Systemic Inflammatory Response Index and Futile Recanalization in Patients with Ischemic Stroke Undergoing Endovascular Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
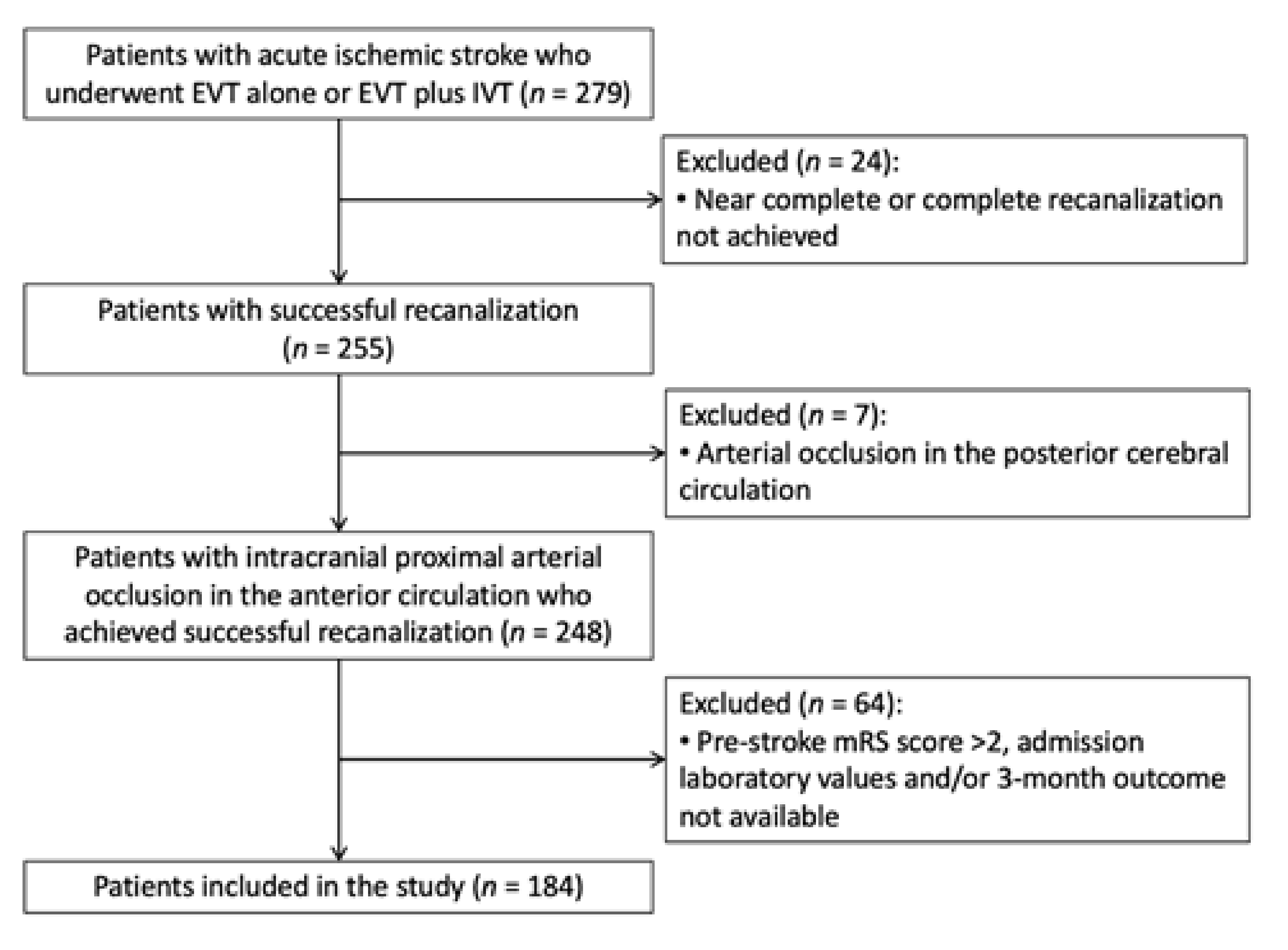
2. Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Statistical Analysis
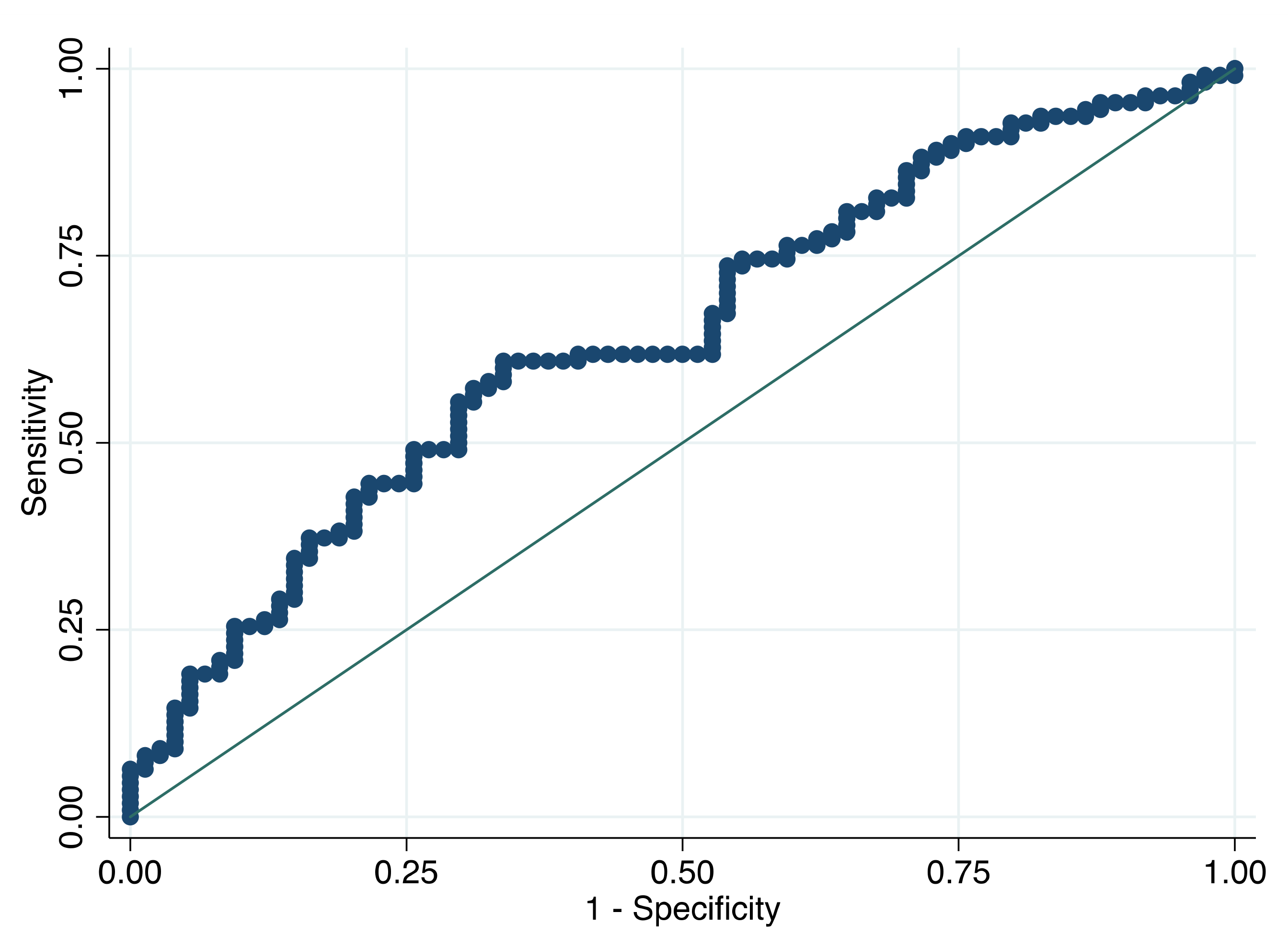
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krueger, H.; Koot, J.; Hall, R.E.; O’Callaghan, C.; Bayley, M.; Corbett, D. Prevalence of individuals experiencing the effects of stroke in Canada: Trends and projections. Stroke 2015, 46, 2226–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lattanzi, S.; Coccia, M.; Pulcini, A.; Cagnetti, C.; Galli, F.L.; Villani, L.; Campa, S.; Dobran, M.; Polonara, G.; Ceravolo, M.G.; et al. Endovascular treatment and cognitive outcome after anterior circulation ischemic stroke. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, S.; Rinaldi, C.; Cagnetti, C.; Foschi, N.; Norata, D.; Broggi, S.; Rocchi, C.; Silvestrini, M. Predictors of Pharmaco-Resistance in Patients with Post-Stroke Epilepsy. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.M.; Saleem, M.A.; Qureshi, A. Rates and predictors of futile recanalization in patients undergoing endovascular treatment in a multicenter clinical trial. Neuroradiology 2018, 60, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansueto, G.; Costa, D.; Capasso, E.; Varavallo, F.; Brunitto, G.; Caserta, R.; Esposito, S.; Niola, M.; Sardu, C.; Marfella, R.; et al. The dating of thrombus organization in cases of pulmonary embolism: An autopsy study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2019, 19, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisicaro, F.; Di Napoli, M.; Liberto, A.; Fanella, M.; Di Stasio, F.; Pennisi, M.; Bella, R.; Lanza, G.; Mansueto, G. Neurological Sequelae in Patients with COVID-19: A Histopathological Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrez, R.; Ali, C.; Toutirais, O.; Le Mauff, B.; Defer, G.; Dirnagl, U.; Vivien, D. Stroke and the immune system: From pathophysiology to new therapeutic strategies. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simats, A.; García-Berrocoso, T.; Montaner, J. Neuroinflammatory biomarkers: From stroke diagnosis and prognosis to therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2016, 1862, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.J.; Sung, J.H.; Lee, D.H. Systemic Inflammation Response Index and Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index Are Associated with Clinical Outcomes in Patients Treated with Mechanical Thrombectomy for Large Artery Occlusion. World Neurosurg. 2021, 153, 105861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świtońska, M.; Piekuś-Słomka, N.; Słomka, A.; Sokal, P.; Żekanowska, E.; Lattanzi, S. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Symptomatic Hemorrhagic Transformation in Ischemic Stroke Patients Undergoing Revascularization. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangari, R.; Zanier, E.R.; Torgano, G.; Bersano, A.; Beretta, S.; Beghi, E.; Casolla, B.; Checcarelli, N.; Lanfranconi, S.; Maino, A.; et al. Early ficolin-1 is a sensitive prognostic marker for functional outcome in ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, Z.; Hao, D.; Song, Y.; Zhuang, L.; Wang, Q.; Yu, X. Systemic inflammatory response index as an independent risk factor for ischemic stroke in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A retrospective study based on propensity score matching. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Yi, H.J.; Lee, D.H.; Sung, J.H. Systemic Inflammation Response Index and Systemic Immune-inflammation Index for Pre-dicting the Prognosis of Patients with Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 30, 105861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashida, R.T.; Furlan, A.J.; Roberts, H.; Tomsick, T.; Connors, B.; Barr, J.; Dillon, W.; Warach, S.; Broderick, J.; Tilley, B.; et al. Trial design and reporting standards for intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2003, 34, e109–e137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wityk, R.J.; Pessin, M.S.; Kaplan, R.F.; Caplan, L.R. Serial assessment of acute stroke using the NIH Stroke Scale. Stroke 1994, 25, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lattanzi, S.; Cagnetti, C.; Pulcini, A.; Morelli, M.; Maffei, S.; Provinciali, L.; Silvestrini, M. The P-wave terminal force in embolic strokes of undetermined source. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 375, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, S.; Pulcini, A.; Corradetti, T.; Rinaldi, C.; Zedde, M.L.; Ciliberti, G.; Silvestrini, M. Prediction of Outcome in Embolic Strokes of Undetermined Source. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 104–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lattanzi, S.; Rinaldi, C.; Pulcini, A.; Corradetti, T.; Angelocola, S.; Zedde, M.L.; Ciliberti, G.; Silvestrini, M. Clinical phenotypes of embolic strokes of undetermined source. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, P.A.; Demchuk, A.M.; Zhang, J.; Buchan, A.M. Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy. Lancet 2000, 355, 1931–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, J.L.; Marotta, C.A. Outcomes validity and reliability of the modified Rankin scale: Implications for stroke clinical trials: A literature review and synthesis. Stroke 2007, 38, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, X.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Duan, W.; Liu, L. Futile Recanalization after Endovascular Therapy in Acute Ischemic Stroke. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S. Applied Logistic Regression, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Iadecola, C.; Anrather, J. The immunology of stroke: From mechanisms to translation. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Yang, G.; Li, G. Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: Role of inflammatory cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anrather, J.; Iadecola, C. Inflammation and Stroke: An Overview. Neuroradio 2016, 13, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, S.; Di Napoli, M.; Ricci, S.; Divani, A.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases in Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Neuroradio 2020, 17, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, S.F.; Denorme, F.; Langhauser, F.; Geuss, E.; Fluri, F.; Kleinschnitz, C. Thromboinflammation in Stroke Brain Damage. Stroke 2016, 47, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ames, A., 3rd; Wright, R.L.; Kowada, M.; Thurston, J.M.; Majno, G. Cerebral ischemia. II. The no-reflow phenomenon. Am. J. Pathol. 1968, 52, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stoll, G.; Nieswandt, B. Thrombo-inflammation in acute ischaemic stroke-implications for treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, M.A.; Lo, E.H.; Iadecola, C. The Science of Stroke: Mechanisms in Search of Treatments. Neuron 2010, 67, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meisel, C.; Schwab, J.; Prass, K.; Meisel, A.; Dirnagl, U. Central nervous system injury-induced immune deficiency syndrome. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, A.; Urra, X.; Planas, A.M. Infection after acute ischemic stroke: A manifestation of brain-induced immunodepression. Stroke 2007, 38, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogelgesang, A.; Grunwald, U.; Langner, S.; Jack, R.; Bröker, B.; Kessler, C.; Dressel, A. Analysis of Lymphocyte Subsets in Patients with Stroke and Their Influence on Infection After Stroke. Stroke 2008, 39, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urra, X.; Cervera, Á.; Villamor, N.; Planas, A.; Chamorro, Á. Harms and benefits of lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with acute stroke. Neuroradio 2009, 158, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wu, H.; Klebe, D.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J. Regulatory T Cell in Stroke: A New Paradigm for Immune Regulation. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 689827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brait, V.H.; Arumugam, T.; Drummond, G.; Sobey, C.G. Importance of T Lymphocytes in Brain Injury, Immunodeficiency, and Recovery after Cerebral Ischemia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 32, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, Y.; Shen, J.; Chen, S.-C.; Chen, J.-X.; Xia, Y.-P. Prognostic value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in acute ischemic stroke after reperfusion therapy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, S.; Cagnetti, C.; Provinciali, L.; Silvestrini, M. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and neurological deterioration following acute cerebral hemorrhage. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 57489–57494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lattanzi, S.; Cagnetti, C.; Rinaldi, C.; Angelocola, S.; Provinciali, L.; Silvestrini, M. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio improves outcome prediction of acute intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 387, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, O.C.; Haring, H.P.; Trenkler, J.; Nolte, C.H.; Bohner, G.; Reich, A.; Wiesmann, M.; Bussmeyer, M.; Mpotsaris, A.; Neumann-Haefelin, T. Age dependency of successful recanalization in anterior circulation stroke: The ENDOSTROKE study. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 36, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, N.; Lin, Z.; Huang, K.; Pan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Ji, Z.; Pan, S. Biomarkers of Unfavorable Outcome in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients with Successful Re-canalization by Endovascular Thrombectomy. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 49, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedraza, M.I.; De Lera, M.; Bos, D.; Calleja, A.I.; Cortijo, E.; Gómez-Vicente, B.; Reyes, J.; Coco-Martín, M.B.; Calonge, T.; Agulla, J.; et al. Brain Atrophy and the Risk of Futile Endovascular Reperfusion in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Futile Recanalization | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| No (n = 74) | Yes (n = 110) | ||
| Demographics | |||
| Age (years) | 64 [53–76] | 79 [69–83] | <0.001 a |
| Male sex | 39 (52.7) | 48 (43.6) | 0.227 b |
| Clinical history | |||
| Current smoking | 17 (23.0) | 22 (20.0) | 0.629 b |
| Hypertension | 38 (51.4) | 79 (71.8) | 0.005 b |
| Diabetes mellitus | 6 (8.1) | 17 (15.5) | 0.140 b |
| Dyslipidemia | 36 (48.7) | 48 (43.6) | 0.503 b |
| Coronary artery disease | 17 (23.0) | 17 (15.5) | 0.198 b |
| Clinical assessment at admission | |||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 134.9 (20.9) | 140.3 (19.6) | 0.076 c |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 75.9 (11.3) | 78.8 (12.5) | 0.112 c |
| NIHSS score | 15 [10–18] | 16 [13–18] | 0.011 a |
| ASPECT value | 9 [7–10] | 8 [7–10] | 0.939 a |
| Location of intracranial occlusion | 0.349 b | ||
| Internal carotid artery | 13 (17.8) | 16 (14.6) | |
| * Internal carotid artery terminus | 1 (1.4) | 5 (4.6) | |
| Middle cerebral artery | |||
| M1 segment | 51 (68.9) | 68 (61.8) | |
| M2 segment | 9 (12.2) | 21 (19.1) | |
| Serum glucose (mg/dL) | 110 [87–131] | 116 [99–140] | 0.071 a |
| White blood cell count (×109/L) | 9310 [7360–12,020] | 9985 [7980–12,170] | 0.244 a |
| Absolute neutrophil count (×109/L) | 6910 [5050–9500] | 8040 [5990–10,140] | 0.071 a |
| Absolute monocyte count (×109/L) | 590 [430–800] | 675 [510–870] | 0.066 a |
| Absolute lymphocyte count (×109/L) | 1325 [970–1970] | 1130 [750–1580] | 0.012 a |
| SIRI (×109/L) | 3.3 [1.6–5.3] | 4.6 [2.4–8.3] | <0.001 a |
| Treatment | |||
| Intravenous thrombolysis | 50 (67.6) | 60 (54.6) | 0.077 b |
| Mechanical thrombectomy | 0.606 b | ||
| Stent-retrievers | 38 (51.4) | 60 (54.5) | |
| Aspiration catheters | 25 (33.8) | 30 (27.3) | |
| Both | 11 (14.9) | 20 (18.2) | |
| Dependent Variable | * Adjusted OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.07 (1.04–1.10) | <0.001 |
| Male sex | 0.85 (0.42–1.73) | 0.661 |
| History of hypertension | 1.28 (0.62–2.67) | 0.507 |
| Baseline NIHSS score | 1.10 (1.02–1.19) | 0.013 |
| ASPECT value | 1.02 (0.80–1.30) | 0.871 |
| Admission SIRI | 1.08 (1.01–1.17) | 0.028 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lattanzi, S.; Norata, D.; Divani, A.A.; Di Napoli, M.; Broggi, S.; Rocchi, C.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; Mansueto, G.; Silvestrini, M. Systemic Inflammatory Response Index and Futile Recanalization in Patients with Ischemic Stroke Undergoing Endovascular Treatment. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091164
Lattanzi S, Norata D, Divani AA, Di Napoli M, Broggi S, Rocchi C, Ortega-Gutierrez S, Mansueto G, Silvestrini M. Systemic Inflammatory Response Index and Futile Recanalization in Patients with Ischemic Stroke Undergoing Endovascular Treatment. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(9):1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091164
Chicago/Turabian StyleLattanzi, Simona, Davide Norata, Afshin A. Divani, Mario Di Napoli, Serena Broggi, Chiara Rocchi, Santiago Ortega-Gutierrez, Gelsomina Mansueto, and Mauro Silvestrini. 2021. "Systemic Inflammatory Response Index and Futile Recanalization in Patients with Ischemic Stroke Undergoing Endovascular Treatment" Brain Sciences 11, no. 9: 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091164
APA StyleLattanzi, S., Norata, D., Divani, A. A., Di Napoli, M., Broggi, S., Rocchi, C., Ortega-Gutierrez, S., Mansueto, G., & Silvestrini, M. (2021). Systemic Inflammatory Response Index and Futile Recanalization in Patients with Ischemic Stroke Undergoing Endovascular Treatment. Brain Sciences, 11(9), 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11091164








