Influence of Epilepsy Characteristics on the Anxiety Occurrence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Neurological Assessment
2.3. Psychological Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients Sociodemographic and Clinical Data
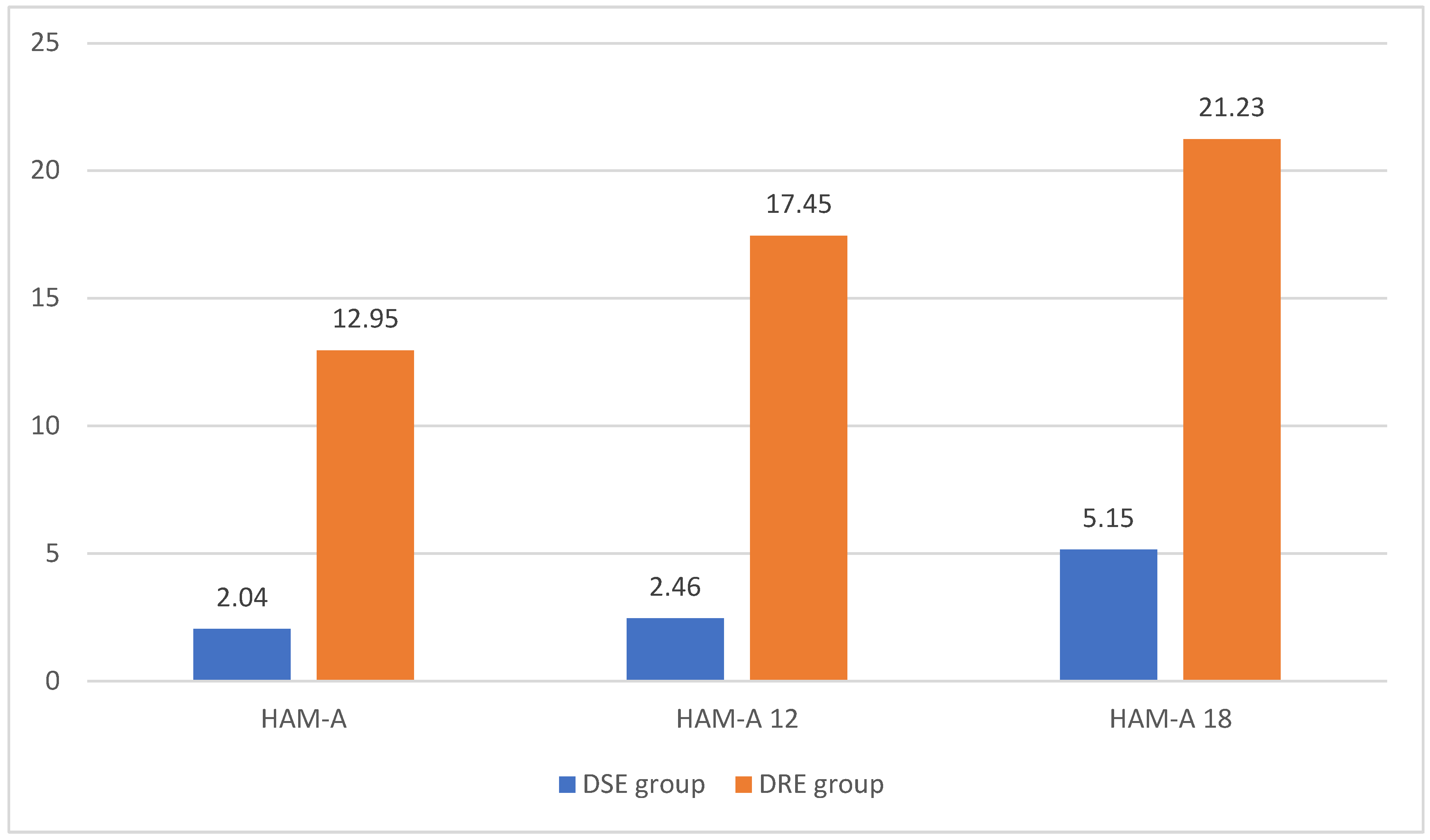
3.2. Higher HAM-A Score in Patients with DRE
3.3. The Influence of Illness Duration, Drug Responsivity, and Epilepsy Type on Anxiety in Patients with Drug-Resistant Epilepsy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kedare, J.S.; Baliga, S.P. Management of Psychiatric Disorders in Patients of Epilepsy. Indian J. Psychiatry 2022, 64, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, A.J.; Sharpe, L.; Hunt, C.; Gandy, M. Anxiety and depressive disorders in people with epilepsy: A meta-analysis. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljunggren, S.; Winblad, S.; Hällgren Graneheim, U.; Malmgren, K.; Ozanne, A. Experiences of emotional and psychosocial functioning after frontal lobe resection for epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 121 Pt A, 108077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saniya, K.L.; Patil, B.G.; Chavan, M.D.; Prakash, K.G.; Sailesh, K.S.; Archana, R.; Johny, M. Neuroanatomical Changes in Brain Structures Related to Cognition in Epilepsy: An Update. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2017, 8, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staba, R.J.; Stead, M.; Worrell, G.A. Electrophysiological biomarkers of epilepsy. Neurotherapeutics 2014, 11, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, A.; Vizjak, K.; Rakusa, M. Cognitive Impairment in People with Epilepsy. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, L.J.; Wishart, A.; Brodie, M.J. Psychiatric side effects and antiepileptic drugs: Observations from prospective audits. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 71 Pt A, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgu, R.S.; Ciobanu, A.M.; Danasel, R.I.; Panea, C.A. Psychiatric comorbidities in adult patients with epilepsy [A systematic review]. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanner, A.M. Management of psychiatric and neurological comorbidities in epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 12, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Xu, H.; Laursen, T.M.; Vestergaard, M.; Mortensen, P.B. Risk for schizophrenia and schizophrenia-like psychosis among patients with epilepsy: Population based cohort study. BMJ 2005, 331, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingray, C.; McGonigal, A.; Kotwas, I.; Micoulaud-Franchi, J.A. The Relationship Between Epilepsy and Anxiety Disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 29, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauh, R.; Domschke, K.; Hirsch, M.; Schulze-Bonhage, A. Listening to anxiety in persons with epilepsy. Development of an integrative assessment model based on qualitative interviews. Epilepsy Behav. 2023, 145, 109319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.M.; Noviello, C.M.; Teng, J.; Walsh, R.M.; Kim, J.J.; Hibbs, R.E. Structure of a human synaptic GABAA receptor. Nature 2018, 559, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salpekar, J.A.; Basu, T.; Thangaraj, S.; Maguire, J. The intersections of stress, anxiety and epilepsy. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2020, 152, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmazer-Hanke, D.; O’Loughlin, E.; McDermott, K. Contribution of amygdala pathology to comorbid emotional disturbances in temporal lobe epilepsy. J. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 94, 486–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleymanova, E.M. Behavioral comorbidities of epilepsy and neuroinflammation: Evidence from experimental and clinical studies. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 117, 107869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, C.; Cavalleri, G.L.; Delanty, N. Exploring the genetic overlap between psychiatric illness and epilepsy: A review. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 102, 106669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauh, R.; Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Metternich, B. Assessment of Anxiety in Patients With Epilepsy: A Literature Review. Front. Neurol. 2022, 25, 836321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, B.; Smith, J.; Tang, Y.; Illes, P.; Engel, T. Beyond Seizure Control: Treating Comorbidities in Epilepsy via Targeting of the P2X7 Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimiskidis, V.K.; Valeta, T. Epilepsy and anxiety: Epidemiology, classification, aetiology, and treatment. Epileptic Disord. 2012, 14, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephson, C.B.; Jetté, N. Psychiatric comorbidities in epilepsy. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2017, 29, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavrilovic, A.; Toncev, G.; Boskovic, M.T.; Vesic, K.; Ilic, Z.J.; Gavrilovic, J. Impact of epilepsy duration, seizure control and EEG abnormalities on cognitive impairment in drug-resistant epilepsy patients. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2019, 119, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.S.; Acevedo, C.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Bogacz, A.; Cross, J.H.; Elger, C.E.; Engel, J., Jr.; Forsgren, L.; French, J.A.; Glynn, M.; et al. ILAE official report: A practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, I.E.; Berkovic, S.; Capovilla, G.; Connolly, M.B.; French, J.; Guilhoto, L.; Hirsch, E.; Jain, S.; Mathern, G.W.; Moshé, S.L.; et al. ILAE classification of the epilepsies: Position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, P.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Berg, A.T.; Brodie, M.J.; Allen Hauser, W.; Mathern, G.; Moshé, S.L.; Perucca, E.; Wiebe, S.; French, J. Definition of drug resistant epilepsy: Consensus proposal by the ad hoc Task Force of the ILAE Commission on Therapeutic Strategies. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 1069–1077, Erratum in Epilepsia 2010, 51, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, M.A.; Harden, C.L. Epilepsy and Anxiety. Epilepsy Behav. 2006, 1, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br. J. Med. Psychol. 1959, 32, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, E.; Pyatka, N.; Burant, C.J.; Sajatovic, M. Systematic Literature Review of Psychiatric Comorbidities in Adults with Epilepsy. J. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 17, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mula, M.; Kanner, A.M.; Jetté, N.; Sander, J.W. Psychiatric Comorbidities in People with Epilepsy. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2021, 11, e112–e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, E.B.; de Oliveira Cardoso, T.A.M.; Yasuda, C.L.; Cendes, F. Depressive disorders in patients with pharmaco-resistant mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, M.H.; Yasuda, C.L.; Coan, A.C.; Kanner, A.M.; Cendes, F. Concurrent mood and anxiety disorders are associated with pharmacoresistant seizures in patients with MTLE. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, C.; Francomme, L.; Vignal, J.P.; Jacquot, C.; Schwan, R.; Tyvaert, L.; Maillard, L.; Hingray, C. Interictal psychiatric comorbidities of drug-resistant focal epilepsy: Prevalence and influence of the localization of the epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 94, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, C.; Schoendienst, M.; Trentowska, M.; May, T.W.; Pohlmann-Eden, B.; Tuschen-Caffier, B.; Schrecke, M.; Fueratsch, N.; Witte-Boelt, K.; Ebner, A. Prevalence of anxiety disorders in patients with refractory focal epilepsy—A prospective clinic based survey. Epilepsy Behav. 2010, 17, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugała-Iwaniuk, M.; Sławińska, K.; Bochyńska, A.; Konopko, M.; Rola, R.; Ryglewicz, D.; Sienkiewicz-Jarosz, H. The prevalence of depressive and anxiety symptoms in Polish epilepsy patients—The context of pharmaco-resistance. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 114 Pt A, 107522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munger Clary, H.M.; Snively, B.M.; Hamberger, M.J. Anxiety is common and independently associated with clinical features of epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 85, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinti, V.; Dell’Isola, G.B.; Tascini, G.; Mencaroni, E.; Cara, G.D.; Striano, P.; Verrotti, A. Temporal Lobe Epilepsy and Psychiatric Comorbidity. Front Neurol. 2021, 12, 775781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schraegle, W.A.; Titus, J.B. The relationship of seizure focus with depression, anxiety, and health-related quality of life in children and adolescents with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 68, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.S. Depression in temporal lobe epilepsy: A review of prevalence, clinical features, and management considerations. Epilepsy Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 809843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Krishnan, V. Depression and Anxiety in the Epilepsies: From Bench to Bedside. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benevides, M.L.; Costa Nunes, J.; Guarnieri, R.; Melo, H.; Lunardi, M.; Neves Linhares, M.; Kupek, E.; Wolf, P.; Lin, K.; Walz, R. Anxiety and depressive symptoms long after mesial temporal epilepsy surgery: A prospective study. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 118, 107936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingaman, N.; Ferguson, L.; Thompson, N.; Reyes, A.; McDonald, C.R.; Hermann, B.P.; Arrotta, K.; Busch, R.M. The relationship between mood and anxiety and cognitive phenotypes in adults with pharmacoresistant temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 3331–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattorusso, A.; Matricard, S.; Mencaroni, E.; Dell’Isola, G.B.; Di Cara, G.; Striano, P.; Verrotti, A. The Pharmacoresistant Epilepsy: An Overview on Existant and New Emerging Therapies. Front Neurol. 2021, 22, 674483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmstaedter, C. Behavioral aspects of frontal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy 2001, 2, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.K.; Lu, J.; Ungvari, G.S.; Wong, K.S.; Kwan, P. Anxiety symptoms in patients with frontal lobe epilepsy versus generalized epilepsy. Seizure 2012, 21, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Thompson, S.A.; Duncan, J.S.; Smith, S.J. Partial seizures presenting as panic attacks. BMJ 2000, 21, 1002–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroniadou-Anderjaska, V.; Fritsch, B.; Qashu, F.; Braga, M.F. Pathology and pathophysiology of the amygdala in epileptogenesis and epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2008, 78, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolls, E.T. Emotion, motivation, decision-making, the orbitofrontal cortex, anterior cingulate cortex, and the amygdala. Brain Struct. Funct. 2023, 228, 1201–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheena, M.K.; Jimmy, J.; Burkhouse, K.L.; Klumpp, H. Anterior cingulate cortex activity during attentional control corresponds with rumination in depression and social anxiety. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2021, 30, 111385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochcovitch, M.D.; da Rocha Freire, R.C.; Garcia, R.F.; Nardi, A.E. A systematic review of fMRI studies in generalized anxiety disorder: Evaluating its neural and cognitive basis. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 167, 336–342, Erratum in J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 167, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arend, J.; Kegler, A.; Caprara, A.L.F.; Almeida, C.; Gabbi, P.; Pascotini, E.T.; de Freitas, L.A.V.; Miraglia, C.; Bertazzo, T.L.; Palma, R.; et al. Depressive, inflammatory, and metabolic factors associated with cognitive impairment in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 6, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Zhang, M.; Hao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, C. Neuroinflammation mechanisms of neuromodulation therapies for anxiety and depression. Transl. Psychiatry 2023, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Guo, D. Interictal cytokine levels were correlated to seizure severity of epileptic patients: A retrospective study on 1218 epileptic patients. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtimäki, K.A.; Keränen, T.; Huhtala, H.; Hurme, M.; Ollikainen, J.; Honkaniemi, J.; Palmio, J.; Peltola, J. Regulation of IL-6 system in cerebrospinal fluid and serum compartments by seizures: The effect of seizure type and duration. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 152, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caprara, A.L.F.; Rissardo, J.P.; Leite, M.T.B.; Silveira, J.O.F.; Jauris, P.G.M.; Arend, J.; Kegler, A.; Royes, L.F.F.; Fighera, M.R. Course and prognosis of adult-onset epilepsy in Brazil: A cohort study. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 105, 106969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimiskidis, V.K.; Triantafyllou, N.I.; Kararizou, E.; Gatzonis, S.S.; Fountoulakis, K.N.; Siatouni, A.; Loucaidis, P.; Pseftogianni, D.; Vlaikidis, N.; Kaprinis, G.S. Depression and anxiety in epilepsy: The association with demographic and seizure-related variables. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 30, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekharan, S.V.; Menon, R.; Cherian, A.; Radhakrishnan, A. Effect of seizure viewing on psychological outcome in persons with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 114 Pt A, 107605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehn, L.B.; Pfäfflin, M.; Brückner, S.; Lutz, M.T.; Steinhoff, B.J.; Mayer, T.; Bien, C.G.; Nussbeck, F.W.; May, T.W. Relationships of depression and anxiety symptoms with seizure frequency: Results from a multicenter follow-up study. Seizure 2017, 53, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruenbaum, B.F.; Sandhu, M.R.S.; Bertasi, R.A.O.; Bertasi, T.G.O.; Schonwald, A.; Kurup, A.; Gruenbaum, S.E.; Freedman, I.G.; Funaro, M.C.; Blumenfeld, H.; et al. Absence seizures and their relationship to depression and anxiety: Evidence for bidirectionality. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 1041–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.K.; Jones, J.E.; Seidenberg, M.; Hermann, B.P. The relative impact of anxiety, depression, and clinical seizure features on health-related quality of life in epilepsy. Epilepsia 2004, 45, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigussie, K.; Lemma, A.; Sertsu, A.; Asfaw, H.; Kerebih, H.; Abdeta, T. Depression, anxiety and associated factors among people with epilepsy and attending outpatient treatment at primary public hospitals in northwest Ethiopia: A multicenter cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2021, 13, e0256236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | DSE Group | DRE Group | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 38.18 ± 16.43 | 35.61 ± 12.52 | p = 0.659 |
| Sex (male/female) | 27/25 | 50/53 | p = 0.820 |
| Mean duration in illneses (years) | 9.56 ± 7.31 | 10.48 ± 758 | p = 0.459 |
| Genelalized epilepsy | 23 (44.2%) | 48 (46.6%) | p = 0.913 |
| Focal epilepsy | 29 (55.8%) | 53 (53.4%) | |
| Temporal | 17 (58.6%) | 33 (59.3%) | |
| Frontal | 11(37.9%) | 16 (29.8%) | |
| Parietal | / | 2 (3.6%) | |
| Occipital | 1 (3.4%) | 4 (7.3%) | |
| Poor seizure control | / | 25 (24.3%) | |
| Medium seizure control | / | 63 (61.2%) | |
| Good seizure control | 12 (23.1%) | 9 (8.7%) | |
| Rare seizures | 12 (23.1%) | 5 (4.9%) | |
| Remmision | 28 (53.8%) | 1 (0.9%) | |
| Monotherapy | 52 (100) | / | |
| Duotherapy | / | 73 (70.9%) | |
| Polytherapy | / | 30 (29.1%) | |
| Topiramate | 5 (9.6%) | 23 (23.3%) | |
| Levetiracetam | 20 (38.5%) | 97 (94.2%) | |
| Carbamazepine | 12 (23.1%) | 44 (42.7%) | |
| Phenobarbiton | 2 (3.8%) | 10 (9,7%) | |
| Lamotrigine | 7 (13.5%) | 28 (27.2%) | |
| Valproat acid | 6 (11.5%) | 33 (32.%) | |
| Seizure freedom > 1 month | 52 (96.2%) | 9 (8.7%) | |
| Seizure freedom 10 days > month | 2 (3.8%) | 43 (41.7%) | |
| Seizure freedom < 10 days | / | 51 (49.5%) |
| Explanatory | Unstandardized | Standardized | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Coefficient ± SE | Coefficient | ||
| Drug responsivity | 13.369 ± 6.644 | 0.460 | 2.012 | 0.048 * |
| Type of epilepsy | −3.122 ± 1.620 | −0.185 | −1.927 | 0.058 * |
| Illness duration | −0.607 ± 0.199 | −0.303 | 3.048 | 0.003 * |
| Seizures control | 1.034 ± 2.219 | 0.104 | 0.466 | 0.642 |
| EEG findings | −1.239 ± 0.17 | −0.103 | −1.014 | 0.314 |
| Categories | Explanatory Variables | B | SE | Wald | p | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anxiety | EEG findings | 0.716 | 0.366 | 3.826 | 0.05 | 0.99–4.912 |
| Baseline | ||||||
| Anxiety 12 | Drug responsivity | −5.169 | 1.991 | 6.738 | 0.009 | 0.000–0.282 |
| Epilepsy duration | 0.126 | 0.051 | 6.064 | 0.014 | 0.798–0.975 | |
| Type of epilepsy | 0.021 | 0.525 | 3.780 | 0.052 | 0.992–7.763 | |
| Anxiety 18 | Drug responsivity | −5.131 | 1.906 | 7.250 | 0.007 | 0.00–0.248 |
| Epilepsy duration | −0.139 | 9.053 | 6.980 | 0.008 | 0.785–0.965 | |
| Type of epilepsy | 0.588 | 0.411 | 2.502 | 0.152 | 0.805–4.028 | |
| EEG findings | −0.045 | 0.333 | 0.018 | 0.892 | 0.498–1.834 | |
| Seizure control | −0.336 | 0.606 | 0.308 | 0.579 | 0.218–2.341 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gavrilovic, A.; Gavrilovic, J.; Ilic Zivojinovic, J.; Jeličić, L.; Radovanovic, S.; Vesic, K. Influence of Epilepsy Characteristics on the Anxiety Occurrence. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090858
Gavrilovic A, Gavrilovic J, Ilic Zivojinovic J, Jeličić L, Radovanovic S, Vesic K. Influence of Epilepsy Characteristics on the Anxiety Occurrence. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(9):858. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090858
Chicago/Turabian StyleGavrilovic, Aleksandar, Jagoda Gavrilovic, Jelena Ilic Zivojinovic, Ljiljana Jeličić, Snezana Radovanovic, and Katarina Vesic. 2024. "Influence of Epilepsy Characteristics on the Anxiety Occurrence" Brain Sciences 14, no. 9: 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090858
APA StyleGavrilovic, A., Gavrilovic, J., Ilic Zivojinovic, J., Jeličić, L., Radovanovic, S., & Vesic, K. (2024). Influence of Epilepsy Characteristics on the Anxiety Occurrence. Brain Sciences, 14(9), 858. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14090858






