A Comparison of the Safety, Efficacy, and Accuracy of Frame-Based versus Remebot Robot-Assisted Stereotactic Systems for Biopsy of Brainstem Tumors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
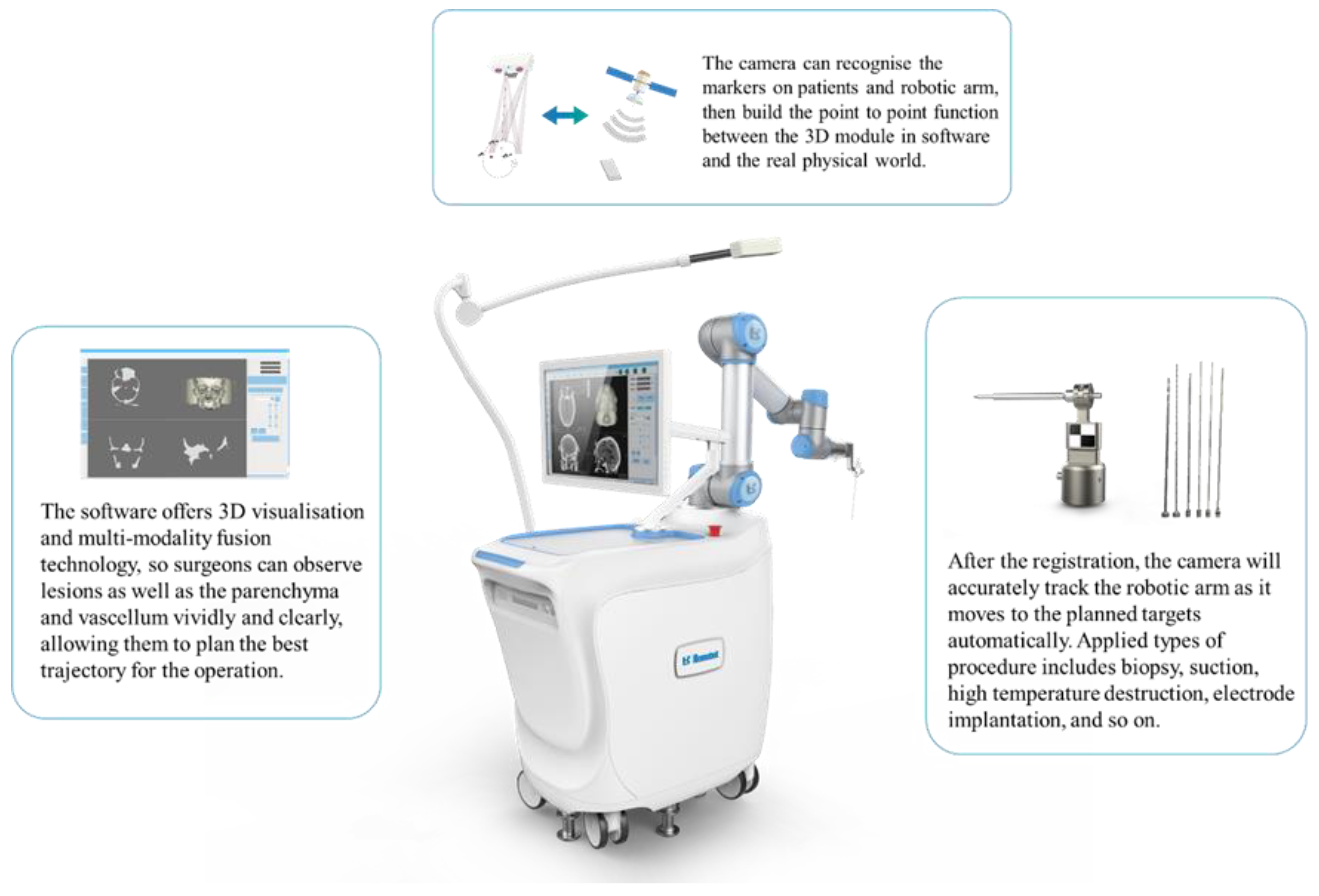
2.2. Surgical Procedure
2.3. Data Acquisition
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
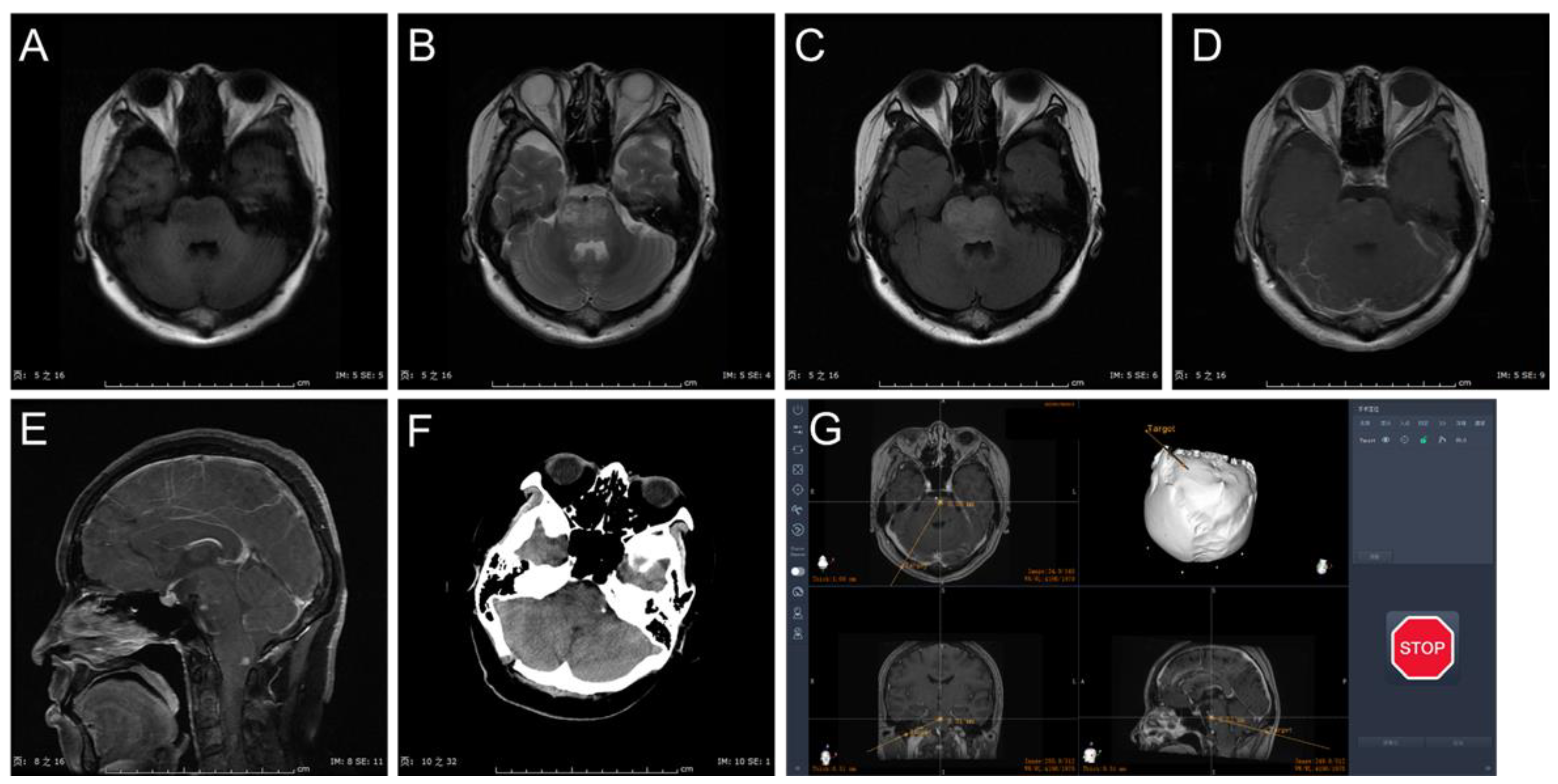
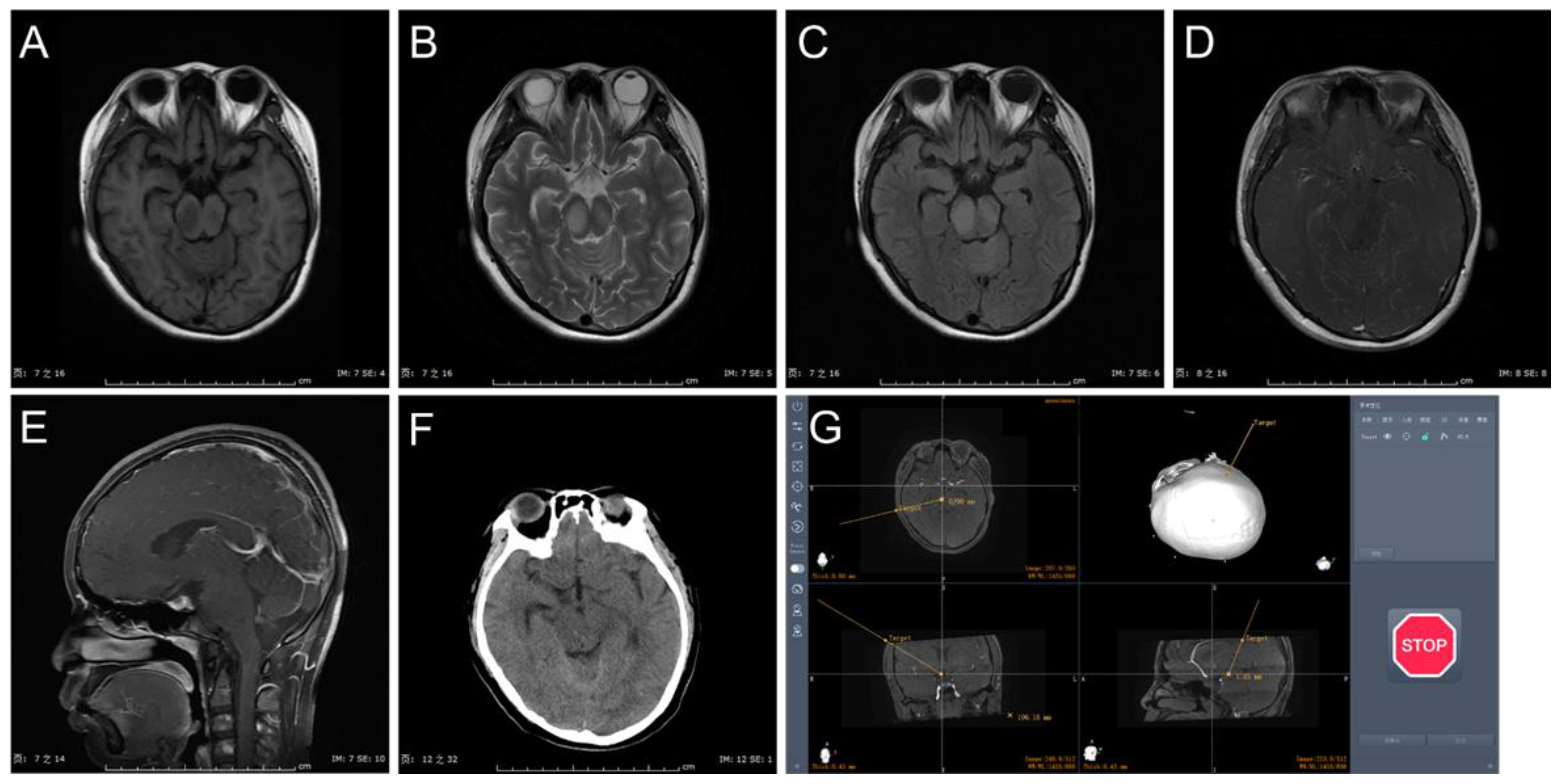
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Procedure and Complications
3.3. Histopathology
3.4. Treatment and Follow-Up
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Price, M.; Ryan, K.; Edelson, J.; Neff, C.; Cioffi, G.A.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Pediatric Brain Tumor Foundation Childhood and Adolescent Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2014–2018. Neuro-Oncol. 2022, 24, iii1–iii38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Price, M.; Neff, C.; Cioffi, G.A.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2015–2019. Neuro-Oncol. 2022, 24, v1–v95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Gao, P.; Liu, W.; Hu, F.; Jiang, W.; Lei, T.; Shu, K. A comparison of the efficacy, safety, and duration of frame-based and Remebot robot-assisted frameless stereotactic biopsy. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 35, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Hu, F.; Jiang, W.; Lei, T.; Shu, K. Effect of Robot-Assisted Neuroendoscopic Hematoma Evacuation Combined Intracranial Pressure Monitoring for the Treatment of Hypertensive Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 722924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Chan, T.M.; Santiago-Dieppa, D.R.; Yekula, A.; Sanchez, C.E.; Elster, J.D.; Crawford, J.R.; Levy, M.L.; Gonda, D.D. Robot-assisted stereotactic biopsy of pediatric brainstem and thalamic lesions. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2020, 27, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machetanz, K.; Grimm, F.; Wang, S.; Schuhmann, M.U.; Tatagiba, M.; Gharabaghi, A.; Naros, G. Rediscovery of the transcerebellar approach: Improving the risk-benefit ratio in robot-assisted brainstem biopsies. Neurosurg. Focus 2022, 52, E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peciu-Florianu, I.; Legrand, V.; Monfilliette-Djelad, A.; Maurage, C.-A.; Vannod-Michel, Q.; Blond, S.; Touzet, G.; Reyns, N. Frameless robot-assisted stereotactic biopsies for lesions of the brainstem—A series of 103 consecutive biopsies. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2022, 157, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, E.; Parvaresh, M.; Bahrami, M.; Fattahi, A. An Experience with Frame-Based Stereotactic Biopsy of Posterior Fossa Lesions via Transcerebellar Route. World Neurosurg. 2020, 136, e380–e385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatab, S.; Spliet, W.; Woerdeman, P.A. Frameless image-guided stereotactic brain biopsies: Emphasis on diagnostic yield. Acta Neurochir. 2014, 156, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Air, E.L.; Leach, J.L.; Warnick, R.; McPherson, C.M. Comparing the risks of frameless stereotactic biopsy in eloquent and noneloquent regions of the brain: A retrospective review of 284 cases. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 820–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, T.M.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Larson, P.S.; Alexander, E.; Gleason, P.L.; Schwartz, R.B.; Jolesz, F.A.; Black, P.M. Frameless Stereotactic Neurosurgery Using Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Stereotactic Brain Biopsy. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capitanio, J.F.; Camporesi, S.; Franzin, A.; Barzaghi, L.R.; Picozzi, P.; Mortini, P. Inverted positioning of Leksell Frame G for very low posterior fossa and brain stem lesions biopsies. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 2019, 63, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guberinic, A.; Elshout, R.V.D.; Kozicz, T.; ter Laan, M.; Henssen, D. Overview of the microanatomy of the human brainstem in relation to the safe entry zones. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 137, 1524–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodworth, G.F.; McGirt, M.J.; Samdani, A.; Garonzik, I.; Olivi, A.; Weingart, J.D. Frameless image-guided stereotactic brain biopsy procedure: Diagnostic yield, surgical morbidity, and comparison with the frame-based technique. J. Neurosurg. 2006, 104, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yeung, C.; Radmanesh, A.; Wiemann, R.; Black, P.M.; Golby, A.J. Comparative Effectiveness of Frame-Based, Frameless, and Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging–Guided Brain Biopsy Techniques. World Neurosurg. 2015, 83, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradac, O.; Steklacova, A.; Nebrenska, K.; Vrana, J.; de Lacy, P.; Benes, V. Accuracy of VarioGuide Frameless Stereotactic System Against Frame-Based Stereotaxy: Prospective, Randomized, Single-Center Study. World Neurosurg. 2017, 104, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekelis, K.; Radwan, T.A.; Desai, A.; Roberts, D.W. Frameless robotically targeted stereotactic brain biopsy: Feasibility, diagnostic yield, and safety. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 116, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kickingereder, P.; Willeit, P.; Simon, T.; Ruge, M.I. Diagnostic Value and Safety of Stereotactic Biopsy for Brainstem Tumors. Neurosurgery 2013, 72, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Goumnerova, L.C.; Manley, P.; Chi, S.N.; Neuberg, D.; Puligandla, M.; Fangusaro, J.; Goldman, S.; Tomita, T.; Alden, T.; et al. Prospective feasibility and safety assessment of surgical biopsy for patients with newly diagnosed diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Neuro-Oncol. 2018, 20, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamisch, C.; Kickingereder, P.; Fischer, M.; Simon, T.; Ruge, M.I. Update on the diagnostic value and safety of stereotactic biopsy for pediatric brainstem tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 735 cases. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2017, 20, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coca, H.; Cebula, H.; Benmekhbi, M.; Chenard, M.; Entz-Werle, N.; Proust, F. Diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas in children: Interest of robotic frameless assisted biopsy. A technical note. Neurochirurgie 2016, 62, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carai, A.; Mastronuzzi, A.; De Benedictis, A.; Messina, R.; Cacchione, A.; Miele, E.; Randi, F.; Esposito, G.; Trezza, A.; Colafati, G.S.; et al. Robot-Assisted Stereotactic Biopsy of Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma: A Single-Center Experience. World Neurosurg. 2017, 101, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitanza, N.A.; Biery, M.C.; Myers, C.; Ferguson, E.; Zheng, Y.; Girard, E.J.; Przystal, J.M.; Park, G.; Noll, A.; Pakiam, F.; et al. Optimal therapeutic targeting by HDAC inhibition in biopsy-derived treatment-naïve diffuse midline glioma models. Neuro-Oncol. 2021, 23, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Broniscer, A.; McEachron, T.A.; Lu, C.; Paugh, B.S.; Becksfort, J.; Qu, C.; Ding, L.; Huether, R.; Parker, M.; et al. Somatic histone H3 alterations in pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas and non-brainstem glioblastomas. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartzentruber, J.; Korshunov, A.; Liu, X.-Y.; Jones, D.T.W.; Pfaff, E.; Jacob, K.; Sturm, D.; Fontebasso, A.M.; Khuong-Quang, D.-A.; Tönjes, M.; et al. Driver mutations in histone H3.3 and chromatin remodelling genes in paediatric glioblastoma. Nature 2012, 482, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz-Bose, R.; Monje, M. Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: Molecular landscape and emerging therapeutic targets. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2019, 31, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majzner, R.G.; Ramakrishna, S.; Yeom, K.W.; Patel, S.; Chinnasamy, H.; Schultz, L.M.; Richards, R.M.; Jiang, L.; Barsan, V.; Mancusi, R.; et al. GD2-CAR T cell therapy for H3K27M-mutated diffuse midline gliomas. Nature 2022, 603, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, V.M.; Power, E.A.; Zhang, L.; Daniels, D.J. Liquid biopsy for diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: An update. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2019, 24, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Remebot Robot Group (n = 22) | Frame-Based Group (n = 11) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD), years | 17.3 ± 18.7 | 32.8 ± 17.1 | 0.027 |
| Sex ratio (male/female) | 7:15 | 7:4 | 0.136 |
| Symptoms | |||
| Vertigo | 5 | 4 | 0.438 |
| Ataxia | 8 | 5 | 0.714 |
| Motor deficit and/or sensory deficit | 5 | 4 | 0.438 |
| IIP | 7 | 4 | >0.999 |
| Region of biopsy | |||
| Midbrain | 2 | 6 | 0.008 |
| Pons | 20 | 5 | 0.008 |
| Remebot Robot Group (n = 22) | Frame-Based Group (n = 11) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trajectory (supra: infratentorial) | 2/20 | 6/5 | 0.032 |
| Trajectory length, mm | 71.27 ± 1.49 | 91.11 ± 5.71 | <0.001 |
| Total procedure duration, mean, min | 84.73 ± 2.19 | 124.5 ± 2.78 | <0.001 |
| Operation time, mean, min | 44.14 ± 1.40 | 45.45 ± 2.67 | 0.632 |
| Complication | 2/20 | 2:9 | 0.586 |
| Histopathological Finding | Remebot Robot Group (n = 22) | Frame-Based Group (n = 11) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic yield | 21/22 | 10/11 | >0.999 |
| Diffuse low-grade glioma | 11 | 5 | |
| Diffuse high-grade glioma | 8 | 4 | |
| Diffuse large B cell lymphoma | 1 | 1 | |
| Nonconclusive diagnosis | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Wu, S.; Huang, K.; Li, R.; Jiang, W.; Wang, J.; Shu, K.; Lei, T. A Comparison of the Safety, Efficacy, and Accuracy of Frame-Based versus Remebot Robot-Assisted Stereotactic Systems for Biopsy of Brainstem Tumors. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020362
Li C, Wu S, Huang K, Li R, Jiang W, Wang J, Shu K, Lei T. A Comparison of the Safety, Efficacy, and Accuracy of Frame-Based versus Remebot Robot-Assisted Stereotactic Systems for Biopsy of Brainstem Tumors. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(2):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020362
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chaoxi, Shiqiang Wu, Kuan Huang, Ran Li, Wei Jiang, Junwen Wang, Kai Shu, and Ting Lei. 2023. "A Comparison of the Safety, Efficacy, and Accuracy of Frame-Based versus Remebot Robot-Assisted Stereotactic Systems for Biopsy of Brainstem Tumors" Brain Sciences 13, no. 2: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020362
APA StyleLi, C., Wu, S., Huang, K., Li, R., Jiang, W., Wang, J., Shu, K., & Lei, T. (2023). A Comparison of the Safety, Efficacy, and Accuracy of Frame-Based versus Remebot Robot-Assisted Stereotactic Systems for Biopsy of Brainstem Tumors. Brain Sciences, 13(2), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13020362








