Neurobiological and Microbiota Alterations After Bariatric Surgery: Implications for Hunger, Appetite, Taste, and Long-Term Metabolic Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Mechanisms of Hunger and Appetite Regulation in the Brain
4. Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Brain Responses to Hunger and Appetite
4.1. Hormonal Changes After Surgery
4.2. Brain Imaging Studies Post-Surgery
4.3. Neuroplasticity in Appetite Regulation
5. Alterations in Food Intake Behavior After Surgery
5.1. Changes in Food Preferences
5.2. Mechanisms Underlying Decreased Cravings and Changes in Reward-Related Eating Behavior
5.3. Psychological Factors Influencing Food Intake
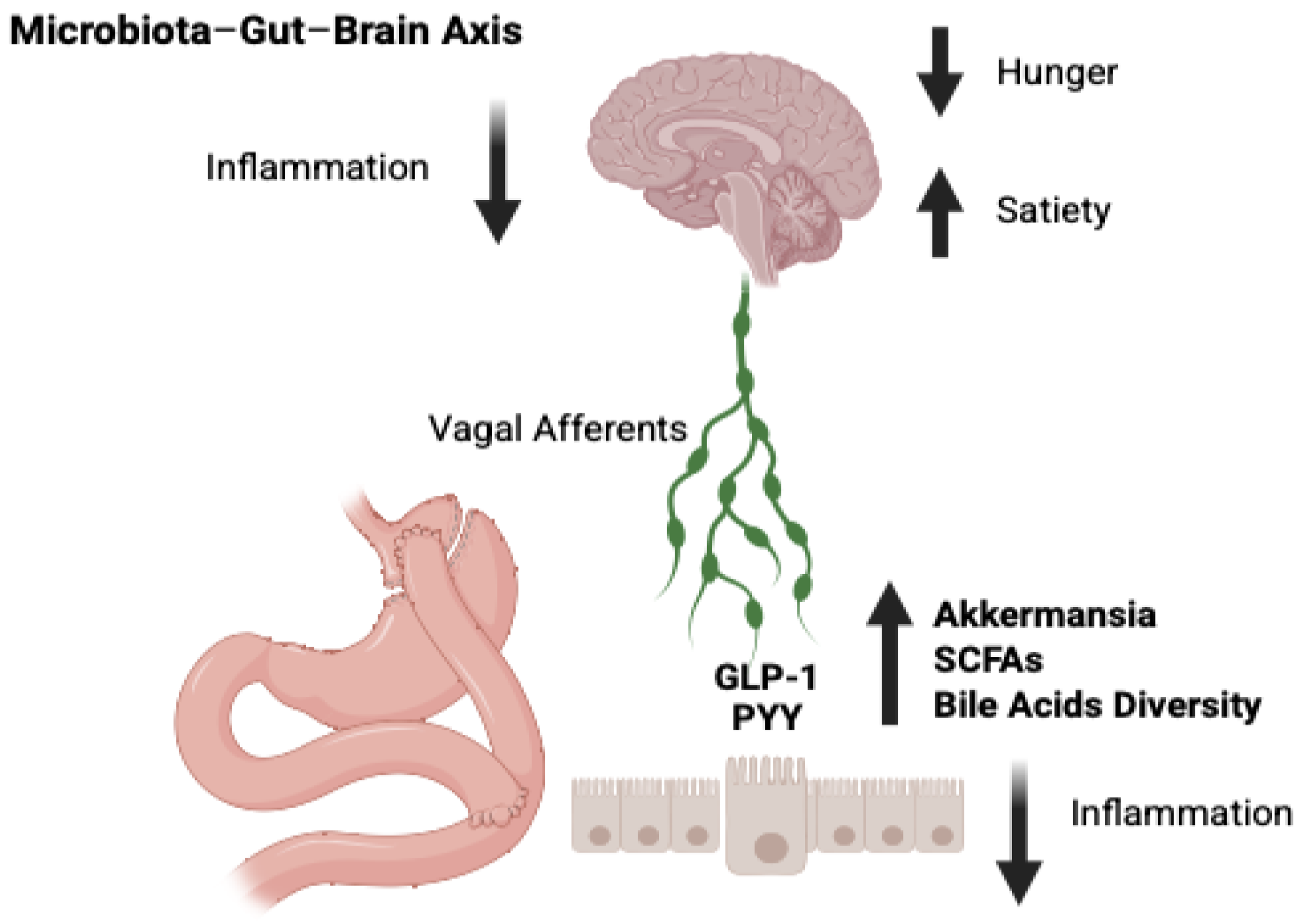
6. Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Microbiota and Its Role in Appetite Regulation
6.1. Alterations in Gut Microbiota Composition
6.2. Microbiota’s Influence on Appetite, Food Intake, and Taste Perception
6.3. Mechanisms of Microbiota-Induced Changes in Neurohormonal Signals
6.4. Implications for Long-Term Dietary Habits
7. Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Taste Perception
7.1. Changes in Taste Sensitivity
7.2. Taste Preferences and Food Choices
7.3. Neural Mechanisms of Taste Modulation
8. Long-Term Implications for Weight Maintenance and Metabolic Health
9. Discussion
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BAs | bile acids |
| BMI | body mass index |
| BS | bariatric surgery |
| BPD/DS | bilio-pancreatic diversion with duodenal switch |
| BPD | bilio-pancreatic diversion without duodenal switch |
| CDC | Center of Disease Control |
| DEBQ | Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire |
| FXR | farnesoid X receptor |
| GB | gastric banding |
| GI | gastrointestinal |
| GM | grey matter |
| GLP-1 | glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| LCA | lithocholic acid |
| LSG | laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy |
| NST | nucleus of the solitary tract |
| NPY | neuropeptide Y |
| PYY | peptide tyrosine-tyrosine |
| RYGB | Roux-en-Y gastric bypass |
| SMD | Standard Media Deviation |
| SCFAs | short-chain fatty acids |
| SG | sleeve gastrectomy |
| TFEQ | Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire |
| TGR5 | takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5 |
| WL | weight loss |
| WM | white matter |
| WR | weight regain |
References
- Lin, X.; Li, H. Obesity: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, S.; Sockalingam, S.; Dash, S. Obesity as a multisystem disease: Trends in obesity rates and obesity-related complications. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23 (Suppl. S1), 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias-Toral, E.; Garcia-Velasquez, E.; de Los Angeles Carignano, M.; Rodriguez-Veintimilla, D.; Alvarado-Aguilera, I.; Bautista-Litardo, N. Polycystic ovary syndrome and obesity: Clinical aspects and nutritional management. Minerva Endocrinol. 2022, 47, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapela, S.P.; Simancas-Racines, A.; Ceriani, F.; Martinuzzi, A.L.N.; Russo, M.P.; Zambrano, A.K.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Verde, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Katsanos, C.S.; et al. Obesity and Obesity-Related Thyroid Dysfunction: Any Potential Role for the Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD)? Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2024, 13, 194–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godos, J.; Lanza, G.; Ferri, R.; Caraci, F.; Cano, S.S.; Elio, I.; Micek, A.; Castellano, S.; Grosso, G. Relation between dietary inflammatory potential and sleep features: Systematic review of observational studies. Med. J. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, S.; Irfan, W.; Jameel, A.; Ahmed, S.; Shahid, R.K. Obesity and cancer: A current overview of epidemiology, pathogenesis, outcomes, and management. Cancers 2023, 15, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piché, M.-E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.-P. Obesity phenotypes, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.-P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: A scientific statement from the american heart association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatterale, F.; Longo, M.; Naderi, J.; Raciti, G.A.; Desiderio, A.; Miele, C.; Beguinot, F. Chronic adipose tissue inflammation linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias-Pereira, R.; Zuk, J.B.; Khavaran, H. Plant bioactive compounds from Mediterranean diet improve risk factors for metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 74, 403–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrea, L.; Pugliese, G.; Frias-Toral, E.; Napolitano, B.; Laudisio, D.; Aprano, S.; Ceriani, F.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. Is there a relationship between the ketogenic diet and sleep disorders? Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 73, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, V.; Neves, J.S.; Salazar, D.; Ferreira, M.J.; Oliveira, S.C.; Souteiro, P.; Pedro, J.; Magalhães, D.; Varela, A.; Belo, S.; et al. Long-Term Weight Loss and Metabolic Syndrome Remission after Bariatric Surgery: The Effect of Sex, Age, Metabolic Parameters and Surgical Technique—A 4-Year Follow-Up Study. Obes. Facts 2019, 12, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, C.; Marchetti, C.; Monami, M.; Mannucci, E.; Cresci, B. Efficacy and effects of bariatric surgery in the treatment of obesity: Network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 2815–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verde, L.; Frias-Toral, E.; Cardenas, D. Editorial: Environmental factors implicated in obesity. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1171507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spivak, H.; Sakran, N.; Dicker, D.; Rubin, M.; Raz, I.; Shohat, T.; Blumenfeld, O. Different effects of bariatric surgical procedures on dyslipidemia: A registry-based analysis. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2017, 13, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, F.M.; Oliveira, J.; Preto, J.; Saavedra, A.; Costa, M.M.; Magalhães, D.; Lau, E.; Bettencourt-Silva, R.; Freitas, P.; Varela, A.; et al. The effect of bariatric surgery type on lipid profile: An age, sex, body mass index and excess weight loss matched study. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.M.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Docimo, S.; Pryo, A.D.; Spaniolas, K. Bariatric surgery lowers the risk of major cardiovascular events. Ann. Surg. 2022, 276, e417–e424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarno, G.; Calabrese, P.; Frias-Toral, E.; Ceriani, F.; Fuchs-Tarlovsky, V.; Spagnuolo, M.; Cucalón, G.; Córdova, L.Á.; Schiavo, L.; Pilone, V. The relationship between preoperative weight loss and intra and post-bariatric surgery complications: An appraisal of the current preoperative nutritional strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 10230–10238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Pugliese, G.; Muscogiuri, G.; Laudisio, D.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. New-generation anti-obesity drugs: Naltrexone/bupropion and liraglutide. An update for endocrinologists and nutritionists. Minerva Endocrinol. 2020, 45, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, M.; Topal, B.; Sanches, E.E.; DE Jongh, F.W.; Cagiltay, E.; Celik, A.; Ribeiro, R.; Parmar, C.; Ugale, S.; Proczko, M.; et al. The effects of glucagon like peptide-1 (GLP-1) on cardiac remodeling: Exploring the role of medication and physiological modulation after metabolic surgery. Minerva Endocrinol. 2022, 47, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, C.-Q.; Huang, Z.-P.; Sheng, Y.; Zou, D.-J. Effects of bariatric surgery on glycemic and lipid metabolism, surgical complication and quality of life in adolescents with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2017, 13, 2037–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoar, S.; Mahmoudzadeh, H.; Naderan, M.; Bagheri-Hariri, S.; Wong, C.; Parizi, A.S.; Shoar, N. Long-Term Outcome of Bariatric Surgery in Morbidly Obese Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 950 Patients with a Minimum of 3 years Follow-Up. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 3110–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, L.; Pilone, V.; Rossetti, G.; Barbarisi, A.; Cesaretti, M.; Iannelli, A. A 4-Week Preoperative Ketogenic Micronutrient-Enriched Diet Is Effective in Reducing Body Weight, Left Hepatic Lobe Volume, and Micronutrient Deficiencies in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery: A Prospective Pilot Study. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robberecht, H.; De Bruyne, T.; Hermans, N. Effect of various diets on biomarkers of the metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-H.; Stoll, C.R.T.; Song, J.; Varela, J.E.; Eagon, C.J.; Colditz, G.A. The effectiveness and risks of bariatric surgery: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis, 2003–2012. JAMA Surg. 2014, 149, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, P.E.; Hindle, A.; Brennan, L.; Skinner, S.; Burton, P.; Smith, A.; Crosthwaite, G.; Brown, W. Long-Term Outcomes After Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Weight Loss at 10 or More Years for All Bariatric Procedures and a Single-Centre Review of 20-Year Outcomes After Adjustable Gastric Banding. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garb, J.; Welch, G.; Zagarins, S.; Kuhn, J.; Romanelli, J. Bariatric surgery for the treatment of morbid obesity: A meta-analysis of weight loss outcomes for laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding and laparoscopic gastric bypass. Obes. Surg. 2009, 19, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrano, F.M.; Iossa, A.; Di Lorenzo, N.; Silecchia, G.; Kontouli, K.-M.; Mavridis, D.; Alarçon, I.; Felsenreich, D.M.; Sanchez-Cordero, S.; Di Vincenzo, A.; et al. EAES rapid guideline: Systematic review, network meta-analysis, CINeMA and GRADE assessment, and European consensus on bariatric surgery-extension 2022. Surg. Endosc. 2022, 36, 1709–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannelli, A.; Treacy, P.; Sebastianelli, L.; Schiavo, L.; Martini, F. Perioperative complications of sleeve gastrectomy: Review of the literature. J. Minim. Access Surg. 2019, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggins, T.; Guidozzi, N.; Welbourn, R.; Ahmed, A.R.; Markar, S.R. Association of bariatric surgery with all-cause mortality and incidence of obesity-related disease at a population level: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, L.; Scalera, G.; Sergio, R.; De Sena, G.; Pilone, V.; Barbarisi, A. Clinical impact of Mediterranean-enriched-protein diet on liver size, visceral fat, fat mass, and fat-free mass in patients undergoing sleeve gastrectomy. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2015, 11, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, C.; Li, M.; Qiu, L.; Shen, J.; Bu, X. Effects of anesthesia methods on insulin, blood glucose, immune and postoperative infection of gastric cancer patients complicated with diabetes mellitus. Minerva Endocrinol. 2018, 43, 388–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrok, H.B.; Ramadan, A.A.; Hamed, I.M.; Mohamed, D.A. Obesity as inducer of cognitive function decline via dysbiosis of gut microbiota in rats. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabesh, M.R.; Eghtesadi, M.; Abolhasani, M.; Maleklou, F.; Ejtehadi, F.; Alizadeh, Z. Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Prescription of Supplements in Pre- and Post-bariatric Surgery Patients: An Updated Comprehensive Practical Guideline. Obes. Surg. 2023, 33, 2557–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, S.; Yasumatsu, K.; Inoue, M.; Iwata, S.; Yoshida, R.; Shigemura, N.; Yanagawa, Y.; Drucker, D.J.; Margolskee, R.F.; Ninomiya, Y. Glucagon-like peptide-1 is specifically involved in sweet taste transmission. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 2268–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Alsheikh, A.S.; Alabdulkader, S.; Johnson, B.; Goldstone, A.P.; Miras, A.D. Effect of obesity surgery on taste. Nutrients 2022, 14, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Penney, N.; Darzi, A.; Purkayastha, S. Taste Changes after Bariatric Surgery: A Systematic Review. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 3321–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, P.; Das, S.K.; Salinardi, T.; Robinson, L.; Saltzman, E.; Scott, T.; Pittas, A.G.; Roberts, S.B. Relationship of cravings with weight loss and hunger. Results from a 6 month worksite weight loss intervention. Appetite 2013, 69, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, J.; Awada, D.; Naim, N.; Al-Jawaldeh, A.; Haidar Ahmad, H.; Mortada, H.; Hoteit, M. Impact of bariatric surgery on the healthy eating index, binge eating behavior and food craving in a middle eastern population: A lebanese experience. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, G.; Dai, S.; Tong, Q.; Liu, B. Determination of glucosamine and galactosamine in food by liquid chromatography with pre-column derivatization. Food Agric. Immunol. 2022, 33, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinou, E.; Stefanova, I.; Iosif, E.; Angelidi, A.M. Neurohormonal Changes in the Gut-Brain Axis and Underlying Neuroendocrine Mechanisms following Bariatric Surgery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunchai, T.; Thunapong, W.; Yasom, S.; Wanchai, K.; Eaimworawuthikul, S.; Metzler, G.; Lungkaphin, A.; Pongchaidecha, A.; Sirilun, S.; Chaiyasut, C.; et al. Decreased microglial activation through gut-brain axis by prebiotics, probiotics, or synbiotics effectively restored cognitive function in obese-insulin resistant rats. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visioli, F.; Marangoni, F.; Poli, A.; Ghiselli, A.; Martini, D. Nutrition and health or nutrients and health? Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 73, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassano, A. The Physiology of Hunger. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoye, A.H.K.; Vondrasek, J.D.; Neph, S.E. Validation of the SmartPlate for detecting food weight and type. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 74, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, S.; Lv, X.; Xiao, X.; Huang, Y.; Tong, X.; Lai, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, D. Integrated double signal amplification systems with ELISA assay for sensitive detection of tylosin in food. Food Agric. Immunol. 2024, 35, 2292971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J. Hunger, ghrelin and the gut. Brain Res. 2018, 1693, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler, L.K.; Lam, D.D. An appetite for life: Brain regulation of hunger and satiety. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 37, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Long, C.; Li, L.; Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Xiong, M.; Zhao, J.; Feng, Z.; Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; et al. Development of a novel polyclonal antibody against bovine αS1 -casein IgE epitopes for prediction of potential allergenicity of milk in foods. Food Agric. Immunol. 2023, 34, 2222932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, Y.; Atasoy, D.; Sternson, S.M. AGRP neurons are sufficient to orchestrate feeding behavior rapidly and without training. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Ma, D.; Fan, Y.; Gao, C.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Hao, Z. Environmental carbon tetrachloride exposure disrupts the liver structure and metabolic detoxification function in mice via p38MAPK/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. Food Agric. Immunol. 2022, 33, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasricha, P.J. Hunger games: Is your stomach making you fat? Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafferty, R.A.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. Emerging therapeutic potential for peptide YY for obesity-diabetes. Peptides 2018, 100, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamah, S.; Hajnal, A.; Covasa, M. Influence of bariatric surgery on gut microbiota composition and its implication on brain and peripheral targets. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionut, V.; Burch, M.; Youdim, A.; Bergman, R.N. Gastrointestinal hormones and bariatric surgery-induced weight loss. Obesity 2013, 21, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perakakis, N.; Farr, O.M.; Mantzoros, C.S. Leptin in Leanness and Obesity: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, I.S.; Bullmore, E.; Keogh, J.; Gillard, J.; O’Rahilly, S.; Fletcher, P.C. Leptin regulates striatal regions and human eating behavior. Science 2007, 317, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, J.; Guan, B. Change in Adipokines and Gastrointestinal Hormones After Bariatric Surgery: A Meta-analysis. Obes. Surg. 2023, 33, 789–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Hreins, E.; Foldi, C.J.; Oldfield, B.J.; Stefanidis, A.; Sumithran, P.; Brown, R.M. Gut-brain mechanisms underlying changes in disordered eating behaviour after bariatric surgery: A review. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 733–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najim, W.; Docherty, N.G.; le Roux, C.W. Food intake and eating behavior after bariatric surgery. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1113–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavo, L.; Sans, A.; Scalera, G.; Barbarisi, A.; Iannelli, A. Why preoperative weight loss in preparation for bariatric surgery is important. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 2790–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneau, M.; McKay, B.; Brooks, E.; Doucet, É.; Baillot, A. Gut peptides before and following Roux-En-Y gastric bypass: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2024, 25, e13702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, K.; Webb, D.-L.; Diaz Tartera, H.O.; Hellström, P.M.; Sundbom, M. Impact of biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch on glucose homeostasis and gut hormones and their correlations with appetite. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2022, 18, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, L.; Scalera, G.; Pilone, V.; De Sena, G.; Quagliariello, V.; Iannelli, A.; Barbarisi, A. A Comparative Study Examining the Impact of a Protein-Enriched Vs Normal Protein Postoperative Diet on Body Composition and Resting Metabolic Rate in Obese Patients after Sleeve Gastrectomy. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J.; Madsbad, S.; Bojsen-Møller, K.N.; Dirksen, C.; Svane, M. New Lessons from the gut: Studies of the role of gut peptides in weight loss and diabetes resolution after gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy. Peptides 2024, 176, 171199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baboumian, S.; Pantazatos, S.P.; Kothari, S.; McGinty, J.; Holst, J.; Geliebter, A. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) of Neural Responses to Visual and Auditory Food Stimuli Pre and Post Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) and Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG). Neuroscience 2019, 409, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, G.; Ji, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ji, W.; Yu, J.; Han, Y.; Cui, G.; Wang, H.; et al. Habenula volume and functional connectivity changes following laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for obesity treatment. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 95, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessi, J.; Dzemidzic, M.; Harezlak, J.; Kareken, D.A.; Considine, R.V. Neural processing of sweet taste in reward regions is reduced following bariatric surgery. Obesity 2024, 32, 1709–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdulkader, S.; Al-Alsheikh, A.S.; Miras, A.D.; Goldstone, A.P. Obesity surgery and neural correlates of human eating behaviour: A systematic review of functional MRI studies. Neuroimage Clin. 2024, 41, 103563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, V.; Demetriou, L.; Behary, P.; Alexiadou, K.; Scholtz, S.; Tharakan, G.; Miras, A.D.; Purkayastha, S.; Ahmed, A.R.; Bloom, S.R.; et al. Weight Loss by Low-Calorie Diet Versus Gastric Bypass Surgery in People With Diabetes Results in Divergent Brain Activation Patterns: A Functional MRI Study. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ji, G.; Hu, Y.; Xu, M.; Jin, Q.; Liu, L.; von Deneen, K.M.; Zhao, J.; Chen, A.; Cui, G.; et al. Bariatric surgery in obese patients reduced resting connectivity of brain regions involved with self-referential processing. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 4755–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rullmann, M.; Preusser, S.; Poppitz, S.; Heba, S.; Gousias, K.; Hoyer, J.; Schütz, T.; Dietrich, A.; Müller, K.; Hankir, M.K.; et al. Adiposity related brain plasticity induced by bariatric surgery. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, J.C.E.; Jove, M.; Gonzalo, H.; Pamplona, R.; Portero-Otin, M. Nutridynamics: Mechanism(s) of action of bioactive compounds and their effects. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 66 (Suppl. S1), S22–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochner, C.N.; Kwok, Y.; Conceição, E.; Pantazatos, S.P.; Puma, L.M.; Carnell, S.; Teixeira, J.; Hirsch, J.; Geliebter, A. Selective reduction in neural responses to high calorie foods following gastric bypass surgery. Ann. Surg. 2011, 253, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, E.J.; Malik, M.S.; Whitford-Bartle, T.; Waters, G.M. The effects of bariatric surgery on psychological aspects of eating behaviour and food intake in humans. Appetite 2020, 150, 104575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moizé, V.L.; Pi-Sunyer, X.; Mochari, H.; Vidal, J. Nutritional pyramid for post-gastric bypass patients. Obes. Surg. 2010, 20, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwer, D.B.; Wadden, T.A.; Moore, R.H.; Baker, A.W.; Gibbons, L.M.; Raper, S.E.; Williams, N.N. Preoperative eating behavior, postoperative dietary adherence, and weight loss after gastric bypass surgery. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2008, 4, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, R.; Stekhoven, D.J.; Leupold, U.; Marti, W.R. Linear mixed effects analysis reveals the significant impact of preoperative diet success on postoperative weight loss in gastric bypass surgery. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 2473–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, N.; Al-Najim, W.; le Roux, C.W.; Docherty, N.G. Shifts in food preferences after bariatric surgery: Observational reports and proposed mechanisms. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brolin, R.E.; Robertson, L.B.; Kenler, H.A.; Cody, R.P. Weight loss and dietary intake after vertical banded gastroplasty and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Ann. Surg. 1994, 220, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyot, E.; Dougkas, A.; Nazare, J.-A.; Bagot, S.; Disse, E.; Iceta, S. A systematic review and meta-analyses of food preference modifications after bariatric surgery. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nance, K.; Acevedo, M.B.; Pepino, M.Y. Changes in taste function and ingestive behavior following bariatric surgery. Appetite 2020, 146, 104423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, L.; Aliberti, S.M.; Calabrese, P.; Senatore, A.M.; Severino, L.; Sarno, G.; Iannelli, A.; Pilone, V. Changes in Food Choice, Taste, Desire, and Enjoyment 1 Year after Sleeve Gastrectomy: A Prospective Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakeri, R.; Batterham, R.L. Potential mechanisms underlying the effect of bariatric surgery on eating behaviour. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2018, 25, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepino, M.Y.; Bradley, D.; Eagon, J.C.; Sullivan, S.; Abumrad, N.A.; Klein, S. Changes in taste perception and eating behavior after bariatric surgery-induced weight loss in women. Obesity 2014, 22, E13–E20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umabiki, M.; Tsuzaki, K.; Kotani, K.; Nagai, N.; Sano, Y.; Matsuoka, Y.; Kitaoka, K.; Okami, Y.; Sakane, N.; Higashi, A. The improvement of sweet taste sensitivity with decrease in serum leptin levels during weight loss in obese females. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2010, 220, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nance, K.; Eagon, J.C.; Klein, S.; Pepino, M.Y. Effects of Sleeve Gastrectomy vs. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass on Eating Behavior and Sweet Taste Perception in Subjects with Obesity. Nutrients 2017, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, M.J.; King, W.C.; Kalarchian, M.A.; Hinerman, A.; Marcus, M.D.; Yanovski, S.Z.; Mitchell, J.E. Eating pathology and associations with long-term changes in weight and quality of life in the longitudinal assessment of bariatric surgery study. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2018, 51, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barstad, L.H.; Johnson, L.K.; Borgeraas, H.; Hofsø, D.; Svanevik, M.; Småstuen, M.C.; Hertel, J.K.; Hjelmesæth, J. Changes in dietary intake, food tolerance, hedonic hunger, binge eating problems, and gastrointestinal symptoms after sleeve gastrectomy compared with after gastric bypass; 1-year results from the Oseberg study—A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 117, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, E.; Dovey, T.M. Validation of the Dutch Eating Behaviour Questionnaire (DEBQ) among Maltese women. Appetite 2016, 107, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, E.J.; Rehman, J.; Pepper, L.B.; Walters, E.R. Obesity and eating disturbance: The role of TFEQ restraint and disinhibition. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, D.S.; da Silva, T.S.; Leal, P.R.F.; Lopes, K.G.; Kraemer-Aguiar, L.G. Early Changes in Eating Behavior Patterns and Their Relationship with Weight Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horbach, T.; Thalheimer, A.; Seyfried, F.; Eschenbacher, F.; Schuhmann, P.; Meyer, G. abiliti Closed-Loop Gastric Electrical Stimulation System for Treatment of Obesity: Clinical Results with a 27-Month Follow-Up. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 1779–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.; Wilms, B.; Veit, R.; Ernst, B.; Thurnheer, M.; Kullmann, S.; Fritsche, A.; Birbaumer, N.; Preissl, H.; Schultes, B. Altered brain activity in severely obese women may recover after Roux-en Y gastric bypass surgery. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, J.J.; Madsbad, S.; Bojsen-Møller, K.N.; Svane, M.S.; Jørgensen, N.B.; Dirksen, C.; Martinussen, C. Mechanisms in bariatric surgery: Gut hormones, diabetes resolution, and weight loss. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2018, 14, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, W.C.; Hinerman, A.S.; Belle, S.H.; Wahed, A.S.; Courcoulas, A.P. Comparison of the performance of common measures of weight regain after bariatric surgery for association with clinical outcomes. JAMA 2018, 320, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, A. “When the honeymoon is over, the real work begins”: Gastric bypass patients’ weight loss trajectories and dietary change experiences. Soc. Sci. Med. 2016, 151, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsbad, S.; Dirksen, C.; Holst, J.J. Mechanisms of changes in glucose metabolism and bodyweight after bariatric surgery. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrea, L.; Verde, L.; Schiavo, L.; Sarno, G.; Camajani, E.; Iannelli, A.; Caprio, M.; Pilone, V.; Colao, A.; Muscogiuri, G. Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) as Pre-Operative First-Line Dietary Therapy in Patients with Obesity Who Are Candidates for Bariatric Surgery. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmiento-Andrade, Y.; Suárez, R.; Quintero, B.; Garrochamba, K.; Chapela, S.P. Gut microbiota and obesity: New insights. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1018212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobârcă, D.; Cătoi, A.F.; Copăescu, C.; Miere, D.; Crișan, G. Bariatric surgery in obesity: Effects on gut microbiota and micronutrient status. Nutrients 2020, 12, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, G.; Pampaloni, I. Gut Microbiota and Gastrointestinal Symptoms in the Global Assessment of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: A Narrative Review of Current Evidence and Practical Implications. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisano, S.; Campisciano, G.; Silvestri, M.; Guerra, M.; Giuricin, M.; Casagranda, B.; Comar, M.; de Manzini, N. Changes in Gut Microbiota Composition after Bariatric Surgery: A New Balance to Decode. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2020, 24, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, D.A.; Pedreros, J.P.; Turiel, D.; Quezada, N.; Pimentel, F.; Escalona, A.; Garrido, D. Distinct patterns in the gut microbiota after surgical or medical therapy in obese patients. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, J.T.; Mocanu, V.; Park, H.; Laffin, M.; Hotte, N.; Karmali, S.; Birch, D.W.; Madsen, K.L. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy induce substantial and persistent changes in microbial communities and metabolic pathways. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2050636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.K.; O’Sullivan, J.M.; Plank, L.D.; Murphy, R. Altered gut microbiome after bariatric surgery and its association with metabolic benefits: A systematic review. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019, 15, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.-P.; Liu, C.-Q.; Qi, L.; Sheng, Y.; Zou, D.-J. Modulation of the gut microbiome: A systematic review of the effect of bariatric surgery. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Osadchiy, V.; Mayer, E.A. Brain-gut-microbiome interactions in obesity and food addiction. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottari, B.; Castellone, V.; Neviani, E. Probiotics and Covid-19. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 72, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvucci, E. The human-microbiome superorganism and its modulation to restore health. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 70, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gu, M.; Sun, H.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. The Potential of Gut Microbiota in Prediction of Stroke-Associated Pneumonia. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B.; Callaghan, B.P.; Rivera, L.R.; Cho, H.-J. The enteric nervous system and gastrointestinal innervation: Integrated local and central control. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 817, 39–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiqian, D.; Jiachan, Z.; Wenjing, C.; Luyao, L.; Meng, L.; Changtao, W. Paecilomyces cicadae: A systematic overview of the biological activities and potential mechanisms of its active metabolites. Food Agric. Immunol. 2023, 34, 2243059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, C.; Iwasaki, Y.; Yada, T. Short-chain fatty acids suppress food intake by activating vagal afferent neurons. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 57, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Xin, M.; Lin, J.; Xie, J.; Lin, R.; Peng, Z.; Guo, J.; Bai, W. Banana starch intervention ameliorates diabetes-induced mood disorders via modulation of the gut microbiota-brain axis in diabetic rats. Food Agric. Immunol. 2022, 33, 377–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, A.A.; Shah, Z.A. A review of the consequences of gut microbiota in neurodegenerative disorders and aging. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sánchez, M.A.; Balaguer-Román, A.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.E.; Almansa-Saura, S.; García-Zafra, V.; Ferrer-Gómez, M.; Frutos, M.D.; Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.; Ruiz-Alcaraz, A.J.; Núñez-Sánchez, M.Á.; et al. Plasma short-chain fatty acid changes after bariatric surgery in patients with severe obesity. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2023, 19, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciacca, S.; Lo Giudice, A.; Asmundo, M.G.; Cimino, S.; Alshatwi, A.A.; Morgia, G.; Ferro, M.; Russo, G.I. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet and prostate cancer severity. Med. J. Nutr. Metab. 2023, 16, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tong, F.; Wu, B.; Dong, X. Radiation-Induced Brain Injury: Mechanistic Insights and the Promise of Gut-Brain Axis Therapies. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukorako, P.; Lemoine, N.; Biertho, L.; Lebel, S.; Roy, M.-C.; Plamondon, J.; Tchernof, A.; Varin, T.V.; Anhê, F.F.; St-Pierre, D.H.; et al. Consistent gut bacterial and short-chain fatty acid signatures in hypoabsorptive bariatric surgeries correlate with metabolic benefits in rats. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawthon, C.R.; Kirkland, R.A.; Pandya, S.; Brinson, N.A.; de La Serre, C.B. Non-neuronal crosstalk promotes an inflammatory response in nodose ganglia cultures after exposure to byproducts from gram positive, high-fat-diet-associated gut bacteria. Physiol. Behav. 2020, 226, 113124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhi, T.; Li, S.; Xia, J.; Tian, Y.; Ma, A.; Jia, Y. Untargeted metabolomics revealed the product formation rules of two fermented walnut milk. Food Agric. Immunol. 2023, 34, 6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z. Changes in fasting bile acid profiles after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy. Medicine 2021, 100, e23939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lin, H.; Shen, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Yuan, M.; Yuan, M.; Jia, S.; Cao, Z.; Wu, C.; et al. Gut microbiota regulates postprandial GLP-1 response via ileal bile acid-TGR5 signaling. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2274124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Jankiewicz, A.; Guzmán-Quevedo, O.; Fénelon, V.S.; Zizzari, P.; Quarta, C.; Bellocchio, L.; Tailleux, A.; Charton, J.; Fernandois, D.; Henricsson, M.; et al. Hypothalamic bile acid-TGR5 signaling protects from obesity. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1483–1492.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinert, R.E.; Peterli, R.; Keller, S.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C.; Drewe, J.; Peters, T.; Beglinger, C. Bile acids and gut peptide secretion after bariatric surgery: A 1-year prospective randomized pilot trial. Obesity 2013, 21, E660–E668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.; Fan, J.; Xu, Q.; Gu, D.; Shi, B.; Wang, D.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y. Different iron sources affected haemoglobin and myoglobin synthesis, and gene expression related to iron metabolism in skeletal muscle in piglets. Food Agric. Immunol. 2023, 34, 2247182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmiguel, C.P.; Jacobs, J.; Gupta, A.; Ju, T.; Stains, J.; Coveleskie, K.; Lagishetty, V.; Balioukova, A.; Chen, Y.; Dutson, E.; et al. Surgically induced changes in gut microbiome and hedonic eating as related to weight loss: Preliminary findings in obese women undergoing bariatric surgery. Psychosom. Med. 2017, 79, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.-M.; Huang, W.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Quan, W.; Niu, G.-Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, M.-X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, L.-P.; Zhao, W.-J.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila Is Beneficial to a Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease, via Alleviated Neuroinflammation and Promoted Neurogenesis, with Involvement of SCFAs. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xu, R.; Li, X.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Chen, W. Unexpected immunoregulation effects of D-lactate, different from L-lactate. Food Agric. Immunol. 2022, 33, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, A.; Lv, J.; Su, Y. The inflammatory mechanism of parkinson’s disease: Gut microbiota metabolites affect the development of the disease through the gut–brain axis. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, C.R.; Albaugh, V.L.; Abumrad, N.N. Metabolic effects of bile acids: Potential role in bariatric surgery. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 8, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterli, R.; Wölnerhanssen, B.; Peters, T.; Devaux, N.; Kern, B.; Christoffel-Courtin, C.; Drewe, J.; von Flüe, M.; Beglinger, C. Improvement in glucose metabolism after bariatric surgery: Comparison of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: A prospective randomized trial. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, T.R.; Jirapinyo, P.; Thompson, C.C. Effect of Sleeve Gastrectomy on Ghrelin, GLP-1, PYY, and GIP Gut Hormones: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann. Surg. 2020, 272, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaugh, V.L.; Banan, B.; Antoun, J.; Xiong, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ping, J.; Alikhan, M.; Clements, B.A.; Abumrad, N.N.; Flynn, C.R. Role of Bile Acids and GLP-1 in Mediating the Metabolic Improvements of Bariatric Surgery. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1041–1051.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutoukidis, D.A.; Jebb, S.A.; Zimmerman, M.; Otunla, A.; Henry, J.A.; Ferrey, A.; Schofield, E.; Kinton, J.; Aveyard, P.; Marchesi, J.R. The association of weight loss with changes in the gut microbiota diversity, composition, and intestinal permeability: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2020068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Montoliu, L.; Rodríguez-Peña, M.-M.; Puig, R.; Astiarraga, B.; Guerrero-Pérez, F.; Virgili, N.; López-Urdiales, R.; Osorio, J.; Monseny, R.; Lazzara, C.; et al. A specific gut microbiota signature is associated with an enhanced GLP-1 and GLP-2 secretion and improved metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes after metabolic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1181744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.S.; Cho, C.H.; Yun, M.S.; Jang, S.J.; You, H.J.; Kim, J.-H.; Han, D.; Cha, K.H.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, K.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila secretes a glucagon-like peptide-1-inducing protein that improves glucose homeostasis and ameliorates metabolic disease in mice. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.N.; Luo, J.N.; Harris, D.A.; Aliakbarian, H.; Yao, L.; Paik, D.; Subramaniam, R.; Adhikari, A.A.; Vernon, A.H.; Kiliç, A.; et al. A microbial metabolite remodels the gut-liver axis following bariatric surgery. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 408–424.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Haase, N.; Haange, S.-B.; Sucher, R.; Münzker, J.; Jäger, E.; Schischke, K.; Seyfried, F.; von Bergen, M.; Hankir, M.K.; et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass contributes to weight loss-independent improvement in hypothalamic inflammation and leptin sensitivity through gut-microglia-neuron-crosstalk. Mol. Metab. 2021, 48, 101214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Wang, W.; Chen, B.; Li, A.; Song, G.; Cheng, J.; Qiao, L.; Zhu, R.; Min, Y. Dietary supplemental synbiotic—Yucca extract compound preparation modulates production performance, immune status and faecal microflora diversity in laying hens. Food Agric. Immunol. 2022, 33, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankir, M.K.; Seyfried, F.; Miras, A.D.; Cowley, M.A. Brain Feeding Circuits after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.; de Souza, A.L.; Batista, G.A.; Duran, L.F.T.; Fernandes, D.P.; Molina, V.B.C.; Gonçalves, R.; Giorgetti, J.S.; Chaim, E.A.; Alegre, S.M. GLP-1: 10-year follow-up after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2022, 407, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard Nielsen, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Just Christensen, B.; Ritz, C.; le Roux, C.W.; Berg Schmidt, J.; Sjödin, A. Bariatric surgery does not affect food preferences, but individual changes in food preferences may predict weight loss. Obesity 2018, 26, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittrell, H.; Graber, W.; Mariani, E.; Czaja, K.; Hajnal, A.; Di Lorenzo, P.M. Taste and odor preferences following Roux-en-Y surgery in humans. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashkoori, N.; Ibrahim, B.; Shahsavan, M.; Shahmiri, S.S.; Pazouki, A.; Amr, B.; Kermansaravi, M. Alterations in taste preferences one year following sleeve gastrectomy, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, and one anastomosis gastric bypass: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilone, V.; Tramontano, S.; Cutolo, C.; Marchese, F.; Pagano, A.M.; Di Spirito, F.; Schiavo, L. Clinical factors correlated with vitamin D deficiency in patients with obesity scheduled for bariatric surgery: A single center experience. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2020, 90, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behary, P.; Miras, A.D. Food preferences and underlying mechanisms after bariatric surgery. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2015, 74, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galazzi, E.; Persani, L.G. Differential diagnosis between constitutional delay of growth and puberty, idiopathic growth hormone deficiency and congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: A clinical challenge for the pediatric endocrinologist. Minerva Endocrinol. 2020, 45, 354–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.R.; Aghababian, A.; Papantoni, A.; Veldhuizen, M.G.; Kamath, V.; Harris, C.; Moran, T.H.; Carnell, S.; Steele, K.E. One Year Follow-Up of Taste-Related Reward Associations with Weight Loss Suggests a Critical Time to Mitigate Weight Regain Following Bariatric Surgery. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Fayos, A.C.; García-Martínez, A.; Herrera-Martínez, A.D.; Jiménez-Vacas, J.M.; Vázquez-Borrego, M.C.; Castaño, J.P.; Picó, A.; Gahete, M.D.; Luque, R.M. Molecular determinants of the response to medical treatment of growth hormone secreting pituitary neuroendocrine tumors. Minerva Endocrinol. 2019, 44, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Ansari, W.; Elhag, W. Weight Regain and Insufficient Weight Loss After Bariatric Surgery: Definitions, Prevalence, Mechanisms, Predictors, Prevention and Management Strategies, and Knowledge Gaps—A Scoping Review. Obes. Surg. 2021, 31, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöström, L.; Lindroos, A.-K.; Peltonen, M.; Torgerson, J.; Bouchard, C.; Carlsson, B.; Dahlgren, S.; Larsson, B.; Narbro, K.; Sjöström, C.D.; et al. Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2683–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, S.J.; Priya, P.; Mahawar, K.K.; Shah, S.; Indian Bariatric Surgery Outcome Reporting (IBSOR) Group. Weight Regain after Bariatric Surgery—A Multicentre Study of 9617 Patients from Indian Bariatric Surgery Outcome Reporting Group. Obes. Surg. 2019, 29, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, A.; Dadar, M.; Pelletier, M.; Zeighami, Y.; Garcia-Garcia, I.; Iceta, S.; Yau, Y.; Nadeau, M.; Marceau, S.; Biertho, L.; et al. Neuroanatomical changes in white and grey matter after sleeve gastrectomy. Neuroimage 2020, 213, 116696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custers, E.; Vreeken, D.; Kleemann, R.; Kessels, R.P.C.; Duering, M.; Brouwer, J.; Aufenacker, T.J.; Witteman, B.P.L.; Snabel, J.; Gart, E.; et al. Long-Term Brain Structure and Cognition Following Bariatric Surgery. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2355380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Miegueu, P.; Lapointe, M.; Poirier, P.; Martin, J.; Bastien, M.; Tiwari, S.; Cianflone, K. Acute post-bariatric surgery increase in orexin levels associates with preferential lipid profile improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigdem Arica, P.; Kocael, A.; Tabak, O.; Taskin, M.; Zengin, K.; Uzun, H. Plasma ghrelin, leptin, and orexin—A levels and insulin resistance after laparoscopic gastric band applications in morbidly obese patients. Minerva Med. 2013, 104, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, C.; Mudd, J.; Hawkins, M. Neuroprotective effects of leptin in the context of obesity and metabolic disorders. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 72 Pt A, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.C.S.; da Silva, N.R.; Santos Gonçalves, V.S.; Corgosinho, F.C.; de Carvalho, K.M.B.; Horst, M.A. The influence of single nucleotide polymorphisms on body weight trajectory after bariatric surgery: A systematic review. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2023, 12, 280–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Izhak, M.; Eshel, A.; Cohen, R.; Madar-Shapiro, L.; Meiri, H.; Wachtel, C.; Leung, C.; Messick, E.; Jongkam, N.; Mavor, E.; et al. Projection of Gut Microbiome Pre- and Post-Bariatric Surgery To Predict Surgery Outcome. mSystems 2021, 6, e0136720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaiss, C.A.; Itav, S.; Rothschild, D.; Meijer, M.T.; Levy, M.; Moresi, C.; Dohnalová, L.; Braverman, S.; Rozin, S.; Malitsky, S.; et al. Persistent microbiome alterations modulate the rate of post-dieting weight regain. Nature 2016, 540, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Brain Region | RYGB Effects | LSG Effects | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC) [67,68,69,71] | ↑↑ activation | ↑↑ activation, though less pronounced than RYGB. | RYGB results in better gains in cognitive control. |
| Nucleus Accumbens (NAc) and Striatum [67,68,69,71] | ↓↓ Food cue reactivity, indicating lower reward sensitivity to food. | Variable effects, prevailing ↓↓ activity but less consistency. | RYGB has a greater influence on ↓↓ food-related reward processing. |
| Hypothalamus and Thalamus [67,68,69,71] | ↑↑ Functional connectivity is linked to ↑↑ hunger regulation. | A moderate ↑ in connectivity | RYGB exhibits better normalization of hunger-related signals. |
| Para hippocampal/Fusiform Gyrus [67,68,69,71] | ↓↓ activity in response to high-energy meal cues, indicating less attention to calorie-dense foods. | ↓↓ activation | RYGB causes a greater ↓↓ of high-energy food cue processing. |
| Before Bariatric Surgery [101,102] | After Bariatric Surgery [105,106,107,108] |
|---|---|
| ↓ Bacteroidetes | ↑ Bacteroidetes |
| ↑ Firmicutes | ↓ Firmicutes |
| ↑ Proteobacteria | |
| ↑ Verrucomicrobia (Akkermansia) |
| Taste Domain | Objectives | Mechanism | Effect of BS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensory [88,152,153] | Transmits taste stimuli to the thalamus and primary taste cortex, responsible for identifying and discriminating flavors. | Nerve fibers of the tongue transmit taste stimuli to the thalamus and the primary taste cortex. | No effect |
| Hedonic [88,152,153] | Integrates sensory input and modulates desire, reward, or aversion to flavors through cortical and mesolimbic system feedback. | Processes sensory input (stimuli from the tongue, vision, and olfactory nerves in the secondary taste cortex, generating feedback with the primary cortex and the mesolimbic system) and modulates reward pathways via dopamine secretion, reducing the drive for sweet or fatty foods. | ↓ dopamine secretion |
| Physiological [88,152,153] | Regulates digestive processes, such as salivation and hormone secretion | Neuroendocrine stimulation. | ↑ GLP-1 and PYY which participate in dopamine secretion |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chapela, S.; Alvarez-Córdova, L.; Martinuzzi, A.; Suarez, R.; Gonzalez, V.; Manrique, E.; Castaño, J.; Rossetti, G.; Cobellis, L.; Pilone, V.; et al. Neurobiological and Microbiota Alterations After Bariatric Surgery: Implications for Hunger, Appetite, Taste, and Long-Term Metabolic Health. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040363
Chapela S, Alvarez-Córdova L, Martinuzzi A, Suarez R, Gonzalez V, Manrique E, Castaño J, Rossetti G, Cobellis L, Pilone V, et al. Neurobiological and Microbiota Alterations After Bariatric Surgery: Implications for Hunger, Appetite, Taste, and Long-Term Metabolic Health. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(4):363. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040363
Chicago/Turabian StyleChapela, Sebastián, Ludwig Alvarez-Córdova, Andres Martinuzzi, Rosario Suarez, Victoria Gonzalez, Ezequiel Manrique, Janeth Castaño, Gianluca Rossetti, Luigi Cobellis, Vincenzo Pilone, and et al. 2025. "Neurobiological and Microbiota Alterations After Bariatric Surgery: Implications for Hunger, Appetite, Taste, and Long-Term Metabolic Health" Brain Sciences 15, no. 4: 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040363
APA StyleChapela, S., Alvarez-Córdova, L., Martinuzzi, A., Suarez, R., Gonzalez, V., Manrique, E., Castaño, J., Rossetti, G., Cobellis, L., Pilone, V., Frias-Toral, E., & Schiavo, L. (2025). Neurobiological and Microbiota Alterations After Bariatric Surgery: Implications for Hunger, Appetite, Taste, and Long-Term Metabolic Health. Brain Sciences, 15(4), 363. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040363







