Cerebral Perfusion Pressure in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Survivors and Non-Survivors: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy—Information Sources
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Selection Process
2.4. Data Collection Process
2.5. Evidence Synthesis
2.6. Risk of Bias Assessment
3. Results
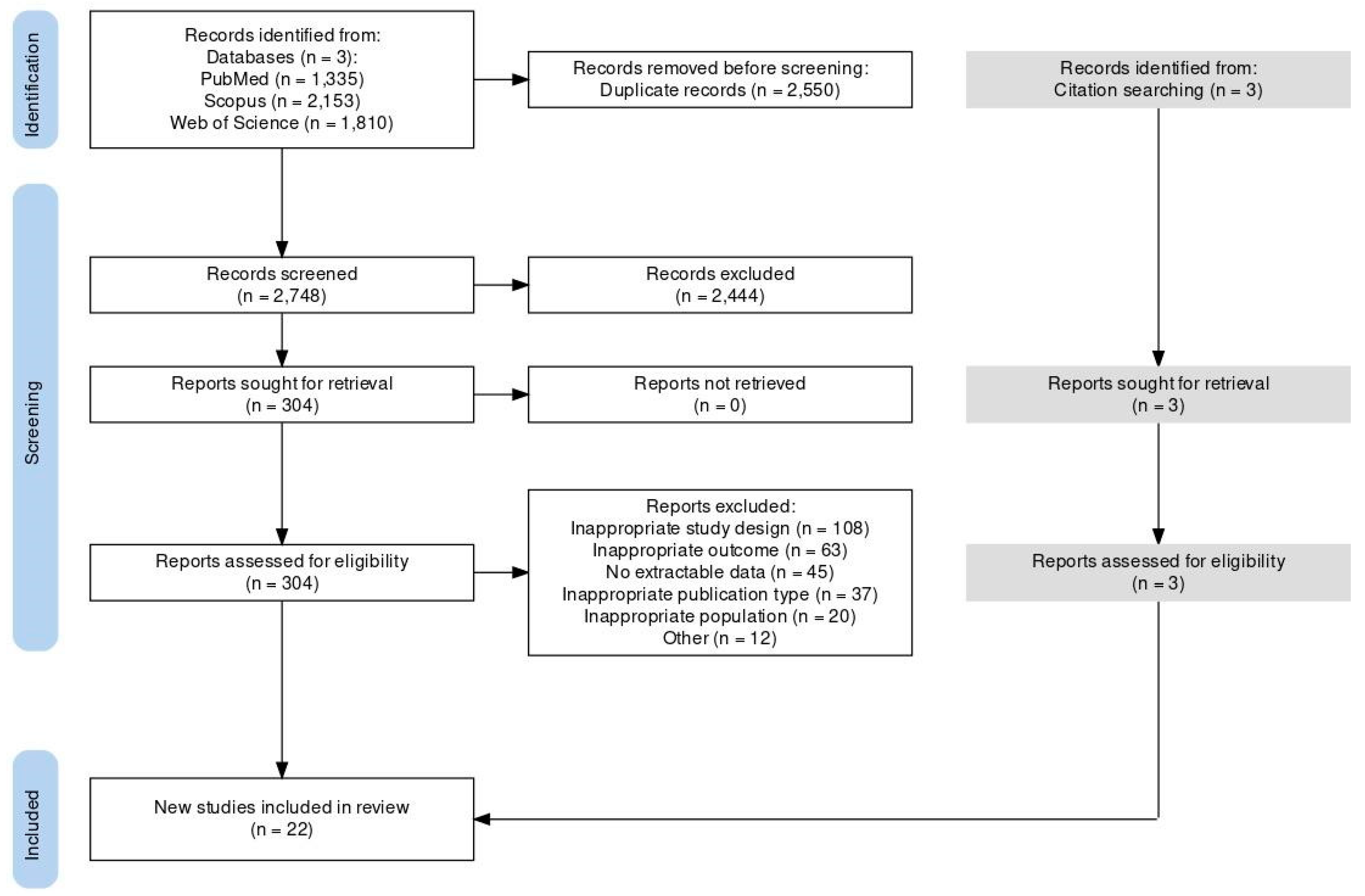
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Eligible Studies
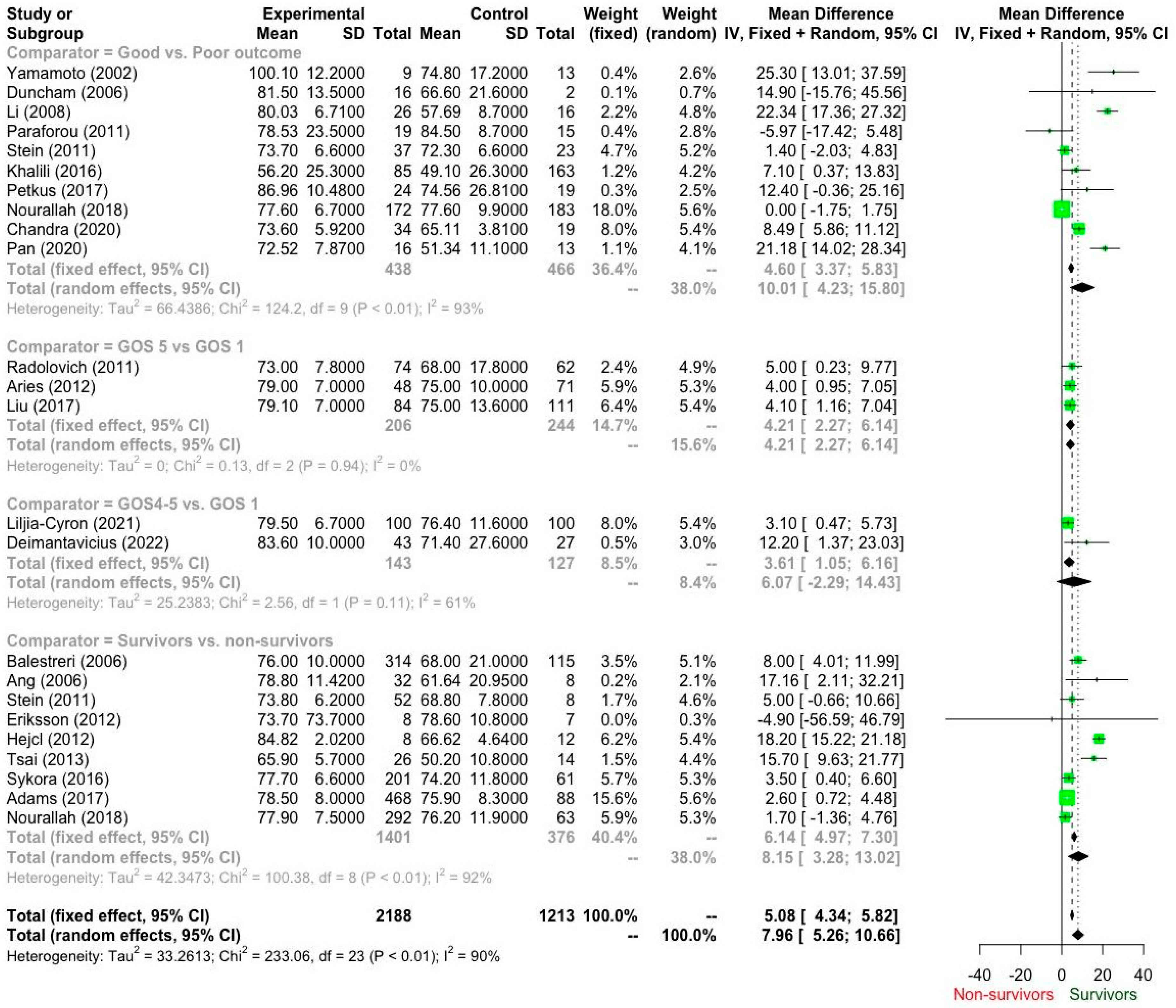
3.3. Pooled Estimates
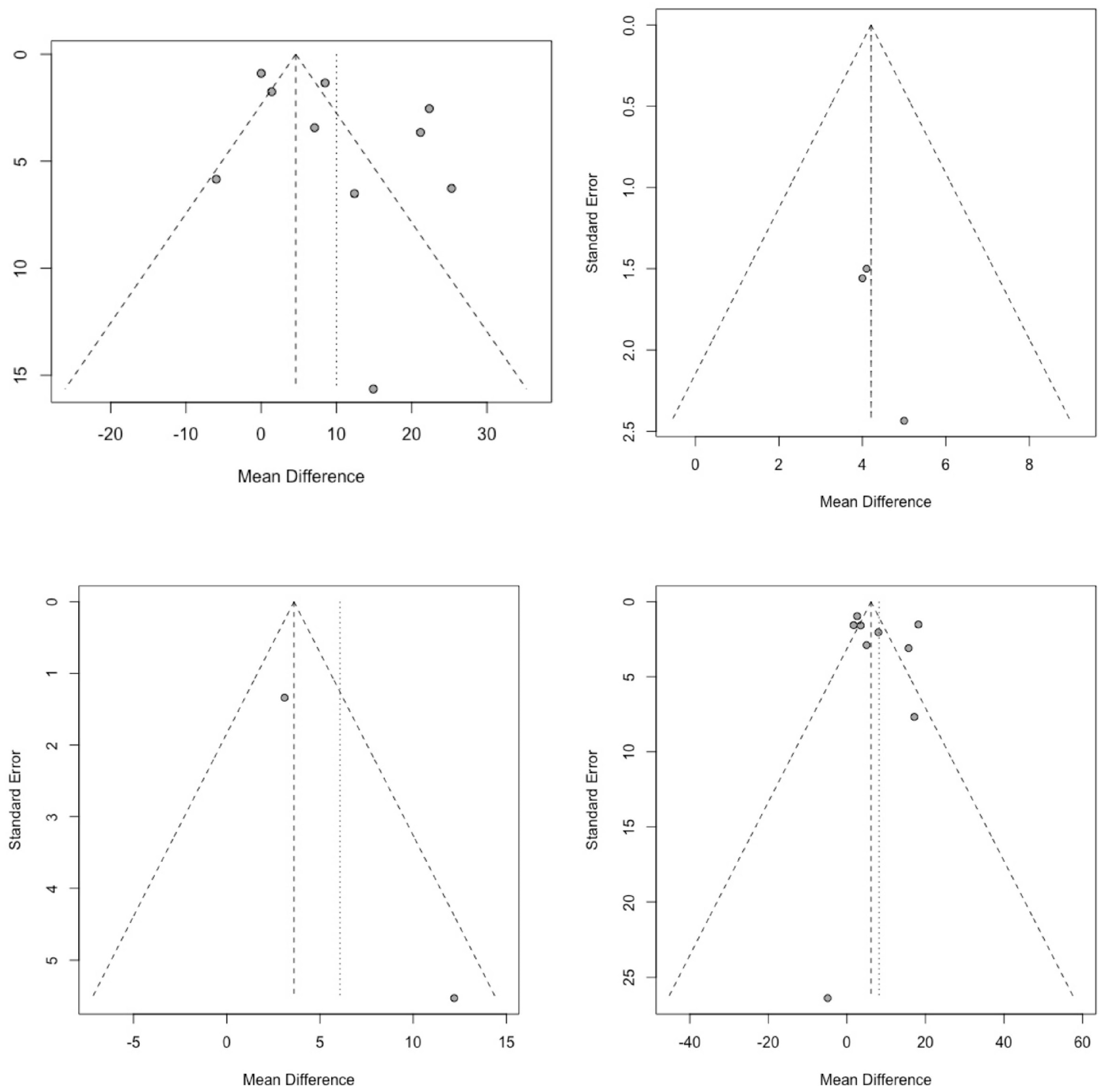
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
3.4.1. Survivors vs. Non-Survivors: Subgroup Analysis by Country/Region
3.4.2. Poor vs. Good Outcome: Subgroup Analysis by Country
4. Discussion
4.1. Overview of Our Findings
4.2. Comparison with the Literature
4.3. Implementation of Our Findings
4.4. CPP and LMICs
4.5. Gaps in the Literature
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, H.; Feng, Y.; Shen, J.; Rao, T.; Dai, H.; Zhong, W.; Zhao, G. Global burden of traumatic brain injury in 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2021. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2025, 68, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capizzi, A.; Woo, J.; Verduzco-Gutierrez, M. Traumatic brain injury: An overview of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and medical management. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 104, 213–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, G.S.; Engel, D.C.; Butcher, I.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Lu, J.; Mushkudiani, N.; Hernández, A.V.; Marmarou, A.; Maas, A.I.R.; Murray, G.D. Prognostic value of secondary insults in traumatic brain injury: Results from the IMPACT study. J. Neurotrauma 2007, 24, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, A.I.; Stocchetti, N.; Bullock, R. Moderate and severe traumatic brain injury in adults. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, N.; Totten, A.M.; O’Reilly, C.; Ullman, J.S.; Hawryluk, G.W.; Bell, M.J.; Ghajar, J. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury, fourth edition. Neurosurgery 2017, 80, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, I.R.; Treadwell, L.; Mendelow, A.D.; Sinar, E.J. Determination of threshold cerebral perfusion pressure in patients with severe head injury. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2001, 76, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, K.Y.; Froese, L.; Gomez, A.; Sainbhi, A.S.; Vakitbilir, N.; Ibrahim, Y.; Zeiler, F.A. Intracranial pressure monitoring and treatment thresholds in acute neural injury: A narrative review of the historical achievements, current state, and future perspectives. Neurotrauma Rep. 2023, 4, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, L.A.; Andrews, P.J. Monitoring the injured brain: ICP and CBF. Br. J. Anaesth. 2006, 97, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Huang, G.; Gao, L.; Tan, H.; Liao, X. Effect of intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure on outcome prediction of severe traumatic brain injury. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2000, 3, 226–230. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Moher, D. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 88, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.r-project.org (accessed on 22 February 2024).
- The Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. Newcastle–Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale (NOS). Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 22 February 2024).
- Yamamoto, T.; Mori, K.; Maeda, M. Assessment of prognostic factors in severe traumatic brain injury patients treated by mild therapeutic cerebral hypothermia therapy. Neurol. Res. 2002, 24, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balestreri, M.; Czosnyka, M.; Hutchinson, P.; Steiner, L.A.; Hiler, M.; Smielewski, P.; Pickard, J.D. Impact of intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure on severe disability and mortality after head injury. Neurocrit. Care 2006, 4, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, B.T.; Wong, J.; Lee, K.K.; Wang, E.; Ng, I. Temporal changes in cerebral tissue oxygenation with cerebrovascular pressure reactivity in severe traumatic brain injury. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunham, C.M.; Sosnowski, C.; Porter, J.M.; Siegal, J.; Kohli, C. Correlation of noninvasive cerebral oximetry with cerebral perfusion in the severe head injured patient: A pilot study. J. Trauma 2002, 52, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.L.; Zhi, D.S.; Wang, Q.; Huang, H.L. Extracellular glycerol in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2008, 11, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraforou, T.; Paterakis, K.; Fountas, K.; Paraforos, G.; Chovas, A.; Tasiou, A.; Mpakopoulou, M.; Papadopoulos, D.; Karavellis, A.; Komnos, A. Cerebral perfusion pressure, microdialysis biochemistry and clinical outcome in patients with traumatic brain injury. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, D.M.; Hu, P.F.; Brenner, M.; Sheth, K.N.; Liu, K.H.; Xiong, W.; Aarabi, B.; Scalea, T.M. Brief episodes of intracranial hypertension and cerebral hypoperfusion are associated with poor functional outcome after severe traumatic brain injury. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2011, 71, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radolovich, D.K.; Aries, M.J.; Castellani, G.; Corona, A.; Lavinio, A.; Smielewski, P.; Pickard, J.D.; Czosnyka, M. Pulsatile intracranial pressure and cerebral autoregulation after traumatic brain injury. Neurocrit. Care 2011, 15, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aries, M.J.; Czosnyka, M.; Budohoski, K.P.; Steiner, L.A.; Lavinio, A.; Kolias, A.G.; Hutchinson, P.J.; Brady, K.M.; Menon, D.K.; Pickard, J.D.; et al. Continuous determination of optimal cerebral perfusion pressure in traumatic brain injury. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 2456–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, E.A.; Barletta, J.F.; Figueroa, B.E.; Bonnell, B.W.; Vanderkolke, W.E.; McAllen, K.J.; Ott, M.M. Cerebral perfusion pressure and intracranial pressure are not surrogates for brain tissue oxygenation in traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 120, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejčl, A.; Bolcha, M.; Procházka, J.; Hušková, E.; Sameš, M. Elevated intracranial pressure, low cerebral perfusion pressure, and impaired brain metabolism correlate with fatal outcome after severe brain injury. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2012, 73, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.H.; Huang, T.Y.; Kung, S.S.; Su, Y.F.; Hwang, S.L.; Lieu, A.S. Intraoperative intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure for predicting surgical outcome in severe traumatic brain injury. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2013, 29, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykora, M.; Czosnyka, M.; Liu, X.; Donnelly, J.; Nasr, N.; Diedler, J.; Hutchinson, P.; Menon, D.; Smielewski, P. Autonomic impairment in severe traumatic brain injury: A multimodal neuromonitoring study. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, H.; Sadraei, N.; Niakan, A.; Ghaffarpasand, F.; Sadraei, A. Role of intracranial pressure monitoring in management of patients with severe traumatic brain injury: Results of a large Level I trauma center in Southern Iran. World Neurosurg. 2016, 94, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkus, V.; Preiksaitis, A.; Krakauskaite, S.; Zubaviciute, E.; Rocka, S.; Rastenyte, D.; Vosylius, S.; Ragauskas, A. Benefit on optimal cerebral perfusion pressure targeted treatment for traumatic brain injury patients. J. Crit. Care 2017, 41, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Donnelly, J.; Czosnyka, M.; Aries, M.J.H.; Brady, K.; Cardim, D.; Robba, C.; Cabeleira, M.; Kim, D.J.; Haubrich, C.; et al. Cerebrovascular pressure reactivity monitoring using wavelet analysis in traumatic brain injury patients: A retrospective study. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, H.; Donnelly, J.; Czosnyka, M.; Smielewski, P.; Hutchinson, P. Pressure reactivity-based optimal cerebral perfusion pressure in a traumatic brain injury cohort. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2018, 126, 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Nourallah, B.; Zeiler, F.A.; Calviello, L.; Smielewski, P.; Czosnyka, M. Critical thresholds for intracranial pressure vary over time in non-craniectomised traumatic brain injury patients. Acta Neurochir. 2018, 160, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.V.; Goda, A. Role of intraoperative intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure measurement for predicting surgical outcome in severe traumatic brain injury. Indian J. Neurotrauma 2020, 17, 121–129. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zhao, P.; Ding, J.; Ren, Z.; Xu, J. Significance of ICP-related parameters for the treatment and outcome of severe traumatic brain injury. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 0300060520941291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilja-Cyron, A.; Zeiler, F.A.; Beqiri, E.; Cabeleira, M.; Smielewski, P.; Czosnyka, M. Optimal cerebral perfusion pressure based on intracranial pressure-derived indices of cerebrovascular reactivity: Which one is better for outcome prediction in moderate/severe traumatic brain injury? Acta Neurochir. 2021, 163, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Deimantavicius, M.; Chaleckas, E.; Boere, K.; Putnynaite, V.; Tamosuitis, T.; Tamasauskas, A.; Kavaliauskas, M.; Rocka, S.; Preiksaitis, A.; Vosylius, S.; et al. Feasibility of the optimal cerebral perfusion pressure value identification without a delay that is too long. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Chu, H. Quantifying publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2018, 74, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brain Trauma Foundation; American Association of Neurological Surgeons; Congress of Neurological Surgeons; Joint Section on Neurotrauma and Critical Care, AANS/CNS. Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury (2007, 4th ed.). J. Neurotrauma 2007, 24 (Suppl. S1), S1–S106. [Google Scholar]
- Wettervik, T.S.; Howells, T.; Hillered, L.; Rostami, E.; Lewén, A.; Enblad, P. Autoregulatory or fixed cerebral perfusion pressure targets in traumatic brain injury: Determining which is better from an energy metabolic perspective. Neurocrit. Care 2021, 35, 238–252. [Google Scholar]
- Bögli, S.Y.; Olakorede, I.; Beqiri, E.; Chen, X.; Lavinio, A.; Hutchinson, P.; Smielewski, P. Cerebral perfusion pressure targets after traumatic brain injury: A reappraisal. Crit. Care 2025, 29, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel-Castilla, L.; Gasco, J.; Nauta, H.J.W.; Okonkwo, D.O.; Robertson, C.S. Cerebral pressure autoregulation in traumatic brain injury. Neurosurg. Focus 2008, 25, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C.S.; Valadka, A.B.; Hannay, H.J.; Contant, C.F.; Gopinath, S.P.; Cormio, M.; Uzura, M.; Grossman, R.G. Prevention of secondary ischemic insults after severe head injury. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 27, 2086–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, F.A.; Howells, T.; Hillered, L.; Rostami, E.; Lewén, A.; Enblad, P. Continuous multimodal neuromonitoring in traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2023, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, J.L.; Chua, K.C.; Manesh, S.; Sivaraju, A.; Lang, M.J.; Becker, K.J.; Stevens, R.D. Management of severe traumatic brain injury across resource settings: Consensus-based recommendations. Neurocrit. Care 2021, 35, 535–547. [Google Scholar]
- Stocchetti, N.; Zanier, E.R.; Carbonara, M. Brain metabolism after traumatic brain injury: The role of brain tissue oxygen monitoring and microdialysis. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 583, 100–106. [Google Scholar]
| Database | Search String |
|---|---|
| Pubmed | (((“CPP”) OR (“cerebral perfusion pressure”)) OR (“neuromonitoring”)) AND ((((“cranial trauma”) OR (“head trauma”)) OR (“traumatic brain injury”)) OR (“TBI”)) |
| Scopus | ((TITLE-ABS-KEY (“cerebral perfusion pressure”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“CPP”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“neuromonitoring”))) AND ((TITLE-ABS-KEY (“head trauma”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“cranial trauma”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“traumatic brain injury”) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (“TBI”))) |
| WoS | https://www.webofscience.com/wos/woscc/summary/2bd7d46a-331b-4e0c-9253-a6f0539535d3-c9e9b418/relevance/1 (accessed on 22 February 2024) |
| Authors | Definition of Cases | Representativenes of Cases | Selection of Controls | Definition of Controls | Comparability | Ascertainment of Exposure | Same Method of Ascertainment in Cases and Controls | Non-Reposnse Rate | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yamamoto (2002) [14] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Balestreri (2006) [15] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Ang (2006) [16] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Duncham (2006) [17] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Li (2008) [18] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Paraforou (2011) [19] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Stein (2011) [20] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Radolovich (2011) [21] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Aries (2012) [22] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Eriksson (2012) [23] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Hejcl (2012) [24] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Tsai (2013) [25] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Sykora (2016) [26] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Khalili (2016) [27] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Petkus (2017) [28] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Liu (2017) [29] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Adams (2017) [30] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Nourallah (2018) [31] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Chandra (2020) [32] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Pan (2020) [33] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Liljia-Cyron (2021) [34] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Deimantavicius (2022) [35] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Parameter | Starting Grade | Risk of Bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Impressision | Publication Bias | Magnitude of Effect | Dose Response | Confounding Factors | Final Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Survivors vs. non-survivors | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ** |
| Good vs. Poor outcome | 2 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | * |
| GOS 5 vs. GOS 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ** |
| GOS4–5 vs. GOS 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ** |
| Authors | Country | SD | Patient | n | Intervention | Comparators | Outcome | Follow-up | NOS | Enrollment Period | Targeted CPP | Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yamamoto (2002) [14] | Japan | RCC | sTBI | 22 | CIM | Good vs. Poor outcome | GOS | NR | 7 | 1993–2000 | 70 mmHg | NR |
| Balestreri (2006) [15] | UK | RCC | sTBI | 429 | CIM | Survivors vs. non-survivors | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 1992–2004 | 60–70 mmHg | Mixed |
| Ang (2006) [16] | Singapore | PCC | sTBI | 40 | CIM | Survivors vs. non-survivors | Mortality | 6 months | 7 | Jan 2001–Dec 2004 | NR | Mixed |
| Duncham (2006) [17] | USA | PCC | sTBI | 18 | CIM | Good vs. Poor outcome | GCS | At discharge | 7 | 2003–2005 | >60 mmHg | Mixed |
| Li (2008) [18] | China | RCC | sTBI | 42 | CIM | Good vs. Poor outcome | GOS | NR | 7 | 2004–2007 | 70 mmHg | NR |
| Paraforou (2011) [19] | Greece | RCC | sTBI | 34 | CIM | Good vs. Poor outcome | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 2006–2009 | 70 mmHg | NR |
| Stein (2011) [20] | USA | RCC | sTBI | 60 | CIM | Survivors vs. non-survivors and Good vs. Poor outcome | GOSE | 6 months | 7 | 2005–2009 | >60 mmHg | Mixed |
| Radolovich (2011) [21] | UK | RCC | sTBI | 136 | CIM | GOS 5 vs. GOS 1 | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 2000–2008 | NR | NR |
| Aries (2012) [22] | UK | RCC | sTBI | 119 | CIM | GOS 5 vs. GOS 1 | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 2003–2009 | CPP | NR |
| Eriksson (2012) [23] | USA | RCC | sTBI | 15 | CIM | Survivors vs. non-survivors | Mortality | At discharge | 7 | 2005–2010 | NR | Mixed |
| Hejcl (2012) [24] | Czechia | RCC | sTBI | 20 | CIM | Survivors vs. non-survivors | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 2005–2010 | NR | Mixed |
| Tsai (2013) [25] | Taiwan | RCC | sTBI | 40 | CIM | Survivors vs. non-survivors | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 2006– 2007 | >60 mmHg | Mixed |
| Sykora (2016) [26] | Mullticentric | RCC | sTBI | 262 | CIM | Survivors vs. non-survivors | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 2008–2012 | NR | NR |
| Khalili (2016) [27] | Iran | RCC | sTBI | 248 | CIM | Good vs. Poor outcome | GOSE | 6 months | 7 | 2004–2007 | >70 mmHg | Mixed |
| Petkus (2017) [28] | Lithuania | RCC | sTBI | 43 | CIM | Good vs. Poor outcome | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 2012–2015 | CPPopt | NR |
| Liu (2017) [29] | UK | RCC | sTBI | 195 | CIM | GOS 5 vs. GOS 1 | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 2004–2007 | 60–70 mmHg | No DC |
| Adams (2017) [30] | UK | RCC | sTBI | 556 | CIM | Survivors vs. non-survivors | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 2004–2013 | NR | NR |
| Nourallah (2018) [31] | UK | RCC | sTBI | 355 | CIM | Survivors vs. non-survivors and Good vs. Poor outcome | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 2012–2016 | >60 mmHg | No DC |
| Chandra (2020) [32] | India | RCC | sTBI | 53 | CIM | Good vs. Poor outcome | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 2015–2018 | NR | NR |
| Pan (2020) [33] | China | RCC | sTBI | 29 | CIM | Good vs. Poor outcome | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 2014–2017 | ICP threshold | NR |
| Liljia-Cyron (2021) [34] | UK | RCC | sTBI | 200 | CIM | GOS4–5 vs. GOS 1 | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 2004–2007 | >60 mmHg | NR |
| Deimantavicius (2022) [35] | Lithuania | RCC | sTBI | 70 | CIM | GOS4–5 vs. GOS 1 | GOS | 6 months | 7 | 2017–2020 | 60–70 mmHg | NR |
| Country/Region | k | Mean Effect | 95% Confidence Interval | τ2 | τ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UK | 3 | 77.52 | 76.18; 78.87 | 1.20 | 1.09 |
| Singapore | 1 | 78.80 | 74.84; 82.76 | - | - |
| USA | 2 | 73.80 | 72.12; 75.48 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Czechia | 1 | 84.82 | 83.42; 86.22 | - | - |
| Taiwan | 1 | 65.90 | 63.71; 68.09 | - | - |
| Multicentric | 1 | 77.70 | 76.79; 78.61 | - | - |
| Country | k | Mean Effect | 95% Confidence Interval | τ2 | τ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Japan | 1 | 100.10 | 92.13; 108.07 | - | - |
| USA | 2 | 76.95 | 69.41; 84.48 | 24.14 | 4.91 |
| China | 2 | 76.42 | 69.06; 83.77 | 25.40 | 5.04 |
| Greece | 1 | 78.53 | 67.96; 89.10 | - | - |
| Iran | 1 | 56.20 | 50.82; 61.58 | - | - |
| Lithuania | 1 | 86.96 | 82.77; 91.15 | - | - |
| UK | 1 | 77.60 | 76.60; 78.60 | - | - |
| India | 1 | 73.60 | 71.61; 75.59 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karagianni, M.; Brotis, A.G.; Vrettou, C.S.; Goupou, K.; Stranjalis, G.; Fountas, K.N. Cerebral Perfusion Pressure in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Survivors and Non-Survivors: A Meta-Analysis. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111161
Karagianni M, Brotis AG, Vrettou CS, Goupou K, Stranjalis G, Fountas KN. Cerebral Perfusion Pressure in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Survivors and Non-Survivors: A Meta-Analysis. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(11):1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111161
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaragianni, Maria, Alexandros G. Brotis, Charikleia S. Vrettou, Kerasia Goupou, George Stranjalis, and Kostas N. Fountas. 2025. "Cerebral Perfusion Pressure in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Survivors and Non-Survivors: A Meta-Analysis" Brain Sciences 15, no. 11: 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111161
APA StyleKaragianni, M., Brotis, A. G., Vrettou, C. S., Goupou, K., Stranjalis, G., & Fountas, K. N. (2025). Cerebral Perfusion Pressure in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury Survivors and Non-Survivors: A Meta-Analysis. Brain Sciences, 15(11), 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111161









