Diffusion Measures of Subcortical Structures Using High-Field MRI
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. MRI Acquisition
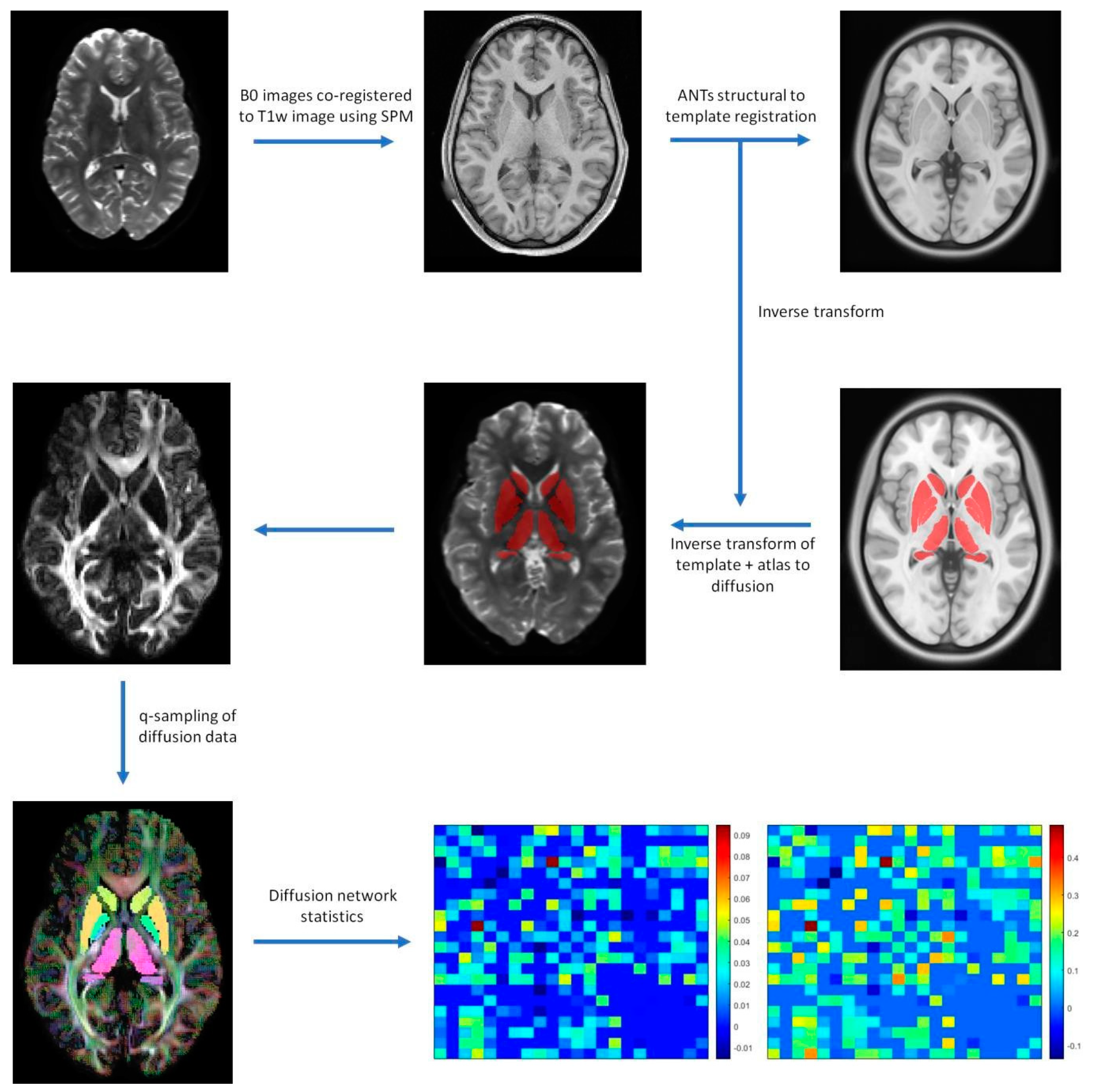
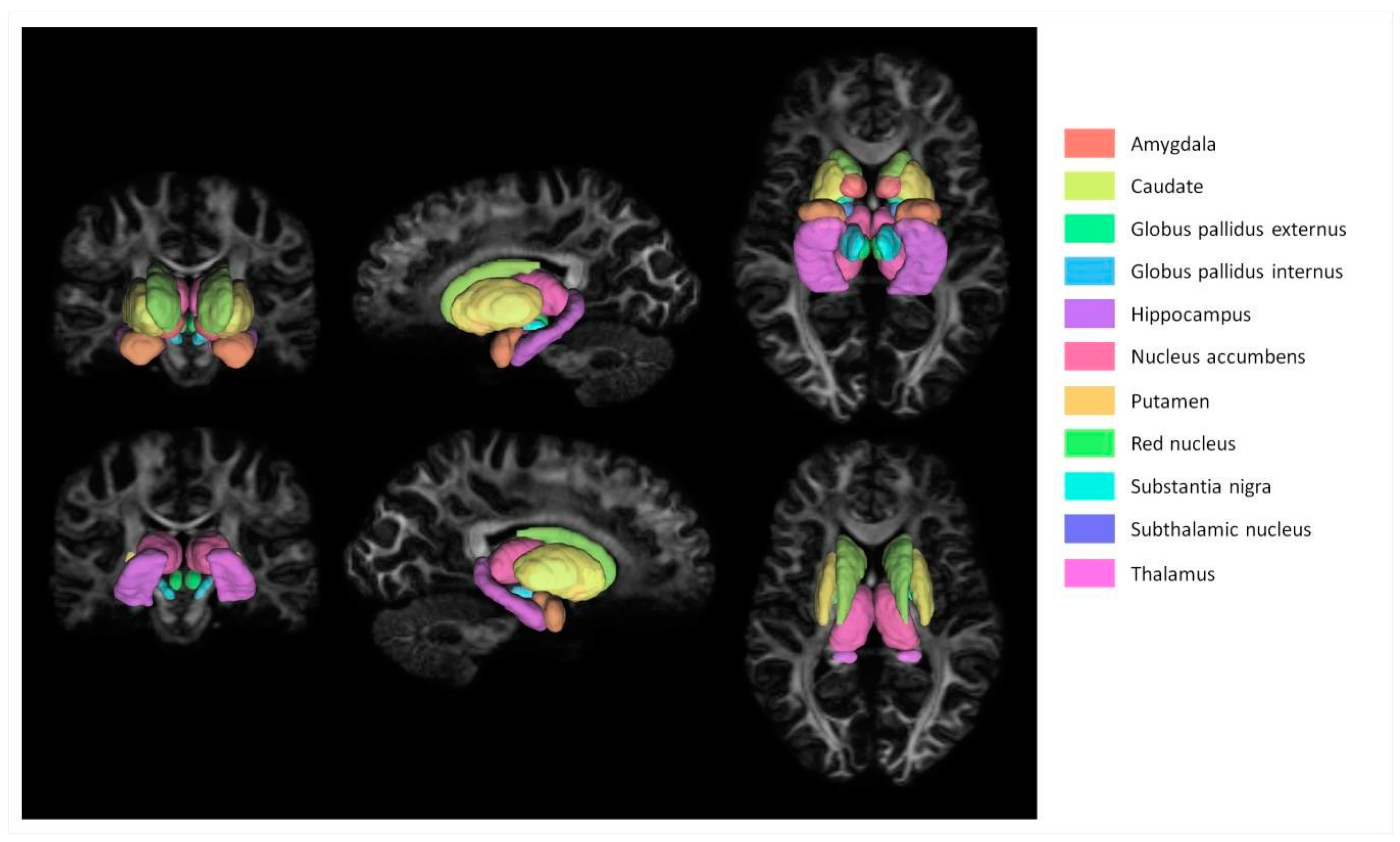
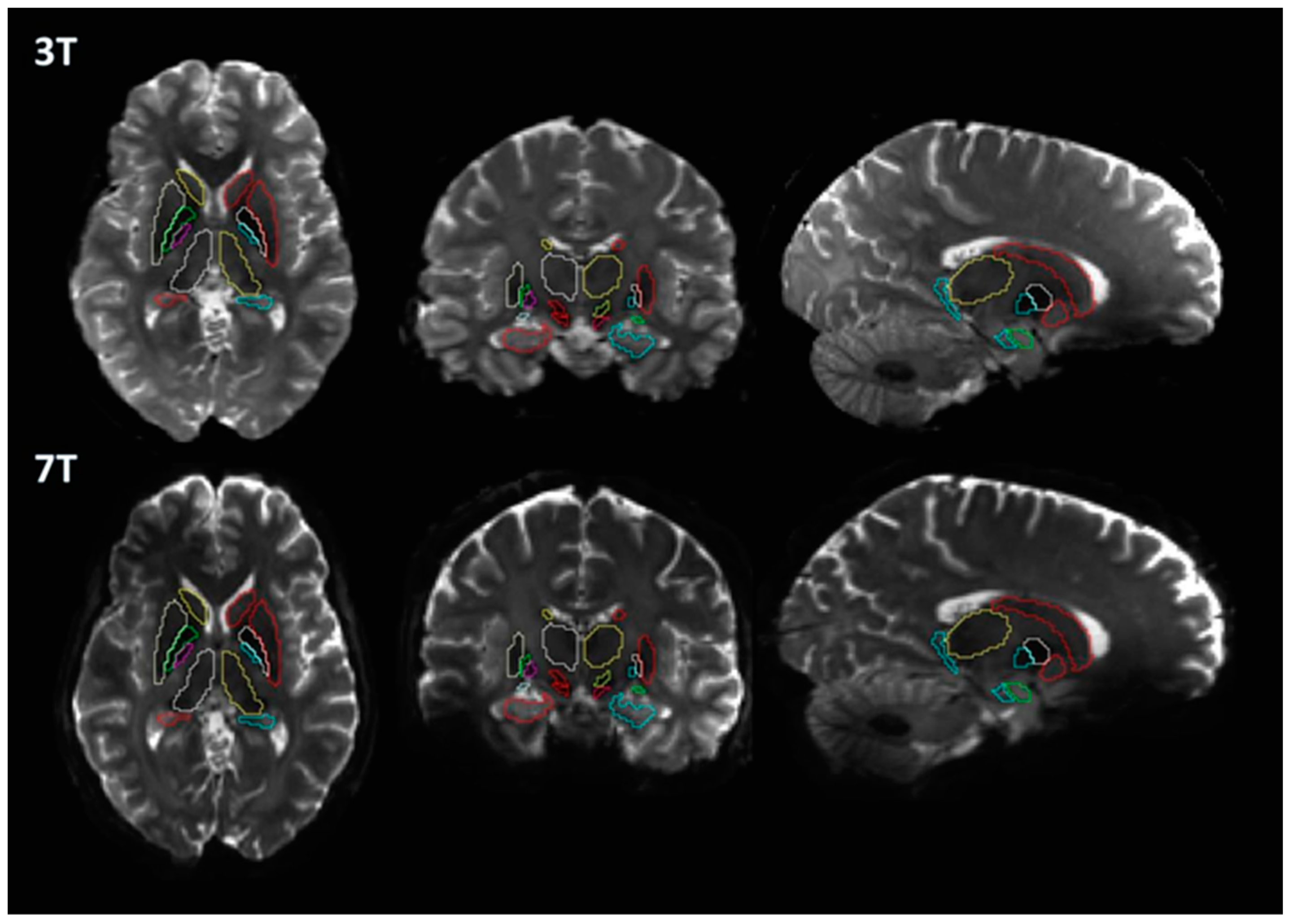
2.3. Image Processing
2.4. Diffusion Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Surmeier, D.J.; Obeso, J.A.; Halliday, G.M. Selective neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 7013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, M.; Murata, J.I.; Uesugi, H.; Kikuchi, S.; Saito, H.; Tashiro, K.; Sawamura, Y. Two-year follow-up of chronic stimulation of the posterior subthalamic white matter for tremor-dominant Parkinson’s disease. Neurosurgery 2005, 56, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temel, Y.; Kessels, A.; Tan, S.; Topdag, A.; Boon, P.; Visser-Vandewalle, V. Behavioural changes after bilateral subthalamic stimulation in advanced Parkinson disease: A systematic review. Park. Relat. Disord. 2006, 12, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.K.; Knösche, T.R.; Turner, R. White matter integrity, fiber count, and other fallacies: The do’s and don’ts of diffusion MRI. NeuroImage 2013, 73, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barisano, G.; Sepehrband, F.; Ma, S.; Jann, K.; Cabeen, R.; Wang, D.J.; Toga, A.W.; Law, M. Clinical 7 T MRI: Are we there yet? A review about magnetic resonance imaging at ultra-high field. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20180492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Hernández-Fernández, M.; Vu, A.T.; Andersson, J.L.; Moeller, S.; Yacoub, E.; Lenglet, C.; Ugurbil, K.; Behrens, T.E.; Jbabdi, S. Fusion in diffusion MRI for improved fibre orientation estimation: An application to the 3T and 7T data of the Human Connectome Project. NeuroImage 2016, 134, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Essen, D.C.; Smith, S.M.; Barch, D.M.; Behrens, T.E.; Yacoub, E.; Ugurbil, K.; Wu-Minn HCP Consortium. The WU-Minn human connectome project: An overview. NeuroImage 2013, 80, 62–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, A.; Kühn, A.A. Lead-DBS: A toolbox for deep brain stimulation electrode localizations and visualizations. NeuroImage 2015, 107, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, F.C.; Wedeen, V.J.; Tseng, W.Y. Generalized q-sampling imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar]
- Nowacki, A.; Nguyen, T.K.; Tinkhauser, G.; Petermann, K.; Debove, I.; Wiest, R.; Pollo, C. Accuracy of different three-dimensional subcortical human brain atlases for DBS–lead localisation. NeuroImage 2018, 20, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewert, S.; Horn, A.; Finkel, F.; Li, N.; Kühn, A.A.; Herrington, T.M. Optimization and comparative evaluation of nonlinear deformation algorithms for atlas-based segmentation of DBS target nuclei. NeuroImage 2019, 184, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uğurbil, K.; Xu, J.; Auerbach, E.J.; Moeller, S.; Vu, A.T.; Duarte-Carvajalino, J.M.; Lenglet, C.; Wu, X.; Schmitter, S.; Van de Moortele, P.F.; et al. Pushing spatial and temporal resolution for functional and diffusion MRI in the Human Connectome Project. NeuroImage 2013, 80, 80–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, M.F.; Sotiropoulos, S.N.; Wilson, J.A.; Coalson, T.S.; Fischl, B.; Andersson, J.L.; Xu, J.; Jbabdi, S.; Webster, M.; Polimeni, J.R.; et al. The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the Human Connectome Project. NeuroImage 2013, 80, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tournier, J.D.; Smith, R.; Raffelt, D.; Tabbara, R.; Dhollander, T.; Pietsch, M.; Christiaens, D.; Jeurissen, B.; Yeh, C.H.; Connelly, A. MRtrix3: A fast, flexible and open software framework for medical image processing and visualisation. NeuroImage 2019, 202, 116–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, A.; Li, N.; Dembek, T.A.; Kappel, A.; Boulay, C.; Ewert, S.; Tietze, A.; Husch, A.; Perera, T.; Neumann, W.J.; et al. Lead-DBS v2: Towards a comprehensive pipeline for deep brain stimulation imaging. NeuroImage 2019, 184, 293–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tustison, N.J.; Avants, B.B.; Cook, P.A.; Zheng, Y.; Egan, A.; Yushkevich, P.A.; Gee, J.C. N4ITK: Improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avants, B.B.; Epstein, C.L.; Grossman, M.; Gee, J.C. Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: Evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Med. Image Anal. 2008, 12, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Fonov, V.; Chakravarty, M.M.; Beriault, S.; Al Subaie, F.; Sadikot, A.; Pike, G.B.; Bertrand, G.; Collins, D.L. A dataset of multi-contrast population-averaged brain MRI atlases of a Parkinson’s disease cohort. Data Brief 2017, 12, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, F.C.; Verstynen, T.D.; Wang, Y.; Fernández-Miranda, J.C.; Tseng, W.Y. Deterministic diffusion fiber tracking improved by quantitative anisotropy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, A.; Neumann, W.J.; Degen, K.; Schneider, G.H.; Kühn, A.A. Toward an electrophysiological“sweet spot” for deep brain stimulation in the subthalamic nucleus. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 3377–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, A.; Wichmann, T. Pathophysiology of parkinsonism. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 1459–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patriat, R.; Niederer, J.; Kaplan, J.; Amundsen Huffmaster, S.; Petrucci, M.; Eberly, L.; Harel, N.; MacKinnon, C. Morphological changes in the subthalamic nucleus of people with mild-to-moderate parkinson’s disease: A 7T MRI study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagae, L.M.; Honce, J.M.; Tanabe, J.; Shelton, E.; Sillau, S.H.; Berman, B.D. Microstructural changes within the basal ganglia differ between Parkinson disease subtypes. Front. Neuroanat. 2016, 23, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mole, J.P.; Subramanian, L.; Bracht, T.; Morris, H.; Metzler-Baddeley, C.; Linden, D.E. Increased fractional anisotropy in the motor tracts of Parkinson’s disease suggests compensatory neuroplasticity or selective neurodegeneration. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 3327–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Burock, M.A. Diffusion tensor imaging in Parkinson’s disease and Parkinsonian syndrome: A systematic review. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 531993. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cousineau, M.; Jodoin, P.M.; Morency, F.C.; Rozanski, V.; Grand’Maison, M.; Bedell, B.J.; Descoteaux, M. A test-retest study on Parkinson’s PPMI dataset yields statistically significant white matter fascicles. NeuroImage Clin. 2017, 16, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faivre, F.; Sánchez-Catalán, M.J.; Dovero, S.; Bido, S.; Joshi, A.; Bezard, E.; Barrot, M. Ablation of the tail of the ventral tegmental area compensates symptoms in an experimental model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 139, 104818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theilmann, R.J.; Reed, J.D.; Song, D.D.; Huang, M.X.; Lee, R.R.; Litvan, I.; Harrington, D.L. White-matter changes correlate with cognitive functioning in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurol. 2013, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.C.; Heng, H.S.; Ng, S.Y.; Tan, L.C.; Chan, L.L.; Tan, E.K. White matter microstructural characteristics in newly diagnosed Parkinson’s disease: An unbiased whole-brain study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Mueller, B.A.; Jahanshad, N.; Jin, Y.; Lenglet, C.; Yacoub, E.; Sapiro, G.; Ugurbil, K.; Harel, N.; Toga, A.W.; et al. Magnetic resonance field strength effects on diffusion measures and brain connectivity networks. Brain Connect. 2013, 3, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| ROI | Mean 3T FA | Mean 7T FA | Student T Test p 3T FA > 7T FA | Mean 3T MD (×10−3) | Mean 7T MD (×10−3) | Student T Test p 3T MD > 7T MD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left amygdala | 0.189 | 0.184 | 0.645 | 0.748 | 0.669 | 0.098 |
| Left caudate | 0.164 | 0.175 | 0.719 | 0.679 | 0.620 | 0.359 |
| Left globus pallidus externus | 0.242 | 0.189 | 0.013 | 0.514 | 0.424 | 0.032 |
| Left globus pallidus internus | 0.250 | 0.196 | 0.597 | 0.525 | 0.433 | 0.890 |
| Left hippocampus | 0.168 | 0.157 | 0.351 | 0.788 | 0.712 | 0.632 |
| Left nucleus accumbens | 0.169 | 0.149 | 0.701 | 0.677 | 0.659 | 0.215 |
| Left putamen | 0.188 | 0.175 | 0.471 | 0.627 | 0.569 | 0.032 |
| Left red nucleus | 0.329 | 0.304 | 0.332 | 0.554 | 0.457 | 0.394 |
| Left substantia nigra | 0.346 | 0.343 | 0.001 | 0.584 | 0.409 | 0.006 |
| Left subthalamic nucleus | 0.347 | 0.294 | 0.030 | 0.534 | 0.426 | 0.635 |
| Left thalamus | 0.269 | 0.248 | 0.753 | 0.631 | 0.583 | 0.252 |
| Right amygdala | 0.169 | 0.175 | 0.509 | 0.757 | 0.667 | 0.001 |
| Right caudate | 0.177 | 0.161 | 0.017 | 0.677 | 0.608 | 0.748 |
| Right globus pallidus externus | 0.230 | 0.250 | 0.176 | 0.532 | 0.384 | 0.207 |
| Right globus pallidus internus | 0.200 | 0.215 | 0.070 | 0.511 | 0.377 | 0.162 |
| Right hippocampus | 0.169 | 0.156 | 0.578 | 0.767 | 0.709 | 0.847 |
| Right nucleus accumbens | 0.171 | 0.147 | 0.490 | 0.665 | 0.642 | 0.810 |
| Right putamen | 0.200 | 0.186 | 0.325 | 0.629 | 0.546 | 0.941 |
| Right red nucleus | 0.320 | 0.323 | 0.357 | 0.550 | 0.433 | 0.082 |
| Right substantia nigra | 0.480 | 0.400 | 0.743 | 0.535 | 0.397 | 0.001 |
| Right subthalamic nucleus | 0.402 | 0.325 | 0.692 | 0.493 | 0.405 | <0.001 |
| Right thalamus | 0.272 | 0.254 | 0.595 | 0.636 | 0.573 | 0.472 |
| ROI | Mean3T AD (×10−3) | Mean7T AD (×10−3) | Student T Test p 3T AD > 7T AD | Mean3T RD (×10−3) | Mean7T RD (×10−3) | Student T Test p 3T RD > 7T RD |
| Left amygdala | 0.897 | 0.798 | 0.084 | 0.673 | 0.605 | 0.126 |
| Left caudate | 0.788 | 0.730 | 0.400 | 0.625 | 0.566 | 0.343 |
| Left globus pallidus externus | 0.636 | 0.500 | 0.043 | 0.452 | 0.386 | 0.033 |
| Left globus pallidus internus | 0.657 | 0.513 | 0.636 | 0.460 | 0.393 | 0.943 |
| Left hippocampus | 0.922 | 0.824 | 0.570 | 0.722 | 0.656 | 0.742 |
| Left nucleus accumbens | 0.788 | 0.756 | 0.375 | 0.621 | 0.611 | 0.162 |
| Left putamen | 0.751 | 0.675 | 0.040 | 0.565 | 0.516 | 0.090 |
| Left red nucleus | 0.751 | 0.605 | 0.018 | 0.455 | 0.383 | 0.985 |
| Left substantia nigra | 0.813 | 0.568 | 0.066 | 0.470 | 0.329 | <0.001 |
| Left subthalamic nucleus | 0.717 | 0.560 | 0.067 | 0.442 | 0.359 | 0.749 |
| Left thalamus | 0.804 | 0.731 | 0.873 | 0.544 | 0.510 | 0.159 |
| Right amygdala | 0.888 | 0.789 | 0.013 | 0.691 | 0.607 | 0.002 |
| Right caudate | 0.800 | 0.708 | 0.751 | 0.615 | 0.559 | 0.925 |
| Right globus pallidus externus | 0.655 | 0.479 | 0.477 | 0.470 | 0.336 | 0.186 |
| Right globus pallidus internus | 0.612 | 0.450 | 0.800 | 0.460 | 0.340 | 0.065 |
| Right hippocampus | 0.898 | 0.821 | 0.925 | 0.701 | 0.654 | 0.788 |
| Right nucleus accumbens | 0.774 | 0.734 | 0.872 | 0.611 | 0.597 | 0.603 |
| Right putamen | 0.762 | 0.655 | 0.537 | 0.563 | 0.492 | 0.743 |
| Right red nucleus | 0.738 | 0.581 | 0.004 | 0.456 | 0.360 | 0.297 |
| Right substantia nigra | 0.850 | 0.589 | 0.001 | 0.377 | 0.301 | 0.432 |
| Right subthalamic nucleus | 0.711 | 0.548 | <0.001 | 0.384 | 0.334 | 0.037 |
| Right thalamus | 0.814 | 0.721 | 0.132 | 0.547 | 0.498 | 0.861 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, H.-M. Diffusion Measures of Subcortical Structures Using High-Field MRI. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030391
Baek H-M. Diffusion Measures of Subcortical Structures Using High-Field MRI. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(3):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030391
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Hyeon-Man. 2023. "Diffusion Measures of Subcortical Structures Using High-Field MRI" Brain Sciences 13, no. 3: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030391
APA StyleBaek, H.-M. (2023). Diffusion Measures of Subcortical Structures Using High-Field MRI. Brain Sciences, 13(3), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13030391




