The Mammalian Locus Coeruleus Complex—Consistencies and Variances in Nuclear Organization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
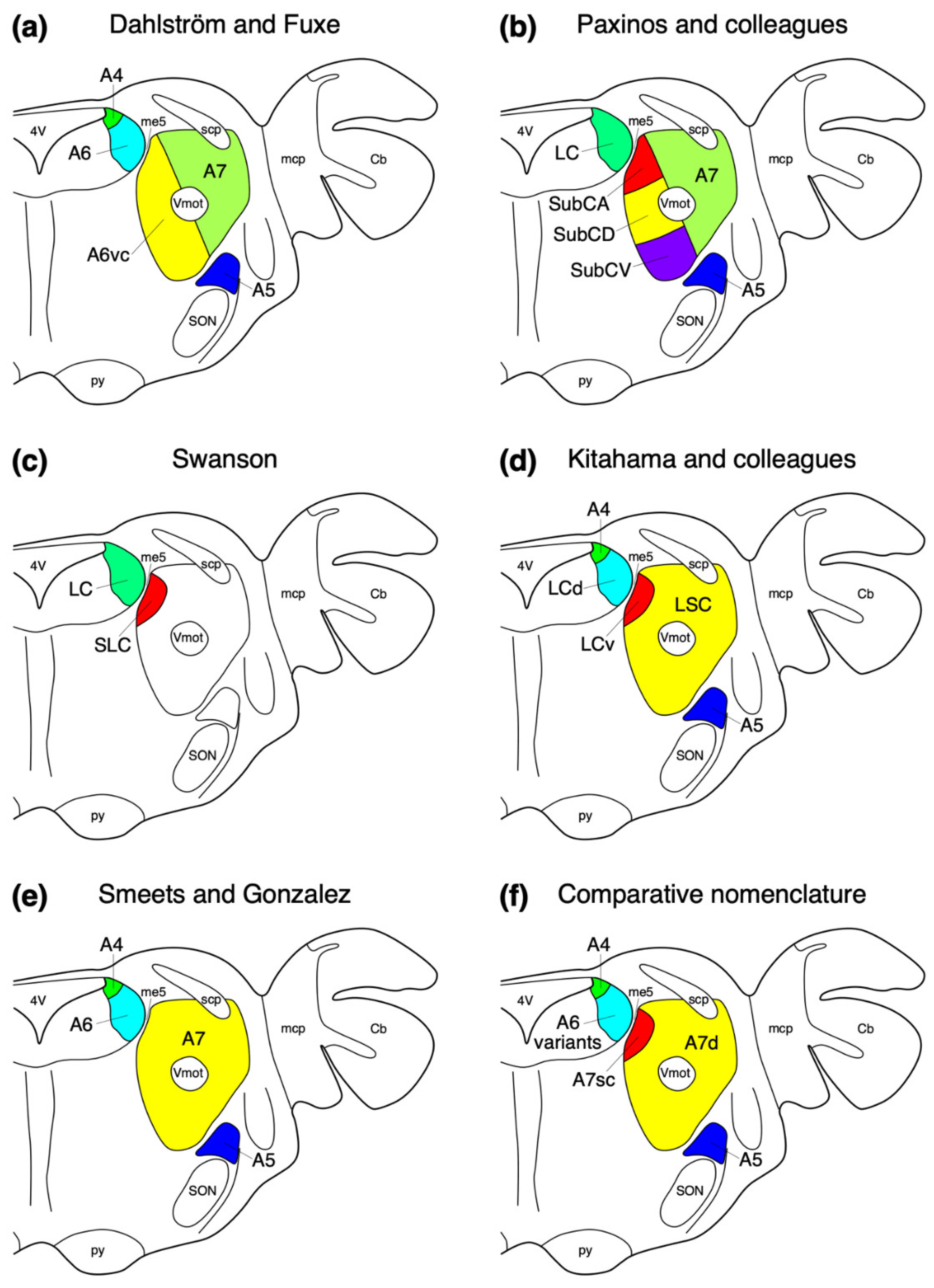
2. Location, Nuclear Parcellation, and Nomenclature of the Locus Coeruleus Complex in Laboratory Rodents
3. Noradrenergic Neurons (A4 and A6 Nuclei) within the Periventricular Grey Matter of the Laboratory Rodent Rostral Hindbrain
4. Noradrenergic Neurons (A5 and A7) within the Parvicellular Reticular Nucleus of the Rostral Hindbrain
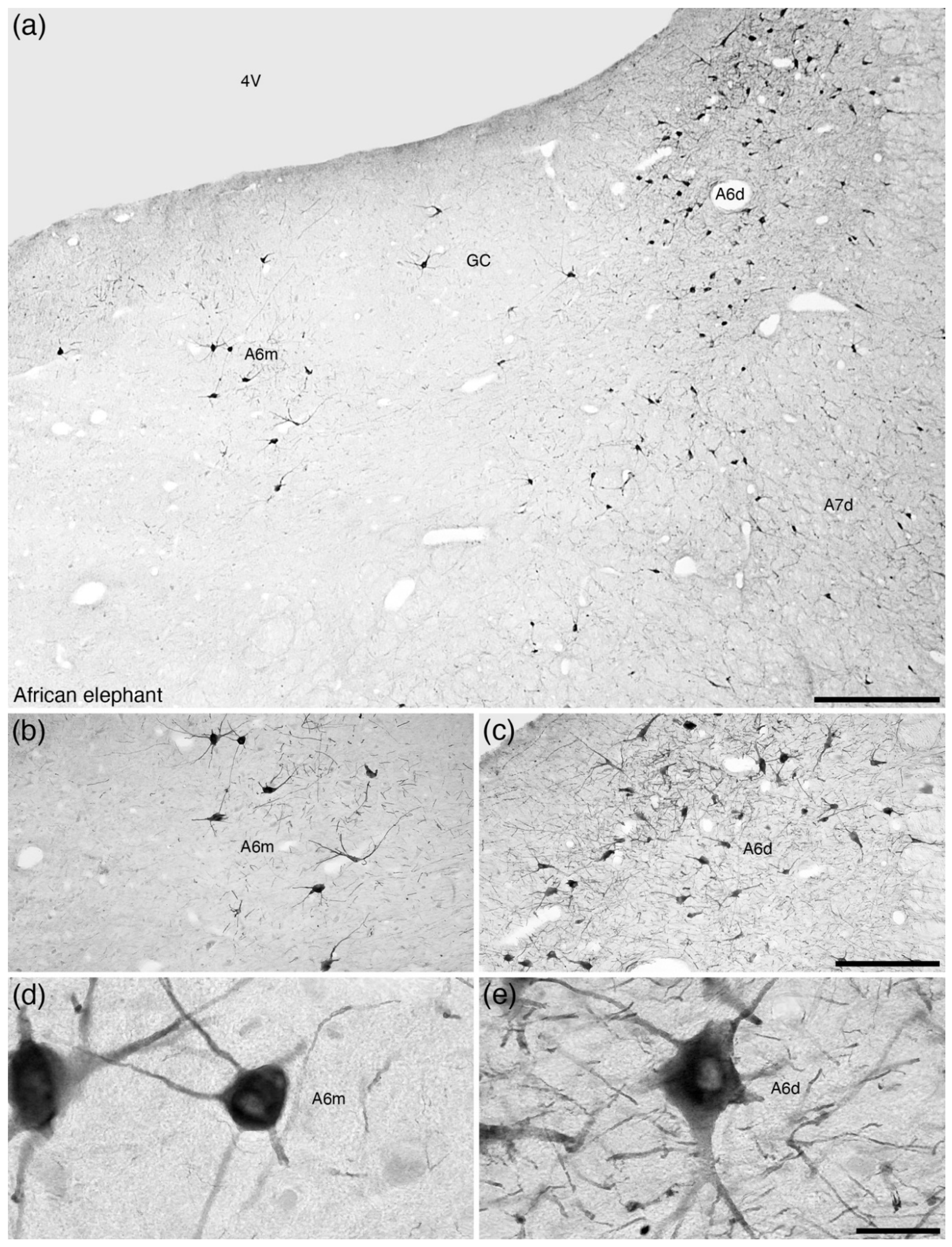
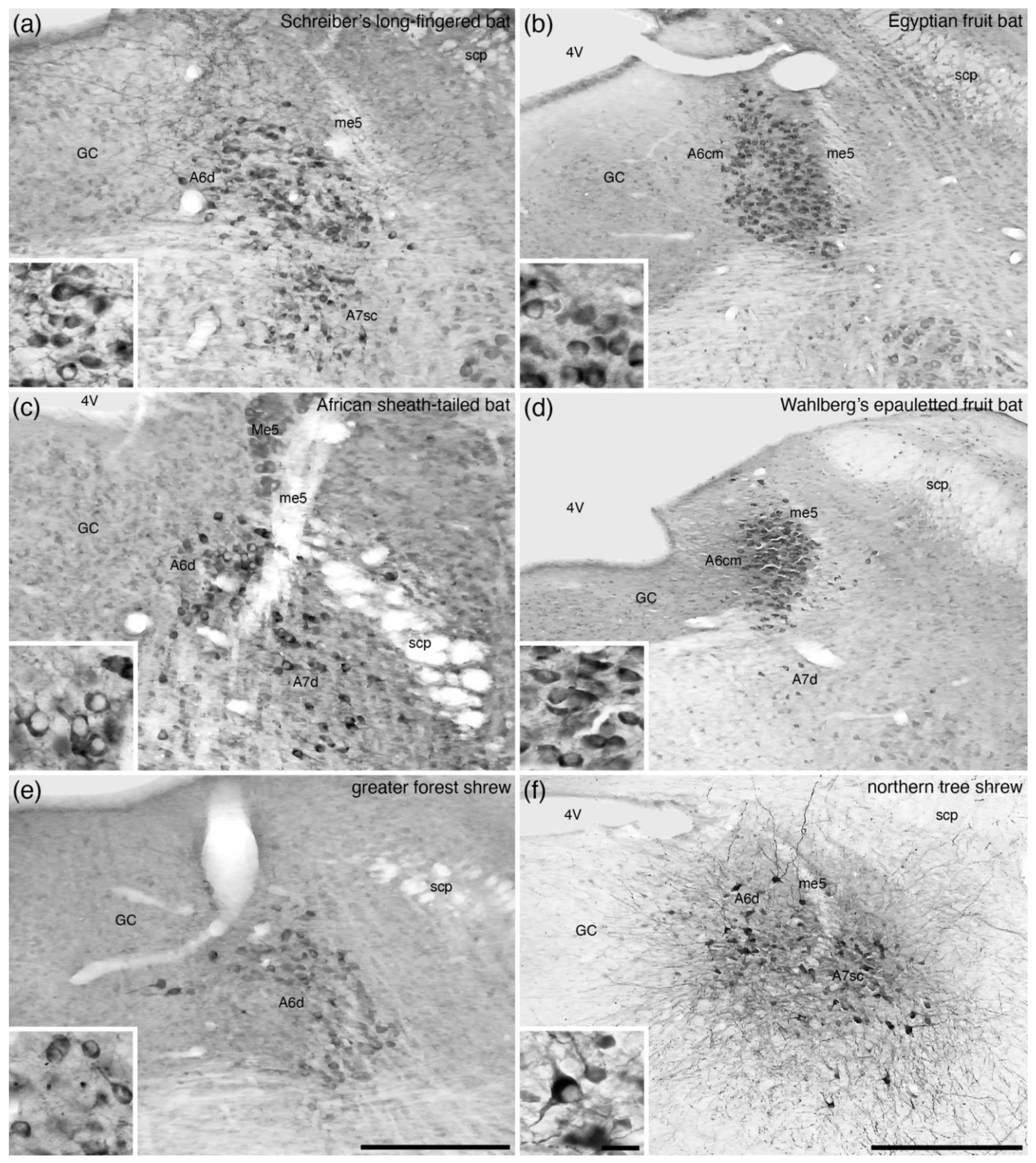
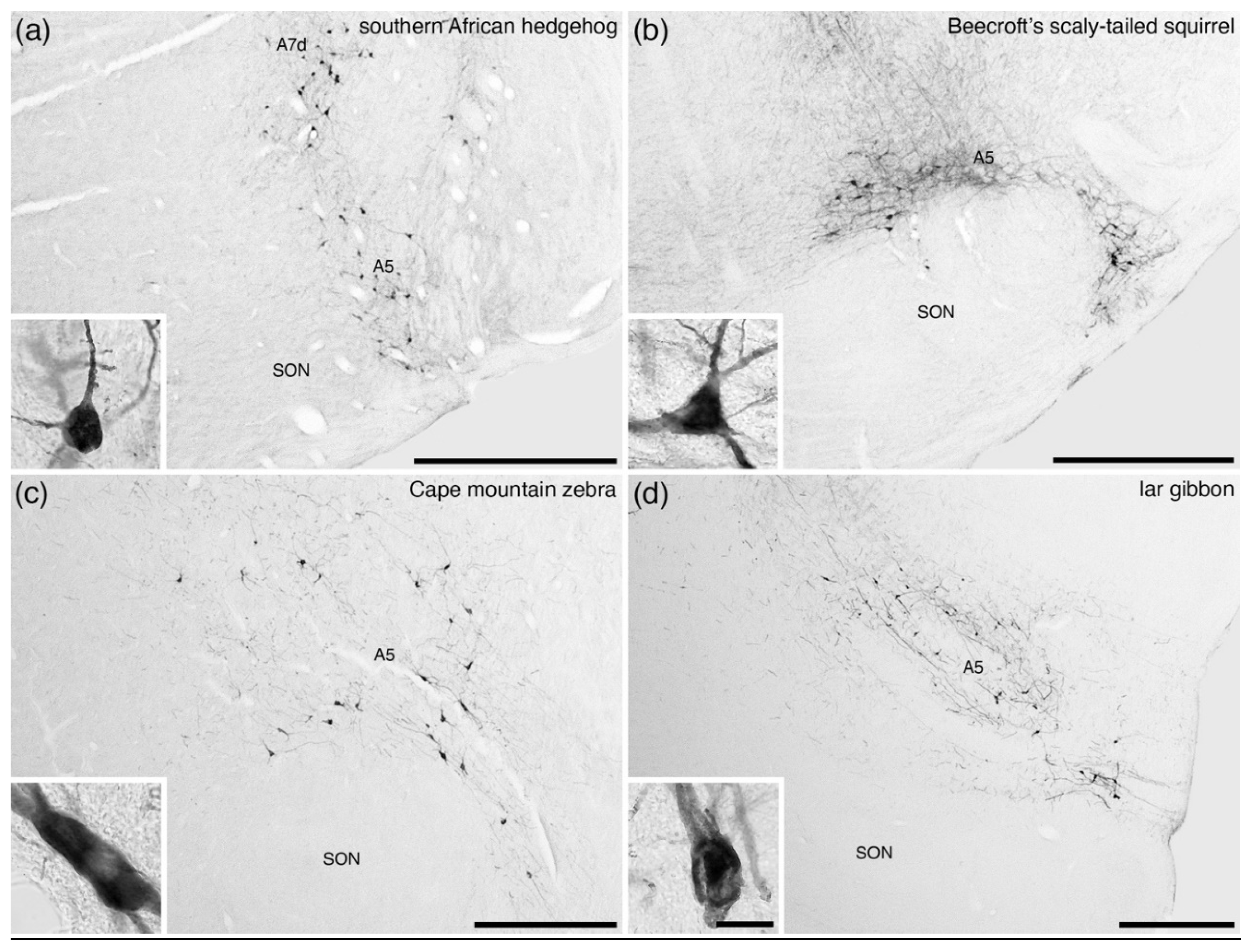
5. Location, Nuclear Parcellation, and Nomenclature of the Locus Coeruleus Complex in Other Mammals
6. The A4 Nucleus (Dorsomedial Division of the Locus Coeruleus)
7. The A6 Nucleus (Locus Coeruleus)
8. The A5 Nucleus (Fifth Arcuate Nucleus)
9. The A7 Nuclei (Subcoeruleus)
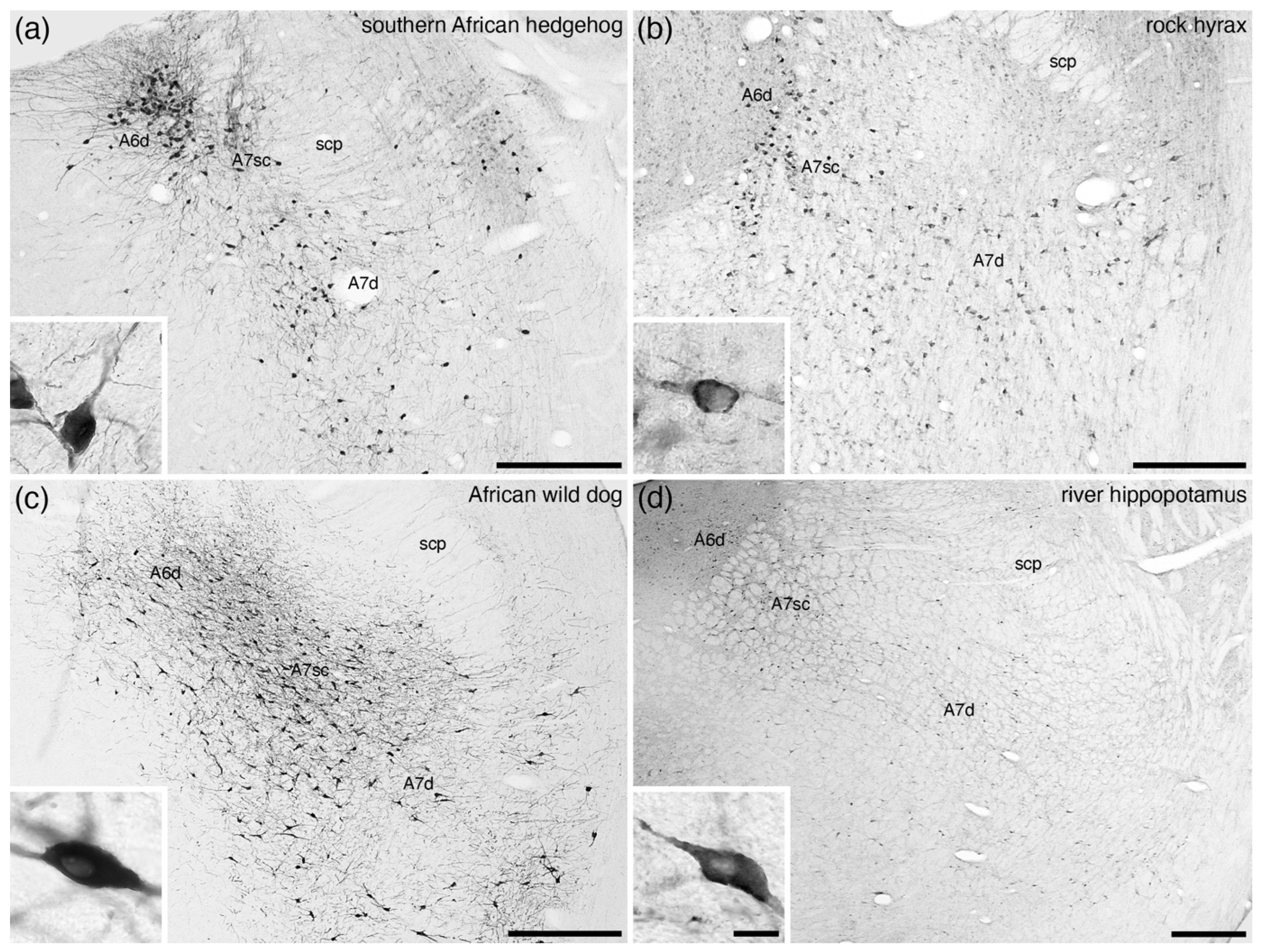
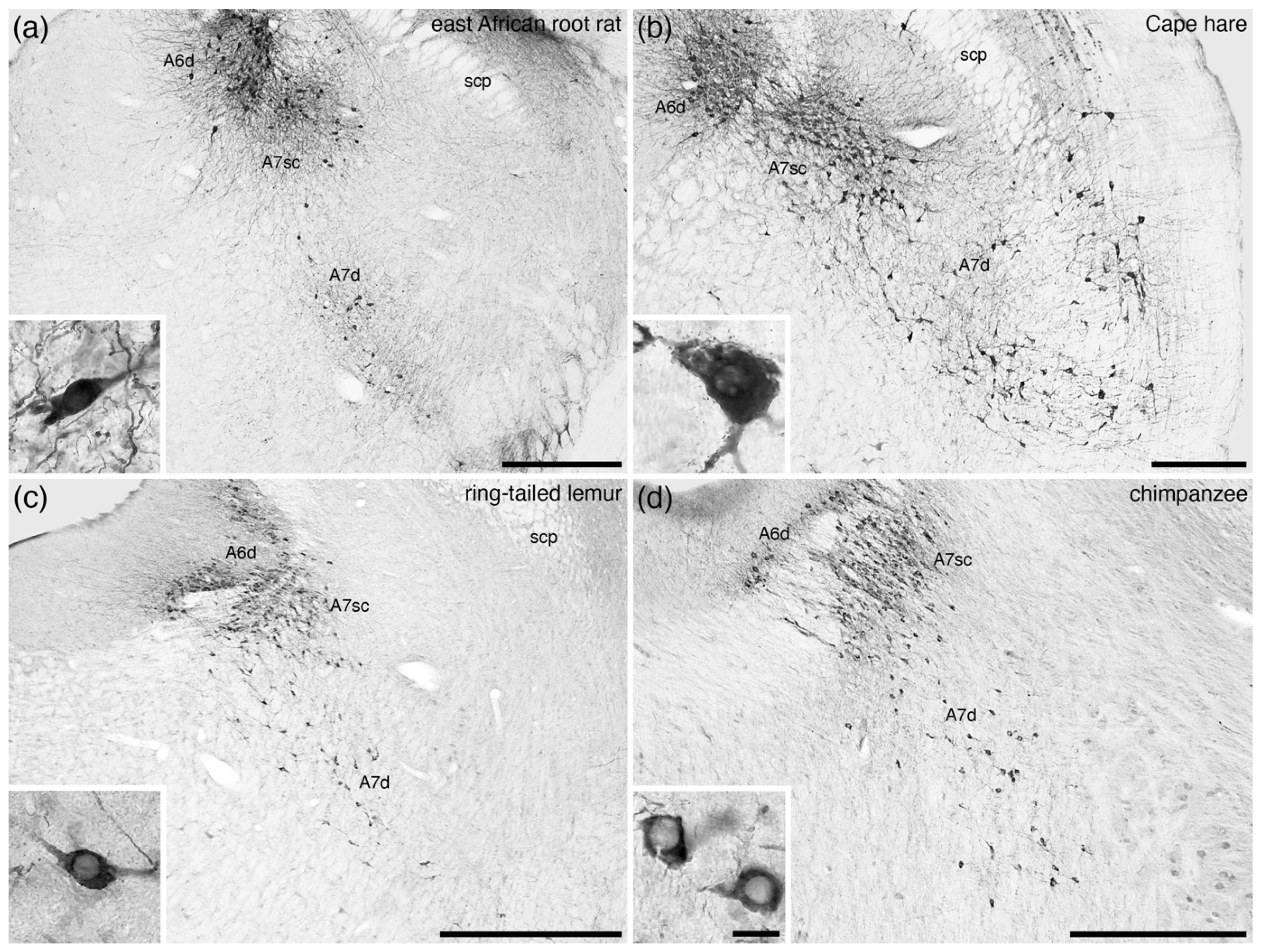
10. Consistencies in the Organization of the Mammalian Locus Coeruleus Complex
11. Variations in the Organization of the Mammalian Locus Coeruleus Complex
12. Gaps in Our Comparative Knowledge of the Mammalian Locus Coeruleus Complex
13. How Does the Nuclear Definition of the LC Complex Developed in the Laboratory Rodent Brain Accommodate Variations in Mammalian Species?
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tubbs, R.S.; Loukas, M.; Shoja, M.M.; Mortazavi, M.M.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A. Félix Vicq d’Azyr (1746–1794): Early founder of neuroanatomy and royal French physician. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2011, 27, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dahlström, A.; Fuxe, K. Evidence for the existence of monoamine-containing neurons in the central nervous system. I. Demonstration of monoamines in the cell bodies of brain stem neurons. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 1964, 232, 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Smeets, W.J.A.J.; González, A. Catecholamine systems in the brain of vertebrates: New perspectives through a comparative approach. Brain Res. Rev. 2000, 33, 308–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuxe, K. Evidence for the existence of monoamine neurons in the central nervous system. IV. Distribution of monoamine nerve terminals in the central nervous system. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 1965, 247, 37–80. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, B.E.; Moore, R.Y. Ascending projections of the locus coeruleus in the rat. II. Autoradiographic study. Brain Res. 1977, 127, 23–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, L.W.; Hartman, B.K. The central adrenergic system. An immunofluorescence study of the location of cell bodies and their efferent connections in the rat utilizing dopamine-beta-hydroxylase as a marker. J. Comp. Neurol. 1975, 163, 467–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, S.D.; Plummer, N.W.; de Marchena, J.; Jensen, P. Developmental origins of central norepinephrine neuron diversity. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, L.A.; Miyamichi, K.; Gao, X.J.; Beier, K.T.; Weissbourd, B.; DeLoach, K.E.; Ren, J.; Ibanes, S.; Malenka, R.C.; Kremer, E.J.; et al. Viral-genetic tracing of the input-output organization of a central noradrenaline circuit. Nature 2015, 524, 88094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aston-Jones, G.; Cohen, J.D. An integrative theory of locus-coeruleus-norepinephrine function: Adaptive gain and optimal performance. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 28, 403–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aston-Jones, G.; Waterhouse, B. Locus coeruleus: From global projection system to adaptive regulation of behavior. Brain Res. 2016, 1645, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poe, G.R.; Foote, S.; Eschenko, O.; Johansen, J.P.; Bouret, S.; Aston-Jones, G.; Harley, C.W.; Manahan-Vaughan, D.; Weinshenker, D.; Valentino, R.; et al. Locus coeruleus: A new look at the blue spot. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 644–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manger, P.R.; Fahringer, H.M.; Pettigrew, J.D.; Siegel, J.M. The distribution and morphological characteristics of catecholaminergic cells in the brain of monotremes as revealed by tyrosine hydroxylase immunohistochemistry. Brain Behav. Evol. 2002, 60, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutcher, K.A.; Humbertson, A.O. The organization of monoamine neurons within the brainstem of the North America opossum (Didelphis virginiana). J. Comp. Neurol. 1978, 179, 195–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patzke, N.; Bertelsen, M.F.; Fuxe, K.; Manger, P.R. Nuclear organization of cholinergic, catecholaminergic serotonergic and orexinergic systems in the brain of the Tasmanian devil (Sarcophilus harrisii). J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2014, 61–62, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieters, R.P.; Gravett, N.; Fuxe, K.; Manger, P.R. Nuclear organization of cholinergic, putative catecholaminergic and serotonergic nuclei in the brain of the eastern rock elephant shrew, Elephantulus myurus. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2010, 39, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvey, T.; Patzke, N.; Kaswera, C.; Gilissen, E.; Bennett, N.C.; Manger, P.R. Nuclear organisation of some immunohistochemically identifiable neural systems in three Afrotherian species—Potomogale velox, Amblysomus hottentotus and Petrodromus tetradactylus. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2013, 50–51, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gravett, N.; Bhagwandin, A.; Fuxe, K.; Manger, P.R. Nuclear organization and morphology of cholinergic, putative catecholaminergic and serotonergic neurons in the brain of the rock hyrax, Procavia capensis. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2009, 38, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maseko, B.C.; Patzke, N.; Fuxe, K.; Manger, P.R. Architectural organization of the African elephant diencephalon and brainstem. Brain Behav. Evol. 2013, 82, 83–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvey, T.; Patzke, N.; Bennett, N.C.; Kaswera-Kyamakya, C.; Gilissen, E.; Alagaili, A.N.; Mohammed, O.B.; Pettigrew, J.D.; Manger, P.R. Nuclear organisation of some immunohistochemically identifiable neural systems in five species of insectivore—Crocidura cyanea, Crocidura olivieri, Sylvisorex ollula, Paraechinus aethiopicus and Atelerix frontalis. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2016, 72, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michaloudi, H.C.; Papdopoulus, G.C. Noradrenergic and dopaminergic systems in the central nervous system of the hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus). J. Hirnforsch. 1996, 37, 319–350. [Google Scholar]
- Maseko, B.C.; Manger, P.R. Distribution and morphology of cholinergic, catecholaminergic and serotonergic neurons in the brain of Schreiber’s long-fingered bat, Miniopterus schreibersii. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2007, 34, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, J.L.; Dell, L.A.; Bhagwandin, A.; Jillani, N.E.; Pettigrew, J.D.; Manger, P.R. Nuclear organization of cholinergic, putative catecholaminergic and serotonergic systems in the brains of five microchiropteran species. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2010, 40, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maseko, B.C.; Bourne, J.A.; Manger, P.R. Distribution and morphology of cholinergic, putative catecholaminergic and serotonergic neurons in the brain of the Egyptian rousette flying fox, Rousettus aegyptiacus. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2007, 34, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell, L.A.; Kruger, J.L.; Bhagwandin, A.; Jillani, N.E.; Pettigrew, J.D.; Manger, P.R. Nuclear organization of cholinergic, putative catecholaminergic and serotonergic systems in the brains of two megachiropteran species. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2010, 40, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, A.; Bhagwandin, A.; Ajao, M.S.; Ihunwo, A.O.; Fuxe, K.; Manger, P.R. Brain of the tree pangolin (Manis tricuspis). III. The unusual locus coeruleus complex. J. Comp. Neurol. 2018, 526, 2570–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dormer, K.J.; Anwar, M.; Ashlock, S.R.; Ruggiero, D.A. Organization of presumptive catecholamine-synthesizing neurons in the canine medulla oblongata. Brain Res. 1993, 601, 41–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, S.; Bhagwandin, A.; Bertelsen, M.F.; Patzke, N.; Engler, G.; Engel, A.K.; Manger, P.R. Regional distribution of cholinergic, catecholaminergic, serotonergic and orexinergic neurons in the brain of two carnivore species: The feliform banded mongoose (Mungos mungo) and the caniform domestic ferret (Mustela putorius furo). J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2017, 82, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitras, D.; Parent, A. Atlas of the distribution of monoamine-containing nerve cell bodies in the brain stem of the cat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1978, 179, 699–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bux, F.; Bhagwandin, A.; Fuxe, K.; Manger, P.R. Organization of cholinergic, putative catecholaminergic and serotonergic nuclei in the diencephalon, midbrain and pons of sub-adult male giraffes. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2010, 39, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malungo, I.B.; Gravett, N.; Bhagwandin, A.; Davimes, J.G.; Manger, P.R. A preliminary description of the sleep-related neural systems in the brain of the blue wildebeest, Connochaetes taurinus. Anat. Rec. 2020, 303, 1977–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davimes, J.G.; Alagaili, A.N.; Bennett, N.C.; Mohammed, O.B.; Bhagwandin, A.; Manger, P.R.; Gravett, N. Neurochemical organization and morphology of the sleep related nuclei in the brain of the Arabian oryx, Oryx leucoryx. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2017, 81, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillet, Y.; Thibault, J. Catecholamine-containing neurons in the sheep brainstem and diencephalon: Immunohistochemical study with tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and dopamine-ß-hydroxylase (DBH) antibodies. J. Comp. Neurol. 1989, 290, 69–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manger, P.R.; Ridgway, S.H.; Siegel, J.M. The locus coeruleus complex of the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) as revealed by tyrosine hydroxylase immunohistochemistry. J. Sleep Res. 2003, 12, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sacchini, S.; Arbelo, M.; Bombardi, C.; Fernandez, A.; Cozzi, B.; Bernaldo de Quiros, Y.; Herraez, P. Locus coeruleus complex of the family Delphinidae. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dell, L.A.; Patzke, N.; Spocter, M.A.; Siegel, J.M.; Manger, P.R. Organization of the sleep-related neural systems in the brain of the harbour porpoise (Phocoena phocoena). J. Comp. Neurol. 2016, 524, 1999–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell, L.A.; Karlsson, K.; Patzke, N.; Spocter, M.A.; Siegel, J.M.; Manger, P.R. Organization of the sleep-related neural systems in the brain of the minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata). J. Comp. Neurol. 2016, 524, 2018–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell, L.A.; Patzke, N.; Spocter, M.A.; Bertelsen, M.F.; Siegel, J.M.; Manger, P.R. Organization of the sleep-related neural systems in the brain of the river hippopotamus (Hippopotamus amphibius): A most unusual cetartiodactyl species. J. Comp. Neurol. 2016, 524, 2036–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos, P.; Arroyo-Jimenez, M.M.; Lozano, G.; Aguilar, L.A.; Covenas, R. Mapping of tyrosine hydroxylase in the alpaca (Lama pacos) brainstem and colocalization with CGRP. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2011, 41, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hökfelt, T.; Martensonm, R.; Björklund, A.; Kleinau, S.; Goldstein, M. Distributional maps of tyrosine-hydroxylase-immunoreactive neurons in the rat brain. In Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy; Björklund, A., Hökfelt, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; Volume 2, pp. 277–379. [Google Scholar]
- Satoh, J.; Irino, M.; Martin, P.M.; Mailman, R.B.; Suzuki, K. Neurochemical and immunocytochemical studies of catecholamine system in the brindled mouse. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1991, 50, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhorst, V.G.J.M.; Ulfhake, B. The organization of the brainstem and spinal cord of the mouse: Relationships between monoaminergic, cholinergic, and spinal projection systems. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2006, 31, 2–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, J.L.; Patzke, N.; Fuxe, K.; Bennett, N.C.; Manger, P.R. Nuclear organization of cholinergic, catecholaminergic, serotonergic and orexinergic systems in the brain of the African pygmy mouse (Mus minutoides): Organizational complexity is preserved in small brains. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2012, 44, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moon, D.J.; Maseko, B.C.; Ihunwo, A.O.; Fuxe, K.; Manger, P.R. Distribution and morphology of catecholaminergic and serotonergic neurons in the brain of the highveld gerbil, Tatera brantsii. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2007, 34, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweigers, J.; Bhagwandin, A.; Spocter, M.A.; Kaswera-Kyamakya, C.; Gilissen, E.; Manger, P.R.; Maseko, B.C. Nuclear organisation of cholinergic, catecholaminergic, serotonergic and orexinergic neurons in two relatively large-brained rodent species—The springhare (Pedetes capensis) and Beecroft’s scaly-tailed squirrel (Anomolurus beecrofti). J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2017, 86, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limacher, A.; Bhagwandin, A.; Fuxe, K.; Manger, P.R. Nuclear organization and morphology of cholinergic, putative catecholaminergic and serotonergic neurons in the brain of the Cape porcupine (Hystrix africaeaustralis): Increased brain size does not lead to increased organizational complexity. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2008, 36, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwarika, S.; Maseko, B.C.; Ihunwo, A.O.; Fuxe, K.; Manger, P.R. Distribution and morphology of putative catecholaminergic and serotonergic neurons in the brain of the greater canerat, Thryonomys swinderianus. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2008, 35, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.; Fuxe, K.; Manger, P.R. Nuclear parcellation of certain immunohistochemically identifiable neuronal systems in the midbrain and pons of the highveld molerat (Cryptomys hottentotus). J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2006, 31, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwandin, A.; Fuxe, K.; Bennett, N.C.; Manger, P.R. Nuclear organization and morphology of cholinergic, putative catecholaminergic and serotonergic neurons in the brain of two species of African mole-rat. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2008, 35, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blessing, W.W.; Chalmers, J.P.; Howe, P.R.C. Distribution of catecholamine-containing cell bodies in the rabbit central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 1978, 179, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvey, T.; Alagaili, A.N.; Bertelsen, M.F.; Bhagwandin, A.; Pettigrew, J.D.; Manger, P.R. Nuclear organization of some immunohistochemically identifiable neural systems in two species of the Euarchontoglires: A Lagomorph, Lepus capensis, and a Scandentia, Tupaia belangeri. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2015, 70, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murray, H.M.; Dominguez, W.F.; Martinez, J.E. Catecholamine neurons in the brain stem o the tree shrew (Tupaia). Brain Res. Bull. 1982, 9, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvey, T.; Patzke, N.; Kaswera-Kyamakya, C.; Gilissen, E.; Bertelsen, M.F.; Pettigrew, J.D.; Manger, P.R. Organization of cholinergic, catecholaminergic, serotonergic and orexinergic nuclei in three strepsirrhine primates: Galago demidoff, Perodicticus potto and Lemur catta. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2015, 70, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobowitz, D.M.; MacLean, P.D. A brainstem atlas of catecholaminergic neurons and serotonergic perikaryal in a pygmy primate (Cebuella pygmaea). J. Comp. Neurol. 1978, 177, 397–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felten, D.L.; Laties, A.M.; Carpenter, M.B. Monoamine-containing cell bodies in the squirrel monkey brain. Am. J. Anat. 1974, 139, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, J.E.; Di Carlo, V. Fluorescence histochemistry of monoamine-containing cell bodies in the brain stem of the squirrel monkey (Saimiri sciureus). II. Catecholamine-containing groups. J. Comp. Neurol. 1974, 153, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garver, D.L.; Sladek, J.R. Monoamine distribution in primate brain. I. Catecholamine-containing perikaryal in the brain stem of Macaca speciosa. J. Comp. Neurol. 1975, 159, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schofield, S.P.; Everitt, B.J. The organisation of catecholamine-containing neurons in the brain of the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). J. Anat. 1981, 132, 391–418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, V.M.; Bhagwandin, A.; Swiegers, J.; Bertelsen, M.F.; Hård, T.; Sherwood, C.C.; Manger, P.R. Nuclear organization of catecholaminergic neurons in the brains of a lar gibbon and a chimpanzee. Anat. Rec. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogerts, B. A brainstem atlas of catecholaminergic neurons in man, using melanin as a natural marker. J. Comp. Neurol. 1981, 197, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, J.; Goldstein, M.; Markey, K.; Brandeis, L. Human brainstem catecholamine neuronal anatomy as indicated by immunocytochemistry with antibodies to tyrosine hydroxylase. Neuroscience 1983, 8, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahama, K.; Sakamoto, N.; Jouvet, A.; Nagatsu, I.; Pearson, J. Dopamine-ß-hydroxylase and tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive neurons in the human brainstem. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1996, 10, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manger, P.R.; Cort, J.; Ebrahim, N.; Goodman, A.; Henning, J.; Karolia, M.; Rodrigues, S.L.; Štrkalj, G. Is 21st century neuroscience too focussed on the rat/mouse model of brain function and dysfunction? Front. Neuranat. 2008, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 5th ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Paxinos, G.; Carrive, P.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.Y. Chemoarchitectonic Atlas of the Rat Brainstem; Academic Press: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, L.W. Brain maps 4.0—Structure of the rat brain: An open access atlas with global nervous system nomenclature ontology and flatmaps. J. Comp. Neurol. 2018, 526, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitahama, K.; Nagatsu, I.; Pearson, J. Catecholamine systems in mammalian midbrain and hindbrain: Theme and variations. In Phylogeny and Development of Catecholamine Systems in the CNS of Vertebrates; Smeets, W.J.A.J., Reiner, A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; pp. 183–205. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, L.; Fuxe, K. On the projections from the locus coeruleus noradrenaline neurons: The cerebellar innervation. Brain Res. 1971, 28, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, R.L.; Sutin, J. Projections of the locus coeruleus and adjacent pontine tegmentum in the cat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1976, 165, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.E.; Halaris, A.E.; McIlhany, M.; Moore, R.Y. Ascending projections of the locus coeruleus in the rat. I. Axonal transport in central noradrenaline neurons. Brain Res. 1977, 127, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipley, M.T.; Halloran, F.J.; de la Torre, J. Surprisingly rich projection from locus coeruleus to the olfactory bulb in the rat. Brain Res. 1985, 329, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aston-Jones, G. Chapter 11—Locus coeruleus, A5 and A7 noradrenergic cell groups. In The Rat Nervous System, 3rd ed.; Paxinos, G., Ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 259–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruinstroop, E.; Cano, G.; Vanderhorst, V.G.J.M.; Cavalcante, J.C.; Wirth, J.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Saper, C.B. Spinal projections of the A5, A6 (locus coeruleus) and A7 noradrenergic cells groups in rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 520, 1985–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plummer, N.W.; Scappini, E.L.; Smith, K.G.; Tucker, C.J.; Jensen, P. Two subpopulations of noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus complex distinguished by expression of the dorsal neural tube marker Pax7. Front. Neuroanat. 2017, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.W.; Das, M.; Oyarzabal, E.A.; Cheng, Q.; Plummer, N.W.; Smith, K.G.; Jones, G.K.; Malawsky, D.; Yakel, J.L.; Shih, Y.Y.I.; et al. Genetic identification of a population of noradrenergic neurons implicated in attenuation of stress-related responses. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 710–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upham, N.S.; Esselstyn, J.A.; Jetz, W. Inferring the mammal tree: Species-level sets of phylogenies for questions in ecology, evolution, and conservation. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettigrew, J.D.; Jamieson, B.G.M.; Robson, S.K.; Hall, L.S.; McNally, K.I.; Cooper, H.M. Phylogenetic relations between microbats, megabats and primates (Mammalia: Chiroptera and Primates). Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1989, 325, 489–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, S. Preclinical research: Make mouse studies work. Nature 2014, 507, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, L.A.; Greek, R. Human stakeholders and the use of animals in drug development. Bus. Soc. Rev. 2018, 123, 3–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pound, P.; Ritskes-Hoitinga, M. Is it possible to overcome issues of external validity in preclinical animal research? Why most animal models are bound to fail. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Subclass | Clade/ Superorder | Order | Species Number | Scientific Name | Common Name | Nuclei of the Locus Coeruleus Complex | Source(s) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A4 | A5 | A6d | A6cr | A6cp | A6cm | A6m | A7sc | A7d | |||||||
| Prototheria | Monotremata | 3 | Ornithorhynchus anatinus | Platypus | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [12] | |
| Tachyglossus aculeatus | Short-beaked echidna | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [12] | ||||
| Metatheria | Ameridelphia | Didelphimorphia | 108 | Didelphis virginiana | Virginia opossum | - | ? | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [13] |
| Paucituberculata | 7 | No data | |||||||||||||
| Australidelphia | Microbiotheria | 1 | No data | ||||||||||||
| Dasyuromorphia | 75 | Sarcophilus harrisii | Tasmanian devil | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [14] | ||
| Notoryctemorphia | 2 | No data | |||||||||||||
| Peramelemorphia | 24 | No data | |||||||||||||
| Diprotodontia | 137 | No data | |||||||||||||
| Eutheria | Xenarthra | Cingulata | 22 | No data | |||||||||||
| Pilosa | 9 | No data | |||||||||||||
| Afrotheria | Tublidentata | 1 | No data | ||||||||||||
| Macroscelidea | 20 | Elephantulus myurus | Eastern rock elephant shrew | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [15] | ||
| Petrodromus tetradactylus | Four-toed sengi | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [16] | ||||
| Afrosoricida | 30 | Potomogale velox | Giant otter shrew | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [16] | ||
| Echinops telfairi | Lesser hedgehog tenrec | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | P.O. | ||||
| Amblysomus hottentotus | Hottentot golden mole | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [16] | ||||
| Chrysochloris asiatica | Cape golden mole | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | P.O. | ||||
| Hyracoidea | 7 | Procavia capensis | Rock hyrax | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [17] | ||
| Proboscidea | 3 | Loxodonta africana | African bush elephant | - | P | P | - | - | - | P | P | P | [18] | ||
| Sirenia | 4 | No data | |||||||||||||
| Laurasiatheria | Eulipotyphla | 399 | Paraechinus aethiopicus | Desert hedgehog | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [19] | |
| Atelerix frontalis | Southern African hedgehog | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [19] | ||||
| Erinaceus europeaus | European hedgehog | ? | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [20] | ||||
| Crocidura olivieri | African giant shrew | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [19] | ||||
| Crocidura cyanea | Reddish-grey musk shrew | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [19] | ||||
| Sylvisorex ollula | Greater forest shrew | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [19] | ||||
| Microchiroptera | 1200+ | Miniopterus schreibersii | Schreiber’s long-fingered bat | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [21] | ||
| Chaerophon pumilis | Little free-tailed bat | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [22] | ||||
| Hipposideros commersoni | Commerson’s leaf-nosed bat | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [22] | ||||
| Cardioderma cor | Heart-nosed bat | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [22] | ||||
| Coleura afra | African sheath-tailed bat | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [22] | ||||
| Triaenops persicus | Persian trident bat | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [22] | ||||
| Megachiroptera | 190+ | Rousettus aegyptiacus | Egyptian rousette | P | P | P | - | - | P | - | P | P | [23] | ||
| Eidolon helvum | Straw-coloured fruit bat | P | P | P | - | - | P | - | P | P | [24] | ||||
| Epomophorus wahlbergi | Wahlberg’s epauletted fruit bat | P | P | P | - | - | P | - | P | P | [24] | ||||
| Philodota | 7 | Manis tricuspis | Tree pangolin | - | P | - | - | - | - | - | P | P | [25] | ||
| Carnivora | 270 | Canis familiaris | Domestic dog | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [26] | ||
| Lycaon pictus | African wild dog | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | P.O. | ||||
| Mustela putorius | Domestic ferret | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [27] | ||||
| Felis cattus | Domestic cat | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [28] | ||||
| Acinonyx jubatus | Cheetah | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | P.O. | ||||
| Mungos mungo | Banded mongoose | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [27] | ||||
| Perissodactyla | 16 | Equus africanus asinus | Domestic donkey | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | P.O. | ||
| Equus caballus | Domestic horse | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | P.O. | ||||
| Equus zebra zebra | Cape mountain zebra | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | P.O. | ||||
| Equus quagga | Plains zebra | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | P.O. | ||||
| Tapirus indicus | Malayan tapir | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | P.O. | ||||
| Cetartiodactyla | 220 | Giraffa camelopardalis | Giraffe | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [29] | ||
| Connochaetes taurinus | Blue wildbeest | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [30] | ||||
| Oryx leucoryx | Arabian oryx | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [31] | ||||
| Ovis aries | Domestic sheep | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [32] | ||||
| Tursiops truncatus | Bottlenose dolphin | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [33] | ||||
| Globicephala macrorhynchus | Short-finned pilot whale | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [34] | ||||
| Grampus griseus | Risso’s dolphin | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [34] | ||||
| Stenella coeruleoalba | Striped dolphin | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [34] | ||||
| Stenella frontalis | Atlantic spotted dolphin | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [34] | ||||
| Delphinus delphis | Common dolphin | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [34] | ||||
| Phocoena phocoena | Harbour porpoise | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [35] | ||||
| Balaenoptera acutorostrata | Minke whale | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [36] | ||||
| Hippopotamus amphibius | River hippopotamus | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [37] | ||||
| Lama pacos | Alpaca | - | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [38] | ||||
| Euarchontoglires | Rodentia | 2200+ | Rattus norvegicus | Laboratory rat | P | P | - | P | - | - | - | P | P | [2,39] | |
| Mus musculus | Laboratory mouse | P | P | - | P | - | - | - | P | P | [40,41] | ||||
| Mus minutoides | Pygmy mouse | P | P | - | P | - | - | - | P | P | [42] | ||||
| Tatera brantsii | Highveld gerbil | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [43] | ||||
| Tachyoryctes splendens | East African mole-rat | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | P.O. | ||||
| Pedetes capensis | Springhare | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [44] | ||||
| Anomalurus beecrofti | Beecroft’s scaly-tailed squirrel | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [44] | ||||
| Hystrix africaeaustralis | Crested porcupine | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [45] | ||||
| Thryonomys swinderianus | Greater cane rat | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [46] | ||||
| Cryptomys hottentotus | Highveld mole-rat | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [47,48] | ||||
| Bathyergus suillus | Cape dune mole-rat | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [48] | ||||
| Georhychus capensis | Cape mole-rat | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | P.O. | ||||
| Dasyprocta primnolopha | Black-rumped agouti | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | P.O. | ||||
| Lagomorpha | 87 | Oryctolagus cuniculus | Domestic rabbit | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [49] | ||
| Lepus capensis | Cape hare | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [50] | ||||
| Scandentia | 19 | Tupaia belangeri | Northern tree shrew | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [50] | ||
| Tupaia glis | Common tree shrew | P | P | P | - | - | - | - | P | P | [51] | ||||
| Dermoptera | 2 | No data | |||||||||||||
| Primates | 300+ | Galago demidoff | Prince Demidoff’s bushbaby | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | P | [52] | ||
| Perodicticus potto | Potto | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | P | [52] | ||||
| Lemur catta | Ring-tailed lemur | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | P | [52] | ||||
| Cebuella pygmaea | Pygmy marmoset | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | P | [53] | ||||
| Saimiri sciureus | Common squirrel monkey | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | P | [54,55] | ||||
| Macaca speciosa | Stump-tailed macaque | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | P | [56] | ||||
| Macaca mulatta | Rhesus macaque | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | P | [57] | ||||
| Hylobates lar | Lar gibbon | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | P | [58] | ||||
| Pan troglodytes | Chimpanzee | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | P | [58] | ||||
| Homo sapiens | Human | P | P | P | - | P | - | - | P | P | [59,60,61] | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manger, P.R.; Eschenko, O. The Mammalian Locus Coeruleus Complex—Consistencies and Variances in Nuclear Organization. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111486
Manger PR, Eschenko O. The Mammalian Locus Coeruleus Complex—Consistencies and Variances in Nuclear Organization. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(11):1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111486
Chicago/Turabian StyleManger, Paul R., and Oxana Eschenko. 2021. "The Mammalian Locus Coeruleus Complex—Consistencies and Variances in Nuclear Organization" Brain Sciences 11, no. 11: 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111486
APA StyleManger, P. R., & Eschenko, O. (2021). The Mammalian Locus Coeruleus Complex—Consistencies and Variances in Nuclear Organization. Brain Sciences, 11(11), 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111486






