A Study on Hemodynamic and Brain Network Characteristics During Upper Limb Movement in Children with Cerebral Hemiplegia Based on fNIRS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection and Grouping of Research Subjects
2.2. Basic Information About the Subjects
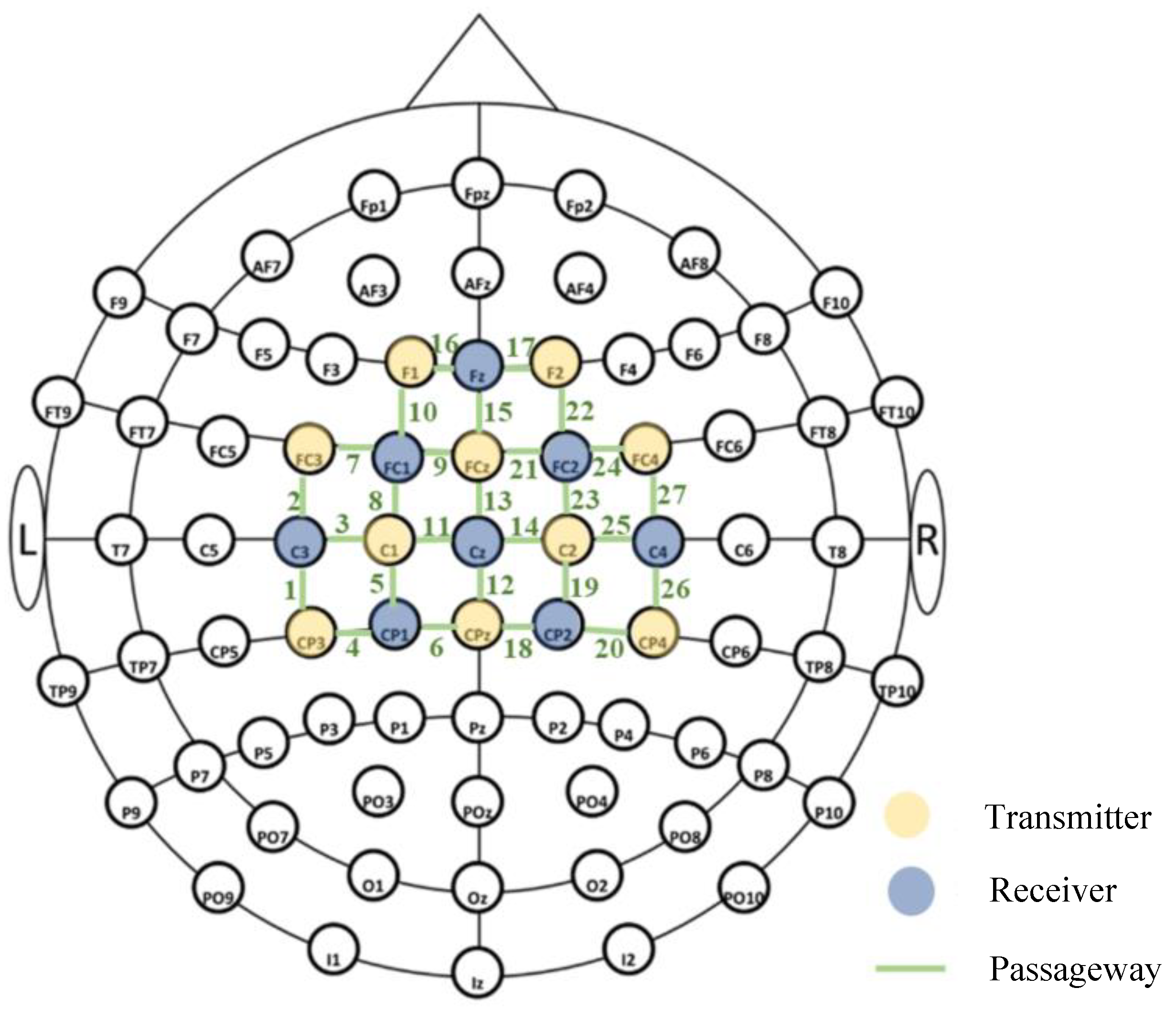
2.3. Experimental Equipment and Parameter Settings
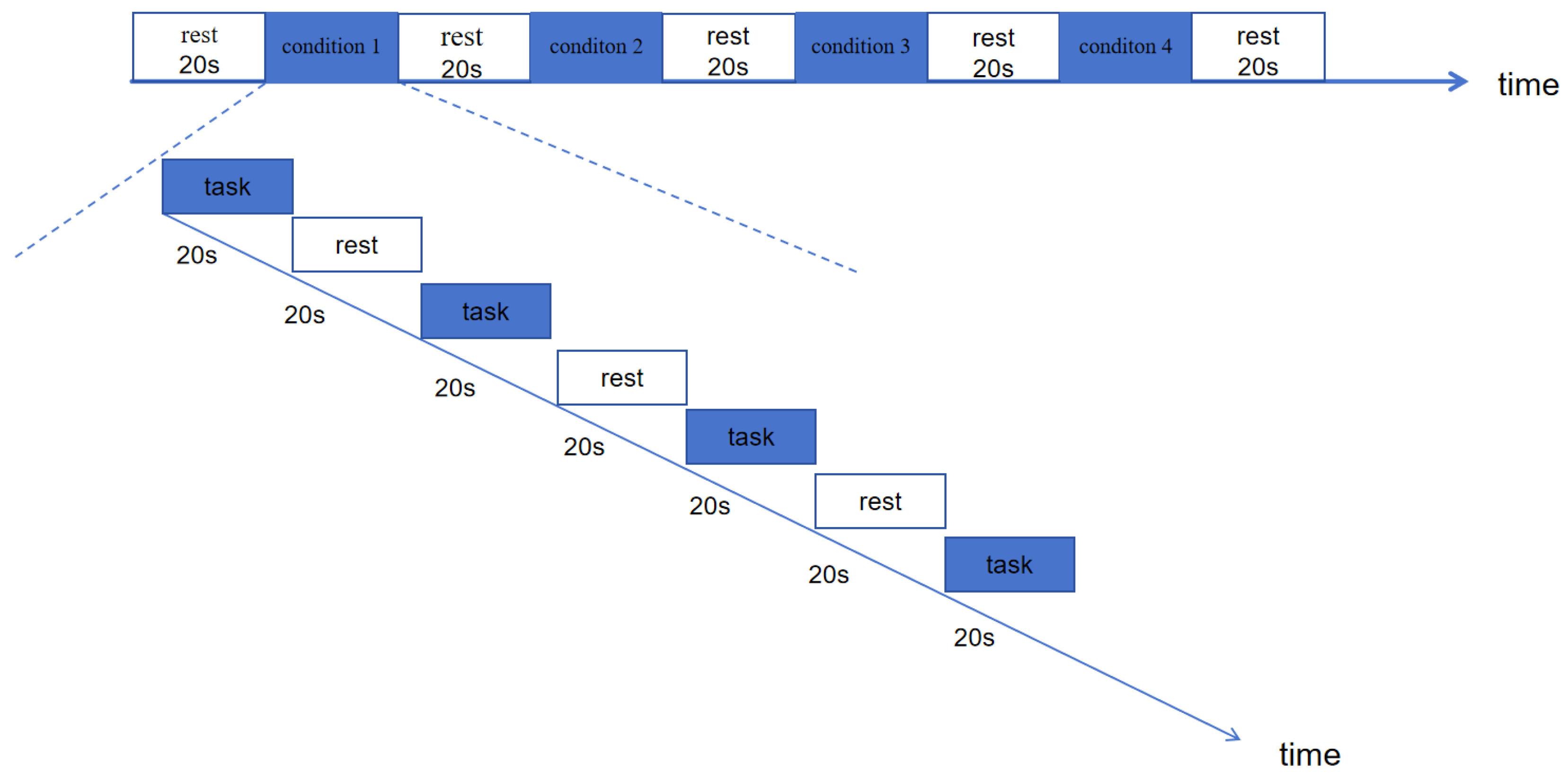
2.4. Task Paradigm and Testing Process
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
2.5.1. fNIRS Preprocessing
2.5.2. Brain Activation Analysis
2.5.3. Cortical Connectivity Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
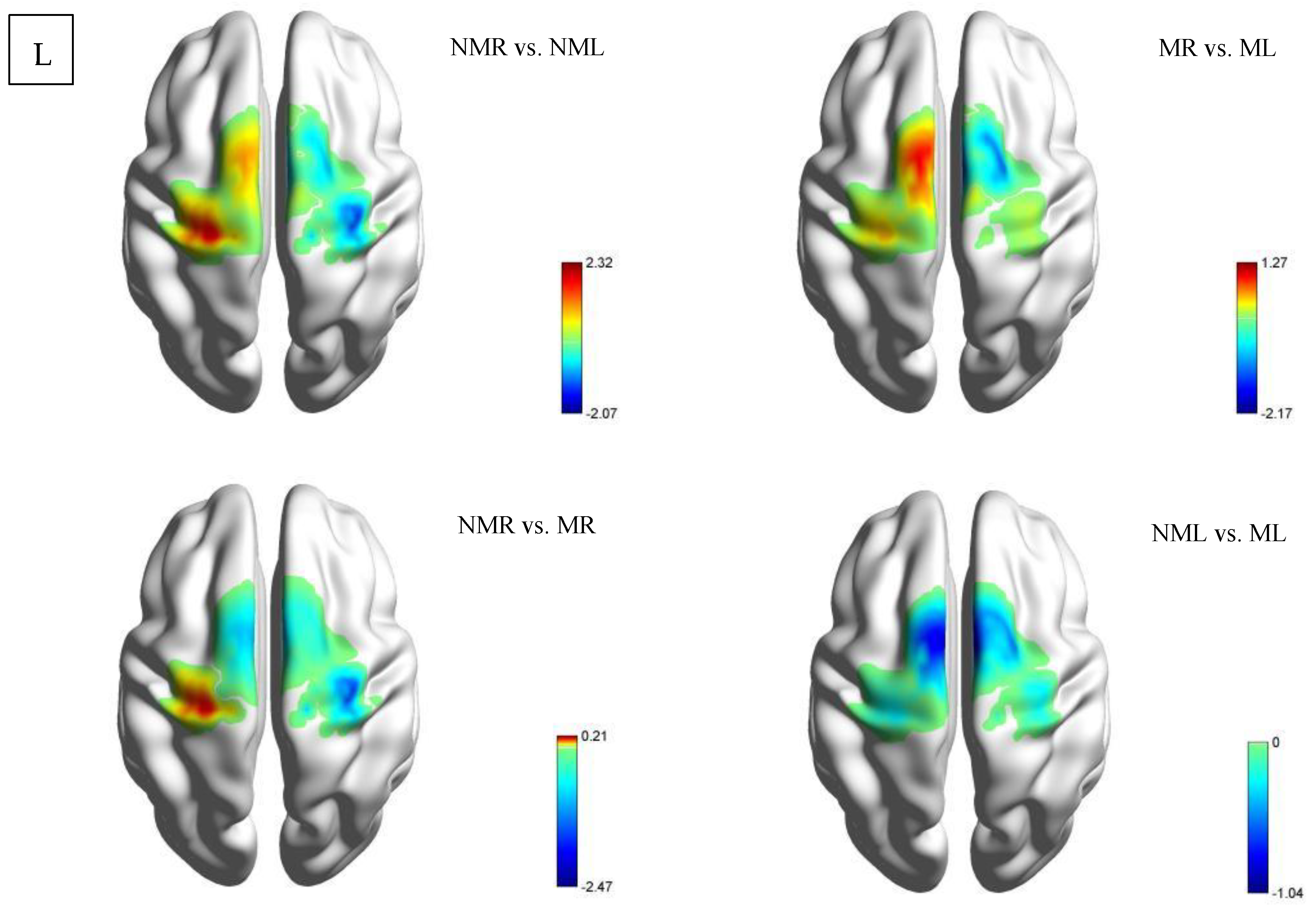
3.1. Brain Activation Differences
3.1.1. Activation Status of Each ROI Based on β Values (Intra-Group Comparison)
HCP Group
CD Group
3.1.2. Activation Status of Each ROI Based on β Values (Between-Group Comparison)
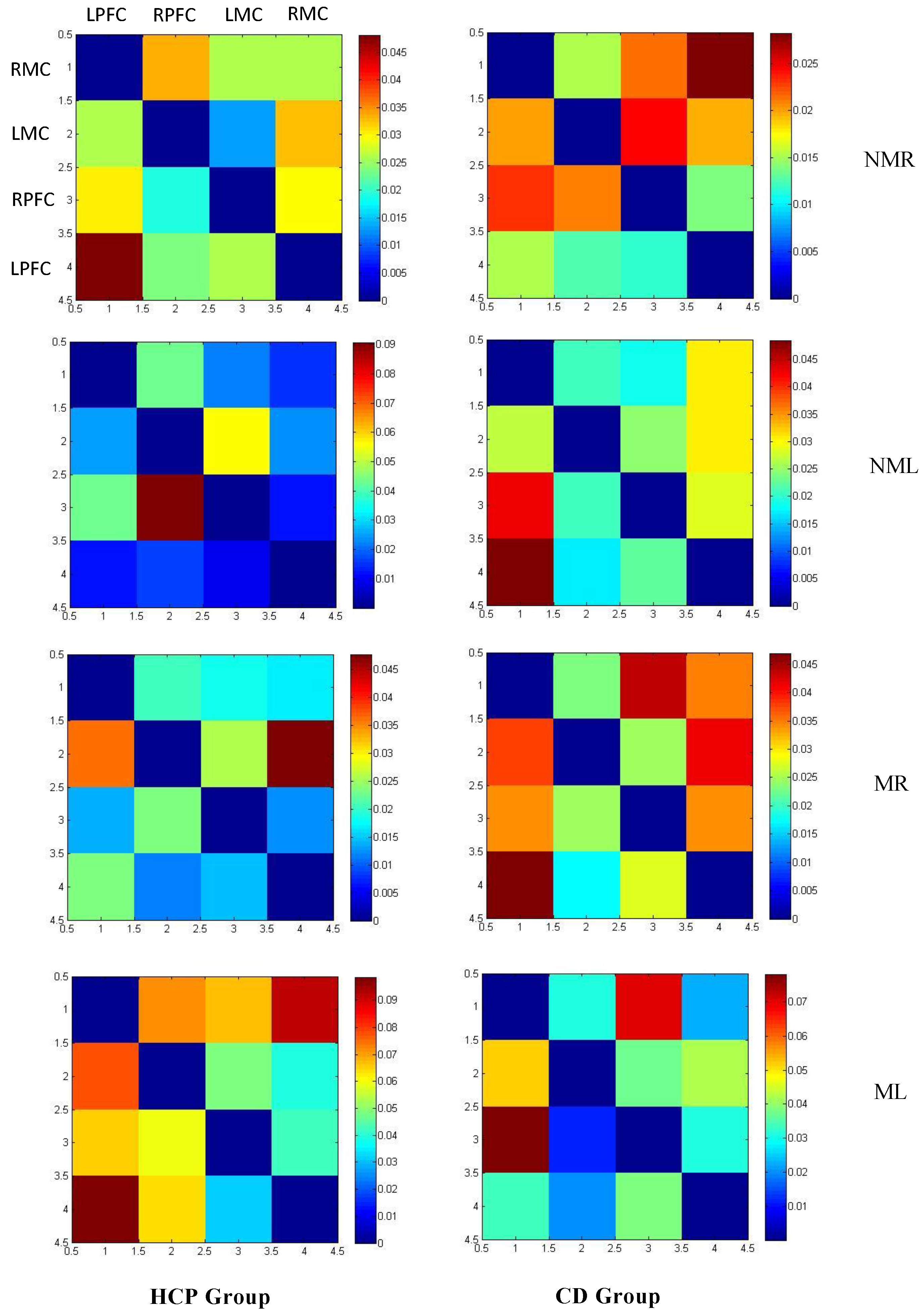
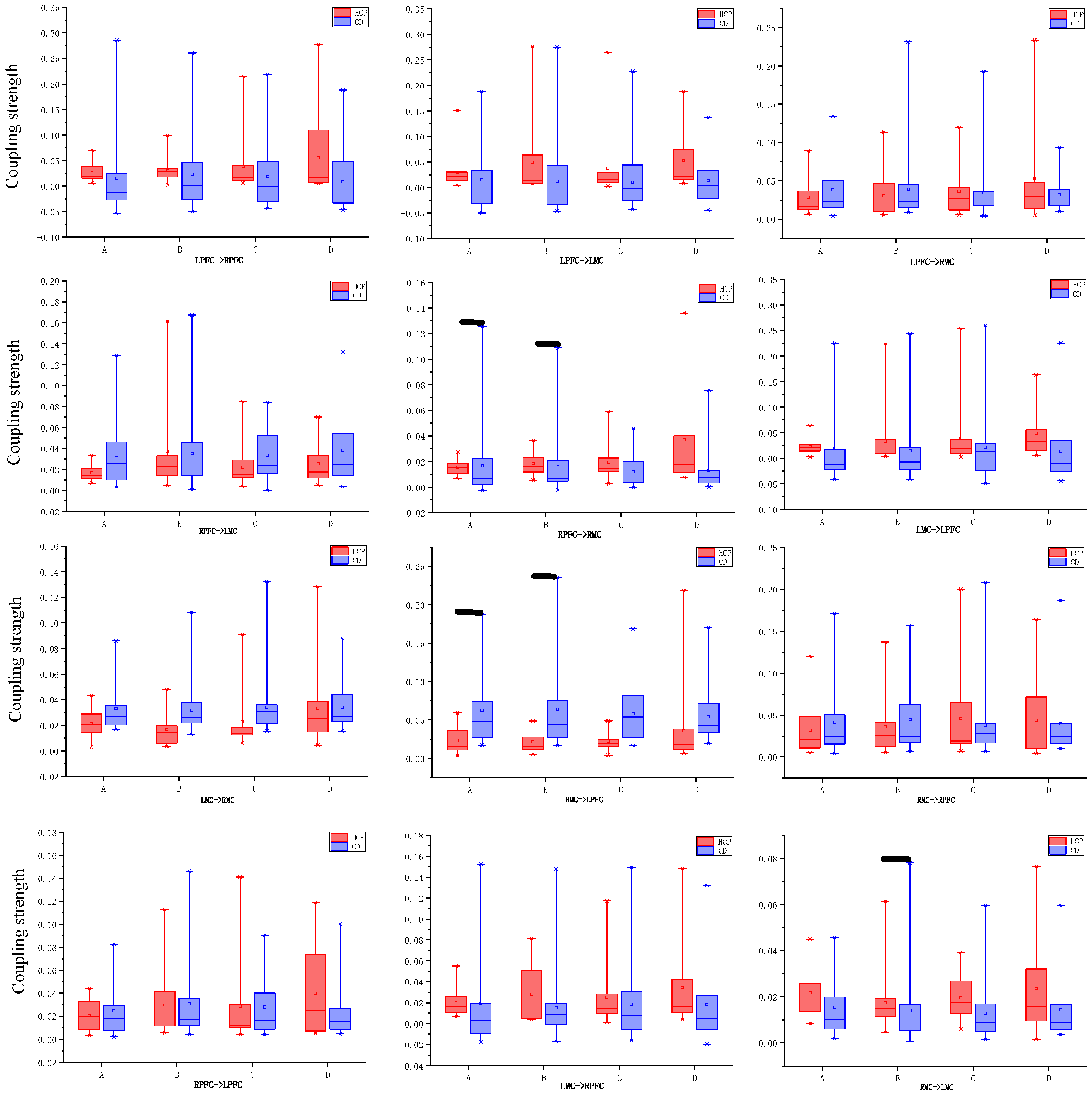
3.2. Direction and Coupling Strength of Effective Connectivity in the Cortex
3.2.1. Connection Direction
3.2.2. Coupling Strength
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paul, S.; Nahar, A.; Bhagawati, M.; Kunwar, A.J. A review on recent advances of cerebral palsy. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 2622310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekteshi, S.; Monbaliu, E.; McIntyre, S.; Saloojee, G.; Hilberink, S.R.; Tatishvili, N.; Dan, B. Towards functional improvement of motor disorders associated with cerebral palsy. Lancet Neurol. 2023, 22, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dar, H.; Stewart, K.; McIntyre, S.; Paget, S. Multiple motor disorders in cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2024, 66, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demont, A.; Gedda, M.; Lager, C.; de Lattre, C.; Gary, Y.; Keroulle, E.; Feuillerat, B.; Caudan, H.; Sancelme, Z.; Isapof, A.; et al. Evidence-based, implementable motor rehabilitation guidelines for individuals with cerebral palsy. Neurology 2022, 99, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, S.; Goldsmith, S.; Webb, A.; Ehlinger, V.; Julsen Hollung, S.; McConnell, K.; Arnaud, C.; Smithers-Sheedy, H.; Oskoui, M.; Khandaker, G.; et al. Global prevalence of cerebral palsy: A systematic analysis. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2022, 64, 1494–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qiu, H.; Jiang, Z. Epidemiological characteristics of cerebral palsy in children in 12 provinces and municipalities in China. Chin. J. Pract. Pediatr. 2018, 33, 378–383. [Google Scholar]
- Arnaud, C.; Ehlinger, V.; Perraud, A.; Kinsner-Ovaskainen, A.; Klapouszczak, D.; Himmelmann, K.; Petra, M.; Rackauskaite, G.; Lanzoni, M.; Platt, M.J.; et al. Public health indicators for cerebral palsy: A European collaborative study of the Surveillance of Cerebral Palsy in Europe network. Paediatr. Perinat. Epidemiol. 2023, 37, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.R.; Neelakantan, M.; Pandher, K.; Merrick, J. Cerebral palsy in children: A clinical overview. Transl. Pediatr. 2020, 9 (Suppl. S1), S125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weeke, L.C.; Groenendaal, F.; Mudigonda, K.; Blennow, M.; Lequin, M.H.; Meiners, L.C.; van Haastert, I.C.; Benders, M.J.; Hallberg, B.; de Vries, L.S. A Novel Magnetic Resonance Imaging Score Predicts Neurodevelopmental Outcome After Perinatal Asphyxia and Therapeutic Hypothermia. J. Pediatr. 2018, 192, 33–40.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, I.; An, Y.; Min, S.; Park, C. Therapeutic effects of metaverse rehabilitation for cerebral palsy: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Huang, M.; Yin, Y.; Gui, D.; Gu, Y.; Zhuang, T.; Chen, C.; Huo, K. Risk factors of cerebral palsy in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Pediatr. 2022, 11, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, S.; Ye, J.C. Statistical analysis of fNIRS data: A comprehensive review. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 72–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, T.; Biondi, M. fNIRS in the developmental sciences. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Cogn. Sci. 2015, 6, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yücel, M.A.; Lühmann, A.; Scholkmann, F.; Gervain, J.; Dan, I.; Ayaz, H.; Boas, D.; Cooper, R.J.; Culver, J.; Elwell, C.E.; et al. Best practices for fNIRS publications. Neurophotonics 2021, 8, 012101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, N.; Hong, K.S. fNIRS-based brain-computer interfaces: A review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Quaresima, V. A brief review on the history of human functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) development and fields of application. Neuroimage 2012, 63, 921–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishburn, F.A.; Norr, M.E.; Medvedev, A.V.; Vaidya, C.J. Sensitivity of fNIRS to cognitive state and load. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastmond, C.; Subedi, A.; De, S.; Intes, X. Deep learning in fNIRS: A review. Neurophotonics 2022, 9, 041411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinti, P.; Tachtsidis, I.; Hamilton, A.; Hirsch, J.; Aichelburg, C.; Gilbert, S.; Burgess, P.W. The present and future use of functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) for cognitive neuroscience. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1464, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshi, Y. Hemodynamic signals in fNIRS. Prog. Brain Res. 2016, 225, 153–179. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.; Nie, Z.; Zhang, T.; Xu, G.; Sun, A.; Chen, T.; Lv, Y. FNIRS based study of brain network characteristics in children with cerebral palsy during bilateral lower limb movement. Med. Phys. 2024, 51, 4434–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, M.J.; Wilson, T.W.; Arpin, D.J. An fNIRS exploratory investigation of the cortical activity during gait in children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy. Brain Dev. 2014, 36, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpetuini, D.; Russo, E.F.; Cardone, D.; Palmieri, R.; Filippini, C.; Tritto, M.; Pellicano, F.; De Santis, G.P.; Calabrò, R.S.; Merla, A.; et al. Identification of functional cortical plasticity in children with cerebral palsy associated to robotic-assisted gait training: An fNIRS study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukal-Moulton, T.; de Campos, A.C.; Alter, K.E.; Huppert, T.J.; Damiano, D.L. Relationship between sensorimotor cortical activation as assessed by functional near infrared spectroscopy and lower extremity motor coordination in bilateral cerebral palsy. NeuroImage Clin. 2018, 20, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licea, J.; Khan, O.A.; Singh, T.; Modlesky, C.M. Prefrontal cortex hemodynamic activity during a test of lower extremity functional muscle strength in children with cerebral palsy: A functional near-infrared spectroscopy study. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2024, 59, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Campos, A.C.; Sukal-Moulton, T.; Huppert, T.; Alter, K.; Damiano, D.L. Brain activation patterns underlying upper limb bilateral motor coordination in unilateral cerebral palsy: An fNIRS study. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivito, G.; Dayan, M.; Battistoni, V.; Clausi, S.; Cercignani, M.; Molinari, M.; Leggio, M.; Bozzali, M. Bilateral effects of unilateral cerebellar lesions as detected by voxel based morphometry and diffusion imaging. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, M.I.S.; Russo, C.; Masson, R.; Sebastiano, D.R.; Baranello, G.; Turati, C.; Bolognini, N. Motor learning in unilateral cerebral palsy and the influence of corticospinal tract reorganization. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2020, 27, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koechlin, E.; Basso, G.; Pietrini, P.; Panzer, S.; Grafman, J. The role of the anterior prefrontal cortex in human cognition. Nature 1999, 399, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astafiev, S.V.; Stanley, C.M.; Shulman, G.L.; Corbetta, M. Extrastriate body area in human occipital cortex responds to the performance of motor actions. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcreff, L.; Fluss, J.; Allali, G.; Valenza, N.; Aminian, K.; Newman, C.J.; Armand, S. The effects of dual tasks on gait in children with cerebral palsy. Gait Posture 2019, 70, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurz, M.J.; Heinrichs-Graham, E.; Arpin, D.J.; Becker, K.M.; Wilson, T.W. Aberrant synchrony in the somatosensory cortices predicts motor performance errors in children with cerebral palsy. J. Neurophysiol. 2014, 111, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukal-Moulton, T.; Krosschell, K.J.; Gaebler-Spira, D.J.; Dewald, J.P. Motor impairments related to brain injury timing in early hemiparesis. Part II: Abnormal upper extremity joint torque synergies. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2014, 28, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill-Rowley, K.; Rose, J. Etiology of impaired selective motor control: Emerging evidence and its implications for research and treatment in cerebral palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, G.; Huo, C.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Li, W. Cortical hemodynamic response and networks in children with cerebral palsy during upper limb bilateral motor training. J. Biophotonics 2023, 16, e202200326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Peng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, P.; Chen, D.; Nie, D.; Liu, H.; Liu, P. Structure of brain grey and white matter in infants with spastic cerebral palsy and periventricular white matter injury. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2023, 66, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Jin, C.; Wang, M.; Liu, C.; Chan, K.C.; Yang, J. Early Diagnosis of Spastic Cerebral Palsy in Infants with Periventricular White Matter Injury Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 40, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumura, K.; Sugawara, K.; Tanabe, S.; Ushiba, J.; Tomita, Y. Influence of mirror therapy on human motor cortex. Int. J. Neurosci. 2007, 117, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Groups | Number of Males | Age (M ± SD) | Height (M ± SD) | Weight (M ± SD) | GMFCS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCP (n = 14) | 6 | 8.34 (1.495) | 140.55 (17.02) | 37.341 (16.5214) | I |
| CD (n = 28) | 14 | 7.5 (2.767) | 115.5 (40.319) | 44.186 (37.1998) | N/A |
| Area of Interest (ROIs) | fNIRS Channel |
|---|---|
| left frontal lobe, LPFC | 7–10, 16 |
| right frontal lobe, RPFC | 15, 17, 21–24 |
| left motor area, LMC | 1–6, 11 |
| right motor area, RMC | 12–14, 18–20, 25–27 |
| ROIs | NMR vs. NML | MR vs. ML | NMR vs. MR | NML vs. ML | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M ± SD | t | p | M ± SD | t | p | M ± SD | t | p | M ± SD | t | p | |
| LPFC | −1.008 ± 4.095 | −0.921 | 0.374 | −1.51 ± 3.252 | −1.737 | 0.106 | 1.76 ± 5.574 | 1.181 | 0.259 | 1.258 ± 7.456 | 0.631 | 0.539 |
| RPFC | −3.651 ± 11.942 | −1.144 | 0.273 | −2.421 ± 6.376 | −1.421 | 0.179 | 0.418 ± 2.596 | 0.603 | 0.557 | 1.648 ± 9.462 | 0.652 | 0.526 |
| LMC | −1.128 ± 2.764 | −1.527 | 0.025 * | −1.033 ± 3.227 | −1.197 | 0.253 | 1.177 ± 2.728 | 1.613 | 0.131 | 1.272 ± 4.713 | 1.01 | 0.331 |
| RMC | 2.685 ± 11.699 | 0.859 | 0.406 | −1.674 ± 2.584 | −2.425 | 0.031 * | 0.912 ± 3.884 | 0.878 | 0.396 | −3.447 ± 11.12 | −1.16 | 0.267 |
| ROIs | NMR vs. NML | MR vs. ML | NMR vs. MR | NML vs. ML | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M ± SD | t | p | M ± SD | t | p | M ± SD | t | p | M ± SD | t | p | |
| LPFC | 0.72 ± 2.848 | 1.362 | 0.184 | 1.222 ± 5.187 | 1.269 | 0.215 | −1.044 ± 4.999 | −1.125 | 0.27 | −0.543 ± 2.808 | −1.041 | 0.307 |
| RPFC | −1.405 ± 5.312 | −1.424 | 0.165 | −1.648 ± 4.085 | −2.173 | 0.038 * | −1.851 ± 10.411 | −0.957 | 0.347 | −2.094 ± 11.523 | −0.978 | 0.336 |
| LMC | 1.505 ± 9.193 | 2.317 | 0.028 * | 0.618 ± 5.503 | 0.605 | 0.55 | 0.17 ± 4.422 | 0.207 | 0.837 | −0.716 ± 10.36 | −0.372 | 0.712 |
| RMC | −0.244 ± 4.492 | −2.068 | 0.048 * | 0.336 ± 7.09 | 0.255 | 0.8 | −1.237 ± 2.692 | −2.474 | 0.02 * | −0.657 ± 7.563 | −0.468 | 0.644 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. A Study on Hemodynamic and Brain Network Characteristics During Upper Limb Movement in Children with Cerebral Hemiplegia Based on fNIRS. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101031
Zhang Y, Xu Y. A Study on Hemodynamic and Brain Network Characteristics During Upper Limb Movement in Children with Cerebral Hemiplegia Based on fNIRS. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(10):1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101031
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuling, and Yaqi Xu. 2025. "A Study on Hemodynamic and Brain Network Characteristics During Upper Limb Movement in Children with Cerebral Hemiplegia Based on fNIRS" Brain Sciences 15, no. 10: 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101031
APA StyleZhang, Y., & Xu, Y. (2025). A Study on Hemodynamic and Brain Network Characteristics During Upper Limb Movement in Children with Cerebral Hemiplegia Based on fNIRS. Brain Sciences, 15(10), 1031. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15101031





