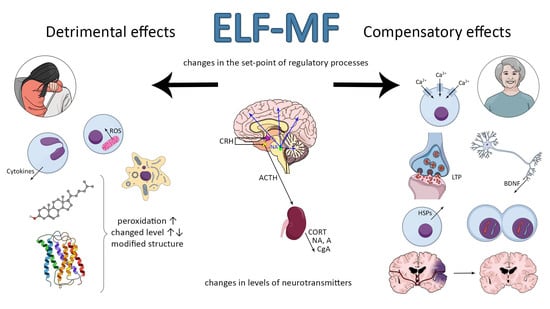
Extremely Low-Frequency Magnetic Field as a Stress Factor—Really Detrimental?—Insight into Literature from the Last Decade
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Stress—A Factor Determining the Function of Organism at All Levels of Organization
3. Molecular Stress Response to ELF-MF
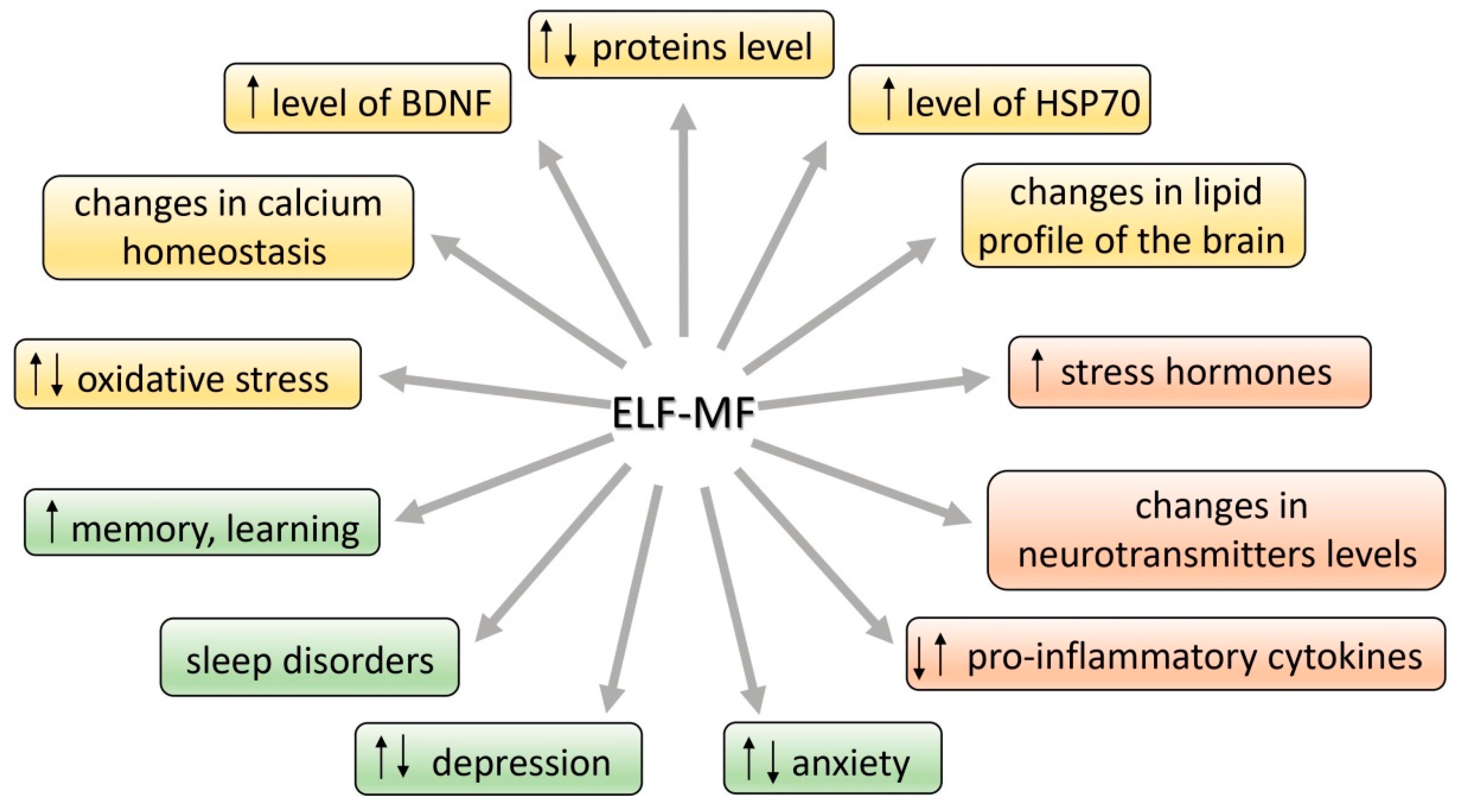
3.1. Proteins and Lipids
3.2. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Status
3.3. Neuroprotective Proteins: Hsp70 and BDNF
3.4. Plasticity, Neurogenesis, Proliferation, and Differentiation
4. ELF-MF-Induced Changes in Levels of Neurotransmitters, Hormones, and Cytokines
5. Association between ELF-MF Exposure and Emotional Behavior and Wellbeing
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- SCENIHR (Scientific Committee on Emerging and Newly Identified Health Risks). Potential Health Effects of Exposure to Electromagnetic Fields (EMF); European Commission: Luxembourg, 2015; pp. 1–288. [Google Scholar]
- Touitou, Y.; Selmaoui, B. The effects of extremely low-frequency magnetic fields on melatonin and cortisol, two marker rhythms of the circadian system. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 14, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgi, G.; Lecciso, M.; Capri, M.; Lukas Yani, S.; Virelli, A.; Bersani, F.; Del Re, B. An evaluation of genotoxicity in human neuronal-type cells subjected to oxidative stress under an extremely low frequency pulsed magnetic field. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2014, 775, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, M.W.; Kock, M.D.; Westerink, R.H. Assessment of the neurotoxic potential of exposure to 50Hz extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields (ELF-EMF) in naive and chemically stressed PC12 cells. Neurotoxicology 2014, 44, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golbach, L.A.; Philippi, J.G.; Cuppen, J.J.; Savelkoul, H.F.; Verburg-van Kemenade, B.M. Calcium signalling in human neutrophil cell lines is not affected by low-frequency electromagnetic fields. Bioelectromagnetics 2015, 36, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, M.; Nakamura, A.; Hondou, T.; Miyata, H. Evaluation of cell viability, DNA single-strand breaks, and nitric oxide production in LPS-stimulated macrophage RAW264 exposed to a 50-Hz magnetic field. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2016, 92, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Lv, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Hua, J.; Zeng, Q. Extremely Low Frequency Magnetic Fields Do Not Induce DNA Damage in Human Lens Epithelial Cells In Vitro. Anat. Rec. 2016, 299, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burman, O.; Marsella, G.; Di Clemente, A.; Cervo, L. The effect of exposure to low frequency electromagnetic fields (EMF) as an integral part of the housing system on anxiety-related behaviour, cognition and welfare in two strains of laboratory mouse. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baan, R.; Grosse, Y.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Islami, F.; Galichet, L.; Straif, K.; et al. Carcinogenicity of radiofrequency electromagnetic fields. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szemerszky, R.; Zelena, D.; Barna, I.; Bárdos, G. Stress-related endocrinological and psychopathological effects of short- and long-term 50Hz electromagnetic field exposure in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2010, 81, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, M.; Goodman, R. Electromagnetic fields stress living cells. Pathophysiology 2009, 16, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasset, I.; Medina, F.J.; Jimena, I.; Agüera, E.; Gascón, F.; Feijóo, M.; Sánchez-López, F.; Luque, E.; Peña, J.; Drucker-Colín, R.; et al. Neuroprotective effects of extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields on a Huntington’s disease rat model: Effects on neurotrophic factors and neuronal density. Neuroscience 2012, 209, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, M.S.; Lisanby, S.H.; Avery, D.; McDonald, W.M.; Durkalski, V.; Pavlicova, M.; Anderson, B.; Nahas, Z.; Bulow, P.; Zarkowski, P.; et al. Daily left prefrontal transcranial magnetic stimulation therapy for major depressive disorder: A sham-controlled randomized trial. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinabadi, M.B.; Khanjani, N.; Ebrahimi, M.H.; Haji, B.; Abdolahfard, M. The effect of chronic exposure to extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields on sleep quality, stress, depression and anxiety. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2019, 38, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedghi, H.; Zare, S.; Hayatgeibi, H.; Alivandi, S.; Ebadi, A.G. Effects of 50 HZ Magnetic Field on Some Factors of Immune System in the Male Guinea Pigs. Am. J. Immunol. 2005, 1, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaoka, K.; Kitamura, M.; Aoi, S.; Shimizu, N.; Yoshizaki, K. Chronic exposure to an extremely low-frequency magnetic field induces depression-like behavior and corticosterone secretion without enhancement of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in mice. Bioelectromagnetics 2013, 34, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sámano, J.; Flores-Poblano, A.; Verdugo-Díaz, L.; Juárez-Oropeza, M.A.; Torres-Durán, P.V. Extremely low frequency electromagnetic field exposure and restraint stress induce changes on the brain lipid profile of Wistar rats. BMC Neurosci. 2018, 19, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S. Physiology and neurobiology of stress and adaptation: Central role of the brain. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 873–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajós-Korcsok, E.; Robinson, D.D.; Yu, J.H.; Fitch, C.S.; Walker, E.; Merchant, K.M. Rapid habituation of hippocampal serotonin and norepinephrine release and anxiety-related behaviors, but not plasma corticosterone levels, to repeated footshock stress in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 74, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selye, H. The Stress of Life; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Selye, H. Stress without Distress; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus, R.S.; Folkman, S. Stress, Appraisal, and Coping; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Mattson, M.P. Hormesis provides a generalized quantitative estimate of biological plasticity. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2011, 5, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, A.; Bauer, M.A.; Kroemer, G.; Madeo, F.; Carmona-Gutierrez, D. When less is more: Hormesis against stress and disease. Microb. Cell 2014, 1, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugers, H.J.; Karst, H.; Joels, M. Interactions between noradrenaline and corticosteroids in the brain: From electrical activity to cognitive performance. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierzchała-Koziec, K.; Zubel-Łojek, J.; Ocłoń, E.; Latacz, A.; Kępys, B. Emotional stress induces sex-specific sympatho-adrenomedullary responses in lambs. Acta Biol. Crac. Série Zool. 2015, 57, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Tafet, G.E.; Bernardini, R. Psychoneuroendocrinological links between chronic stress and depression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 27, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesse, R.M.; Bhatnagar, S.; Young, E.A. Evolutionary Origins and Functions of the Stress Response. In Stress: Concepts, Cognition, Emotion, and Behavior; Fink, G., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; Volume 1, pp. 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Black, C.N.; Bot, M.; Révész, D.; Scheffer, P.G.; Penninx, B. The association between three major physiological stress systems and oxidative DNA and lipid damage. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 80, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kloet, E.R.; Vreugdenhil, E.; Oitzl, M.S.; Joëls, M. Brain corticosteroid receptor balance in health and disease. Endocr. Rev. 1998, 19, 269–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogalska, J. Mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors in hippocampus: Their impact on neurons survival and behavioral impairment after neonatal brain injury. Vitam. Horm. 2010, 82, 391–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnett, M.G.; Muglia, L.M.; Laryea, G.; Muglia, L.J. Genetic Approaches to Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Regulation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushak, P. Temporal stability of chemical hormesis (CH): Is CH just a temporary stop on the road to thresholds and toxic responses? Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1446–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuccurazzu, B.; Leone, L.; Podda, M.V.; Piacentini, R.; Riccardi, E.; Ripoli, C.; Azzena, G.B.; Grassi, C. Exposure to extremely low-frequency (50 Hz) electromagnetic fields enhances adult hippocampal neurogenesis in C57BL/6 mice. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 226, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaki, A.; Khalili, A.; Salehi, I.; Shahidi, S.; Sarihi, A. Effects of exposure to an extremely low frequency electromagnetic field on hippocampal long-term potentiation in rat. Brain Res. 2014, 1564, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, O. Disturbance of the immune system by electromagnetic fields-A potentially underlying cause for cellular damage and tissue repair reduction which could lead to disease and impairment. Pathophysiology 2009, 16, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corallo, C.; Battisti, E.; Albanese, A.; Vannoni, D.; Leoncini, R.; Landi, G.; Gagliardi, A.; Landi, C.; Carta, S.; Nuti, R.; et al. Proteomics of human primary osteoarthritic chondrocytes exposed to extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields (ELF EMFs) and to therapeutic application of musically modulated electromagnetic fields (TAMMEF). Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2014, 33, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.S.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Yang, C.J.; Lian, H.Y.; Cai, P. Gene expression and reproductive abilities of male Drosophila melanogaster subjected to ELF-EMF exposure. Mutat. Res. 2013, 758, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merla, C.; Liberti, M.; Consales, C.; Denzi, A.; Apollonio, F.; Marino, C.; Benassi, B. Evidences of plasma membrane-mediated ROS generation upon ELF exposure in neuroblastoma cells supported by a computational multiscale approach. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2019, 1861, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, R.; Lakshmi, N.K.; Bhargava, S.C.; Ahuja, Y.R. Epinephrine, DNA integrity and oxidative stress in workers exposed to extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields (ELF-EMFs) at 132 kV substations. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2015, 34, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; He, M.; Xu, S.; Chen, C.; Pi, H.; Gao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, M.; et al. Comparison of the genotoxic effects induced by 50 Hz extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields and 1800 MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic fields in GC-2 cells. Radiat. Res. 2015, 183, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Luo, X.; Duan, Y.; Duan, W.; Zhang, H.; He, Y.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Neuroprotective effects of lotus seedpod procyanidins on extremely low frequency electromagnetic field-induced neurotoxicity in primary cultured hippocampal neurons. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 82, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroni, L.; Tocco, I.; De Pieri, A.; Menarin, M.; Fermi, E.; Piattelli, A.; Gardin, C.; Zavan, B. Pulsed magnetic therapy increases osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells only if they are pre-committed. Life Sci. 2016, 152, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat, N.; Abdolmaleki, P.; Parnian, J.; Behmanesh, M. The expression of pluripotency and neuronal differentiation markers under the influence of electromagnetic field and nitric oxide. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 85, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, M.; Cetiner, S.; Zencir, S.; Unlukurt, I.; Kahraman, I.; Topcu, Z. Oxidative stress and apoptosis in relation to exposure to magnetic field. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 59, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juszczak, K.; Kaszuba-Zwoinska, J.; Thor, P.J. Pulsating electromagnetic field stimulation of urothelial cells induces apoptosis and diminishes necrosis: New insight to magnetic therapy in urology. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 63, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Hasanzadeh, H.; Seyyedi, S.; Ghoujeghi, F.; Semnani, V.; Zali, H. Proteomic Analysis of Extremely Low-Frequency ElectroMagnetic Field (ELF-EMF) with Different Intensities in Rats Hippocampus. Arch. Neurosci. 2018, 5, e62954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.L.; Ye, Z.M. Extremely low frequency electromagnetic field induces apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells via oxidative stress. J. Zhejiang Univ. 2015, 44, 323–328. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zuo, H.; Wang, D.; Peng, R.; Song, T.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Improvement of spatial memory disorder and hippocampal damage by exposure to electromagnetic fields in an Alzheimer’s disease rat model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Tong, J.; Yu, L.; Zhang, J. EMF protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia-induced injury via heat shock protein 70 activation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 248, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W.; Yin, C.; Ci, L.; Zhao, R.; Yang, X. Short communication: Salivary haptoglobin and chromogranin A as non-invasive markers during restraint stress in pigs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 114, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’amico, M.A.; Ghinassi, B.; Izzicupo, P.; Manzoli, L.; Di Baldassarre, A. Biological function and clinical relevance of chromogranin A and derived peptides. Endocr. Connect. 2014, 3, R45–R54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touitou, Y.; Lambrozo, J.; Mauvieux, B.; Riedel, M. Evaluation in humans of ELF-EMF exposure on chromogranin A, a marker of neuroendocrine tumors and stress. Chronobiol. Int. 2020, 37, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corraliza-Gomez, M.; Sanchez, D.; Ganfornina, M.D. Lipid-Binding Proteins in Brain Health and Disease. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sámano, J.; Torres-Durán, P.V.; Juárez-Oropeza, M.A.; Verdugo-Díaz, L. Effect of acute extremely low frequency electromagnetic field exposure on the antioxidant status and lipid levels in rat brain. Arch. Med. Res. 2012, 43, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, S.A.; Salehi, I.; Shykhi, T.; Zare, S.; Komaki, A. Effects of exposure to extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields on spatial and passive avoidance learning and memory, anxiety-like behavior and oxidative stress in male rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 359, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Liao, Y.; Cai, P. Lipidomic alteration and stress-defense mechanism of soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans in response to extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shu, Y.; Zhai, C.; Zhu, Y.; Gong, S.; Cui, Y.; Wang, J.F. Chronic unpredictable stress impairs endogenous antioxidant defense in rat brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 584, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pejic, S.; Stojikjkovic, V.; Todorovic, A.; Gavrilovic, L.; Pavlovic, I.; Popovic, N.; Pajovic, S.B. Antioxidant Enzymes in Brain Cortex of Rats Exposed to Acute, Chronic and Combined Stress. Folia Biol. 2016, 64, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, K.K.; Kumar, R. Stress, oxidative injury and disease. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 30, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frahm, J.; Mattsson, M.O.; Simkó, M. Exposure to ELF magnetic fields modulate redox related protein expression in mouse macrophages. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 192, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garip, A.I.; Akan, Z. Effect of ELF-EMF on number of apoptotic cells; correlation with reactive oxygen species and HSP. Acta Biol. Hung. 2010, 61, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannerling, A.C.; Simkó, M.; Mild, K.H.; Mattsson, M.O. Effects of 50-Hz magnetic field exposure on superoxide radical anion formation and HSP70 induction in human K562 cells. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2010, 49, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannoni, D.; Albanese, A.; Battisti, E.; Aceto, E.; Giglioni, S.; Corallo, C.; Carta, S.; Ferrata, P.; Fioravanti, A.; Giordano, N. In vitro exposure of human osteoarthritic chondrocytes to ELF fields and new therapeutic application of musically modulated electromagnetic fields: Biological evidence. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2012, 26, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Calcabrini, C.; Mancini, U.; De Bellis, R.; Diaz, A.R.; Martinelli, M.; Cucchiarini, L.; Sestili, P.; Stocchi, V.; Potenza, L. Effect of extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields on antioxidant activity in the human keratinocyte cell line NCTC 2544. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2017, 64, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tang, C.; Liao, Y.; Yang, C.; Cai, P. Coupling of oxidative stress responses to tricarboxylic acid cycle and prostaglandin E2 alterations in Caenorhabditis elegans under extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2018, 94, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdag, M.Z.; Dasdag, S.; Ulukaya, E.; Uzunlar, A.K.; Kurt, M.A.; Taşkin, A. Effects of extremely low-frequency magnetic field on caspase activities and oxidative stress values in rat brain. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2010, 138, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goraca, A.; Ciejka, E.; Piechota, A. Effects of extremely low frequency magnetic field on the parameters of oxidative stress in heart. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 61, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Budziosz, J.; Stanek, A.; Sieroń, A.; Witkoś, J.; Cholewka, A.; Sieroń, K. Effects of Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Field on Oxidative Stress in Selected Structures of the Central Nervous System. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 1427412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; He, Y.; Lu, R.; Zhang, R.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. The preventive effect of lotus seedpod procyanidins on cognitive impairment and oxidative damage induced by extremely low frequency electromagnetic field exposure. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 1252–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Chen, M.; Duan, Y.; Duan, W.; Zhang, H.; He, Y.; Yin, C.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Chemoprotective action of lotus seedpod procyanidins on oxidative stress in mice induced by extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field exposure. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 82, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, N.Z.; Paunović, M.G.; Peulić, A.S. Anxiety-like behavioural effects of extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field in rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 21693–21699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Sámano, J.; Torres-Durán, P.V.; Juárez-Oropeza, M.A.; Elías-Viñas, D.; Verdugo-Díaz, L. Effects of acute electromagnetic field exposure and movement restraint on antioxidant system in liver, heart, kidney and plasma of Wistar rats: A preliminary report. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2010, 86, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzay, D.; Ozer, C.; Sirav, B.; Canseven, A.G.; Seyhan, N. Oxidative effects of extremely low frequency magnetic field and radio frequency radiation on testes tissues of diabetic and healthy rats. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2017, 118, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Helaly, M.; Abu-Hashem, E. Oxidative stress, melatonin level, and sleep insufficiency among electronic equipment repairers. Indian J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2010, 14, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Sun, C. Effects of dietary green tea polyphenol supplementation on the health of workers exposed to high-voltage power lines. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 46, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinabadi, M.B.; Khanjani, N. The Effect of Extremely Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields on the Prevalence of Musculoskeletal Disorders and the Role of Oxidative Stress. Bioelectromagnetics 2019, 40, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morabito, C.; Rovetta, F.; Bizzarri, M.; Mazzoleni, G.; Fanò, G.; Mariggiò, M.A. Modulation of redox status and calcium handling by extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields in C2C12 muscle cells: A real-time, single-cell approach. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 48, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehnert, S.; Fentz, A.K.; Schreiner, A.; Birk, J.; Wilbrand, B.; Ziegler, P.; Reumann, M.K.; Wang, H.; Falldorf, K.; Nussler, A.K. Extremely low frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields cause antioxidative defense mechanisms in human osteoblasts via induction of •O2- and H2O2. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patruno, A.; Tabrez, S.; Pesce, M.; Shakil, S.; Kamal, M.A.; Reale, M. Effects of extremely low frequency electromagnetic field (ELF-EMF) on catalase, cytochrome P450 and nitric oxide synthase in erythro-leukemic cells. Life Sci. 2015, 121, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewicka, M.; Henrykowska, G.A.; Pacholski, K.; Szczęsny, A.; Dziedziczak-Buczyńska, M.; Buczyński, A. The impact of electromagnetic radiation of different parameters on platelet oxygen metabolism—In vitro studies. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 24, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Im, S.H.; Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, H.M.; Lee, H.J.; Park, G.S. A 60 Hz uniform electromagnetic field promotes human cell proliferation by decreasing intracellular reactive oxygen species levels. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, M.; Kamal, M.A.; Patruno, A.; Costantini, E.; D’Angelo, C.; Pesce, M.; Greig, N.H. Neuronal cellular responses to extremely low frequency electromagnetic field exposure: Implications regarding oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falone, S.; Marchesi, N.; Osera, C.; Fassina, L.; Comincini, S.; Amadio, M.; Pascale, A. Pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) prevents pro-oxidant effects of H2O2 in SK-N-BE(2) human neuroblastoma cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2016, 92, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichoń, N.; Bijak, M.; Miller, E.; Saluk, J. Extremely low frequency electromagnetic field (ELF-EMF) reduces oxidative stress and improves functional and psychological status in ischemic stroke patients. Bioelectromagnetics 2017, 38, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichoń, N.; Rzeźnicka, P.; Bijak, M.; Miller, E.; Miller, S.; Saluk, J. Extremely low frequency electromagnetic field reduces oxidative stress during the rehabilitation of post-acute stroke patients. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 27, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulda, S.; Gorman, A.M.; Hori, O.; Samali, A. Cellular Stress Responses: Cell Survival and Cell Death. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimani, A.F.; Zulkifli, I.; Omar, A.R.; Raha, A.R. The relationship between adrenocortical function and Hsp70 expression in socially isolated Japanese quail. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2012, 161, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirulli, F.; Alleva, E. The NGF saga: From animal models of psychosocial stress to stress-related psychopathology. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2009, 30, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagena, H.; Hansen, N.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. β-Adrenergic Control of Hippocampal Function: Subserving the Choreography of Synaptic Information Storage and Memory. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 1349–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaroli, A.; Chessa, M.G.; Bavestrello, G.; Bianco, B. Effects of an extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field on stress factors: A study in Dictyostelium discoideum cells. Eur. J. Protistol. 2013, 49, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Shepherd, S.; Sharkh, S.; Jackson, C.W.; Newland, P.L. Exposure to extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields alters the behaviour, physiology and stress protein levels of desert locusts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeni, O.; Simkó, M.; Scarfi, M.R.; Mattsson, M.O. Cellular Response to ELF-MF and Heat: Evidence for a Common Involvement of Heat Shock Proteins? Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Masison, D.C. Hsp70 structure, function, regulation and influence on yeast prions. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, F.P.; Zhou, X.; Morisaki, J.; Jurivich, D. Electromagnetic field therapy delays cellular senescence and death by enhancement of the heat shock response. Exp. Gerontol. 2008, 43, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutzeit, H.O. Biological Effects of ELF-EMF Enhanced Stress Response: New Insights and New Questions. Electro Magn. 2001, 20, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.; Lin-Ye, A.; Geddis, M.S.; Wickramaratne, P.J.; Hodge, S.E.; Pantazatos, S.P.; Blank, M.; Ambron, R.T. Extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields activate the ERK cascade, increase hsp70 protein levels and promote regeneration in Planaria. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2009, 85, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, M.; Morici, J.F.; Zanoni, M.B.; Bekinschtein, P. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: A Key Molecule for Memory in the Healthy and the Pathological Brain. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathina, S.; Das, U.N. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its clinical implications. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 11, 1164–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Hu, X.; Sun, H.; Tian, J. Pulsed electromagnetic field enhances brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression through L-type voltage-gated calcium channel- and Erk-dependent signaling pathways in neonatal rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neurochem. Int. 2014, 75, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichoń, N.; Bijak, M.; Czarny, P.; Miller, E.; Synowiec, E.; Sliwinski, T.; Saluk-Bijak, J. Increase in Blood Levels of Growth Factors Involved in the Neuroplasticity Process by Using an Extremely Low Frequency Electromagnetic Field in Post-stroke Patients. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urnukhsaikhan, E.; Mishig-Ochir, T.; Kim, S.C.; Park, J.K.; Seo, Y.K. Neuroprotective Effect of Low Frequency-Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields in Ischemic Stroke. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 1360–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A.; Few, A.P. Calcium channel regulation and presynaptic plasticity. Neuron 2008, 59, 882–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardeshirylajimi, A.; Soleimani, M. Enhanced growth and osteogenic differentiation of Induced Pluripotent Stem cells by Extremely Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Field. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 61, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Grassi, C.; D’Ascenzo, M.; Torsello, A.; Martinotti, G.; Wolf, F.; Cittadini, A.; Azzena, G.B. Effects of 50 Hz electromagnetic fields on voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and their role in modulation of neuroendocrine cell proliferation and death. Cell Calcium 2004, 35, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.L.; Yang, N.; He, C.; Li, H.L.; Li, C.; Chen, F.; Xiong, J.X.; Hu, Z.A.; Zhang, J. Exposure to extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields alters the calcium dynamics of cultured entorhinal cortex neurons. Environ. Res. 2014, 135, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.C.; Ge, J.L.; Guo, B.; Guo, J.; Hao, M.; Wu, Y.C.; Lin, Y.A.; La, T.; Yao, P.T.; Mei, Y.A.; et al. Extremely Low Frequency Electromagnetic Fields Facilitate Vesicle Endocytosis by Increasing Presynaptic Calcium Channel Expression at a Central Synapse. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.R.; Lu, J.M.; Yao, J.J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Ling, C.; Mei, Y.A. Neuritin reverses deficits in murine novel object associative recognition memory caused by exposure to extremely low-frequency (50 Hz) electromagnetic fields. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.G.; Fei, Z.; Zhong, J.; Wei, L.Z.; Long, Q.F.; Liu, W.P. Acute neuroprotective effects of extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields after traumatic brain injury in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 516, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhaie, M.H.; Soleimani, M.; Pourheydar, B.; Majd, Z.; Atefimanesh, P.; Asl, S.S.; Mehdizadeh, M. Effects of Extremely Low-Frequency Electromagnetic Fields on Neurogenesis and Cognitive Behavior in an Experimental Model of Hippocampal Injury. Behav. Neurol. 2017, 2017, 9194261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, J.F.; Lazar, C.; Nowé, A.; Hinsenkamp, M. Statistical validation of the acceleration of the differentiation at the expense of the proliferation in human epidermal cells exposed to extremely low frequency electric fields. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2013, 111, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Loreto, S.; Falone, S.; Caracciolo, V.; Sebastiani, P.; D’Alessandro, A.; Mirabilio, A.; Zimmitti, V.; Amicarelli, F. Fifty hertz extremely low-frequency magnetic field exposure elicits redox and trophic response in rat-cortical neurons. J. Cell Physiol. 2009, 219, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, E.; Farahzadi, R. Zinc Sulphate Mediates the Stimulation of Cell Proliferation of Rat Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Under High Intensity of EMF Exposure. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 184, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Chung, S.J.; Lim, C.H.; Oh, K.W.; Sohn, U.D.; Park, E.S.; Jeong, J.H. Extremely low frequency magnetic field modulates the level of neurotransmitters. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 19, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieroń, A.; Labus, Ł.; Nowak, P.; Cieślar, G.; Brus, H.; Durczok, A.; Zagził, T.; Kostrzewa, R.M.; Brus, R. Alternating extremely low frequency magnetic field increases turnover of dopamine and serotonin in rat frontal cortex. Bioelectromagnetics 2004, 25, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isogawa, K.; Fujiki, M.; Akiyoshi, J.; Tsutsumi, T.; Horinouchi, Y.; Kodama, K.; Nagayama, H. Anxiety induced by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation is suppressed by chronic treatment of paroxetine in rats. Pharmacopsychiatry 2003, 36, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janać, B.; Tovilović, G.; Tomić, M.; Prolić, Z.; Radenović, L. Effect of continuous exposure to alternating magnetic field (50 Hz, 0.5 mT) on serotonin and dopamine receptors activity in rat brain. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2009, 28, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jadidi, M.; Firoozabadi, S.M.; Rashidy-Pour, A.; Sajadi, A.A.; Sadeghi, H.; Taherian, A.A. Acute exposure to a 50 Hz magnetic field impairs consolidation of spatial memory in rats. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2007, 88, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschenlohr, H.; Ellis, P.; Hesketh, R.; Metcalfe, J. Gene expression profiles in white blood cells of volunteers exposed to a 50 Hz electromagnetic field. Radiat. Res. 2012, 178, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, S.M.; Sahraei, H.; Yaghmaei, P.; Tavakoli, H. Effects of electromagnetic radiation exposure on stress-related behaviors and stress hormones in male wistar rats. Biomol. Ther. 2014, 22, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, E.; Nafisi, S.; Zare, S. The effects of electromagnetic fields on plasma levels of corticosterone, free-T3, free-T4 malonyldialdehyde in white male rabbit with normal diet and hyperchlostrol diet. Vet. Res. Forum 2011, 2, 222–225. [Google Scholar]
- Afhami, M.; Bahaoddini, A.; Saadat, M. P20: Investigation the Effect of EMF on Plasma Levels of Corticosterone, Testosterone and Testicular Gene Expression of Gstt1 of Male Rats. Shefaye Khatam 2016, 4, 43. [Google Scholar]
- de Kleijn, S.; Ferwerda, G.; Wiese, M.; Trentelman, J.; Cuppen, J.; Kozicz, T.; de Jager, L.; Hermans, P.W.; Verburg-van Kemenade, B.M. A short-term extremely low frequency electromagnetic field exposure increases circulating leukocyte numbers and affects HPA-axis signaling in mice. Bioelectromagnetics 2016, 37, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, R.M.; Mostafa, Y.M.; Ennaceur, A. Effects of exposure to extremely low-frequency magnetic field of 2 G intensity on memory and corticosterone level in rats. Physiol. Behav. 2002, 76, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszlo, A.M.; Ladanyi, M.; Boda, K.; Csicsman, J.; Bari, F.; Serester, A.; Molnar, Z.; Sepp, K.; Galfi, M.; Radacs, M. Effects of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields on turkeys. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, R.; Hou, G.; Li, D.; Yuan, T.F. A possible change process of inflammatory cytokines in the prolonged chronic stress and its ultimate implications for health. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 780616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverman, M.N.; Pearce, B.D.; Biron, C.A.; Miller, A.H. Immune modulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis during viral infection. Viral. Immunol. 2005, 18, 41–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyszkowska, J.; Jędrzejewski, T.; Piotrowski, J.; Wojciechowska, A.; Stankiewicz, M.; Kozak, W. Evaluation of the influence of in vivo exposure to extremely low-frequency magnetic fields on the plasma levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in rats. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2018, 94, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichoń, N.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Miller, E.; Sliwinski, T.; Synowiec, E.; Wigner, P.; Bijak, M. Evaluation of the effects of extremely low frequency electromagnetic field on the levels of some inflammatory cytokines in post-stroke patients. J. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 51, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahaki, H.; Jabarivasal, N.; Sardanian, K.; Zamani, A. Effects of Various Densities of 50 Hz Electromagnetic Field on Serum IL-9, IL-10, and TNF-α Levels. Int. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2020, 11, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, E.Y.; Kalynchuk, L.E. Behavioral and neurobiological consequences of prolonged glucocorticoid exposure in rats: Relevance to depression. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 34, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, S.; He, L.; Ye, K. Anxiogenic effect of chronic exposure to extremely low frequency magnetic field in adult rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 434, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaeed, I.; Al-Somali, F.; Sakhnini, L.; Aljarallah, O.S.; Hamdan, R.M.; Bubishate, S.A.; Sarfaraz, Z.K.; Kamal, A. Autism-relevant social abnormalities in mice exposed perinatally to extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 37, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpinar, M.A.; Kalkan, M.T.; Tuncel, H. The 50 Hz (10 mT) sinusoidal magnetic field: Effects on stress-related behavior of rats. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2012, 113, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balassa, T.; Szemerszky, R.; Bárdos, G. Effect of short-term 50 Hz electromagnetic field exposure on the behavior of rats. Acta Physiol. Hung. 2009, 96, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.H.; Shi, H.M.; Liu, T.T.; Xu, Y.C.; Ye, K.P.; Wang, S. Effects of extremely low frequency magnetic field on anxiety level and spatial memory of adult rats. Chin. Med. J. 2011, 124, 3362–3366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mattar, F.A.; Bareedy, M.H.; El-Dosouky, M.E.M.; Zaghloul, M.S.; Mahmod, M.S.M. Effects of 6 Weeks Exposure of 3.5 mT (ELF EMF) on Some Animal behaviors in White Albino Rat (Sprague Dawley) Pups. Zagazig Vet. J. 2014, 42, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Ruan, G.; Chaugai, S.; Chen, C.; Wang, D.W. Effects of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields (100μT) on behaviors in rats. Neurotoxicology 2016, 52, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boscolo, P.; Di Giampaolo, L.; Di Donato, A.; Antonucci, A.; Paiardini, G.; Morelli, S.; Vasile, R.; Spagnoli, G.; Reale, M.; Dadorante, V.; et al. The immune response of women with prolonged exposure to electromagnetic fields produced by radiotelevision broadcasting stations. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2006, 19 (Suppl. 4), 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, R.M.; Narasimhan, M.; Sanacora, G.; Miano, A.P.; Hoffman, R.E.; Hu, X.S.; Charney, D.S.; Boutros, N.N. A randomized clinical trial of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in the treatment of major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2000, 47, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janać, B.; Pesić, V.; Jelenković, A.; Vorobyov, V.; Prolić, Z. Different effects of chronic exposure to ELF magnetic field on spontaneous and amphetamine-induced locomotor and stereotypic activities in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2005, 67, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roszkowski, M.; Manuella, F.; von Ziegler, L.; Durán-Pacheco, G.; Moreau, J.L.; Mansuy, I.M.; Bohacek, J. Rapid stress-induced transcriptomic changes in the brain depend on beta-adrenergic signaling. Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuis, S.J.; Lipp, C.T. Electromagnetic hypersensitivity: Fact or fiction? Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 414, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klimek, A.; Rogalska, J. Extremely Low-Frequency Magnetic Field as a Stress Factor—Really Detrimental?—Insight into Literature from the Last Decade. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020174
Klimek A, Rogalska J. Extremely Low-Frequency Magnetic Field as a Stress Factor—Really Detrimental?—Insight into Literature from the Last Decade. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(2):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020174
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlimek, Angelika, and Justyna Rogalska. 2021. "Extremely Low-Frequency Magnetic Field as a Stress Factor—Really Detrimental?—Insight into Literature from the Last Decade" Brain Sciences 11, no. 2: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020174
APA StyleKlimek, A., & Rogalska, J. (2021). Extremely Low-Frequency Magnetic Field as a Stress Factor—Really Detrimental?—Insight into Literature from the Last Decade. Brain Sciences, 11(2), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020174