Effect of a Plant-Based Nootropic Supplement on Perceptual Decision-Making and Brain Network Interdependencies: A Randomised, Double-Blinded, and Placebo-Controlled Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
What effect does a commercially available nootropic supplement have on perceptual decision-making performance (i.e., the ability to make rapid decisions based on sensory information) and brain network interdependencies (i.e., the collective interactions between brain regions)?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Recruitment, Selection, and Randomisation Schedule
2.2. Interventional Compound
2.3. Experimental Task
2.4. Stimuli
2.5. Behavioural Task
2.6. EEG Recording and Pre-Processing
2.7. Higher-Order Brain Network Interdependencies
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
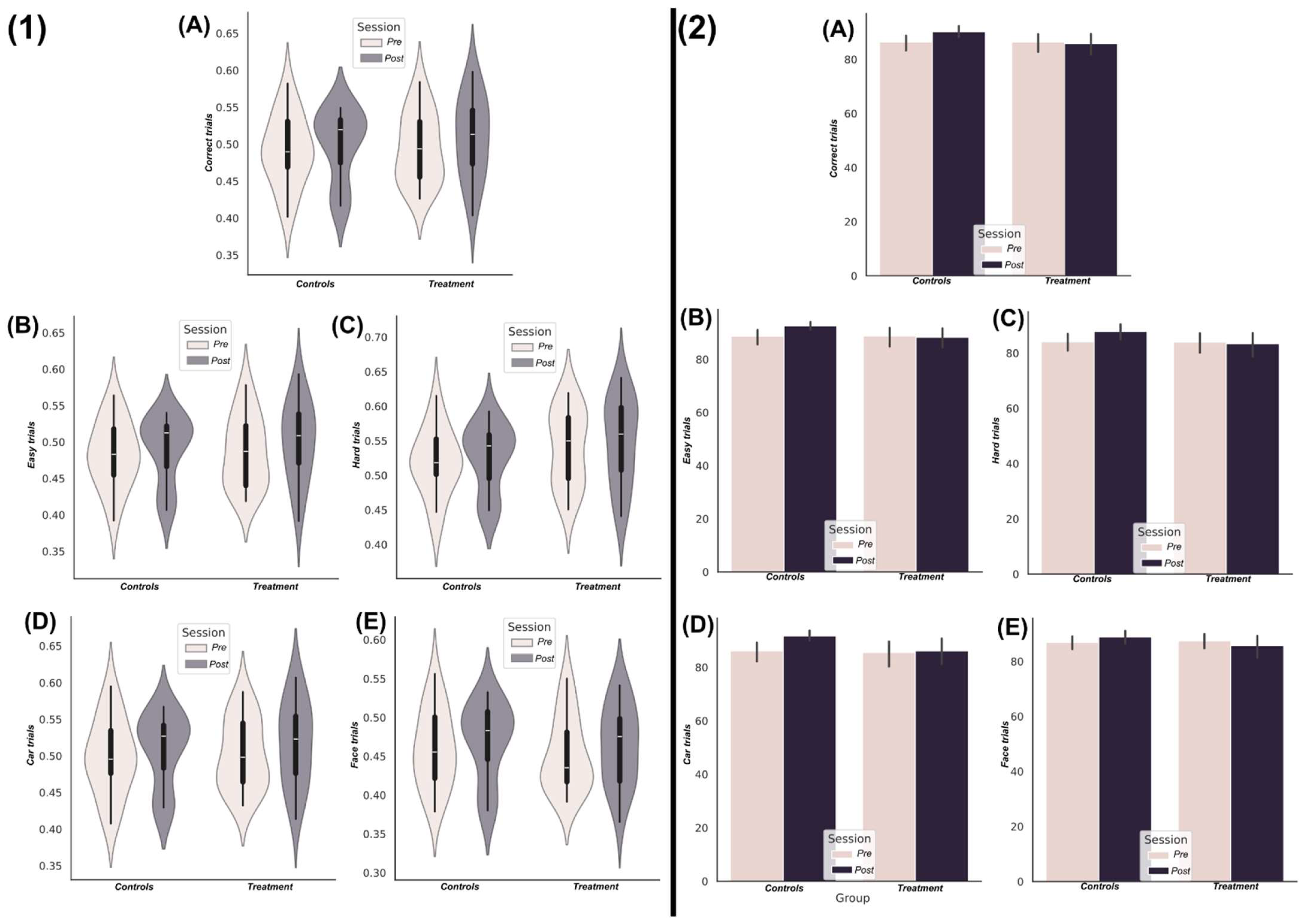
3.1. Nootropic Supplementation Did Not Improve Perceptual Decision-Making Performance
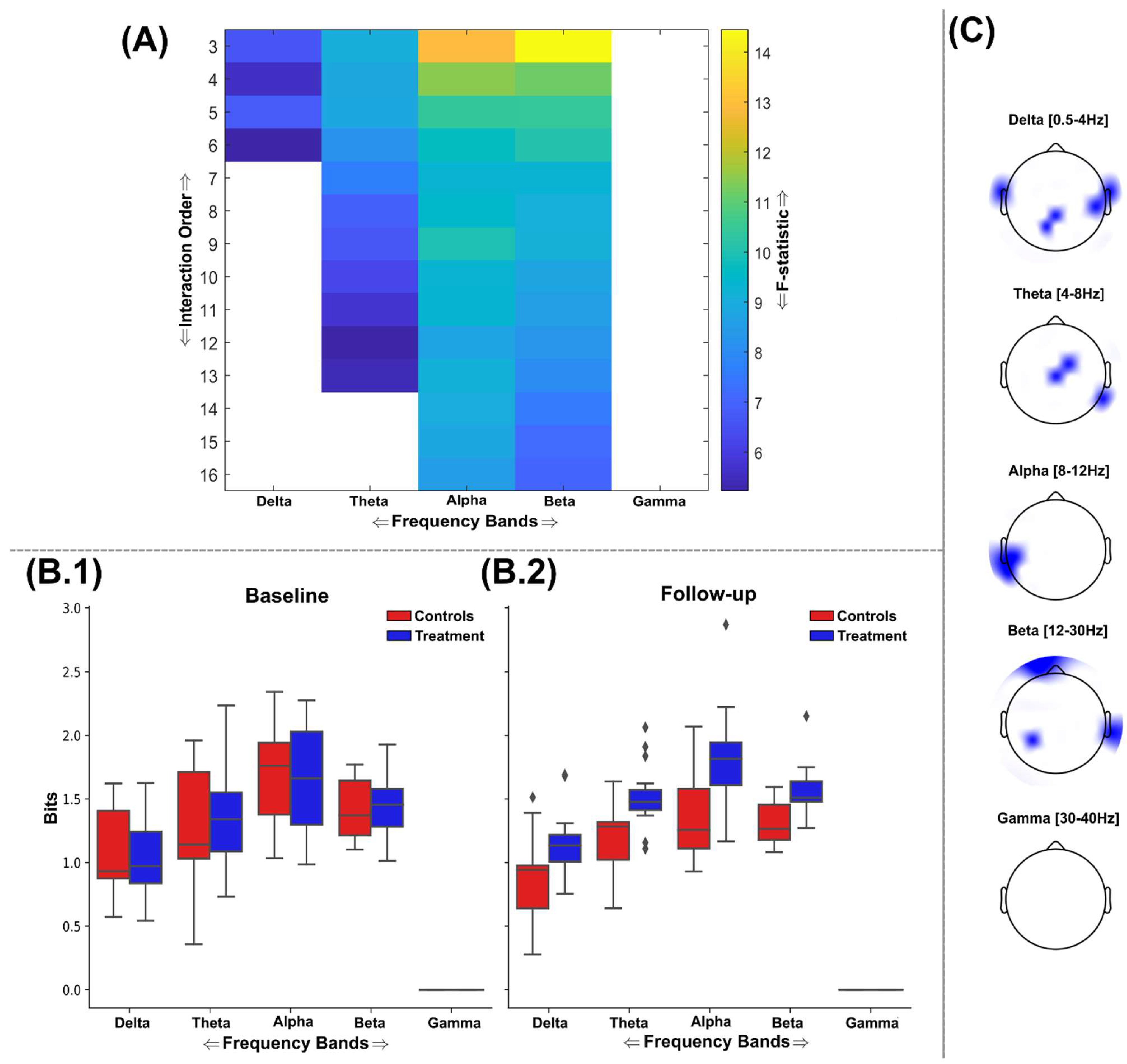
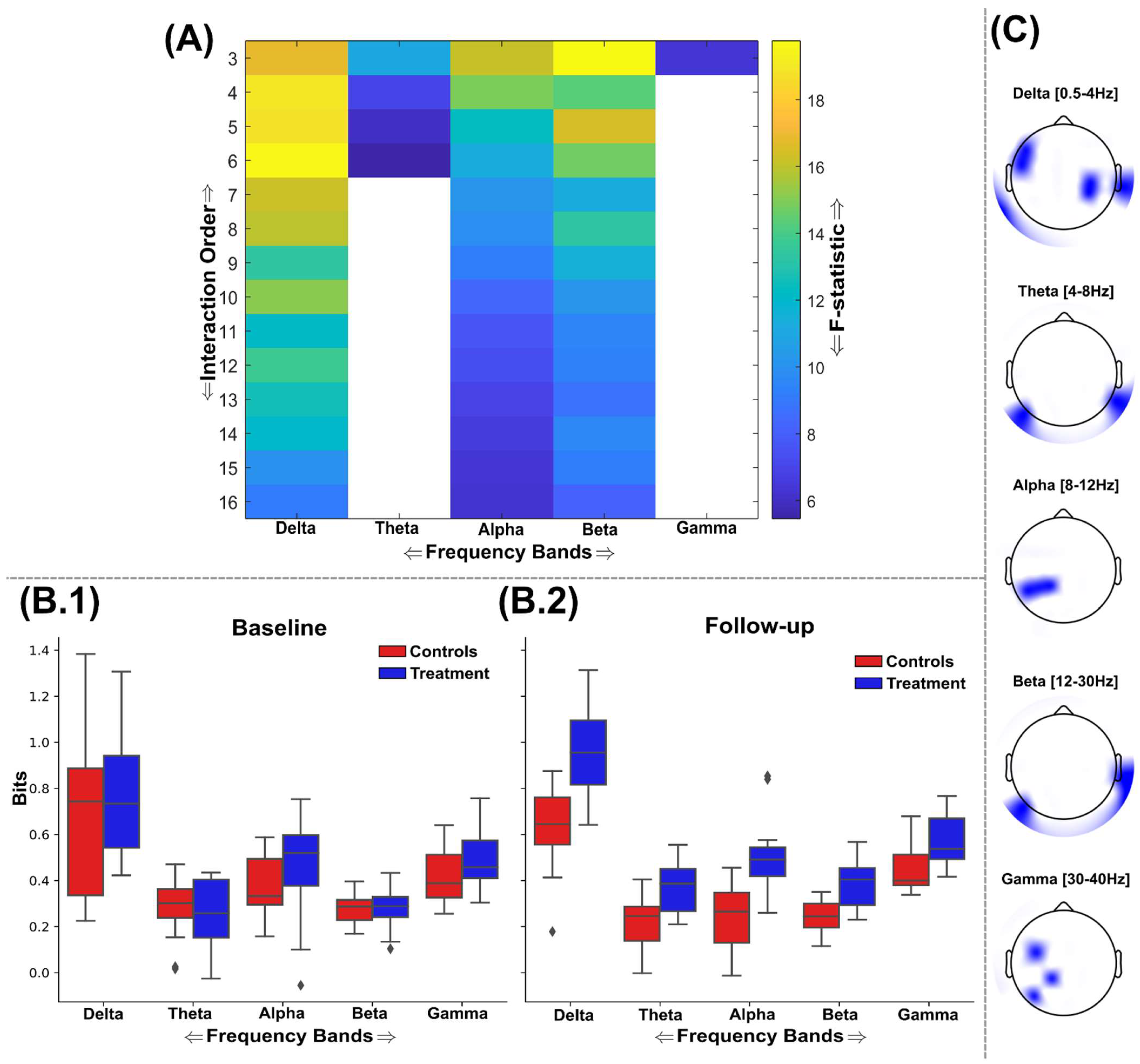
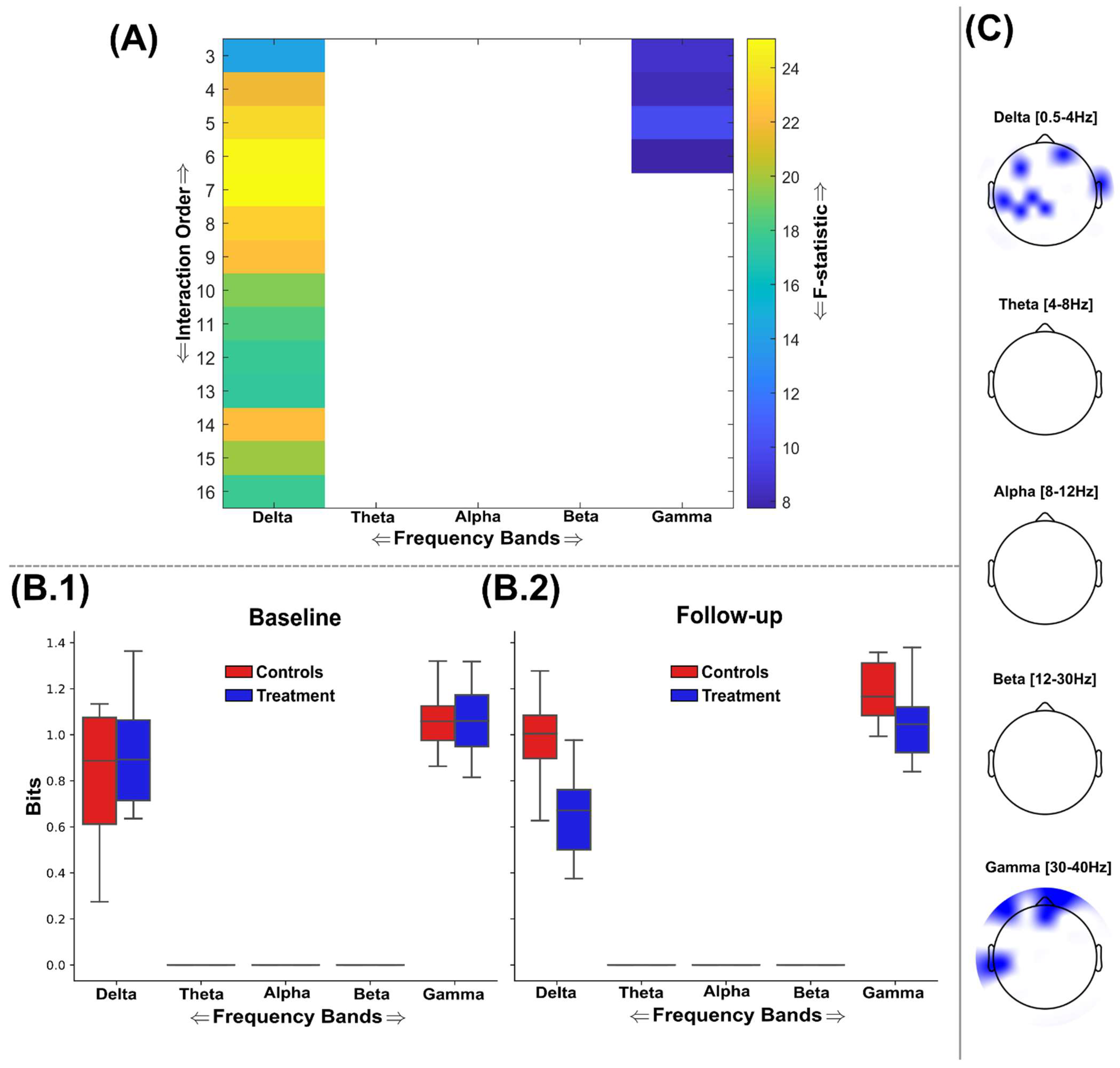
3.2. Information Sharing Across Brain Networks Is Enhanced Following Nootropic Supplementation
3.3. Natural Nootropic Supplement Increases Both the Redundancy and Synergy Between Brain Regions
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malík, M.; Tlustoš, P. Nootropics as cognitive enhancers: Types, dosage and side effects of smart drugs. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, S.; Guirguis, A.; Fergus, S.; Schifano, F. The use and impact of cognitive enhancers among university students: A systematic review. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaco, A.M.; Ribeiro, J.; Nørgaard, L.S. Exploring the use of cognitive enhancement substances among Portuguese university students. Explor. Res. Clin. Soc. Pharm. 2022, 5, 100097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schifano, F.; Catalani, V.; Sharif, S.; Napoletano, F.; Corkery, J.M.; Arillotta, D.; Fergus, S.; Vento, A.; Guirguis, A. Benefits and harms of ‘smart drugs’(nootropics) in healthy individuals. Drugs 2022, 82, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaami, S.; Rinaldi, R.; Bersani, G.; Del Rio, A.; Ciallella, C.; Marinelli, E. Nootropics use in the workplace. Psychiatric and ethical aftermath towards the new frontier of bioengineering. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roe, A.L.; Venkataraman, A. The safety and efficacy of botanicals with nootropic effects. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiroma, S.M.; Taib, C.N.; Moklas, M.A.; Baharuldin, M.T.; Amom, Z.; Jagadeesan, S. The use of nootropics in Alzheimer’s disease: Is there light at the end of the tunnel? Biomed. Res. Ther. 2019, 6, 2937–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorca, C.; Mulet, M.; Arévalo-Caro, C.; Sanchez, M.Á.; Perez, A.; Perrino, M.; Bach-Faig, A.; Aguilar-Martínez, A.; Vilella, E.; Gallart-Palau, X.; et al. Plant-derived nootropics and human cognition: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 5521–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandalise, F.; Roda, E.; Ratto, D.; Goppa, L.; Gargano, M.L.; Cirlincione, F.; Priori, E.C.; Venuti, M.T.; Pastorelli, E.; Savino, E.; et al. Hericium erinaceus in neurodegenerative diseases: From bench to bedside and beyond, how far from the shoreline? J. Fungi 2023, 9, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.J.; Foley, A.G.; O’connell, A.W.; Regan, C.M. Chronic exposure of rats to cognition enhancing drugs produces a neuroplastic response identical to that obtained by complex environment rearing. Neuropsychopharmacology 2006, 31, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyov, V.; Kaptsov, V.; Kovalev, G.; Sengpiel, F. Effects of nootropics on the EEG in conscious rats and their modification by glutamatergic inhibitors. Brain Res. Bull. 2011, 85, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malík, M.; Tlustoš, P. Nootropic herbs, shrubs, and trees as potential cognitive enhancers. Plants 2023, 12, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Saha, S.C.; Sunita, K.; Majumder, M.; Ghorai, M.; Mane, A.B.; Prasanth, D.A.; Kumar, P.; Pandey, D.K.; Al-Tawaha, A.R.; et al. Promising botanical-derived monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors: Pharmacological aspects and structure-activity studies. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 146, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, N.A.; Mat Taib, C.N.; Mohd Moklas, M.A.; Adenan, M.I.; Hidayat Baharuldin, M.T.; Basir, R. Establishing natural nootropics: Recent molecular enhancement influenced by natural nootropic. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 4391375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, E.L.; Jackson, P.A.; Khan, J.; Forster, J.; Heiner, F.; Feistel, B.; Suarez, C.G.; Pischel, I.; Kennedy, D.O. The acute and chronic cognitive and cerebral blood flow effects of a Sideritis scardica (Greek mountain tea) extract: A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled, parallel groups study in healthy humans. Nutrients 2018, 10, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDaniel, M.A.; Maier, S.F.; Einstein, G.O. “Brain-specific” nutrients: A memory cure? Psychol. Sci. Public Interest 2002, 3, 12–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, D.S.; Kulkarni, S.K. Possible role of nitric oxide in the nootropic and antiamnesic effects of neurosteroids on aging-and dizocilpine-induced learning impairment. Brain Res. 1998, 799, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasikumar, P.; Aswathy, M.; Prem, P.T.; Radhakrishnan, K.V.; Chakrapani, P.S. Plant derived bioactive compounds and their potential to enhance adult neurogenesis. Phytomedicine Plus 2022, 2, 100191. [Google Scholar]
- Bonetti, F.; Brombo, G.; Zuliani, G. Nootropics, functional foods, and dietary patterns for prevention of cognitive decline. In Nutrition and Functional Foods for Healthy Aging; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 211–232. [Google Scholar]
- Drachman, D.A. Aging of the brain, entropy, and Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2006, 67, 1340–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aanerud, J.; Borghammer, P.; Chakravarty, M.M.; Vang, K.; Rodell, A.B.; Jonsdottir, K.Y.; Møller, A.; Ashkanian, M.; Vafaee, M.S.; Iversen, P.; et al. Brain energy metabolism and blood flow differences in healthy aging. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, W.I.; Bormann, M.K.; Shen, M.; Kim, D.; Forester, B.; Park, Y.; So, J.; Seo, H.; Sonntag, K.C.; Cohen, B.M. Brain cells derived from Alzheimer’s disease patients have multiple specific innate abnormalities in energy metabolism. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 5702–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, T.M.; Leech, J.; de Bros, G.B.; Murphy, C.A.; Budson, A.E.; Vassey, E.A.; Solomon, P.R. A randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled, parallel group, efficacy study of alpha BRAIN® administered orally. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2016, 31, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rootman, J.M.; Kiraga, M.; Kryskow, P.; Harvey, K.; Stamets, P.; Santos-Brault, E.; Kuypers, K.P.; Walsh, Z. Psilocybin microdosers demonstrate greater observed improvements in mood and mental health at one month relative to non-microdosing controls. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canter, P.H.; Ernst, E. Ginkgo biloba is not a smart drug: An updated systematic review of randomised clinical trials testing the nootropic effects of G. biloba extracts in healthy people. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2007, 22, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomeroy, D.E.; Tooley, K.L.; Probert, B.; Wilson, A.; Kemps, E. A systematic review of the effect of dietary supplements on cognitive performance in healthy young adults and military personnel. Nutrients 2020, 12, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, K.R.; Sweetnam, H.; Kondel, T.K. Is Ginkgo biloba a cognitive enhancer in healthy individuals? A meta-analysis. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2012, 27, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, M.J. Does caffeine intake enhance absolute levels of cognitive performance? Psychopharmacology 1993, 110, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott-Imboden, C.; Gonzalez, Y.; Utley, A. Efficacy of the nootropic supplement Mind Lab Pro on memory in adults: Double blind, placebo-controlled study. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2023, 38, e2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancheva, S.L.; Petkov, V.D.; Hadjiivanova, C.I.; Petkov, V.V. Age-related changes of the effects of a group of nootropic drugs on the content of rat brain biogenic monoamines. Gen. Pharmacol. 1991, 22, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, B.; Stemmler, M.B.; Friston, K.J. Information and efficiency in the nervous system—A synthesis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenon, A.; Solopchuk, O.; Pezzulo, G. An information-theoretic perspective on the costs of cognition. Neuropsychologia 2019, 123, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philiastides, M.G.; Sajda, P. Temporal characterization of the neural correlates of perceptual decision making in the human brain. Cereb. Cortex 2006, 16, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolam, J.; Diaz, J.A.; Andrews, M.; Coats, R.O.; Philiastides, M.G.; Astill, S.L.; Delis, I. A drift diffusion model analysis of age-related impact on multisensory decision-making processes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzen, L.; Delis, I.; De Sousa, G.; Kayser, C.; Philiastides, M.G. Auditory information enhances post-sensory visual evidence during rapid multisensory decision-making. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delis, I.; Onken, A.; Schyns, P.G.; Panzeri, S.; Philiastides, M.G. Space-by-time decomposition for single-trial decoding of M/EEG activity. Neuroimage 2016, 133, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oostenveld, R.; Fries, P.; Maris, E.; Schoffelen, J.M. FieldTrip: Open source software for advanced analysis of MEG, EEG, and invasive electrophysiological data. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 156869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leske, S.; Dalal, S.S. Reducing power line noise in EEG and MEG data via spectrum interpolation. Neuroimage 2019, 189, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, F.; Pernier, J.; Bertrand, O.; Echallier, J.F. Spherical splines for scalp potential and current density mapping. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1989, 72, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilming, N.; Murphy, P.R.; Meyniel, F.; Donner, T.H. Large-scale dynamics of perceptual decision information across human cortex. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nottage, J.F.; Horder, J. State-of-the-art analysis of high-frequency (gamma range) electroencephalography in humans. Neuropsychobiology 2016, 72, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, R.; Rosas, F.E.; Whelan, R.; Fittipaldi, S.; Santamaria-Garcia, H.; Cruzat, J.; Birba, A.; Moguilner, S.; Tagliazucchi, E.; Prado, P.; et al. Genuine high-order interactions in brain networks and neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 175, 105918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S. Information theoretical analysis of multivariate correlation. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1960, 4, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Sun, H. Nonnegative entropy measures of multivariate symmetric correlations. Inf. Control 1978, 36, 133–156. [Google Scholar]
- Rosas, F.E.; Mediano, P.A.; Gastpar, M.; Jensen, H.J. Quantifying high-order interdependencies via multivariate extensions of the mutual information. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 100, 032305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, S.A.; Plumbley, M.D. A measure of statistical complexity based on predictive information. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1012.1890. [Google Scholar]
- Ince, R.A.; Giordano, B.L.; Kayser, C.; Rousselet, G.A.; Gross, J.; Schyns, P.G. A statistical framework for neuroimaging data analysis based on mutual information estimated via a gaussian copula. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 1541–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawilowsky, S.S. New effect size rules of thumb. J. Mod. Appl. Stat. Methods 2009, 8, 597–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatica, M.; Cofré, R.; Mediano, P.A.; Rosas, F.E.; Orio, P.; Diez, I.; Swinnen, S.P.; Cortes, J.M. High-order interdependencies in the aging brain. Brain Connect. 2021, 11, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, R. Effective analysis of reaction time data. Psychol. Rec. 2008, 58, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, R.A.; Paton, A.T.; Kay, J.W.; Schyns, P.G. Bayesian inference of population prevalence. eLife 2021, 10, e62461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proca, A.M.; Rosas, F.E.; Luppi, A.I.; Bor, D.; Crosby, M.; Mediano, P.A. Synergistic information supports modality integration and flexible learning in neural networks solving multiple tasks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2024, 20, e1012178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, A.I.; Rosas, F.E.; Mediano, P.A.; Menon, D.K.; Stamatakis, E.A. Information decomposition and the informational architecture of the brain. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2024, 28, 352–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.R.; D’Esposito, M. The segregation and integration of distinct brain networks and their relationship to cognition. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 12083–12094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combrisson, E.; Basanisi, R.; Neri, M.; Auzias, G.; Petri, G.; Marinazzo, D.; Panzeri, S.; Brovelli, A. Higher-order and distributed synergistic functional interactions encode information gain in goal-directed learning. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, A.I.; Mediano, P.A.; Rosas, F.E.; Holland, N.; Fryer, T.D.; O’Brien, J.T.; Rowe, J.B.; Menon, D.K.; Bor, D.; Stamatakis, E.A. A synergistic core for human brain evolution and cognition. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luppi, A.I.; Mediano, P.A.; Rosas, F.E.; Allanson, J.; Pickard, J.; Carhart-Harris, R.L.; Williams, G.B.; Craig, M.M.; Finoia, P.; Owen, A.M.; et al. A synergistic workspace for human consciousness revealed by integrated information decomposition. eLife 2024, 12, RP88173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigam, S.; Pojoga, S.; Dragoi, V. Synergistic coding of visual information in columnar networks. Neuron 2019, 104, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, N.; Strong, S.P.; Koberle, R.; Bialek, W.; Steveninck, R.R. Synergy in a neural code. Neural Comput. 2000, 12, 1531–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorist, M.M.; Tops, M. Caffeine, fatigue, and cognition. Brain Cogn. 2003, 53, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Panda, R.; Sharma, K.; Adarsh, A.; Annen, J.; Martial, C.; Faymonville, M.E.; Laureys, S.; Sombrun, C.; Ganesan, R.A.; et al. Changes in high-order interaction measures of synergy and redundancy during non-ordinary states of consciousness induced by meditation, hypnosis, and auto-induced cognitive trance. NeuroImage 2024, 293, 120623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Tang, Y.Y.; Tang, R.; Posner, M.I. Improving creativity performance by short-term meditation. Behav. Brain Funct. 2014, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.; Malinowski, P. Meditation, mindfulness and cognitive flexibility. Conscious. Cogn. 2009, 18, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmony, T. The functional significance of delta oscillations in cognitive processing. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, T.; Steffen, A.; Weisz, N.; Miller, G.A.; Rockstroh, B. Cross-frequency dynamics of neuromagnetic oscillatory activity: Two mechanisms of emotion regulation. Psychophysiology 2012, 49, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Nutrition Facts | Amount per Serving |
|---|---|
| Vitamin B6 | 2.5 mg |
| Vitamin B9 | 100 mcg |
| Vitamin B12 | 7.5 mcg |
| Citicoline | 250 mg |
| Bacopa monnieri | 150 mg |
| Organic lion’s mane mushroom | 500 mg |
| Phosphatidylserine | 100 mg |
| N-Acetyl L-Tyrosine | 175 mg |
| L-Theanine | 100 mg |
| Rhodiola rosea | 50 mg |
| Maritime pine bark extract | 75 mg |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
O’Reilly, D.; Bolam, J.; Delis, I.; Utley, A. Effect of a Plant-Based Nootropic Supplement on Perceptual Decision-Making and Brain Network Interdependencies: A Randomised, Double-Blinded, and Placebo-Controlled Study. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030226
O’Reilly D, Bolam J, Delis I, Utley A. Effect of a Plant-Based Nootropic Supplement on Perceptual Decision-Making and Brain Network Interdependencies: A Randomised, Double-Blinded, and Placebo-Controlled Study. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(3):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030226
Chicago/Turabian StyleO’Reilly, David, Joshua Bolam, Ioannis Delis, and Andrea Utley. 2025. "Effect of a Plant-Based Nootropic Supplement on Perceptual Decision-Making and Brain Network Interdependencies: A Randomised, Double-Blinded, and Placebo-Controlled Study" Brain Sciences 15, no. 3: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030226
APA StyleO’Reilly, D., Bolam, J., Delis, I., & Utley, A. (2025). Effect of a Plant-Based Nootropic Supplement on Perceptual Decision-Making and Brain Network Interdependencies: A Randomised, Double-Blinded, and Placebo-Controlled Study. Brain Sciences, 15(3), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15030226







