Disrupted Effective Connectivity within the Fronto-Thalamic Circuit in Pontine Infarction: A Spectral Dynamic Causal Modeling Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Demographic and Clinical Data
2.3. MRI Acquisition
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. MRI Data Preprocessing
2.4.2. Spectral Dynamic Causal Modeling Analysis
2.4.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Data
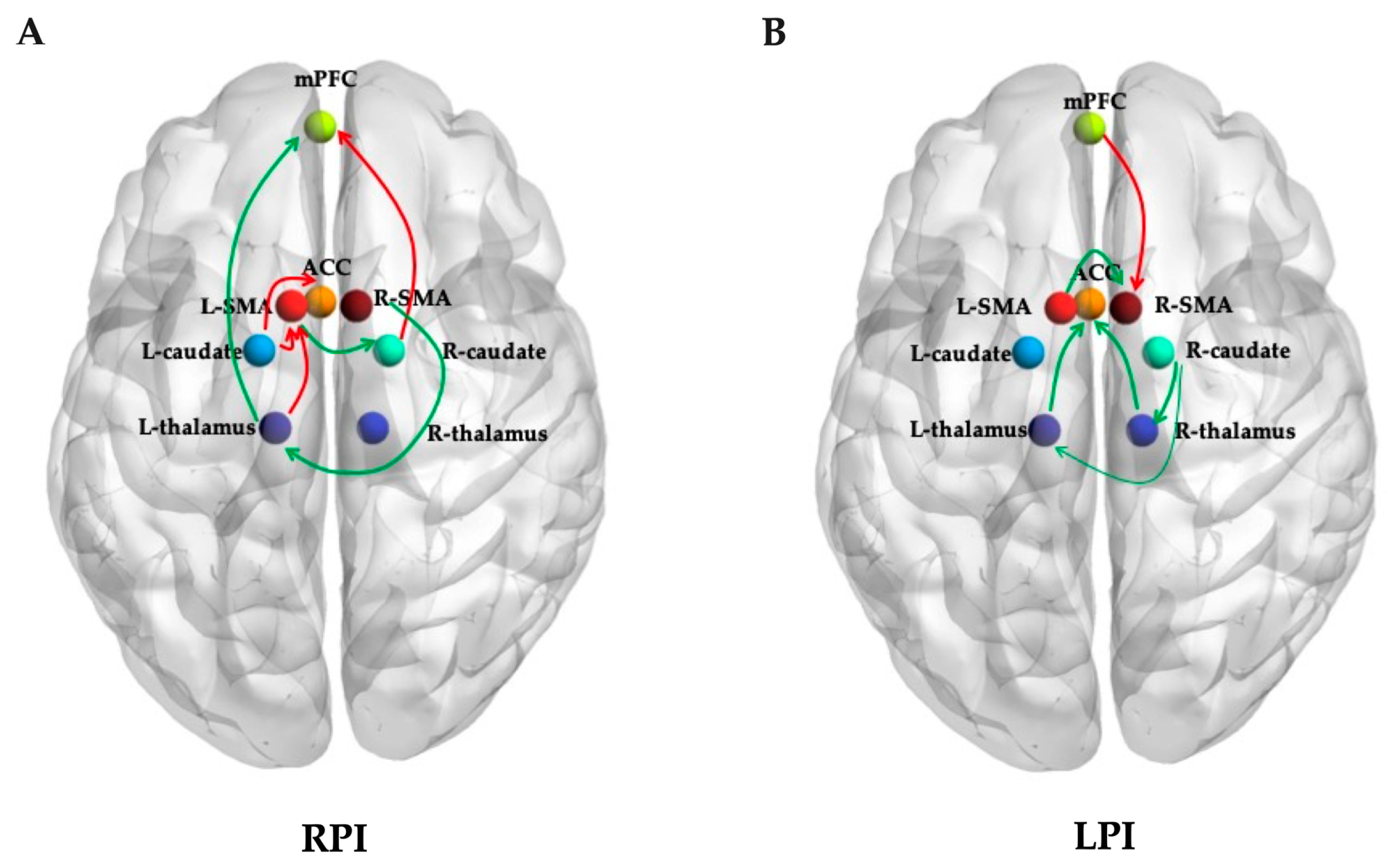
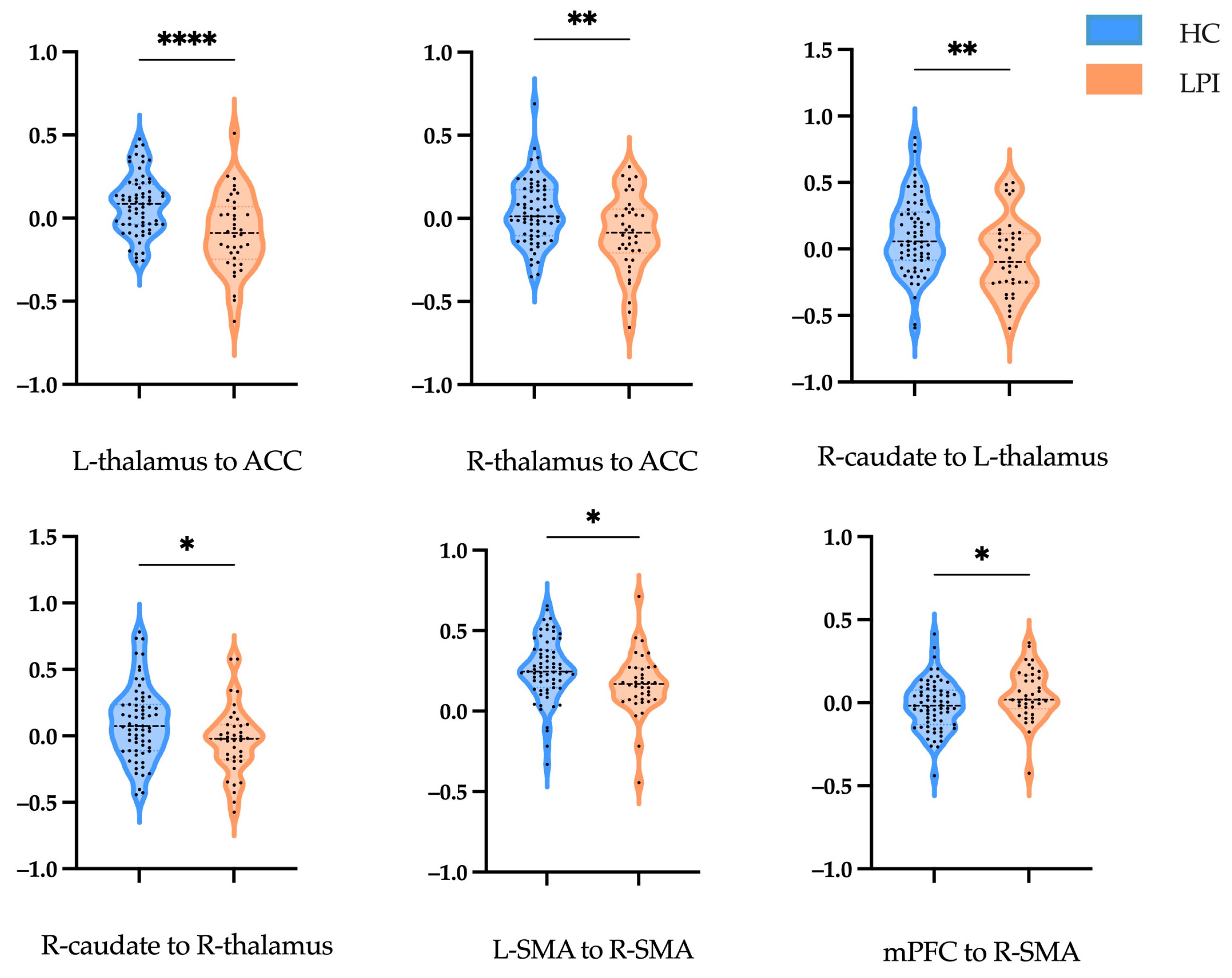
3.2. Effective Connectivity Analysis
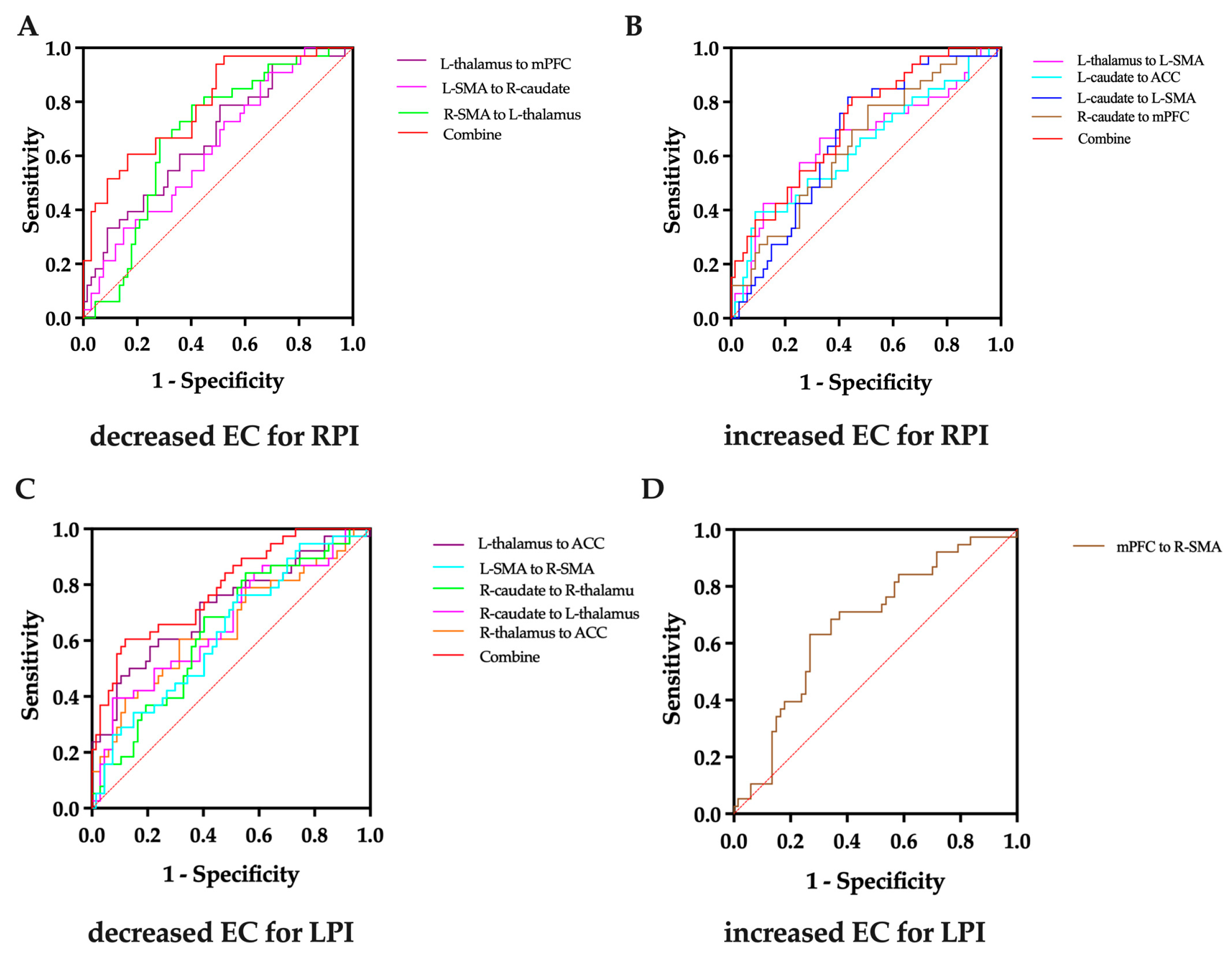
3.3. Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve
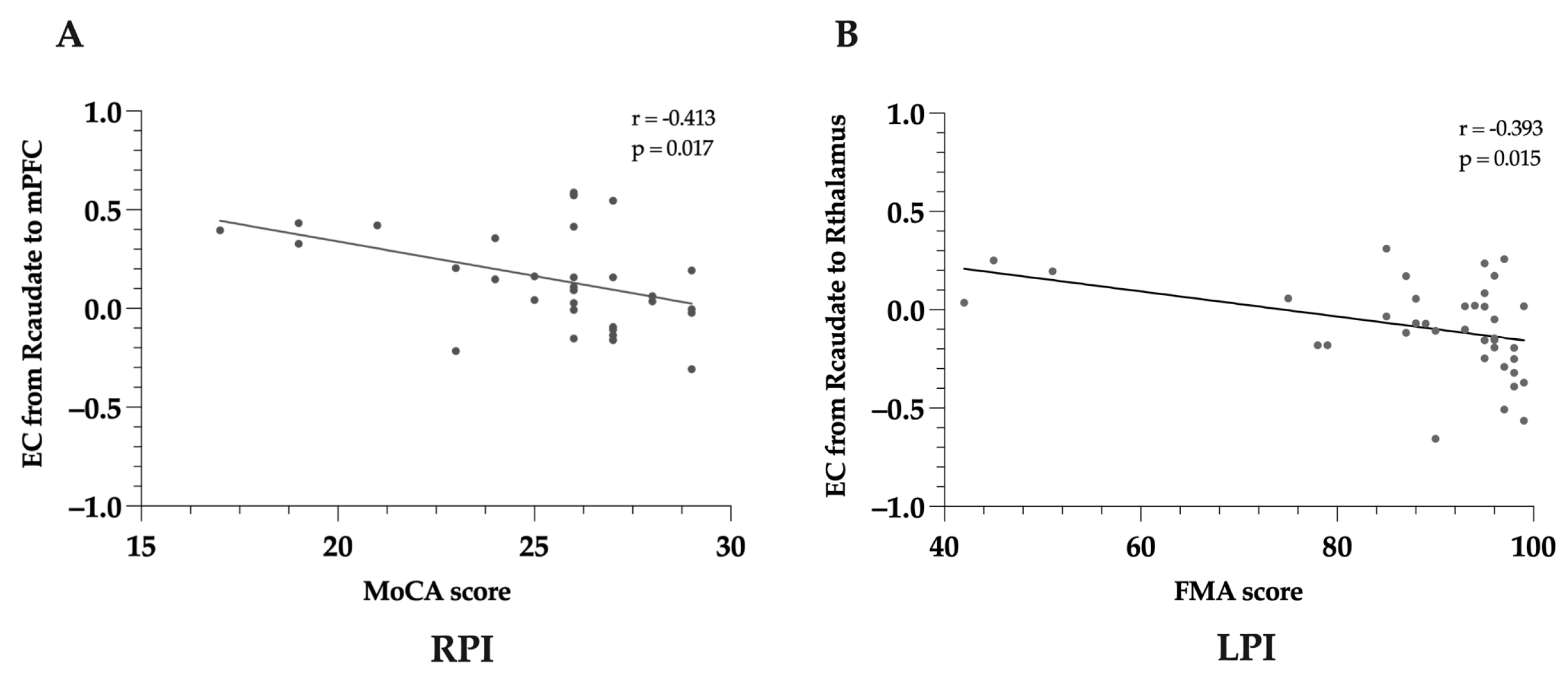
3.4. Correlation Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACC | Anterior cingulate cortex | mPFC | Medial prefrontal cortex |
| EC | Effective connectivity | NIHSS | National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale |
| FMA | Fugl–Meyer Assessment | PI | Pontine infarction |
| GMV | Gray matter volume | RPI | Right pontine infarction |
| HC | Healthy control | rs-fMRI | Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging |
| LPI | Left pontine infarction | spDCM | Spectral dynamic causal modeling |
| MoCA | Montreal Cognitive Assessment | SMA | Supplementary motor area |
References
- Fonarow, G.C.; Reeves, M.J.; Zhao, X.; Olson, D.M.; Smith, E.E.; Saver, J.L.; Schwamm, L.H. Age-Related Differences in Characteristics, Performance Measures, Treatment Trends, and Outcomes in Patients With Ischemic Stroke. Circulation 2010, 121, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Caplan, L.R. Clinical Stroke Syndromes. In Intracranial Atherosclerosis: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment; Frontiers of Neurology and Neuroscience; Karger Publishers: Basel, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 72–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Jia, X.; Zhang, M.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Shan, Y.; Ma, Q.; Qian, T.; Wang, J.; Lu, J.; et al. Correlation of Longitudinal Gray Matter Volume Changes and Motor Recovery in Patients After Pontine Infarction. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Dai, Y.Q.; Wu, H.T.; Luo, L.Y.; Wei, L.; Zhou, L.; Lin, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.J.; Lu, Z.Q. Predictors of Early Neurologic Deterioration in Acute Pontine Infarction. Stroke 2020, 51, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeshima, S.; Osawa, A.; Miyazaki, Y.; Takeda, H.; Tanahashi, N. Functional outcome in patients with pontine infarction after acute rehabilitation. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 33, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Miao, P.; Wang, K.; Wang, C.; Cheng, J. Disrupted Regional Cerebral Blood Flow and Functional Connectivity in Pontine Infarction: A Longitudinal MRI Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 577899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payabvash, S.; Benson, J.C.; Tyan, A.E.; Taleb, S.; McKinney, A.M. Multivariate Prognostic Model of Acute Stroke Combining Admission Infarct Location and Symptom Severity: A Proof-of-Concept Study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, C.; Liu, G.; Xing, S.; Xie, C.; Peng, K.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Pei, Z.; et al. Longitudinal Cortical Volume Changes Correlate With Motor Recovery in Patients After Acute Local Subcortical Infarction. Stroke 2013, 44, 2795–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Guo, J.; Wei, Y.; Wang, K.; Miao, P.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J. Voxel-Mirrored Homotopic Connectivity Associated With Change of Cognitive Function in Chronic Pontine Stroke. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 621767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, S.M. Thalamus plays a central role in ongoing cortical functioning. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.; Kyeong, S.; Kang, H.; Kim, D.H. Bihemispheric changes associated with cognition in patients with chronic brainstem stroke. Neuroreport 2019, 30, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Guo, J.; Cheng, J.; Han, T.; Miao, P.; Cao, C.; Yu, C. Structural Alterations in Chronic Capsular versus Pontine Stroke. Radiology 2017, 285, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Geng, W.; Shang, S.A.; Shi, M.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, P.; Yin, X.; Chen, Y.C. Alterations of brain network topology and structural connectivity-functional connectivity coupling in capsular versus pontine stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K.J.; Harrison, L.; Penny, W. Dynamic causal modelling. NeuroImage 2003, 19, 1273–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, B.; Bai, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Leung, H.C.; Tian, P.; Zhang, L.; Guo, F.; Cui, L.B.; et al. Abnormal resting state effective connectivity within the default mode network in major depressive disorder: A spectral dynamic causal modeling study. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, S.; Housley, S.N.; Wu, D.; Dhamala, M.; James, G.A.; Butler, A.J. Dominance of the Unaffected Hemisphere Motor Network and Its Role in the Behavior of Chronic Stroke Survivors. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos-Leite, A.J.; Ridgway, G.R.; Silveira, C.; Norton, A.; Reis, S.; Friston, K.J. Dysconnectivity Within the Default Mode in First-Episode Schizophrenia: A Stochastic Dynamic Causal Modeling Study With Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Schizophr. Bull. 2014, 41, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, P.; Liu, J.; Wei, S.; Wei, Y.; Han, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Altered resting-state neurovascular coupling in patients with pontine infarction. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 179, 112241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Guo, J.; Miao, P.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; et al. Altered static and dynamic spontaneous neural activity in patients with ischemic pontine stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1131062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çavdar, S.; Köse, B.; Altınöz, D.; Özkan, M.; Güneş, Y.C.; Algın, O. The brainstem connections of the supplementary motor area and its relations to the corticospinal tract: Experimental rat and human 3-tesla tractography study. Neurosci. Lett. 2023, 798, 137099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-W.; Lin, P.; Yao, P.-S.; Zheng, S.-F.; Kang, D.-Z. Structure and function of corticospinal projection originating from supplementary motor area. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, T.; Hensel, L.; Rehme, A.K.; Tscherpel, C.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Fink, G.R.; Grefkes, C.; Volz, L.J. Early motor network connectivity after stroke: An interplay of general reorganization and state-specific compensation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 5230–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, M.T.; Barcia, C.; Navarro, J. Functional anatomy of thalamus and basal ganglia. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2002, 18, 386–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreitzer, A.C.; Malenka, R.C. Striatal Plasticity and Basal Ganglia Circuit Function. Neuron 2008, 60, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcauter, S.; Lin, W.; Smith, J.K.; Short, S.J.; Goldman, B.D.; Reznick, J.S.; Gilmore, J.H.; Gao, W. Development of Thalamocortical Connectivity during Infancy and Its Cognitive Correlations. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 9067–9075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badke D’Andrea, C.; Marek, S.; Van, A.N.; Miller, R.L.; Earl, E.A.; Stewart, S.B.; Dosenbach, N.U.F.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Laumann, T.O.; Fair, D.A.; et al. Thalamo-cortical and cerebello-cortical functional connectivity in development. Cereb. Cortex 2023, 33, 9250–9262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Sabate, C.; Gonzalez, A.; Perez-Darias, J.C.; Morales, I.; Sole-Sabater, M.; Rodriguez, M. Causality methods to study the functional connectivity in brain networks: The basal ganglia-thalamus causal interactions. Brain Imaging Behav. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintzen, A.; Pelzer, E.A.; Tittgemeyer, M. Thalamic interactions of cerebellum and basal ganglia. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 223, 569–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pozzo-Miller, L. Dysfunction of the corticostriatal pathway in autism spectrum disorders. J. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 98, 2130–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etkin, A.; Egner, T.; Kalisch, R. Emotional processing in anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortex. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2011, 15, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Wang, J.; Qiu, S.; Chen, P.; Luo, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y. Common and distinct patterns of intrinsic brain activity alterations in major depression and bipolar disorder: Voxel-based meta-analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harel, M.; Perini, I.; Kämpe, R.; Alyagon, U.; Shalev, H.; Besser, I.; Sommer, W.H.; Heilig, M.; Zangen, A. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Alcohol Dependence: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled Proof-of-Concept Trial Targeting the Medial Prefrontal and Anterior Cingulate Cortices. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 91, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
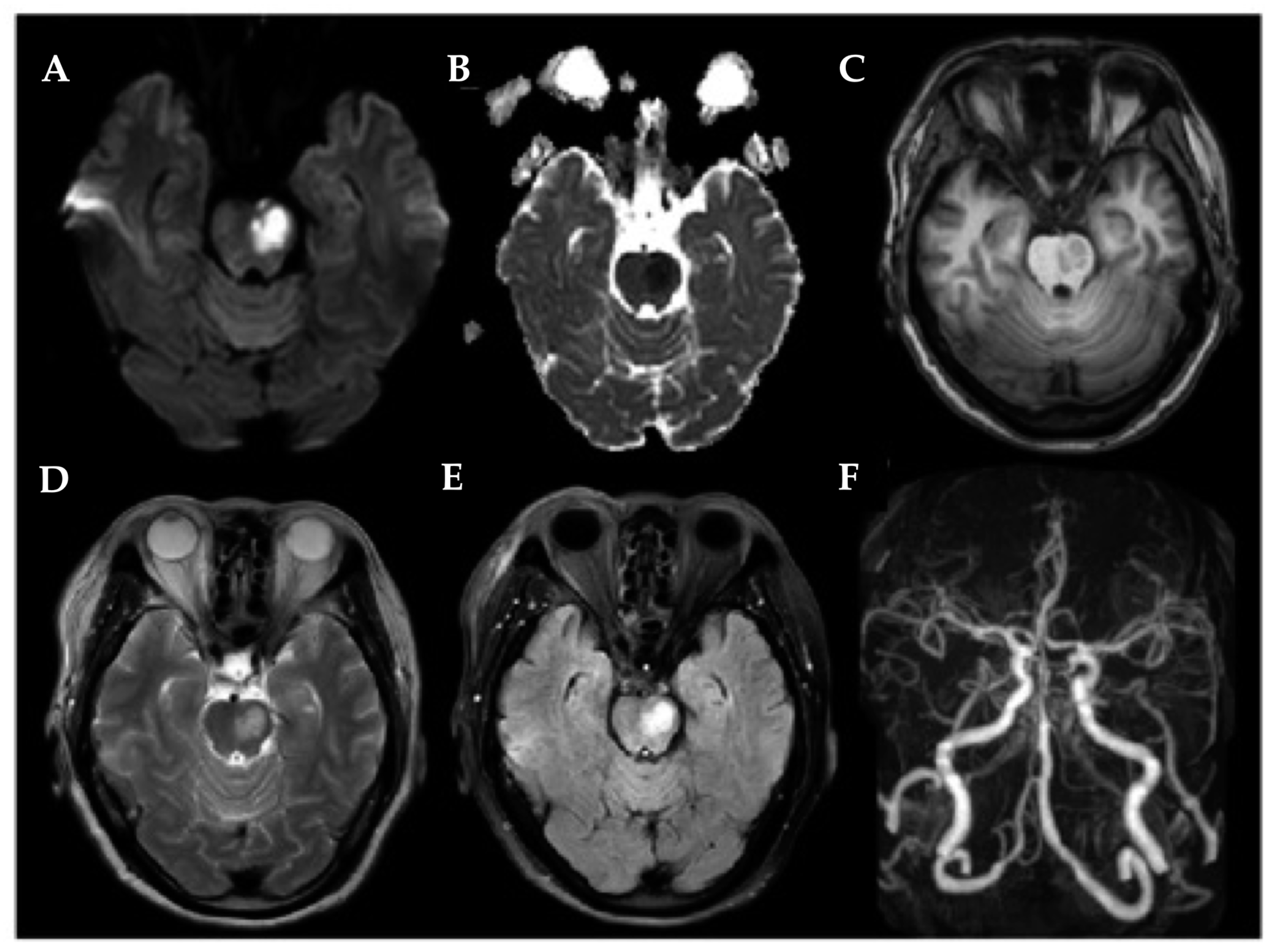
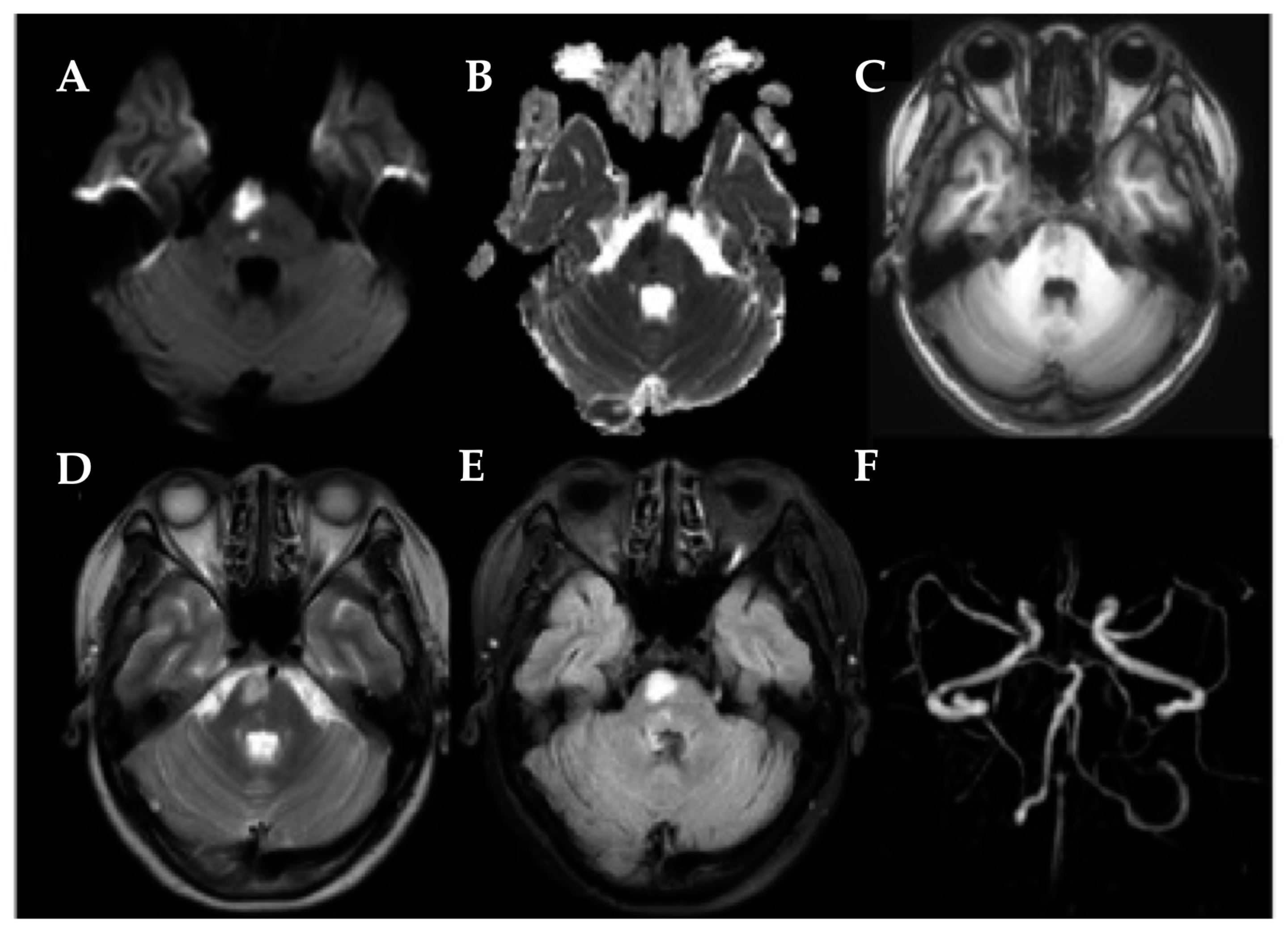
| RPI (n = 33) | LPI (n = 38) | HCs (n = 67) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 65.76 ± 8.98 | 64.53 ± 10.64 | 61.84 ± 6.60 | 0.067 |
| Gender (male/female) | 21/12 | 26/12 | 45/22 | 0.906 |
| Education (years) | 10.06 ± 1.82 | 10.95 ± 2.21 | 10.97 ± 1.87 | 0.319 |
| NIHSS score | 3.12 ± 2.26 | 3.50 ± 2.29 | - | 0.486 |
| FMA score | 85.68 ± 14.62 | 88.79 ± 14.09 | - | 0.349 |
| MoCA score | 25.45 ± 2.91 | 25.47 ± 3.59 | 26.09 ± 2.672 | 0.016 * |
| Connection | Connectivity Strength (Mean ± SD) | p-Value | t | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCs | RPI | |||
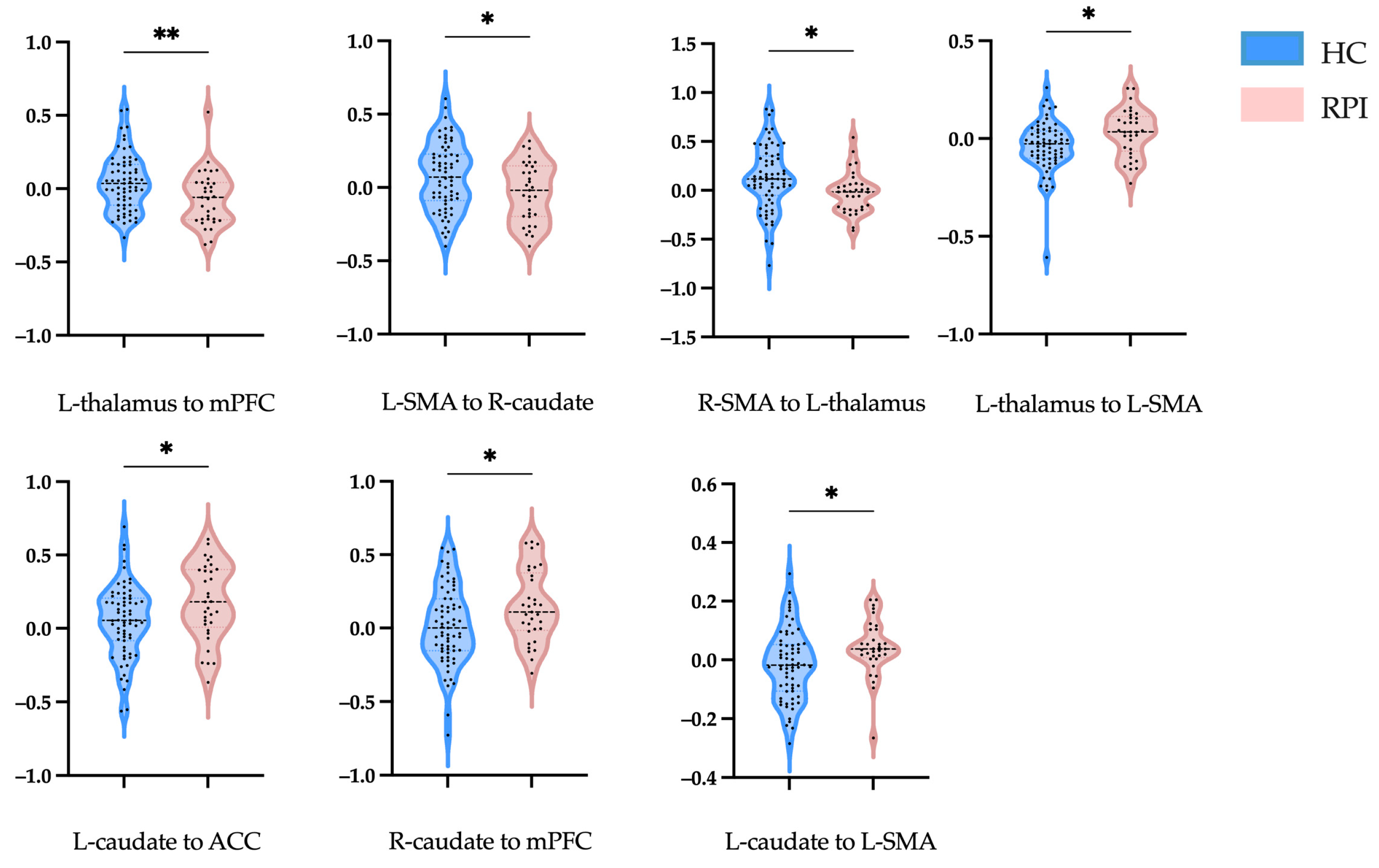
| L-thalamus to mPFC | 0.424 ± 0.192 | −0.066 ± 0.185 | 0.008 | 2.737 |
| L-SMA to R-caudate | 0.074 ± 0.231 | −0.032 ± 0.202 | 0.027 | 2.246 |
| R-SMA to L-thalamus | 0.126 ± 0.326 | −0.028 ± 0.207 | 0.005 | 2.882 |
| L-thalamus to L-SMA | −0.039 ± 0.128 | −0.295 ± 0.121 | 0.010 | −2.634 |
| L-caudate to ACC | 0.053 ± 0.249 | 0.177 ± 0.259 | 0.023 | −2.310 |
| L-caudate to LSMA | −0.016 ± 0.119 | 0.042 ± 0.094 | 0.016 | −2.441 |
| R-caudate to mPFC | 0.014 ± 0.264 | 0.148 ± 0.246 | 0.016 | −2.454 |
| Connection | Connectivity Strength (Mean ± SD) | p-Value | t | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCs | LPI | |||
| L-thalamus to ACC | −0.812 ± 0.179 | −0.088 ± 0.229 | <0.001 | 4.205 |
| R-thalamus to ACC | 0.036 ± 0.190 | −0.091 ± 0.229 | 0.003 | 3.035 |
| R-caudate to L-thalamus | 0.103 ± 0.291 | −0.066 ± 0.286 | 0.005 | 2.868 |
| R-caudate to R-thalamus | 0.098 ± 0.277 | −0.034± 0.254 | 0.015 | 2.422 |
| L-SMA to R-SMA | 0.260 ± 0.192 | 0.166 ± 0.188 | 0.017 | 2.425 |
| mPFC to R-SMA | −0.015 ± 0.149 | 0.049 ± 0.152 | 0.038 | −2.101 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Mao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, M.; Geng, W.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yin, X. Disrupted Effective Connectivity within the Fronto-Thalamic Circuit in Pontine Infarction: A Spectral Dynamic Causal Modeling Study. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14010045
Chen H, Mao Q, Zhang Y, Shi M, Geng W, Ma Y, Chen Y, Yin X. Disrupted Effective Connectivity within the Fronto-Thalamic Circuit in Pontine Infarction: A Spectral Dynamic Causal Modeling Study. Brain Sciences. 2024; 14(1):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14010045
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Huiyou, Qianqian Mao, Yujie Zhang, Mengye Shi, Wen Geng, Yuehu Ma, Yuchen Chen, and Xindao Yin. 2024. "Disrupted Effective Connectivity within the Fronto-Thalamic Circuit in Pontine Infarction: A Spectral Dynamic Causal Modeling Study" Brain Sciences 14, no. 1: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14010045
APA StyleChen, H., Mao, Q., Zhang, Y., Shi, M., Geng, W., Ma, Y., Chen, Y., & Yin, X. (2024). Disrupted Effective Connectivity within the Fronto-Thalamic Circuit in Pontine Infarction: A Spectral Dynamic Causal Modeling Study. Brain Sciences, 14(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14010045





