VGF and Its Derived Peptides in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. ALS
1.2. Neuropeptides
1.3. VGF Precursor Protein and Its Derived Peptides
1.4. Methods
2. VGF Expression and Changes in ALS Nervous System
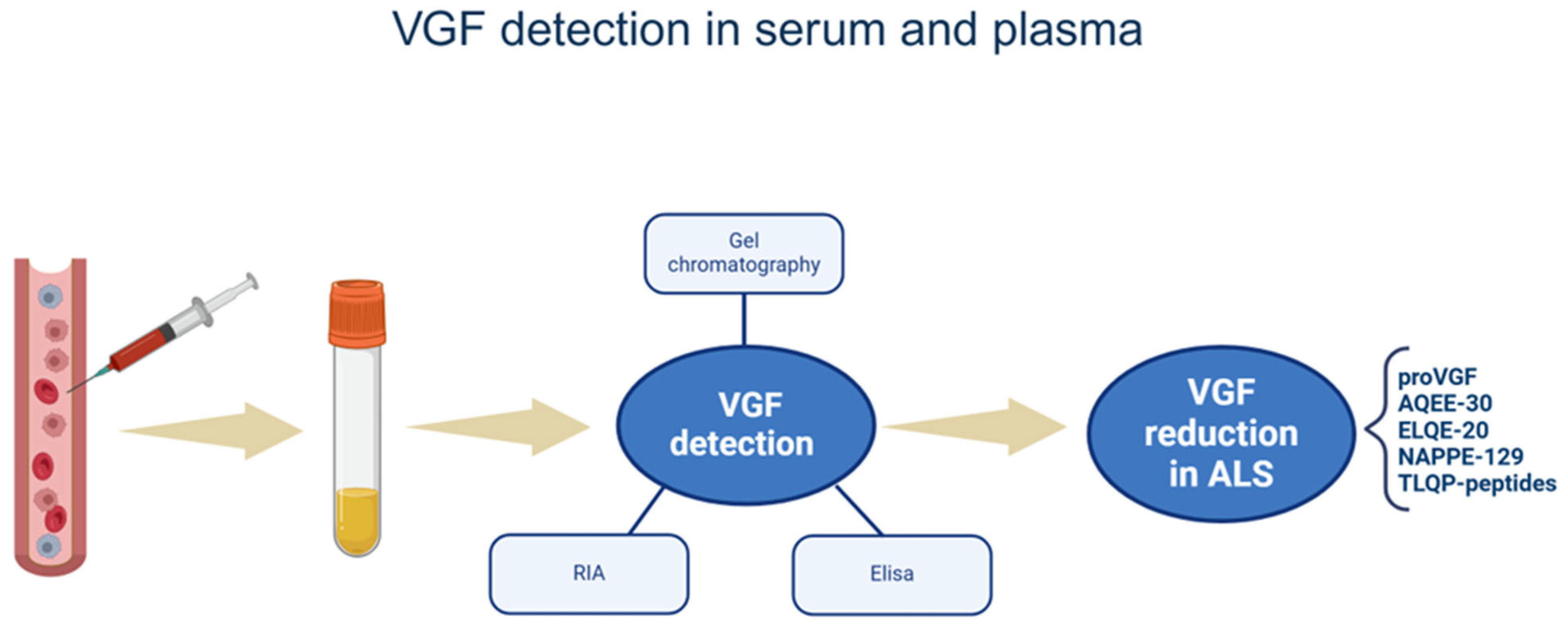
3. VGF Changes in CSF, Serum, and Plasma of ALS Patients
3.1. VGF Changes in CSF
3.2. VGF Changes in Serum and Plasma
4. VGF Role in ALS Mechanisms
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, R.H.; Al-Chalabi, A. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brotman, R.G.; Moreno-Escobar, M.C.; Joseph, J.; Munakomi, S.; Pawar, G. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, N.L.; Van Dyke, J.; Nashold, L.; Satriotomo, I.; Suzuki, M.; Mitchell, G.S. Ventilatory Control in ALS. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2013, 189, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garnier, M.; Camdessanché, J.-P.; Cassereau, J.; Codron, P. From Suspicion to Diagnosis: Exploration Strategy for Suspected Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Ann. Med. 2024, 56, 2398199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Masrori, P.; Van Damme, P. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Clinical Review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 1918–1929. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, P.M.; Al-Chalabi, A. Clinical Genetics of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: What Do We Really Know? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 603–615. [Google Scholar]
- Lill, C.M.; Abel, O.; Bertram, L.; Al-Chalabi, A. Keeping up with Genetic Discoveries in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: The ALSoD and ALSGene Databases. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2011, 12, 238–249. [Google Scholar]
- Vidovic, M.; Müschen, L.H.; Brakemeier, S.; Machetanz, G.; Naumann, M.; Castro-Gomez, S. Current State and Future Directions in the Diagnosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Cells 2023, 12, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, H.; Vullaganti, M.; Kwan, J. Advances in Molecular Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. BMJ 2023, 383, e075037. [Google Scholar]
- Bellingham, M.C. A Review of the Neural Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Efficiency of Riluzole in Treating Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: What Have We Learned in the Last Decade? CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2011, 17, 4–31. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, K.; Itoyama, Y.; Sobue, G.; Tsuji, S.; Aoki, M.; Doyu, M.; Hamada, C.; Kondo, K.; Yoneoka, T.; Akimoto, M.; et al. Confirmatory Double-Blind, Parallel-Group, Placebo-Controlled Study of Efficacy and Safety of Edaravone (MCI-186) in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2014, 15, 610–617. [Google Scholar]
- Everett, W.H.; Bucelli, R.C. Tofersen for SOD1 ALS. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2024, 14, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Chalabi, A.; Hardiman, O.; Kiernan, M.C.; Chiò, A.; Rix-Brooks, B.; Van Den Berg, L.H. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Moving towards a New Classification System. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riancho, J.; Bosque-Varela, P.; Perez-Pereda, S.; Povedano, M.; De Munaín, A.L.; Santurtun, A. The Increasing Importance of Environmental Conditions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2018, 62, 1361–1374. [Google Scholar]
- Zufiría, M.; Gil-Bea, F.J.; Fernández-Torrón, R.; Poza, J.J.; Muñoz-Blanco, J.L.; Rojas-García, R.; Riancho, J.; De Munain, A.L. ALS: A Bucket of Genes, Environment, Metabolism and Unknown Ingredients. Prog. Neurobiol. 2016, 142, 104–129. [Google Scholar]
- Sturmey, E.; Malaspina, A. Blood Biomarkers in ALS: Challenges, Applications and Novel Frontiers. Acta Neuro Scand. 2022, 146, 375–388. [Google Scholar]
- Bowser, R.; Turner, M.R.; Shefner, J. Biomarkers in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Opportunities and Limitations. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 631–638. [Google Scholar]
- Foerster, B.R.; Pomper, M.G.; Callaghan, B.C.; Petrou, M.; Edden, R.A.E.; Mohamed, M.A.; Welsh, R.C.; Carlos, R.C.; Barker, P.B.; Feldman, E.L. An Imbalance Between Excitatory and Inhibitory Neurotransmitters in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Revealed by Use of 3-T Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 1009. [Google Scholar]
- Walczak-Nowicka, Ł.J.; Herbet, M. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases and the Role of Acetylcholinesterase in Their Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreux-Varoquaux, O.; Bensimon, G.; Lacomblez, L.; Salachas, F.; Pradat, P.F.; Le Forestier, N.; Marouan, A.; Dib, M.; Meininger, V. Glutamate Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Reappraisal Using a New HPLC Method with Coulometric Detection in a Large Cohort of Patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 193, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, A.F. Overview of Neuropeptides: Awakening the Senses? Headache 2017, 57, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Dockray, G.J. The Biosynthesis of Regulatory Peptides. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1987, 136 Pt 2, S9–S15. [Google Scholar]
- De-Miguel, F.F.; Leon-Pinzon, C.; Torres-Platas, S.G.; del-Pozo, V.; Hernández-Mendoza, G.A.; Aguirre-Olivas, D.; Méndez, B.; Moore, S.; Sánchez-Sugía, C.; García-Aguilera, M.A.; et al. Extrasynaptic Communication. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 638858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Pol, A.N. Neuropeptide Transmission in Brain Circuits. Neuron 2012, 76, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Yin, S.; Jang, R.; Wang, J.; Xue, Z.; Xu, T. NeuroPep: A Comprehensive Resource of Neuropeptides. Database 2015, 2015, bav038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S. A Short History, Principles, and Types of ELISA, and Our Laboratory Experience with Peptide/Protein Analyses Using ELISA. Peptides 2015, 72, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, H. Monoplex and Multiplex Immunoassays: Approval, Advancements, and Alternatives. Comp. Clin. Path. 2021, 31, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellanti, R.; Keddie, S.; Lunn, M.P.; Rinaldi, S. Ultrasensitive Assay Technology and Fluid Biomarkers for the Evaluation of Peripheral Nerve Disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2024, 95, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xiang, R.; Horváth, C.; Wilkins, J.A. The Role of Liquid Chromatography in Proteomics. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1053, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catherman, A.D.; Skinner, O.S.; Kelleher, N.L. Top Down Proteomics: Facts and Perspectives. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 445, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Po, A.; Eyers, C.E. Top-Down Proteomics and the Challenges of True Proteoform Characterization. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 22, 3663–3675. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, B.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, F. The Utility of Proteases in Proteomics, from Sequence Profiling to Structure and Function Analysis. Proteomics 2023, 23, 2200132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salton, S.R.J.; Fischberg, D.J.; Dong, K.W. Structure of the Gene Encoding VGF, a Nervous System-Specific mRNA that is Rapidly and Selectively Induced by Nerve Growth Factor in PC12 Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 2335–2349. [Google Scholar]
- Alder, J.; Thakker-Varia, S.; Bangasser, D.A.; Kuroiwa, M.; Plummer, M.R.; Shors, T.J.; Black, I.B. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor-Induced Gene Expression Reveals Novel Actions of VGF in Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10800–10808. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eagleson, K.L.; Fairfull, L.D.; Salton, S.R.J.; Levitt, P. Regional Differences in Neurotrophin Availability Regulate Selective Expression of VGF in the Developing Limbic Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 9315–9324. [Google Scholar]
- Hawley, R.; Scheibe, R.; Wagner, J. NGF Induces the Expression of the VGF Gene through a cAMP Response Element. J. Neurosci. 1992, 12, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar]
- Possenti, R.; Di Rocco, G.; Nasi, S.; Levi, A. Regulatory Elements in the Promoter Region of Vgf, a Nerve Growth Factor-Inducible Gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 3815–3819. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, G.-L.; Levi, A.; Possenti, R. A Novel Neuroendocrine Gene Product: Selective VGF8a Gene Expression and Immuno-Localisation of the VGF Protein in Endocrine and Neuronal Populations. Mol. Brain Res. 1992, 13, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, G.-L.; Possenti, R. Vgf A Neurotrophin-Inducible Gene Expressed in Neuroendocrine Tissues. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 7, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancia, C.; Noli, B.; Boido, M.; Pilleri, R.; Boi, A.; Puddu, R.; Marrosu, F.; Vercelli, A.; Bongioanni, P.; Ferri, G.-L.; et al. TLQP Peptides in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Possible Blood Biomarkers with a Neuroprotective Role. Neuroscience 2018, 380, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.E.; Brameld, J.M.; Jethwa, P.H. Neuroendocrine Role for VGF. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, G.L.; Gaudio, R.M.; Cossu, M.; Rinaldi, A.M.; Polak, J.M.; Berger, P.; Possenti, R. The “VGF” Protein in Rat Adenohypophysis: Sex Differences and Changes during the Estrous Cycle and after Gonadectomy. Endocrinology 1995, 136, 2244–2251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Possenti, R.; Rinaldi, A.M.; Ferri, G.-L.; Borboni, P.; Trani, E.; Levi, A. Expression, Processing, and Secretion of the Neuroendocrine VGF Peptides by INS-1 Cells*. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 3727–3735. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cocco, C.; Brancia, C.; Pirisi, I.; D’Amato, F.; Noli, B.; Possenti, R.; Ferri, G.-L. VGF Metabolic-Related Gene: Distribution of Its Derived Peptides in Mammalian Pancreatic Islets. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2007, 55, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, K.; Osaki, T.; Minamino, N. Large-Scale Identification of Endogenous Secretory Peptides Using Electron Transfer Dissociation Mass Spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 700–709. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, K.; Satomi, Y.; Takao, T.; Minamino, N. Snapshot Peptidomics of the Regulated Secretory Pathway. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2009, 8, 1638–1647. [Google Scholar]
- Bresciani, E.; Possenti, R.; Coco, S.; Rizzi, L.; Meanti, R.; Molteni, L.; Locatelli, V.; Torsello, A. TLQP-21, A VGF-Derived Peptide Endowed of Endocrine and Extraendocrine Properties: Focus on In Vitro Calcium Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocco, C.; Noli, B.; Manconi, B.; Contini, C.; Manca, E.; Pisanu, C.; Meloni, A.; Manchia, M.; Paribello, P.; Chillotti, C.; et al. Lower Plasma Levels of Selective VGF (Non-Acronymic) Peptides in Bipolar Disorder: Comparative Analysis Reveals Distinct Patterns across Mood Disorders and Healthy Controls. Neuropsychobiology 2024, 83, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancia, C.; Noli, B.; Boido, M.; Boi, A.; Puddu, R.; Borghero, G.; Marrosu, F.; Bongioanni, P.; Orrù, S.; Manconi, B.; et al. VGF Protein and Its C-Terminal Derived Peptides in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Human and Animal Model Studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164689. [Google Scholar]
- Canu, N.; Possenti, R.; Ricco, A.S.; Rocchi, M.; Levi, A. Cloning, Structural Organization Analysis, and Chromosomal Assignment of the Human Gene for the Neurosecretory Protein VGF. Genomics 1997, 45, 443–446. [Google Scholar]
- Bartolomucci, A.; Possenti, R.; Mahata, S.K.; Fischer-Colbrie, R.; Loh, Y.P.; Salton, S.R.J. The Extended Granin Family: Structure, Function, and Biomedical Implications. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 755–797. [Google Scholar]
- Jethwa, P.H.; Warner, A.; Nilaweera, K.N.; Brameld, J.M.; Keyte, J.W.; Carter, W.G.; Bolton, N.; Bruggraber, M.; Morgan, P.J.; Barrett, P.; et al. VGF-Derived Peptide, TLQP-21, Regulates Food Intake and Body Weight in Siberian Hamsters. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 4044–4055. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jethwa, P.H.; Ebling, F.J.P. Role of VGF-Derived Peptides in the Control of Food Intake, Body Weight and Reproduction. Neuroendocrinology 2008, 88, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bozdagi, O.; Rich, E.; Tronel, S.; Sadahiro, M.; Patterson, K.; Shapiro, M.L.; Alberini, C.M.; Huntley, G.W.; Salton, S.R.J. The Neurotrophin-Inducible Gene Vgf Regulates Hippocampal Function and Behavior through a Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor-Dependent Mechanism. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 9857–9869. [Google Scholar]
- Thakker-Varia, S.; Krol, J.J.; Nettleton, J.; Bilimoria, P.M.; Bangasser, D.A.; Shors, T.J.; Black, I.B.; Alder, J. The Neuropeptide VGF Produces Antidepressant-Like Behavioral Effects and Enhances Proliferation in the Hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 12156–12167. [Google Scholar]
- Noda, Y.; Shimazawa, M.; Tanaka, H.; Tamura, S.; Inoue, T.; Tsuruma, K.; Hara, H. VGF and Striatal Cell Damage in in Vitro and in Vivo Models of Huntington’s Disease. Pharmacol. Res. Perspec 2015, 3, e00140. [Google Scholar]
- Hunsberger, J.G.; Newton, S.S.; Bennett, A.H.; Duman, C.H.; Russell, D.S.; Salton, S.R.; Duman, R.S. Antidepressant Actions of the Exercise-Regulated Gene VGF. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1476–1482. [Google Scholar]
- El Gaamouch, F.; Audrain, M.; Lin, W.-J.; Beckmann, N.; Jiang, C.; Hariharan, S.; Heeger, P.S.; Schadt, E.E.; Gandy, S.; Ehrlich, M.E.; et al. VGF-Derived Peptide TLQP-21 Modulates Microglial Function through C3aR1 Signaling Pathways and Reduces Neuropathology in 5xFAD Mice. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020, 15, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.; Shi, M.; Jin, J.; Albin, R.L.; Lieberman, A.; Gearing, M.; Lin, B.; Pan, C.; Yan, X.; Kashima, D.T.; et al. Proteomics Identification of Proteins in Human Cortex Using Multidimensional Separations and MALDI Tandem Mass Spectrometer. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 1818–1823. [Google Scholar]
- Zanon, A.; Rakovic, A.; Blankenburg, H.; Doncheva, N.T.; Schwienbacher, C.; Serafin, A.; Alexa, A.; Weichenberger, C.X.; Albrecht, M.; Klein, C.; et al. Profiling of Parkin-Binding Partners Using Tandem Affinity Purification. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78648. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, J.P.; Ethier, E.C.; Novielli, A.; Malone, A.; Ramirez, C.E.; Salloum, L.; Trombetta, B.A.; Kivisäkk, P.; Bremang, M.; Selzer, S.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid and Brain Proteoforms of the Granin Neuropeptide Family in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2023, 34, 649–667. [Google Scholar]
- Karayel, O.; Winter, S.V.; Padmanabhan, S.; Kuras, Y.I.; Vu, D.T.; Tuncali, I.; Merchant, K.; Wills, A.-M.; Scherzer, C.R.; Mann, M. Proteome Profiling of Cerebrospinal Fluid Reveals Biomarker Candidates for Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Steenoven, I.; Noli, B.; Cocco, C.; Ferri, G.-L.; Oeckl, P.; Otto, M.; Koel-Simmelink, M.J.A.; Bridel, C.; Van Der Flier, W.M.; Lemstra, A.W.; et al. VGF Peptides in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virreira Winter, S.; Karayel, O.; Strauss, M.T.; Padmanabhan, S.; Surface, M.; Merchant, K.; Alcalay, R.N.; Mann, M. Urinary Proteome Profiling for Stratifying Patients with Familial Parkinson’s Disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocco, C.; Corda, G.; Lisci, C.; Noli, B.; Carta, M.; Brancia, C.; Manca, E.; Masala, C.; Marrosu, F.; Solla, P.; et al. VGF Peptides as Novel Biomarkers in Parkinson’s Disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2020, 379, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hölttä, M.; Minthon, L.; Hansson, O.; Holmén-Larsson, J.; Pike, I.; Ward, M.; Kuhn, K.; Rüetschi, U.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. An Integrated Workflow for Multiplex CSF Proteomics and Peptidomics—Identification of Candidate Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.S.; Bal, L.C.; Winschel, I.; Manca, E.; Walkenhorst, M.; Sevgili, B.; Sonner, J.K.; Di Liberto, G.; Mayer, C.; Binkle-Ladisch, L.; et al. The NR4A2/VGF Pathway Fuels Inflammation-Induced Neurodegeneration via Promoting Neuronal Glycolysis. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e177692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumi, R.; Petri, S.; Siwy, J.; Latosinska, A.; Raad, J.; Zürbig, P.; Skripuletz, T.; Mischak, H.; Beige, J. Small Peptide CSF Fingerprint of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0302280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, T.; Koizumi, S.; Takagi, A.; Hatori, T.; Kuwabara, K.; Fujino, O.; Fukunaga, Y. Identification of a Novel Biomarker Candidate, a 4.8-kDa Peptide Fragment from a Neurosecretory Protein VGF Precursor, by Proteomic Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid from Children with Acute Encephalopathy Using SELDI-TOF-MS. BMC Neurol. 2011, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Lange, D.J.; Ho, L.; Bonini, S.; Shao, B.; Salton, S.R.; Thomas, S.; Pasinetti, G.M. Vgf Is a Novel Biomarker Associated with Muscle Weakness in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), with a Potential Role in Disease Pathogenesis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 5, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Noda, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Nakamura, S.; Ito, J.; Kakita, A.; Hara, H.; Shimazawa, M. Identification of VGF Nerve Growth Factor Inducible-Producing Cells in Human Spinal Cords and Expression Change in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Li, S.; Li, X.-J.; Yang, W. New Pathogenic Insights from Large Animal Models of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Protein Cell 2022, 13, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pasinetti, G.M.; Ungar, L.H.; Lange, D.J.; Yemul, S.; Deng, H.; Yuan, X.; Brown, R.H.; Cudkowicz, M.E.; Newhall, K.; Peskind, E.; et al. Identification of Potential CSF Biomarkers in ALS. Neurology 2006, 66, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijte, D.; McDonnell, L.A.; Balog, C.I.A.; Bossers, K.; Deelder, A.M.; Swaab, D.F.; Verhaagen, J.; Mayboroda, O.A. A Novel Peptidomics Approach to Detect Markers of Alzheimer’s Disease in Cerebrospinal Fluid. Methods 2012, 56, 500–507. [Google Scholar]
- Skillbäck, T.; Delsing, L.; Synnergren, J.; Mattsson, N.; Janelidze, S.; Nägga, K.; Kilander, L.; Hicks, R.; Wimo, A.; Winblad, B.; et al. CSF/Serum Albumin Ratio in Dementias: A Cross-Sectional Study on 1861 Patients. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 59, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, G.; Na, C.H.; Renuse, S.; Madugundu, A.K.; Albert, M.; Moghekar, A.; Pandey, A. Quantitative Proteomic Profiling of Cerebrospinal Fluid to Identify Candidate Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2019, 13, 1800105. [Google Scholar]
- Barschke, P.; Oeckl, P.; Steinacker, P.; Al Shweiki, M.R.; Weishaupt, J.H.; Landwehrmeyer, G.B.; Anderl-Straub, S.; Weydt, P.; Diehl-Schmid, J.; Danek, A.; et al. Different CSF Protein Profiles in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia with C9orf72 Hexanucleotide Repeat Expansion. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 91, 503–511. [Google Scholar]
- Pingle, S.C.; Lin, F.; Anekoji, M.S.; Patro, C.P.K.; Datta, S.; Jones, L.D.; Kesari, S.; Ashili, S. Exploring the Role of Cerebrospinal Fluid as Analyte in Neurologic Disorders. Future Sci. OA 2023, 9, FSO851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.W. Complications of lumbar puncture. Neurol. Clin. 1998, 16, 83–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazawa, M.; Tanaka, H.; Ito, Y.; Morimoto, N.; Tsuruma, K.; Kadokura, M.; Tamura, S.; Inoue, T.; Yamada, M.; Takahashi, H.; et al. An Inducer of VGF Protects Cells against ER Stress-Induced Cell Death and Prolongs Survival in the Mutant SOD1 Animal Models of Familial ALS. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15307. [Google Scholar]
- Noda, Y.; Motoyama, S.; Nakamura, S.; Shimazawa, M.; Hara, H. Neuropeptide VGF-Derived Peptide LQEQ-19 Has Neuroprotective Effects in an In Vitro Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 897–904. [Google Scholar]
- Corda, G.; Noli, B.; Manconi, B.; Brancia, C.; Pellegrini, M.; Naro, F.; Olianas, A.; Ferri, G.-L.; Cocco, C. TLQP-21 Changes in Response to a Glucose Load. Tissue Cell 2021, 68, 101471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noli, B.; Brancia, C.; Corda, G.; Ferri, G.-L.; Cocco, C. Dynamic of TLQP-Peptides upon Fasting. Tissue Cell 2020, 65, 101368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dalbøge, L.S.; Jacobsen, J.M.; Mehrotra, S.; Mercer, A.J.; Cox, N.; Liu, F.; Bennett, C.M.; Said, M.; Tang-Christensen, M.; Raun, K.; et al. Evaluation of VGF Peptides as Potential Anti-Obesity Candidates in Pre-Clinical Animal Models. Peptides 2021, 136, 170444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cocco, C.; Manai, A.L.; Manca, E.; Noli, B. Brain-Biomarker Changes in Body Fluids of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, E.; Noli, B.; Corda, G.; El-Hassani, M.; Manai, A.; Sanna, F.; Argiolas, A.; Melis, M.R.; Manconi, B.; Contini, C.; et al. VGF Modifications Related to Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration Induced by the Pesticide Fipronil in Adult Male Rats. Ann. Anat.-Anat. Anz. 2024, 252, 152194. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.Y.; Osman, J.; Low, T.Y.; Jamal, R. Plasma/Serum Proteomics: Depletion Strategies for Reducing High-Abundance Proteins for Biomarker Discovery. Bioanalysis 2019, 11, 1799–1812. [Google Scholar]


| Reference | Method | Antibody | VGF Peptide/Protein | VGF Sequence | Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [71] | Immunohistochemistry | Non-identified | proVGF | VGF1–617 | h. spinal cord |
| [49] | SEC/HPLC-MS/ELISA Immunohistochemistry | VGF C-terminus | proVGF | VGF1–617 | |
| NAPP-129 | VGF486–617 | ||||
| NAPP-19 | VGF486–504 | ||||
| AQEE-13 | VGF586–602 | m. spinal cord | |||
| ELQE-20 | VGF353–372 | ||||
| [40] | SEC/ELISA | TLQP | proVGF | VGF1–617 | |
| Immunohistochemistry | NAPP-129 | VGF486–617 | |||
| TLQP-21, -30, -42, -62 | VGF556–577/556–587/556–598/556–617 | ||||
| [73] | SELDI-MS | - | ARQN-13 | VGF398–410 | |
| [70] | ELISA sandwich | VGF588–617 and VGF78–340 | proVGF | VGF78–617 | |
| [68] | CE-MS, LC-MS/MS | - | PPGR-39 | VGF24–62 | h. CSF |
| AVPG-13 (N)APPE-19 | VGF47–59 VGF487–504 | ||||
| [70] | RIA | AQEE-30 | AQEE-30 | VGF586–617 | m. CSF |
| [49] | SEC/ELISA | VGF C-terminus | proVGF | VGF1–617 | |
| NAPP-129 | VGF486–617 | ||||
| [40] | SEC/ELISA | TLQP | proVGF | VGF1–617 | h. blood |
| NAPP-129 | VGF486–617 | ||||
| TLQP-21, -30, -42, -62 | VGF556–577/556–587/556–598/556–617 | ||||
| [70] | RIA | AQEE-30 | AQEE-30 | VGF586–617 | |
| [49] | SEC/ELISA | VGF C-terminus | proVGF | VGF1–617 | |
| NAPP-129 | VGF486–617 | ||||
| TLQP-62 | VGF556–617 | m. blood | |||
| AQEE-30 | VGF586–617 | ||||
| [40] | ELISA | TLQP | proVGF | ||
| NAPP-129 | VGF486–617 | ||||
| TLQP-21, -30, -42, -62 | VGF556–577/556–587/556–598/556–617 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manai, A.L.; Caria, P.; Noli, B.; Contini, C.; Manconi, B.; Etzi, F.; Cocco, C. VGF and Its Derived Peptides in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040329
Manai AL, Caria P, Noli B, Contini C, Manconi B, Etzi F, Cocco C. VGF and Its Derived Peptides in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(4):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040329
Chicago/Turabian StyleManai, Antonio Luigi, Paola Caria, Barbara Noli, Cristina Contini, Barbara Manconi, Federica Etzi, and Cristina Cocco. 2025. "VGF and Its Derived Peptides in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis" Brain Sciences 15, no. 4: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040329
APA StyleManai, A. L., Caria, P., Noli, B., Contini, C., Manconi, B., Etzi, F., & Cocco, C. (2025). VGF and Its Derived Peptides in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Brain Sciences, 15(4), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15040329







