A Novel Method for the Locomotion Control of a Rat Robot via the Electrical Stimulation of the Ventral Tegmental Area and Nigrostriatal Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
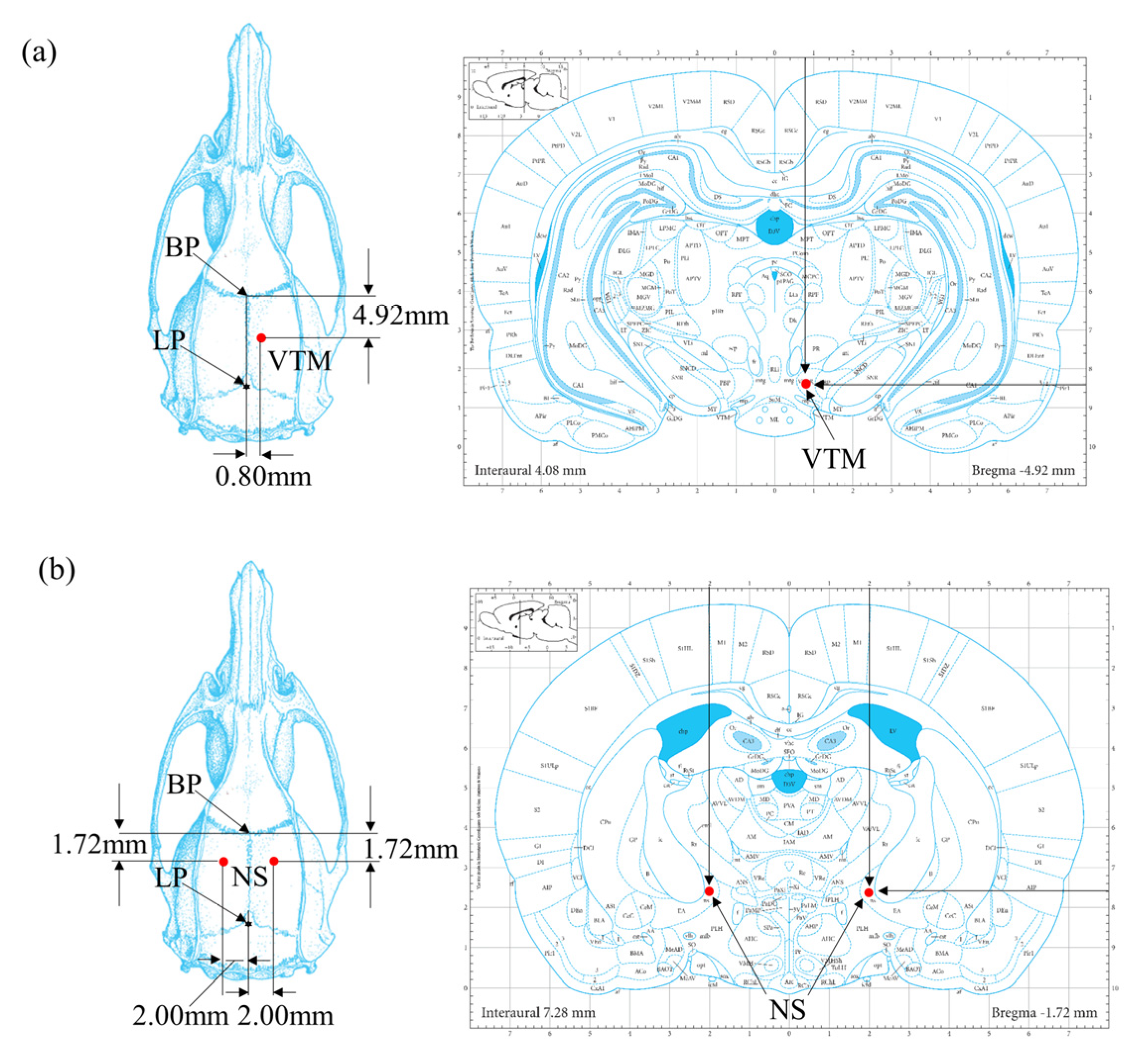
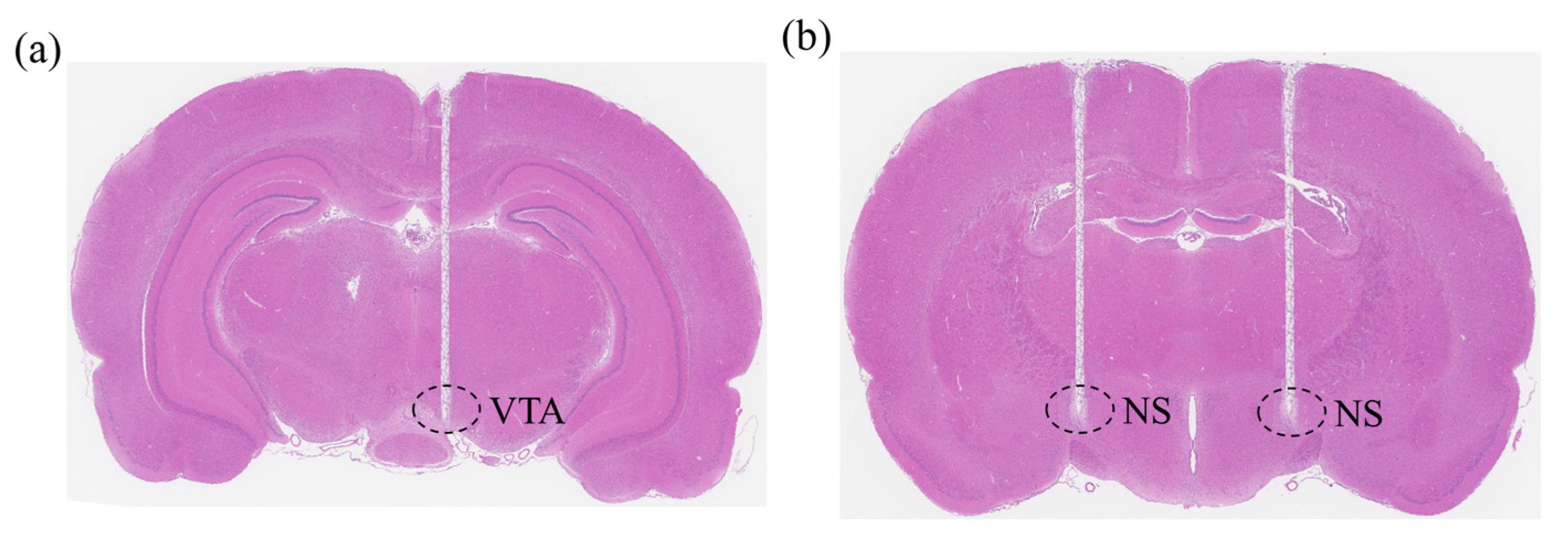
2.2. Surgical Procedures
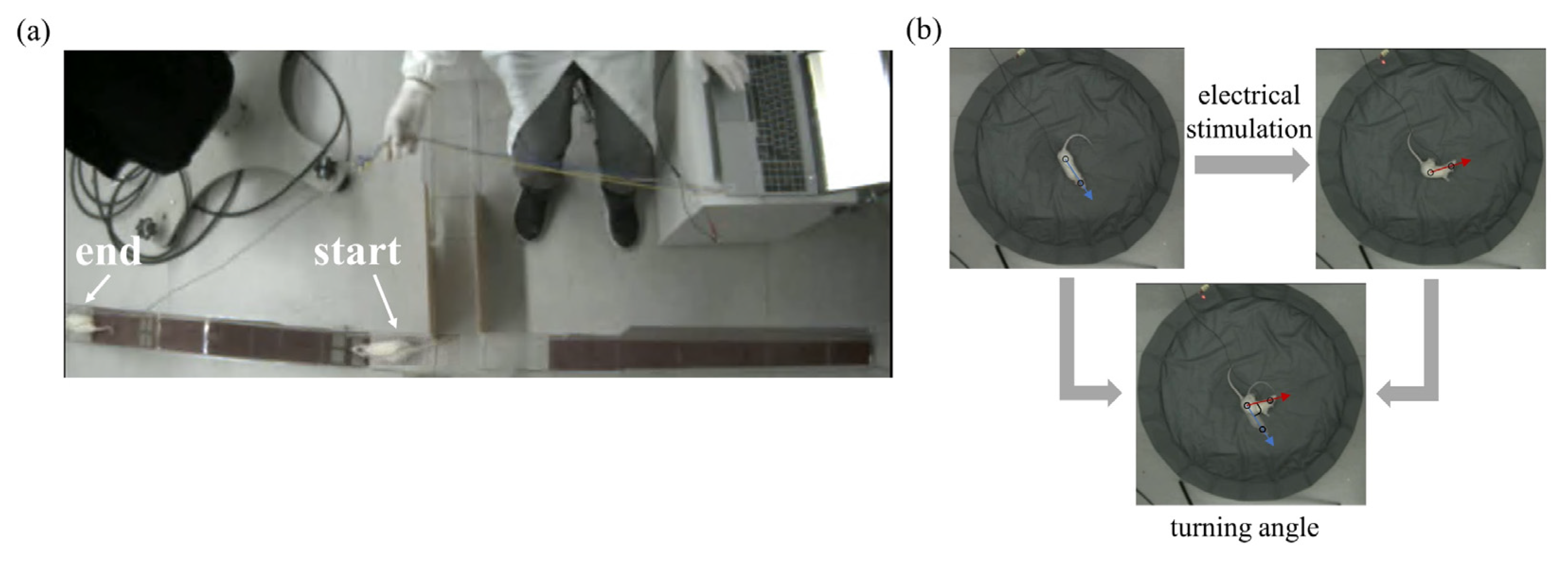
2.3. Electrical Stimulation and Behavioral Testing Platform
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
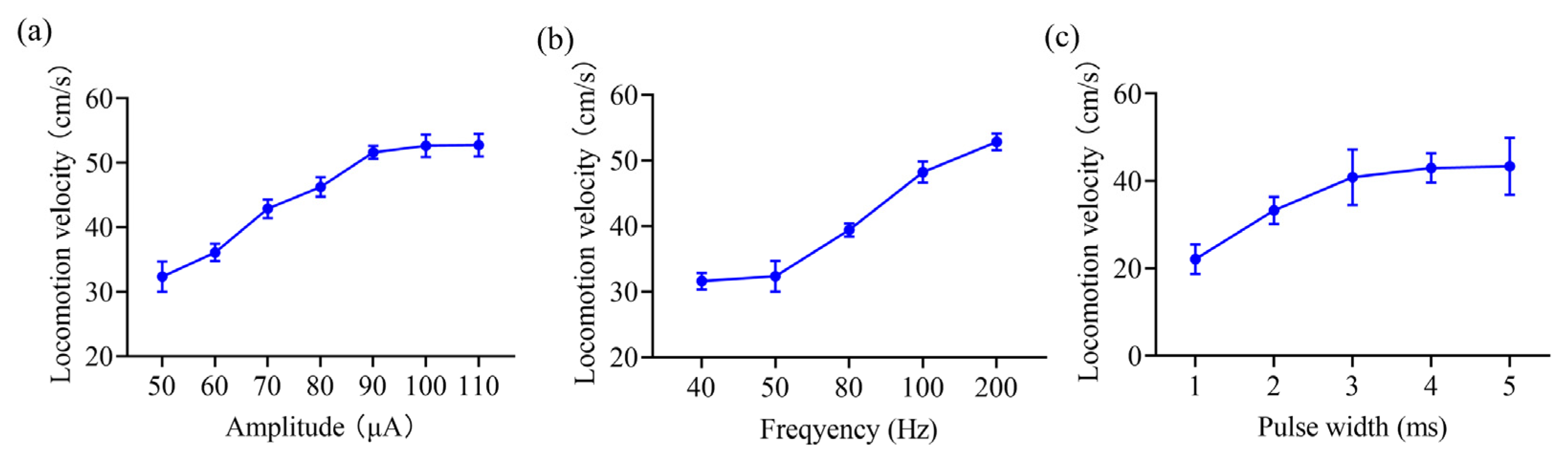
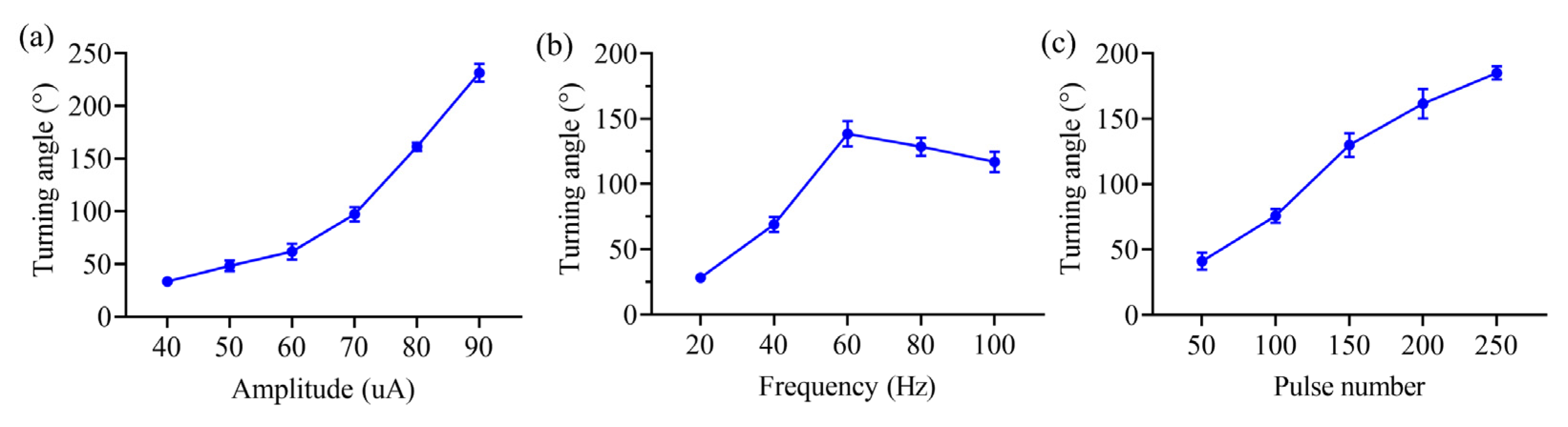
3.1. Inclined Movement Control in Rats Based on Stimulation of the VTA
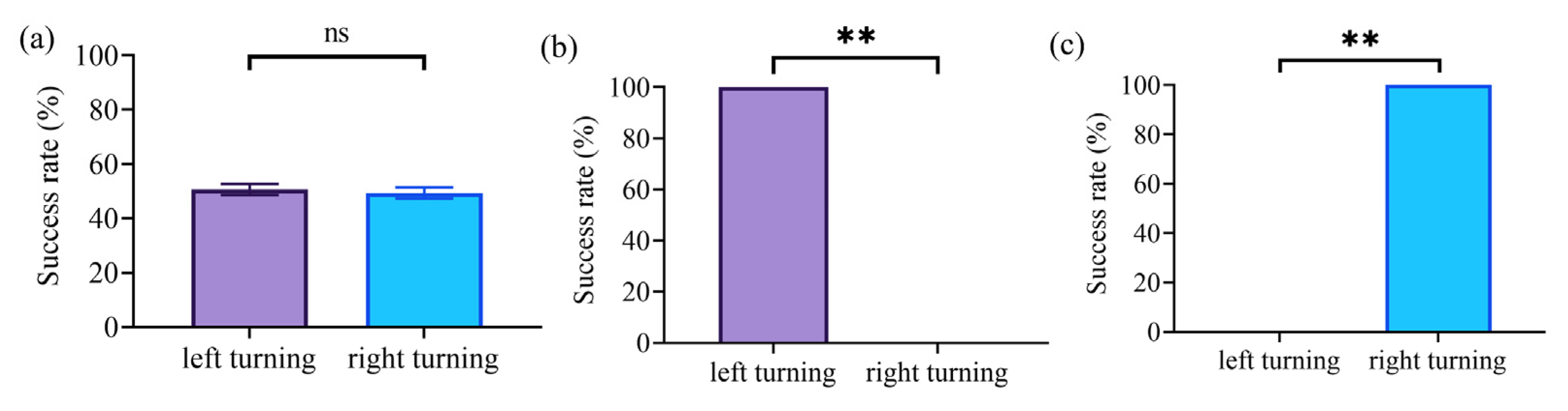
3.2. Turning Movement Control in Rats Based on NS Pathway Stimulation
4. Discussion
4.1. Electrical Stimulation of the VTA Induces Stable Inclined Movement
4.2. Electrical Stimulation of the NS Pathway Induces Immediate Turning Movements
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Latif, T.; Bozkurt, A. Line following terrestrial insect biobots. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 972–975. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Zhao, J.; Ma, Z.; Wang, W.; Yan, S.; Jin, Y.; Fang, Y. Experimental Verification on Steering Flight of Honeybee by Electrical Stimulation. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2022, 2022, 9895837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo-Doan, T.T.; Dung, V.T.; Sato, H. A Cyborg Insect Reveals a Function of a Muscle in Free Flight. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2022, 2022, 9780504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmkuhle, M.; Vetter, R.; Parikh, H.; Carrier, J.; Kipke, D. Implantable neural interfaces for characterizing population responses to odorants and electrical stimuli in the nurse shark, Ginglymostoma cirratum. Chem. Senses 2006, 31, A14. [Google Scholar]
- Wenbo, W.; Ce, G.; Jiurong, S.; Zhendong, D. Locomotion Elicited by Electrical Stimulation in the Midbrain of the Lizard Gekko gecko. In Intelligent Unmanned Systems: Theory and Applications; Budiyono, A., Riyanto, B., Joelianto, E., Eds.; Studies in Computational Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 192, pp. 145–153. ISBN 978-3-642-00263-2. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Dai, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Tang, Y. Modulating Motor Behaviors by Electrical Stimulation of Specific Nuclei in Pigeons. J. Bionic Eng. 2015, 12, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwar, S.K.; Xu, S.; Hawley, E.S.; Weiss, S.A.; Moxon, K.A.; Chapin, J.K. Rat navigation guided by remote control. Nature 2002, 417, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Li, D.; Lin, R.; Yang, Z.; Yang, G.; Zhong, T.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Bao, H.; et al. A battery-free anti-inflammatory brain remote for spatiotemporal guiding movement of mice. Appl. Mater. Today 2024, 37, 102141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, R.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Su, X. A New Robo-Animals Navigation Method Guided by the Remote Control. In Proceedings of the 2009 2nd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics, Tianjin, China, 17–19 October 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Yu, C.; Jia, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zheng, X. Using dlPAG-evoked immobile behavior in animal-robotics navigation. In Proceedings of the 2010 5th International Conference on Computer Science & Education, Hefei, China, 24–27 August 2010; pp. 1295–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Khajei, S.; Shalchyan, V.; Daliri, M.R. Ratbot navigation using deep brain stimulation in ventral posteromedial nucleus. Bioengineered 2019, 10, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.; Lee, J.C.T.; Zheng, X. A novel turning behavior control method for rat-robot through the stimulation of ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 298, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xu, K.; Gong, Y.; Zheng, N.; Zheng, X.; Pan, G. Automatic Training of Rat Cyborgs for Navigation. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 2016, 6459251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Zheng, X. Automatic navigation for rat-robots with modeling of the human guidance. J. Bionic Eng. 2013, 10, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Zheng, X. An automatic control model for rat-robot. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 7413–7416. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, H.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Qu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Xu, K.; Zheng, X. Optogenetics Based Rat–Robot Control: Optical Stimulation Encodes “Stop” and “Escape” Commands. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 1851–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.C.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.M.; Zheng, X.X.; Xu, K.D. A Rat-Robot Control System Based on Optogenetics. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 461, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Qu, Y.; Guo, S.; Shi, Z.; Xu, K.; Zheng, X. Encode the STOP command by photo-stimulation for precise control of rat-robot. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 2172–2175. [Google Scholar]
- Majkutewicz, I.; Cecot, T.; Jerzemowska, G.; Myślińska, D.; Plucińska, K.; Trojniar, W.; Wrona, D. Lesion of the ventral tegmental area amplifies stimulation-induced Fos expression in the rat brain. Brain Res. 2010, 1320, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S.M.; Famous, K.R.; Sadri-Vakili, G.; Kumaresan, V.; Schmidt, H.D.; Bass, C.E.; Terwilliger, E.F.; Cha, J.-H.J.; Pierce, R.C. CaMKII: A biochemical bridge linking accumbens dopamine and glutamate systems in cocaine seeking. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björklund, A.; Dunnett, S.B. Dopamine neuron systems in the brain: An update. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Marsden, C. What do the basal ganglia do? Lancet 1998, 351, 1801–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsden, C.D. What do the basal ganglia tell premotor cortical areas? Ciba Found. Symp. 1987, 132, 282–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kr, B.; Sj, C. The Striosome and Matrix Compartments of the Striatum: A Path through the Labyrinth from Neurochemistry toward Function. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Lammers, J.H.; Meelis, W.; Kruk, M.R.; van der Poel, A.M. Hypothalamic substrates for brain stimulation-induced grooming, digging and circling in the rat. Brain Res. 1987, 418, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuthnott, G.W.; Ungerstedt, U. Turning behavior induced by electrical stimulation of the nigro-neostriatal system of the rat. Exp. Neurol. 1975, 47, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, D.H. Motor responses induced by stimulation of the substantia nigra. Exp. Neurol. 1973, 41, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, D.H.; Hires, S.A.; Guo, Z.V.; Li, N.; Yu, J.; Sun, Q.-Q.; Huber, D.; Svoboda, K. Neural coding during active somatosensation revealed using illusory touch. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, M.-Y.; Han, X.; Zhao, T.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Lu, G.-Y.; Wu, N.; Song, R.; Li, J. Re-examining the role of ventral tegmental area dopaminergic neurons in motor activity and reinforcement by chemogenetic and optogenetic manipulation in mice. Metab. Brain Dis. 2019, 34, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Murris, S.R.; Isa, K.; Onoe, H.; Koshimizu, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Vanduffel, W.; Isa, T. Divergent Whole Brain Projections from the Ventral Midbrain in Macaques. Cereb. Cortex 2021, 31, 2913–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosp, J.A.; Nolan, H.E.; Luft, A.R. Topography and collateralization of dopaminergic projections to primary motor cortex in rats. Exp. Brain Res. 2015, 233, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Inoue, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Ishida, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Isa, T.; Takada, M.; Nishimura, Y. A multisynaptic pathway from the ventral midbrain toward spinal motoneurons in monkeys. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 1731–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.V.; Tsien, J.Z. Conjunctive Processing of Locomotor Signals by the Ventral Tegmental Area Neuronal Population. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.-S.; Steffensen, S.C.; Henriksen, S.J. Discharge Profiles of Ventral Tegmental Area GABA Neurons during Movement, Anesthesia, and the Sleep–Wake Cycle. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puryear, C.B.; Kim, M.J.; Mizumori, S.J.Y. Conjunctive encoding of movement and reward by ventral tegmental area neurons in the freely navigating rodent. Behav. Neurosci. 2010, 124, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbuthnott, G.W.; Crow, T.J. Relation of contraversive turning to unilateral release of dopamine from the nigrostriatal pathway in rats. Exp. Neurol. 1971, 30, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, C.A.; Basso, M.A. Optogenetic activation of the inhibitory nigro-collicular circuit evokes contralateral orienting movements in mice. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Training Procedure | Accuracy | Steering Consistency | Long-Term Stability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1BF [7] | 1–2 weeks | No strong correlation between steering angle and stimulus parameters | More consistent steering direction | about one week |
| VPM [11,12] | no training | Steering angle is parametrically controllable, but continuous electrical stimulation inhibits steering behavior in rats. | The VPM stimulation may create contralateral or ipsilateral turning behaviors. | about one month |
| Our method | no training | Steering angle is parametrically controllable. | More consistent steering direction | about one month |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Liu, H.; Li, G.; Lang, Y.; Tang, R.; Yang, F. A Novel Method for the Locomotion Control of a Rat Robot via the Electrical Stimulation of the Ventral Tegmental Area and Nigrostriatal Pathway. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040348
Li B, Liu H, Li G, Lang Y, Tang R, Yang F. A Novel Method for the Locomotion Control of a Rat Robot via the Electrical Stimulation of the Ventral Tegmental Area and Nigrostriatal Pathway. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(4):348. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040348
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bo, Honghao Liu, Guanghui Li, Yiran Lang, Rongyu Tang, and Fengbao Yang. 2025. "A Novel Method for the Locomotion Control of a Rat Robot via the Electrical Stimulation of the Ventral Tegmental Area and Nigrostriatal Pathway" Brain Sciences 15, no. 4: 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040348
APA StyleLi, B., Liu, H., Li, G., Lang, Y., Tang, R., & Yang, F. (2025). A Novel Method for the Locomotion Control of a Rat Robot via the Electrical Stimulation of the Ventral Tegmental Area and Nigrostriatal Pathway. Brain Sciences, 15(4), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040348





