Error in Figure
In the original publication [1], there was a mistake in the published Figure 7. The image of Figure 9 was mistakenly used as Figure 7, leading to the duplication of Figures 7 and 9. The corrected Figure 7 appears below. The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected. This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
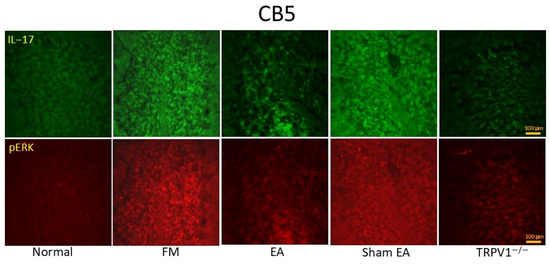
Figure 7.
Immunofluorescence staining (n = 2) showing the increased signals of IL-17RA and pERK in the FM groups. EA and TRPV1 deletion could reverse these effects. CB5 = cerebellum lobe V. CON = control. FM = intermittent cold stress (ICS)-induced FM-like mice model. EA = electroacupuncture. Sham = sham EA. Trpv1−/− = transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 gene knock out. IL-17RA = interleukin-17 receptor A. pERK = phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase.
Reference
- Yeh, Y.-A.; Liao, H.-Y.; Hsiao, I.-H.; Hsu, H.-C.; Lin, Y.-W. Electroacupuncture Reduced Fibromyalgia-Pain-like Behavior through Inactivating Transient Receptor Potential V1 and Interleukin-17 in Intermittent Cold Stress Mice Model. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).