Plasma Heparin-Binding Protein as a Predictor of Functional Recovery and a Potential Therapeutic Target in Acute Anterior Circulation Large-Vessel Occlusion Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Clinical Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Laboratory Findings
3.3. Associations of HBP with Poor Outcomes
3.4. Comparative and Predictive Value of HBP for Poor 90-Day Functional Outcomes
3.5. Assessment of Model Improvement and Overfitting for Model 3
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC-LVO | anterior circulation large-vessel occlusion |
| AIS | acute ischemic stroke |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| CI | confidence interval |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CTA | computed tomography angiography |
| FBG | fasting blood glucose |
| HbA1c | glycated hemoglobin |
| HBP | heparin-binding protein |
| HDL | high-density lipoprotein |
| HCY | homocysteine |
| HT | hemorrhagic transformation |
| ICH | intracranial hemorrhage |
| ICA | internal carotid artery |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| LMR | lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio |
| LDL | low-density lipoprotein |
| LVO | large-vessel occlusion |
| MCA | middle cerebral artery |
| mRS | modified Rankin Scale |
| MT | mechanical thrombectomy |
| NLR | neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| NIHSS | National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale |
| OR | odds ratio |
| PLR | platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| SAA | serum amyloid A |
| sICH | symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage |
| SD | standard deviation |
| TIA | transient ischemic attack |
| TG | triglycerides |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| TOAST | Trial of ORG 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment |
| TC | total cholesterol |
References
- Global, Regional, and National Burden of Stroke and Its Risk Factors, 1990-2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Ashutosh, P.J.; Diogo, C.H.; Alain, B.; Ronald, F.B.; Parita, B.; Dileep, R.Y.; Marc, R.; Christophe, C.; Ricardo, A.H.; et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 Hours after Stroke with a Mismatch between Deficit and Infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinel, T.R.; Kaesmacher, J.; Mosimann, P.J.; Seiffge, D.; Jung, S.; Mordasini, P.; Arnold, M.; Goeldlin, M.; Hajdu, S.D.; Olivé-Gadea, M.; et al. Association of Initial Imaging Modality and Futile Recanalization after Thrombectomy. Neurology 2020, 17, e2331–e2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, Y.; Yang, L.; Ren, C.; Li, C.; Xu, J.; Guo, W.; Zhao, W.; Ji, X. The Effect of Systemic Inflammatory Response on Mechanical Thrombectomy Is Partly Mediated by Pre-Thrombectomy Cerebral Edema in Acute Stroke Patients. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2025, 4, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zeng, L.; Ge, A.; Wang, S.; Zeng, J.; Yuan, X.; Mei, Z.; Wang, G.; Ge, J. A Systematic Review of the Research Progress of Non-Coding Rna in Neuroinflammation and Immune Regulation in Cerebral Infarction/Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 930171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadecola, C.; Anrather, J. The Immunology of Stroke: From Mechanisms to Translation. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuyama, J.; Nakamura, A.; Ooboshi, H.; Yoshimura, A.; Shichita, T. Pivotal Role of Innate Myeloid Cells in Cerebral Post-Ischemic Sterile Inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2018, 40, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jickling, G.C.; Liu, D.; Ander, B.P.; Stamova, B.; Zhan, X.; Sharp, F.R. Targeting Neutrophils in Ischemic Stroke: Translational Insights from Experimental Studies. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 888–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Yu, H.; Yang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Bai, X.; Wang, R.; Cao, Y.; Xu, H.; Luo, H.; Lu, L.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Released by Neutrophils Impair Revascularization and Vascular Remodeling after Stroke. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteley, W.; Jackson, C.; Lewis, S.; Lowe, G.; Rumley, A.; Sandercock, P.; Wardlaw, J.; Dennis, M.; Sudlow, C. Association of Circulating Inflammatory Markers with Recurrent Vascular Events after Stroke: A Prospective Cohort Study. Stroke 2011, 42, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, B.H.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Saver, J.L.; Bang, O.Y.; Yun, S.W.; Starkman, S.; Ali, L.K.; Kim, D.; Villablanca, J.P.; Salamon, N.; et al. Early Neutrophilia Is Associated with Volume of Ischemic Tissue in Acute Stroke. Stroke 2008, 39, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Song, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, S.; Deng, L.; Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Liu, M. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Poor Outcomes after Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Cohort Study and Systematic Review. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 406, 116445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.W.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, J.S.; Kwon, H.M.; Lee, Y.S.; Ko, S.B.; Yoon, B.W. High Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Stroke-Associated Pneumonia. Stroke 2018, 49, 1886–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liao, C.; Liu, Q. Prognostic Value of Tnf-A, Pct, Il-8, and Hbp, Combined with Apache Ii Score in Patients with Sepsis. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2025, 19, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.S.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Gad, H.; Antar, M.; Elgazar, A.; Anil, V.; Diedrich, D.A.; Laudanski, K. Longitudinal Analysis of Traditional Inflammatory Markers (Il-6, Crp) Juxtaposed with Heparin-Binding Protein (Hbp) and Serum Amyloid a Protein Component (Saa) During Acute Infection and Convalescence from Covid-19 Infection in the Context of Initial Viral Load and Markers of Tissue Destruction. J. Immunol. Res. 2025, 2025, 8881752. [Google Scholar]
- Linder, A.; Soehnlein, O.; Akesson, P. Roles of Heparin-Binding Protein in Bacterial Infections. J. Innate Immun. 2010, 2, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.; Linder, A. Heparin-Binding Protein: A Key Player in the Pathophysiology of Organ Dysfunction in Sepsis. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 281, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tydén, J.; Herwald, H.; Sjöberg, F.; Johansson, J. Increased Plasma Levels of Heparin-Binding Protein on Admission to Intensive Care Are Associated with Respiratory and Circulatory Failure. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Jiang, B.; Hu, D.; Zhao, M. Heparin-Binding Protein: A Novel Biomarker Linking Four Different Cardiovascular Diseases. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 9575373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, N.; Olofsson, A.M.; Herwald, H.; Iversen, L.F.; Lundgren-Åkerlund, E.; Hedqvist, P.; Arfors, K.-E.; Flodgaard, H.; Lindbom, L. Heparin-Binding Protein (Hbp/Cap37): A Missing Link in Neutrophil-Evoked Alteration of Vascular Permeability. Nat. Med. 2021, 7, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, Á.; Dirnagl, U.; Urra, X.; Planas, A.M. Neuroprotection in Acute Stroke: Targeting Excitotoxicity, Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress, and Inflammation. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candelario-Jalil, E.; Dijkhuizen, R.M.; Magnus, T. Neuroinflammation, Stroke, Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction, and Imaging Modalities. Stroke 2022, 53, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, L.; Ma, X. Transforming Growth Factor-Β Receptor Type 2 Is Required for Heparin-Binding Protein-Induced Acute Lung Injury and Vascular Leakage for Transforming Growth Factor-Β/Smad/Rho Signaling Pathway Activation. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinel, T.R.; Lerch, C.; Fischer, U.; Beyeler, M.; Mujanovic, A.; Kurmann, C.; Siepen, B.; Scutelnic, A.; Müller, M.; Goeldlin, M.; et al. Multivariable Prediction Model for Futile Recanalization Therapies in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Neurology 2022, 99, e1009–e1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, G. Predictive Role of a Combined Model for Futile Recanalization in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Front. Neurol. 2025, 16, 1566842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, A.; Akesson, P.; Brink, M.; Studahl, M.; Björck, L.; Christensson, B. Heparin-Binding Protein: A Diagnostic Marker of Acute Bacterial Meningitis. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, G.; Li, F.; Cheng, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhang, J. Usefulness of the Heparin-Binding Protein Level to Diagnose Sepsis and Septic Shock According to Sepsis-3 Compared with Procalcitonin and C Reactive Protein: A Prospective Cohort Study in China. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e026527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.; Kahn, F.; Wiebe, E.; Gustafsson, P.; Kander, T.; Mellhammar, L.; Bentzer, P.; Linder, A. The Dynamics of Circulating Heparin-Binding Protein: Implications for Its Use as a Biomarker. J. Innate Immun. 2022, 14, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
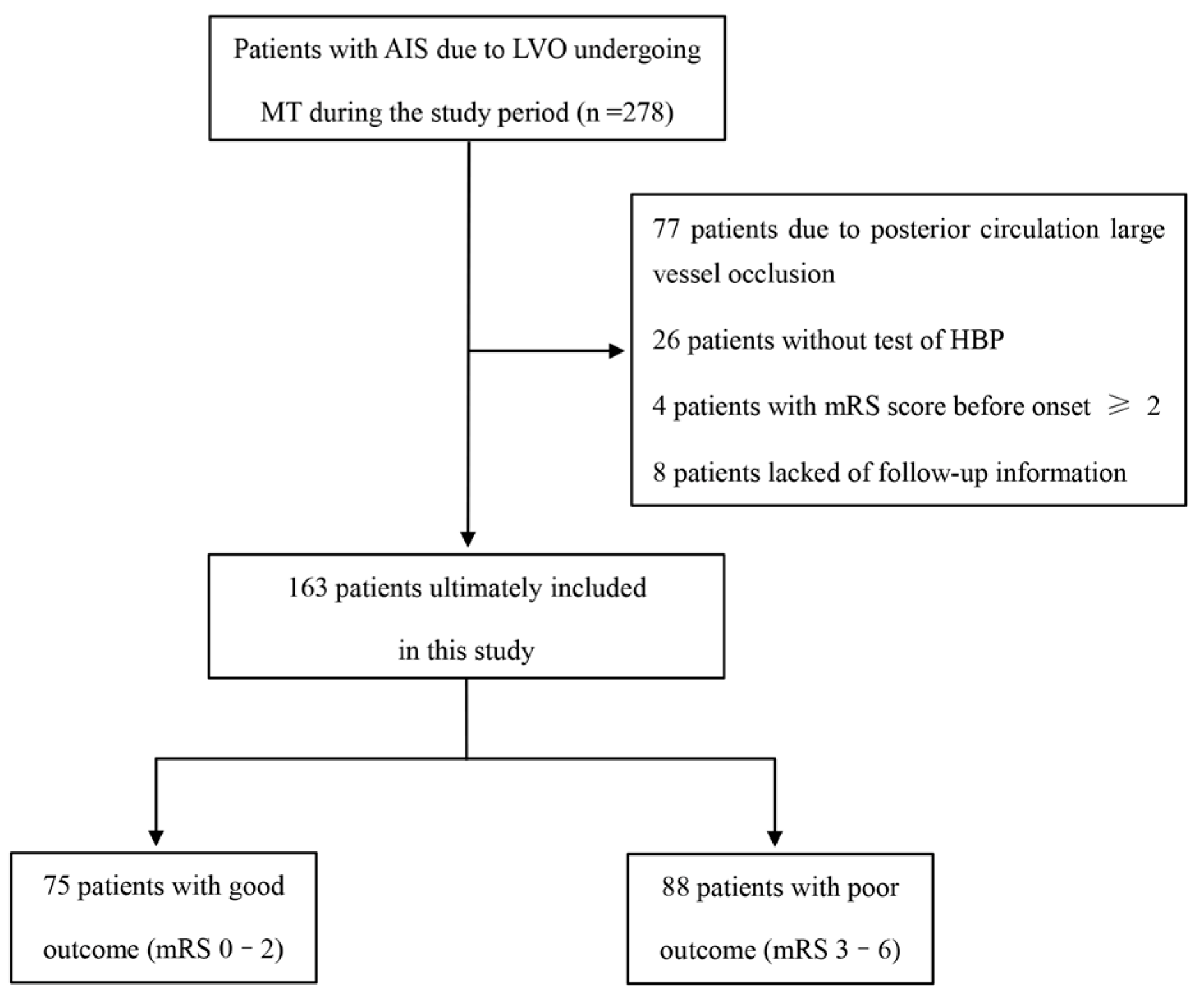
| 90-Day Functional Outcome | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Overall n = 163 | mRS 0–2 n = 75 | mRS 3–6 n = 88 | p Value |
| Baseline characteristics | ||||
| Age, years | 73 (66–79) | 71 (65.75–80.75) | 75 (68.75–82.25) | 0.036 |
| Sex, Men, n (%) | 114 (69.9) | 50 (66.7) | 64 (72.7) | 0.400 |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 60 (36.8) | 28 (17.2) | 32 (19.6) | 0.898 |
| Medical history, n (%) | ||||
| Hypertension | 109 (66.9) | 49 (65.3) | 60 (68.2) | 0.700 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 50 (30.7) | 22 (29.3) | 28 (31.8) | 0.732 |
| Previous TIA/stroke | 36 (22.1) | 14 (18.7) | 22 (25.0) | 0.331 |
| Cardiovascular disease, | 26 (16.0) | 16 (21.3) | 10 (11.4) | 0.083 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 5 1(31.3) | 16 (21.3) | 35 (39.8) | 0.110 |
| Initial clinical assessment | ||||
| Baseline NIHSS score | 14.07 ± 6.32 | 11.99 ± 5.54 | 15.83 ± 6.42 | <0.001 |
| Baseline glucose, mmol/L, median (IQR) | 7.20 (6.30–9.25) | 6.50 (5.83–7.78) | 7.70 (6.40–10.38) | 0.100 |
| Stroke etiology, n (%) | ||||
| Large-artery atherosclerosis | 74 (45.4) | 42 (56.0) | 32 (36.4) | 0.012 |
| Cardioembolism | 75 (46.0) | 28 (37.3) | 47 (53.4) | 0.400 |
| Others | 14 (8.6) | 5 (6.7) | 9 (10.2) | 0.419 |
| Site of occlusion [n, (%)] | ||||
| Distal ICA, M1, M2 occlusion | 124 (76.1) | 62 (82.7) | 62 (70.5) | |
| Tandem occlusion | 39 (23.9) | 13 (17.3) | 26 (29.5) | 0.069 |
| Procedural characteristics, n (%) | ||||
| Intravenous thrombolysis | 41 (25.2) | 19 (25.3) | 22 (25.0) | 0.961 |
| Unknown symptom onset, n (%) | 58 (35.6) | 26 (34.7) | 32 (36.4) | 0.822 |
| Onset-to-door, min, median (IQR) | 180 (120–300) | 180 (120–293) | 225 (180–300) | 0.385 |
| Onset-to-groin, mean (SD) | 419.33 ± 165.99 | 402.62 ± 178.51 | 434.25 ± 154.06 | 0.267 |
| Procedure duration, min, median (IQR) | 110 (80–140) | 105 (83–140) | 115 (85–146) | 0.158 |
| Clinical outcomes, n (%) | ||||
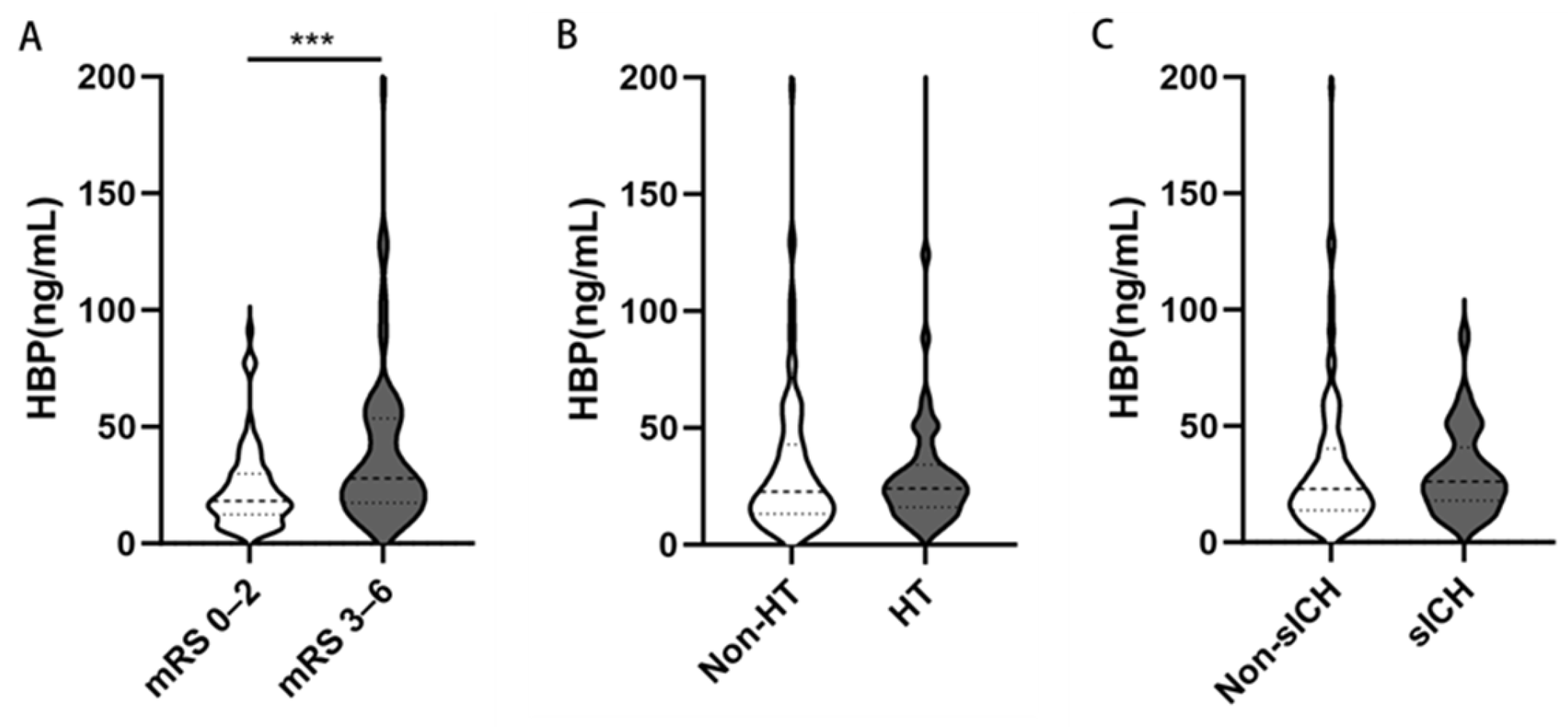
| HT | 50 (30.7) | 11 (14.7) | 39 (44.3) | <0.001 |
| sICH | 32 (19.6) | 7 (9.3) | 25 (28.4) | 0.002 |
| Variables | 90-Day Functional Outcome | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall n = 163 | mRS 0–2 n = 75 | mRS 3–6 n = 88 | p-Value | |
| Hematological parameters | ||||
| White blood cell, ×109/L, median (IQR) | 9.00 (7.46–10.76) | 8.07 (6.48–9.91) | 9.57 (8.35–12.18) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil, ×109/L, median (IQR) | 7.49 (5.94–9.51) | 6.53 (4.81–8.00) | 8.29 (6.76–10.76) | <0.001 |
| Lymphocyte, ×109/L, median (IQR) | 0.81 (0.60–1.25) | 0.86 (0.61–1.43) | 0.82 (0.59–1.08) | 0.323 |
| Monocyte, ×109/L, median (IQR) | 0.46 (0.33–0.62) | 0.41 (0.23–0.58) | 0.48 (0.37–0.65) | <0.001 |
| Red blood cell, ×1012/L, mean (SD) | 4.03 ± 0.62 | 4.04 ± 0.61 | 4.01 ± 0.64 | 0.74 |
| Hemoglobin, g/L, median (IQR) | 126(112–137) | 127 (112–140) | 125 (113–136) | 0.494 |
| Platelet count, ×109/L, median (IQR) | 174 (145–235) | 171 (153–229) | 179 (135–246) | 0.757 |
| Biochemical markers | ||||
| Triglycerides (mmol/L), median (IQR) | 1.33 (0.93–1.99) | 1.23 (0.83–1.94) | 1.41 (0.99–2.07) | 0.288 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L), mean (SD) | 3.81 ± 0.95 | 3.87 ± 0.90 | 3.76 ± 0.99 | 0.467 |
| HDL (mmol/L), mean (SD) | 1.06 ± 0.29 | 1.07 ± 0.33 | 1.06 ± 0.26 | 0.773 |
| LDL (mmol/L), mean (SD) | 2.25 ± 0.82 | 2.26 ± 0.82 | 2.24 ± 0.83 | 0.415 |
| D-dimer(mg/L), median (IQR) | 1.55 (0.75–3.85) | 1.09 (0.57–2.55) | 1.80 (0.95–4.22) | 0.002 |
| Homocysteine (µmol/L), median (IQR) | 12.70 (9.40–19.50) | 11.30 (8.65–14.85) | 15.00 (10.80–21.40) | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol), median (IQR) | 6.00 (5.70–6.93) | 5.90 (5.70–6.80) | 6.20 (5.80–7.00) | 0.839 |
| Inflammatory biomarkers | ||||
| CRP (mg/L), median (IQR) | 10.96 (4.40–23.13) | 7.22 (2.74–15.91) | 13.15 (6.32–23.74) | 0.004 |
| SAA (mg/L), median (IQR) | 21.19 (8.01–59.42) | 8.73 (8.00–32.07) | 31.92 (11.47–75.38) | <0.001 |
| HBP (ng/mL), median (IQR) | 23.11 (14.78–40.25) | 18.42 (12.03–30.84) | 28.80 (18.48–53.94) | <0.001 |
| NLR, median (IQR) | 9.81 (5.41–13.48) | 6.82 (4.92–10.67) | 10.76 (6.41–15.94) | <0.001 |
| LMR, median (IQR) | 1.93 (1.31–3.12) | 2.38 (1.70–4.00) | 1.61 (1.1–2.40) | <0.001 |
| PLR, median (IQR) | 213 (148–316) | 202 (137–290) | 228 (168–356) | 0.045 |
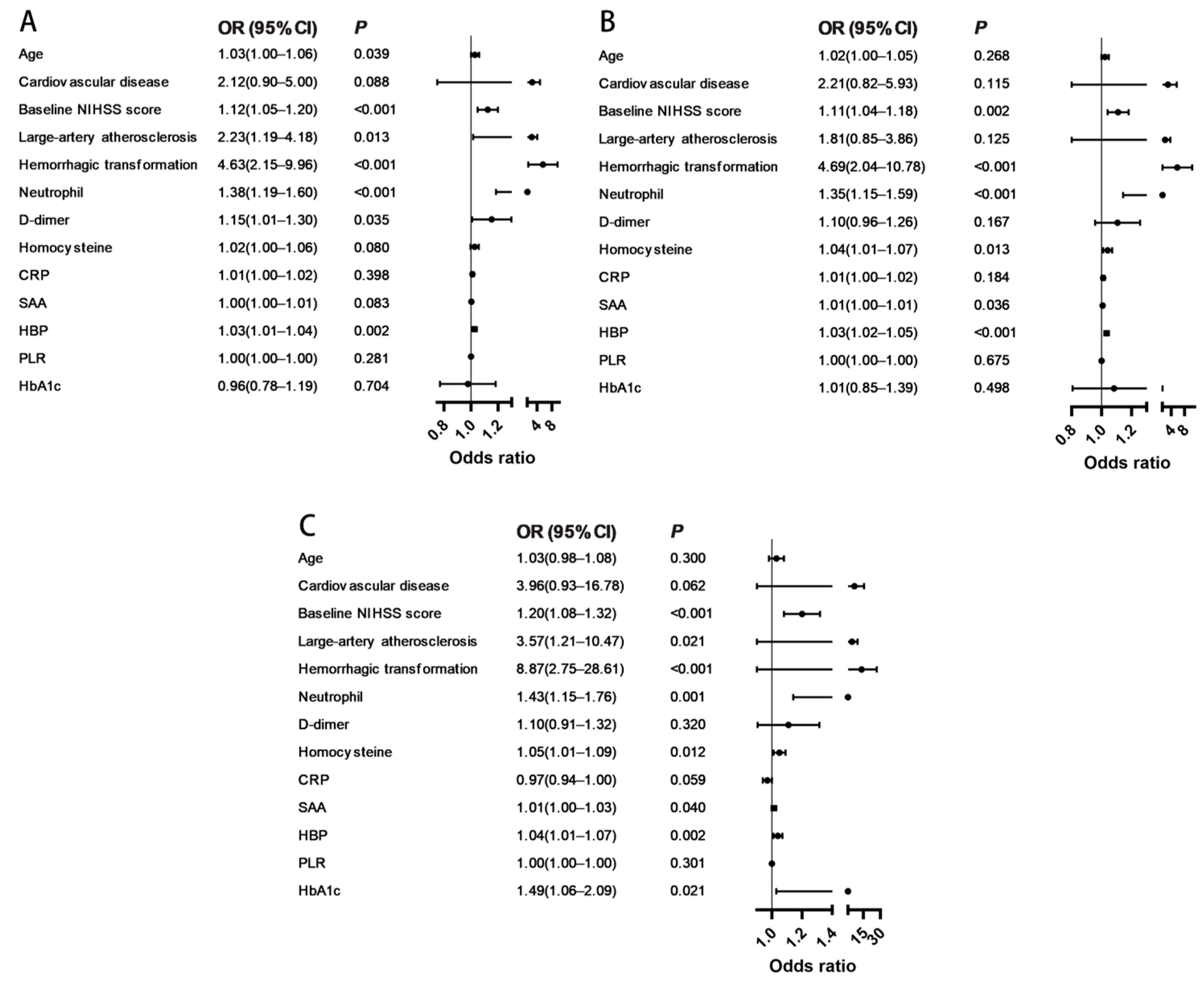
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age | 1.03 (1.00–1.06) | 0.039 | 1.02 (1.00–1.05) | 0.268 | 1.03 (0.98–1.08) | 0.300 |
| Baseline NIHSS score | 1.12 (1.05–1.20) | <0.001 | 1.11 (1.04–1.18) | 0.002 | 1.20 (1.08–1.32) | <0.001 |
| Large-artery atherosclerosis | 2.23 (1.19–4.18) | 0.013 | 1.81 (0.85–3.86) | 0.125 | 3.57 (1.21–10.47) | 0.021 |
| Hemorrhagic transformation | 4.63 (2.15–9.96) | <0.001 | 4.69 (2.04–10.78) | <0.001 | 8.87 (2.75–28.61) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil | 1.38 (1.19–1.60) | <0.001 | 1.35 (1.15–1.59) | <0.001 | 1.43 (1.15–1.76) | 0.001 |
| D-dimer | 1.15 (1.01–1.30) | 0.035 | 1.10 (0.96–1.26) | 0.167 | 1.10 (0.91–1.32) | 0.320 |
| Homocysteine | 1.02 (1.00–1.06) | 0.080 | 1.04 (1.01–1.07) | 0.013 | 1.05 (1.01–1.09) | 0.012 |
| SAA | 1.00 (1.00–1.01) | 0.083 | 1.01 (1.00–1.01) | 0.036 | 1.01 (1.00–1.03) | 0.040 |
| HBP | 1.03 (1.01–1.04) | 0.002 | 1.03 (1.02–1.05) | <0.001 | 1.04 (1.01–1.07) | 0.002 |
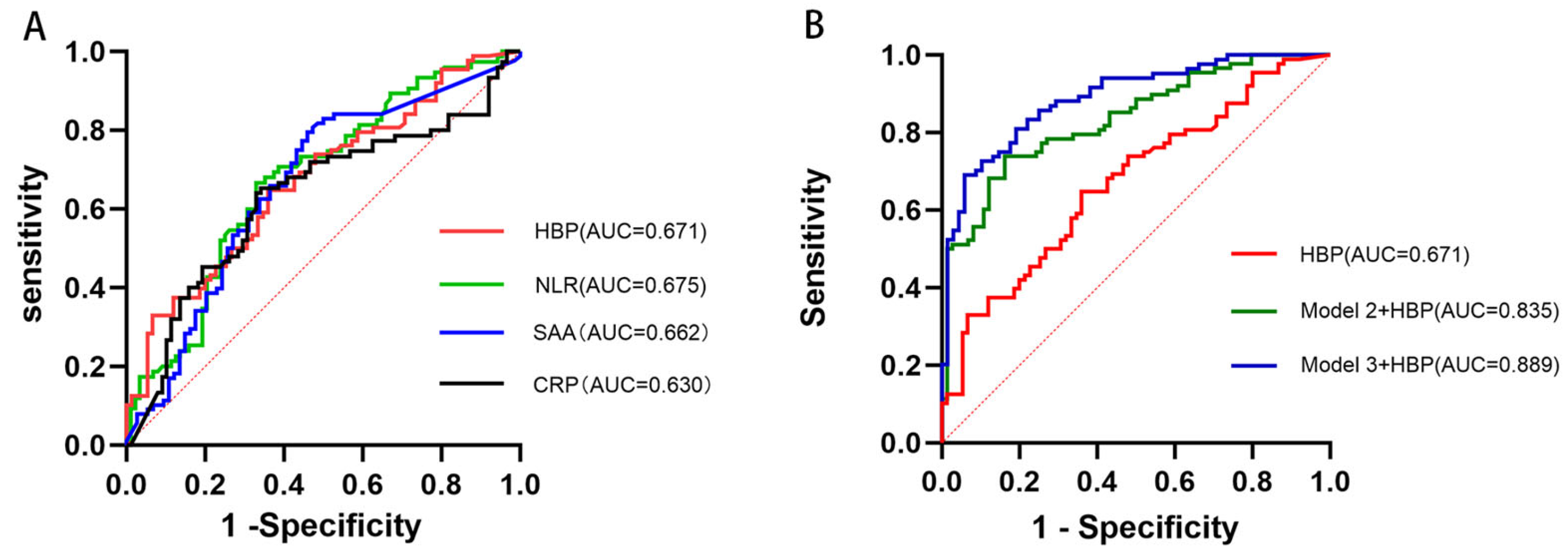
| Model | Original AUC (95% CI) | 10-Fold Cross-Validation AUC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Model 1 (HBP) | 0.671 (0.590–0.754) | 0.690 (0.606–0.775) |
| Model 2 + HBP | 0.835 (0.774–0.896) | 0.819 (0.798–0.840) |
| Model 3 + HBP | 0.889 (0.838–0.940) | 0.844 (0.794–0.894) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.; An, H.; Yin, Y.; Huang, D. Plasma Heparin-Binding Protein as a Predictor of Functional Recovery and a Potential Therapeutic Target in Acute Anterior Circulation Large-Vessel Occlusion Stroke. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111216
Wu C, An H, Yin Y, Huang D. Plasma Heparin-Binding Protein as a Predictor of Functional Recovery and a Potential Therapeutic Target in Acute Anterior Circulation Large-Vessel Occlusion Stroke. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(11):1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111216
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chao, Hedi An, You Yin, and Dongya Huang. 2025. "Plasma Heparin-Binding Protein as a Predictor of Functional Recovery and a Potential Therapeutic Target in Acute Anterior Circulation Large-Vessel Occlusion Stroke" Brain Sciences 15, no. 11: 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111216
APA StyleWu, C., An, H., Yin, Y., & Huang, D. (2025). Plasma Heparin-Binding Protein as a Predictor of Functional Recovery and a Potential Therapeutic Target in Acute Anterior Circulation Large-Vessel Occlusion Stroke. Brain Sciences, 15(11), 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111216





