Granger-Causality-Based Multi-Frequency Band EEG Graph Feature Extraction and Fusion for Emotion Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Overview of the GC Method
2.2. Overviews of Graph Convolutional Neural Networks (GCN)
3. The Proposed GC-F-GCN Scheme for EEG Emotion Recognition
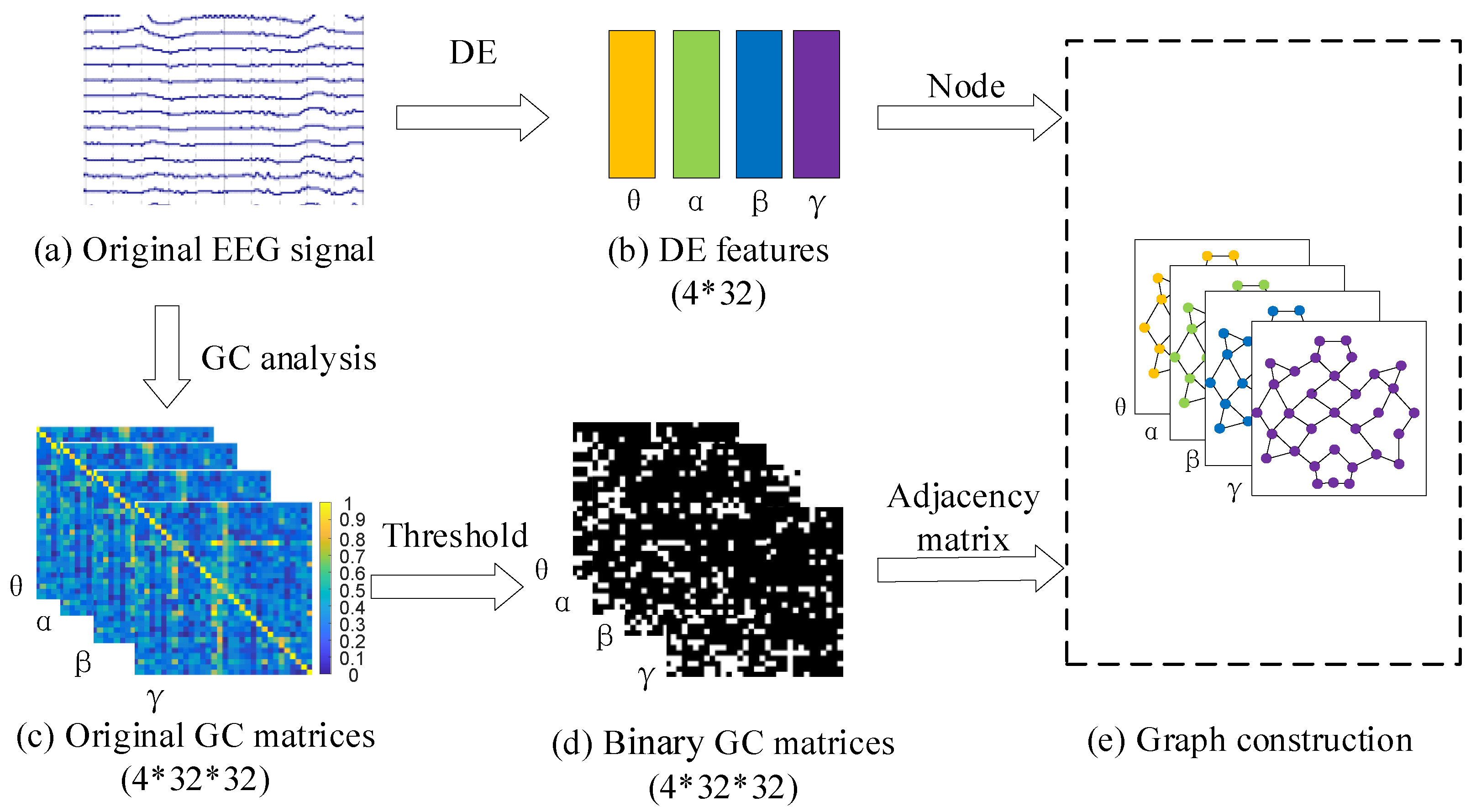
3.1. Preprocessing of EEG Signals
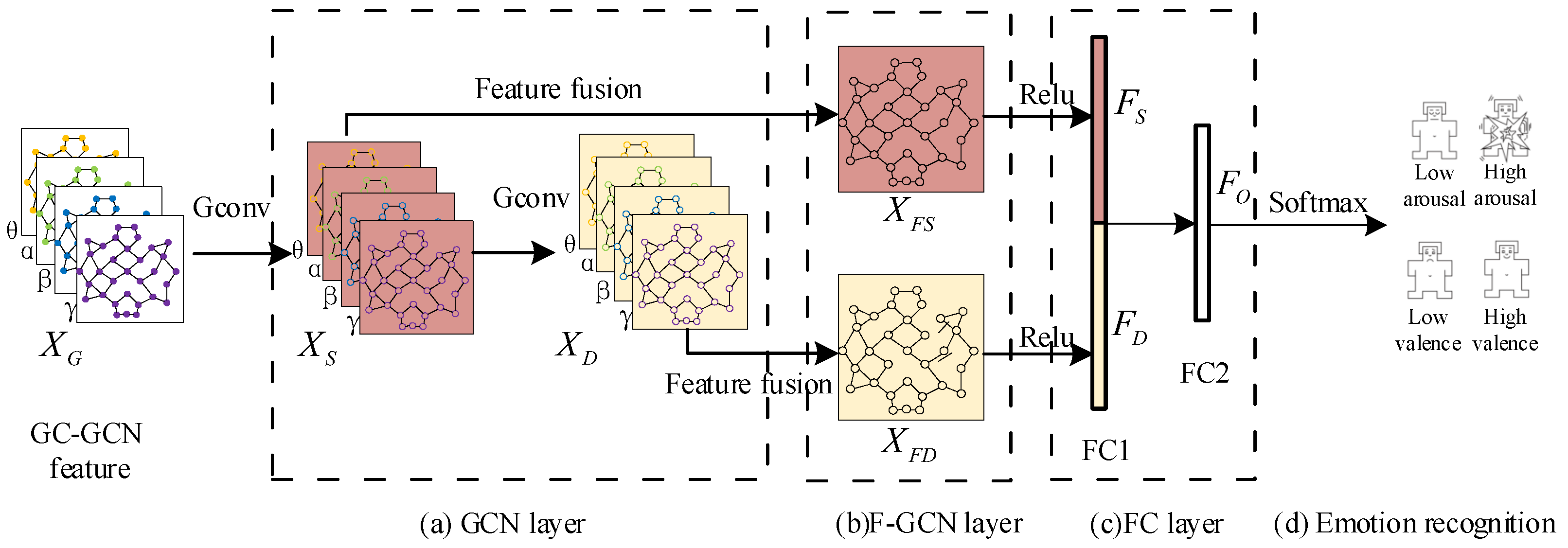
3.2. The Construction of GC-GCN Graph Feature
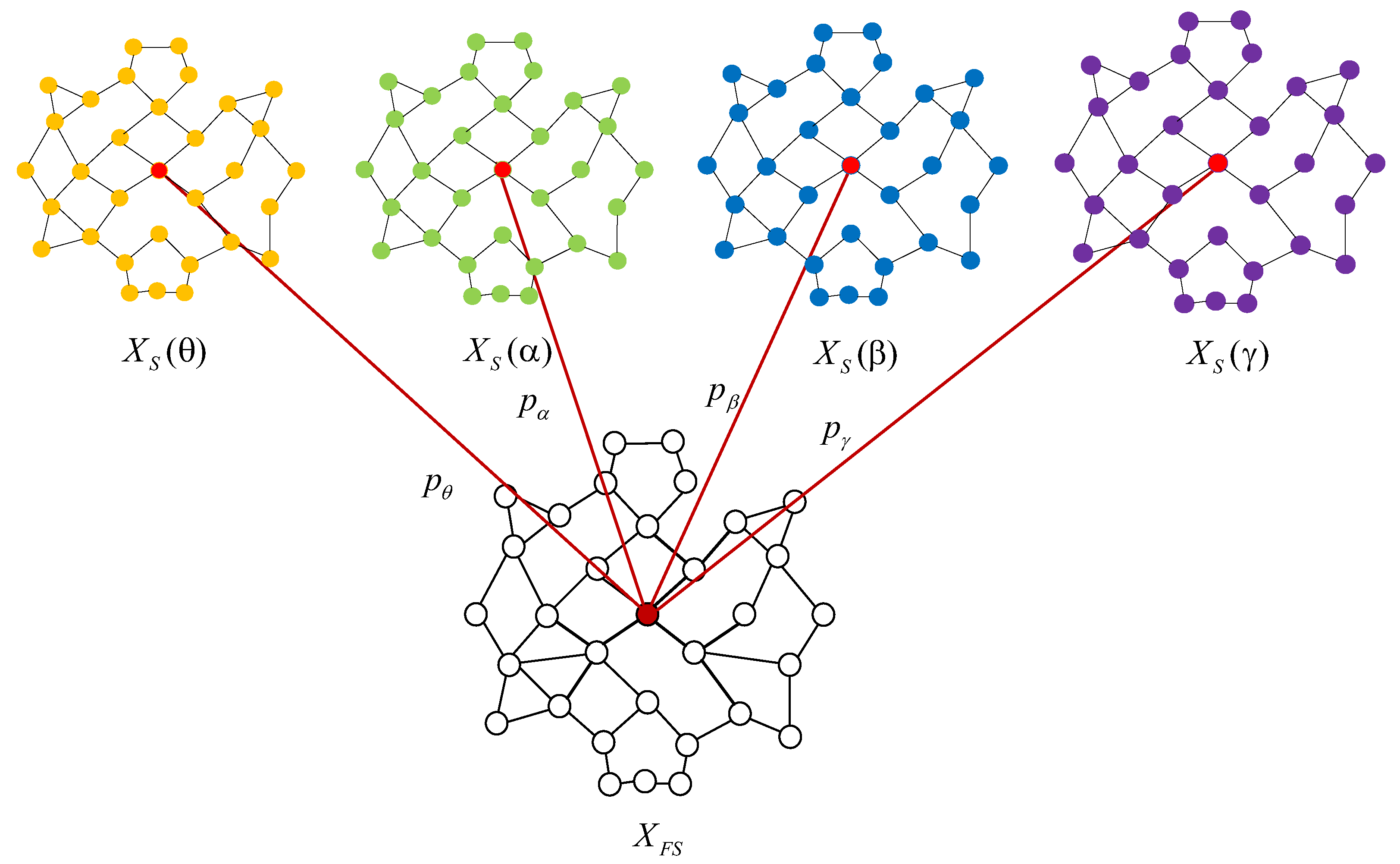
3.3. Multi-Frequency Band Graph Feature Fusion Method
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. The Emotion Recognition Performance of the GC-GCN Graph Feature
4.2. The Performance of the GC-F-GCN Feature Fusion Method
4.3. Performance Comparisons for Latest GCN Graph Feature
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| GC | Granger causality |
| GCN | Graph convolutional neural network |
| GC-GCN | GC-based GCN graph feature |
| GC-F-GCN | Multi-frequency band GC-GCN feature fusion method |
| PLV | Phase Locking Value |
| SGC-GCN | Shallow graph feature |
| DGC-GCN | Deep graph feature |
| SDGC-GCN | Shallow and deep cascade graph feature |
| SGC-F-GCN | Shallow fusion feature |
| DGC-F-GCN | Deep fusion feature |
| SDGC-F-GCN | Shallow and deep fusion feature |
References
- Zhang, J.H.; Yin, Z.; Chen, P.; Nichele, P. Emotion recognition using multi-modal data and machine learning techniques: A tutorial and review. Inf. Fusion 2020, 59, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Li, F.; Li, P.; Yi, C.; Li, C.; Tao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Si, Y.; Yao, D.; Yin, G.; et al. A survey of brain network analysis by electroencephalographic signals. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2022, 16, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Pato, V.M.; Sánchez, C.N.; Domínguez-Soberanes, J.; Méndoza-Pérez, D.E.; Velázquez, R. A Multisensor Data Fusion Approach for Predicting Consumer Acceptance of Food Products. Foods 2020, 9, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.Z.; He, Y.; Zang, Y.F.; Weng, X.C. Modulation of functional connectivity during the resting state and the motor task. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2004, 22, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.L.; Lu, B.L. Investigating critical frequency bands and channels for EEG-based emotion recognition with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Auton. Ment. Dev. 2015, 7, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Xiao, R.L.; Cui, W.J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, G.D. Application of EEG-based machine learning in emotion recognition: A Review. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Wu, Q.; Fu, Y.Z.; Chen, X.W. Continuous convolutional neural network with 3d input for EEG-based emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Siem Reap, Cambodia, 13–16 December 2018; pp. 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Dai, G.; Lin, G. EEG-based emotion recognition using 4D convolutional recurrent neural network. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2020, 14, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, G.J.; Yan, C. EEG emotion recognition based on the 3D-CNN and spatial-frequency attention mechanism. J. Xidian Univ. 2022, 49, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defferrard, M.; Bresson, X.; Vandergheynst, P. Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; pp. 3844–38523. [Google Scholar]
- Levie, R.; Monti, F.; Bresson, X.; Bronstein, M. Cayleynets: Graph convolutional neural networks with complex rational spectral filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 67, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M.; Vandergheynst, P. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.Q.; Zheng, X.W.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.C. EEG emotion recognition using fusion model of graph convolutional neural networks and LSTM. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 100, 106954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.F.; Zheng, W.M.; Song, P.; Cui, Z. EEG emotion recognition using dynamical graph convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2018, 11, 32–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.F.; Zheng, W.M.; Liu, S.Y.; Zong, Y.; Cui, Z.; Li, Y. Graph-Embedded Convolutional Neural Network for Image-based EEG Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2021, 10, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Liu, X.C.; Li, J.H.; Xu, T.; Bezerianos, A.; Sun, Y.; Wan, F. Driving fatigue recognition with functional connectivity based on phase synchronization. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2020, 13, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.L.; Li, M.; Ju, X.Y.; Liu, Y.D. Applying Multiple Functional Connectivity Features in GCN for EEG-Based Human Identification. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, M.; Sun, A.; Liu, J.J.; Men, H. A fast Pearson graph convolutional network combined with electronic nose to identify the origin of rice. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 21175–21183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Tong, Y.; Heng, X. Phase-locking value-based graph convolutional neural networks for emotion recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 93711–93722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhao, Y.F.; Shan, X.C.; Wei, H.L.; Guo, Y.Z.; Chen, L.Y.; Erkoyuncu, A.J.; Sarrigiannis, P.G. Brain Functional and Effective Connectivity Based on Electroencephalography Recordings: A Review. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2022, 43, 860–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, R.; Bortoletto, M.; Miniussi, C. Integrating TMS, EEG, and MRI as an approach for studying brain connectivity. Neuroscientist 2020, 26, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.E.; Chen, C.J.; Hsieh, C.J.; Wang, J.L.; Lee, J.S. Emotional EEG Classification Using Connectivity Features and Convolutional Neural Networks. Neural Netw. 2020, 132, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.T.; Headley, D.B.; Mill, R.D.; Sanchez-Romero, R.; Uddin, L.Q.; Marinazzo, D.; Lurie, D.J.; Valdés-Sosa, P.A.; Hanson, S.J.; Biswal, B.B.; et al. Advancing functional connectivity research from association to causation. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.W.J. Investigating Causal Relations by Econometric Models and Cross-Spectral Methods. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1969, 10, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Wang, X.K.; Potter, T.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, Y.C. Single-trial EEG emotion recognition using Granger Causality/Transfer Entropy analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 346, 108904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.Z.; Qiu, M.; Li, M.H.; Jin, X.Y.; Zhu, L. Causal Graph Convolutional Neural Network for Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2022; Early Access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.Y.; Peng, Y.; Kong, W.Z.; Dai, G.J. Multi-scale frequency bands ensemble learning for EEG-based emotion recognition. Sensors 2021, 21, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.L.; Liu, W.; Lu, Y.F.; Lu, B.L.; Cichocki, A. Emotionmeter: A Multimodal Framework for Recognizing Human Emotions. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.D.; Xie, L.; Chai, B.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H. Spatial-frequency convolutional self-attention network for EEG emotion recognition. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 122, 108740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.W.; Shi, M.; Ye, M.W.; Xu, B.W.; Chen, Z.D.; Ren, Q.S. 4D attention-based neural network for EEG emotion recognition. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2022, 16, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tong, H.H.; Xu, J.J.; Maciejewski, R. Graph convolutional networks: Algorithms, applications and open challenges. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computational Data and Social Networks, Shanghai, China, 18–12 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Tong, H.H.; Xu, J.J.; Maciejewski, R. Graph convolutional networks: A comprehensive review. Comput. Soc. Netw. 2019, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelstra, S.; Muhl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Lee, J.S.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Pun, T.; Nijholt, A.; Patras, L. DEAP: A Database for Emotion Analysis Using Physiological Signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2011, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, G.J.; Huang, L.X.; Sun, Y. EEG emotion recognition based on cross-frequency granger causality feature extraction and fusion in the left and right hemispheres. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 974673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.C.; Jiao, Y.Y.; Lu, B.L. Differential entropy feature for EEG-based vigilance estimation. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 6627–6630. [Google Scholar]

| k | Arousal | Valence | Arousal–Valence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 91.35 ± 5.37 | 91.34 ± 5.45 | 86.90 ± 8.23 |
| 20% | 91.56 ± 5.14 | 91.66 ± 5.25 | 87.21 ± 8.31 |
| 30% | 91.22 ± 5.53 | 92.01 ± 5.23 | 86.71 ± 8.10 |
| 40% | 91.15 ± 5.34 | 91.23 ± 5.52 | 86.93 ± 8.45 |
| 50% | 91.55 ± 5.33 | 91.46 ± 5.57 | 87.31 ± 8.78 |
| 60% | 91.82 ± 4.82 | 91.27 ± 5.88 | 86.80 ± 9.1 |
| 70% | 91.73 ± 5.66 | 91.25 ± 4.79 | 87.38 ± 7.94 |
| 80% | 91.48 ± 5.21 | 91.91 ± 4.88 | 87.30 ± 9.06 |
| 90% | 91.38 ± 5.26 | 91.60 ± 5.09 | 86.87 ± 8.91 |
| Emotion | Adjacency Matrix | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arousal | Random | 71.89 ± 5.44 | 72.12 ± 5.80 | 71.22 ± 5.78 | 71.54 ± 4.87 | 87.45 ± 5.53 |
| Distance | 71.42 ± 5.93 | 72.52 ± 6.24 | 75.32 ± 6.24 | 75.10 ± 5.74 | 87.23 ± 5.17 | |
| PLV [19] | 72.31 ± 5.24 | 71.78 ± 5.17 | 71.44 ± 4.80 | 71.95 ± 5.58 | 90.89 ± 4.68 | |
| GC-GCN | 72.58 ± 5.16 | 78.09 ± 5.94 | 78.68 ± 5.82 | 79.55 ± 5.56 | 91.82 ± 4.82 | |
| Valence | Random | 69.92 ± 6.46 | 69.71 ± 6.65 | 69.42 ± 6.50 | 69.80 ± 5.46 | 87.31 ± 4.75 |
| Distance | 70.61 ± 6.36 | 70.67 ± 6.26 | 70.33 ± 7.12 | 69.89 ± 5.75 | 87.58 ± 5.42 | |
| PLV [19] | 69.94 ± 6.22 | 69.34 ± 6.24 | 70.56 ± 6.33 | 70.50 ± 5.83 | 90.35 ± 5.02 | |
| GC-GCN | 78.06 ± 5.84 | 78.25 ± 5.01 | 76.85 ± 6.37 | 77.66 ± 5.45 | 92.01 ± 5.23 | |
| Arousal–Valence | Random | 55.92 ± 9.24 | 54.35 ± 8.34 | 53.80+9.38 | 55.34+9.29 | 83.88 ± 9.00 |
| Distance | 54.51 ± 9.57 | 54.90 ± 8.28 | 54.00 ± 8.40 | 55.27 ± 9.57 | 83.86 ± 8.66 | |
| PLV [19] | 53.76 ± 8.96 | 54.88 ± 9.51 | 70.36 ± 6.22 | 71.07 ± 70.1 | 85.64 ± 7.99 | |
| GC-GCN | 71.47 ± 4.93 | 72.07 ± 5.07 | 71.97 ± 4.36 | 72.09 ± 5.19 | 87.38 ± 7.94 |
| Features | Arousal | Valence | Arousal–Valence |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGC-GCN | 92.12 ± 3.06 | 90.71 ± 5.00 | 87.53 ± 2.91 |
| DGC-GCN | 91.82 ± 4.82 | 92.01 ± 5.23 | 87.38 ± 7.94 |
| SDGC-GCN | 93.58 ± 5.78 | 93.25 ± 4.22 | 92.38 ± 3.05 |
| SGC-GCN | 97.12 ± 2.53 | 97.11 ± 2.30 | 97.13 ± 2.66 |
| DGC-GCN | 97.41 ± 3.29 | 98.23 ± 1.38 | 97.78 ± 3.26 |
| SDGC-F-GCN | 97.91 ± 2.50 | 98.46 ± 1.16 | 98.15 ± 2.39 |
| Emotion | Method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arousal | SVM | 74.19 ± 8.55 | 76.05 ± 8.68 | 80.10 ± 8.47 | 83.74 ± 7.17 | 84.20 ± 9.39 |
| ANN | 77.72 ± 10.82 | 89.60 ± 7.73 | 87.14 ± 8.38 | 86.67 ± 7.01 | 92.87 ± 5.45 | |
| DGGCN [14] | 72.63 ± 5.59 | 72.33 ± 5.77 | 72.23 ± 5.75 | 72.43 ± 5.85 | 88.56 ± 5.98 | |
| PGCNN [19] | 72.31 ± 5.24 | 71.78 ± 5.17 | 71.44 ± 4.80 | 71.95 ± 5.58 | 90.89 ± 4.68 | |
| Causal-GCN [26] | 72.24 ± 5.41 | 71.93 ± 5.19 | 72.15 ± 4.98 | 72.61 ± 5.20 | 88.48 ± 5.71 | |
| GC-GCN | 72.58 ± 5.16 | 78.09 ± 5.94 | 78.68 ± 5.82 | 79.55 ± 5.56 | 91.82 ± 4.82 | |
| GC-F-GCN | 84.14 ± 7.61 | 93.45 ± 5.42 | 92.62 ± 5.60 | 91.69 ± 4.72 | 97.91 ± 2.50 | |
| Valence | SVM | 67.68 ± 9.42 | 72.79 ± 9.14 | 77.17 ± 11.80 | 78.76 ± 11.02 | 83.43 ± 11.50 |
| ANN | 78.63 ± 10.13 | 89.65 ± 6.81 | 87.73 ± 6.07 | 87.90 ± 5.38 | 92.28 ± 6.12 | |
| DGGCN [14] | 72.64 ± 5.49 | 72.25 ± 5.94 | 71.79 ± 4.86 | 72.27 ± 5.79 | 88.36 ± 5.48 | |
| PGCNN [19] | 69.94 ± 6.22 | 69.34 ± 6.24 | 70.56 ± 6.33 | 70.50 ± 5.83 | 90.35 ± 5.02 | |
| Causal-GCN [26] | 71.92 ± 5.63 | 71.95 ± 5.36 | 71.69 ± 5.40 | 71.96 ± 5.62 | 88.46 ± 5.11 | |
| GC-GCN | 78.06 ± 5.84 | 78.25 ± 5.01 | 76.85 ± 6.37 | 77.66 ± 5.45 | 92.01 ± 5.23 | |
| GC-F-GCN | 84.02 ± 8.01 | 84.19 ± 7.86 | 83.98 ± 7.83 | 83.82 ± 7.76 | 98.46 ± 1.16 | |
| arousal–Valence | SVM | 69.54 ± 14.10 | 78.61 ± 11.44 | 82.31 ± 9.67 | 86.95 ± 7.89 | 87.68 ± 6.98 |
| ANN | 69.03 ± 13.05 | 68.64 ± 14.39 | 62.34 ± 16.20 | 60.78 ± 14.05 | 87.53 ± 12.25 | |
| DGGCN [14] | 72.65 ± 5.60 | 73.15 ± 5.86 | 72.65 ± 5.59 | 73.00 ± 5.29 | 82.40 ± 9.32 | |
| PGCNN [19] | 53.76 ± 8.96 | 54.88 ± 9.51 | 70.36 ± 6.22 | 71.07 ± 70.1 | 85.64 ± 7.99 | |
| Causal-GCN [26] | 73.10 ± 5.39 | 73.22 ± 5.37 | 73.14 ± 5.37 | 73.39 ± 6.29 | 82.35 ± 9.23 | |
| GC-GCN | 71.47 ± 4.93 | 72.07 ± 5.07 | 71.97 ± 4.36 | 72.09 ± 5.19 | 87.38 ± 7.94 | |
| GC-F-GCN | 77.28 ± 11.96 | 77.20 ± 12.68 | 77.07 ± 12.10 | 77.05 ± 12.32 | 98.15 ± 2.39 |
| Model | Arousal | Valence | Arousal–Valence | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Times (s) | Parameters | Times (s) | Parameters | Times (s) | |
| DGGCN [14] | 4338 | 15 | 4338 | 15 | 4404 | 16 |
| PGCNN [19] | 4274 | 16 | 4274 | 16 | 4340 | 16 |
| Causal-GCN [26] | 4402 | 17 | 4402 | 17 | 4468 | 18 |
| GC-GCN | 4218 | 25 | 4218 | 26 | 4284 | 29 |
| GC-F-GCN | 4970 | 123 | 24,970 | 124 | 25,076 | 126 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Q. Granger-Causality-Based Multi-Frequency Band EEG Graph Feature Extraction and Fusion for Emotion Recognition. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121649
Zhang J, Zhang X, Chen G, Zhao Q. Granger-Causality-Based Multi-Frequency Band EEG Graph Feature Extraction and Fusion for Emotion Recognition. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(12):1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121649
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jing, Xueying Zhang, Guijun Chen, and Qing Zhao. 2022. "Granger-Causality-Based Multi-Frequency Band EEG Graph Feature Extraction and Fusion for Emotion Recognition" Brain Sciences 12, no. 12: 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121649
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhang, X., Chen, G., & Zhao, Q. (2022). Granger-Causality-Based Multi-Frequency Band EEG Graph Feature Extraction and Fusion for Emotion Recognition. Brain Sciences, 12(12), 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121649






