The Significance of NLRP Inflammasome in Neuropsychiatric Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
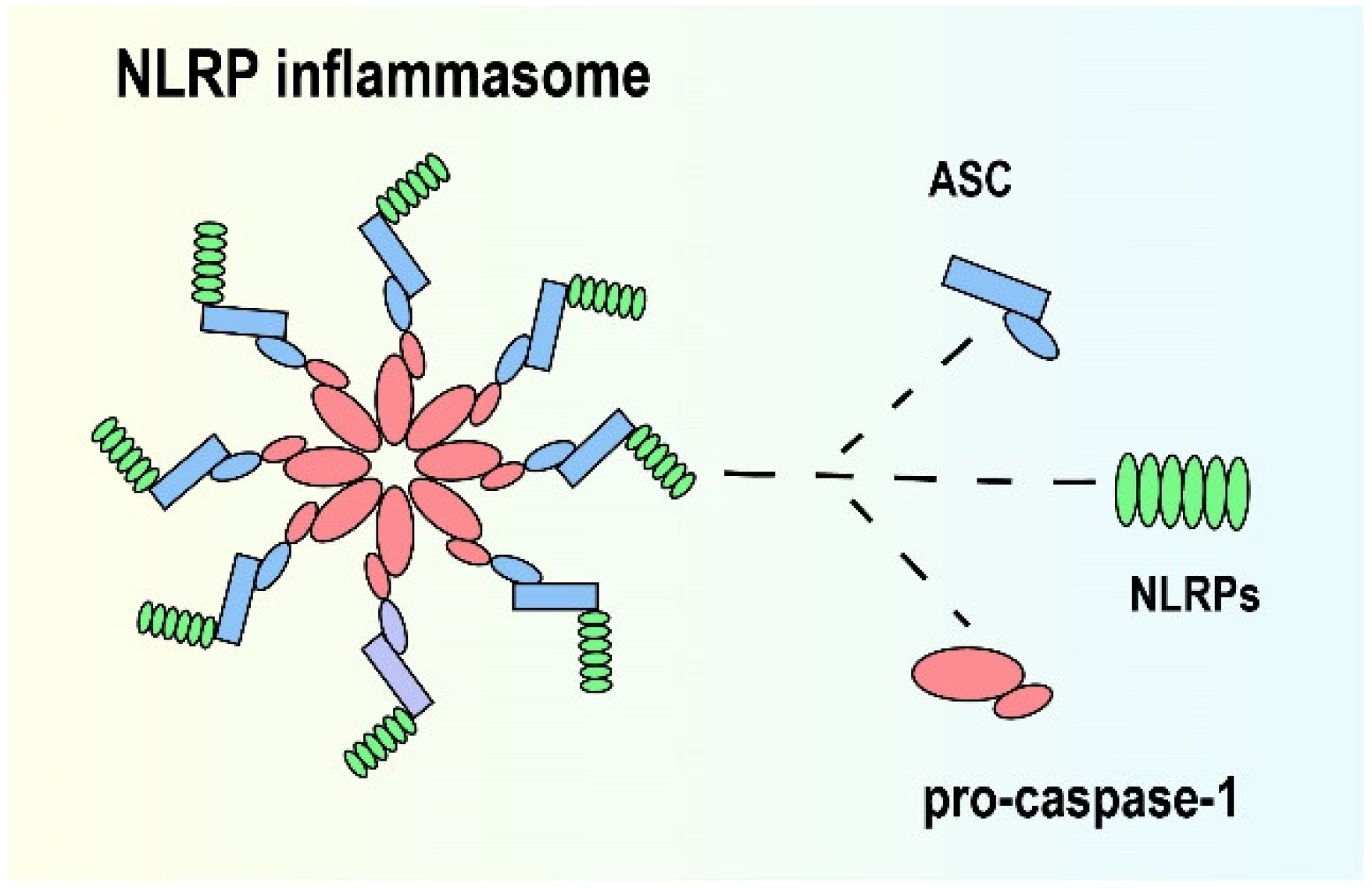
2. NLRP Inflammasome
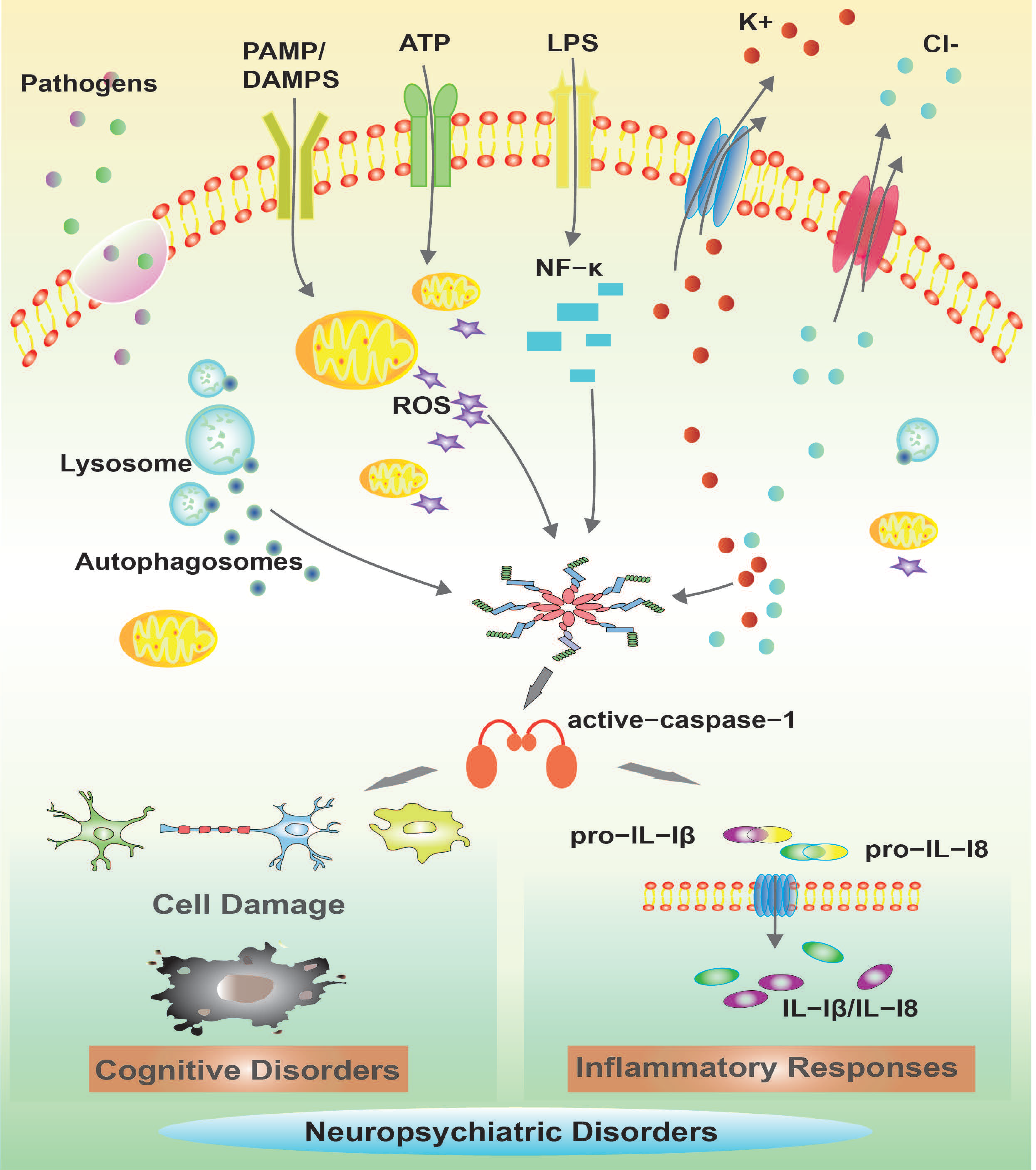
3. Roles of NLRP Inflammasome in Neuropsychiatric Disorders
3.1. Alzheimer’s Disease
3.2. Parkinson’s Disease
3.3. Huntington’s Disease
3.4. Depression
3.5. Drug Use Disorder
4. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amor, S.; Peferoen, L.A.N.; Vogel, D.Y.S.; Breur, M.; van der Valk, P.; Baker, D.; van Noort, J.M. Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases—An update. Immunology 2014, 142, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, J.; Nutma, E.; van der Valk, P.; Amor, S. Inflammation in CNS neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology 2018, 154, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Jiang, Z.; Bi, G.; Nomura, K.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Cai, B.; Zhou, J.-M.; He, S.Y.; Xin, X.-F. Pattern-recognition receptors are required for NLR-mediated plant immunity. Nature 2021, 592, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toldo, S.; Abbate, A. The NLRP3 inflammasome in acute myocardial infarction. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sok, S.P.M.; Ori, D.; Wada, A.; Okude, H.; Kawasaki, T.; Momota, M.; Nagoor, N.H.; Kawai, T. 1′-Acetoxychavicol acetate inhibits NLRP3-dependent inflammasome activation via mitochondrial ROS suppression. Int. Immunol. 2021, 33, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.G.; Muruve, D.A.; Power, C. Inflammasomes in the CNS. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; McManus, R.M.; Latz, E. Inflammasome signalling in brain function and neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloudizargari, M.; Moradkhani, F.; Asghari, N.; Fallah, M.; Asghari, M.H.; Moghadamnia, A.A.; Abdollahi, M. NLRP inflammasome as a key role player in the pathogenesis of environmental toxicants. Life Sci. 2019, 231, 116585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepp, O.; Galluzzi, L.; Kroemer, G. Mitochondrial control of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, Z.; Han, X.; Wang, D.; Jiang, Q.; Ding, J.; Xiao, M.; Wang, C.; Lu, M.; Hu, G. Dopamine D2 receptor restricts astrocytic NLRP3 inflammasome activation via enhancing the interaction of β-arrestin2 and NLRP3. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 2037–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Dietrich, W.D.; Keane, R.W. Activation and regulation of cellular inflammasomes: Gaps in our knowledge for central nervous system injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, K.V.; Deng, M.; Ting, J.P.Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaron, J.R.; Gangaraju, S.; Rao, M.Y.; Kong, X.; Zhang, L.; Su, F.; Tian, Y.; Glenn, H.L.; Meldrum, D.R. K(+) regulates Ca(2+) to drive inflammasome signaling: Dynamic visualization of ion flux in live cells. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasomes. Cell 2010, 140, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.E.; Smith, D.E. The IL-1 family: Regulators of immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, C.; Kneser, L.; Fiedler, R.; Beckert, J.; Wildgrube, S.; Seibert, E.; Fick, S.; Schafer, C.; Markau, S.; Trojanowicz, B.; et al. Pyroptosis: A Common Feature of Immune Cells of Haemodialysis Patients. Toxins 2021, 13, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdette, B.E.; Esparza, A.N.; Zhu, H.; Wang, S. Gasdermin D in pyroptosis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2768–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, B.A.; Dixit, V.M.; Power, C. Fiery Cell Death: Pyroptosis in the Central Nervous System. Trends Neurosci. 2020, 43, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohsfield, L.A.; Najafi, A.R.; Ghorbanian, Y.; Soni, N.; Hingco, E.E.; Kim, S.J.; Jue, A.D.; Swarup, V.; Inlay, M.A.; Green, K.N. Effects of long-term and brain-wide colonization of peripheral bone marrow-derived myeloid cells in the CNS. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothhammer, V.; Borucki, D.M.; Tjon, E.C.; Takenaka, M.C.; Chao, C.-C.; Ardura-Fabregat, A.; de Lima, K.A.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Hewson, P.; Staszewski, O.; et al. Microglial control of astrocytes in response to microbial metabolites. Nature 2018, 557, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.-H.; Wu, Y.-F.; Lin, Q.; Wang, D.-P.; Hai, J. URB597 protects against NLRP3 inflammasome activation by inhibiting autophagy dysfunction in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, P.B.; Sonowal, H.; Shukla, K.; Srivastava, S.K.; Ramana, K.V. Aldose Reductase Mediates NLRP3 Inflammasome-Initiated Innate Immune Response in Hyperglycemia-Induced Thp1 Monocytes and Male Mice. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 3661–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pétrilli, V.; Papin, S.; Dostert, C.; Mayor, A.; Martinon, F.; Tschopp, J. Activation of the NALP3 inflammasome is triggered by low intracellular potassium concentration. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ktistakis, N.T.; Tooze, S.A. Digesting the Expanding Mechanisms of Autophagy. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahama, M.; Akira, S.; Saitoh, T. Autophagy limits activation of the inflammasomes. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.M.; Kanneganti, T.-D. Regulation of lysosomal dynamics and autophagy by CTSB/cathepsin B. Autophagy 2016, 12, 2504–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Sun, S.; Sun, Y.; Song, Q.; Zhu, J.; Song, N.; Chen, M.; Sun, T.; Xia, M.; Ding, J.; et al. Small molecule-driven NLRP3 inflammation inhibition via interplay between ubiquitination and autophagy: Implications for Parkinson disease. Autophagy 2019, 15, 1860–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, D.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; Ma, M.; Xue, Z.; Lv, J.; Liu, H.; Xi, Q.; et al. Mir223 restrains autophagy and promotes CNS inflammation by targeting ATG16L1. Autophagy 2019, 15, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhang, B.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, D.; Huang, R.; Li, W.; Li, W. Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against neuronal degeneration induced by chronic dexamethasone treatment by inhibiting NLRP-1 inflammasomes in mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Su, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chen, M.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Ding, S.; Fang, Z.; Li, W.; et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 alleviates Aβ deposition by inhibiting NADPH oxidase 2 activation in APP/PS1 mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Zhao, F.; Chojnacki, J.E.; Fulp, J.; Klein, W.L.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, X. NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibitor Ameliorates Amyloid Pathology in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 1977–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atluri, V.S.R.; Tiwari, S.; Rodriguez, M.; Kaushik, A.; Yndart, A.; Kolishetti, N.; Yatham, M.; Nair, M. Inhibition of Amyloid-Beta Production, Associated Neuroinflammation, and Histone Deacetylase 2-Mediated Epigenetic Modifications Prevent Neuropathology in Alzheimer’s Disease Model. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, E.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Xiong, H. Inflammasome Activation by Methamphetamine Potentiates Lipopolysaccharide Stimulation of IL-1β Production in Microglia. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, C.; Dorothee, G.; Hunot, S.; Martin, E.; Monnet, Y.; Duchamp, M.; Dong, Y.; Legeron, F.P.; Leboucher, A.; Burnouf, S.; et al. Hippocampal T cell infiltration promotes neuroinflammation and cognitive decline in a mouse model of tauopathy. Brain 2017, 140, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Gong, Q.; Shi, J.; Li, F. Osthole improves cognitive function of vascular dementia rats: Reducing Aβ deposition via inhibition NLRP3 inflammasome. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Q.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Yang, P.F.; Yuan, Y.H.; Chen, N.H. Amyloidogenic proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases activate the NLRP3 inflammasome. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 49, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, G.; Jaehne, E.J.; Corrigan, F.; Toben, C.; Baune, B.T. Inflammasomes in neuroinflammation and changes in brain function: A focused review. Front. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawhinney, L.J.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Dale, G.A.; Keane, R.W.; Bramlett, H.M. Heightened inflammasome activation is linked to age-related cognitive impairment in Fischer 344 rats. BMC Neurosci. 2011, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.M.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Sheng, S.; Li, J.J.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, F. Ellagic Acid Protects Dopamine Neurons via Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Microglia. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 2963540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Ren, R.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, X.; Ablat, N.; Pu, X. Neuroprotective Effects of Safflower Flavonoid Extract in 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Model of Parkinson’s Disease May Be Related to its Anti-Inflammatory Action. Molecules 2020, 25, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wei, Y.Z.; He, X.M.; Li, D.D.; Wang, G.Q.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, F. Naringenin Produces Neuroprotection Against LPS-Induced Dopamine Neurotoxicity via the Inhibition of Microglial NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Wang, M.; Jia, Y.; Tian, D.; Liu, A.; Wang, W.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Yang, Q.; Liu, R.; et al. Echinacoside protects dopaminergic neurons by inhibiting NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1β signaling pathway in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 164, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comi, G.; Jeffery, D.; Kappos, L.; Montalban, X.; Boyko, A.; Rocca, M.A.; Filippi, M. Placebo-controlled trial of oral laquinimod for multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leem, Y.-H.; Park, J.-S.; Park, J.-E.; Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, H.-S. Papaverine Exerts Neuroprotective Effect by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in an MPTP-Induced Microglial Priming Mouse Model Challenged with LPS. Biomol. Ther. 2021, 29, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Chen, P.-H.; Siecinski, S.; Li, Q.-J.; Liu, C.; Steinman, L.; Gregory, S.G.; Benner, E.; Shinohara, M.L. An interferon-β-resistant and NLRP3 inflammasome-independent subtype of EAE with neuronal damage. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1599–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, H.; Lin, B.; Chen, Y.; Deng, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhou, R. RRx-001 ameliorates inflammatory diseases by acting as a potent covalent NLRP3 inhibitor. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Xiao, Z.; Huang, J.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Li, W. Disulfiram inhibits oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome activation to prevent LPS-induced cardiac injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 105, 108545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larose, T.L.; Chen, Y.; Camargo, C.A.; Langhammer, A.; Romundstad, P.; Mai, X.-M. Factors associated with vitamin D deficiency in a Norwegian population: The HUNT Study. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2014, 68, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, H.L.; Frenkel, D. Immunology and immunotherapy of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Luehmann, M.; Spires-Jones, T.L.; Prada, C.; Garcia-Alloza, M.; de Calignon, A.; Rozkalne, A.; Koenigsknecht-Talboo, J.; Holtzman, D.M.; Bacskai, B.J.; Hyman, B.T. Rapid appearance and local toxicity of amyloid-β plaques in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2008, 451, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halle, A.; Hornung, V.; Petzold, G.C.; Stewart, C.R.; Monks, B.G.; Reinheckel, T.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Latz, E.; Moore, K.J.; Golenbock, D.T. The NALP3 inflammasome is involved in the innate immune response to amyloid-beta. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Mejias, E.; Navarro, V.; Jimenez, S.; Sanchez-Mico, M.; Sanchez-Varo, R.; Nunez-Diaz, C.; Trujillo-Estrada, L.; Davila, J.C.; Vizuete, M.; Gutierrez, A.; et al. Soluble phospho-tau from Alzheimer’s disease hippocampus drives microglial degeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 897–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz, M.; Priller, J.; Sisodia, S.S.; Ransohoff, R.M. Heterogeneity of CNS myeloid cells and their roles in neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ising, C.; Heneka, M.T. Functional and structural damage of neurons by innate immune mechanisms during neurodegeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucin, K.M.; Wyss-Coray, T. Immune Activation in Brain Aging and Neurodegeneration: Too Much or Too Little? Neuron 2009, 64, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, S.; Sakata, K.; McDonald, M.P.; Liao, F.-F.; Ishrat, T. ER stress associated TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome activation in hippocampus of human Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 148, 105104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, L.; Dong, X.; Han, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, J.; Li, W. SOCE-mediated NFAT1-NOX2-NLRP1 inflammasome involves in lipopolysaccharide-induced neuronal damage and Aβ generation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 3183–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, R.; van der Lee, S.J.; Naj, A.C.; Bellenguez, C.; Badarinarayan, N.; Jakobsdottir, J.; Kunkle, B.W.; Boland, A.; Raybould, R.; Bis, J.C.; et al. Rare coding variants in PLCG2, ABI3, and TREM2 implicate microglial-mediated innate immunity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griciuc, A.; Serrano-Pozo, A.; Parrado, A.R.; Lesinski, A.N.; Asselin, C.N.; Mullin, K.; Hooli, B.; Choi, S.H.; Hyman, B.T.; Tanzi, R.E. Alzheimer’s disease risk gene CD33 inhibits microglial uptake of amyloid beta. Neuron 2013, 78, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, L.; Shang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Jin, S.; Guo, Z.; Wang, X. Concurrent suppression of Aβ aggregation and NLRP3 inflammasome activation for treating Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 2971–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, V.; Dye, R.; Pakavathkumar, P.; Foveau, B.; Flores, J.; Hyman, B.; Ghetti, B.; Koller, B.H.; LeBlanc, A.C. Neuronal NLRP1 inflammasome activation of Caspase-1 coordinately regulates inflammatory interleukin-1-beta production and axonal degeneration-associated Caspase-6 activation. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 1676–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Chen, Y.; Shen, X.; Xu, T.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ding, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, Y.; et al. Inhibition of NOX2-NLRP1 signaling pathway protects against chronic glucocorticoids exposure-induced hippocampal neuronal damage. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 74, 105721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, G.; Zeng, X.; Li, L. Thioredoxin-1 inhibits amyloid-β-induced activation of NLRP1/caspase-1/GSDMD pyroptotic pathway in PC12 cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 3445–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, R.; Hu, D.; Sun, X.; Fujioka, H.; Lundberg, K.; Chan, E.R.; Wang, Q.; Xu, R.; Flanagan, M.E.; et al. Oligodendroglial glycolytic stress triggers inflammasome activation and neuropathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb8680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Xiao, D.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, B.; Long, Z.; Yu, L.; He, G. Enhanced Autolysosomal Function Ameliorates the Inflammatory Response Mediated by the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 629891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.-Q.; Pan, R.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, X.-G.; Wu, J.-M.; Yu, L.; Law, B.Y.-K.; Ai, W.; Yu, C.-L.; Qin, D.-L.; et al. Lychee seed polyphenol inhibits Aβ-induced activation of NLRP3 inflammasome via the LRP1/AMPK mediated autophagy induction. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Zhou, X.-G.; Tang, Y.; Wu, J.-M.; Sun, Y.-S.; Teng, J.-F.; Pan, R.; Law, B.Y.-K.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, W.-Q.; et al. Lychee seed polyphenol protects the blood-brain barrier through inhibiting Aβ(25-35)-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation via the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1-mediated autophagy in bEnd.3 cells and APP/PS1 mice. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 954–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi, S.; Shamsi, S. MCC950 in the treatment of NLRP3-mediated inflammatory diseases: Latest evidence and therapeutic outcomes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 106, 108595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, S.S.; Guerrero-Munoz, M.J.; Castillo-Carranza, D.L. Tau Oligomers: Cytotoxicity, Propagation, and Mitochondrial Damage. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usenovic, M.; Niroomand, S.; Drolet, R.E.; Yao, L.; Gaspar, R.C.; Hatcher, N.G.; Schachter, J.; Renger, J.J.; Parmentier-Batteur, S. Internalized Tau Oligomers Cause Neurodegeneration by Inducing Accumulation of Pathogenic Tau in Human Neurons Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 14234–14250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskar, K.; Konerth, M.; Kokiko-Cochran, O.N.; Cardona, A.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Lamb, B.T. Regulation of tau pathology by the microglial fractalkine receptor. Neuron 2010, 68, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheedy, F.J.; Grebe, A.; Rayner, K.J.; Kalantari, P.; Ramkhelawon, B.; Carpenter, S.B.; Becker, C.E.; Ediriweera, H.N.; Mullick, A.E.; Golenbock, D.T.; et al. CD36 coordinates NLRP3 inflammasome activation by facilitating intracellular nucleation of soluble ligands into particulate ligands in sterile inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ising, C.; Venegas, C.; Zhang, S.; Scheiblich, H.; Schmidt, S.V.; Vieira-Saecker, A.; Schwartz, S.; Albasset, S.; McManus, R.M.; Tejera, D.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation drives tau pathology. Nature 2019, 575, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.S.; Tan, L.; Jiang, T.; Zhu, X.C.; Wang, H.F.; Jia, C.D.; Yu, J.T. Amyloid-beta induces NLRP1-dependent neuronal pyroptosis in models of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.M.; Fowler, S.W.; Miller, D.K.; Sun, A.Y.; Weisman, G.A.; Wood, W.G.; Sun, G.Y.; Simonyi, A.; Schachtman, T.R. Spatial learning and memory impairment and increased locomotion in a transgenic amyloid precursor protein mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 222, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanneganti, T.-D.; Özören, N.; Body-Malapel, M.; Amer, A.; Park, J.-H.; Franchi, L.; Whitfield, J.; Barchet, W.; Colonna, M.; Vandenabeele, P.; et al. Bacterial RNA and small antiviral compounds activate caspase-1 through cryopyrin/Nalp3. Nature 2006, 440, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Allen, H.; Banerjee, S.; Franklin, S.; Herzog, L.; Johnston, C.; Seshadri, T. Mice Deficient in IL-lp-Converting Enzyme Are Defective in Production of Mature IL-lp and Resistant to Endotoxic Shock. Cell Death Dis. 1995, 80, 401–411. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, M.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, T.; Teruyoshi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xue, C. Eicosapentaenoic Acid-Enriched Phosphatidylcholine Mitigated Abeta1-42-Induced Neurotoxicity via Autophagy-Inflammasome Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13767–13774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kong, L.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J. Osthole decreases tau protein phosphorylation via PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2019, 217, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kip, E.; Parr-Brownlie, L. Reducing neuroinflammation via therapeutic compounds and lifestyle to prevent or delay progression of Parkinson’s disease.Prevention of neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 78, 101618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massano, J.; Bhatia, K.P. Clinical approach to Parkinson’s disease: Features, diagnosis, and principles of management. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Med. 2012, 2, a008870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faustini, G.; Longhena, F.; Bruno, A.; Bono, F.; Grigoletto, J.; La Via, L.; Barbon, A.; Casiraghi, A.; Straniero, V.; Valoti, E.; et al. Alpha-synuclein/synapsin III pathological interplay boosts the motor response to methylphenidate. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 138, 104789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasser, T. Molecular pathogenesis of Parkinson disease: Insights from genetic studies. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2009, 11, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapira, A.H.; Bezard, E.; Brotchie, J.; Calon, F.; Collingridge, G.L.; Ferger, B.; Hengerer, B.; Hirsch, E.; Jenner, P.; Le Novere, N.; et al. Novel pharmacological targets for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicik, A.; Tuzun, E.; Erdogdu, E.; Bilgic, B.; Tufekcioglu, Z.; Ozturk-Isik, E.; Hanagasi, H.; Gurvit, H. Neuroinflammation Mediators are Reduced in Sera of Parkinson’s Disease Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Noro Psikiyatr. Ars. 2020, 57, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuttitta, G.; Cibella, F.; Bellia, V.; Grassi, V.; Cossi, S.; Bucchieri, S.; Bonsignore, G. Changes in FVC During Methacholine-Induced Bronchoconstriction in Elderly Patients With Asthma: Bronchial Hyperresponsiveness and Aging. Chest 2001, 119, 1685–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, M.J.; Gwinn, K.; Singleton, A.; Hardy, J. Parkinson’s disease and alpha-synuclein expression. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 2160–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, T.; Pei, Z.; Miller, D.S.; Wu, X.; Block, M.L.; Wilson, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Hong, J.S.; et al. Aggregated alpha-synuclein activates microglia: A process leading to disease progression in Parkinson’s disease. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, M.; Du, R.H.; Qiao, C.; Jiang, C.Y.; Zhang, K.Z.; Ding, J.H.; Hu, G. MicroRNA-7 targets Nod-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome to modulate neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Callaway, J.B.; Ting, J.P.Y. Inflammasomes: Mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panicker, N.; Sarkar, S.; Harischandra, D.S.; Neal, M.; Kam, T.I.; Jin, H.; Saminathan, H.; Langley, M.; Charli, A.; Samidurai, M.; et al. Fyn kinase regulates misfolded alpha-synuclein uptake and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in microglia. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 1411–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codolo, G.; Plotegher, N.; Pozzobon, T.; Brucale, M.; Tessari, I.; Bubacco, L.; de Bernard, M. Triggering of inflammasome by aggregated alpha-synuclein, an inflammatory response in synucleinopathies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, R.; Albornoz, E.A.; Christie, D.C.; Langley, M.R.; Kumar, V.; Mantovani, S.; Woodruff, T.M. Inflammasome inhibition prevents α-synuclein pathology and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaah4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litteljohn, D.; Mangano, E.; Clarke, M.; Bobyn, J.; Moloney, K.; Hayley, S. Inflammatory Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration in Toxin-Based Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Parkinson’s Dis. 2011, 2011, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, C.C.; Pott Godoy, M.C.; Tarelli, R.; Chertoff, M.; Depino, A.M.; Pitossi, F.J. Progressive neurodegeneration and motor disabilities induced by chronic expression of IL-1beta in the substantia nigra. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 24, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siew, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Chen, C.; Soong, B.; Wu, Y.; Chang, C.; Chan, Y.; Lin, C.; et al. Galectin-3 is required for the microglia-mediated brain inflammation in a model of Huntington’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panicker, N.; Kam, T.-I.; Wang, H.; Neifert, S.; Chou, S.-C.; Kumar, M.; Brahmachari, S.; Jhaldiyal, A.; Hinkle, J.T.; Akkentli, F.; et al. Neuronal NLRP3 is a parkin substrate that drives neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 2022, 110, 2422–2437.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piancone, F.; Saresella, M.; La Rosa, F.; Marventano, I.; Meloni, M.; Navarro, J.; Clerici, M. Inflammatory Responses to Monomeric and Aggregated alpha-Synuclein in Peripheral Blood of Parkinson Disease Patients. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 639646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, M.E.; Ambrose, C.M.; Duyao, M.P.; Myers, R.H.; Lin, C.; Srinidhi, L.; Harper, P.S. A Novel Gene Containing a Trinucleotide Repeat That Is Expanded and Unstable on Huntington’s Disease Chromosomes. Cell 1993, 72, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinsky, G.V. SNP-guided microRNA maps (MirMaps) of 16 common human disorders identify a clinically accessible therapy reversing transcriptional aberrations of nuclear import and inflammasome pathways. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 3564–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Wang, S.-F.; Weng, I.C.; Hong, M.-H.; Lo, T.-H.; Jan, J.-T.; Hsu, L.-C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Liu, F.-T. Galectin-3 Enhances Avian H5N1 Influenza A Virus–Induced Pulmonary Inflammation by Promoting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Chen, M.; Fan, Y.; Ding, J.; Lu, M.; Hu, G. Inhibition of the hepatic Nlrp3 protects dopaminergic neurons via attenuating systemic inflammation in a MPTP/p mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Gao, Y.; Nie, K.; Wang, L. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor meditates MPP+/MPTP-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation in microglia cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao = J. South. Med. Univ. 2021, 41, 972–979. [Google Scholar]
- Marcellino, D.; Suárez-Boomgaard, D.; Sánchez-Reina, M.D.; Aguirre, J.A.; Yoshitake, T.; Yoshitake, S.; Hagman, B.; Kehr, J.; Agnati, L.F.; Fuxe, K.; et al. On the role of P2X7 receptors in dopamine nerve cell degeneration in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease: Studies with the P2X7 receptor antagonist A-438079. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, G.N.; Zhang, H.; Sharma, A.; Ren, X. Innate immunity receptors in depression and suicide: Upregulated NOD-like receptors containing pyrin (NLRPs) and hyperactive inflammasomes in the postmortem brains of people who were depressed and died by suicide. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2021, 46, E538–E547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhu, X.; Mi, W.; Maoying, Q.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y. Hippocampal PKR/NLRP1 Inflammasome Pathway Is Required for the Depression-Like Behaviors in Rats with Neuropathic Pain. Neuroscience 2019, 412, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Boyle, M. Neuroscience of Addiction: Relevance to Prevention and Treatment. Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northrop, N.A.; Halpin, L.E.; Yamamoto, B.K. Peripheral ammonia and blood brain barrier structure and function after methamphetamine. Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudiasl, G.R.; Abbaszadeh, H.A.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Abdollahifar, M.A.; Khoramgah, M.S.; Niknazar, S.; Darabi, S.; Roozbahany, N.A. Nod-like receptor protein 3 and nod-like receptor protein 1 inflammasome activation in the hippocampal region of postmortem methamphetamine chronic user. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2019, 120, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, M.W.; Stevens, B. Microglia emerge as central players in brain disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Huang, E.; Tai, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Chen, R.; Liu, C.; Lin, Z.; Wang, H.; et al. Nupr1 Modulates Methamphetamine-Induced Dopaminergic Neuronal Apoptosis and Autophagy through CHOP-Trib3-Mediated Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Signaling Pathway. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Du, L.; Zhou, R.; Wu, X.; Shen, K.; Yao, H. Molecular mechanisms underlying the involvement of the sigma-1 receptor in methamphetamine-mediated microglial polarization. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Shen, K.; Bai, Y.; Chao, J.; Hu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, H. Involvement of NLRP3 inflammasome in methamphetamine-induced microglial activation through miR-143/PUMA axis. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 301, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, H.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Si, Z.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y. The effect of the NLRP1 inflammasome on methamphetamine-induced cognitive impairment in rats. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2022, 237, 109537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wen, D.; Gao, J.; Xie, B.; Yu, H.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Jing, W.; Cong, B.; Ma, C. Methamphetamine induces GSDME-dependent cell death in hippocampal neuronal cells through the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Brain Res. Bull 2020, 162, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, S.; Chitti, S.V.P.; Nair, M.P.N.; Saxena, S.K. Interactive effects of cocaine on HIV infection: Implication in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder and neuroAIDS. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraj, A.; Periyasamy, P.; Guo, M.-L.; Chivero, E.T.; Callen, S.; Buch, S. Mitigation of cocaine-mediated mitochondrial damage, defective mitophagy and microglial activation by superoxide dismutase mimetics. Autophagy 2020, 16, 289–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivero, E.T.; Thangaraj, A.; Tripathi, A.; Periyasamy, P.; Guo, M.-L.; Buch, S. NLRP3 Inflammasome Blockade Reduces Cocaine-Induced Microglial Activation and Neuroinflammation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 2215–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pedrajas, R.; Ramírez-Lamelas, D.T.; Muriach, B.; Sánchez-Villarejo, M.V.; Almansa, I.; Vidal-Gil, L.; Romero, F.J.; Barcia, J.M.; Muriach, M. Cocaine promotes oxidative stress and microglial-macrophage activation in rat cerebellum. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirshahrokhi, K.; Niapour, A. Methylsulfonylmethane protects against ethanol-induced brain injury in mice through the inhibition of oxidative stress, proinflammatory mediators and apoptotic cell death. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 106, 108638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, C.J.; Drew, P.D. Inflammatory responses to alcohol in the CNS: Nuclear receptors as potential therapeutics for alcohol-induced neuropathologies. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blednov, Y.A.; Benavidez, J.M.; Black, M.; Leiter, C.R.; Osterndorff-Kahanek, E.; Johnson, D.; Borghese, C.M.; Hanrahan, J.R.; Johnston, G.A.; Chebib, M.; et al. GABAA receptors containing rho1 subunits contribute to in vivo effects of ethanol in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Wang, X.; Ji, Z.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.P.; Chang, C.H.; Li, R.; Zhang, H.; Nel, A.E.; Xia, T. NADPH Oxidase-Dependent NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and its Important Role in Lung Fibrosis by Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Small 2015, 11, 2087–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.B.; Park, H.H. Purification and analysis of the interactions of caspase-1 and ASC for assembly of the inflammasome. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 2883–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proell, M.; Gerlic, M.; Mace, P.D.; Reed, J.C.; Riedl, S.J. The CARD plays a critical role in ASC foci formation and inflammasome signalling. Biochem. J. 2013, 449, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyet, J.L.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Tnani, M.; Razmara, M.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Alnemri, E.S. Identification of Ipaf, a human caspase-1-activating protein related to Apaf-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 28309–28313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippai, D.; Bala, S.; Petrasek, J.; Csak, T.; Levin, I.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Szabo, G. Alcohol-induced IL-1β in the brain is mediated by NLRP3/ASC inflammasome activation that amplifies neuroinflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Bare, D.; DeSantiago, J.; Zhao, W.; Mei, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ginsburg, K.; Solaro, R.; Wolska, B.; Bers, D.; et al. JNK2, a Newly-Identified SERCA2 Enhancer, Augments an Arrhythmic [Ca] Leak-Load Relationship. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Lee, H.; Jung, Y.; Kim, J.; Chae, C.; Kim, S.; Han, H. Ethanol-activated CaMKII signaling induces neuronal apoptosis through Drp1-mediated excessive mitochondrial fission and JNK1-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2020, 18, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tong, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Downregulation of ROCK2 attenuates alcohol-induced inflammation and oxidative stress in astrocytes. Int. J. Neurosci. 2020, 132, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Su, L.-Y.; Sun, C.; Jiao, L.; Miao, Y.; Xu, M.; Luo, R.; Zuo, X.; Zhou, R.; Zheng, P.; et al. Melatonin alleviates morphine analgesic tolerance in mice by decreasing NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Redox Biol. 2020, 34, 101560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Huang, M.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Luo, L.; Xu, X.; Xu, L.; Shi, H.; Xu, Y.; et al. Microglial TLR4-induced TAK1 phosphorylation and NLRP3 activation mediates neuroinflammation and contributes to chronic morphine-induced antinociceptive tolerance. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 165, 105482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Kong, H.; Pan, Y.-B.; Jiang, L.; Pan, X.-X.; Hu, L.; Qian, Y.-N.; Jiang, C.-Y.; Liu, W.-T. Procyanidins alleviates morphine tolerance by inhibiting activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F. NSAID Exposure and Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease: An Updated Meta-Analysis From Cohort Studies. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.; Armbruster, K.; Silva, J.; Widell, D.J.; Cheng, F. The Association between the Usage of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Cognitive Status: Analysis of Longitudinal and Cross-Sectional Studies from the Global Alzheimer’s Association Interactive Network and Transcriptomic Data. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Structure | Model | Findings | Clinical Advance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rg1 | 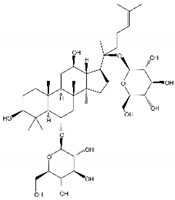 | APP/PS1 mice | hippocampus and cortex of mice Aβ↓. | [30,31] | |
| JC-124 | 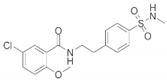 | CRND8 APP transgenic mice (TgCRND8) | Aβ, Aβ1-42↓ | [32,33,34] | |
| MCC950 (CRID3) | 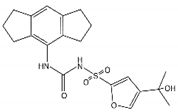 | In vitro cell culture model of Alzheimer’s disease (SH-APP cells); METH use disorder. | caspase-1 and IL-1β levels, tau, Aβ↓; Capase-1, lysosomal histone B activity, ROS↓. | [35] | |
| Osthole |  | APP/PS1 double transfected mice | hippocampal tau↓ | [36,37] | |
| Probenecid | 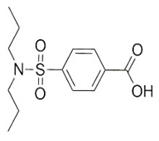 | Aged rats | Inflammasome activation↓ spatial learning performance↑. | [38,39] | |
| EA (Ellagic acid) | 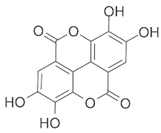 | LPS induced rat DA neuronal (MN9D, BV-2 cell line) damage model. NLRP3 siRNA. | Neuroprotection. | [40] | |
| SAFE (Safflower Flavonoid Extract) | 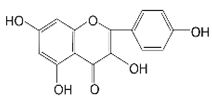 | 6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced rat model of Parkinson’s disease | NLRP3 inflammasome activation ↓ | [41] | |
| NAR(Naringin) |  | Rat nigral stereotaxic injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). NLRP3 siRNA. | Neuroprotection. | [42] | |
| ECH(Echinacoside) | 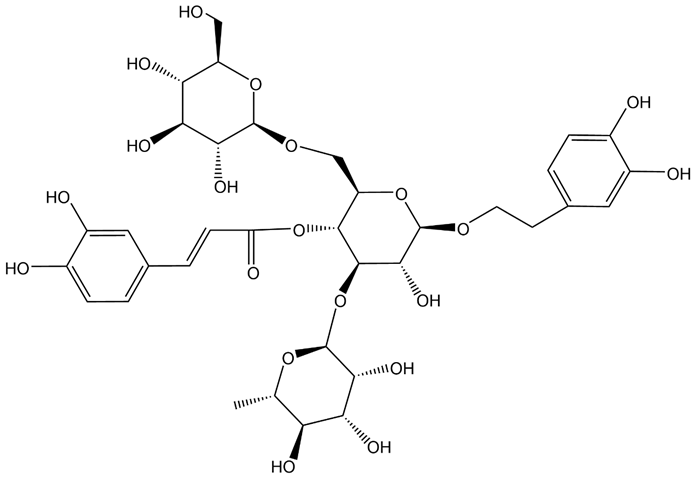 | Mice model of Parkinson’s disease | NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1β signaling pathway↓. | [43] | |
| Laquinimod | 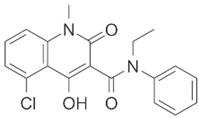 | Parkinson’s disease | [44] | ||
| PAP(Papaverine) | 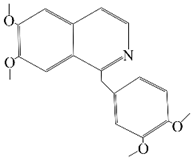 | Mice model mice of Huntington’s disease | Regulation of NF-κB and CREB signaling pathways to inhibit NLRP3. | [45] | |
| RRx-001 | 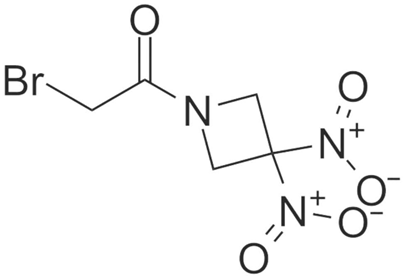 | Hunting’s disease | NLRP3↓. | [46,47] | |
| DSF(Disulfiram) | 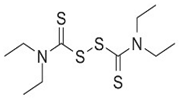 | Alcohol use disorder | ROS and NLRP3↓ | Alcohol use disorder | [48] |
| Cod liver oil | 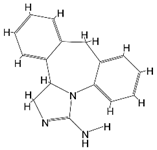 | Alcohol consumption↓ | Alcohol use disorder | [49] |
| Diseases | Drugs | Pathways | Pathological Changes | Performance | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s disease | Rg1, JC-124, CR2D3, EPA-PC, OST, Probenecid | K+/Ca2+-NLRP-Caspase1-IL-1β | Aβ deposition, tau protein entanglement. | Loss of memory function and cognitive decline. | [51,53,56,63,65] | |
| Parkinson’s disease | EA, SAFE, NAR, ECH, Laquinimod | a-Syn-NLRP-Caspase1 | Decrease in dopaminergic neurons and formation of Lewy bodies. | The Campaign Triad. | [83,89,95,97,100] | |
| Huntington’s disease | PAP, MCC950 | Gal3-NLRP3-IL-1β | Inclusion body formation, brain atrophy. | Motor, cognitive impairment. | [101,102,104,105] | |
| Depression | caspase3-NLRP-IL-1β | Inflammatory lesion. | Persistent depression and loss of interest. | [109,110] | ||
| Drug use disorder | METH | MCC950 | NLRP-Caspase-1-IL-1β | ASC protein aggregation and increased autophagosomes. | Cognitive dysfunction, schizophrenia. | [114,115,117,119] |
| Cocaine | MCC950 | ROS/NLRP | Oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. | Nervous and mental injury. | [120,123] | |
| Alcohol | Cod liver oil, VX765 | CaMKII/JNK1-NLRP1 | Lysosomal and mitochondrial damage. | Central nervous system lesions, behavioral disorders. | [125,127] | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.; Qian, L.; Luo, H.; Li, X.; Ruan, Y.; Fan, R.; Si, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, Y. The Significance of NLRP Inflammasome in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081057
Shen Y, Qian L, Luo H, Li X, Ruan Y, Fan R, Si Z, Chen Y, Li L, Liu Y. The Significance of NLRP Inflammasome in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(8):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081057
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yao, Liyin Qian, Hu Luo, Xiaofang Li, Yuer Ruan, Runyue Fan, Zizhen Si, Yunpeng Chen, Longhui Li, and Yu Liu. 2022. "The Significance of NLRP Inflammasome in Neuropsychiatric Disorders" Brain Sciences 12, no. 8: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081057
APA StyleShen, Y., Qian, L., Luo, H., Li, X., Ruan, Y., Fan, R., Si, Z., Chen, Y., Li, L., & Liu, Y. (2022). The Significance of NLRP Inflammasome in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Brain Sciences, 12(8), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081057







