Optimizing and Predicting Antidepressant Efficacy in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder Using Multi-Omics Analysis and the Opade AI Prediction Tools
Abstract
1. Introduction
Objective
2. Study Design
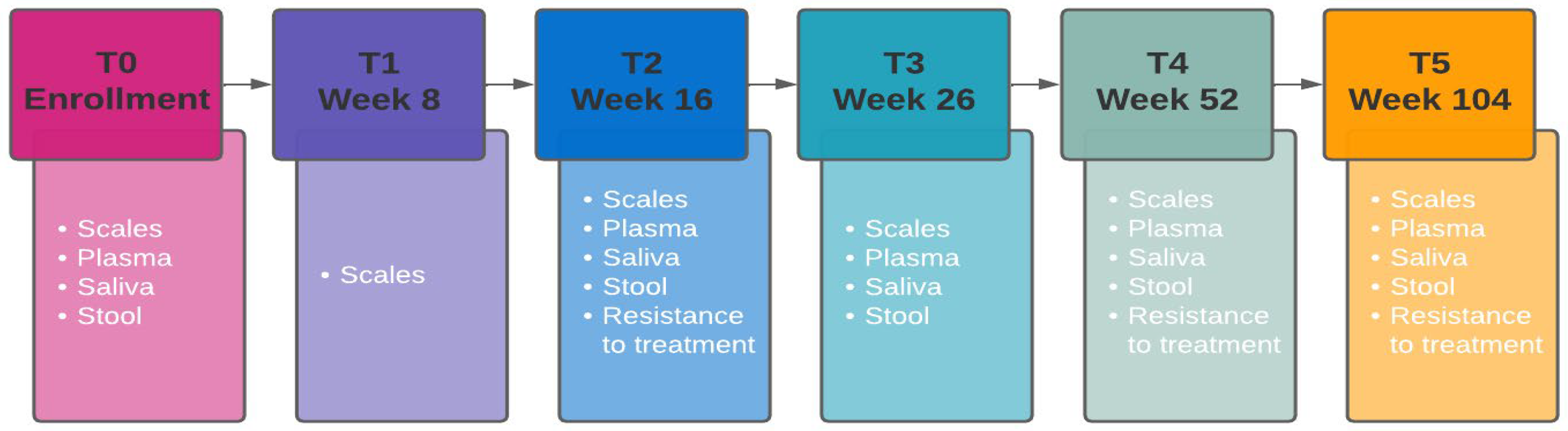
2.1. Setting and Participants
2.2. Serological Markers
2.3. Lipoprotein Profiling
2.4. Microbiome Profiling
2.5. Transcriptomics
2.6. Epigenomics
2.7. Metabolomic Profile
2.8. Pharmacogenetic and Long qt Phenotype
2.9. Hormonal/Cortisol Analysis
2.10. Psychometric Rating Scales
2.11. Assessment of Personal Resources
2.12. Assessment of Real-Life Functioning and Quality of Life
2.13. Treatment-Resistant Depression
2.14. Assessment of Cognitive Functions
2.15. Electroencephalographic Evaluation
2.16. Evaluation of Antidepressant Response
2.17. Remission Assessment
3. Device Used in the Study
Digital Patient Empowerment Tool: Turning Stories into Data
4. Factors of Interest
4.1. Environmental
4.2. Genetics and Epigenetics
4.3. Microbiome/Metabolome
5. Statistical Approach
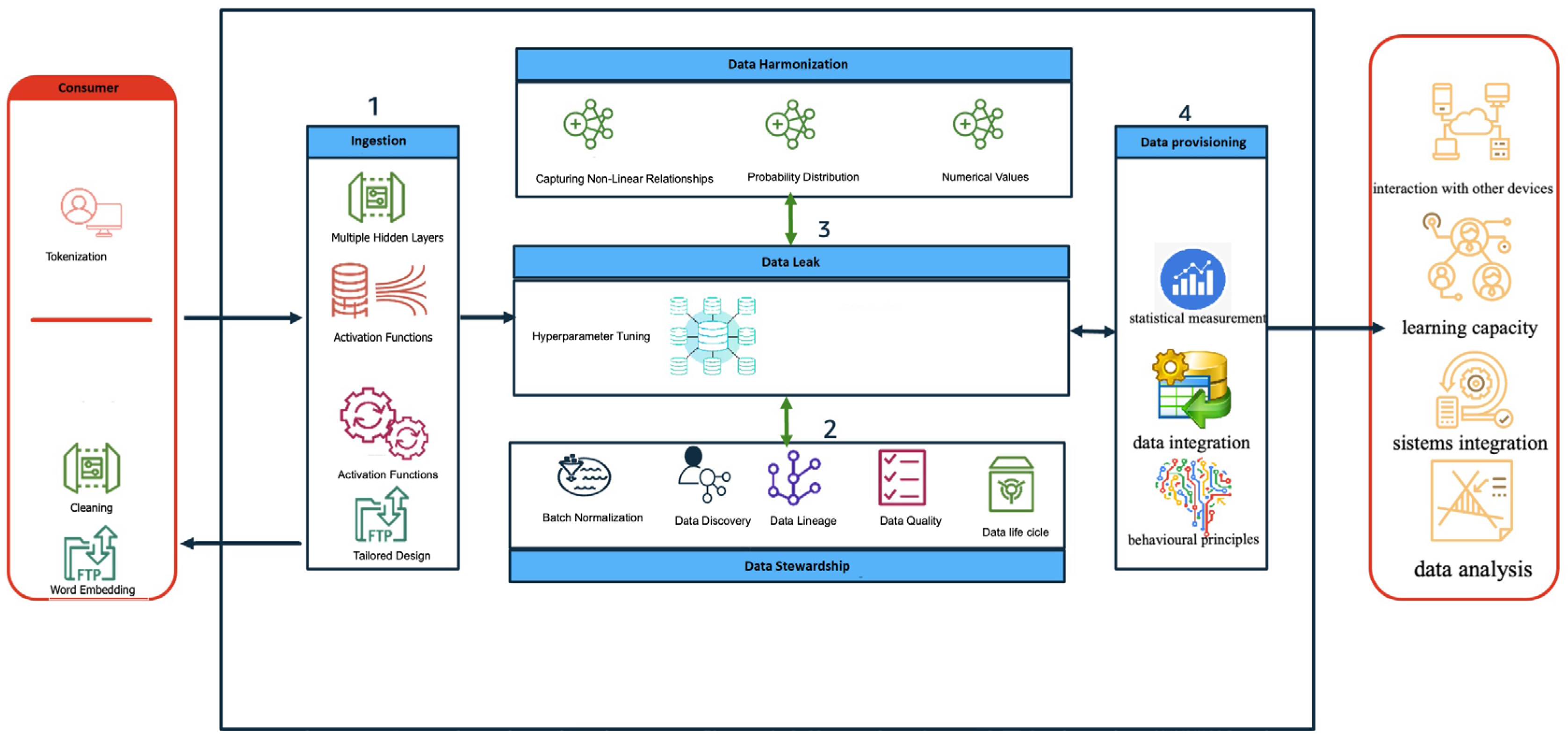
5.1. Artificial Intelligence Modelling
5.2. Data Protection
6. Discussion
7. Ethics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation. Global Health Data Exchange (GHDx). Available online: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results/ (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- Malhi, G.S.; Das, P.; Outhred, T.; Irwin, L.; Morris, G.; Hamilton, A.; Lynch, K.; Mannie, Z. Understanding suicide: Focusing on its mechanisms through a lithium lens. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 241, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroel, M.A.; Terlizzi, E.P. Symptoms of Depression among Adults: United States, 2019; NCHS Data Brief No. 379; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hasin, D.S.; Sarvet, A.L.; Meyers, J.L.; Saha, T.D.; Ruan, W.J.; Stohl, M.; Grant, B.F. Epidemiology of Adult DSM-5 Major Depressive Disorder and Its Specifiers in the United States. JAMA Psychiatry 2018, 75, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.C. The Costs of Depression. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.; Mokonogho, J.; Kumar, A. Racial and ethnic differences in depression: Current perspectives. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santomauro, D.F.; Herrera, A.M.M.; Shadid, J.; Zheng, P.; Ashbaugh, C.; Pigott, D.M.; Abbafati, C.; Adolph, C.; Amlag, J.O.; Aravkin, A.Y.; et al. Global prevalence and burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2021, 398, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego-Ruiz, A.; Borrego, J.J. An updated overview on the relationship between human gut microbiome dysbiosis and psychiatric and psychological disorders. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 128, 110861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialek, K.; Czarny, P.; Strycharz, J.; Sliwinski, T. Major depressive disorders accompanying autoimmune diseases–Response to treatment. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 95, 109678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beurel, E.; Toups, M.; Nemeroff, C.B. The Bidirectional Relationship of Depression and Inflammation: Double Trouble. Neuron 2020, 107, 234–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, I.D.; Nicholson, J.K. Gut microbiome interactions with drug metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity. Transl. Res. 2017, 179, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lax, E. DNA Methylation as a Therapeutic and Diagnostic Target in Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 759052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, L.M.; Phillips, K.E.; Ho, M.C.; Veldic, M.; Blacker, C.J. The Relationship between DNA Methylation and Antidepressant Medications: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, M.Y.; Michalak, E.E.; Waraich, P.; Anderson, J.E.; Lam, R.W. Is remission of depressive symptoms in primary care a realistic goal? A meta-analysis. BMC Fam. Pract. 2004, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, E.; Daguanno, A.W.; Woolwine, B.J.; Goldsmith, D.R.; Baer, W.M.; Wommack, E.C.; Felger, J.C.; Miller, A.H. Antidepressant treatment resistance is associated with increased inflammatory markers in patients with major depressive disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 95, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voineskos, D.; Daskalakis, Z.J.; Blumberger, D.M. Management of Treatment-Resistant Depression: Challenges and Strategies. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadam, H.; Pihlak, A.; Jaago, M.; Pupina, N.; Rähni, A.; Toots, M.; Vaheri, A.; Nieminen, J.K.; Siuko, M.; Tienari, P.J.; et al. Identification of two highly antigenic epitope markers predicting multiple sclerosis in optic neuritis patients. EBioMedicine 2021, 64, 103211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadam, H.; Pihlak, A.; Kivil, A.; Pihelgas, S.; Jaago, M.; Adler, P.; Vilo, J.; Vapalahti, O.; Neuman, T.; Lindholm, D.; et al. Prostaglandin D2 Receptor DP1 Antibodies Predict Vaccine-induced and Spontaneous Narcolepsy Type 1: Large-scale Study of Antibody Profiling. EBioMedicine 2018, 29, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Míguez, A.; Beghini, F.; Cumbo, F.; McIver, L.J.; Thompson, K.N.; Zolfo, M.; Manghi, P.; Dubois, L.; Huang, K.D.; Thomas, A.M.; et al. Extending and improving metagenomic taxonomic profiling with uncharacterized species using MetaPhlAn 4. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beghini, F.; McIver, L.J.; Blanco-Míguez, A.; Dubois, L.; Asnicar, F.; Maharjan, S.; Mailyan, A.; Manghi, P.; Scholz, M.; Thomas, A.M.; et al. Integrating taxonomic, functional, and strain-level profiling of diverse microbial communities with bioBakery 3. eLife 2021, 10, e65088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.-M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis: Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajković, G.; Starčević, V.; Latas, M.; Leštarević, M.; Ille, T.; Bukumirić, Z.; Marinković, J. Reliability of the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression: A meta-analysis over a period of 49 years. Psychiatry Res. 2011, 189, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuevo, R.; Dunn, G.; Dowrick, C.; Vázquez-Barquero, J.L.; Casey, P.; Dalgard, O.S.; Lehtinen, V.; Ayuso-Mateos, J.L. Cross-cultural equivalence of the Beck Depression Inventory: A five-country analysis from the ODIN study. J. Affect. Disord. 2009, 114, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.B.W.; Kobak, K.A. Development and reliability of a structured interview guide for the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (SIGMA). Br. J. Psychiatry 2008, 192, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, M.; Dellepiane, M.; Benvenuti, A.; Feloukatzis, K.; Skondra, N.; Dell’Osso, L.; Steingrímsson, S. Swedish Version of Mood Spectrum Self-Report Questionnaire: Psychometric Properties of Lifetime and Last-week Version. Clin. Pract. Epidemiol. Ment. Health 2016, 12, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boyd, J.E.; Adler, E.P.; Otilingam, P.G.; Peters, T. Internalized Stigma of Mental Illness (ISMI) Scale: A multinational review. Compr. Psychiatry 2014, 55, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aas, I.M. Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF): Properties and frontier of current knowledge. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen-Bauer, K.; Gowers, S.; Aalen, O.O.; Bilenberg, N.; Brann, P.; Garralda, E.; Merry, S.; Heyerdahl, S. Cross-National Reliability of Clinician-Rated Outcome Measures in Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services. Adm. Policy Ment. Health 2007, 34, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.K.; Gandek, B.; Aaronson, N.K.; Acquadro, C.; Alonso, J.; Apolone, G.; Bullinger, M.; Bjorner, J.; Fukuhara, S.; Kaasa, S.; et al. Cross-Cultural Comparisons of the Content of SF-36 Translations across 10 Countries. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1998, 51, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varni, J.W.; Seid, M.; Kurtin, P.S. PedsQLTM 4.0: Reliability and Validity of the Pediatric Quality of Life InventoryTM Version 4.0 Generic Core Scales in Healthy and Patient Populations. Med. Care 2001, 39, 800–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravens-Sieberer, U.; Herdman, M.; Devine, J.; Otto, C.; Bullinger, M.; Rose, M.; Klasen, F. The European KIDSCREEN approach to measure quality of life and well-being in children: Development, current application, and future advances. Qual. Life Res. 2014, 23, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, M. Assessment of Physical Activity: An International Perspective. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2000, 71, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, R.S.; Alsuwaidan, M.; Baune, B.T.; Berk, M.; Demyttenaere, K.; Goldberg, J.F.; Gorwood, P.; Ho, R.; Kasper, S.; Kennedy, S.H.; et al. Treatment-resistant depression: Definition, prevalence, detection, management, and investigational interventions. World Psychiatry 2023, 22, 394–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, P.L.; Roiser, J.P.; Riedel, W.J.; Blackwell, A.D. Cognitive impairment in depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 2029–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowie, C.R.; Harvey, P.D. Cognitive deficits and functional outcome in schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2006, 2, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Égerházi, A.; Berecz, R.; Bartók, E.; Degrell, I. Automated Neuropsychological Test Battery (CANTAB) in mild cognitive impairment and in Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 31, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, H.-J. Outcomes in major depressive disorder: The evolving concept of remission and its implications for treatment. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 9, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, J.; Rebinsky, R.; Suresh, R.; Kubic, S.; Carter, A.; Cunningham, J.E.A.; Ker, A.; Williams, K.; Sorin, M. Scoping review to evaluate the effects of peer support on the mental health of young adults. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e061336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schick, A.; Feine, J.; Morana, S.; Maedche, A.; Reininghaus, U. Validity of Chatbot Use for Mental Health Assessment: Experimental Study. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2022, 10, e28082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Alrazaq, A.A.; Rababeh, A.; Alajlani, M.; Bewick, B.M.; Househ, M. Effectiveness and Safety of Using Chatbots to Improve Mental Health: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med Internet Res. 2020, 22, e16021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Gennaro, M.; Krumhuber, E.G.; Lucas, G. Effectiveness of an Empathic Chatbot in Combating Adverse Effects of Social Exclusion on Mood. Front. Psychol. 2020, 10, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.-Z.; Song, X.-S.; Ma, J.-S. Gene × environment interaction in major depressive disorder. World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 9368–9375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Yang, B.; Rothschild, G.; Mann, J.J.; Sanford, L.D.; Tang, X.; Huang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W. Epigenetic regulation in major depression and other stress-related disorders: Molecular mechanisms, clinical relevance and therapeutic potential. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, A.A.; Bailey, M.T. Stressed to the Core: Inflammation and Intestinal Permeability Link Stress-Related Gut Microbiota Shifts to Mental Health Outcomes. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 95, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madison, A.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Stress, depression, diet, and the gut microbiota: Human–bacteria interactions at the core of psychoneuroimmunology and nutrition. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2019, 28, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahai, H.; Khurshid, A. Statistics in Epidemiology: Methods, Techniques, and Applications; CRC Press, Inc: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, F.; Scherer, M.; Assenov, Y.; Lutsik, P.; Walter, J.; Lengauer, T.; Bock, C. RnBeads 2.0: Comprehensive analysis of DNA methylation data. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, T.R.; Smith, R.G.; Hackinger, S.; Schalkwyk, L.C.; Uher, R.; McGuffin, P.; Mill, J.; Tansey, K.E. DNA methylation in interleukin-11 predicts clinical response to antidepressants in GENDEP. Transl. Psychiatry 2013, 3, e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaeian, N.; Gurina, R.; Saltykova, O.A.; Hezla, L.; Nohurov, M.; Kashyzadeh, K.R. Novel GA-Based DNN Architecture for Identifying the Failure Mode with High Accuracy and Analyzing Its Effects on the System. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, C. Trends in using deep learning algorithms in biomedical prediction systems. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1256351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaria, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of deep learning: Concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, P.P. Hyperparameter Tuning: The Art of Fine-Tuning Machine and Deep Learning Models to Improve Metric Results. In Applied Data Science in Tourism; Egger, R., Ed.; Tourism on the Verge; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 231–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Abuhmed, T.; El-Sappagh, S.; Muhammad, K.; Alonso-Moral, J.M.; Confalonieri, R.; Guidotti, R.; Del Ser, J.; Díaz-Rodríguez, N.; Herrera, F. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): What we know and what is left to attain Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence. Inf. Fusion 2023, 99, 101805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramspek, C.L.; Jager, K.J.; Dekker, F.W.; Zoccali, C.; Van Diepen, M. External validation of prognostic models: What, why, how, when and where? Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linden, A. Measuring diagnostic and predictive accuracy in disease management: An introduction to receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. J. Evaluation Clin. Pract. 2006, 12, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Rojas, L.; Porras-Segovia, A.; Dunne, H.; Andrade-González, N.; Cervilla, J.A. Prevalence and correlates of major depressive disorder: A systematic review. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2020, 42, 657–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Inclusion criteria:
|
Exclusion criteria:
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corrivetti, G.; Monaco, F.; Vignapiano, A.; Marenna, A.; Palm, K.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Frigola-Capell, E.; Leen, V.; Ibarrola, O.; Amil, B.; et al. Optimizing and Predicting Antidepressant Efficacy in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder Using Multi-Omics Analysis and the Opade AI Prediction Tools. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14070658
Corrivetti G, Monaco F, Vignapiano A, Marenna A, Palm K, Fernández-Arroyo S, Frigola-Capell E, Leen V, Ibarrola O, Amil B, et al. Optimizing and Predicting Antidepressant Efficacy in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder Using Multi-Omics Analysis and the Opade AI Prediction Tools. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(7):658. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14070658
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorrivetti, Giulio, Francesco Monaco, Annarita Vignapiano, Alessandra Marenna, Kaia Palm, Salvador Fernández-Arroyo, Eva Frigola-Capell, Volker Leen, Oihane Ibarrola, Burak Amil, and et al. 2024. "Optimizing and Predicting Antidepressant Efficacy in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder Using Multi-Omics Analysis and the Opade AI Prediction Tools" Brain Sciences 14, no. 7: 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14070658
APA StyleCorrivetti, G., Monaco, F., Vignapiano, A., Marenna, A., Palm, K., Fernández-Arroyo, S., Frigola-Capell, E., Leen, V., Ibarrola, O., Amil, B., Caruson, M. M., Chiariotti, L., Palacios-Ariza, M. A., Hoekstra, P. J., Chiang, H.-Y., Floareș, A., Fagiolini, A., & Fasano, A. (2024). Optimizing and Predicting Antidepressant Efficacy in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder Using Multi-Omics Analysis and the Opade AI Prediction Tools. Brain Sciences, 14(7), 658. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14070658









