Delayed Intracerebral Hematoma after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in the Context of Ruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformation: A Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Original Clinical Series
2.1.1. Assessment Tools
2.1.2. Ethics
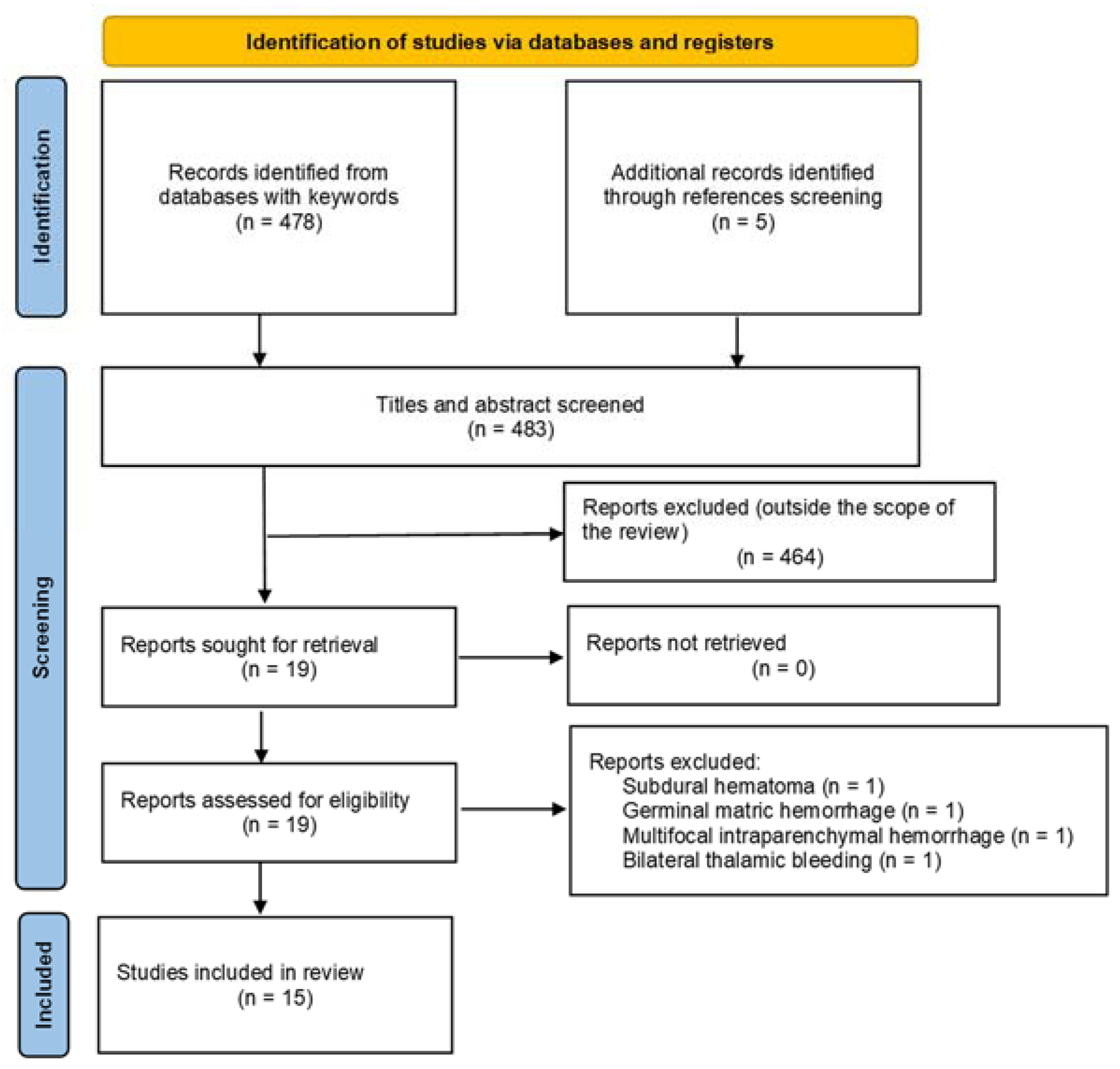
2.2. PRISMA Systematic Literature Review
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Series
3.2. Literature Review Analysis
- The median delay between the EVD/VPS procedure and the hemorrhagic complication was 5 days (range from 2 to 15 days).
- DICH patients were rather young, with a median age of 61 years (range from 17 to 84 years).
- A slight male predominance was noted, with a gender ratio of 1.3 M/F.
- The most prevalent underlying pathologies in DICH patients were as follows: (a) neurovascular disorders accounted for 47% of the cases, including conditions such as spontaneous intracerebral hematoma and subarachnoid hemorrhage resulting from ruptured vascular malformations. (b) Traumatic brain injuries constituted 23% of the cases. (c) Normal-pressure hydrocephalus was observed in 20% of the cases. (d) Other pathologies, such as brain tumors and central nervous system infectious diseases, were less frequently reported, with respective incidences of 5% and 3% of the patient population.
- The majority of DICH cases were symptomatic, accounting for 66% of patients. This symptomatic presentation correlated with an unfavorable prognosis in 44% of cases, with a Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS) score of 3 or less, indicating poor outcomes. Surgical management was pursued for 22% of all patients, while 3% unfortunately succumbed to their condition before a surgical procedure could be performed. Conservative medical management or therapeutic abstention were approaches adopted for most patients.
4. Discussion
4.1. Hemorrhagic Complications in the Ventricular Shunting Procedure
- The location of the hematoma was consistently distant from the arteriovenous malformation (AVM) nidus, surrounding the trajectory of the ventricular catheter.
- The occurrence of the hemorrhagic complication transpired several weeks after the initial AVM rupture and several days after the placement of the VPS.
- Catheter-related DICH manifested in all 10 cases without any evident coagulation disorders or other identifiable risk factors.
- Age older than 75 years;
- Anticoagulation/antiplatelet therapy;
- Other coagulation disorders;
- Iterative manipulations during surgery (many drain insertion attempts) surgical difficulties;
- Larger diameter of the inserted catheter;
- And postoperative valve manipulation/pressure changing.
4.2. DICH
4.3. Arteriovenous Malformations and Physio-Pathological Mechanisms
4.4. Hydrocephalus Management in Ruptured bAVM Patients
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gross, B.A.; Rosalind Lai, P.M.; Du, R. Hydrocephalus after Arteriovenous Malformation Rupture. FOC 2013, 34, E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilard, V.; Metayer, T.; Gakuba, C.; Langlois, O.; Proust, F.; Emery, E.; Gaberel, T. Intraventricular Hemorrhage Related to AVM Rupture: Description, Outcomes and Impact of Intraventricular Fibrinolysis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 164, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirmani, A.; Sarmast, A.; Bhat, A. Role of External Ventricular Drainage in the Management of Intraventricular Hemorrhage; Its Complications and Management. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2015, 6, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukamachi, A.; Koizumi, H.; Nukui, H. Postoperative Intracerebral Hemorrhages: A Survey of Computed Tomographic Findings after 1074 Intracranial Operations. Surg. Neurol. 1985, 23, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sussman, E.S.; Kellner, C.P.; Nelson, E.; McDowell, M.M.; Bruce, S.S.; Bruce, R.A.; Zhuang, Z.; Connolly, E.S. Hemorrhagic Complications of Ventriculostomy: Incidence and Predictors in Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Clinical Article. JNS 2014, 120, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniker, A.H.; Vaynman, A.Y.; Karimi, R.J.; Sabit, A.O.; Holland, B. Hemorrhagic Complications Of External Ventricular Drainage. Oper. Neurosurg. 2006, 59, ONS-419–ONS-425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, A.; Shinohara, A.; Munekata, K.; Maki, Y. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt. Surg. Neurol. 1985, 24, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Xu, L.; Yang, P.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. Characteristics of Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Insertion. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 42693–42699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Chen, X.; Yu, B.; Shen, L.; Zhang, X. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage Secondary to Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt: A Retrospective Study. World Neurosurg. 2017, 107, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, Y.-L.; Yang, S.-X.; Wang, Y.-R. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage Secondary to Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt: A Case Report and Literature Review. Medicine 2015, 94, e2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Liu, Q.; Ying, G.; Zhu, X. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage Secondary to Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt: Two Case Reports and a Literature Review. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 9, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hou, K.; Suo, S.; Gao, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G. Symptomatic Intracerebral Hemorrhage Secondary to Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in Adults without Bleeding Tendency. World Neurosurg. 2017, 106, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savitz, M.H.; Bobroff, L.M. Low Incidence of Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage Secondary to Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Insertion. J. Neurosurg. 1999, 91, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-T.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Lv, H.-T.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.-H. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage after Ventriculo-Peritoneal Shunt Procedure: Two Case Reports and a Review of Literature. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 6093–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teasdale, G.; Jennett, B. Assessment of Coma and Impaired Consciousness. A Practical Scale. Lancet 1974, 2, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennett, B. Assessment of Outcome after Severe Brain Damage: A Practical Scale. Lancet 1975, 305, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, C.M.; Kistler, J.P.; Davis, J.M. Relation of Cerebral Vasospasm to Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Visualized by Computerized Tomographic Scanning. Neurosurgery 1980, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spetzler, R.F.; Martin, N.A. A Proposed Grading System for Arteriovenous Malformations. J. Neurosurg. 1986, 65, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibbaro, S.; Tacconi, L. Safety of Deep Venous Thrombosis Prophylaxis with Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin in Brain Surgery. Prospective Study on 746 Patients. Surg. Neurol. 2008, 70, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibbaro, S.; Cebula, H.; Todeschi, J.; Fricia, M.; Vigouroux, D.; Abid, H.; Kourbanhoussen, H.; Pop, R.; Nannavecchia, B.; Gubian, A.; et al. Evolution of Prophylaxis Protocols for Venous Thromboembolism in Neurosurgery: Results from a Prospective Comparative Study on Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin, Elastic Stockings, and Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Devices. World Neurosurg. 2018, 109, e510–e516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganau, M.; Prisco, L.; Cebula, H.; Todeschi, J.; Abid, H.; Ligarotti, G.; Pop, R.; Proust, F.; Chibbaro, S. Risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis in Neurosurgery: State of the Art on Prophylaxis Protocols and Best Clinical Practices. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 45, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganau, M.; Ligarotti, G.K.I.; Meloni, M.; Chibbaro, S. Efficacy and Safety Profiles of Mechanical and Pharmacological Thromboprophylaxis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, S224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snow, R.B.; Zimmerman, R.D.; Devinsky, O. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunting. Neurosurgery 1986, 19, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derdeyn, C.P.; Delashaw, J.B.; Broaddus, W.C.; Jane, J.A. Detection of Shunt-Induced Intracerebral Hemorrhage by Postoperative Skull Films: A Report of Two Cases. Neurosurgery 1988, 22, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascalchi, M. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage after CSF Shunt for Communicating “Normal-Pressure” Hydrocephalus. Case Report. Ital. J. Neurol. Sci. 1991, 12, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcázar, L.; Alfaro, R.; Tamarit, M.; Gómez-Angulo, J.C.; Ortega, J.M.; Aragonés, P.; Jerez, P.; Salazar, F.; Del Pozo, J.M. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Insertion. Case Report and Literature Review. Neurocirugía 2007, 18, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaki, K.; Uchiyama, N.; Hayashi, Y.; Hamada, J. Intracerebral Hemorrhage Secondary to Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Insertion -Four Case Reports—Four Case Reports. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2010, 50, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musali, S.R.; Manne, S.; Beniwal, H.K.; Butkuri, N.; Gollapudi, P.R.; Nandigama, P.K. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage after Placement of a Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in a Case of Hydrocephalus: A Rare Case Report and Review of Literature. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2019, 10, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.K.; Cha, S.H.; Choi, B.K.; Lee, J.I.; Yun, E.Y.; Choi, C.H. Hemorrhage Rates Associated with Two Methods of Ventriculostomy: External Ventricular Drainage vs. Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Procedure. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2014, 54, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.; Tummala, R.P. Risk Factors for Hemorrhage Associated with External Ventricular Drain Placement and Removal. JNS 2017, 126, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, H.; Li, F.; Chen, M.; Chen, P. A New Inflammatory Parameter Can Predict Delayed Intracranial Hemorrhage Following Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Mesa-Tejada, R.; Quick, C.M.; Bollen, A.W.; Joshi, S.; Pile-Spellman, J.; Lawton, M.T.; Young, W.L. Evidence of Increased Endothelial Cell Turnover in Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Neurosurgery 2001, 49, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moftakhar, P.; Hauptman, J.S.; Malkasian, D.; Martin, N.A. Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Part 1: Cellular and Molecular Biology. FOC 2009, 26, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Choi, E.-J.; McDougall, C.M.; Su, H. Brain Arteriovenous Malformation Modeling, Pathogenesis, and Novel Therapeutic Targets. Transl. Stroke Res. 2014, 5, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlikowska, L.; Tran, M.N.; Achrol, A.S.; McCulloch, C.E.; Ha, C.; Lind, D.L.; Hashimoto, T.; Zaroff, J.; Lawton, M.T.; Marchuk, D.A.; et al. Polymorphisms in Genes Involved in Inflammatory and Angiogenic Pathways and the Risk of Hemorrhagic Presentation of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Stroke 2004, 35, 2294–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Sugita, Y.; Nakashima, S.; Okada, Y.; Yoshitomi, M.; Kimura, Y.; Miyoshi, H.; Morioka, M.; Ohshima, K. Alternatively Activated Macrophages Play an Important Role in Vascular Remodeling and Hemorrhaging in Patients with Brain Arteriovenous Malformation. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

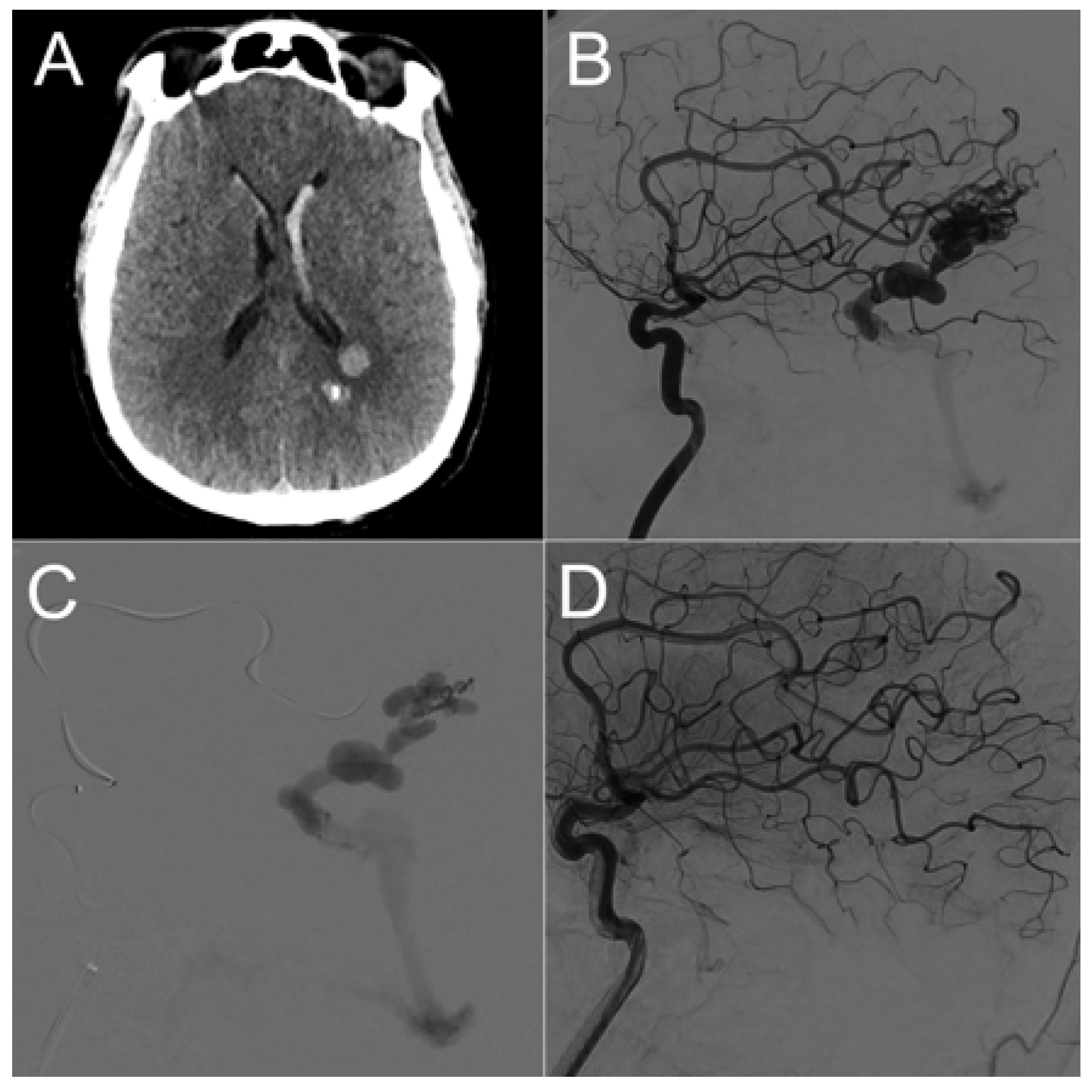
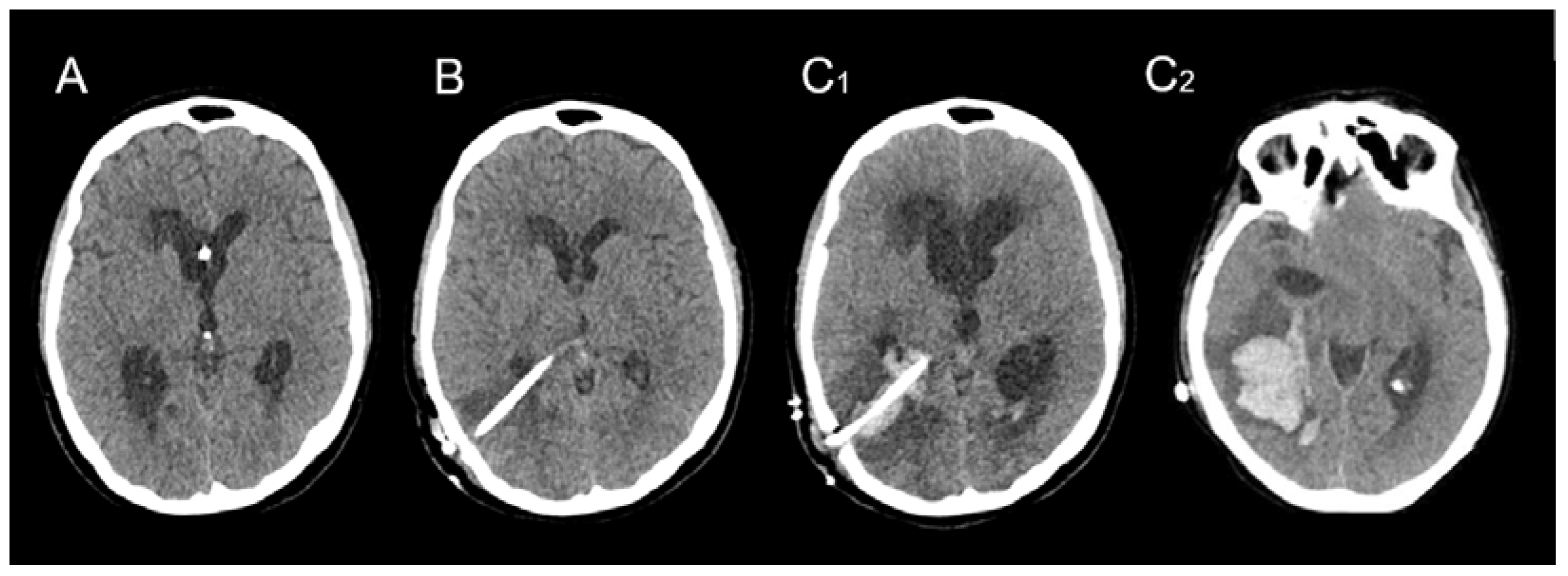

| Sex | Age | AVM Location | Spetzler–Martin Grade | Draining Vein(s) | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 21 | Left parieto-occipital | 3 | Lateral sinus | Embolization |
| M | 40 | Left parietal | 3 | Straight sinus | Embolization |
| F | 37 | Left cerebellar | 3 | Sigmoid sinus | Embolization |
| F | 58 | Right cerebellar | 3 | Vein of Galen, inferior petrous sinus | Embolization |
| F | 29 | Right parietal | 3 | Superior sagittal sinus | Surgery |
| M | 30 | Right parietal | 2 | Superior sagittal sinus | Surgery |
| F | 57 | Right frontal | 3 | Vein of Galen | Embolization |
| M | 61 | Left basifrontal | 3 | Vein of Galen | Embolization |
| F | 48 | Left temporo-parietal | 2 | Superior sagittal sinus | Embolization + Surgery |
| F | 34 | Left temporal | 3 | Superior sagittal sinus, lateral sinus | Embolization + Surgery |
| Series | Number of Patients | Onset Day of Hemorrhage | Age | Gender | Localization of the Ventricular Catheter | Primary Disease Leading to Hydrocephalus | Symptomatic | Management | Glasgow Outcome Scale |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matsumura et al. (1985) [7] | 1 | 7 | 17 | M | AH | TBI | Yes | Surgery | 5 |
| Snow et al. (1986) [25] | 1 | 7 | 43 | F | AH | NPH | Yes | - | - |
| Derdeyn et al. (1988) [26] | 2 | 2 | 56 | M | PH | TBI | Yes | Surgery | 4 |
| 2 | 73 | F | AH | NPH | Yes | Conservative | 4 | ||
| Mascalchi et al. (1991) [27] | 1 | 15 | 68 | M | AH | ICH | Yes | Conservative | 1 |
| Savitz et al. (1999) [13] | 2 | 2 | - | - | PH | - | No | Conservative | - |
| 2 | - | - | PH | - | No | Conservative | - | ||
| Alcazar et al. (2007) [28] | 1 | 6 | 64 | F | PH | SAH | Yes | Surgery | 1 |
| Misaki et al. (2010) [29] | 2 | 5 | 55 | M | PH | SAH | No | Conservative | - |
| 3 | 64 | M | PH | SAH | No | Conservative | - | ||
| Zhou et al. (2012) [11] | 2 | 5 | 32 | F | AH | NPH | Yes | Death before surgery | 1 |
| 3 | 58 | M | AH | TBI | Yes | Conservative | 4 | ||
| Ma et al. (2015) [10] | 1 | 8 | 67 | M | AH | TBI | Yes | Palliative care | - |
| Guo et al. (2017) [9] | 20 | 3 | 58 | F | - | SAH | Yes | Conservative | 4 |
| 3 | 54 | M | - | ICH | Yes | Conservative | 1 | ||
| 3 | 61 | M | - | TBI | Yes | Conservative | 3 | ||
| 4 | 61 | M | - | Tumoral | Yes | Conservative | 1 | ||
| 4 | 75 | M | - | ICH | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 5 | 84 | F | - | TBI | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 6 | 48 | F | - | SAH | Yes | Surgery | 1 | ||
| 6 | 61 | M | - | NPH | Yes | Surgery | 1 | ||
| 6 | 62 | M | - | TBI | Yes | Surgery | 2 | ||
| 6 | 78 | M | - | NPH | No | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 7 | 64 | F | - | SAH | Yes | Conservative | 4 | ||
| 7 | 65 | F | - | Tumoral | No | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 7 | 76 | F | - | ICH | Yes | Surgery | 2 | ||
| 8 | 66 | M | - | TBI | No | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 8 | 69 | M | - | NPH | No | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 9 | 57 | F | - | SAH | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 9 | 69 | M | - | NPH | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 9 | 72 | M | - | NPH | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 10 | 33 | M | - | ICH | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 10 | 30 | M | - | ICH | Yes | Conservative | 4 | ||
| Gong et al. (2017) [8] | 12 | 3 | 62 | M | AH | ICH | Yes | Death before surgery | 1 |
| 3 | 64 | F | PH | TBI | - | Conservative | 3 | ||
| 7 | 76 | M | AH | SAH | - | Conservative | 3 | ||
| 3 | 50 | M | AH | SAH | Yes | Surgery | 2 | ||
| 4 | 61 | F | AH | TBI | - | Conservative | 4 | ||
| 5 | 67 | M | AH | Infectious | - | Conservative | 3 | ||
| 7 | 65 | M | AH | NPH | No | Conservative | 4 | ||
| 4 | 61 | M | AH | NPH | - | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 3 | 60 | M | AH | TBI | - | Conservative | 4 | ||
| 4 | 53 | F | PH | SAH | - | Surgery | 2 | ||
| 5 | 68 | F | AH | NPH | - | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 5 | 61 | M | AH | SAH | - | Surgery | 3 | ||
| Hou et al. (2017) [12] | 4 | 9 | 56 | F | AH | Tumoral | Yes | Surgery | 1 |
| 2 | 48 | M | AH | TBI | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 3 | 65 | M | PH | NPH | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 4 | 51 | F | AH | TBI | Yes | Conservative | 1 | ||
| Musali et al. (2019) [30] | 1 | 7 | 56 | F | PH | Infectious | Yes | Conservative | 1 |
| Wang et al. [14] (2021) | 2 | 9 | 49 | F | PH | SAH | Yes | Conservative | 5 |
| 6 | 76 | F | PH | TBI | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| Present study | 10 | 2 | 21 | M | PH | AVM | Yes | Conservative | 4 |
| 2 | 44 | M | PH | AVM | Yes | Conservative | 1 | ||
| 3 | 37 | F | PH | AVM | No | Surgery | 4 | ||
| 4 | 58 | F | PH | AVM | Yes | Surgery | 3 | ||
| 5 | 29 | F | PH | AVM | Yes | Conservative | 3 | ||
| 5 | 30 | M | PH | AVM | Yes | Conservative | 1 | ||
| 5 | 57 | F | PH | AVM | No | Surgery | 3 | ||
| 6 | 61 | M | PH | AVM | No | Conservative | 1 | ||
| 6 | 48 | F | PH | AVM | Yes | Conservative | 1 | ||
| 6 | 34 | F | PH | AVM | Yes | Conservative | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dannhoff, G.; Chibbaro, S.; Mallereau, C.-H.; Ganau, M.; Agbo-Ponzo, M.; Santin, M.d.N.; Ollivier, I.; Pop, R.; Proust, F.; Todeschi, J. Delayed Intracerebral Hematoma after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in the Context of Ruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformation: A Literature Review. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13081159
Dannhoff G, Chibbaro S, Mallereau C-H, Ganau M, Agbo-Ponzo M, Santin MdN, Ollivier I, Pop R, Proust F, Todeschi J. Delayed Intracerebral Hematoma after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in the Context of Ruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformation: A Literature Review. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(8):1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13081159
Chicago/Turabian StyleDannhoff, Guillaume, Salvatore Chibbaro, Charles-Henry Mallereau, Mario Ganau, Martial Agbo-Ponzo, Marie des Neiges Santin, Irène Ollivier, Raoul Pop, François Proust, and Julien Todeschi. 2023. "Delayed Intracerebral Hematoma after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in the Context of Ruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformation: A Literature Review" Brain Sciences 13, no. 8: 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13081159
APA StyleDannhoff, G., Chibbaro, S., Mallereau, C.-H., Ganau, M., Agbo-Ponzo, M., Santin, M. d. N., Ollivier, I., Pop, R., Proust, F., & Todeschi, J. (2023). Delayed Intracerebral Hematoma after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in the Context of Ruptured Brain Arteriovenous Malformation: A Literature Review. Brain Sciences, 13(8), 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13081159







