Inhibition of Microglial Activation by Amitriptyline and Doxepin in Interferon-β Pre-Treated Astrocyte–Microglia Co-Culture Model of Inflammation †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Treatment of Cultures
2.3. MTT (3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide) Assay
2.4. Immunocytochemistry
2.5. Nitric Oxide (NO) Assay
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Data Analyses and Statistics
3. Results
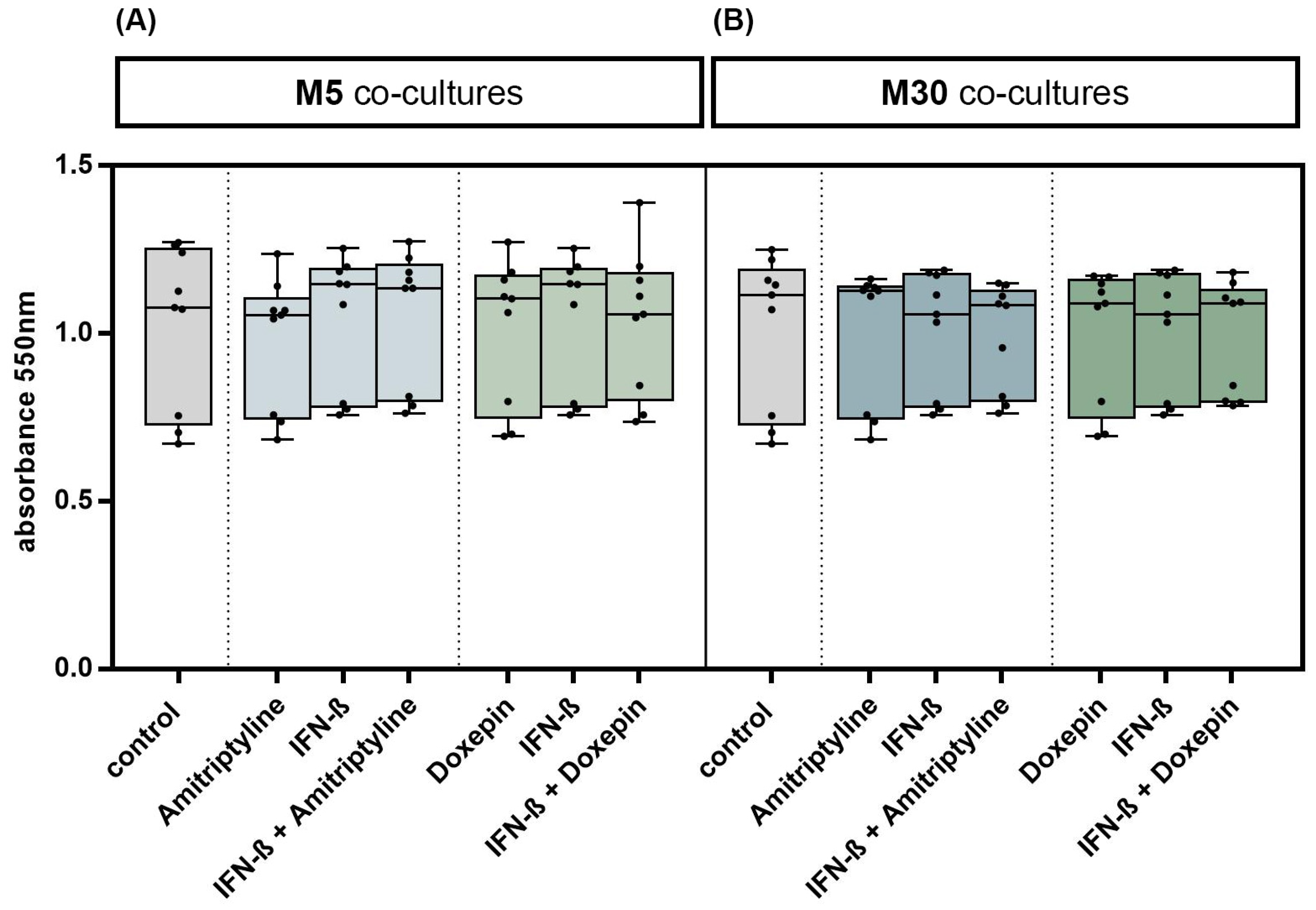
3.1. Effects of Doxepin, Amitriptyline and IFN-β on Glial Cell Viability
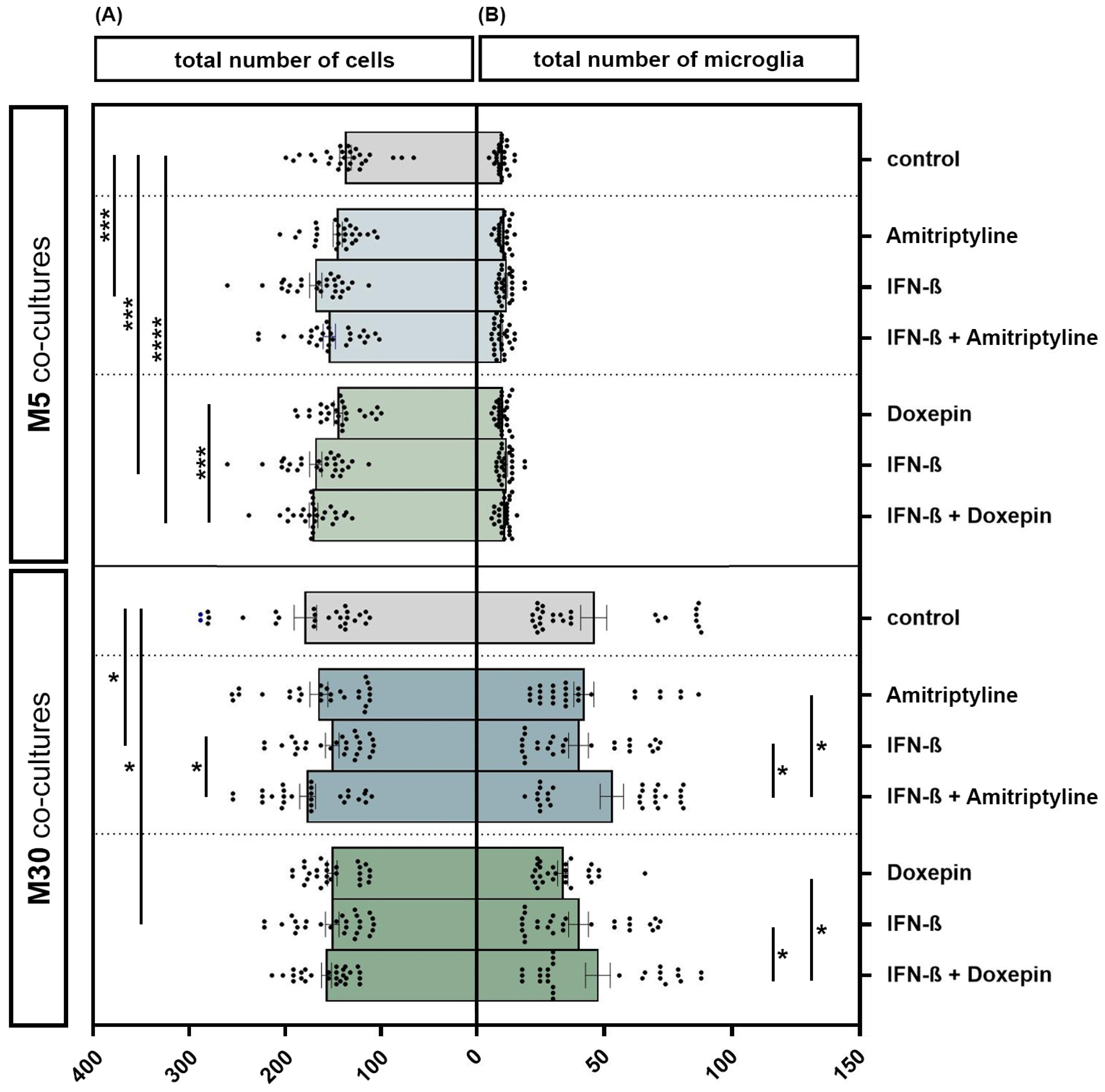
3.2. Influence of Doxepin, Amitriptyline and IFN-β on Cell Numbers in Different Set-Ups of Astrocyte–Microglia Co-Culture Model of Inflammation
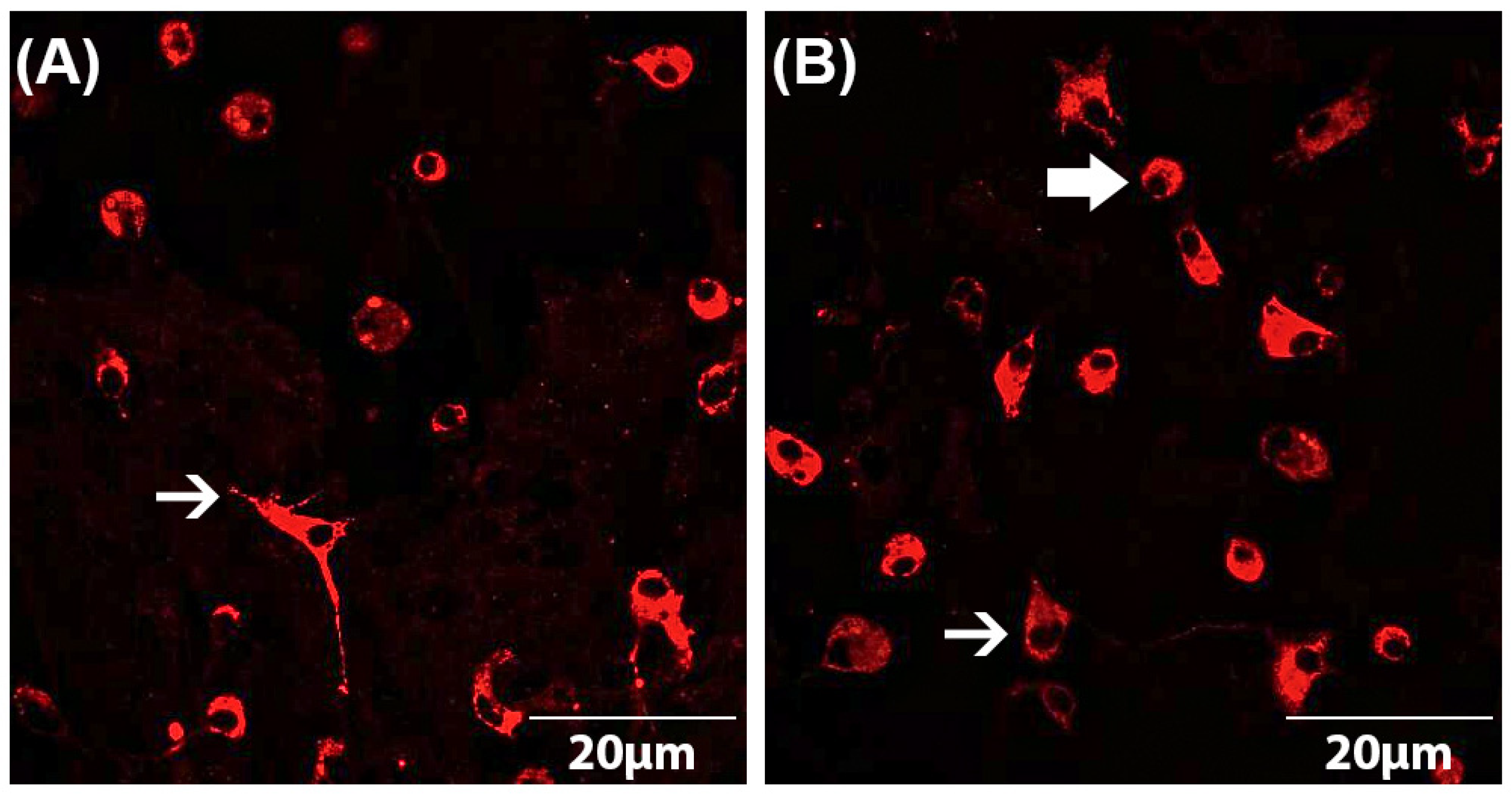
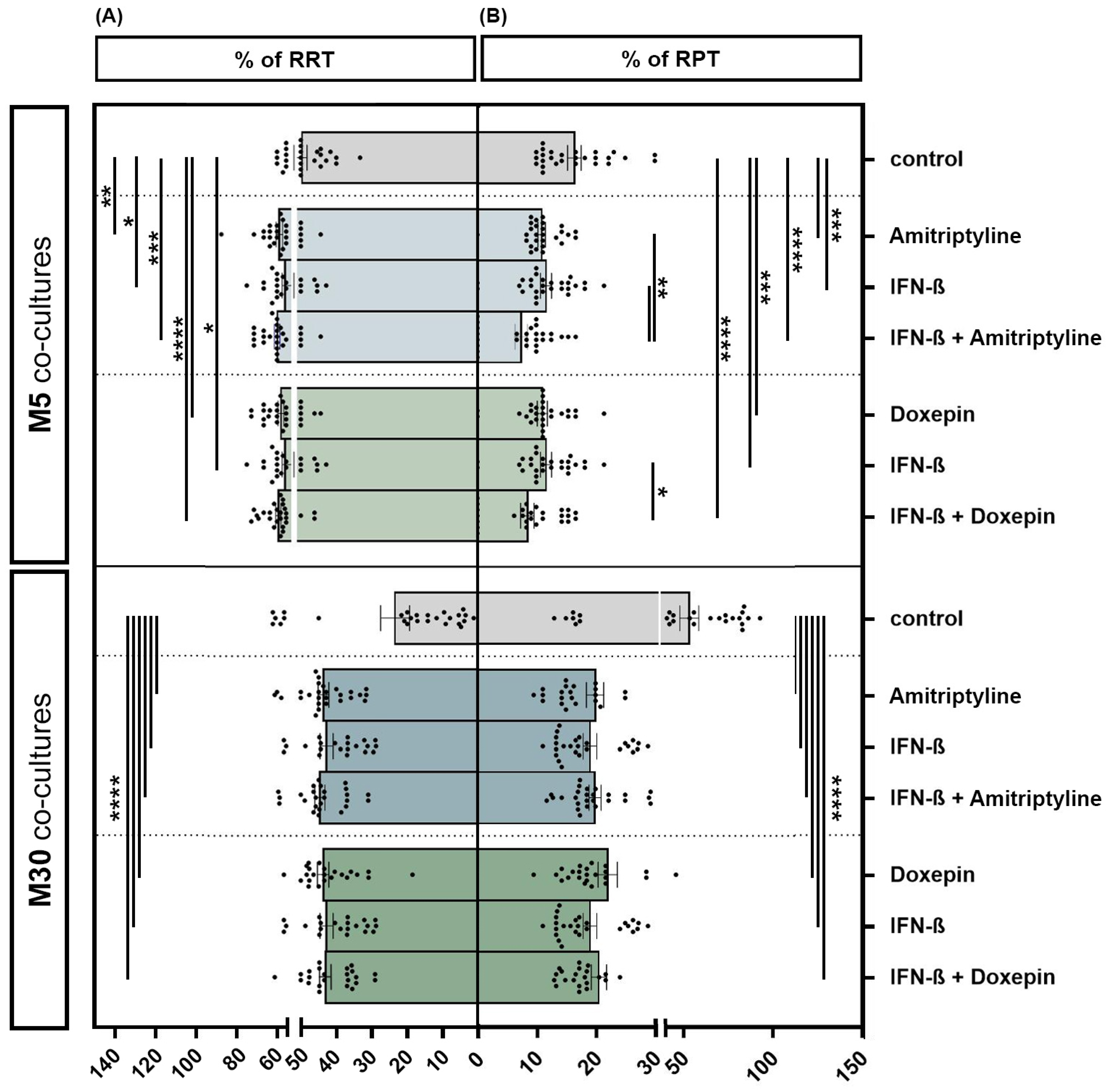
3.3. Effects of Doxepin, Amitriptyline and IFN-β on Microglial Activation under Physiological and Pathological Conditions
3.4. Effects of Doxepin, Amitriptyline and IFN-β on Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 in M5 and M30 Astrocyte–Microglia Co-Cultures
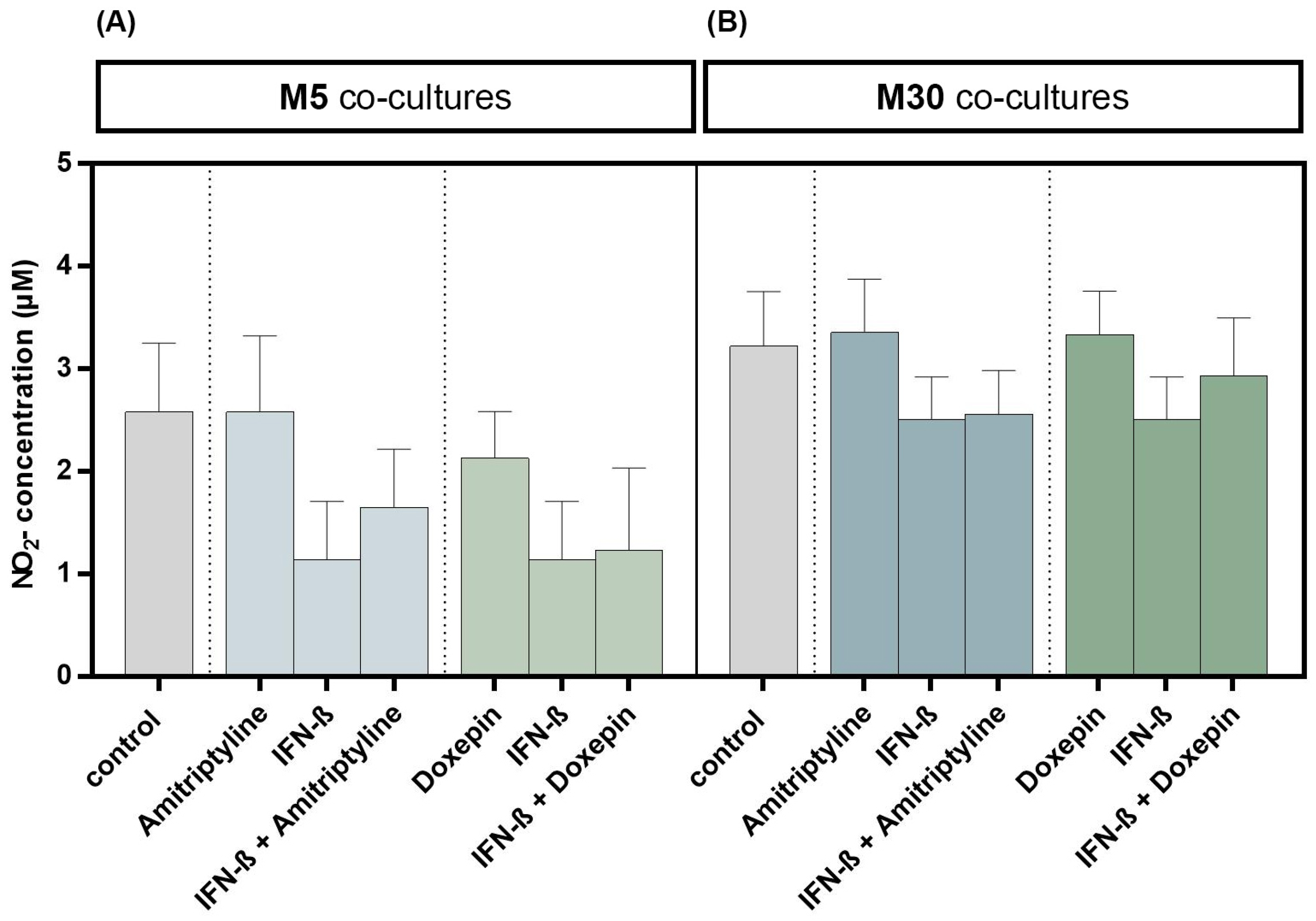
3.5. Effects of Doxepin, Amitriptyline and IFN-β on NO Concentration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sospedra, M.; Martin, R. Immunology of Multiple Sclerosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 683–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, M.; Bar-Or, A.; Piehl, F.; Preziosa, P.; Solari, A.; Vukusic, S.; Rocca, M.A. Multiple Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kleijn, K.M.A.; Martens, G.J.M. Molecular Effects of FDA-Approved Multiple Sclerosis Drugs on Glial Cells and Neurons of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrzavy, T.; Hametner, S.; Wimmer, I.; Butovsky, O.; Weiner, H.L.; Lassmann, H. Loss of “homeostatic” Microglia and Patterns of Their Activation in Active Multiple Sclerosis. Brain 2017, 140, 1900–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustmann, P.M.; Haase, C.G.; Romberg, S.; Hinkerohe, D.; Szlachta, D.; Smikalla, D.; Krause, D.; Dermietzel, R. Microglia Activation Influences Dye Coupling and Cx43 Expression of the Astrocytic Network. Glia 2003, 42, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapp, B.D.; Nave, K.A. Multiple Sclerosis: An Immune or Neurodegenerative Disorder? Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 31, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallaur, A.P.; Oliveira, S.R.; Simao, A.N.C.; De Almeida, E.R.D.; Morimoto, H.K.; Lopes, J.; De Carvalho Jennings Pereira, W.L.; Andrade, R.M.; Pelegrino, L.M.; Borelli, S.D.; et al. Cytokine Profile in Relapsing-remitting Multiple Sclerosis Patients and the Association between Progression and Activity of the Disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooi, E.J.; Strijbis, E.M.M.; Van Der Valk, P.; Geurts, J.J.G. Heterogeneity of Cortical Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis: Clinical and Pathologic Implications. Neurology 2012, 79, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perriot, S.; Mathias, A.; Perriard, G.; Canales, M.; Jonkmans, N.; Merienne, N.; Meunier, C.; El Kassar, L.; Perrier, A.L.; Laplaud, D.A.; et al. Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Astrocytes Are Differentially Activated by Multiple Sclerosis-Associated Cytokines. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 11, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, M.A.; Quintana, F.J. Regulation of Astrocyte Functions in Multiple Sclerosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a029009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, W.M.; Chevillotte, M.D.; Rice, C.M. Interferon-Stimulated Genes: A Complex Web of Host Defenses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakimovski, D.; Kolb, C.; Ramanathan, M.; Zivadinov, R.; Weinstock-Guttman, B. Interferon β for Multiple Sclerosis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a032003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieseier, B.C. The Mechanism of Action of Interferon-β in Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis. CNS Drugs 2011, 25, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of Type I Interferon Responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheu, S.; Ali, S.; Mann-Nüttel, R.; Richter, L.; Arolt, V.; Dannlowski, U.; Kuhlmann, T.; Klotz, L.; Alferink, J. Interferon β-Mediated Protective Functions of Microglia in Central Nervous System Autoimmunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.; O’Donoghue, S.; Counihan, T.; McDonald, C.; Calabresi, P.A.; Ahmed, M.A.S.; Kaplin, A.; Hallahan, B. Neuropsychiatric Syndromes of Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinstein, A. Multiple Sclerosis and Depression. Mult. Scler. 2011, 17, 1276–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinstein, A.; Magalhaes, S.; Richard, J.F.; Audet, B.; Moore, C. The Link between Multiple Sclerosis and Depression. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, P.; Piehl, F. Fatigue and Depression in Multiple Sclerosis: Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Interventions. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2016, 134 (Suppl. 200), 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba Palé, L.; León Caballero, J.; Samsó Buxareu, B.; Salgado Serrano, P.; Pérez Solà, V. Systematic Review of Depression in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis and Its Relationship to Interferonβ Treatment. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2017, 17, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franscina Pinto, E.; Andrade, C. Interferon-Related Depression: A Primer on Mechanisms, Treatment, and Prevention of a Common Clinical Problem. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaro, C.; Gamberini, G.; Masuccio, F.G. Depression in Multiple Sclerosis: Epidemiology, Aetiology, Diagnosis and Treatment. CNS Drugs 2018, 32, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowlati, Y.; Herrmann, N.; Swardfager, W.; Liu, H.; Sham, L.; Reim, E.K.; Lanctôt, K.L. A Meta-Analysis of Cytokines in Major Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rial, D.; Lemos, C.; Pinheiro, H.; Duarte, J.M.; Gonçalves, F.Q.; Real, J.I.; Prediger, R.D.; Gonçalves, N.; Gomes, C.A.; Canas, P.M.; et al. Depression as a Glial-Based Synaptic Dysfunction. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brites, D.; Fernandes, A. Neuroinflammation and Depression: Microglia Activation, Extracellular Microvesicles and MicroRNA Dysregulation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherder, R.; Kant, N.; Wolf, E.T.; Pijnenburg, B.; Scherder, E.J.A. Psychiatric and Physical Comorbidities and Pain in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. J. Pain Res. 2018, 11, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiest, K.M.; Walker, J.R.; Bernstein, C.N.; Graff, L.A.; Zarychanski, R.; Abou-Setta, A.M.; Patten, S.B.; Sareen, J.; Bolton, J.M.; Marriott, J.J.; et al. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Interventions for Depression and Anxiety in Persons with Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2016, 5, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, E.W.; Daniels, R.N. Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Amitriptyline. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.A.; Derry, S.; Aldington, D.; Cole, P.; Wiffen, P.J. Amitriptyline for Neuropathic Pain in Adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD008242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, W.F.; Chung, K.F.; Yung, K.P.; Ng, T.H.Y. Doxepin for Insomnia: A Systematic Review of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials. Sleep Med. Rev. 2015, 19, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.; Siddiqui, M.A.A.; Wagstaff, A.J.; McCormack, P.L. Low-Dose Doxepin: In the Treatment of Insomnia. CNS Drugs 2010, 24, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz, L.; Richardson, J.S.; Mukerji, S. Doxepin, a Tricyclic Antidepressant, Binds to Normal, Intact Astroglial Cells in Cultures and Inhibits the Isoproterenol-Induced Increase in Cyclic AMP Production. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1980, 58, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zychowska, M.; Rojewska, E.; Makuch, W.; Przewlocka, B.; Mika, J. The Influence of Microglia Activation on the Efficacy of Amitriptyline, Doxepin, Milnacipran, Venlafaxine and Fluoxetine in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 749, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mika, J.; Jurga, A.M.; Starnowska, J.; Wasylewski, M.; Rojewska, E.; Makuch, W.; Kwiatkowski, K.; Malek, N.; Przewlocka, B. Effects of Chronic Doxepin and Amitriptyline Administration in Naïve Mice and in Neuropathic Pain Mice Model. Neuroscience 2015, 294, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obuchowicz, E.; Kowalski, J.; Labuzek, K.; Krysiak, R.; Pendzich, J.; Herman, Z.S. Amitriptyline and Nortriptyline Inhibit Interleukin-1 Release by Rat Mixed Glial and Microglial Cell Cultures. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2006, 9, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera, E.; Ubhi, K.; Mante, M.; Rockenstein, E.; Masliah, E. Antidepressants Reduce Neuroinflammatory Responses and Astroglial Alpha-Synuclein Accumulation in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Multiple System Atrophy. Glia 2014, 62, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa Tomaz, V.; Chaves Filho, A.J.M.; Cordeiro, R.C.; Jucá, P.M.; Soares, M.V.R.; Barroso, P.N.; Cristino, L.M.F.; Jiang, W.; Teixeira, A.L.; de Lucena, D.F.; et al. Antidepressants of Different Classes Cause Distinct Behavioral and Brain Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Changes in Mice Submitted to an Inflammatory Model of Depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 268, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambach, H.; Hinkerohe, D.; Prochnow, N.; Stienen, M.N.; Moinfar, Z.; Haase, C.G.; Hufnagel, A.; Faustmann, P.M. Glia and Epilepsy: Experimental Investigation of Antiepileptic Drugs in an Astroglia/Microglia Co-Culture Model of Inflammation. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvace, F.; Faustmann, T.J.; Faustmann, P.M.; Ismail, F.S. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Lacosamide in an Astrocyte-Microglia Co-Culture Model of Inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 915, 174696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustmann, T.J.; Corvace, F.; Faustmann, P.M.; Ismail, F.S. Effects of Lamotrigine and Topiramate on Glial Properties in an Astrocyte-Microglia Co-Culture Model of Inflammation. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022, 25, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, F.S.; Corvace, F.; Faustmann, P.M.; Faustmann, T.J. Pharmacological Investigations in Glia Culture Model of Inflammation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 805755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinkerohe, D.; Smikalla, D.; Haghikia, A.; Heupel, K.; Haase, C.G.; Dermietzel, R.; Faustmann, P.M. Effects of Cytokines on Microglial Phenotypes and Astroglial Coupling in an Inflammatory Coculture Model. Glia 2005, 52, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmar, P.; Haghikia, A.; Dermietzel, R.; Faustmann, P.M. Venlafaxine Exhibits an Anti-Inflammatory Effect in an Inflammatory Co-Culture Model. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008, 11, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghikia, A.; Ladage, K.; Hinkerohe, D.; Vollmar, P.; Heupel, K.; Dermietzel, R.; Faustmann, P.M. Implications of Antiinflammatory Properties of the Anticonvulsant Drug Levetiracetam in Astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinkerohe, D.; Wolfkühler, D.; Haghikia, A.; Meier, C.; Faustmann, P.M.; Schlegel, U. Dexamethasone Differentially Regulates Functional Membrane Properties in Glioma Cell Lines and Primary Astrocytes In Vitro. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 103, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stienen, M.N.; Haghikia, A.; Dambach, H.; Thöne, J.; Wiemann, M.; Gold, R.; Chan, A.; Dermietzel, R.; Faustmann, P.M.; Hinkerohe, D.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Anticonvulsant Drug Levetiracetam on Electrophysiological Properties of Astroglia Are Mediated via TGFβ1 Regulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corvace, F.; Faustmann, T.J.; Heckers, S.; Faustmann, P.M.; Ismail, F.S. Experimental Investigations of Monomethyl and Dimethyl Fumarate in an Astrocyte-Microglia Co-Culture Model of Inflammation. Pharmacology 2023, 108, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuschle, M.; Härtter, S.; Hiemke, C.; Standhardt, H.; Heuser, I. Doxepin and Its Metabolites in Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid in Depressed Patients. Psychopharmacology 1997, 131, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanin, I.; Koslow, S.H.; Kocsis, J.H.; Bowden, C.L.; Brunswick, D.; Frazer, A.; Carl, J.; Robins, E. Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels of Amitriptyline, Nortriptyline, Imipramine and Desmethylimipramine. Relationship to Plasma Levels and Treatment Outcome. J. Affect. Disord. 1985, 9, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomburg, R.; Remane, D.; Fassbender, K.; Maurer, H.H.; Spiegel, J. Doxepin Concentrations in Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid. J. Neural Transm. 2011, 118, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruga, I.; Hartwig, S.; Thöne, J.; Hovemann, B.; Gold, R.; Juckel, G.; Linker, R.A. Inflammation Modulates Anxiety in an Animal Model of Multiple Sclerosis. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 220, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheuermann, K.; Orellano, L.A.A.; Viana, C.T.R.; Machado, C.T.; Lazari, M.G.T.; Capettini, L.S.A.; Andrade, S.P.; Campos, P.P. Amitriptyline Downregulates Chronic Inflammatory Response to Biomaterial in Mice. Inflammation 2021, 44, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, F.; Zhu, J.; Duan, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yao, K.; Bo, J.; Zu, H. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Doxepin Hydrochloride against LPS-Induced C6-Glioma Cell Inflammatory Reaction by PI3K-Mediated Akt Signaling. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azadbakht, A.A.; Radahmadi, M.; Javanmard, S.H.; Reisi, P. The Effects of Doxepin on Stress-Induced Learning, Memory Impairments, and TNF-α Level in the Rat Hippocampus. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 460. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, M.; Shinohara, M.L. The Role of Interferon-β in the Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis and Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis-in the Perspective of Inflammasomes. Immunology 2013, 139, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teige, I.; Treschow, A.; Teige, A.; Mattsson, R.; Navikas, V.; Leanderson, T.; Holmdahl, R.; Issazadeh-Navikas, S. IFN-Beta Gene Deletion Leads to Augmented and Chronic Demyelinating Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 4776–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragoso, Y.D.; Frota, E.R.C.; Lopes, J.S.; Noal, J.S.; Giacomo, M.C.; Gomes, S.; Gonçalves, M.V.M.; Da Gama, P.D.; Finkelsztejn, A. Severe Depression, Suicide Attempts, and Ideation during the Use of Interferon Beta by Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 33, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.O.; Si, Q.; Zhou, J.N.; Pestell, R.G.; Brosnan, C.F.; Locker, J.; Lee, S.C. Interferon-Beta Activates Multiple Signaling Cascades in Primary Human Microglia. J. Neurochem. 2002, 81, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.; Seguin, R.; Magnus, T.; Papadimitriou, C.; Toyka, K.V.; Antel, J.P.; Gold, R. Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Inflammatory Cells by Microglia and Its Therapeutic Implications: Termination of CNS Autoimmune Inflammation and Modulation by Interferon-Beta. Glia 2003, 43, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo-Silva, D.; Carriche, G.M.; Castro, A.G.; Roque, S.; Saraiva, M. Interferon-β Regulates the Production of IL-10 by Toll-like Receptor-Activated Microglia. Glia 2017, 65, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanokuchi, J.; Mizuno, T.; Kato, H.; Mitsuma, N.; Suzumura, A. Effects of Interferon-β on Microglial Functions as Inflammatory and Antigen Presenting Cells in the Central Nervous System. Neuropharmacology 2004, 46, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, N.; Everson, J.; Pariante, C.M.; Borsini, A. Modulation of Microglial Activation by Antidepressants. J. Psychopharmacol. 2022, 36, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashioka, S. Antidepressants and Neuroinflammation: Can Antidepressants Calm Glial Rage Down? Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Salam, O.M.E.; Youssef Morsy, S.M.; Sleem, A.A. The Effect of Different Antidepressant Drugs on Oxidative Stress after Lipopolysaccharide Administration in Mice. EXCLI J. 2011, 10, 290. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, F.T.S.; de Souza, M.R.M.; de Carvalho Lima, C.N.; da Silva, F.E.R.; da Silva Costa, D.V.; dos Santos, C.C.; Miyajima, F.; de Sousa, F.C.F.; Vasconcelos, S.M.M.; Barichello, T.; et al. Major Depression Model Induced by Repeated and Intermittent Lipopolysaccharide Administration: Long-Lasting Behavioral, Neuroimmune and Neuroprogressive Alterations. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 107, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrill, J.E.; Ignarro, L.J.; Sherman, M.P.; Melinek, J.; Lane, T.E. Microglial Cell Cytotoxicity of Oligodendrocytes Is Mediated through Nitric Oxide. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 2132–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, E.; Yagi, G.; Nakaki, T.; Kanba, S.; Asai, M. Elevated Plasma Nitrate Levels in Depressive States. J. Affect. Disord. 2001, 63, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vismari, L.; Alves, G.J.; Muscará, M.N.; Palermo-Neto, J. A Possible Role to Nitric Oxide in the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Amitriptyline. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2012, 34, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisaoka-Nakashima, K.; Miyano, K.; Matsumoto, C.; Kajitani, N.; Abe, H.; Okada-Tsuchioka, M.; Yokoyama, A.; Uezono, Y.; Morioka, N.; Nakata, Y.; et al. Tricyclic Antidepressant Amitriptyline-Induced Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Production Involves Pertussis Toxin-Sensitive Gαi/o Activation in Astroglial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 13678–13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barca, O.; Devesa-Peleteiro, P.; Seoane, M.; Señarís, R.M.; Arce, V.M. Bimodal Effect of Interferon-β on Astrocyte Proliferation and Survival: Importance of Nuclear Factor-ΚB. J. Neuroimmunol. 2010, 226, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, J.I.; Berens, M.E.; Shapiro, J.R.; Treasurywala, S.; Floyd-Smith, G. Interferon-Beta Inhibits Proliferation and Progression through S Phase of the Cell Cycle in Five Glioma Cell Lines. J. Neurooncol. 1996, 30, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, G.; Happe, S.; Evers, S.; Hermann, W.; Jansen, S.; Kallweit, U.; Muntean, M.-L.; Pöhlau, D.; Riemann, D.; Saletu, M.; et al. Insomnia in Neurological Diseases. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2021, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faustmann, T.J.; Wawrzyniak, M.; Faustmann, P.M.; Corvace, F.; Ismail, F.S. Inhibition of Microglial Activation by Amitriptyline and Doxepin in Interferon-β Pre-Treated Astrocyte–Microglia Co-Culture Model of Inflammation. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030493
Faustmann TJ, Wawrzyniak M, Faustmann PM, Corvace F, Ismail FS. Inhibition of Microglial Activation by Amitriptyline and Doxepin in Interferon-β Pre-Treated Astrocyte–Microglia Co-Culture Model of Inflammation. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(3):493. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030493
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaustmann, Timo Jendrik, Marisa Wawrzyniak, Pedro M. Faustmann, Franco Corvace, and Fatme Seval Ismail. 2023. "Inhibition of Microglial Activation by Amitriptyline and Doxepin in Interferon-β Pre-Treated Astrocyte–Microglia Co-Culture Model of Inflammation" Brain Sciences 13, no. 3: 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030493
APA StyleFaustmann, T. J., Wawrzyniak, M., Faustmann, P. M., Corvace, F., & Ismail, F. S. (2023). Inhibition of Microglial Activation by Amitriptyline and Doxepin in Interferon-β Pre-Treated Astrocyte–Microglia Co-Culture Model of Inflammation. Brain Sciences, 13(3), 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030493





