Unveiling the Truth in Pain: Neural and Behavioral Distinctions Between Genuine and Deceptive Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Questionnaires and Interoception Assessment
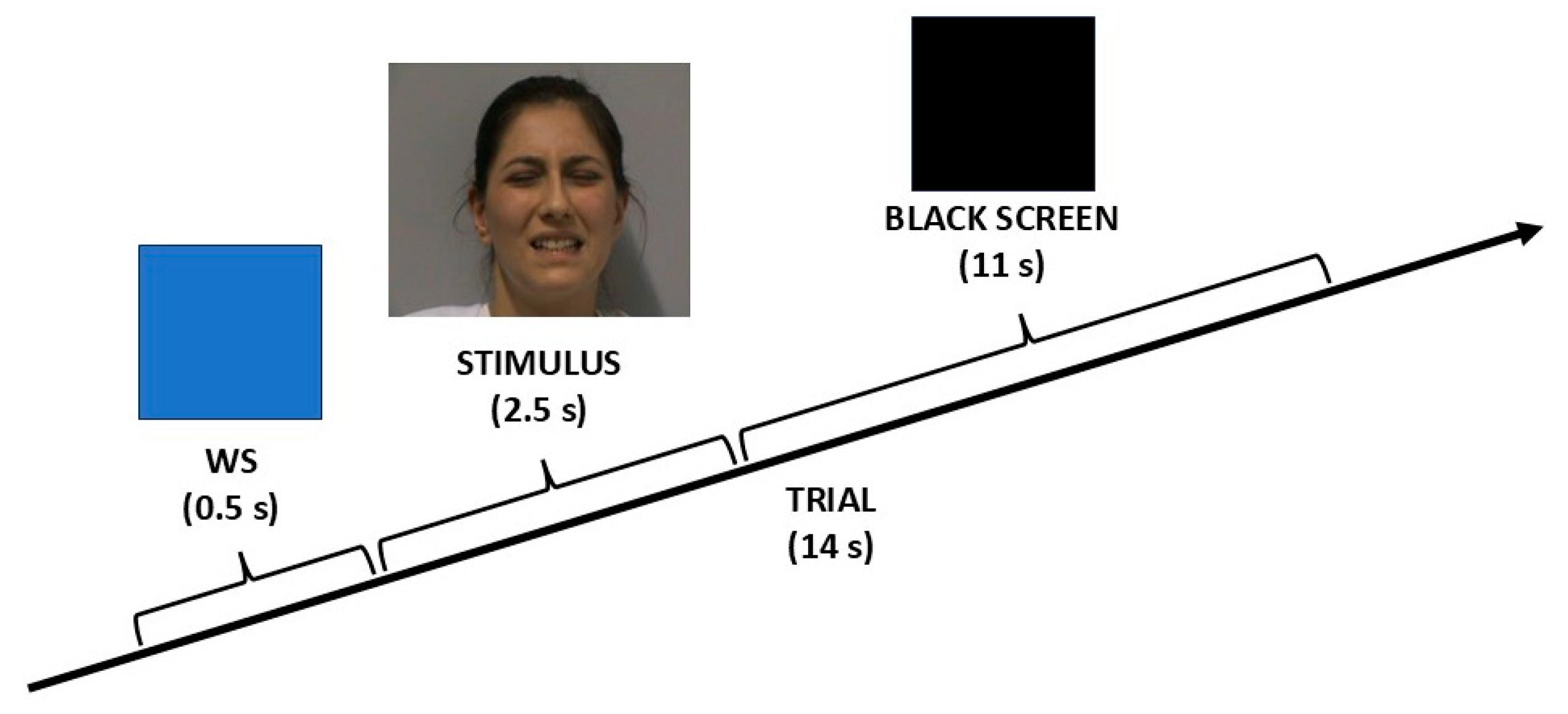
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Stimuli
2.5. fMRI Data Acquisition
2.6. Behavioral Data Analysis
2.7. fMRI Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Behavioral Results
3.1.1. Questionnaires and Interoception Assessment
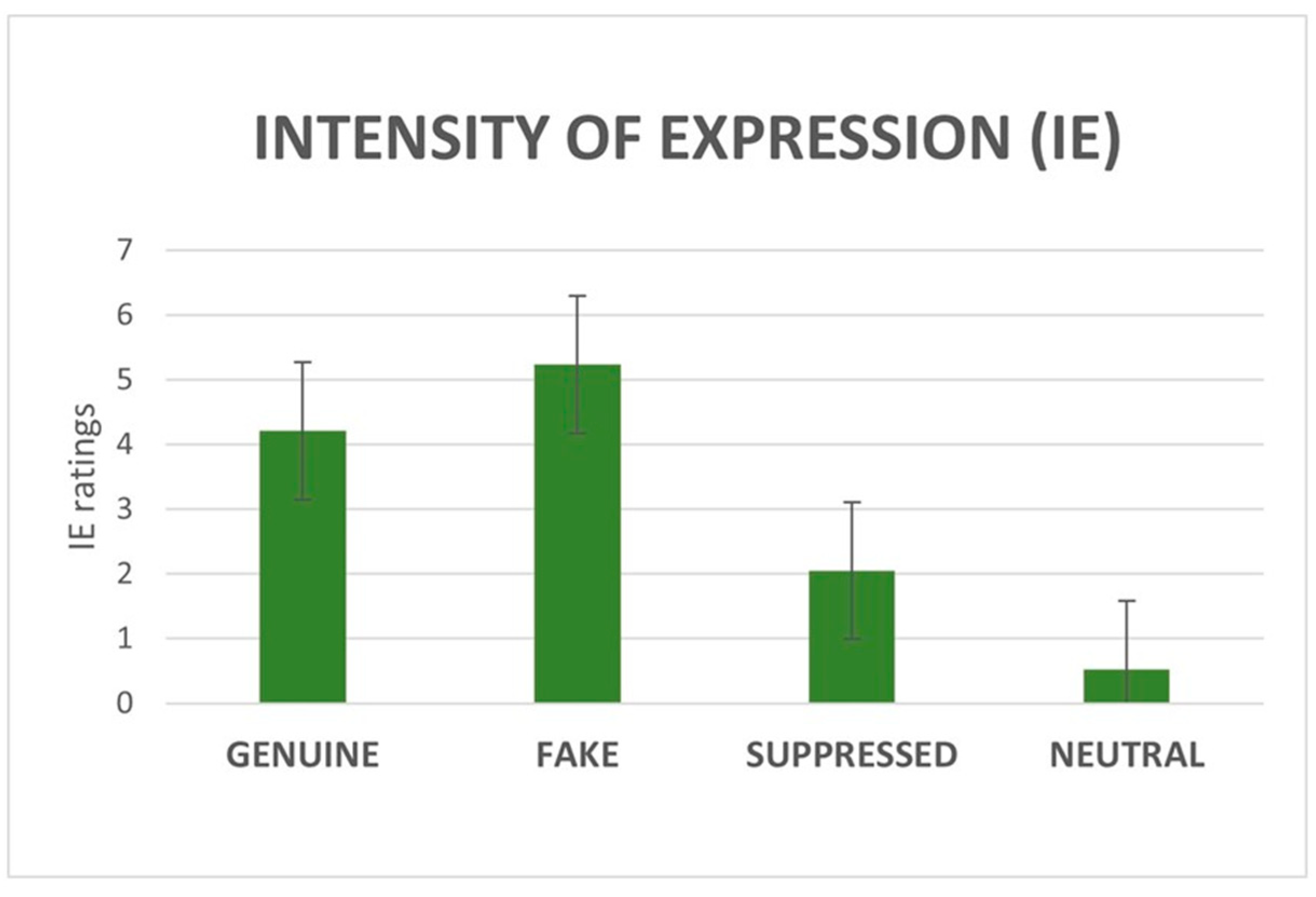
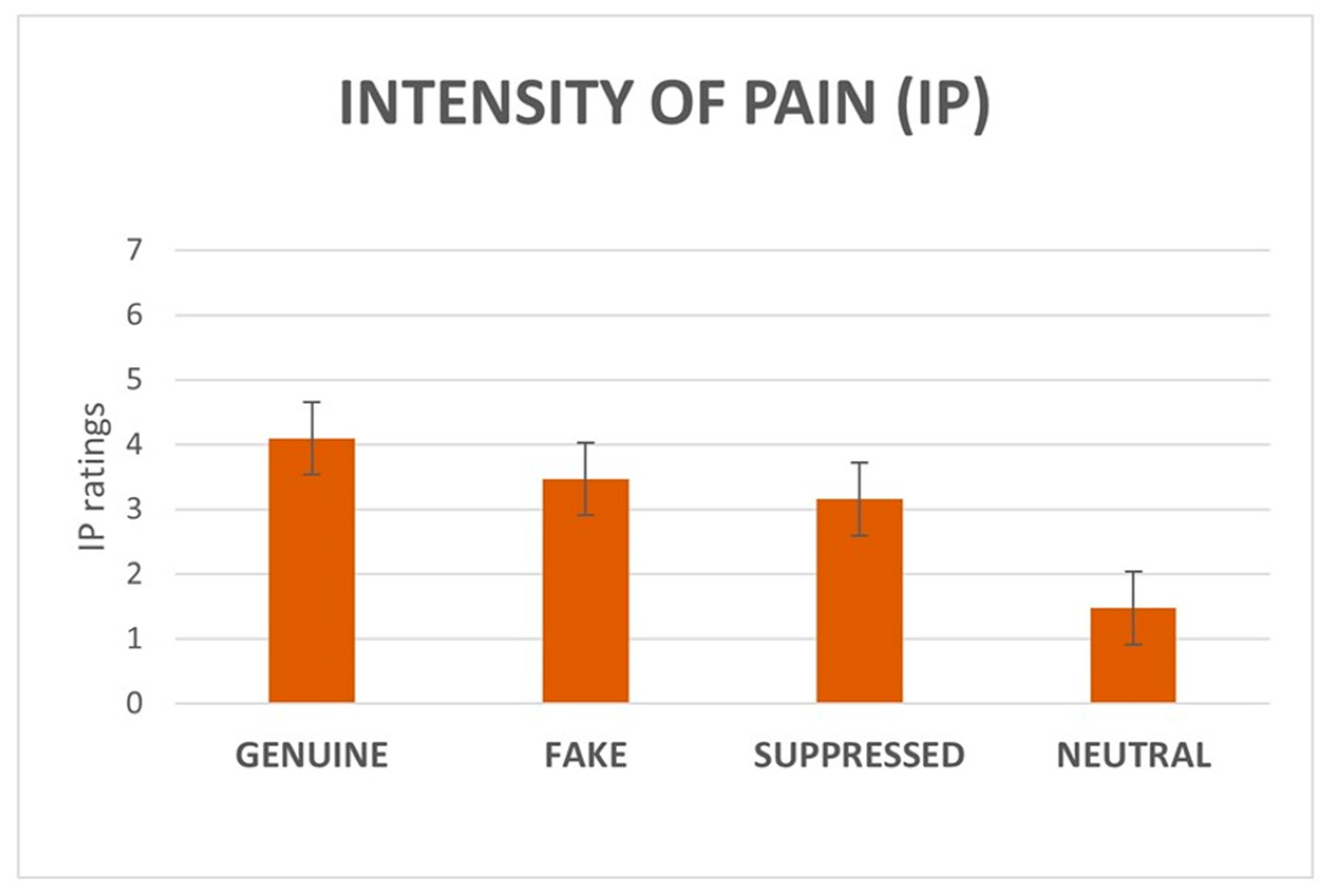
3.1.2. IE and IP Ratings
3.2. fMRI Results
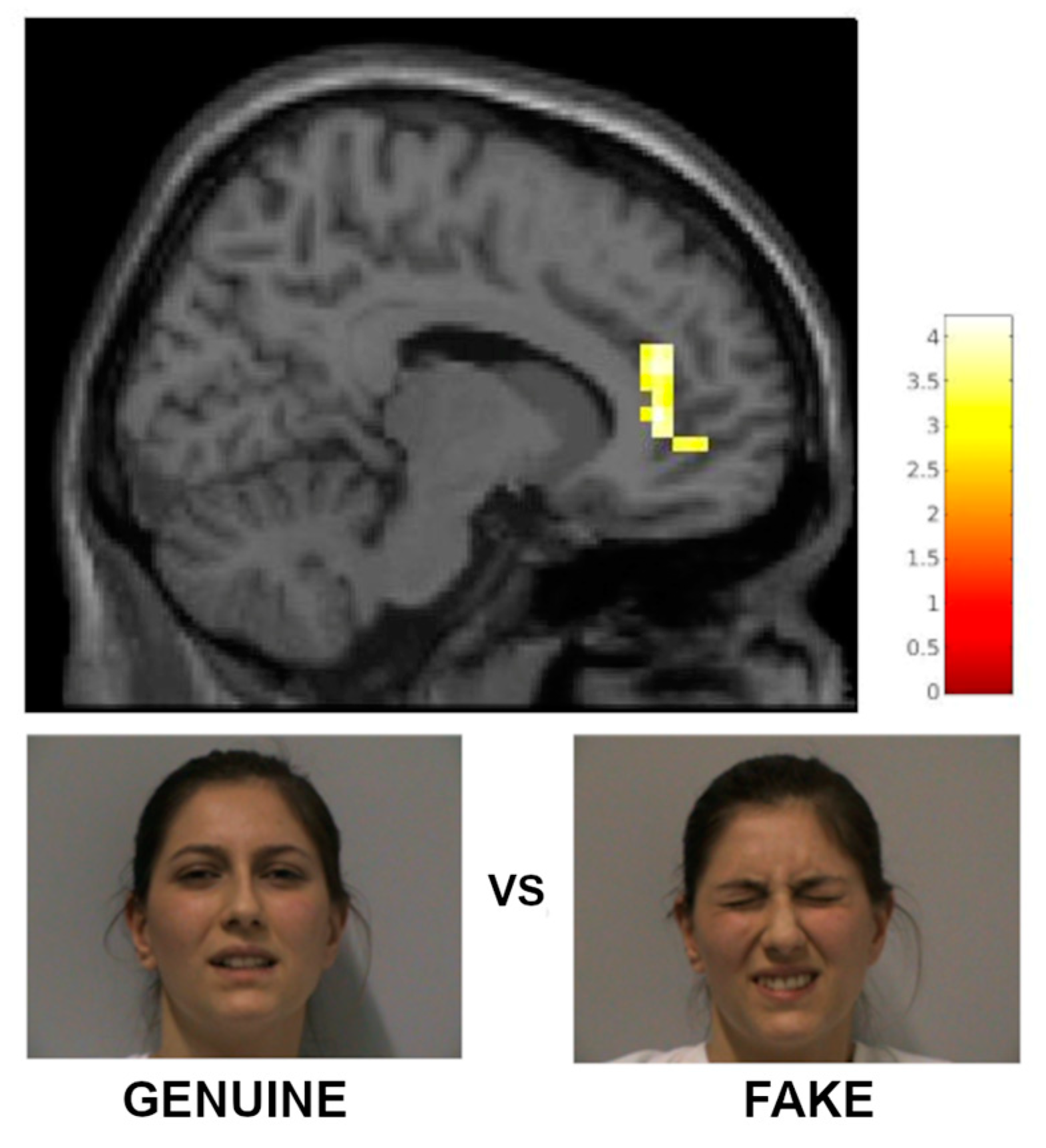
3.2.1. fMRI Results with a Priori Categorization
3.2.2. Parametric Analysis with a Posteriori Categorization
3.2.3. Correlations with Questionnaires and Interoception
4. Discussion
4.1. Behavioral Findings
4.2. Functional Imaging Findings
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | Anterior cingulate cortex |
| AI | Anterior insula |
| aMCC | Anterior mid-cingulate cortex |
| BOLD | Blood oxygenation level-dependent |
| EQ | Empathy quotient |
| fMRI | Functional magnetic resonance imaging |
| FP | Fake pain |
| GLM | General linear model |
| GP | Genuine pain |
| IA | Interoceptive accuracy |
| IASP | International association for the study of pain |
| IE | Intensity of the facial expression |
| IFG | Inferior frontal gyrus |
| IP | Intensity of the pain |
| IPL | Inferior parietal lobe |
| IRI | Interpersonal reactivity index |
| M | Mean |
| MFG | Middle frontal gyrus |
| MNI | Montreal neurological institute |
| MPFC | Medial prefrontal cortex |
| N | Neutral |
| NRS | Numerical rating scale |
| pACC | Pregenual anterior cingulate cortex |
| PCS | Pain catastrophizing scale |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SMG | Supramarginal gyrus |
| SP | Suppressed pain |
| SPM | Statistical parametric mapping |
| STS | Superior temporal sulcus |
| TAS-20 | Toronto alexithymia scale 20 |
| TE | Echo time |
| TR | Repetition time |
| WS | Warning signal |
References
- Raja, S.N.; Carr, D.B.; Cohen, M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Flor, H.; Gibson, S.; Keefe, F.J.; Mogil, J.S.; Ringkamp, M.; Sluka, K.A.; et al. The revised International Association for the Study of Pain definition of pain: Concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain 2020, 161, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekman, P. Darwin, deception, and facial expression. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 1000, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, M.S.; Littlewort, G.C.; Frank, M.G.; Lee, K. Automatic decoding of facial movements reveals deceptive pain expressions. Curr. Biol. CB 2014, 24, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarela, M.V.; Hlushchuk, Y.; Williams, A.C.; Schürmann, M.; Kalso, E.; Hari, R. The compassionate brain: Humans detect intensity of pain from another’s face. Cereb. Cortex 2007, 17, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Benuzzi, F.; Lui, F.; Ardizzi, M.; Ambrosecchia, M.; Ballotta, D.; Righi, S.; Pagnoni, G.; Gallese, V.; Porro, C.A. Pain mirrors: Neural correlates of observing self or others’ facial expressions of pain. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blais, C.; Fiset, D.; Furumoto-Deshaies, H.; Kunz, M.; Seuss, D.; Cormier, S. Facial Features Underlying the Decoding of Pain Expressions. J. Pain 2019, 20, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, T.; Seymour, B.; O’Doherty, J.; Kaube, H.; Dolan, R.J.; Frith, C.D. Empathy for pain involves the affective but not sensory components of pain. Science 2004, 303, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de C Williams, A.C. Pain: Behavioural expression and response in an evolutionary framework. Evol. Med. Public Health 2023, 11, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riečanský, I.; Lamm, C. The Role of Sensorimotor Processes in Pain Empathy. Brain Topogr. 2019, 32, 965–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Li, Y.; Luo, L.; Li, L.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X.; Shen, L. The Empathy for Pain Stimuli System (EPSS): Development and preliminary validation. Behav. Res. 2024, 56, 784–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.C. Facial expression of pain: An evolutionary account. Behav. Brain Sci. 2002, 25, 439–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.L.; Craig, K.D. Detecting deception in pain expressions: The structure of genuine and deceptive facial displays. Pain 2002, 98, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stel, M.; van Dijk, E. When do we see that others misrepresent how they feel? Detecting deception from emotional faces with direct and indirect measures. Soc. Influ. 2018, 13, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, C.F.; Robinson, M. The evolution of deception. J. Nonverbal Behav. 1988, 12 Pt 2, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, S.; ten Brinke, L. Reading between the lies: Identifying concealed and falsified emotions in universal facial expressions. Psychol. Sci. 2008, 19, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePaulo, B.M.; Zuckerman, M.; Rosenthal, R. Detecting deception: Modality effects. In Review of Personality and Social Psychology; Wheeler, L., Ed.; Sage: Beverly Hills, CA, USA, 1980; Volume 1, pp. 125–162. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhouli, M.; Al-Nerabieah, Z.; Dashash, M. Analyzing facial action units in children to differentiate genuine and fake pain during inferior alveolar nerve block: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, U.; Kleck, R.E. The cues decoders use in attempting to differentiate emotion-elicited and posed facial expressions. Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 1994, 24, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrij, A.; Mann, S. Telling and detecting lies in a high-stake situation: The case of a convicted murderer. Appl. Cogn. Psychol. 2001, 15, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, C.F.; Levine, T.R.; Hartwig, M. New findings in non-verbal lie detection. In Detecting Deception: Current Challenges and Cognitive Approaches; Granhag, P.A., Vrij, A., Verschuere, B., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 37–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, R.D. Neural correlates of conscious emotional experience. In Cognitive Neuroscience of Emotion; Lane, R.D., Nadel, L., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 345–370. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, N.; Moyal, N.; Lichtenstein-Vidne, L.; Henik, A. Explicit vs. implicit emotional processing: The interaction between processing type and executive control. Cogn. Emot. 2015, 30, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critchley, H.; Daly, E.; Phillips, M.; Brammer, M.; Bullmore, E.; Williams, S.; Van Amelsvoort, T.; Robertson, D.; David, A.; Murphy, D. Explicit and implicit neural mechanisms for processing of social information from facial expressions: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2000, 9, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, F.; Duzzi, D.; Corradini, M.; Serafini, M.; Baraldi, P.; Porro, C.A. Touch or pain? Spatio-temporal patterns of cortical fMRI activity following brief mechanical stimuli. Pain 2008, 138, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.B.; Regenbogen, C.; Ohse, M.C.; Frasnelli, J.; Freiherr, J.; Lundström, J.N. Brain activations during pain: A neuroimaging meta-analysis of patients with pain and healthy controls. Pain 2016, 157, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Larsen, B.; Baller, E.B.; Scott, J.C.; Sharma, V.; Adebimpe, A.; Basbaum, A.I.; Dworkin, R.H.; Edwards, R.R.; Woolf, C.J.; et al. Convergent neural representations of experimentally-induced acute pain in healthy volunteers: A large-scale fMRI meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 112, 300–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treede, R.D.; Kenshalo, D.R.; Gracely, R.H.; Jones, A.K. The cortical representation of pain. Pain 1999, 79, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, B.A. Cingulate cortex in the three limbic subsystems. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 166, pp. 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.D. Psychological and neural mechanisms of the affective dimension of pain. Science 2000, 288, 1769–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favilla, S.; Huber, A.; Pagnoni, G.; Lui, F.; Facchin, P.; Cocchi, M.; Baraldi, P.; Porro, C.A. Ranking brain areas encoding the perceived level of pain from fMRI data. NeuroImage 2014, 90, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botvinick, M.; Jha, A.P.; Bylsma, L.M.; Fabian, S.A.; Solomon, P.E.; Prkachin, K.M. Viewing facial expressions of pain engages cortical areas involved in the direct experience of pain. NeuroImage 2005, 25, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budell, L.; Jackson, P.; Rainville, P. Brain responses to facial expressions of pain: Emotional or motor mirroring? NeuroImage 2010, 53, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Rütgen, M.; Sladky, R.; Lamm, C. Neural dynamics between anterior insular cortex and right supramarginal gyrus dissociate genuine affect sharing from perceptual saliency of pretended pain. eLife 2021, 10, e69994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldfield, R.C. The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaFrance, M.; Banaji, M. Toward a reconsideration of the gender-emotion relationship. In Review of Personality and Social Psychology: Emotions and Social Behavior; Clark, M.S., Ed.; Sage: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1992; Volume 14, pp. 178–202. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.; Carter, J.; Horgan, T. Gender differences in nonverbal communication of emotion. In Gender and Emotion: Social Psychological Perspectives (Studies in Emotion and Social Interaction); Fischer, A., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; pp. 97–117. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, K.J.K.; Hodges, S.D. Gender differences, motivation, and empathic accuracy: When it pays to understand. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2001, 27, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, T.; Seymour, B.; O’Doherty, J.P.; Stephan, K.E.; Dolan, R.J.; Frith, C.D. Empathic neural responses are modulated by the perceived fairness of others. Nature 2006, 439, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preti, A.; Vellante, M.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Zucca, G.; Petretto, D.R.; Masala, C. The empathy quotient: A cross-cultural comparison of the Italian version. Cogn. Neuropsychiatry 2011, 16, 50–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albiero, P.; Ingoglia, S.; Lo Coco, A. Contributo all’adattamento italiano dell’interpersonal reactivity index. Test. Psicom. Metod. 2006, 13, 107–125. [Google Scholar]
- Caretti, V.; La Barbera, D.; Craparo, G. La Toronto Alexithymia Scale (TAS-20). In Alessitimia, Valutazione e Trattamento; Caretti, V., La Barbera, D., Eds.; Astrolabio Ubaldini: Rome, Italy, 2005; pp. 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Monticone, M.; Baiardi, P.; Ferrari, S.; Foti, C.; Mugnai, R.; Pillastrini, P.; Rocca, B.; Vanti, C. Development of the Italian version of the pain catastrophizing scale (PCS-I): Cross-cultural adaptation, factor analysis, reliability, validity and sensitivity to change. Qual. Life Res. 2012, 21, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollatos, O.; Herbert, B.M.; Matthias, E.; Schandry, R. Heart rate response after emotional picture presentation is modulated by interoceptive awareness. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2007, 63, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, B.D.; Galton, H.C.; Morgan, R.; Evans, D.; Oliver, C.; Meyer, M.; Cusack, R.; Lawrence, A.D.; Dalgleish, T. Listening to your heart. How interoception shapes emotion experience and intuitive decision making. Psychol. Sci. 2010, 21, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schandry, R. Heart beat perception and emotional experience. Psychophysiology 1981, 18, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardizzi, M.; Ambrosecchia, M.; Buratta, L.; Ferri, F.; Peciccia, M.; Donnari, S.; Mazzeschi, C.; Gallese, V. Interoception and positive symptoms in schizophrenia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosecchia, M.; Ardizzi, M.; Russo, E.; Ditaranto, F.; Speciale, M.; Vinai, P.; Todisco, P.; Maestro, S.; Gallese, V. Interoception and autonomic correlates during social interactions. Implications for anorexia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollatos, O.; Kurz, A.-L.; Albrecht, J.; Schreder, T.; Kleemann, A.M.; Schöpf, V.; Kopietz, R.; Wiesmann, M.; Schandry, R. Reduced perception of bodily signals in anorexia nervosa. Eat. Behav. 2008, 9, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuerecker, J.; Frodl, T.; Koutsouleris, N.; Zetzsche, T.; Wiesmann, M.; Kleemann, A.M.; Brückmann, H.; Schmitt, G.; Möller, H.J.; Meisenzahl, E.M. Cerebral differences in explicit and implicit emotional processing—An fMRI study. Neuropsychobiology 2007, 56, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, B. Pain: A Precision Signal for Reinforcement Learning and Control. Neuron 2019, 101, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, M.; Oudenhove, L.V.; Dupont, P.; Wager, T.D.; Fukudo, S. Imaging Brain Mechanisms of Functional Somatic Syndromes: Potential as a Biomarker? Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2020, 250, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyron, R.; Quesada, C.; Fauchon, C. Cingulate-mediated approaches to treating chronic pain. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 166, pp. 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, B.A. Pain and emotion interactions in subregions of the cingulate gyrus. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benuzzi, F.; Lui, F.; Duzzi, D.; Nichelli, P.F.; Porro, C.A. Does it look painful or disgusting? Ask your parietal and cingulate cortex. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porro, C.A.; Cettolo, V.; Francescato, M.P.; Baraldi, P. Temporal and intensity coding of pain in human cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 1998, 80, 3312–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haxby, J.V.; Hoffman, E.A.; Gobbini, M.I. The distributed human neural system for face perception. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2000, 4, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbini, M.I.; Haxby, J.V. Neural systems for recognition of familiar faces. Neuropsychologia 2007, 45, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gelder, B.; Snyder, J.; Greve, D.; Gerard, G.; Hadjikhani, N. Fear fosters flight: A mechanism for fear contagion when perceiving emotion expressed by a whole body. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16701–16706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grèzes, J.; Pichon, S.; de Gelder, B. Perceiving fear in dynamic body expressions. NeuroImage 2007, 35, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichon, S.; de Gelder, B.; Grezes, J. Emotional modulation of visual and motor areas by dynamic body expressions of anger. Soc. Neurosci. 2008, 3, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, H.; Christensen, A.; Flash, T.; Giese, M.; Malach, R. Brain activity correlates with emotional perception induced by dynamic avatars. NeuroImage 2015, 122, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitada, R.; Johnsrude, I.S.; Kochiyama, T.; Lederman, S.J. Brain networks involved in haptic and visual identification of facial expressions of emotion: An fMRI study. NeuroImage 2010, 49, 1677–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkheil, P.; Goebel, R.; Schneider, F.; Mathiak, K. Emotion unfolded by motion: A role for parietal lobe in decoding dynamic facial expressions. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2013, 8, 950–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Shinkareva, S.V.; Wedell, D.H. Representations of modality general valence for videos and music derived from fMRI data. Neuroimage 2017, 148, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Xu, J.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, B. Abstract Representations of Emotions Perceived From the Face, Body, and Whole-Person Expressions in the Left Postcentral Gyrus. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhle, J.T.; Kober, H.; Ochsner, K.N.; Mende-Siedlecki, P.; Weber, J.; Hughes, B.L.; Kross, E.; Atlas, L.Y.; McRae, K.; Wager, T.D. Common representation of pain and negative emotion in the midbrain periaqueductal gray. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2013, 8, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.L.; Brunet, E.; Meltzoff, A.N.; Decety, J. Empathy examined through the neural mechanisms involved in imagining how I feel versus how you feel pain. Neuropsychologia 2006, 44, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kross, E.; Berman, M.G.; Mischel, W.; Smith, E.E.; Wager, T.D. Social rejection shares somatosensory representations with physical pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6270–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulbright, R.K.; Troche, C.J.; Skudlarski, P.; Gore, J.C.; Wexler, B.E. Functional MR imaging of regional brain activation associated with the affective experience of pain. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2001, 177, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matharu, M.S.; Bartsch, T.; Ward, N.; Frackowiak, R.S.; Weiner, R.; Goadsby, P.J. Central neuromodulation in chronic migraine patients with suboccipital stimulators: A PET study. Brain 2004, 127 Pt 1, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallese, V. Before and below “theory of mind”: Embodied simulation and the neural correlates of social cognition. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacoboni, M. Imitation, empathy, and Mirror neurons. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2009, 60, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majdandžić, J.; Amashaufer, S.; Hummer, A.; Windischberger, C.; Lamm, C. The selfless mind: How prefrontal involvement in mentalizing with similar and dissimilar others shapes empathy and prosocial behavior. Cognition 2016, 157, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Z.; Li, L. Probing the role of the right inferior frontal gyrus during Pain-Related empathy processing: Evidence from fMRI and TMS. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 1518–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, F.; Koehne, S.; Steinbeis, N.; Dziobek, I.; Singer, T. Preserved Self-other Distinction During Empathy in Autism is Linked to Network Integrity of Right Supramarginal Gyrus. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2016, 46, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukowski, H.; Tik, M.; Silani, G.; Ruff, C.C.; Windischberger, C.; Lamm, C. When differences matter: rTMS/fMRI reveals how differences in dispositional empathy translate to distinct neural underpinnings of self-other distinction in empathy. Cortex 2020, 128, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallon, N.; Roberts, C.; Stancak, A. Shared and distinct functional networks for empathy and pain processing: A systematic review and meta-analysis of fMRI studies. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2020, 15, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naor, N.; Rohr, C.; Schaare, L.H.; Limbachia, C.; Shamay-Tsoory, S.; Okon-Singer, H. The neural networks underlying reappraisal of empathy for pain. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2020, 15, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, J.E.; Thomasson, M.; Voruz, P.; Selosse, G.; Péron, J. Explicit and Implicit Emotion Processing in the Cerebellum: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review. Cerebellum 2023, 22, 852–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerner, K.E.; Chambers, C.T.; Craig, K.D.; Pillai Riddell, R.R.; Parker, J.A. Caregiver accuracy in detecting deception in facial expressions of pain in children. Pain 2013, 154, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samolsky Dekel, B.G.; Gori, A.; Vasarri, A.; Sorella, M.C.; Di Nino, G.; Melotti, R.M. Medical Evidence Influence on Inpatients and Nurses Pain Ratings Agreement. Pain Res. Manag. 2016, 2016, 9267536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hoffman, K.M.; Trawalter, S.; Axt, J.R.; Oliver, M.N. Racial bias in pain assessment and treatment recommendations, and false beliefs about biological differences between blacks and whites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4296–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Genuine | Fake | Suppressed | Neutral | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IE | IP | IE | IP | IE | IP | IE | IP | |
| M | 3.4 | 2.4 | 3.2 | 0.04 | 1.2 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 |
| SD | 1.1 | 1.3 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0 | 0 |
| IE | IP | Condition |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | Neutral |
| ≠0 | 0 | Other |
| ≠0 | ≠0 | Real/Fake/Suppressed (based on the a priori categorization) |
| BA | Side | Cluster | Voxel Level | MNI Coordinates | Talairach Coordinates | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain Areas | k | ZE | x | y | z | x | y | z | ||
| GP vs. FP | ||||||||||
| pregenual anterior cingulate cortex | 32 | r/l | 125 | 3.59 | 12 | 38 | 6 | 12 | 38 | 12 |
| GP vs. SP | ||||||||||
| Cerebellum | l | 67 | 5.01 | −15 | −73 | −46 | −15 | −73 | −35 | |
| 3.72 | −18 | −67 | −30 | −18 | −66 | −22 | ||||
| 2.95 | −21 | −79 | −38 | −21 | −78 | −28 | ||||
| Middle Temporal Gyrus, Superior Temporal Gyrus, Inferior Temporal Gyrus, Inferior Parietal Lobule, Fusiform Gyrus, Middle Occipital Gyrus, Insula, Cuneus | 21, 22, 37, 40 19, 17 | r | 579 | 4.74 | 48 | −37 | 2 | 48 | −36 | 4 |
| 4.54 | 51 | −73 | 2 | 50 | −71 | 5 | ||||
| 4.50 | 57 | −40 | 6 | 56 | −38 | 7 | ||||
| Middle Temporal Gyrus, Superior Temporal Gyrus. Inferior Temporal Gyrus, Middle Occipital Gyrus. | 22, 19 | l | 221 | 4.55 | −54 | −46 | 6 | −53 | −44 | 8 |
| 3.99 | −48 | −70 | 6 | −48 | −68 | 9 | ||||
| 3.21 | −39 | −70 | 6 | −39 | −68 | 9 | ||||
| BA | Side | Cluster | Voxel Level | MNI Coordinates | Talairach Coordinates | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain Areas | k | ZE | x | y | z | x | y | z | ||
| Middle Temporal Gyrus, Superior Temporal Gyrus, Inferior Temporal Gyrus, Middle Occipital Gyrus, Inferior Parietal Lobule, Insula | 21, 22, 20, 19, 39 | r | 599 | 6.98 | 51 | −40 | 6 | 50 | −38 | 7 |
| 6.06 | 48 | −76 | −2 | 48 | −74 | 2 | ||||
| 5.84 | 45 | −31 | −6 | 45 | −30 | −4 | ||||
| Middle Temporal Gyrus, Superior Temporal Gyrus, Temporal Pole | 21, 38 | r | 46 | 5.95 | 54 | 8 | −22 | 53 | 7 | −19 |
| Middle Temporal Gyrus, Superior Temporal Gyrus, Inferior Temporal Gyrus, Middle Occipital Gyrus, Supramarginal Gyrus | 22, 37, 19 | l | 360 | 5.60 | −51 | −73 | 6 | −50 | −70 | 9 |
| 5.58 | −51 | −64 | 6 | −50 | −62 | 9 | ||||
| 5.30 | −57 | −55 | 6 | −56 | −53 | 8 | ||||
| Middle Frontal Gyrus | 46 | r | 33 | 5.43 | 48 | 2 | 42 | 48 | 4 | 38 |
| Inferior Frontal Gyrus, Insula | 47 | r | 64 | 4.85 | 45 | 26 | −2 | 45 | 25 | −3 |
| Inferior Frontal Gyrus | 47 | l | 70 | 4.80 | −48 | 20 | −6 | −48 | 19 | −6 |
| 3.94 | −39 | 26 | −2 | −39 | 25 | −3 | ||||
| Cerebellum | l | 14 | 4.14 | −12 | −76 | −46 | −12 | −76 | −35 | |
| 3.53 | −18 | −82 | −46 | −18 | −81 | −35 | ||||
| Middle Occipital Gyrus, Inferior Occipital Gyrus, Fusiform Gyrus | 18, 37 | r | 41 | 4.03 | 27 | −85 | −6 | 27 | −83 | −1 |
| 3.60 | 27 | −91 | 10 | 27 | −88 | 14 | ||||
| Fusiform Gyrus | 37 | r | 16 | 3.96 | 42 | −43 | −22 | 42 | −43 | −16 |
| BA | Side | Cluster | Voxel Level | MNI Coordinates | Talairach Coordinates | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain Areas | k | ZE | x | y | z | x | y | z | ||
| Mid-cingulate cortex | 24 | l | 15 | 4.68 | −3 | 2 | 38 | −3 | 4 | 35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zanelli, V.; Lui, F.; Casadio, C.; Ricci, F.; Carpentiero, O.; Ballotta, D.; Ambrosecchia, M.; Ardizzi, M.; Gallese, V.; Porro, C.A.; et al. Unveiling the Truth in Pain: Neural and Behavioral Distinctions Between Genuine and Deceptive Pain. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15020185
Zanelli V, Lui F, Casadio C, Ricci F, Carpentiero O, Ballotta D, Ambrosecchia M, Ardizzi M, Gallese V, Porro CA, et al. Unveiling the Truth in Pain: Neural and Behavioral Distinctions Between Genuine and Deceptive Pain. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(2):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15020185
Chicago/Turabian StyleZanelli, Vanessa, Fausta Lui, Claudia Casadio, Francesco Ricci, Omar Carpentiero, Daniela Ballotta, Marianna Ambrosecchia, Martina Ardizzi, Vittorio Gallese, Carlo Adolfo Porro, and et al. 2025. "Unveiling the Truth in Pain: Neural and Behavioral Distinctions Between Genuine and Deceptive Pain" Brain Sciences 15, no. 2: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15020185
APA StyleZanelli, V., Lui, F., Casadio, C., Ricci, F., Carpentiero, O., Ballotta, D., Ambrosecchia, M., Ardizzi, M., Gallese, V., Porro, C. A., & Benuzzi, F. (2025). Unveiling the Truth in Pain: Neural and Behavioral Distinctions Between Genuine and Deceptive Pain. Brain Sciences, 15(2), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15020185







