Cognitive Improvement Effects of Electroacupuncture Combined with Computer-Based Cognitive Rehabilitation in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethical Considerations
2.3. Participant Recruitment
2.4. Participation
2.5. Randomization and Blinding
2.6. Implementation
2.7. Intervention
2.7.1. Electroacupuncture Treatment
2.7.2. RehaCom Cognitive Rehabilitation
2.8. Outcome Measurements
2.9. Sample Size Calculation
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
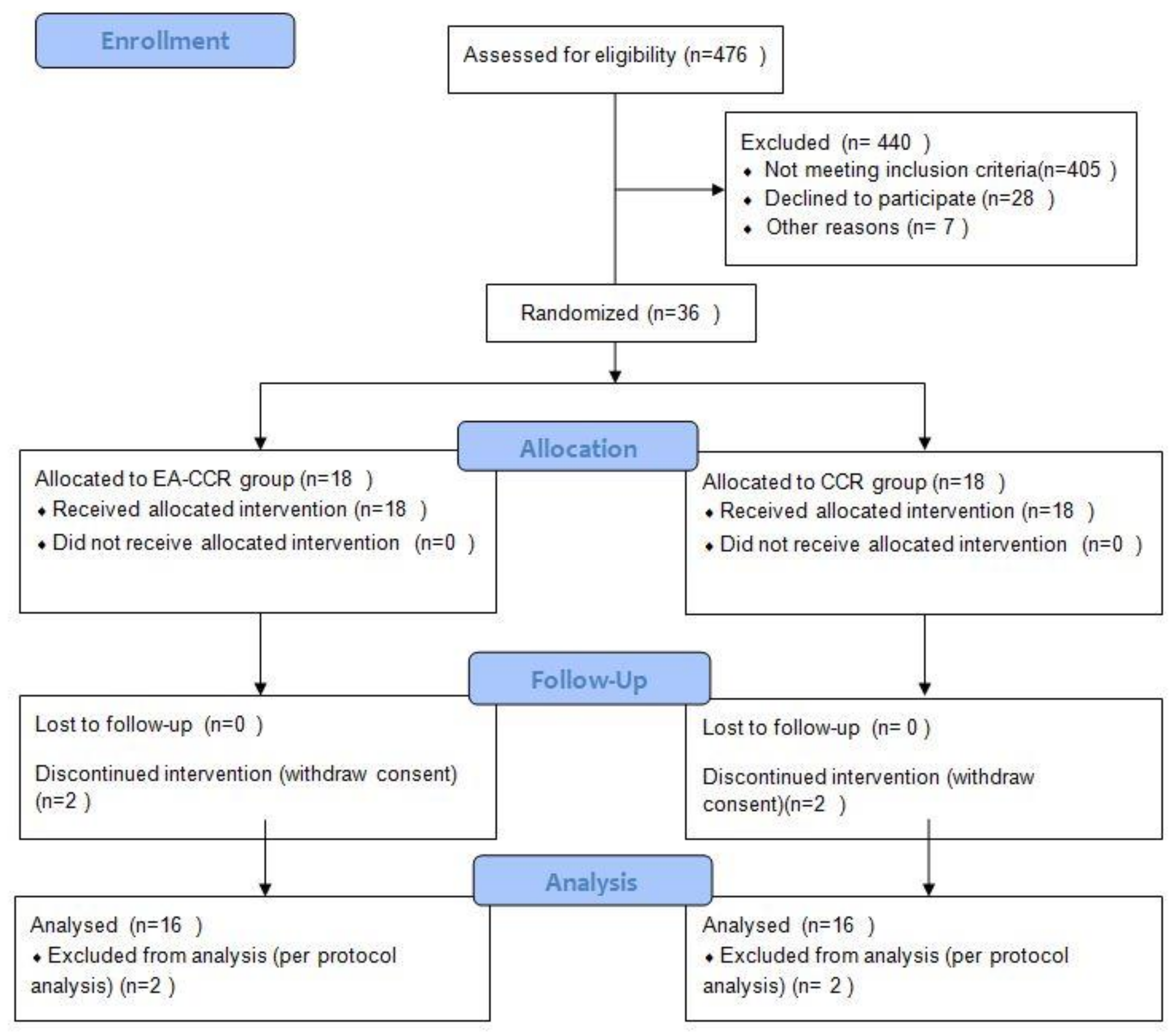
3.1. Particpants
3.2. Baseline Charactersitics
3.3. Primary and Secondary Outcomes
3.4. Safety Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petersen, R.C. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 256, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, R.C.; Smith, G.E.; Waring, S.C.; Ivnik, R.J.; Tangalos, E.G.; Kokmen, E. Mild cognitive impairment: Clinical characterization and outcome. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langa, K.M.; Levine, D.A. The diagnosis and management of mild cognitive impairment: A clinical review. JAMA 2014, 312, 2551–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manly, J.J.; Tang, M.X.; Schupf, N.; Stern, Y.; Vonsattel, J.P.; Mayeux, R. Frequency and course of mild cognitive impairment in a multiethnic community. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, F.; D’Introno, A.; Colacicco, A.M.; Capurso, C.; Del Parigi, A.; Caselli, R.J.; Pilotto, A.; Argentieri, G.; Scapicchio, P.L.; Scafato, E.; et al. Current epidemiology of mild cognitive impairment and other predementia syndromes. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2005, 13, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.O.; Knopman, D.S.; Mielke, M.M.; Cha, R.H.; Pankratz, V.S.; Christianson, T.J.; Geda, Y.E.; Boeve, B.F.; Ivnik, R.J.; Tangalos, E.G.; et al. Higher risk of progression to dementia in mild cognitive impairment cases who revert to normal. Neurology 2014, 82, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshkoor, S.A.; Hamid, T.A.; Mun, C.Y.; Ng, C.K. Mild cognitive impairment and its management in older people. Clin. Interv. Aging 2015, 10, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar-Fuchs, A.; Clare, L.; Woods, B. Cognitive training and cognitive rehabilitation for mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD003260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C.; Lopez, O.; Armstrong, M.J.; Getchius, T.S.D.; Ganguli, M.; Gloss, D.; Gronseth, G.S.; Marson, D.; Pringsheim, T.; Day, G.S.; et al. Practice guideline update summary: Mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 2018, 90, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, T.C.; Morling, J.R. Cholinesterase inhibitors for mild cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD009132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Soobiah, C.; Berliner, S.; Ho, J.M.; Ng, C.H.; Ashoor, H.M.; Chen, M.H.; Hemmelgarn, B.; Straus, S.E. Efficacy and safety of cognitive enhancers for patients with mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. CMAJ 2013, 185, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimova, B.; Maresova, P. Computer-based training programs for older people with mild cognitive impairment and/or dementia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, N.T.; Mowszowski, L.; Naismith, S.L.; Chadwick, V.L.; Lampit, A. Computerized cognitive training in older adults with mild cognitive impairment or dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry 2017, 174, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gates, N.; FiataroneSingh, M.A.; Sachdev, P.S.; Valenzuela, M. The effects of exercise training on cognitive function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2013, 21, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, H.; Qu, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Wu, T.; Xiao, M.; et al. Effects of a specially designed aerobic dance routine on mild cognitive impairment. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 1691–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Wang, X.F. Acupuncture for amnestic mild cognitive impairment: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acupunct. Med. 2016, 34, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, Y.I.; Yoo, H.R.; Jung, I.C. Cognitive improvement effects of electroacupuncture for the treatment of MCI compared with western medications: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, C.Y.; Lee, B.; Suh, H.W.; Chung, S.Y.; Kim, J.W. Efficacy and safety of auricular acupuncture for cognitive impairment and dementia: A systematic review. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 3426079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.K.; Chung, J.Y.; Yoo, D.Y.; Yi, S.S.; Youn, H.Y.; Seong, J.K.; Yoon, Y.S. Comparing the effects of acupuncture and electroacupuncture at Zusanli and Baihui on cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation in the rat hippocampus. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napadow, V.; Makris, N.; Liu, J.; Kettner, N.W.; Kwong, K.K.; Hui, K.K. Effects of electroacupuncture versus manual acupuncture on the human brain as measured by fMRI. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2005, 24, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, L. Observations on the efficacy of electric scalp acupuncture in treating mild cognitive impairment. J. Sichuan Tradit. Chin. Med. 2012, 30, 112–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, F.W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhaou, B.; Chen, W.Y.; Zhu, M.J. Mild cognitive impairment disease treated with electroacupuncture: A multi-center randomized controlled trial. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 2012, 32, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Zheng, L.; Li, H.; Peng, S.; Mao, R.; Xiong, D.; Tan, T. Efficacy of combined treatment of drugs and electric acupuncture on cognitive function of patients with mild cognitive impairment. China Med. Her. 2013, 10, 118–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, L.; Yang, S.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Peng, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, M. Clinical observation on effect of scalp electroacupuncture for mild cognitive impairment. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2013, 33, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.S.; Yokomizo, J.E.; Bottino, C.M. Cognitive intervention in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 1163–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Han, J.Y.; Park, G.C.; Lee, J.S. Effects of electroacupuncture combined with computer-based cognitive rehabilitation on mild cognitive impairment: Study protocol for a pilot randomized controlled trial. Trials 2019, 20, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Western Pacific Region. WHO Standard Acupuncture Point Locations in the Western Pacific Region; Elsevier Korea L.C.C.: Seoul, Korea, 2009; Volume 185, pp. 217–219. [Google Scholar]
- Kueper, J.K.; Speechley, M.; Montero-Odasso, M. The Alzheimer’s disease assessment scale-cognitive subscale (ADAS-cog): Modifications and responsiveness in pre-dementia populations. A narrative review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 63, 423–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, E.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.T.; Park, S.S.; Kim, J.E.; Cha, J.Y.; Seol, I.C.; Choi, Y.E.; Yoo, H.R. Effects of acupuncture on patients with mild cognitive impairment assessed using functional near-infrared spectroscopy on week 12(close-out): A pilot study protocol. Integr. Med. Res. 2018, 7, 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radloff, L.S. The CES-D scale: A self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl. Psychol. Meas. 1977, 1, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, C.W.; Yang, K.Y.; Rho, Y.G.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, E.J.; Yoon, J.L.; Cho, K.H.; Shin, H.C.; Cho, B.R.; Oh, J.R.; et al. The development of Korean activities of daily living (K-ADL) and Korean instrumental activities of daily living (K-IADL) scale. J. Korean Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 6, 107–120. [Google Scholar]
- Herdman, M.; Gudex, C.; Lloyd, A.; Janssen, M.F.; Kind, P.; Parkin, D.; Bonsel, G.; Badia, X. Development and preliminary testing of the new five-level version of EQ-5D (EQ-5D-5L). Qual. Life Res. 2011, 20, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Yang, S.; Tao, J.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Ye, H.; Chen, S.; Hong, W.; Chen, L. Clinical efficacy of acupuncture treatment in combination with RehaCom cognitive training for improving cognitive function in stroke: A 2×2 factorial design randomized controlled trial. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2016, 17, 1114–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, T.; Gan, L.; Zheng, J. Efficacy and safety assessment of acupuncture and nimodipine to treatment mild cognitive impairment after cerebral infarction: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Regional Office for the Western Pacific. WHO International Standard Terminologies on Traditional Medicine in the Western Pacific Region; World Health Organization Regional Office for the Western Pacific: Manila, Philippines, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G.X.; Yang, X.M.; Liu, C.Z.; Wang, L.P. Factors contributing to therapeutic effects evaluated in acupuncture clinical trials. Trials 2012, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| STUDY PERIOD | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enrolment | Allocation | Post-Allocation | Close-Out | ||||||||
| TIMEPOINT | Screening | Visit1-3 | Visit4-6 | Visit7-9 | Visit10-12 | Visit13-15 | Visit16-18 | Visit19-21 | Visit22-24 | Visit25 | |
| Week | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 20 | ||
| ENROLMENT | |||||||||||
| Informed consent | X | ||||||||||
| Sociodemographic profile | X | ||||||||||
| Medical history | X | ||||||||||
| Vital signs | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Inclusion/exclusion criteria | X | ||||||||||
| Allocation | X | ||||||||||
| K-MMSE, MoCA-K | X | ||||||||||
| INTERVENTIONS | |||||||||||
| CCR | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| EA-CCR | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| ASSESSMENTS | |||||||||||
| Change of medical history | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| Safety assessment | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||
| ADAS-K-cog | X | X | X | ||||||||
| MoCA-K | X | X | X | ||||||||
| CES-D | X | X | X | ||||||||
| K-ADL, K-IADL | X | X | X | ||||||||
| EQ-5D-5L | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Dependent Variables | EA-CCR (n = 16) | CCR (n = 16) | p or x2 (P) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) or n (%) | Mean (SD) or n (%) | ||
| Age (y) | 69.94 (5.94) | 74.25 (5.39) | 21.33 (0.166) ǂ |
| Gender (Female) | 14 (87.5) | 14 (87.5) | 0.00 (1.000) ǂ |
| Education | 9.13 (4.83) | 8.69 (5.08) | 4.84 (0.679) ǂ |
| ADAS-K-cog | 11.13 ± 4.10 | 11.19 ± 6.22 | −0.03 (0.973) * |
| MoCA-K | 18.75 ± 2.54 | 19.31 ± 2.92 | −0.58 (0.565) * |
| CES-D | 14.25 ± 5.91 | 11.50 ± 6.94 | 1.21 (0.237) * |
| K-ADL | 7.19 ± 0.40 | 7.13 ± 0.34 | 0.47 (0.640) * |
| K-IADL | 11.00 ± 3.03 | 11.50 ± 3.10 | −0.46 (0.648) * |
| EQ-5D-5L | 6.38 ± 1.36 | 7.31 ± 2.52 | −1.31 (0.201) * |
| Groups | Dependent Variables | Week 0 (M ± SD) | Week 8 (M ± SD) | Week 20 (M ± SD) | Difference (w8-w0) | Z (p) * | Difference (w20-w0) | Z (p) * | x2 (p) ǂ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EA-CCR group (n = 16) | ADAS-K -cog | 11.13 ± 4.10 | 7.19 ± 4.75 | 6.19 ± 3.95 | −3.94 ± 2.57 | −3.42 (0.001) | −4.94 ± 3.45 | −3.42 (0.001) | 21.08 (<0.001) |
| MoCA-K | 18.75 ± 2.54 | 24.25 ± 3.26 | 24.56 ± 4.21 | 5.50 ± 2.48 | −3.53 (<0.001) | 5.81 ± 3.69 | −3.41 (0.001) | 24.10 (<0.001) | |
| CES-D | 14.25 ± 5.91 | 10.94 ± 6.18 | 10.75 ± 6.02 | −3.31 ± 4.77 | −2.39 (0.017) | −3.50 ± 6.20 | −2.01 (0.038) | 7.48 (0.024) | |
| K-ADL | 7.19 ± 0.40 | 7.06 ± 0.25 | 7.13 ± 0.34 | −0.13 ± 0.34 | −1.41 (0.157) | −0.06 ± 0.44 | −0.58 (0.564) | 2.00 (0.368) | |
| K-IADL | 11.00 ± 3.03 | 10.69 ± 1.85 | 10.44 ± 0.96 | −0.31 ± 3.03 | −0.54 (0.593) | −0.56 ± 2.45 | −0.73 (0.465) | 0.15 (0.926) | |
| EQ-5D-5L | 6.38 ± 1.36 | 6.06 ± 1.24 | 5.75 ± 1.00 | 0.31 ± 1.49 | −0.93 (0.351) | 0.63 ± 1.54 | −1.40 (0.161) | 3.56 (0.169) | |
| CCR group (n = 16) | ADAS-K -cog | 11.19 ± 6.22 | 7.38 ± 3.86 | 5.81 ± 2.76 | -3.81 ± 3.47 | −3.33 (0.001) | −5.38 ± 5.19 | −3.42 (0.001) | 19.22 (<0.001) |
| MoCA-K | 19.31 ± 2.92 | 24.19 ± 2.48 | 25.13 ± 1.89 | 4.88 ± 2.45 | −3.53 (<0.001) | 5.81 ± 2.37 | −3.53 (<0.001) | 26.00 (<0.001) | |
| CES-D | 11.50 ± 6.94 | 11.00 ± 6.69 | 9.75 ± 6.77 | −0.50 ± 7.43 | −0.00 (1.00) | −1.75 ± 8.70 | −1.02 (0.306) | 1.86 (0.395) | |
| K-ADL | 7.13 ± 0.34 | 7.06 ± 0.25 | 7.06 ± 0.25 | −0.06 ± 0.25 | −1.00 (0.317) | −0.06 ± 0.25 | −1.00 (0.317) | 2.00 (0.368) | |
| K-IADL | 11.50 ± 3.10 | 11.44 ± 3.08 | 11.62 ± 3.12 | −0.06 ± 0.93 | −0.45 (0.655) | −0.13 ± 1.31 | −0.54 (0.593) | 0.20 (0.905) | |
| EQ-5D-5L | 7.31 ± 2.52 | 6.12 ± 1.24 | 6.31 ± 1.25 | 1.00 ± 2.92 | −2.21 (0.027) | −1.00 ± 2.92 | −1.29 (0.196) | 5.28 (0.071) |
| Dependent Variables | Group (n) | Week 0 (M ± SD) | Week 8 (M ± SD) | Week 20 (M ± SD) | Source | SS | df | Mean Square | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADAS-K-cog | EA-CCR (n = 16) | 11.13 ± 4.10 | 7.19 ± 4.75 | 6.19 ± 3.95 | Time | 461.27 | 2 | 230.64 | 38.16 | <0.001 |
| CCR (n = 16) | 11.19 ± 6.22 | 7.38 ± 3.86 | 5.81 ± 2.76 | Group Time | 1.396 | 2 | 0.70 | 0.12 | 0.891 | |
| MoCA-K | EA-CCR (n = 16) | 18.75 ± 2.54 | 24.25 ± 3.26 | 24.56 ± 4.21 | Time | 651.58 | 2 | 325.79 | 86.11 | <0.001 |
| CCR (n = 16) | 19.31 ± 2.92 | 24.19 ± 2.48 | 25.13 ± 1.89 | Group Time | 2.08 | 2 | 1.04 | 0.28 | 0.760 | |
| CES-D | EA-CCR (n = 16) | 14.25 ± 5.91 | 10.94 ± 6.18 | 10.75 ± 6.02 | Time | 117.77 | 2 | 58.89 | 2.52 | 0.089 |
| CCR (n = 16) | 11.50 ± 6.94 | 11.00 ± 6.69 | 9.75 ± 6.77 | Group Time | 32.27 | 2 | 16.14 | 0.69 | 0.506 | |
| K-ADL | EA-CCR (n = 16) | 7.19 ± 0.40 | 7.06 ± 0.25 | 7.13 ± 0.34 | Time | 0.15 | 2 | 0.07 | 1.75 | 0.183 |
| CCR (n = 16) | 7.13 ± 0.34 | 7.06 ± 0.25 | 7.06 ± 0.25 | Group Time | 0.02 | 2 | 0.01 | 0.25 | 0.780 | |
| K-IADL | EA-CCR (n = 16) | 11.00 ± 3.03 | 10.69 ± 1.85 | 10.44 ± 0.96 | Time | 0.90 | 2 | 0.45 | 0.26 | 0.770 |
| CCR (n = 16) | 11.50 ± 3.10 | 11.44 ± 3.08 | 11.62 ± 3.12 | Group Time | 1.94 | 2 | 0.97 | 0.57 | 0.570 | |
| EQ-5D-5L | EA-CCR (n = 16) | 6.38 ± 1.36 | 6.06 ± 1.24 | 5.75 ± 1.00 | Time | 13.08 | 2 | 6.54 | 3.83 | 0.027 |
| CCR (n = 16) | 7.31 ± 2.52 | 6.12 ± 1.24 | 6.31 ± 1.25 | Group Time | 3.08 | 2 | 1.54 | 0.90 | 0.411 |
| Dependent Variables | Group(n) | Week 0 (M ± SD) | Difference (w8-w0) | Z (p) * | Difference (w20-w0) | Z (p) * | Difference (w20-w8) | Z (p) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADAS-K -cog | EA-CCR (n = 16) | 11.13 ± 4.10 | −3.94 ± 2.57 | −0.38 (0.703) | −4.94 ± 3.45 | −0.21 (0.835) | −1.00 ± 2.66 | −0.25 (0.804) |
| CCR(n = 16) | 11.19 ± 6.22 | −3.81 ± 3.47 | −5.38 ± 5.19 | 1.56 ± 2.83 | ||||
| MoCA-K | EA-CCR (n = 16) | 18.75 ± 2.54 | 5.50 ± 2.48 | −0.72 (0.470) | 5.81 ± 3.69 | −0.23 (0.819) | 0.31 ± 2.98 | −0.74 (0.459) |
| CCR(n = 16) | 19.31 ± 2.92 | 4.88 ± 2.45 | 5.81 ± 2.37 | 0.94 ± 2.26 | ||||
| CES-D | EA-CCR (n = 16) | 14.25 ± 5.91 | −3.31 ± 4.77 | −1.32 (0.186) | −3.50 ± 6.20 | −0.63 (0.533) | −0.19 ± 4.05 | −1.19 (0.234) |
| CCR(n = 16) | 11.50 ± 6.94 | −0.50 ± 7.43 | −1.75 ± 8.70 | −1.25 ± 8.50 | ||||
| K-ADL | EA-CCR (n = 16) | 7.19 ± 0.40 | −0.13 ± 0.34 | −0.60 (0.551) | −0.06 ± 0.44 | −0.03 (0.974) | 0.06 ± 0.25 | −1.00 (0.317) |
| CCR(n = 16) | 7.13 ± 0.34 | −0.06 ± 0.25 | −0.06 ± 0.25 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | ||||
| K-IADL | EA-CCR (n = 16) | 11.00 ± 3.03 | −0.31 ± 3.03 | −0.45 (0.655) | −0.56 ± 2.45 | −0.42 (0.677) | −0.25 ± 1.29 | −0.07 (0.948) |
| CCR(n = 16) | 11.50 ± 3.10 | −0.06 ± 0.93 | −0.13 ± 1.31 | 0.19 ± 1.05 | ||||
| EQ−5D−5L | EA-CCR (n = 16) | 6.38 ± 1.36 | 0.31 ± 1.49 | −1.31 (0.189) | 0.63 ± 1.54 | −0.21(0.832) | −0.31 ± 0.95 | −1.17(0.243) |
| CCR(n = 16) | 7.31 ± 2.52 | −1.19 ± 1.91 | −1.00 ± 2.92 | 0.19 ± 1.68 |
| Dependent Variables | Group (n) | Week 0 (M ± SD) | Week 8 (M ± SD) | Week 20 (M ± SD) | Difference (w8-w0) | Z (p) * | Difference (w20-w0) | Z (p) * | Difference (w20-w8) | Z (p) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADAS-cog | EA-CCR (n = 9) | 11.56 ± 3.94 | 7.56 ± 5.66 | 7.00 ± 4.64 | −4.00 ± 3.24 | −0.70 (0.483) | −4.56 ± 4.03 | −0.94 (0.349) | −0.56 ± 2.74 | −0.80 (0.424) |
| CCR (n = 4) | 7.00 ± 2.94 | 4.75 ± 3.40 | 4.75 ± 3.40 | −2.25 ± 1.71 | −2.25 ± 0.96 | 0.00 ± 2.00 | ||||
| MoCA-K | EA-CCR (n = 9) | 18.33 ± 2.50 | 23.44 ± 3.47 | 23.00 ± 4.33 | 5.11 ± 2.57 | −0.47 (0.639) | 4.67 ± 3.24 | −1.02 (0.308) | −0.44 ± 2.88 | −0.78 (0.438) |
| CCR (n = 4) | 19.75 ± 2.22 | 25.50 ± 2.52 | 26.25 ± 1.71 | 5.75 ± 2.06 | 6.50 ± 1.00 | 0.75 ± 1.26 | ||||
| CES-D | EA-CCR (n = 9) | 13.78 ± 4.47 | 11.22 ± 6.24 | 12.22 ± 4.32 | −2.56 ± 3.64 | −0.16 (0.876) | −1.56 ± 5.27 | −0.70 (0.486) | 1.00 ± 4.72 | −0.46 (0.643) |
| CCR (n = 4) | 10.50 ± 7.59 | 11.50 ± 9.29 | 13.00 ± 7.75 | 1.00 ± 8.68 | 2.50 ± 14.57 | 1.50 ± 16.11 | ||||
| K-ADL | EA-CCR (n = 9) | 7.00 ± 0.00 | 7.00 ± 0.00 | 7.11 ± 0.33 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 (1.000) | 0.11 ± 0.33 | −0.67 (0.505) | 0.11 ± 0.33 | −0.68 (0.505) |
| CCR (n = 4) | 7.00 ± 0.00 | 7.00 ± 0.00 | 7.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | ||||
| K-IADL | EA-CCR (n = 9) | 11.78 ± 3.96 | 11.22 ± 2.39 | 10.78 ± 1.20 | −0.56 ± 4.13 | −0.42 (0.676) | −1.00 ± 3.28 | −0.79 (0.429) | −0.44 ± 1.74 | −0.94 (0.348) |
| CCR (n = 4) | 10.75 ± 1.50 | 10.75 ± 1.50 | 11.75 ± 2.06 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 1.00 ± 2.00 | 1.00 ± 2.00 | ||||
| EQ−5D−5L | EA-CCR (n = 9) | 6.44 ± 1.59 | 5.78 ± 1.09 | 5.33 ± 0.71 | −0.67 ± 1.41 | −0.24 (0.810) | −1.11 ± 1.69 | −0.24 (0.813) | −0.44 ± 1.13 | −0.50 (0.614) |
| CCR (n = 4) | 6.75 ± 2.06 | 6.00 ± 1.41 | 6.50 ± 1.73 | −0.75 ± 0.96 | −0.25 ± 3.10 | 0.50 ± 2.52 |
| Dependent Variables | Group (n) | Week 0 (M ± SD) | Week 8 (M ± SD) | Week 20 (M ± SD) | Difference (w8-w0) | Z (p) * | Difference (w20-w0) | Z (p) * | Difference (w20-w8) | Z (p) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADAS-cog | EA-CCR (n = 7) | 10.57 ± 4.54 | 6.71 ± 3.64 | 5.14 ± 2.85 | −3.86 ± 1.57 | −0.86 (0.931) | −5.43 ± 2.76 | −0.85 (0.932) | −1.57 ± 2.64 | −0.43 (0.668) |
| CCR (n = 12) | 12.58 ± 6.47 | 8.25 ± 3.72 | 6.17 ± 2.55 | −4.33 ± 3.80 | −6.42 ± 5.63 | −2.08 ± 2.94 | ||||
| MoCA-K | EA-CCR (n = 7) | 19.29 ± 2.69 | 25.29 ± 2.87 | 26.57 ± 3.31 | 6.00 ± 2.45 | −1.41 (0.158) | 7.29 ± 3.95 | −1.11 (0.265) | 1.29 ± 3.04 | −0.86 (0.932) |
| CCR (n = 12) | 19.17 ± 3.19 | 23.75 ± 2.42 | 24.75 ± 1.86 | 4.58 ± 2.57 | 5.58 ± 2.68 | 1.00 ± 2.56 | ||||
| CES-D | EA-CCR (n = 7) | 14.86 ± 7.73 | 10.57 ± 6.58 | 8.86 ± 7.63 | −4.29 ± 6.10 | −1.32 (0.188) | −6.00 ± 6.78 | −0.93 (0.352) | −1.71 ± 2.56 | −0.55 (0.579) |
| CCR (n = 12) | 11.83 ± 7.03 | 10.83 ± 6.12 | 8.67 ± 6.40 | −1.00 ± 7.32 | −3.17 ± 6.04 | −2.17 ± 4.91 | ||||
| K-ADL | EA-CCR (n = 7) | 7.43 ± 0.53 | 7.14 ± 0.38 | 7.14 ± 0.38 | −0.29 ± 0.49 | 1.14 (0.256) | −0.29 ± 0.49 | −1.14 (0.258) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | −0.00 (1.000) |
| CCR (n = 12) | 7.17 ± 0.39 | 7.08 ± 0.29 | 7.08 ± 0.29 | −0.08 ± 0.29 | −0.08 ± 0.29 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | ||||
| K-IADL | EA-CCR (n = 7) | 10.00 ± 0.00 | 10.00 ± 0.00 | 10.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | −0.00 (1.000) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | −0.00 (1.000) | −0.00 ± 0.00 | −0.76 (0.445) |
| CCR (n = 12) | 11.75 ± 3.49 | 11.67 ± 3.47 | 11.58 ± 3.48 | −0.08 ± 1.08 | −0.17 ± 0.94 | −0.08 ± 0.29 | ||||
| EQ−5D−5L | EA-CCR (n = 7) | 6.29 ± 1.11 | 6.43 ± 1.40 | 6.29 ± 1.11 | 0.14 ± 1.57 | −1.45 (0.146) | 0.00 ± 1.15 | −0.78 (0.433) | −0.14 ± 0.69 | −0.83 (0.409) |
| CCR (n = 12) | 7.50 ± 2.71 | 6.17 ± 1.19 | 6.25 ± 1.14 | −1.33 ± 2.15 | −1.25 ± 2.96 | 0.08 ± 1.44 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-H.; Han, J.-Y.; Park, G.-C.; Lee, J.-S. Cognitive Improvement Effects of Electroacupuncture Combined with Computer-Based Cognitive Rehabilitation in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120984
Kim J-H, Han J-Y, Park G-C, Lee J-S. Cognitive Improvement Effects of Electroacupuncture Combined with Computer-Based Cognitive Rehabilitation in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(12):984. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120984
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jae-Hong, Jae-Young Han, Gwang-Cheon Park, and Jeong-Soon Lee. 2020. "Cognitive Improvement Effects of Electroacupuncture Combined with Computer-Based Cognitive Rehabilitation in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Brain Sciences 10, no. 12: 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120984
APA StyleKim, J.-H., Han, J.-Y., Park, G.-C., & Lee, J.-S. (2020). Cognitive Improvement Effects of Electroacupuncture Combined with Computer-Based Cognitive Rehabilitation in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Brain Sciences, 10(12), 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120984





