Behavioral and Gene Expression Analysis of Stxbp6-Knockout Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mouse Model
2.2. Genotyping
2.3. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Behavioral Analysis
2.5. Differential Expression (DE) Analysis
2.6. Enrichment Analysis
2.7. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Analysis
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (QRT-PCR)
3. Results
3.1. Global Stxbp6-Knockout Mouse Model
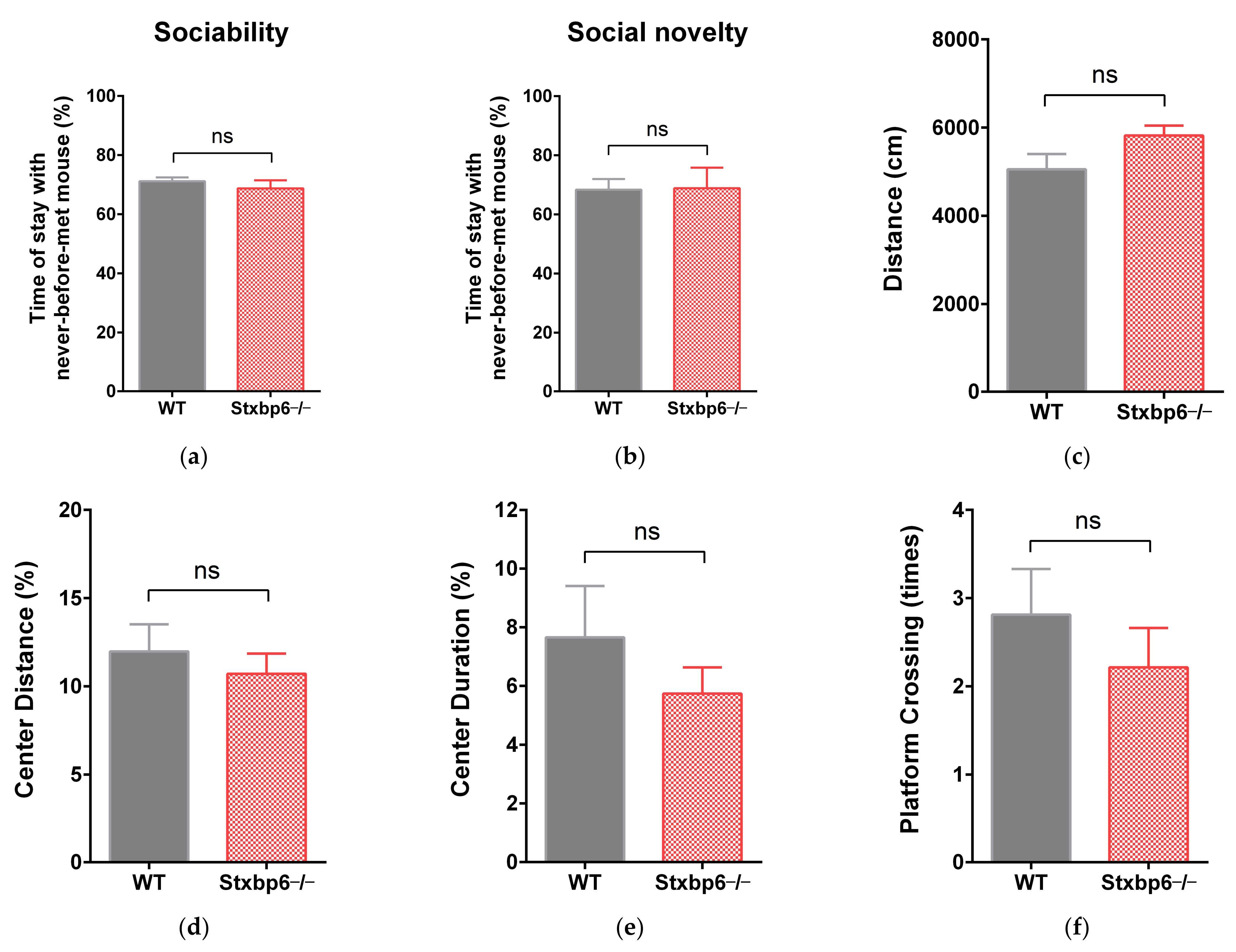
3.2. No Obvious Behavioral Abnormalities Were Observed in Stxbp6-Knockout Mice
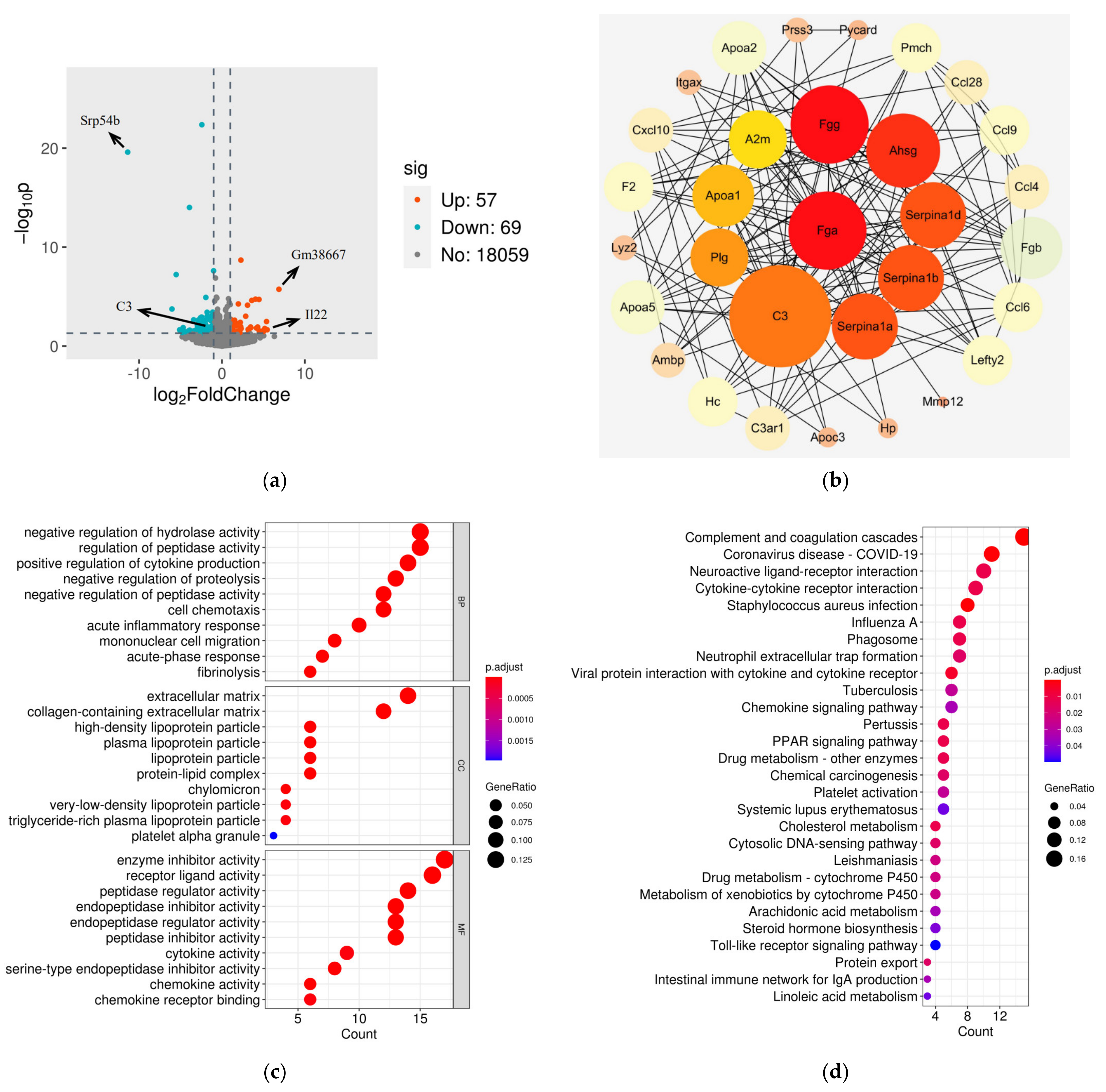
3.3. Comparison of Gene Expression Profiles between Cerebral Cortexes from WT and Stxbp6−/− Mice
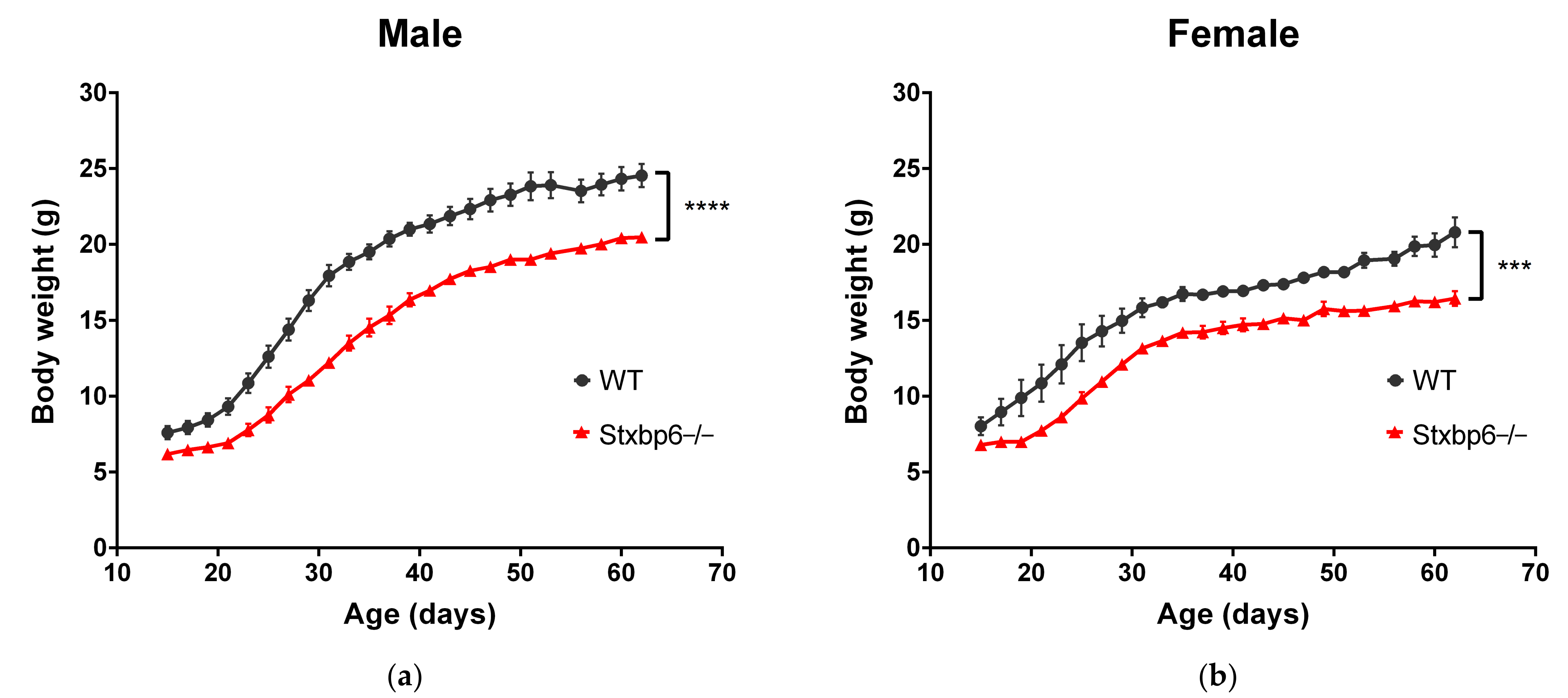
3.4. Stxbp6-Knockout Mice Were Leaner Than Age- and Sex-Matched Wildtype Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Nichols, E.; Alam, T.; Bannick, M.S.; Beghi, E.; Blake, N.; Culpepper, W.J.; Dorsey, E.R.; Elbaz, A.; Ellenbogen, R.G. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Kavalali, E.T. Synaptic vesicle-recycling machinery components as potential therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, M.A.; Xiao, W.; Macosko, J.C.; Chan, C.; Shin, Y.-K.; Bennett, M.K. The synaptic SNARE complex is a parallel four-stranded helical bundle. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Südhof, T.C.; Rothman, J.E. Membrane fusion: Grappling with SNARE and SM proteins. Science 2009, 323, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, S.; Deák, F.; Königstorfer, A.; Mozhayeva, M.; Sara, Y.; Südhof, T.C.; Kavalali, E.T. SNARE function analyzed in synaptobrevin/VAMP knockout mice. Science 2001, 294, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteggia, L.M.; Lin, P.-Y.; Adachi, M.; Kavalali, E.T. Behavioral analysis of SNAP-25 and Synaptobrevin-2 haploinsufficiency in mice. Neuroscience 2019, 420, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardar, G.; Chang, S.; Arancillo, M.; Wu, Y.-J.; Trimbuch, T.; Rosenmund, C. Distinct functions of syntaxin-1 in neuronal maintenance, synaptic vesicle docking, and fusion in mouse neurons. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 7911–7924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, M.; Shi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Fei, J. Brain-specific SNAP-25 deletion leads to elevated extracellular glutamate level and schizophrenia-like behavior in mice. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scales, S.J.; Hesser, B.A.; Masuda, E.S.; Scheller, R.H. Amisyn, a novel syntaxin-binding protein that may regulate SNARE complex assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 28271–28279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constable, J.R.; Graham, M.E.; Morgan, A.; Burgoyne, R.D. Amisyn regulates exocytosis and fusion pore stability by both syntaxin-dependent and syntaxin-independent mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 31615–31623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castermans, D.; Thienpont, B.; Volders, K.; Crepel, A.; Vermeesch, J.R.; Schrander-Stumpel, C.T.; Van de Ven, W.J.; Steyaert, J.G.; Creemers, J.W.; Devriendt, K. Position effect leading to haploinsufficiency in a mosaic ring chromosome 14 in a boy with autism. Eur. J. Human Genet. 2008, 16, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castermans, D.; Volders, K.; Crepel, A.; Backx, L.; De Vos, R.; Freson, K.; Meulemans, S.; Vermeesch, J.R.; Schrander-Stumpel, C.T.; De Rijk, P. SCAMP5, NBEA and AMISYN: Three candidate genes for autism involved in secretion of large dense-core vesicles. Human Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.C.; Do, H.W.; Hastoy, B.; Hugill, A.; Adam, J.; Chibalina, M.V.; Galvanovskis, J.; Godazgar, M.; Lee, S.; Goldsworthy, M. Increased expression of the diabetes gene SOX4 reduces insulin secretion by impaired fusion pore expansion. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1952–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Synowiec, S.; Lu, L.; Yu, Y.; Bretherick, T.; Takada, S.; Yarnykh, V.; Caplan, J.; Caplan, M.; Claud, E.C. Microbiota influence the development of the brain and behaviors in C57BL/6J mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-S.; Heng, Y.; Mou, Z.; Huang, J.-Y.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Chen, N.-H. Reassessment of subacute MPTP-treated mice as animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P. STRING v11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, C.-H.; Chen, S.-H.; Wu, H.-H.; Ho, C.-W.; Ko, M.-T.; Lin, C.-Y. cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T.L. Primer-BLAST: A tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C T method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondratiuk, I.; Jakhanwal, S.; Jin, J.; Sathyanarayanan, U.; Kroppen, B.; Pobbati, A.V.; Krisko, A.; Ashery, U.; Meinecke, M.; Jahn, R. PI (4, 5) P2-dependent regulation of exocytosis by amisyn, the vertebrate-specific competitor of synaptobrevin 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13468–13479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryda, E.C. The Mighty Mouse: The impact of rodents on advances in biomedical research. Mo. Med. 2013, 110, 207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perlman, R.L. Mouse models of human disease: An evolutionary perspective. Evol. Med. Public Health 2016, 2016, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R. Improving animal models for nervous system disorders. Genes Brain Behav. 2012, 11, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGonigle, P. Animal models of CNS disorders. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 87, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaric, I.; Miller, G.; Dear, T.N. Appearances can be deceiving: Phenotypes of knockout mice. Brief. Funct. Genom. Proteom. 2007, 6, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.F.; Ansari, M.A.; Nadeem, A.; Bakheet, S.A.; Alsanea, S.; Al-Hosaini, K.A.; Mahmood, H.M.; Alzahrani, M.Z.; Attia, S.M. Inhibition of tyrosine kinase signaling by tyrphostin AG126 downregulates the IL-21/IL-21R and JAK/STAT pathway in the BTBR mouse model of autism. Neurotoxicology 2020, 77, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagan, K.; Crider, A.; Ahmed, A.O.; Pillai, A. Complement C3 expression is decreased in autism spectrum disorder subjects and contributes to behavioral deficits in rodents. Mol. Neuropsychiatry 2017, 3, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Shen, X.; Lu, F.; Ruan, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhen, J. Reveals new lung adenocarcinoma cancer genes based on gene expression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 16, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Long, J.; Xie, F.; Kang, K.; Shi, Y.; Xu, W.; Wu, X.; Lin, J.; Xu, H.; Du, S. Transcriptomic analysis and identification of prognostic biomarkers in cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Chen, J.Y. Discovery of pathway biomarkers from coupled proteomics and systems biology methods. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, M.; Yokoyama, K.; Seiriki, K.; Naka, Y.; Matsumura, K.; Kondo, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Hayashida, M.; Kasai, A.; Ago, Y. Psychiatric-disorder-related behavioral phenotypes and cortical hyperactivity in a mouse model of 3q29 deletion syndrome. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 2125–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlisle, H.J.; Luong, T.N.; Medina-Marino, A.; Schenker, L.; Khorosheva, E.; Indersmitten, T.; Gunapala, K.M.; Steele, A.D.; O’Dell, T.J.; Patterson, P.H. Deletion of densin-180 results in abnormal behaviors associated with mental illness and reduces mGluR5 and DISC1 in the postsynaptic density fraction. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 16194–16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Hu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Liang, D. Behavioral and Gene Expression Analysis of Stxbp6-Knockout Mice. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040436
Liu C, Hu Q, Chen Y, Wu L, Liu X, Liang D. Behavioral and Gene Expression Analysis of Stxbp6-Knockout Mice. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(4):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040436
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Cong, Qian Hu, Yan Chen, Lingqian Wu, Xionghao Liu, and Desheng Liang. 2021. "Behavioral and Gene Expression Analysis of Stxbp6-Knockout Mice" Brain Sciences 11, no. 4: 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040436
APA StyleLiu, C., Hu, Q., Chen, Y., Wu, L., Liu, X., & Liang, D. (2021). Behavioral and Gene Expression Analysis of Stxbp6-Knockout Mice. Brain Sciences, 11(4), 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11040436





