Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation over the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- Contraindications to tRNS (e.g., scalp skin diseases, history of neurosurgical interventions);
- Neurological comorbidities (excluding PD-MCI);
- Presence of major depressive disorder, using a cutoff of ≥15 on the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale [25];
- Use of psychotropic drugs (e.g., antidepressants, anxiolytics, or neuroleptics) or cognitive enhancers.
2.3. Study Protocol Structure
2.3.1. Baseline Evaluation
- Attention and Orientation ≤ 14.73;
- Memory ≤ 14.47;
- Verbal Fluency ≤ 6.01;
- Language ≤ 18.83;
- Visuospatial Abilities ≤ 10.73.
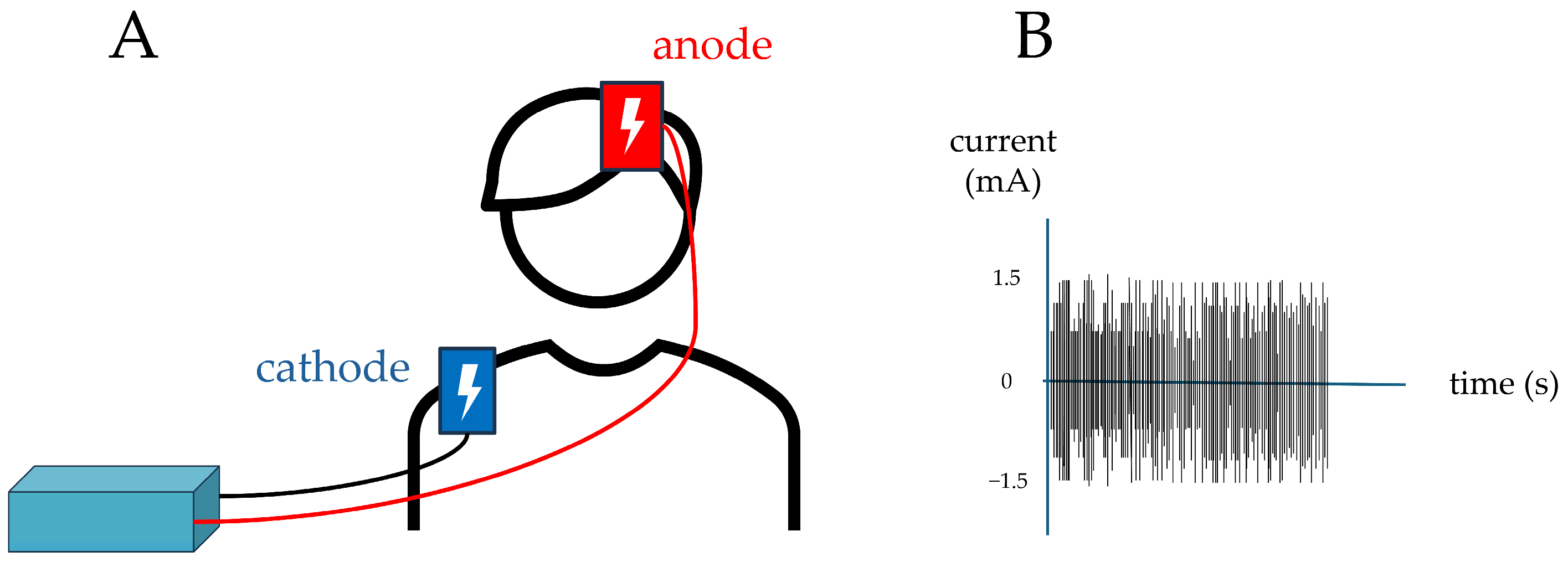
2.3.2. First Stimulation
- Pre-stimulation (T0)
- b.
- Stimulation
- Intensity: 1.5 mA;
- Frequency range: 100–600 Hz;
- Stimulation duration: 900 s (15 min).
- Intensity: 1.5 mA;
- Frequency range: 100–600 Hz;
- Stimulation duration: 900 s (15 min); however, current was delivered only during the first and last 30 s to give participants the impression of being stimulated, as cutaneous sensations are typically perceived mainly at these times during the active protocol.
- c.
- Post-Stimulation (T1)
2.3.3. Second Stimulation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Effect of tRNS Session
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MCI | Mild cognitive impairment |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| MDS | Movement Disorder Society |
| NIBS | Non-invasive brain stimulation |
| tRNS | Transcranial random noise stimulation |
| DLPFC | Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex |
| PDD | Parkinson’s disease dementia |
| TMS | Transcranial magnetic stimulation |
| tACS | Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) |
| ACE-R | Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination-Revised |
| MoCA | Montreal Cognitive Assessment |
| FAB | Frontal Assessment Battery |
| FAS | Phonemic Verbal Fluency Test |
| UPDRS | Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale |
| SD | Standard deviation |
References
- Baschi, R.; Nicoletti, A.; Restivo, V.; Recca, D.; Zappia, M.; Monastero, R. Frequency and Correlates of Subjective Memory Complaints in Parkinson’s Disease with and without Mild Cognitive Impairment: Data from the Parkinson’s Disease Cognitive Impairment Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 63, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarsland, D.; Batzu, L.; Halliday, G.M.; Geurtsen, G.J.; Ballard, C.; Ray Chaudhuri, K.; Weintraub, D. Parkinson Disease-Associated Cognitive Impairment. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monastero, R.; Cicero, C.E.; Baschi, R.; Davì, M.; Luca, A.; Restivo, V.; Zangara, C.; Fierro, B.; Zappia, M.; Nicoletti, A. Mild Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease: The Parkinson’s Disease Cognitive Study (PACOS). J. Neurol. 2018, 265, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, A.; Baschi, R.; Cicero, C.E.; Iacono, S.; Re, V.L.; Luca, A.; Schirò, G.; Monastero, R. Sex and Gender Differences in Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Narrative Review. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2023, 212, 111821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, L.L.; Weintraub, D.; Lemmen, R.; Perera, G.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Svenningsson, P.; Aarsland, D. Risk of Dementia in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mov. Disord. 2024, 39, 1697–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, A.; Luca, A.; Baschi, R.; Cicero, C.E.; Mostile, G.; Davì, M.; Pilati, L.; Restivo, V.; Zappia, M.; Monastero, R. Incidence of Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia in Parkinson’s Disease: The Parkinson’s Disease Cognitive Impairment Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, A.; Luca, A.; Baschi, R.; Cicero, C.E.; Mostile, G.; Davì, M.; La Bianca, G.; Restivo, V.; Zappia, M.; Monastero, R. Vascular Risk Factors, White Matter Lesions and Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease: The PACOS Longitudinal Study. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvan, I.; Goldman, J.G.; Tröster, A.I.; Schmand, B.A.; Weintraub, D.; Petersen, R.C.; Mollenhauer, B.; Adler, C.H.; Marder, K.; Williams-Gray, C.H.; et al. Diagnostic Criteria for Mild Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease: Movement Disorder Society Task Force Guidelines. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarnall, A.J.; Rochester, L.; Burn, D.J. Mild Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease. Age Ageing 2013, 42, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, D.; Tröster, A.I.; Marras, C.; Stebbins, G. Initial Cognitive Changes in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinkelbach, L.; Brambilla, M.; Manenti, R.; Brem, A.-K. Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation in Parkinson’s Disease: Exploiting Crossroads of Cognition and Mood. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 75, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, A.J.; Hardy, J.; Revesz, T. Parkinson’s Disease. Lancet 2009, 373, 2055–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Machado, C.B.; da Silva, L.M.; Gonçalves, A.F.; Andrade, P.R.; Mendes, C.K.T.T.; de Assis, T.J.C.F.; Godeiro Júnior, C.O.; Andrade, S.M. Multisite Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation in Parkinson’s Disease: A Scoping Review. NeuroRehabilitation 2021, 49, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priori, A. Brain Polarization in Humans: A Reappraisal of an Old Tool for Prolonged Non-Invasive Modulation of Brain Excitability. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2003, 114, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priori, A.; Hallett, M.; Rothwell, J.C. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation or Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation? Brain Stimul. Basic Transl. Clin. Res. Neuromodul. 2009, 2, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioni, A.; Baroni, A.; Fregna, G.; Ahmed, I.; Straudi, S. The Effectiveness of Home-Based Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Chronic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Digit. Health 2024, 10, 20552076241292676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, M.A.; Paulus, W. Excitability Changes Induced in the Human Motor Cortex by Weak Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation. J. Physiol. 2000, 527, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filmer, H.L.; Dux, P.E.; Mattingley, J.B. Applications of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation for Understanding Brain Function. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Groen, O.; Potok, W.; Wenderoth, N.; Edwards, G.; Mattingley, J.B.; Edwards, D. Using Noise for the Better: The Effects of Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation on the Brain and Behavior. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 138, 104702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terney, D.; Chaieb, L.; Moliadze, V.; Antal, A.; Paulus, W. Increasing Human Brain Excitability by Transcranial High-Frequency Random Noise Stimulation. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 14147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, F.; Ward, L.M.; Sannita, W.G. Stochastic Resonance and Sensory Information Processing: A Tutorial and Review of Application. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potok, W.; Bächinger, M.; van der Groen, O.; Cretu, A.L.; Wenderoth, N. Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation Acutely Lowers the Response Threshold of Human Motor Circuits. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monastero, R.; Baschi, R.; Nicoletti, A.; Pilati, L.; Pagano, L.; Cicero, C.E.; Zappia, M.; Brighina, F. Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation over the Primary Motor Cortex in PD-MCI Patients: A Crossover, Randomized, Sham-Controlled Study. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoehn, M.M.; Yahr, M.D. Parkinsonism. Neurology 1967, 17, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjelland, I.; Dahl, A.A.; Haug, T.T.; Neckelmann, D. The Validity of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale: An Updated Literature Review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2002, 52, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mioshi, E.; Dawson, K.; Mitchell, J.; Arnold, R.; Hodges, J.R. The Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination Revised (ACE-R): A Brief Cognitive Test Battery for Dementia Screening. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2006, 21, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, M.; Raimo, S.; Tufano, D.; Basile, G.; Grossi, D.; Santangelo, F.; Trojano, L.; Santangelo, G. The Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination Revised (ACE-R) and Its Sub-Scores: Normative Values in an Italian Population Sample. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A Brief Screening Tool for Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, E.N.; Esposito, A.; Gramegna, C.; Gazzaniga, V.; Zago, S.; Difonzo, T.; Appollonio, I.M.; Bolognini, N. The Frontal Assessment Battery (FAB) and Its Sub-Scales: Validation and Updated Normative Data in an Italian Population Sample. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombaugh, T.N.; Kozak, J.; Rees, L. Normative Data Stratified by Age and Education for Two Measures of Verbal Fluency: FAS and Animal Naming. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 1999, 14, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, C.G.; Tilley, B.C.; Shaftman, S.R.; Stebbins, G.T.; Fahn, S.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Poewe, W.; Sampaio, C.; Stern, M.B.; Dodel, R.; et al. Movement Disorder Society-Sponsored Revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): Scale Presentation and Clinimetric Testing Results. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 2129–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregni, F.; Boggio, P.S.; Nitsche, M.; Bermpohl, F.; Antal, A.; Feredoes, E.; Marcolin, M.A.; Rigonatti, S.P.; Silva, M.T.A.; Paulus, W.; et al. Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation of Prefrontal Cortex Enhances Working Memory. Exp. Brain Res. 2005, 166, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, A.; Capitani, E.; Laiacona, M. Raven’s coloured progressive matrices: Normative values on 305 adult normal controls. Funct. Neurol. 1987, 2, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Monaco, M.; Costa, A.; Caltagirone, C.; Carlesimo, G.A. Forward and Backward Span for Verbal and Visuo-Spatial Data: Standardization and Normative Data from an Italian Adult Population. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 34, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.E.B.; do Nascimento Neto, L.I.; Terra, M.B.; Barboza, N.M.; Okano, A.H.; Smaili, S.M. Effectiveness of Acute Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Non-Motor and Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 696, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.B.; Junqué, C.; Bartrés-Faz, D.; Martí, M.J.; Sala-Llonch, R.; Compta, Y.; Falcón, C.; Vendrell, P.; Pascual-Leone, Á.; Valls-Solé, J.; et al. Modulation of Verbal Fluency Networks by Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Stimul. Basic Transl. Clin. Res. Neuromodul. 2013, 6, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggio, P.S.; Ferrucci, R.; Rigonatti, S.P.; Covre, P.; Nitsche, M.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Fregni, F. Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Working Memory in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 249, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doruk, D.; Gray, Z.; Bravo, G.L.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Fregni, F. Effects of TDCS on Executive Function in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 582, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.-I.; Liu, M.N.; Chang, K.C.; Chang, A.; Bai, C.H.; Tseng, C.S.; Walsh, V.; Wang, H.C. Effect of Single-Session Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Cognition in Parkinson’s Disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballol, N.; Martí, M.J.; Tolosa, E. Cognitive Dysfunction and Dementia in Parkinson Disease. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, S358–S366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganath, C.; Cohen, M.X.; Brozinsky, C.J. Working Memory Maintenance Contributes to Long-Term Memory Formation: Neural and Behavioral Evidence. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2005, 17, 994–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, R.; Brambilla, M.; Benussi, A.; Rosini, S.; Cobelli, C.; Ferrari, C.; Petesi, M.; Orizio, I.; Padovani, A.; Borroni, B.; et al. Mild Cognitive Impairment in Parkinson’s Disease Is Improved by Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Combined with Physical Therapy. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenzato, M.; Manenti, R.; Enrici, I.; Gobbi, E.; Brambilla, M.; Alberici, A.; Cotelli, M.S.; Padovani, A.; Borroni, B.; Cotelli, M. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Enhances Theory of Mind in Parkinson’s Disease Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled Study. Transl. Neurodegener. 2019, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biundo, R.; Weis, L.; Fiorenzato, E.; Gentile, G.; Giglio, M.; Schifano, R.; Campo, M.C.; Marcon, V.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Bisiacchi, P.; et al. Double-Blind Randomized Trial of t-DCS versus Sham in Parkinson Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment Receiving Cognitive Training. Brain Stimul. 2015, 8, 1223–1225, Erratum in Brain Stimul. 2016, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Felice, A.; Castiglia, L.; Formaggio, E.; Cattelan, M.; Scarpa, B.; Manganotti, P.; Tenconi, E.; Masiero, S. Personalized Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (TACS) and Physical Therapy to Treat Motor and Cognitive Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Cross-over Trial. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 22, 101768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.L.; Yang, Y.R.; Huang, S.F.; Wang, R.Y. Effects of DLPFC TDCS Followed by Treadmill Training on Dual-Task Gait and Cortical Excitability in Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2024, 38, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, B.; Caridade-Silva, R.; Soares-Guedes, C.; Martins-Macedo, J.; Gomes, E.D.; Monteiro, S.; Teixeira, F.G. Neuroinflammation and Parkinson’s Disease—From Neurodegeneration to Therapeutic Opportunities. Cells 2022, 11, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yan, Q.; Wang, A.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Yao, L. Dual-Target TDCS and Dual-Task Training Modulate Neuroinflammation and Neuroplasticity: Transcriptomic and Behavioral Evidence in Stroke Rehabilitation. Front. Rehabil. Sci. 2025, 6, e1589588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Mean ± SD | Min–Max |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 67.0 ± 7.4 | 55–77 |
| Disease duration (years) | 7.3 ± 4.0 | 1–13 |
| Levodopa dose (mg/day) | 518.7 ± 298.3 | 0–885 |
| Sex | 8 Male (80%)/2 Female (20%) | — |
| Number of participants | 10 | — |
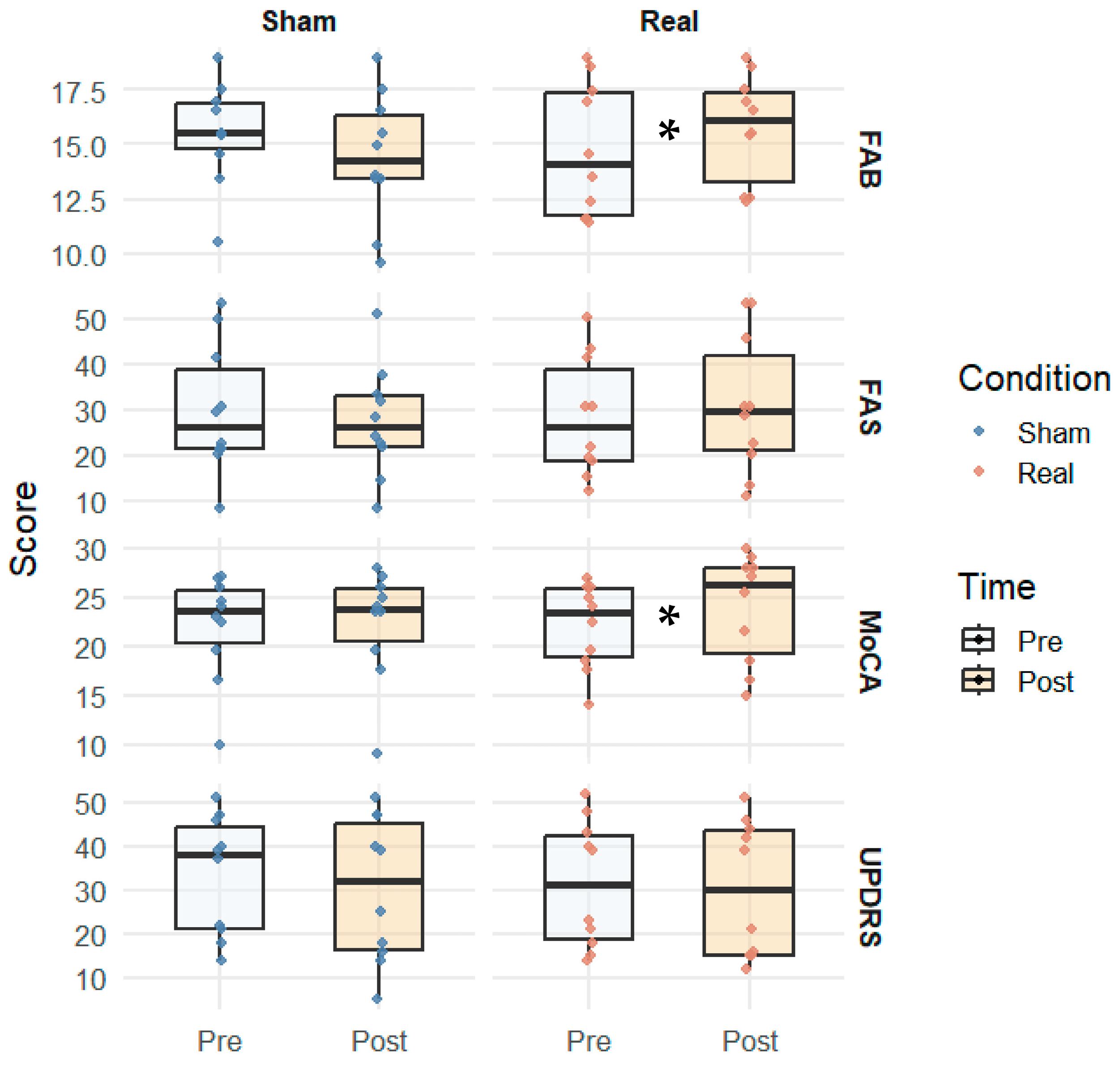
| Test | Real Pre (M ± SD) | Real Post (M ± SD) | p-Value | Sham Pre (M ± SD) | Sham Post (M ± SD) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAB | 14.7 (±2.6) | 15.7 (±2.7) | 0.022 | 15.5 (±2.3) | 14.4 (±2.8) | 0.057 |
| FAS | 28.4 (±12.0) | 31.0 (±12.5) | 0.087 | 30.0 (±10.0) | 27.3 (±11.5) | 0.176 |
| MoCA total | 22.0 (±3.8) | 23.9 (±4.2) | 0.018 | 22.0 (±3.5) | 22.3 (±4.0) | 0.299 |
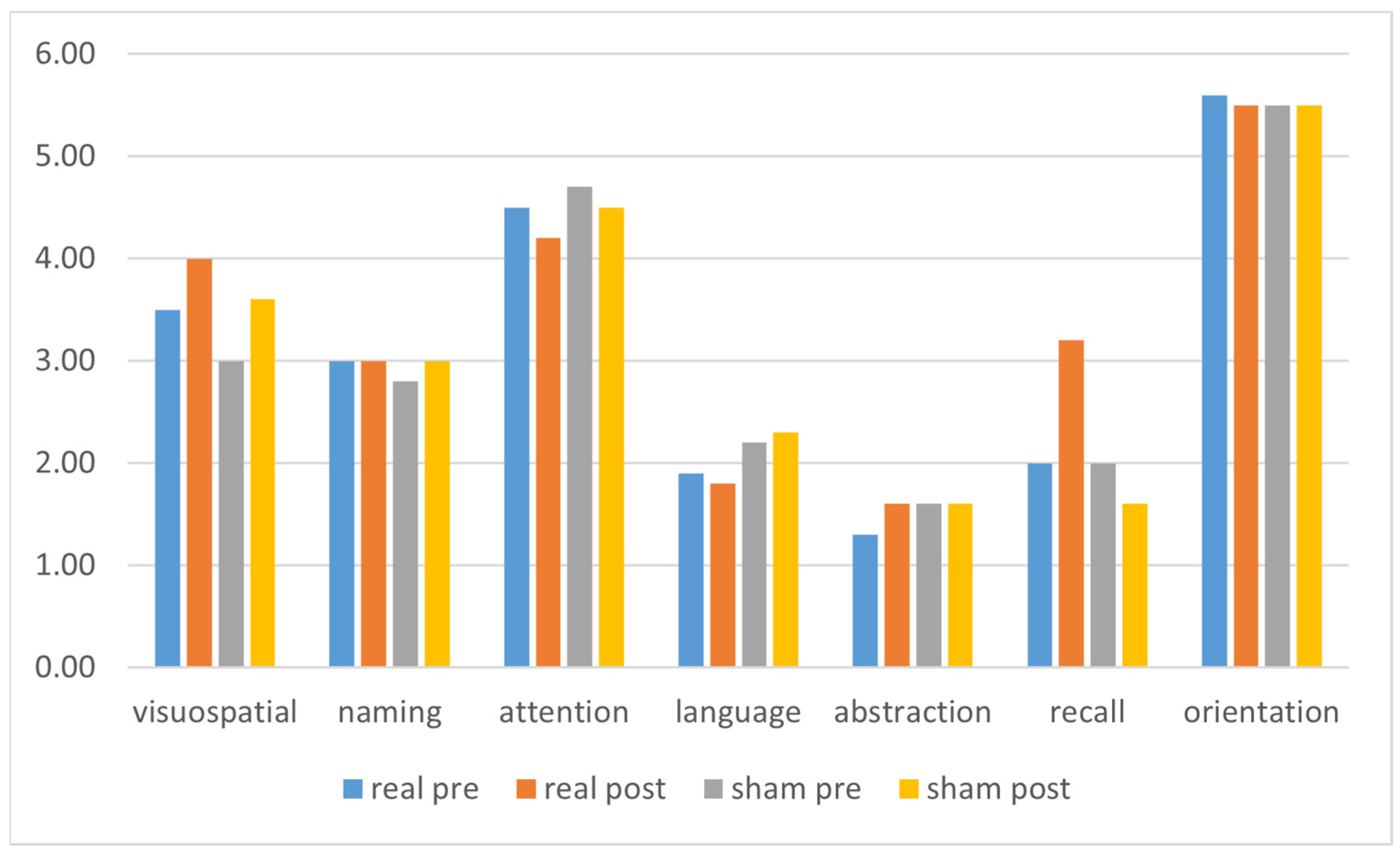
| Visuospatial | 3.5 (±1.1) | 4.0 (±1.0) | 0.168 | 3.0 (±1.0) | 3.6 (±1.2) | 0.048 |
| Naming | 3.0 (±0.0) | 3.0 (±0.0) | na | 2.8 (±0.4) | 3.0 (±0.0) | 0.346 |
| Attention | 4.5 (±1.3) | 4.2 (±1.5) | 0.586 | 4.7 (±1.5) | 4.5 (±1.6) | 0.572 |
| Language | 1.9 (±0.9) | 1.8 (±0.9) | 0.773 | 2.2 (±0.8) | 2.3 (±0.7) | 1.000 |
| Abstraction | 1.3 (±0.8) | 1.6 (±0.7) | 0.233 | 1.6 (±0.7) | 1.6 (±0.6) | 1.000 |
| Recall | 2.0 (±1.2) | 3.2 (±1.3) | 0.061 | 2.0 (±1.0) | 1.6 (±1.0) | 0.265 |
| Orientation | 5.6 (±0.7) | 5.5 (±0.8) | 0.773 | 5.5 (±0.7) | 5.5 (±0.6) | na |
| UPDRS (motor) | 31.3 (±12.5) | 30.1 (±13.2) | 0.114 | 33.5 (±12.0) | 30.2 (±13.0) | 0.611 |
| Parameter | Group | Mean | SD | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
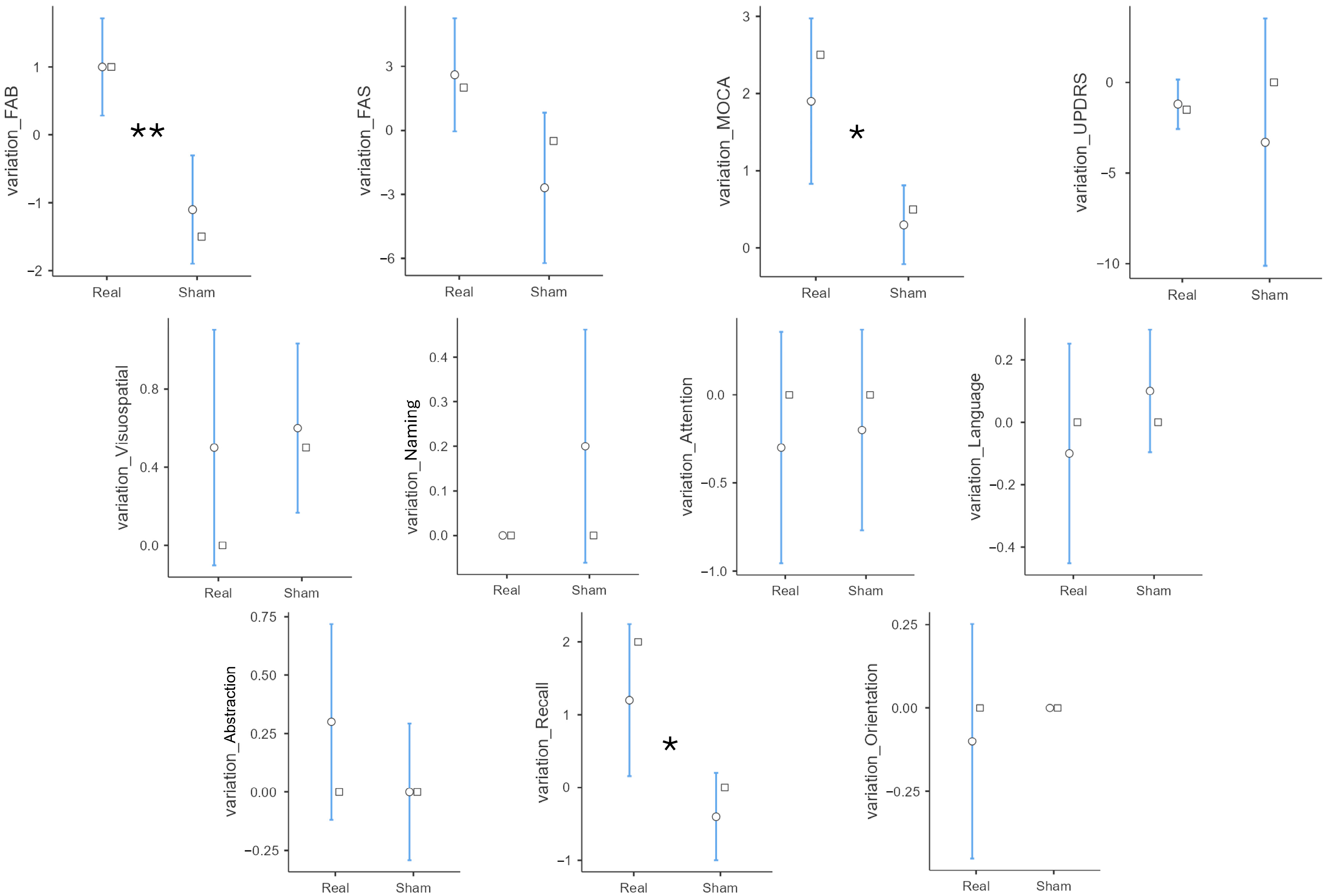
| variation_FAB | Real | 1.00 | 1.15 | 0.001 |
| Sham | −1.10 | 1.29 | ||
| variation_FAS | Real | 2.60 | 4.27 | 0.087 |
| Sham | −2.70 | 5.70 | ||
| variation_MoCA | Real | 1.90 | 1.73 | 0.017 |
| Sham | 0.30 | 0.82 | ||
| variation_Visuospatial | Real | 0.50 | 0.97 | 0.742 |
| Sham | 0.60 | 0.70 | ||
| variation_Naming | Real | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.167 |
| Sham | 0.20 | 0.42 | ||
| variation_Attention | Real | −0.30 | 1.06 | 1.000 |
| Sham | −0.20 | 0.92 | ||
| variation_Language | Real | −0.10 | 0.57 | 0.357 |
| Sham | 0.10 | 0.32 | ||
| variation_Abstraction | Real | 0.30 | 0.67 | 0.244 |
| Sham | 0.00 | 0.47 | ||
| variation_Recall | Real | 1.20 | 1.69 | 0.018 |
| Sham | −0.40 | 0.97 | ||
| variation_Orientation | Real | −0.10 | 0.57 | 0.584 |
| Sham | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||
| variation_UPDRS | Real | −1.20 | 2.20 | 0.444 |
| Sham | −3.30 | 11.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mazzara, D.; Torrente, A.; Alonge, P.; Baschi, R.; Campione, M.; Di Stefano, V.; La Bianca, G.; Brighina, F.; Monastero, R. Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation over the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot Study. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111232
Mazzara D, Torrente A, Alonge P, Baschi R, Campione M, Di Stefano V, La Bianca G, Brighina F, Monastero R. Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation over the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot Study. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(11):1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111232
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazzara, Davide, Angelo Torrente, Paolo Alonge, Roberta Baschi, Marina Campione, Vincenzo Di Stefano, Giuseppe La Bianca, Filippo Brighina, and Roberto Monastero. 2025. "Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation over the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot Study" Brain Sciences 15, no. 11: 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111232
APA StyleMazzara, D., Torrente, A., Alonge, P., Baschi, R., Campione, M., Di Stefano, V., La Bianca, G., Brighina, F., & Monastero, R. (2025). Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation over the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Pilot Study. Brain Sciences, 15(11), 1232. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111232











