The Pre-Interictal Network State in Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. MRI Acquisition
2.3. EEG Recording
2.4. EEG Analysis
2.5. Epoch Selection
- Epochs of brain activity prior to the first interictal epileptiform discharge. We named these epochs as pre-interictal.
- Resting-state (RS) epochs with a difference of at least three minutes from the GSWDs.
2.6. Source Localization
2.7. Regions of Interest
2.8. Cortical Functional Connectivity
2.9. Network Analysis
2.10. Graph Theory Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
2.12. Network Visualization
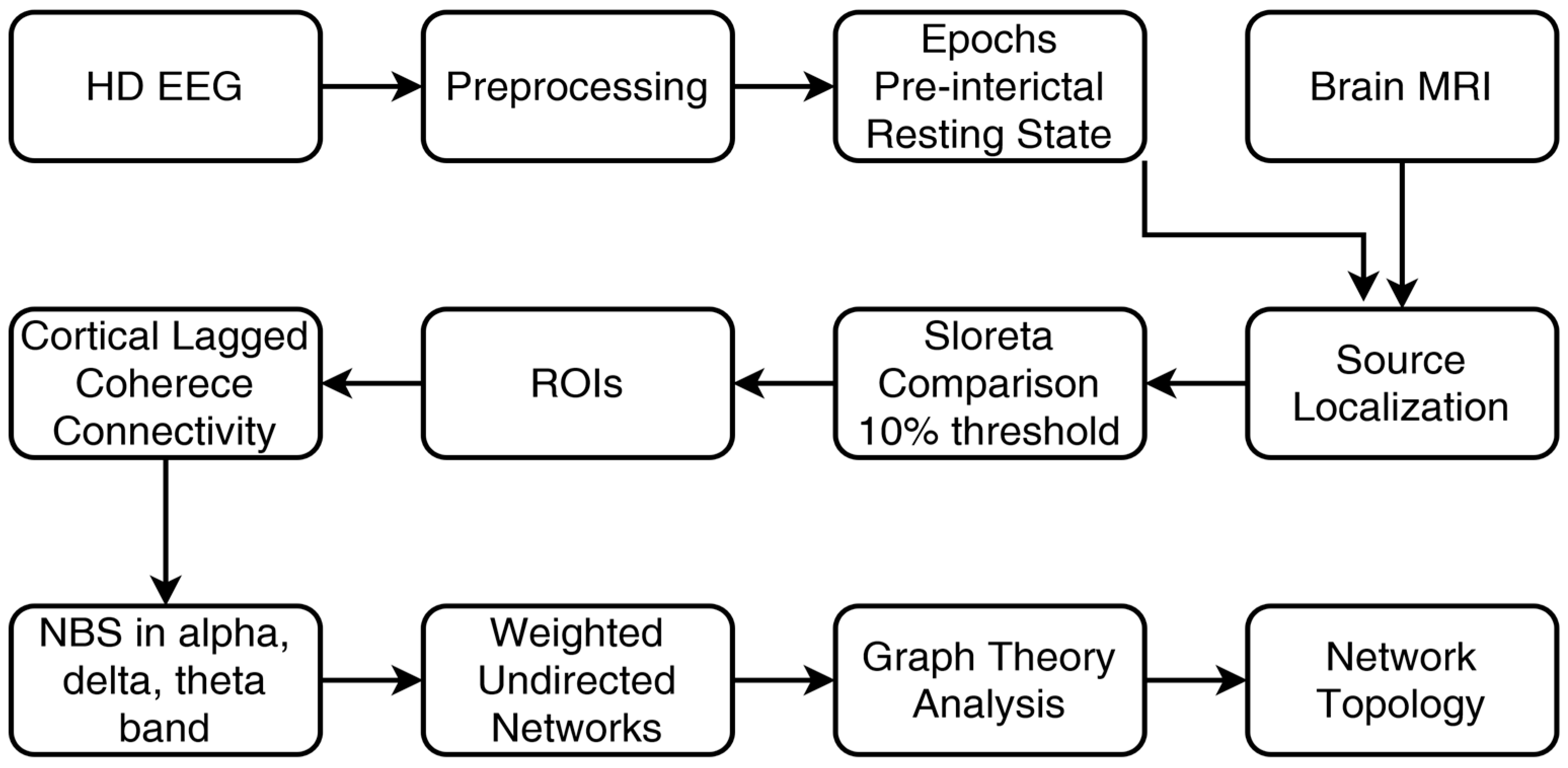
2.13. Methodology Flowchart
3. Results
3.1. Regions of Interest
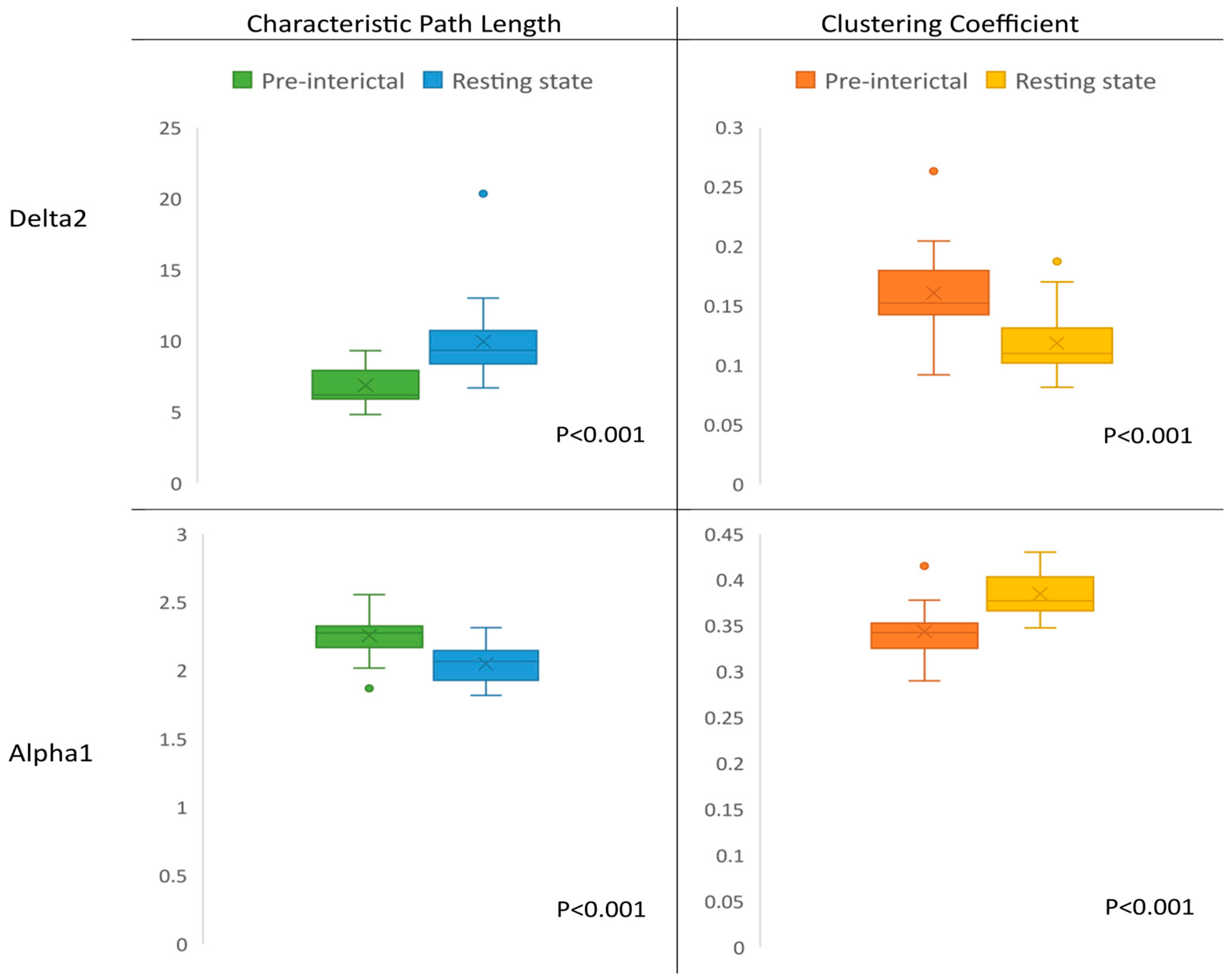
3.2. Network Characteristics
3.3. Node Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vecchio, F.; Miraglia, F.; Maria Rossini, P. Connectome: Graph theory application in functional brain network architecture. Clin. Neurophysiol. Pract. 2017, 2, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, O. Graph theory methods: Applications in brain networks. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 20, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavaty, A.; Ramialison, M.; Currie, P.D. Integrated Value of Influence: An Integrative Method for the Identification of the Most Influential Nodes within Networks. Patterns 2020, 1, 100052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarion, G.; Sparacino, L.; Antonacci, Y.; Faes, L.; Mesin, L. Connectivity Analysis in EEG Data: A Tutorial Review of the State of the Art and Emerging Trends. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiruska, P.; de Curtis, M.; Jefferys, J.G.; Schevon, C.A.; Schiff, S.J.; Schindler, K. Synchronization and desynchronization in epilepsy: Controversies and hypotheses. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, E.; French, J.; Scheffer, I.E.; Bogacz, A.; Alsaadi, T.; Sperling, M.R.; Abdulla, F.; Zuberi, S.M.; Trinka, E.; Specchio, N.; et al. ILAE definition of the Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy Syndromes: Position statement by the ILAE Task Force on Nosology and Definitions. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1475–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerulli Irelli, E.; Leodori, G.; Morano, A.; Di Bonaventura, C. EEG Markers of Treatment Resistance in Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy: From Standard EEG Findings to Advanced Signal Analysis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneviratne, U.; Cook, M.J.; D’Souza, W.J. Electroencephalography in the Diagnosis of Genetic Generalized Epilepsy Syndromes. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeren, H.; van Luijtelaar, G.; Lopes da Silva, F.; Coenen, A. Evolving concepts on the pathophysiology of absence seizures: The cortical focus theory. Arch. Neurol. 2005, 62, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumsky, S.; Greenfield, L.J., Jr. Network analysis of preictal iEEG reveals changes in network structure preceding seizure onset. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotiuchyi, I.; Pernice, R.; Popov, A.; Faes, L.; Kharytonov, V. A Framework to Assess the Information Dynamics of Source EEG Activity and Its Application to Epileptic Brain Networks. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Zhang, T.; Miao, A.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Q.; Hu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, X. Differences Between Interictal and Ictal Generalized Spike-Wave Discharges in Childhood Absence Epilepsy: A MEG Study. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamidis, P.D.; Hellstrand, E.; Lidholm, H.; Abraham-Fuchs, K.; Ioannides, A.A. MFT in complex partial epilepsy: Spatio-temporal estimates of interictal activity. Neuroreport 1995, 7, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Curtis, M.; Jefferys, J.G.R.; Avoli, M. Interictal Epileptiform Discharges in Partial Epilepsy: Complex Neurobiological Mechanisms Based on Experimental and Clinical Evidence. In Jasper’s Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies, 4th ed.; Noebels, J.L., Avoli, M., Rogawski, M.A., Olsen, R.W., Delgado-Escueta, A.V., Eds.; Bethesda: Montgomery County, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vataman, A.; Ciolac, D.; Chiosa, V.; Aftene, D.; Leahu, P.; Winter, Y.; Groppa, S.A.; Gonzalez-Escamilla, G.; Muthuraman, M.; Groppa, S. Dynamic flexibility and controllability of network communities in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 179, 106055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, B.; Puskas, S.; Besenyei, M.; Spisak, T.; Opposits, G.; Hollody, K.; Fogarasi, A.; Fekete, I.; Emri, M. Neurophysiology of juvenile myoclonic epilepsy: EEG-based network and graph analysis of the interictal and immediate preictal states. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 106, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffer, I.E.; Berkovic, S.; Capovilla, G.; Connolly, M.B.; French, J.; Guilhoto, L.; Hirsch, E.; Jain, S.; Mathern, G.W.; Moshe, S.L.; et al. ILAE classification of the epilepsies: Position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadel, F.; Baillet, S.; Mosher, J.C.; Pantazis, D.; Leahy, R.M. Brainstorm: A user-friendly application for MEG/EEG analysis. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2011, 2011, 879716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cheveigne, A.; Nelken, I. Filters: When, Why, and How (Not) to Use Them. Neuron 2019, 102, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chriskos, P.; Frantzidis, C.A.; Gkivogkli, P.T.; Bamidis, P.D.; Kourtidou-Papadeli, C. Achieving Accurate Automatic Sleep Staging on Manually Pre-processed EEG Data Through Synchronization Feature Extraction and Graph Metrics. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comon, P. Independent component analysis, a new concept? Signal Process. 1994, 36, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grech, R.; Cassar, T.; Muscat, J.; Camilleri, K.P.; Fabri, S.G.; Zervakis, M.; Xanthopoulos, P.; Sakkalis, V.; Vanrumste, B. Review on solving the inverse problem in EEG source analysis. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2008, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.M.; Brunet, D. EEG Source Imaging: A Practical Review of the Analysis Steps. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaser, C.; Dahnke, R.; Thompson, P.M.; Kurth, F.; Luders, E.; Initiative, A.s.D.N. CAT—A Computational Anatomy Toolbox for the Analysis of Structural MRI Data. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramfort, A.; Papadopoulo, T.; Olivi, E.; Clerc, M. OpenMEEG: Opensource software for quasistatic bioelectromagnetics. Biomed. Eng. Online 2010, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D. Standardized low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (sLORETA): Technical details. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 24 (Suppl. D), 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Desikan, R.S.; Segonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.T.; Dickerson, B.C.; Blacker, D.; Buckner, R.L.; Dale, A.M.; Maguire, R.P.; Hyman, B.T.; et al. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydöre, S.; Ashrafulla, S.; Joshi, A.A.; Leahy, R.M. A measure of connectivity in the presence of crosstalk. In Proceedings of the 2013 Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 3–6 November 2013; pp. 1848–1852. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Faber, P.; Kinoshita, T.; Kochi, K.; Milz, P.; Keiichiro, N.; Yoshimura, M. A comparison of bivariate frequency domain measures of electrophysiological connectivity. bioRxiv 2018, 459503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindriks, R. Relation between the phase-lag index and lagged coherence for assessing interactions in EEG and MEG data. Neuroimage Rep. 2021, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R. Instantaneous and lagged measurements of linear and nonlinear dependence between groups of multivariate time series: Frequency decomposition. arXiv 2007, arXiv:0711.1455. [Google Scholar]
- Caliandro, P.; Vecchio, F.; Miraglia, F.; Reale, G.; Della Marca, G.; La Torre, G.; Lacidogna, G.; Iacovelli, C.; Padua, L.; Bramanti, P.; et al. Small-World Characteristics of Cortical Connectivity Changes in Acute Stroke. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2017, 31, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, F.; Pappalettera, C.; Miraglia, F.; Alù, F.; Orticoni, A.; Judica, E.; Cotelli, M.; Pistoia, F.; Rossini, P.M. Graph Theory on Brain Cortical Sources in Parkinson’s Disease: The Analysis of ‘Small World’ Organization from EEG. Sensors 2021, 21, 7266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D. Coherence and phase synchronization: Generalization to pairs of multivariate time series, and removal of zero-lag contributions. arXiv 2007, arXiv:0706.1776. [Google Scholar]
- Zalesky, A.; Fornito, A.; Bullmore, E.T. Network-based statistic: Identifying differences in brain networks. Neuroimage 2010, 53, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullmore, E.; Sporns, O. Complex brain networks: Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinov, M.; Sporns, O. Complex network measures of brain connectivity: Uses and interpretations. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, M.; Wang, J.; He, Y. BrainNet Viewer: A network visualization tool for human brain connectomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X. Differences in generation and maintenance between ictal and interictal generalized spike-and-wave discharges in childhood absence epilepsy: A magnetoencephalography study. Epilepsy Behav. 2023, 148, 109440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, N.; Chen, Y.; Tan, Y.; Dong, L.; Xu, P.; Guo, D.; Zhang, T.; Yao, D.; Luo, C. How Alpha Rhythm Spatiotemporally Acts Upon the Thalamus-Default Mode Circuit in Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsy. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 68, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, F.; Siebner, H.R.; Wolff, S.; Muhle, H.; Boor, R.; Granert, O.; Jansen, O.; Stephani, U.; Siniatchkin, M. Changes in activity of striato-thalamo-cortical network precede generalized spike wave discharges. Neuroimage 2008, 39, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luttjohann, A.; van Luijtelaar, G. The role of thalamic nuclei in genetic generalized epilepsies. Epilepsy Res. 2022, 182, 106918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton, Z.; Nagy, O.; Barcsai, L.; Sere, P.; Zsigri, N.; Foldi, T.; Gellert, L.; Berenyi, A.; Crunelli, V.; Lorincz, M.L. Higher-order thalamic nuclei facilitate the generalization and maintenance of spike-and-wave discharges of absence seizures. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 178, 106025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangwiriyasakul, C.; Perani, S.; Centeno, M.; Yaakub, S.N.; Abela, E.; Carmichael, D.W.; Richardson, M.P. Dynamic brain network states in human generalized spike-wave discharges. Brain 2018, 141, 2981–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs-Brichford, E.; Horn, P.S.; Tenney, J.R. Mapping preictal networks preceding childhood absence seizures using magnetoencephalography. J. Child Neurol. 2014, 29, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.; Ossenblok, P.; van Luijtelaar, G. Space–time network connectivity and cortical activations preceding spike wave discharges in human absence epilepsy: A MEG study. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2011, 49, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, B.; Puskas, S.; Besenyei, M.; Kovacs, N.Z.; Spisak, T.; Kis, S.A.; Emri, M.; Hollody, K.; Fogarasi, A.; Kondakor, I.; et al. Valproate treatment normalizes EEG functional connectivity in successfully treated idiopathic generalized epilepsy patients. Epilepsy Res. 2014, 108, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Number of patients | 21 |
| Female/Male N (%) | 10 (48%)/11 (52%) |
| Age in years (mean ± SD) | 29.8 ± 12.4 |
| Age at onset of epilepsy in years (mean ± SD) | 17.1 ± 9.3 |
| IGEs N (%) | |
| CAE | 1 (5%) |
| JAE | 6 (28.5%) |
| GTCSa | 8 (38%) |
| JME | 6 (28.5%) |
| ASMs | |
| Valproic | 8 (43%) |
| Levetiracetam | 4 (19%) |
| ≥2 ASMs | 9 (38%) |
| HD-EEG | |
| Number of channels Pre-interictal epochs (total/mean) | 128 27/1.28 |
| Function | Region of Interest | Hubness Score | Spreading Difference Score | RSN |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spreaders | Precuneus R | Subthr. | 13.366 (p = 0.019) | DMN |
| Posterior cingulate R | Subthr. | 3.717 (p = 0.023) | DMN | |
| Inferior temporal L | Subthr. | 2.439 (p = 0.022) | DAN | |
| Inferior temporal R | Subthr. | 1.924 (p = 0.024) | DAN | |
| Pars opercularis L | Subthr. | 1.912 (p = 0.045) | DAN | |
| Hubs | Caudal anterior cingulate L | 100 | ns | DAN |
| Isthmus cingulate L | 95 | ns | DMN | |
| Medial orbitofrontal L | 92 | ns | DMN | |
| Precuneus L | 91 | ns | DMN | |
| Thalamus L | 85 | ns | ||
| Thalamus R | 74 | ns |
| Function | Region of Interest | Dsync. Degree | RSN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dsync. Nodes | Isthmus cingulate L | 100 | DAN |
| Lateral orbitofrontal R | 87 | DMN | |
| Isthmus cingulate R | 86 | DAN | |
| Rostral anterior cingulate L | 85 | DAN | |
| Pars triangularis R | 75 | DAN | |
| Lateral occipital R | 71 | VIS | |
| Medial orbitofrontal R | 69 | DMN | |
| Middle temporal R | 68 | DAN |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pitetzis, D.; Frantzidis, C.; Psoma, E.; Ketseridou, S.N.; Deretzi, G.; Kalogera-Fountzila, A.; Bamidis, P.D.; Spilioti, M. The Pre-Interictal Network State in Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsies. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121671
Pitetzis D, Frantzidis C, Psoma E, Ketseridou SN, Deretzi G, Kalogera-Fountzila A, Bamidis PD, Spilioti M. The Pre-Interictal Network State in Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsies. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(12):1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121671
Chicago/Turabian StylePitetzis, Dimitrios, Christos Frantzidis, Elizabeth Psoma, Smaranda Nafsika Ketseridou, Georgia Deretzi, Anna Kalogera-Fountzila, Panagiotis D. Bamidis, and Martha Spilioti. 2023. "The Pre-Interictal Network State in Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsies" Brain Sciences 13, no. 12: 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121671
APA StylePitetzis, D., Frantzidis, C., Psoma, E., Ketseridou, S. N., Deretzi, G., Kalogera-Fountzila, A., Bamidis, P. D., & Spilioti, M. (2023). The Pre-Interictal Network State in Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsies. Brain Sciences, 13(12), 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13121671







