Verbal Encoding Deficits Impact Recognition Memory in Atypical “Non-Amnestic” Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Characteristics
2.2. Memory Testing and the Neuropsychological Battery
2.3. Neuroimaging Data Acquisition and Analysis
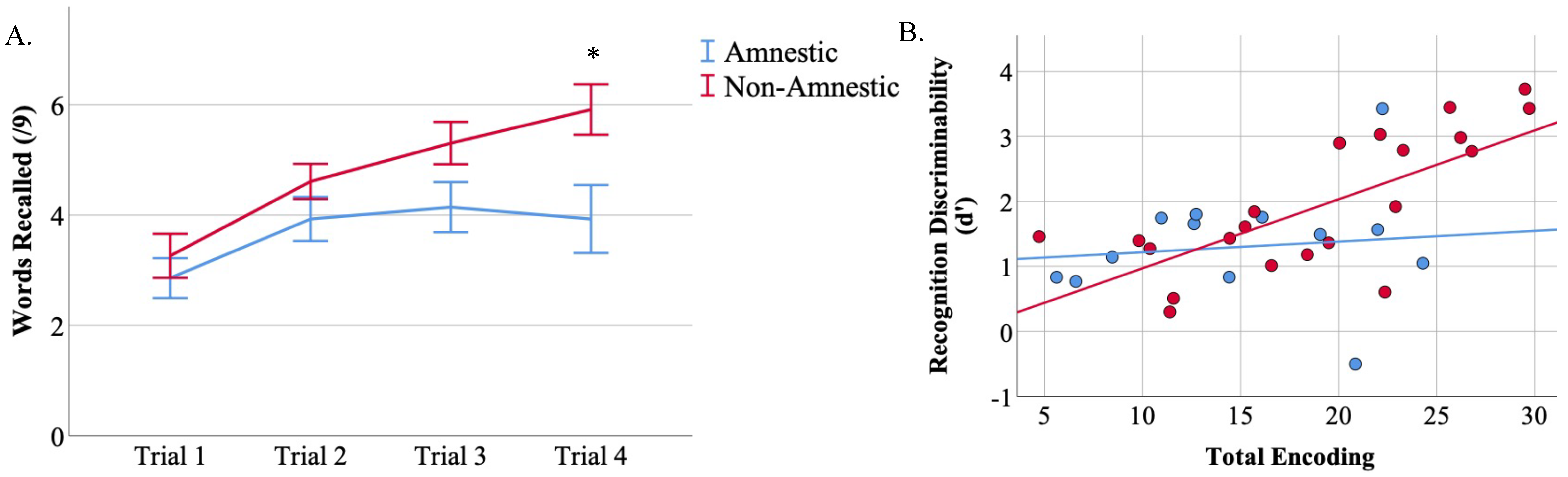
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Cognitive Characteristics
3.2. CVLT-II-SF Performance
3.3. Recognition Memory Is Impaired across Atypical Aß + AD Syndromes
3.4. Total Encoding Is Related to d’ in Non-Amnestic Atypical AD
3.5. Retention Is Related to d’ in Non-Amnestic AD
3.6. Total Encoding and d’ Are Related to Atrophy in Dissociable Cortical Regions
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jack, C.R., Jr.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Feldman, H.H.; Frisoni, G.B.; Hampel, H.; Jagust, W.J.; Johnson, K.A.; Knopman, D.S.; et al. A/T/N: An unbiased descriptive classification scheme for Alzheimer disease biomarkers. Neurology 2016, 87, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crutch, S.J.; Schott, J.M.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Murray, M.; Snowden, J.S.; van der Flier, W.M.; Dickerson, B.C.; Vandenberghe, R.; Ahmed, S.; Bak, T.H.; et al. Consensus classification of posterior cortical atrophy. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 870–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorno-Tempini, M.L.; Hillis, A.E.; Weintraub, S.; Kertesz, A.; Mendez, M.; Cappa, S.F.; Ogar, J.M.; Rohrer, J.D.; Black, S.; Boeve, B.F.; et al. Classification of primary progressive aphasia and its variants. Neurology 2011, 76, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benson, D.F.; Davis, R.J.; Snyder, B.D. Posterior cortical atrophy. Arch. Neurol. 1988, 45, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang-Wai, D.F.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Parisi, J.E.; Crook, R.; Caselli, R.J.; Knopman, D.S.; Petersen, R.C. Clinical, genetic, and neuropathologic characteristics of posterior cortical atrophy. Neurology 2004, 63, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutch, S.J.; Lehmann, M.; Warren, J.D.; Rohrer, J.D. The language profile of posterior cortical atrophy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.; Loane, C.; Bartels, S.; Zamboni, G.; Mackay, C.; Baker, I.; Husain, M.; Thompson, S.; Hornberger, M.; Butler, C. Lateral parietal contributions to memory impairment in posterior cortical atrophy. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 20, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putcha, D.; McGinnis, S.M.; Brickhouse, M.; Wong, B.; Sherman, J.C.; Dickerson, B.C. Executive dysfunction contributes to verbal encoding and retrieval deficits in posterior cortical atrophy. Cortex 2018, 106, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldsman, M.; Zamboni, G.; Butler, C.; Ahmed, S. Attention network dysfunction underlies memory impairment in posterior cortical atrophy. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 22, 101773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Win, K.T.; Pluta, J.; Yushkevich, P.; Irwin, D.J.; McMillan, C.T.; Rascovsky, K.; Wolk, D.; Grossman, M. Neural Correlates of Verbal Episodic Memory and Lexical Retrieval in Logopenic Variant Primary Progressive Aphasia. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramanan, S.; Flanagan, E.; Leyton, C.E.; Villemagne, V.L.; Rowe, C.C.; Hodges, J.R.; Hornberger, M. Non-Verbal Episodic Memory Deficits in Primary Progressive Aphasias are Highly Predictive of Underlying Amyloid Pathology. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 51, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berron, D.; van Westen, D.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Strandberg, O.; Hansson, O. Medial temporal lobe connectivity and its associations with cognition in early Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2020, 143, 1233–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squire, L.R.; Wixted, J.T. The cognitive neuroscience of human memory since H.M. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 259–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Toledo-Morrell, L.; Dickerson, B.; Sullivan, M.P.; Spanovic, C.; Wilson, R.; Bennett, D.A. Hemispheric differences in hippocampal volume predict verbal and spatial memory performance in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Hippocampus 2000, 10, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putcha, D.; Brickhouse, M.; Wolk, D.A.; Dickerson, B.C.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging, I. Fractionating the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test: Distinct roles of large-scale cortical networks in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychologia 2019, 129, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolk, D.A.; Dickerson, B.C. Initiative AsDN. Fractionating verbal episodic memory in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilmore, A.W.; Nelson, S.M.; McDermott, K.B. A parietal memory network revealed by multiple MRI methods. Trends. Cogn. Sci. 2015, 19, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggleton, J.P.; Brown, M.W. Interleaving brain systems for episodic and recognition memory. Trends. Cogn. Sci. 2006, 10, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenbaum, H.; Yonelinas, A.P.; Ranganath, C. The medial temporal lobe and recognition memory. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 30, 123–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yonelinas, A.P.; Aly, M.; Wang, W.C.; Koen, J.D. Recollection and familiarity: Examining controversial assumptions and new directions. Hippocampus 2010, 20, 1178–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wagner, A.D.; Shannon, B.J.; Kahn, I.; Buckner, R.L. Parietal lobe contributions to episodic memory retrieval. Trends. Cogn. Sci. 2005, 9, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonelinas, A.P.; Otten, L.J.; Shaw, K.N.; Rugg, M.D. Separating the brain regions involved in recollection and familiarity in recognition memory. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 3002–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, M.; Rohrer, J.D.; Clarkson, M.J.; Ridgway, G.R.; Scahill, R.I.; Modat, M.; Warren, J.D.; Ourselin, S.; Barnes, J.; Rossor, M.N.; et al. Reduced cortical thickness in the posterior cingulate gyrus is characteristic of both typical and atypical Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ossenkoppele, R.; Cohn-Sheehy, B.I.; La Joie, R.; Vogel, A.C.; Moller, C.; Lehmann, M.; van Berckel, B.N.; Seeley, W.W.; Pijnenburg, Y.; Gorno-Tempini, M.L.; et al. Atrophy patterns in early clinical stages across distinct phenotypes of Alzheimer’s disease. Human Brain Mapping 2015, 36, 4421–4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weintraub, S.; Rogalski, E.; Shaw, E.; Sawlani, S.; Rademaker, A.; Wieneke, C.; Mesulam, M.M. Verbal and nonverbal memory in primary progressive aphasia: The Three Words-Three Shapes Test. Behav. Neurol. 2013, 26, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapolsky, D.; Bakkour, A.; Negreira, A.; Nalipinski, P.; Weintraub, S.; Mesulam, M.M.; Caplan, D.; Dickerson, B.C. Cortical neuroanatomic correlates of symptom severity in primary progressive aphasia. Neurology 2010, 75, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, B.; Lucente, D.E.; MacLean, J.; Padmanabhan, J.; Quimby, M.; Brandt, K.D.; Putcha, D.; Sherman, J.; Frosch, M.P.; McGinnis, S.; et al. Diagnostic evaluation and monitoring of patients with posterior cortical atrophy. Neurodegener Dis. Manag. 2019, 9, 217–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, B.C.; McGinnis, S.M.; Xia, C.; Price, B.H.; Atri, A.; Murray, M.E.; Mendez, M.F.; Wolk, D.A. Approach to atypical Alzheimer’s disease and case studies of the major subtypes. CNS Spectr. 2017, 22, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, J.A.; Burns, J.M.; Hou, C.E.; McKeel, D.W., Jr.; Storandt, M.; Morris, J.C. Progressive posterior cortical dysfunction: A clinicopathologic series. Neurology 2004, 63, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovici, G.D.; Furst, A.J.; Alkalay, A.; Racine, C.A.; O’Neil, J.P.; Janabi, M.; Baker, S.L.; Agarwal, N.; Bonasera, S.J.; Mormino, E.C.; et al. Increased metabolic vulnerability in early-onset Alzheimer’s disease is not related to amyloid burden. Brain 2010, 133, 512–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Fox, N.C.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delis, D.C.; Kramer, J.H.; Kaplan, E.; Ober, B. California Verbal Learning Test: Adult version (CVLT-II): Manual, 2nd ed.; Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Shoup, T.M.; Yokell, D.L.; Rice, P.A.; Jackson, R.N.; Livni, E.; Johnson, K.A.; Brady, T.J.; Vasdev, N. A concise radiosynthesis of the tau radiopharmaceutical, [(18)F]T807. J. Labelled Comp. Radiopharm. 2013, 56, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dale, A.M.; Fischl, B.; Sereno, M.I. Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage 1999, 9, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischl, B.; van der Kouwe, A.; Destrieux, C.; Halgren, E.; Segonne, F.; Salat, D.H.; Busa, E.; Seidman, L.J.; Goldstein, J.; Kennedy, D.; et al. Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2004, 14, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, K.A.; Schultz, A.; Betensky, R.A.; Becker, J.A.; Sepulcre, J.; Rentz, D.; Mormino, E.; Chhatwal, J.; Amariglio, R.; Papp, K.; et al. Tau positron emission tomographic imaging in aging and early Alzheimer disease. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 79, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, J.A.; Hedden, T.; Carmasin, J.; Maye, J.; Rentz, D.M.; Putcha, D.; Fischl, B.; Greve, D.N.; Marshall, G.A.; Salloway, S.; et al. Amyloid-beta associated cortical thinning in clinically normal elderly. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaretz, S.J.; Quimby, M.; Collins, J.; Makris, N.; McGinnis, S.; Schultz, A.; Vasdev, N.; Johnson, K.A.; Dickerson, B.C. Flortaucipir tau PET imaging in semantic variant primary progressive aphasia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 89, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, C.; Makaretz, S.J.; Caso, C.; McGinnis, S.; Gomperts, S.N.; Sepulcre, J.; Gomez-Isla, T.; Hyman, B.T.; Schultz, A.; Vasdev, N.; et al. Association of In Vivo [18F]AV-1451 Tau PET Imaging Results With Cortical Atrophy and Symptoms in Typical and Atypical Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Baker, I.; Husain, M.; Thompson, S.; Kipps, C.; Hornberger, M.; Hodges, J.R.; Butler, C.R. Memory Impairment at Initial Clinical Presentation in Posterior Cortical Atrophy. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 52, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beth, E.H.; Budson, A.E.; Waring, J.D.; Ally, B.A. Response bias for picture recognition in patients with Alzheimer disease. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 2009, 22, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Budson, A.E.; Wolk, D.A.; Chong, H.; Waring, J.D. Episodic memory in Alzheimer’s disease: Separating response bias from discrimination. Neuropsychologia 2006, 44, 2222–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.P.; Stuss, D.; Gillingham, S. Impaired list learning is not a general property of frontal lesions. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2009, 21, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrini, M.; Cappa, S.F.; Rossi, S.; Rossini, P.M.; Miniussi, C. The role of prefrontal cortex in verbal episodic memory: rTMS evidence. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2003, 15, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Demographic | All (n = 37) | Amnestic (n = 14) | PCA (n = 14) | lvPPA (n = 9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 67.1 (8.7) | 61.2 (5.9) | 70.3 (8.4) * | 71.2 (8.3) * |
| Sex Ratio (M:F) | 16M/21F | 7M/7F | 5M/9F | 4M/5F |
| Education (years) | 16.4 (2.6) | 16.9 (2.2) | 16.8 (2.1) | 14.9 (3.5) |
| Handedness (R:L) | 34R/3L | 12R/2L | 14R/0L | 8R/1L |
| CDR Global | CDR 0 (N = 2) CDR 0.5 (N = 21) CDR 1 (N = 14) | CDR 0.5 (N = 8) CDR 1 (N = 6) | CDR 0.5 (N = 7) CDR 1 (N = 7) | CDR 0 (N = 2) CDR 0.5 (N = 6) CDR 1 (N = 1) |
| CVLT-II-SF | All (n = 37) | Amnestic (n = 14) | PCA (n = 14) | lvPPA (n = 9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trial 1 | 3.1 (1.7) | 2.9 (1.3) * | 4.0 (1.7) ^ | 2.1 (1.7) *^ |
| Total Encoding (Sum Trials 1–4) | 17.4 (6.6) | 14.9 (5.9) * | 20.7 (5.6) † | 16.3 (7.6) * |
| SDFR | 3.7 (2.2) | 2.9 (1.9) * | 4.4 (2.5) | 4.0 (2.0) * |
| LDFR | 2.8 (2.6) † | 1.7 (1.9) * | 3.1 (2.9) | 4.1 (2.4) † |
| LDCR | 3.2 (25) | 2.1 (1.9) * | 3.8 (2.7) * | 3.9 (2.8) * |
| Recognition Discriminability (d’) | 1.7 (1.0) | 1.3 (0.8) | 1.9 (1.1) | 1.9 (1.0) |
| Response Bias (C) | −0.1 (0.5) | −0.3 (0.6) | −0.04 (0.3) | −0.02 (0.6) |
| Test | All (n = 37) | Amnestic (n = 14) | PCA (n = 14) | lvPPA (n = 9) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MoCA (out of 30) | 16.2 (6.0) | 14.9 (6.1) | 17.9 (6.2) | 15.5 (5.2) |
| Attention/Executive Functions | ||||
| Longest Digit Span Forward | 5.6 (1.7) | 5.2 (1.1) | 6.7 (1.6) *^ | 4.3 (1.5) ^ |
| Longest Digit Span Backward | 3.3 (1.4) | 2.9 (1.4) | 3.8 (1.4) | 3.2 (1.0) |
| Trails A a | 76.5 (43.9) | 65.7 (36.4) | 127 (24.9) *^ | 44.4 (20.5) ^ |
| Trails B b | 200.1 (62) | 237 (58.3) | 164.5 (10.6) | 190.3 (75) |
| Language | ||||
| Auditory Naming Test (/50) | 42.1 (8.4) | 42.6 (6.7) | 46.9 (3.5) *^ | 33.8 (10.4) *^ |
| Auditory Naming Test with PC | 46.1 (5.6) | 45.9 (5.3) | 48.9 (1.8) | 42 (7.6) |
| MINT (/31) | 22.8 (7.8) | 26.9 (4.5) | 20.1 (9.7) * | 20.1 (6.5) * |
| MINT with SC | 23.3 (7.9) | 27.1 (4.4) | 24 (7.5) | 20.2 (6.6) * |
| MINT with PC | 26.6 (5.4) | 28.5 (3.5) | 26.2 (6.8) | 24.2 (4.6) * |
| Letter Fluency (FAS) | 28.1 (17.8) | 19.3 (9.8) | 44.5 (15.7) * | 23.7 (22.3) |
| Category Fluency (Animals) | 11.4 (5.7) | 9.7 (5.4) | 14.6 (6.1) | 9.3 (3.1) |
| Sentence Repetition (/5) | 3.7 (1.5) | 3.7 (1.4) | 4.8 (0.5) ^ | 2.8 (3.1) ^ |
| Sentence Reading (/5) | 4.5 (0.67) | 4.5 (0.8) | 4.3 (0.6) | 4.5 (0.5) |
| Memory | ||||
| Craft Story Immediate (/44) | 9.5 (5.3) | 7.8 (4.2) | 12.8 (5.9) *^ | 6.9 (3.0) ^ |
| Craft Story Delayed Recall (/44) | 6.2 (5.9) | 2.7 (3.1) | 9.5 (7.2) * | 6.4 (3.7) * |
| Benson Figure Recall (/17) | 5.5 (4.8) | 3.2 (3.9) | 3.8 (5.3) | 9.0 (3.7) * |
| Visuospatial | ||||
| Clock Drawing (/3) | 1.6 (0.7) | 1.6 (0.9) | 1.5 (0.7) | 1.7 (0.5) |
| Benson Figure Copy (/17) | 12.1 (5.6) | 13.7 (4.6) | 5.4 (5.1) *^ | 15.3 (1.5) ^ |
| VOSP Number Location (/10) | 5.8 (2.9) | 6.1 (2.9) | 4 (2.3) ^ | 7.8 (2.5) ^ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Putcha, D.; Carvalho, N.; Dev, S.; McGinnis, S.M.; Dickerson, B.C.; Wong, B. Verbal Encoding Deficits Impact Recognition Memory in Atypical “Non-Amnestic” Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070843
Putcha D, Carvalho N, Dev S, McGinnis SM, Dickerson BC, Wong B. Verbal Encoding Deficits Impact Recognition Memory in Atypical “Non-Amnestic” Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(7):843. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070843
Chicago/Turabian StylePutcha, Deepti, Nicole Carvalho, Sheena Dev, Scott M. McGinnis, Bradford C. Dickerson, and Bonnie Wong. 2022. "Verbal Encoding Deficits Impact Recognition Memory in Atypical “Non-Amnestic” Alzheimer’s Disease" Brain Sciences 12, no. 7: 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070843
APA StylePutcha, D., Carvalho, N., Dev, S., McGinnis, S. M., Dickerson, B. C., & Wong, B. (2022). Verbal Encoding Deficits Impact Recognition Memory in Atypical “Non-Amnestic” Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sciences, 12(7), 843. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070843







