Recent Advances in Progresses and Prospects of IL-37 in Central Nervous System Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. About IL-37
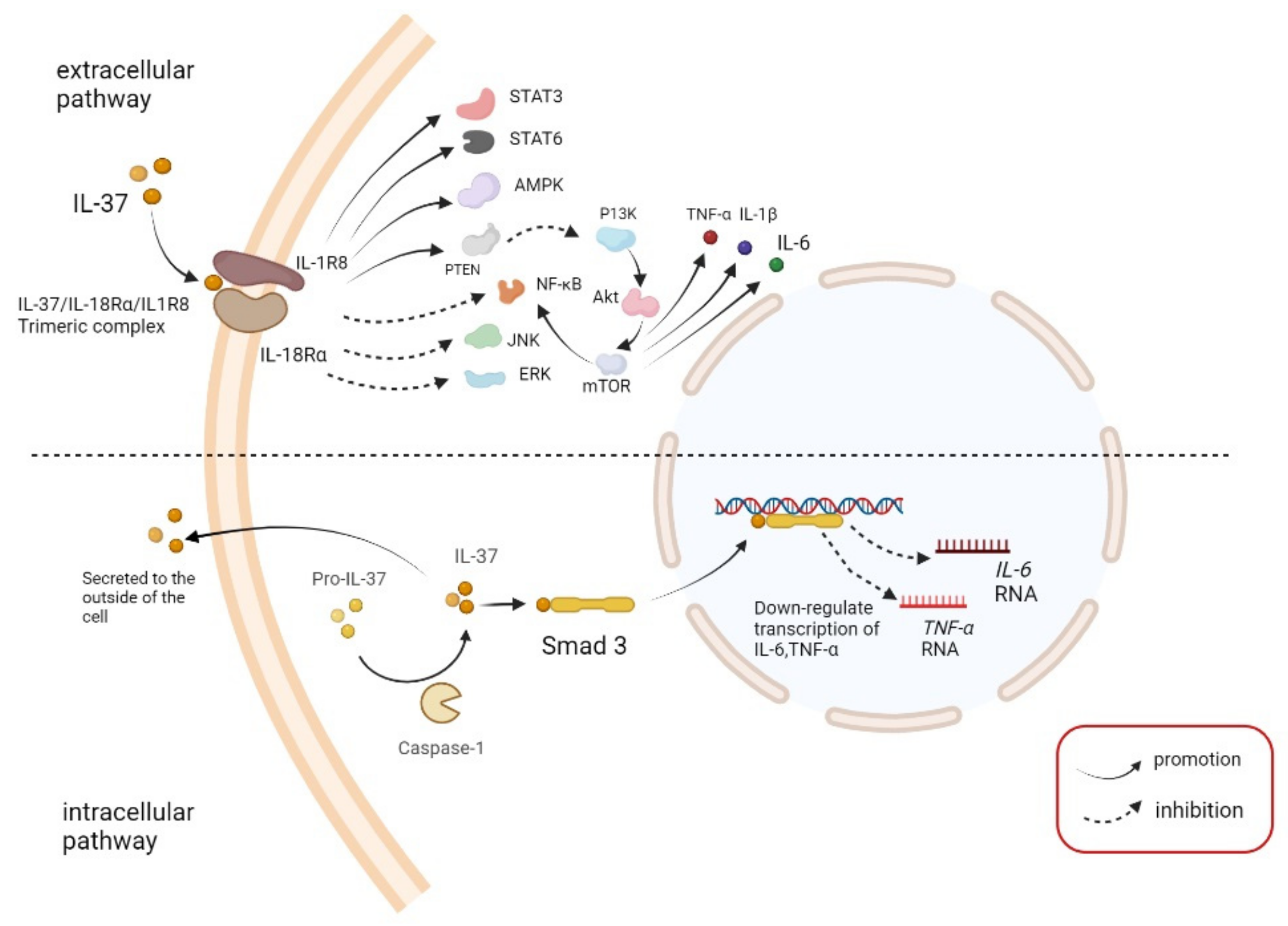
2.1. Function
2.2. Pathway
3. IL-37 in CNS Diseases
3.1. Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI)
3.2. Demyelinating Disease
3.3. Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
3.4. Stroke
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bello, R.O.; Chin, V.K.; Abd Rachman Isnadi, M.F.; Abd Majid, R.; Atmadini Abdullah, M.; Lee, T.Y.; Amiruddin Zakaria, Z.; Hussain, M.K.; Basir, R. The Role, Involvement and Function(s) of Interleukin-35 and Interleukin-37 in Disease Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; McDonnell, P.C.; Lehr, R.; Tierney, L.; Tzimas, M.N.; Griswold, D.E.; Capper, E.A.; Tal-Singer, R.; Wells, G.I.; Doyle, M.L.; et al. Identification and initial characterization of four novel members of the interleukin-1 family. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 10308–10314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boraschi, D.; Lucchesi, D.; Hainzl, S.; Leitner, M.; Maier, E.; Mangelberger, D.; Oostingh, G.J.; Pfaller, T.; Pixner, C.; Posselt, G.; et al. IL-37: A new anti-inflammatory cytokine of the IL-1 family. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2011, 22, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.L.; Renshaw, B.R.; Garka, K.E.; Smith, D.E.; Sims, J.E. Genomic organization of the interleukin-1 locus. Genomics 2002, 79, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A.; Nold-Petry, C.; Nold, M.; Fujita, M.; Li, S.; Kim, S.; Bufler, P. Suppression of innate inflammation and immunity by interleukin-37. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Tan, S.; Wu, D. IL-37 As a Potential Biotherapeutics of Inflammatory Diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2020, 21, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nold, M.F.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Tan, S.; Wu, D. IL-37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ma, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C.; Lei, Y.; Liu, M.; Cao, J. Interleukin-37 as a biomarker of mortality risk in patients with sepsis. J. Infect. 2021, 82, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamee, E.N.; Masterson, J.C.; Jedlicka, P.; McManus, M.; Grenz, A.; Collins, C.B.; Nold, M.F.; Nold-Petry, C.; Bufler, P.; Dinarello, C.A.; et al. Interleukin 37 expression protects mice from colitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16711–16716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.Y.; Zheng, D.F.; Shen, A.; Gu, H.T.; Wei, X.F.; Mou, T.; Zhang, J.B.; Liu, R. IL-37b suppresses epithelial mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting IL-6/STAT3 signaling. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2018, 17, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.E.; Renshaw, B.R.; Ketchem, R.R.; Kubin, M.; Garka, K.E.; Sims, J.E. Four new members expand the interleukin-1 superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abulkhir, A.; Samarani, S.; Amre, D.; Duval, M.; Haddad, E.; Sinnett, D.; Leclerc, J.M.; Diorio, C.; Ahmad, A. A protective role of IL-37 in cancer: A new hope for cancer patients. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 101, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.; Arend, W.; Sims, J.; Smith, D.; Blumberg, H.; O’Neill, L.; Goldbach-Mansky, R.; Pizarro, T.; Hoffman, H.; Bufler, P.; et al. IL-1 family nomenclature. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garlanda, C.; Riva, F.; Polentarutti, N.; Buracchi, C.; Sironi, M.; De Bortoli, M.; Muzio, M.; Bergottini, R.; Scanziani, E.; Vecchi, A.; et al. Intestinal inflammation in mice deficient in Tir8, an inhibitory member of the IL-1 receptor family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3522–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Amo-Aparicio, J.; Neff, C.P.; Tengesdal, I.W.; Azam, T.; Palmer, B.E.; López-Vales, R.; Bufler, P.; Dinarello, C.A. Role for nuclear interleukin-37 in the suppression of innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4456–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.M.; Fujita, M. IL-37: A new player in immune tolerance. Cytokine 2015, 72, 113–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A.; Bufler, P. Interleukin-37. Semin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca-Camarillo, G.; Furuzawa-Carballeda, J.; Yamamoto-Furusho, J.K. Interleukin 35 (IL-35) and IL-37: Intestinal and peripheral expression by T and B regulatory cells in patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Cytokine 2015, 75, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.; Wei-min, L.; Tong, Y.L.; Dong, N.; Sheng, Z.Y.; Yao, Y.M. Expression of IL-37 contributes to the immunosuppressive property of human CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bufler, P.; Gamboni-Robertson, F.; Azam, T.; Kim, S.H.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1 homologues IL-1F7b and IL-18 contain functional mRNA instability elements within the coding region responsive to lipopolysaccharide. Biochem. J. 2004, 381 Pt 2, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Neff, C.P.; Barber, K.; Hong, J.; Luo, Y.; Azam, T.; Palmer, B.E.; Fujita, M.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A.; et al. Extracellular forms of IL-37 inhibit innate inflammation in vitro and in vivo but require the IL-1 family decoy receptor IL-1R8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2497–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballak, D.B.; van Diepen, J.A.; Moschen, A.R.; Jansen, H.J.; Hijmans, A.; Groenhof, G.J.; Leenders, F.; Bufler, P.; Boekschoten, M.V.; Müller, M.; et al. IL-37 protects against obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; zhai, Y.; Ao, L.; Hui, H.; Fullerton, D.A.; Dinarello, C.A.; Meng, X. Interleukin-37 suppresses the inflammatory response to protect cardiac function in old endotoxemic mice. Cytokine 2017, 95, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.; Tsang, M.S.; Kan, L.L.; Li, P.; Chu, I.M.; Lam, C.W.; Wong, C.K. IL-37 Targets TSLP-Primed Basophils to Alleviate Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, Y.S.; Ke, X.; Hu, G.H. IL-37 attenuates allergic process via STAT6/STAT3 pathways in murine allergic rhinitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 69, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xia, L.; Shen, H.; Lu, J. Elevated frequency of IL-37- and IL-18Rα-positive T cells in the peripheral blood of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Cytokine 2018, 110, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragab, D.; Mobasher, S.; Shabaan, E. Elevated levels of IL-37 correlate with T cell activation status in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Cytokine 2019, 113, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, P.; Chen, Z.G.; Zhang, T.T.; Liang, Z.Z.; Zou, X.L.; Yang, H.L.; Li, H.T. IL-37 alleviates house dust mite-induced chronic allergic asthma by targeting TSLP through the NF-κB and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, D.G.; Domenico, J.; Luo, Y.; Reid, A.L.; Zhai, Z.; Gao, D.; Ziman, M.; Dinarello, C.A.; Robinson, A.W.; Fujita, M.; et al. Interleukin-37 is highly expressed in regulatory T cells of melanoma patients and enhanced by melanoma cell secretome. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kulk, N.; Nold, M.F.; Gräf, R.; Kim, S.H.; Reinhardt, D.; Dinarello, C.A.; Bufler, P. The IL-1 family member 7b translocates to the nucleus and down-regulates proinflammatory cytokines. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 5477–5482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulau, A.M.; Nold, M.F.; Li, S.; Nold-Petry, C.A.; Fink, M.; Mansell, A.; Schwerd, T.; Hong, J.; Rubartelli, A.; Dinarello, C.A.; et al. Role of caspase-1 in nuclear translocation of IL-37, release of the cytokine, and IL-37 inhibition of innate immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2650–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Hanning, C.R.; Brigham-Burke, M.R.; Rieman, D.J.; Lehr, R.; Khandekar, S.; Kirkpatrick, R.B.; Scott, G.F.; Lee, J.C.; Lynch, F.J.; et al. Interleukin-1F7B (IL-1H4/IL-1F7) is processed by caspase-1 and mature IL-1F7B binds to the IL-18 receptor but does not induce IFN-gamma production. Cytokine 2002, 18, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, G.; Risser, P.; Mao, W.; Baldwin, D.T.; Zhong, A.W.; Filvaroff, E.; Yansura, D.; Lewis, L.; Eigenbrot, C.; Henzel, W.J.; et al. IL-1H, an interleukin 1-related protein that binds IL-18 receptor/IL-1Rrp. Cytokine 2001, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimsby, S.; Jaensson, H.; Dubrovska, A.; Lomnytska, M.; Hellman, U.; Souchelnytskyi, S. Proteomics-based identification of proteins interacting with Smad3: SREBP-2 forms a complex with Smad3 and inhibits its transcriptional activity. FEBS Lett. 2004, 577, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, K.; Nakanishi, K.; Tsutsui, H. Interleukin-18 in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nold-Petry, C.A.; Lo, C.Y.; Rudloff, L.; Elgass, K.D.; Li, S.; Gantier, M.P.; Lotz-Havla, A.S.; Gersting, S.W.; Cho, S.X.; Lao, J.C.; et al. IL-37 requires the receptors IL-18Rα and IL-1R8 (SIGIRR) to carry out its multifaceted anti-inflammatory program upon innate signal transduction. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novick, D.; Kim, S.; Kaplanski, G.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-18, more than a Th1 cytokine. Semin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, D.; Qin, J.; Zhao, Z.; Qian, Y.; Naramura, M.; Tian, L.; Towne, J.; Sims, J.E.; Stark, G.R.; Li, X. SIGIRR, a negative regulator of Toll-like receptor-interleukin 1 receptor signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bufler, P.; Azam, T.; Gamboni-Robertson, F.; Reznikov, L.L.; Kumar, S.; Dinarello, C.A.; Kim, S.H. A complex of the IL-1 homologue IL-1F7b and IL-18-binding protein reduces IL-18 activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13723–13728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wei, J.; Suber, T.L.; Ye, Q.; Miao, J.; Li, S.; Taleb, S.J.; Tran, K.C.; Tamaskar, A.S.; Zhao, J.; et al. IL-37-induced activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β promotes IL-1R8/Sigirr phosphorylation, internalization, and degradation in lung epithelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 5676–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, B.; Cameron, P.A.; Braaf, S.; Nunn, A.; Fitzgerald, M.C.; Judson, R.T.; Teague, W.J.; Lennox, A.; Middleton, J.W.; Harrison, J.E. Traumatic spinal cord injury in Victoria 2007–2016. Med. J. Aust. 2019, 210, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglis, T.; Banaszek, D.; Rivers, C.S.; Kurban, D.; Ewaniew, N.; Fallah, N.; Waheed, Z.; Christie, S.; Fox, R.; Thiong, J.M.; et al. In-Hospital Mortality for the Elderly with Acute Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2020, 37, 2332–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeitouni, D.; Catalino, M.; Kessler, B.; Pate, V.; Stürmer, T.; Quinsey, C.; Bhowmick, D.A. 1-Year Mortality and Surgery Incidence in Older US Adults with Cervical Spine Fracture. World Neurosurg. 2020, 141, e858–e863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll-Miró, M.; Francos-Quijorna, I.; Santos-Nogueira, E.; Torres-Espin, A.; Bufler, P.; Dinarello, C.A.; López-Vales, R. Beneficial effects of IL-37 after spinal cord injury in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1411–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Cao, S.; Hou, G.; Ma, G.; Shi, B. Association between Serum IL-37 and Spinal Cord Injury: A Prospective Observational Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6664313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amo-Aparicio, J.; Sanchez-Fernandez, A.; Li, S.; Eisenmesser, E.Z.; Garlanda, C.; Dinarello, C.A.; Lopez-Vales, R. Extracellular and nuclear roles of IL-37 after spinal cord injury. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 91, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekerle, H. Lessons from multiple sclerosis: Models, concepts, observations. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67 (Suppl. 3), iii56–iii60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Vidal-Jordana, A.; Montalban, X. Multiple sclerosis: Clinical aspects. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2018, 31, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Fernández, A.; Zandee, S.; Amo-Aparicio, J.; Charabati, M.; Prat, A.; Garlanda, C.; Eisenmesser, E.Z.; Dinarello, C.A.; López-Vales, R. IL-37 exerts therapeutic effects in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through the receptor complex IL-1R5/IL-1R8. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, E.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Mammana, S.; Pennisi, M.; Fagone, P.; Kalfin, R.; Martinovic, V.; Ivanovic, J.; Andabaka, M.; et al. In Silico and In Vivo Analysis of IL37 in Multiple Sclerosis Reveals Its Probable Homeostatic Role on the Clinical Activity, Disability, and Treatment with Fingolimod. Molecules 2019, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouchaki, E.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Dadgostar, E.; Karami, M.; Nikoueinejad, H.; Akbari, H. Correlation of Serum Levels of IL-33, IL-37, Soluble Form of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 (VEGFR2), and Circulatory Frequency of VEGFR2-expressing Cells with Multiple Sclerosis Severity. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017, 16, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farrokhi, M.; Rezaei, A.; Amani-Beni, A.; Etemadifar, M.; Kouchaki, E.; Zahedi, A. Increased serum level of IL-37 in patients with multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2015, 115, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willison, H.J.; Jacobs, B.C.; van Doorn, P.A. Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet 2016, 388, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, E.; Salameh, J. Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Semin. Neurol. 2019, 39, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, B.; Walgaard, C.; Drenthen, J.; Fokke, C.; Jacobs, B.C.; van Doorn, P.A. Guillain-Barré syndrome: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, P.; Sun, X.; Che, Y.; Jiang, Y. Elevated levels of cerebrospinal fluid and plasma interleukin-37 in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 639712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, N.; Van Sweringen, H.L.; Belizaire, R.M.; Quillin, R.C.; Schuster, R.; Blanchard, J.; Burns, J.M.; Tevar, A.D.; Edwards, M.J.; Lentsch, A.B. Interleukin-37 reduces liver inflammatory injury via effects on hepatocytes and non-parenchymal cells. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulau, A.M.; Fink, M.; Maucksch, C.; Kappler, R.; Mayr, D.; Wagner, K.; Bufler, P. In vivo expression of interleukin-37 reduces local and systemic inflammation in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis. Sci. World J. 2011, 11, 2480–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, J.; Perry, G. A Multilevel View of the Development of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuroscience 2021, 457, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, C.; Ding, G.; Heng, Y.; Li, A.; Wang, W.; Hou, H.; Wen, J.; Zhang, Y. The Burden of Alzheimer’s Disease Mortality in the United States 1999–2018. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 82, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2021 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, 327–406. [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, A.; de Strooper, B.; Arancibia-Cárcamo, I.L. Cellular senescence at the crossroads of inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 714–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Campisi, J. Chronic inflammation (inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69 (Suppl. 1), S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppé, J.P.; Patil, C.K.; Rodier, F.; Sun, Y.; Muñoz, D.P.; Goldstein, J.; Nelson, P.S.; Desprez, P.Y. Senescence-associated secretory phenotypes reveal cell-nonautonomous functions of oncogenic RAS and the p53 tumor suppressor. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, 2853–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Pozo, A.; Mielke, M.L.; Gómez-Isla, T.; Betensky, R.A.; Growdon, J.H.; Frosch, M.P.; Hyman, B.T. Reactive glia not only associates with plaques but also parallels tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Tan, M.S.; Yu, J.T.; Tan, L. Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 136. [Google Scholar]
- Czeh, M.; Gressens, P.; Kaindl, A.M. The yin and yang of microglia. Dev. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratchayasakul, W.; Kerdphoo, S.; Petsophonsakul, P.; Pongchaidecha, A.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. Effects of high-fat diet on insulin receptor function in rat hippocampus and the level of neuronal corticosterone. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, L.M.; Lin, C.I.; Chen, Y.H.; Liao, H.; Lin, S.H. A diet containing grape powder ameliorates the cognitive decline in aged rats with a long-term high-fructose-high-fat dietary pattern. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 34, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.A.; Mohamed, R.A.; Abdallah, D.M.; El-Brairy, A.I.; Ahmed, K.A.; El-Abhar, H.S. Palonosetron/Methyllycaconitine Deactivate Hippocampal Microglia 1, Inflammasome Assembly and Pyroptosis to Enhance Cognition in a Novel Model of Neuroinflammation. Molecules 2021, 26, 5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunmokun, G.; Dewanjee, S.; Chakraborty, P.; Valupadas, C.; Chaudhary, A.; Kolli, V.; Anand, U.; Vallamkondu, J.; Goel, P.; Paluru, H.P.R. The Potential Role of Cytokines and Growth Factors in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spooren, A.; Kolmus, K.; Laureys, G.; Clinckers, R.; De Keyser, J.; Haegeman, G.; Gerlo, S. Interleukin-6, a mental cytokine. Brain Res. Rev. 2011, 67, 157–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarty, P.; Jansen-West, K.; Beccard, A.; Ceballos-Diaz, C.; Levites, Y.; Verbeeck, C.; Zubair, A.C.; Dickson, D.; Golde, T.E.; Das, P. Massive gliosis induced by interleukin-6 suppresses Abeta deposition in vivo: Evidence against inflammation as a driving force for amyloid deposition. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belaya, I.; Kucháriková, N.; Górová, V.; Kysenius, K.; Hare, D.J.; Crouch, P.J.; Malm, T.; Atalay, M.; White, A.R.; Liddell, J.R.; et al. Regular Physical Exercise Modulates Iron Homeostasis in the 5xFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutinen, E.M.; Pirttilä, T.; Anderson, G.; Salminen, A.; Ojala, J.O. The Role of Interleukin-18, Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Syndrome in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.T.; Chang, R.C.; Tan, L. Calcium dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease: From mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Prog. Neurobiol. 2009, 89, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrad, R.; Berraïes, A.; Hamdi, B.; Ammar, J.; Hamzaoui, K.; Hamzaoui, A. Anti-inflammatory activity of IL-37 in asthmatic children: Correlation with inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-β, IL-6 and IL-17A. Immunobiology 2016, 221, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Dang, W.; Chen, B.; Qing, Y.; Xie, W.; Zhao, M.; Zhou, J. IL-37 inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in MSU crystal-induced inflammatory response. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Geffen, E.W.; van Caam, A.P.; van Beuningen, H.M.; Vitters, E.L.; Schreurs, W.; van de Loo, F.A.; van Lent, P.L.; Koenders, M.I.; Blaney Davidson, E.N.; van der Kraan, P.M. IL37 dampens the IL1β-induced catabolic status of human OA chondrocytes. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, P.; Sun, R.; Zhang, C. IL-37 inhibits invasion and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer by suppressing the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Lv, F.; Song, L. Interleukin-37 (IL-37) Suppresses Pertussis Toxin-Induced Inflammatory Myopathy in a Rat Model. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 9187–9195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, G.; Dinarello, C.A. Suppression of inflammation and acquired immunity by IL-37. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Peng, S.; Yan, Y.; Ji, P.; Xu, J. IL-37 inhibits M1-like macrophage activation to ameliorate temporomandibular joint inflammation through the NLRP3 pathway. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 3070–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders during 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 877–897. [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Jing, L.; Tian, Y.; Liu, S.; Lin, M.; Du, Z.; Ren, G.; Sun, Q.; Shi, L.; Dai, D.; et al. High prevalence of stroke and uncontrolled associated risk factors are major public health challenges in rural northeast China: A population-based study. Int. J. Stroke 2020, 15, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhu, T.; Li, H.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, N.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Chang, D.; Li, X. Plasma Interleukin-37 is Elevated in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients and Probably Associated With 3-month Functional Prognosis. Clin. Interv. Aging 2020, 15, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, H.; Nan, S. Serum Interleukin-37 Increases in Patients after Ischemic Stroke and Is Associated with Stroke Recurrence. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5546991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.B.; Zeng, Y.Y.; Wang, F.; Cheng, L.; Tang, W.J.; Wang, X.Q. A high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts hemorrhagic transformation of large atherosclerotic infarction in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Aging 2020, 12, 2428–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-de-Puig, I.; Miró-Mur, F.; Ferrer-Ferrer, M.; Gelpi, E.; Pedragosa, J.; Justicia, C.; Urra, X.; Chamorro, A.; Planas, A.M. Neutrophil recruitment to the brain in mouse and human ischemic stroke. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolaczkowska, E.; Kubes, P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilioni, I.; Patel, A.B.; Pantazopoulos, H.; Berretta, S.; Conti, P.; Leeman, S.E.; Theoharides, T.C. IL-37 is increased in brains of children with autism spectrum disorder and inhibits human microglia stimulated by neurotensin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 21659–21665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Huang, Z.; Li, W.; He, S.; Wu, H.; Zhu, J.; Li, R.; Liang, Z.; Chen, Z. IL-37 expression is decreased in patients with hyperhomocysteinemia and protects cells from inflammatory injury by homocysteine. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; An, W.; Yao, Y.; Chen, R.; Zheng, X.; Yang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Jiang, E.; Bie, Y.; et al. Interleukin 37 Expression Inhibits STAT3 to Suppress the Proliferation and Invasion of Human Cervical Cancer Cells. J. Cancer 2015, 6, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Conti, P.; Stellin, L.; Caraffa, A.; Gallenga, C.E.; Ross, R.; Kritas, S.K.; Frydas, I.; Younes, A.; Di Emidio, P.; Ronconi, G. Advances in Mast Cell Activation by IL-1 and IL-33 in Sjögren’s Syndrome: Promising Inhibitory Effect of IL-37. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Zhou, T.; Damsky, W.; Weizman, O.E.; McGeary, M.K.; Hartmann, K.P.; Rosen, C.E.; Fischer, S.; Jackson, R.; Flavell, R.A.; et al. IL-18BP is a secreted immune checkpoint and barrier to IL-18 immunotherapy. Nature 2020, 583, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Yan, B.; Du, J.; Xu, S.; Liu, L.; Pan, C.; Kang, X.; Zhu, S. Recent Advances in Progresses and Prospects of IL-37 in Central Nervous System Diseases. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060723
Li X, Yan B, Du J, Xu S, Liu L, Pan C, Kang X, Zhu S. Recent Advances in Progresses and Prospects of IL-37 in Central Nervous System Diseases. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(6):723. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060723
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinrui, Bing Yan, Jin Du, Shanshan Xu, Lu Liu, Caifei Pan, Xianhui Kang, and Shengmei Zhu. 2022. "Recent Advances in Progresses and Prospects of IL-37 in Central Nervous System Diseases" Brain Sciences 12, no. 6: 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060723
APA StyleLi, X., Yan, B., Du, J., Xu, S., Liu, L., Pan, C., Kang, X., & Zhu, S. (2022). Recent Advances in Progresses and Prospects of IL-37 in Central Nervous System Diseases. Brain Sciences, 12(6), 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12060723




