Granger-Causality-Based Multi-Frequency Band EEG Graph Feature Extraction and Fusion for Emotion Recognition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Overview of the GC Method
2.2. Overviews of Graph Convolutional Neural Networks (GCN)
3. The Proposed GC-F-GCN Scheme for EEG Emotion Recognition
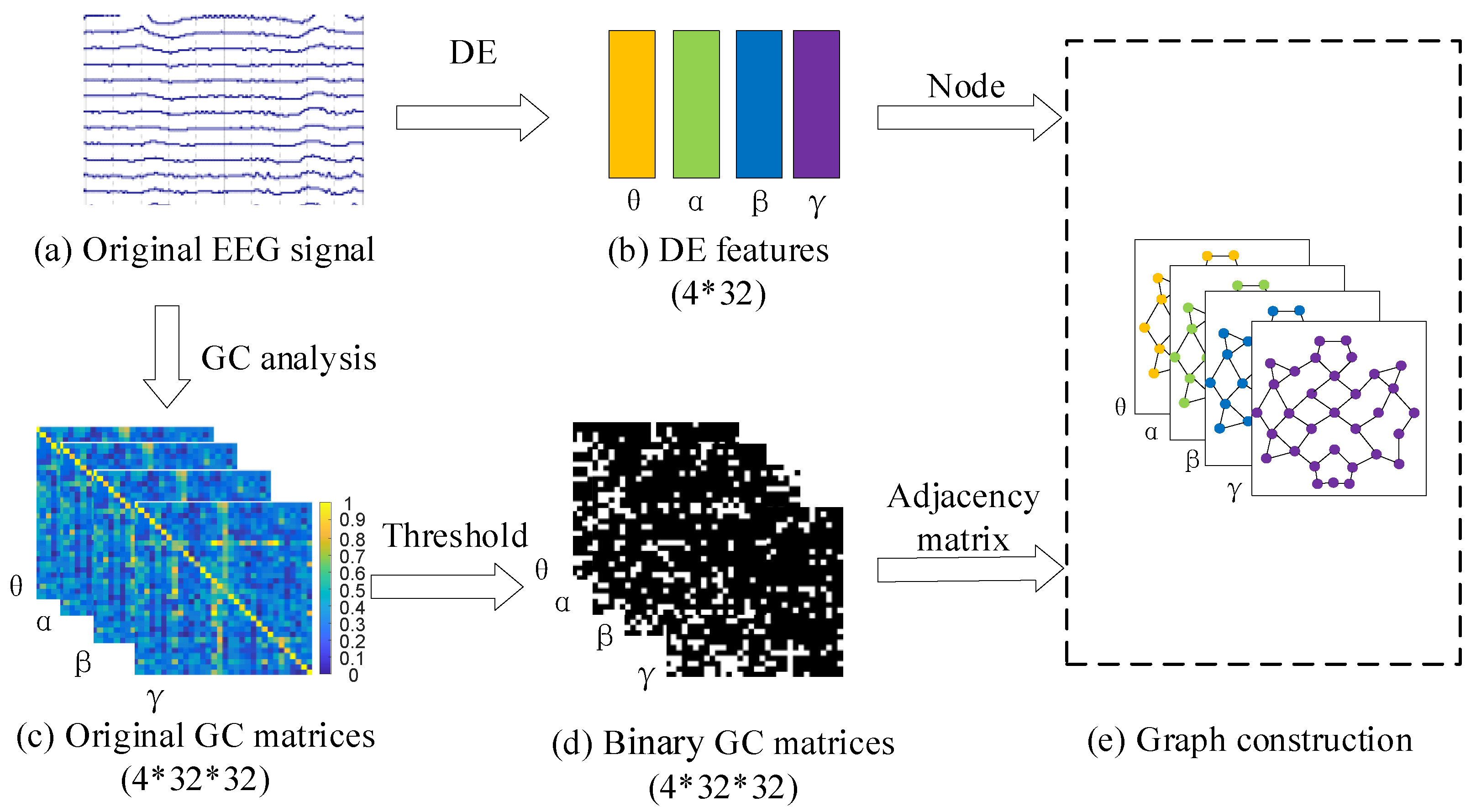
3.1. Preprocessing of EEG Signals
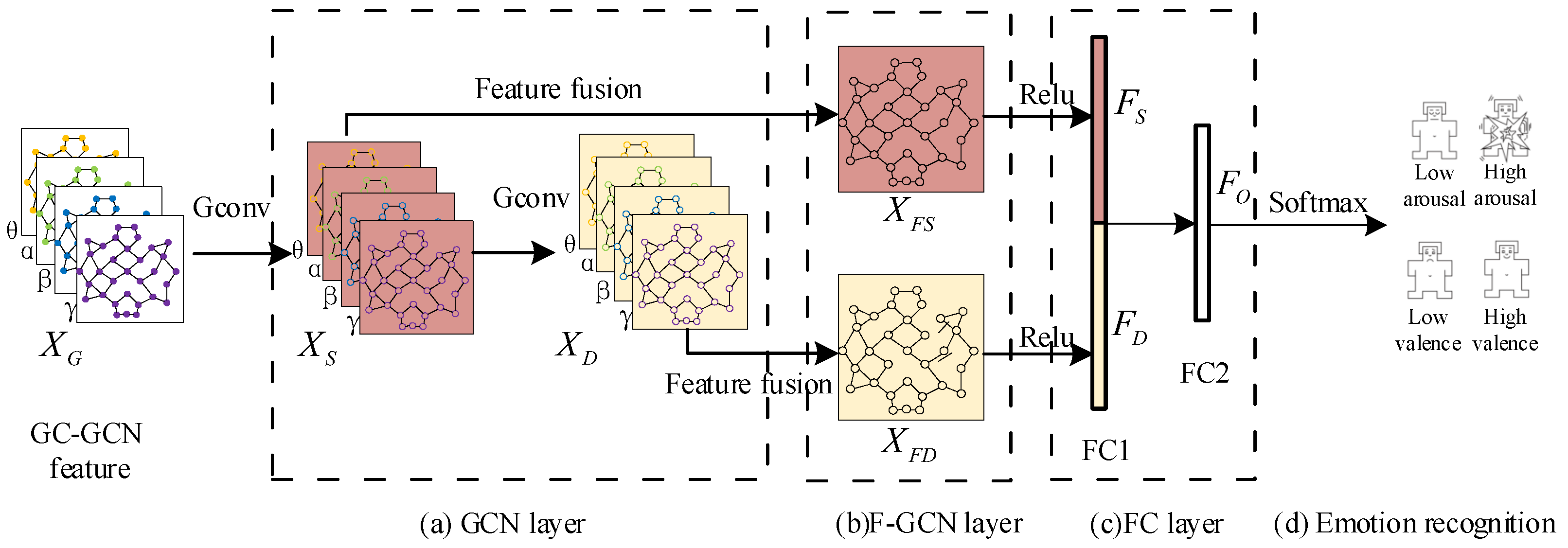
3.2. The Construction of GC-GCN Graph Feature
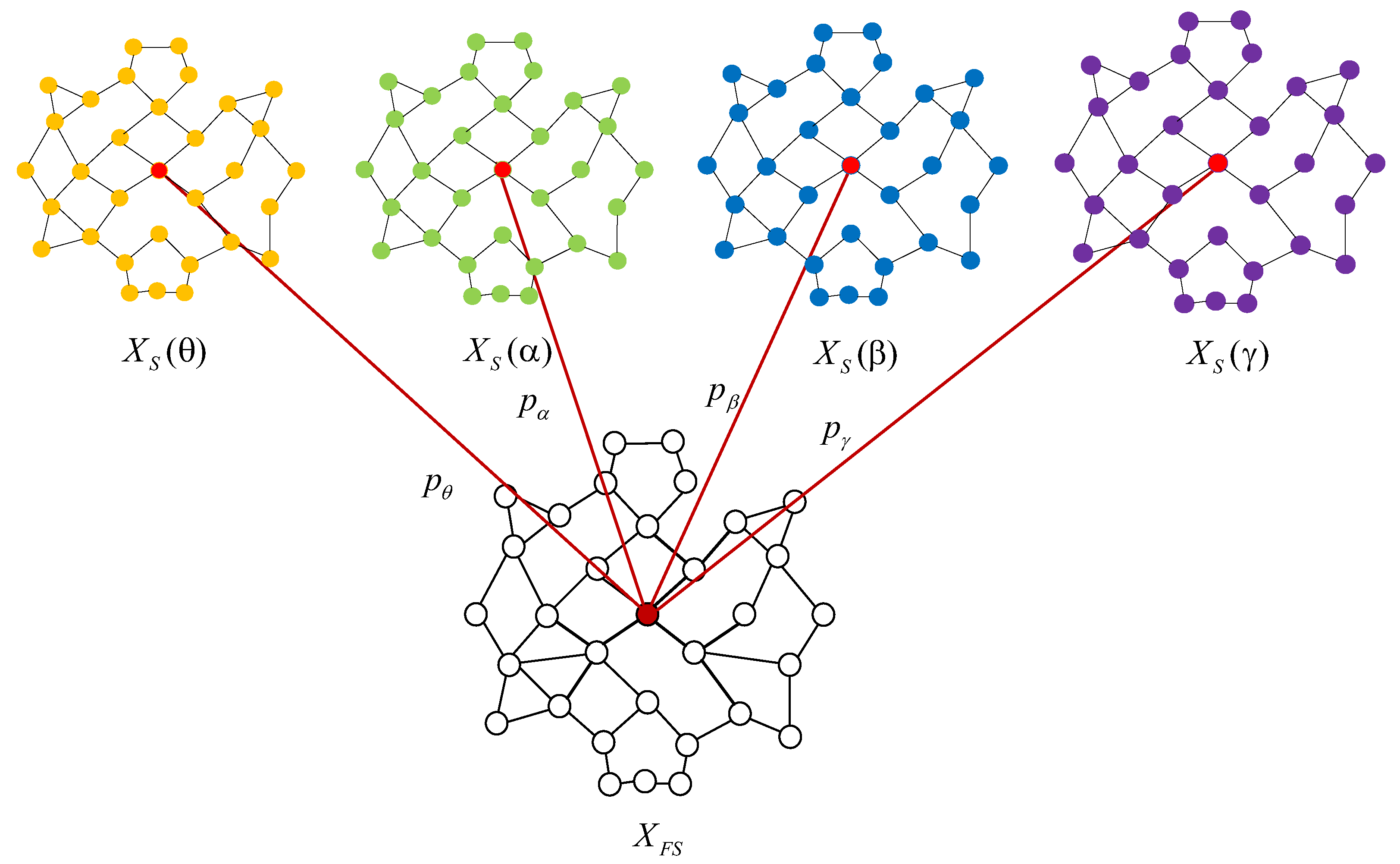
3.3. Multi-Frequency Band Graph Feature Fusion Method
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. The Emotion Recognition Performance of the GC-GCN Graph Feature
4.2. The Performance of the GC-F-GCN Feature Fusion Method
4.3. Performance Comparisons for Latest GCN Graph Feature
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EEG | Electroencephalogram |
| GC | Granger causality |
| GCN | Graph convolutional neural network |
| GC-GCN | GC-based GCN graph feature |
| GC-F-GCN | Multi-frequency band GC-GCN feature fusion method |
| PLV | Phase Locking Value |
| SGC-GCN | Shallow graph feature |
| DGC-GCN | Deep graph feature |
| SDGC-GCN | Shallow and deep cascade graph feature |
| SGC-F-GCN | Shallow fusion feature |
| DGC-F-GCN | Deep fusion feature |
| SDGC-F-GCN | Shallow and deep fusion feature |
References
- Zhang, J.H.; Yin, Z.; Chen, P.; Nichele, P. Emotion recognition using multi-modal data and machine learning techniques: A tutorial and review. Inf. Fusion 2020, 59, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Li, F.; Li, P.; Yi, C.; Li, C.; Tao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Si, Y.; Yao, D.; Yin, G.; et al. A survey of brain network analysis by electroencephalographic signals. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2022, 16, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Pato, V.M.; Sánchez, C.N.; Domínguez-Soberanes, J.; Méndoza-Pérez, D.E.; Velázquez, R. A Multisensor Data Fusion Approach for Predicting Consumer Acceptance of Food Products. Foods 2020, 9, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.Z.; He, Y.; Zang, Y.F.; Weng, X.C. Modulation of functional connectivity during the resting state and the motor task. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2004, 22, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.L.; Lu, B.L. Investigating critical frequency bands and channels for EEG-based emotion recognition with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Auton. Ment. Dev. 2015, 7, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Xiao, R.L.; Cui, W.J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, G.D. Application of EEG-based machine learning in emotion recognition: A Review. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Wu, Q.; Fu, Y.Z.; Chen, X.W. Continuous convolutional neural network with 3d input for EEG-based emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Siem Reap, Cambodia, 13–16 December 2018; pp. 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Dai, G.; Lin, G. EEG-based emotion recognition using 4D convolutional recurrent neural network. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2020, 14, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, G.J.; Yan, C. EEG emotion recognition based on the 3D-CNN and spatial-frequency attention mechanism. J. Xidian Univ. 2022, 49, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defferrard, M.; Bresson, X.; Vandergheynst, P. Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; pp. 3844–38523. [Google Scholar]
- Levie, R.; Monti, F.; Bresson, X.; Bronstein, M. Cayleynets: Graph convolutional neural networks with complex rational spectral filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 67, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M.; Vandergheynst, P. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.Q.; Zheng, X.W.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.C. EEG emotion recognition using fusion model of graph convolutional neural networks and LSTM. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 100, 106954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.F.; Zheng, W.M.; Song, P.; Cui, Z. EEG emotion recognition using dynamical graph convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2018, 11, 32–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, T.F.; Zheng, W.M.; Liu, S.Y.; Zong, Y.; Cui, Z.; Li, Y. Graph-Embedded Convolutional Neural Network for Image-based EEG Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 2021, 10, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Liu, X.C.; Li, J.H.; Xu, T.; Bezerianos, A.; Sun, Y.; Wan, F. Driving fatigue recognition with functional connectivity based on phase synchronization. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2020, 13, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.L.; Li, M.; Ju, X.Y.; Liu, Y.D. Applying Multiple Functional Connectivity Features in GCN for EEG-Based Human Identification. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, M.; Sun, A.; Liu, J.J.; Men, H. A fast Pearson graph convolutional network combined with electronic nose to identify the origin of rice. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 21175–21183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Tong, Y.; Heng, X. Phase-locking value-based graph convolutional neural networks for emotion recognition. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 93711–93722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhao, Y.F.; Shan, X.C.; Wei, H.L.; Guo, Y.Z.; Chen, L.Y.; Erkoyuncu, A.J.; Sarrigiannis, P.G. Brain Functional and Effective Connectivity Based on Electroencephalography Recordings: A Review. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2022, 43, 860–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, R.; Bortoletto, M.; Miniussi, C. Integrating TMS, EEG, and MRI as an approach for studying brain connectivity. Neuroscientist 2020, 26, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.E.; Chen, C.J.; Hsieh, C.J.; Wang, J.L.; Lee, J.S. Emotional EEG Classification Using Connectivity Features and Convolutional Neural Networks. Neural Netw. 2020, 132, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.T.; Headley, D.B.; Mill, R.D.; Sanchez-Romero, R.; Uddin, L.Q.; Marinazzo, D.; Lurie, D.J.; Valdés-Sosa, P.A.; Hanson, S.J.; Biswal, B.B.; et al. Advancing functional connectivity research from association to causation. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.W.J. Investigating Causal Relations by Econometric Models and Cross-Spectral Methods. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1969, 10, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Y.; Wang, X.K.; Potter, T.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, Y.C. Single-trial EEG emotion recognition using Granger Causality/Transfer Entropy analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2020, 346, 108904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.Z.; Qiu, M.; Li, M.H.; Jin, X.Y.; Zhu, L. Causal Graph Convolutional Neural Network for Emotion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2022; Early Access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.Y.; Peng, Y.; Kong, W.Z.; Dai, G.J. Multi-scale frequency bands ensemble learning for EEG-based emotion recognition. Sensors 2021, 21, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.L.; Liu, W.; Lu, Y.F.; Lu, B.L.; Cichocki, A. Emotionmeter: A Multimodal Framework for Recognizing Human Emotions. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 1110–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.D.; Xie, L.; Chai, B.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H. Spatial-frequency convolutional self-attention network for EEG emotion recognition. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 122, 108740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.W.; Shi, M.; Ye, M.W.; Xu, B.W.; Chen, Z.D.; Ren, Q.S. 4D attention-based neural network for EEG emotion recognition. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2022, 16, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tong, H.H.; Xu, J.J.; Maciejewski, R. Graph convolutional networks: Algorithms, applications and open challenges. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Computational Data and Social Networks, Shanghai, China, 18–12 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Tong, H.H.; Xu, J.J.; Maciejewski, R. Graph convolutional networks: A comprehensive review. Comput. Soc. Netw. 2019, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koelstra, S.; Muhl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Lee, J.S.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Pun, T.; Nijholt, A.; Patras, L. DEAP: A Database for Emotion Analysis Using Physiological Signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2011, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, G.J.; Huang, L.X.; Sun, Y. EEG emotion recognition based on cross-frequency granger causality feature extraction and fusion in the left and right hemispheres. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 974673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.C.; Jiao, Y.Y.; Lu, B.L. Differential entropy feature for EEG-based vigilance estimation. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 6627–6630. [Google Scholar]

| k | Arousal | Valence | Arousal–Valence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 91.35 ± 5.37 | 91.34 ± 5.45 | 86.90 ± 8.23 |
| 20% | 91.56 ± 5.14 | 91.66 ± 5.25 | 87.21 ± 8.31 |
| 30% | 91.22 ± 5.53 | 92.01 ± 5.23 | 86.71 ± 8.10 |
| 40% | 91.15 ± 5.34 | 91.23 ± 5.52 | 86.93 ± 8.45 |
| 50% | 91.55 ± 5.33 | 91.46 ± 5.57 | 87.31 ± 8.78 |
| 60% | 91.82 ± 4.82 | 91.27 ± 5.88 | 86.80 ± 9.1 |
| 70% | 91.73 ± 5.66 | 91.25 ± 4.79 | 87.38 ± 7.94 |
| 80% | 91.48 ± 5.21 | 91.91 ± 4.88 | 87.30 ± 9.06 |
| 90% | 91.38 ± 5.26 | 91.60 ± 5.09 | 86.87 ± 8.91 |
| Emotion | Adjacency Matrix | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arousal | Random | 71.89 ± 5.44 | 72.12 ± 5.80 | 71.22 ± 5.78 | 71.54 ± 4.87 | 87.45 ± 5.53 |
| Distance | 71.42 ± 5.93 | 72.52 ± 6.24 | 75.32 ± 6.24 | 75.10 ± 5.74 | 87.23 ± 5.17 | |
| PLV [19] | 72.31 ± 5.24 | 71.78 ± 5.17 | 71.44 ± 4.80 | 71.95 ± 5.58 | 90.89 ± 4.68 | |
| GC-GCN | 72.58 ± 5.16 | 78.09 ± 5.94 | 78.68 ± 5.82 | 79.55 ± 5.56 | 91.82 ± 4.82 | |
| Valence | Random | 69.92 ± 6.46 | 69.71 ± 6.65 | 69.42 ± 6.50 | 69.80 ± 5.46 | 87.31 ± 4.75 |
| Distance | 70.61 ± 6.36 | 70.67 ± 6.26 | 70.33 ± 7.12 | 69.89 ± 5.75 | 87.58 ± 5.42 | |
| PLV [19] | 69.94 ± 6.22 | 69.34 ± 6.24 | 70.56 ± 6.33 | 70.50 ± 5.83 | 90.35 ± 5.02 | |
| GC-GCN | 78.06 ± 5.84 | 78.25 ± 5.01 | 76.85 ± 6.37 | 77.66 ± 5.45 | 92.01 ± 5.23 | |
| Arousal–Valence | Random | 55.92 ± 9.24 | 54.35 ± 8.34 | 53.80+9.38 | 55.34+9.29 | 83.88 ± 9.00 |
| Distance | 54.51 ± 9.57 | 54.90 ± 8.28 | 54.00 ± 8.40 | 55.27 ± 9.57 | 83.86 ± 8.66 | |
| PLV [19] | 53.76 ± 8.96 | 54.88 ± 9.51 | 70.36 ± 6.22 | 71.07 ± 70.1 | 85.64 ± 7.99 | |
| GC-GCN | 71.47 ± 4.93 | 72.07 ± 5.07 | 71.97 ± 4.36 | 72.09 ± 5.19 | 87.38 ± 7.94 |
| Features | Arousal | Valence | Arousal–Valence |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGC-GCN | 92.12 ± 3.06 | 90.71 ± 5.00 | 87.53 ± 2.91 |
| DGC-GCN | 91.82 ± 4.82 | 92.01 ± 5.23 | 87.38 ± 7.94 |
| SDGC-GCN | 93.58 ± 5.78 | 93.25 ± 4.22 | 92.38 ± 3.05 |
| SGC-GCN | 97.12 ± 2.53 | 97.11 ± 2.30 | 97.13 ± 2.66 |
| DGC-GCN | 97.41 ± 3.29 | 98.23 ± 1.38 | 97.78 ± 3.26 |
| SDGC-F-GCN | 97.91 ± 2.50 | 98.46 ± 1.16 | 98.15 ± 2.39 |
| Emotion | Method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arousal | SVM | 74.19 ± 8.55 | 76.05 ± 8.68 | 80.10 ± 8.47 | 83.74 ± 7.17 | 84.20 ± 9.39 |
| ANN | 77.72 ± 10.82 | 89.60 ± 7.73 | 87.14 ± 8.38 | 86.67 ± 7.01 | 92.87 ± 5.45 | |
| DGGCN [14] | 72.63 ± 5.59 | 72.33 ± 5.77 | 72.23 ± 5.75 | 72.43 ± 5.85 | 88.56 ± 5.98 | |
| PGCNN [19] | 72.31 ± 5.24 | 71.78 ± 5.17 | 71.44 ± 4.80 | 71.95 ± 5.58 | 90.89 ± 4.68 | |
| Causal-GCN [26] | 72.24 ± 5.41 | 71.93 ± 5.19 | 72.15 ± 4.98 | 72.61 ± 5.20 | 88.48 ± 5.71 | |
| GC-GCN | 72.58 ± 5.16 | 78.09 ± 5.94 | 78.68 ± 5.82 | 79.55 ± 5.56 | 91.82 ± 4.82 | |
| GC-F-GCN | 84.14 ± 7.61 | 93.45 ± 5.42 | 92.62 ± 5.60 | 91.69 ± 4.72 | 97.91 ± 2.50 | |
| Valence | SVM | 67.68 ± 9.42 | 72.79 ± 9.14 | 77.17 ± 11.80 | 78.76 ± 11.02 | 83.43 ± 11.50 |
| ANN | 78.63 ± 10.13 | 89.65 ± 6.81 | 87.73 ± 6.07 | 87.90 ± 5.38 | 92.28 ± 6.12 | |
| DGGCN [14] | 72.64 ± 5.49 | 72.25 ± 5.94 | 71.79 ± 4.86 | 72.27 ± 5.79 | 88.36 ± 5.48 | |
| PGCNN [19] | 69.94 ± 6.22 | 69.34 ± 6.24 | 70.56 ± 6.33 | 70.50 ± 5.83 | 90.35 ± 5.02 | |
| Causal-GCN [26] | 71.92 ± 5.63 | 71.95 ± 5.36 | 71.69 ± 5.40 | 71.96 ± 5.62 | 88.46 ± 5.11 | |
| GC-GCN | 78.06 ± 5.84 | 78.25 ± 5.01 | 76.85 ± 6.37 | 77.66 ± 5.45 | 92.01 ± 5.23 | |
| GC-F-GCN | 84.02 ± 8.01 | 84.19 ± 7.86 | 83.98 ± 7.83 | 83.82 ± 7.76 | 98.46 ± 1.16 | |
| arousal–Valence | SVM | 69.54 ± 14.10 | 78.61 ± 11.44 | 82.31 ± 9.67 | 86.95 ± 7.89 | 87.68 ± 6.98 |
| ANN | 69.03 ± 13.05 | 68.64 ± 14.39 | 62.34 ± 16.20 | 60.78 ± 14.05 | 87.53 ± 12.25 | |
| DGGCN [14] | 72.65 ± 5.60 | 73.15 ± 5.86 | 72.65 ± 5.59 | 73.00 ± 5.29 | 82.40 ± 9.32 | |
| PGCNN [19] | 53.76 ± 8.96 | 54.88 ± 9.51 | 70.36 ± 6.22 | 71.07 ± 70.1 | 85.64 ± 7.99 | |
| Causal-GCN [26] | 73.10 ± 5.39 | 73.22 ± 5.37 | 73.14 ± 5.37 | 73.39 ± 6.29 | 82.35 ± 9.23 | |
| GC-GCN | 71.47 ± 4.93 | 72.07 ± 5.07 | 71.97 ± 4.36 | 72.09 ± 5.19 | 87.38 ± 7.94 | |
| GC-F-GCN | 77.28 ± 11.96 | 77.20 ± 12.68 | 77.07 ± 12.10 | 77.05 ± 12.32 | 98.15 ± 2.39 |
| Model | Arousal | Valence | Arousal–Valence | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Times (s) | Parameters | Times (s) | Parameters | Times (s) | |
| DGGCN [14] | 4338 | 15 | 4338 | 15 | 4404 | 16 |
| PGCNN [19] | 4274 | 16 | 4274 | 16 | 4340 | 16 |
| Causal-GCN [26] | 4402 | 17 | 4402 | 17 | 4468 | 18 |
| GC-GCN | 4218 | 25 | 4218 | 26 | 4284 | 29 |
| GC-F-GCN | 4970 | 123 | 24,970 | 124 | 25,076 | 126 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Q. Granger-Causality-Based Multi-Frequency Band EEG Graph Feature Extraction and Fusion for Emotion Recognition. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121649
Zhang J, Zhang X, Chen G, Zhao Q. Granger-Causality-Based Multi-Frequency Band EEG Graph Feature Extraction and Fusion for Emotion Recognition. Brain Sciences. 2022; 12(12):1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121649
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jing, Xueying Zhang, Guijun Chen, and Qing Zhao. 2022. "Granger-Causality-Based Multi-Frequency Band EEG Graph Feature Extraction and Fusion for Emotion Recognition" Brain Sciences 12, no. 12: 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121649
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhang, X., Chen, G., & Zhao, Q. (2022). Granger-Causality-Based Multi-Frequency Band EEG Graph Feature Extraction and Fusion for Emotion Recognition. Brain Sciences, 12(12), 1649. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12121649






