A Novel Perspective on Ischemic Stroke: A Review of Exosome and Noncoding RNA Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Inclusion Criteria
3. The Potential Diagnostic Value of Exosomal Noncoding RNAs in Ischemic Stroke
3.1. The Expression Profile of Exosomal Long Noncoding RNAs
3.2. The Expression Profile of Exosomal Circular RNAs
4. The Involvement of Exosomal Noncoding RNAs in the Pathophysiological Process of Ischemic Stroke
4.1. Exosomal Long Noncoding RNAs in the Process of Ischemic Stroke
4.1.1. Exosomal LncRNA RMRP
4.1.2. Exosomal LncRNA MALAT1
4.2. Exosomal Circular RNAs in the Process of Ischemic Stroke
4.2.1. Exosomal CircSHOC2
4.2.2. Exosomal CircRNA-0006896
4.2.3. Exosomal CircOGDH
4.2.4. Exosomal circ_0000647
4.2.5. Exosomal circFUNDC1
4.2.6. Exosomal CircAkap7
4.2.7. Exosomal Circ-Rps5
5. Recent Advances in Exosome Applications in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke
6. Therapeutic Prospects of Exosomal Noncoding RNAs in the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke
7. Future Work and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Stark, B.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Roth, G.A.; Bisignano, C.; Abady, G.G.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abedi, V.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Alonso, A.; Beaton, A.Z.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; Carson, A.P.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2022 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 145, e153–e639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauch, E.C.; Saver, J.L.; Adams, H.P., Jr.; Bruno, A.; Connors, J.J.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Khatri, P.; McMullan, P.W., Jr.; Qureshi, A.I.; Rosenfield, K.; et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the American heart association/American stroke association. Stroke 2018, 49, e46–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, J.H. A comprehensive review on factors influences biogenesis, functions, therapeutic and clinical implications of exosomes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Niel, G.; d’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Du, W.; Liu, J.; Ma, W.; Zhang, L.; Du, Z.; Cai, B. Stem cell-derived exosome in cardiovascular diseases: Macro roles of micro particles. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Cosmopoulos, K.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Hopmans, E.S.; Lindenberg, J.L.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Würdinger, T.; Middeldorp, J.M. Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6328–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, H.; Im, H.; Castro, C.M.; Breakefield, X.; Weissleder, R.; Lee, H. New technologies for analysis of extracellular vesicles. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1917–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Gould, S.J. Exosomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 487–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhu, R. Long noncoding RNAs as diagnostic and therapeutic targets for ischemic stroke. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, R. Circular RNAs: Novel diagnostic and therapeutic targets for ischemic stroke. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhuang, C.; Chen, L. Exosomal long non-coding RNA expression from serum of patients with acute minor stroke. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Qu, M.J.; Wang, K.; Ma, A.J.; Pan, X.D.; Zhu, X.Y. Novel Insights into the Potential Diagnostic Value of Circulating Exosomal IncRNA-Related Networks in Large Artery Atherosclerotic Stroke. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Yin, R.; Xiao, Q.; Ding, Y.; Zhu, X.; Pan, X. Circulating exosomal lncRNAs as predictors of risk and unfavorable prognosis for large artery atherosclerotic stroke. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Huang, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Y.; Liang, B.; Gu, L.; Su, L. Analysis of expression profiles and bioinformatics suggests that plasma exosomal circular RNAs may be involved in ischemic stroke in the Chinese Han population. Metab. Brain Dis. 2022, 37, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Yin, R.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Ma, A.; Pan, X.; Zhu, X. Comprehensive analysis of peripheral exosomal circRNAs in large artery atherosclerotic stroke. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 685741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Hou, R.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Pan, X. Circulating exosomal circRNAs contribute to potential diagnostic value of large artery atherosclerotic stroke. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 830018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Luo, L. Exosomes from Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Ameliorate Ischemic Injuries by Suppressing the RNA Component of Mitochondrial RNA-processing Endoribonuclease via the Induction of miR-206/miR-1-3p Levels. Neuroscience 2021, 476, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Feng, J.; Chen, L. Exosome-shuttled circSHOC2 from IPASs regulates neuronal autophagy and ameliorates ischemic brain injury via the miR-7670-3p/SIRT1 axis. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 657–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Chun, Y.; Lian, Z.Q.; Yong, Z.W.; Lan, Y.M.; Huan, L.; Xi, C.Y.; Juan, L.S.; Qing, Z.W.; Jia, C.; et al. circRNA-0006896-miR1264-DNMT1 axis plays an important role in carotid plaque destabilization by regulating the behavior of endothelial cells in atherosclerosis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zang, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Tan, Z.; Ma, D.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. CircOGDH Is a Penumbra Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 907–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, X.; Xu, T. Circ_0000647 promotes cell injury by modulating miR-126-5p/TRAF3 axis in oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion-induced SK-N-SH cell model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 104, 108464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, H.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; Zhou, D. CircFUNDC1 knockdown alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced human brain microvascular endothelial cell injuries by inhibiting PTEN via miR-375. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 770, 136381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ji, H.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, L.; Lai, X.; Wu, F.; Hu, R.; Yang, X.; Bao, H.; Jiang, M. Exosomes derived from CircAkap7-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect against cerebral ischemic injury. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Tu, Z.; Yang, D.; Hu, M.; Zhou, L.; Li, Q.; Yu, B.; Hou, S. Exosomes from hypoxic pre-treated ADSCs attenuate acute ischemic stroke-induced brain injury via delivery of circ-Rps5 and promote M2 microglia/macrophage polarization. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 769, 136389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Han, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Du, L.; Xu, L.; Wu, F.; et al. Extracellular vesicle–mediated delivery of circular RNA SCMH1 promotes functional recovery in rodent and nonhuman primate ischemic stroke models. Circulation 2020, 142, 556–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Lee, Y.; Lee, M. Hypoxia-specific anti-RAGE exosomes for nose-to-brain delivery of anti-miR-181a oligonucleotide in an ischemic stroke model. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 14166–14178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, T.C.; Morris, K.V.; Weinberg, M.S. Perspectives on the mechanism of transcriptional regulation by long non-coding RNAs. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, H.; Liu, B.; Dun, L.; Lu, C.; Cai, Y.; Wang, H. Suppression of lncRNA RMRP ameliorates oxygen-glucose deprivation/re-oxygenation-induced neural cells injury by inhibiting autophagy and PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated apoptosis. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Bassit, G.; Patel, R.S.; Carter, G.; Shibu, V.; Patel, A.A.; Song, S.; Murr, M.; Cooper, D.R.; Bickford, P.C.; Patel, N.A. MALAT1 in Human Adipose Stem Cells Modulates Survival and Alternative Splicing of PKC δ II in HT22 Cells. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 183–195. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, N.A.; Moss, L.D.; Lee, J.Y.; Tajiri, N.; Acosta, S.; Hudson, C.; Parag, S.; Cooper, D.R.; Borlongan, C.V.; Bickford, P.C. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 in exosomes drives regenerative function and modulates inflammation-linked networks following traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Liu, K.; Hamblin, M.H.; Yin, K.J. Long noncoding RNA Malat1 regulates cerebrovascular pathologies in ischemic stroke. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Zhang, L.; Zu, J.; Wang, Z.; Han, B.; Chen, B.; Cheng, M.; Ju, M.; Li, M.; Shu, G.; et al. Circulating circular RNAs as biomarkers for the diagnosis and prediction of outcomes in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Graf, I.; Kuang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Haupt, M.; Majid, A.; Kilic, E.; Hermann, D.M.; Psychogios, M.N.; Weber, M.S.; et al. Neural progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles enhance blood-brain barrier integrity by NF-κB (Nuclear Factor-κB)-dependent regulation of ABCB1 (ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter B1) in stroke mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 1127–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Jiang, C. Evolution of blood–brain barrier in brain diseases and related systemic nanoscale brain-targeting drug delivery strategies. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2306–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.; Pan, J.J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, G.Y. Native and Bioengineered Exosomes for Ischemic Stroke Therapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, Y.; Hira, K.; Miyamoto, N.; Kijima, C.; Inaba, T.; Hattori, N. Pleiotropic effects of exosomes as a therapy for stroke recovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Chen, W.; Ye, J.; Wang, Y. Potential Role of Exosomes in Ischemic Stroke Treatment. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, T.; Jiang, C. Recent advances in nanomedicines for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1767–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Bai, Y.; Min, S.; Xu, X.; Tang, T.; Ju, S. In vivo monitoring and assessment of exogenous mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in mice with ischemic stroke by molecular imaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Buller, B.; Chopp, M. Exosomes—beyond stem cells for restorative therapy in stroke and neurological injury. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zhang, H.X.; He, C.P.; Fan, S.; Zhu, Y.L.; Qi, C.; Huang, N.P.; Xiao, Z.D.; Lu, Z.H.; Tannous, B.A.; et al. Surface functionalized exosomes as targeted drug delivery vehicles for cerebral ischemia therapy. Biomaterials 2018, 150, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ling, C.L.; Pang, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.X.; Wang, B.S.; Liang, J.M.; Guo, Y.Z.; Qin, J.; Wang, J.X. Direct macromolecular drug delivery to cerebral ischemia area using neutrophil-mediated nanoparticles. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kim, T.J.; Kang, L.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, M.K.; Kim, J.; Ryu, J.H.; Hyeon, T.; Yoon, B.W.; Ko, S.B.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived magnetic extracellular nanovesicles for targeting and treatment of ischemic stroke. Biomaterials 2020, 243, 119942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Cao, L.; He, C.; Ye, Q.; Liang, R.; You, W.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Ye, J.; Tannous, B.A.; et al. Targeted delivery of neural progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles for anti-inflammation after cerebral ischemia. Theranostics 2021, 11, 6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Chen, W.; Waqas, A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Exosomes derived from human neural stem cells stimulated by interferon gamma improve therapeutic ability in ischemic stroke model. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 24, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Fan, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Zang, J.; Ye, J.; Xiao, M.; et al. Exosome-mediated targeted delivery of miR-210 for angiogenic therapy after cerebral ischemia in mice. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Kim, G.; Hwang, D.W.; Lee, M. Delivery of high mobility group box-1 siRNA using brain-targeting exosomes for ischemic stroke therapy. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2019, 15, 2401–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munagala, R.; Aqil, F.; Jeyabalan, J.; Kandimalla, R.; Wallen, M.; Tyagi, N.; Wilcher, S.; Yan, J.; Schultz, D.J.; Spencer, W.; et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of RNA and DNA for gene therapy. Cancer Lett. 2021, 505, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.C.; Wang, Z.L.; Xu, T.; He, Z.Y.; Wei, Y.Q. The approved gene therapy drugs worldwide: From 1998 to 2019. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 40, 107502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H.; Betts, C.; Lakhal, S.; Wood, M.J. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorshkov, A.; Purvinsh, L.; Brodskaia, A.; Vasin, A. Exosomes as natural nanocarriers for RNA-based therapy and prophylaxis. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, T.; Shan, Y.; Li, G.; Ni, X.; Chen, X.; Hu, X.; Lin, L.; Li, Y.; Guan, Y.; et al. Therapeutic reversal of Huntington’s disease by in vivo self-assembled siRNAs. Brain 2021, 144, 3421–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, A.; Grunseich, C. Hitching a ride on exosomes: A new approach for the delivery of siRNA-mediated therapies. Brain 2021, 144, 3286–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 endothelial cell
endothelial cell  migroglia
migroglia  neuron
neuron  SK-N-SH cells
SK-N-SH cells  astrocyte
astrocyte  adipose-derived stem cell. (The italic represents detrimental effect of stroke).
adipose-derived stem cell. (The italic represents detrimental effect of stroke).
 endothelial cell
endothelial cell  migroglia
migroglia  neuron
neuron  SK-N-SH cells
SK-N-SH cells  astrocyte
astrocyte  adipose-derived stem cell. (The italic represents detrimental effect of stroke).
adipose-derived stem cell. (The italic represents detrimental effect of stroke).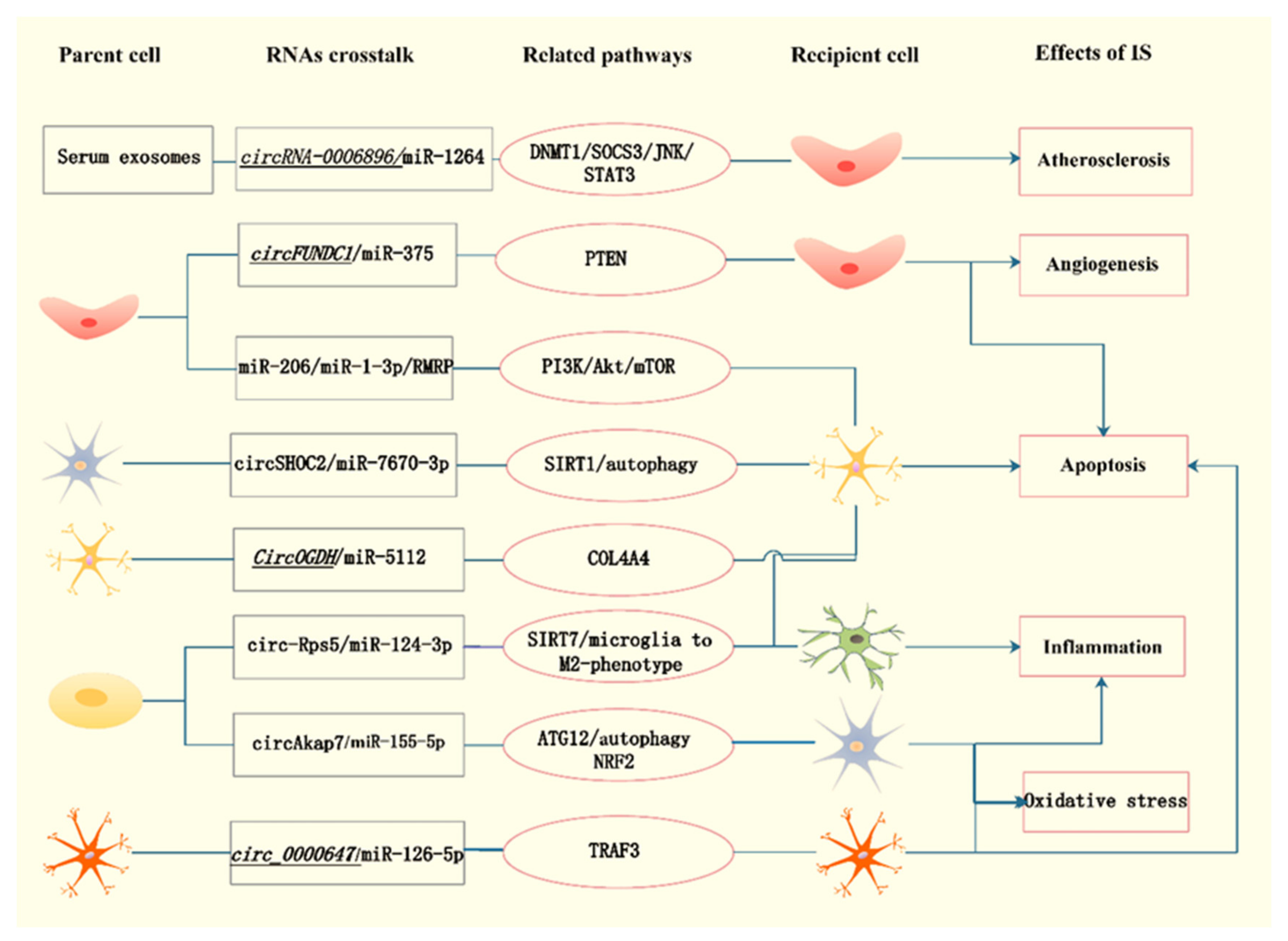
| Models and Tissues | Detection Method | Changes of Expression Profiles | Focal ncRNAs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exosomes from peripheral serum in stroke patients | RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR | 1096 lncRNAs covering 307 showed elevated expression while 789 showed decline | lnc-CRKL-2 and lnc-NTRK3-4 ↑ RPS6KA2-AS1 and lnc-CALM1-7 ↓ | Xu [16] |
| Exosomes from peripheral plasma in stroke patients | HTS and qRT-PCR | 1020 lncRNAs were differentially expressed, 226 lncRNAs increased and 794 lncRNAs decreased levels | Most: novel lnc_000288 ↑; novel lnc_000285 ↓ lnc_002015/hsa-mir342/PTPRC/AAMP; lnc001350/hsa-mir-3127/ST14 | Zhang [17] |
| Exosomes from peripheral plasma in stroke patients | RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR | 319 lncRNAs including 97 increased expression and 222 showed reduction | lnc_000048, lnc_001350 and lnc_016442 ↑ lnc_002015 ↓ | Zhang [18] |
| Exosomes from peripheral plasma in stroke patients | HTS | 3540 circRNAs, 1177 increased expression and 2363 decrease expression | / | Xu [19] |
| Exosomes from peripheral plasma in stroke patients | RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR | 25 circRNAs, 9 circRNAs were significantly upregulated and 16 circRNAs were significantly downregulated | hsa_circ_0000698/hsa_circ_0002775/hsa_circ_0005585/hsa_circ_0043837 ↓; hsa-miR-16 ↑; VWF ↓; novel_circ_0010155 ↓; hsa-miR-939 ↑; septin 9 and MYLK2 ↓ | Xiao [20] |
| Exosomes from peripheral plasma in stroke patients | RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR | 26 circRNAs, 7 circRNAs were significantly upregulated and 19 circRNAs were significantly downregulated | circ_0043837 circ_0001801 | Xiao [21] |
| Source | RNA | Expression | Target/Mechanisms | Function/Effects of Dysregulation | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exosomes from HUVECs subjected to OGD | lncRNA RMRP | / | miR-206, miR-1-3p and RMRP/PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway | Increased cell viability and decreased infarct volume by regulating apoptosis and inducing eNOS activation | Zhong [22] |
| Exosomes from ischemic-preconditioned astrocytes | circSHOC2 | Upregulation | circSHOC2/miR-7670-3p/SIRT1 | Decreased infarct volume and neurobehavioral deficits by reducing neuronal apoptosis via regulating autophagy | Chen [23] |
| Serum exosomes from patients with carotid plaque | circRNA-0006896 | Increased levels in UA group | circRNA-0006896-miR1264-DNMT1/SOCS3/JNK/STAT3 axis | Promoted endothelial cell migration and proliferation, induced plaque destabilization | Yan [24] |
| Exosomes from ischemic mouse primary cortical neurons and plasma of AIS patients | CircOGDH | Upregulation | CircOGDH/miR-5112/COL4A4 | Knockdown relieved neuronal injury by inhibiting apoptosis The expression was positively related to the size of penumbra in AIS patients | Liu [25] |
| Exosomes from OGD/R-induced SK-N-SH cells | circ_0000647 | Upregulation | circ_0000647/miR-126-5p/TRAF3 | Accelerate apoptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress and inhibit cell proliferation | Dai [26] |
| Serum exosomes from AIS patients | circFUNDC1 | Upregulation | circFUNDC1/miR-375/PTEN | Knockdown promoted cell survival and angiogenesis | Bai [27] |
| Exosomes from ADSCs | circAkap7 | / | circAkap7/miR-155-5p/ATG12, NRF2 | Protected against cerebral ischemic injury by promoting autophagy and inhibiting oxidative stress | Xu [28] |
| Exosomes from ADSCs | cir_Rps5 | Upregulation | cir_Rps5/miR-124-3p/SIRT7 axis | Improved ischemic induced cognitive function via decreasing neuronal damage in the hippocampus | Yang [29] |
| RVG-circSCMH1-EVs | circular RNA SCMH1 | / | circSCMH1/MeCP2/Mobp, Igfbp3, Fxyd1, and Prodh | Enhanced functional recovery including promotion of brain plasticity, reduced glial activation, and peripheral immune cell infiltration | Yang [30] |
| RBP-Exo/AMO181a-chol | miR-181a | / | Bcl-2 | Decreased infarct volume by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis | Kim [31] |
| Origin | Cargo | Function | Target | Implication | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neural progenitor cell | / | Inhibited NF-κB signaling pathway | ECs, astrocytes | Enhanced BBB integrity poststroke | Zhang [38] |
| Mesenchymal stromal cell | Curcumin | Biochemically engineered cRGD-Exo | Microglia, neurons, astrocytes. | Inhibited inflammation and cellular apoptosis | Tian [46] |
| Aqueous suspension | / | Constructed cl PGP-PEG-DGL/CAT-Aco NPs ROS-mediated apoptosis | Neuronal cells | Reduce infarct volume through suppressing inflammation | Zhang [47] |
| Mesenchymal stem cell | Therapeutic growth factors | Constructed MSC-IONP-derived magnetic nanovesicles | ECs, neuronal cells, macrophages | Decreased infarction volume and improved motor function via angiogenesis, anti-inflammation and anti-apoptosis | Kim [48] |
| Neural progenitor cell | MiRNAs | Constructed RGD-EV MAPK signal pathway | Microglia | Improved targeting ability to the ischemic lesion and suppressed poststroke inflammation | Tian [49] |
| Neural stem cell | MiRNAs | Constructed IFN-γ-hNSC-Exo | Neurons, microglia | Reduced infarct volume and facilitated the neurological functional recovery by increasing cell proliferation and survival, decreasing cell apoptosis and inflammation | Zhang [50] |
| Mesenchymal stromal cell | MiR-210 | Constructed RGD-Exo | ECs | Improved microvascular angiogenesis by upregulating VEGF expression | Zhang [51] |
| HEK293T cells | HMGB1- siRNA | Constructed RVG-Exo | Neuro2A cells | Reduced infarct volume by suppressing TNF-α expression and cell apoptosis | Kim [52] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Meng, L.; Yin, J.; Wang, L.; Gong, T. A Novel Perspective on Ischemic Stroke: A Review of Exosome and Noncoding RNA Studies. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081000
Wang Q, Chen Y, Meng L, Yin J, Wang L, Gong T. A Novel Perspective on Ischemic Stroke: A Review of Exosome and Noncoding RNA Studies. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(8):1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081000
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qianwen, Yuhui Chen, Lingbing Meng, Jiawen Yin, Li Wang, and Tao Gong. 2022. "A Novel Perspective on Ischemic Stroke: A Review of Exosome and Noncoding RNA Studies" Brain Sciences 12, no. 8: 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081000
APA StyleWang, Q., Chen, Y., Meng, L., Yin, J., Wang, L., & Gong, T. (2022). A Novel Perspective on Ischemic Stroke: A Review of Exosome and Noncoding RNA Studies. Brain Sciences, 12(8), 1000. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12081000






