Short Vestibular and Cognitive Training Improves Oral Reading Fluency in Children with Dyslexia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
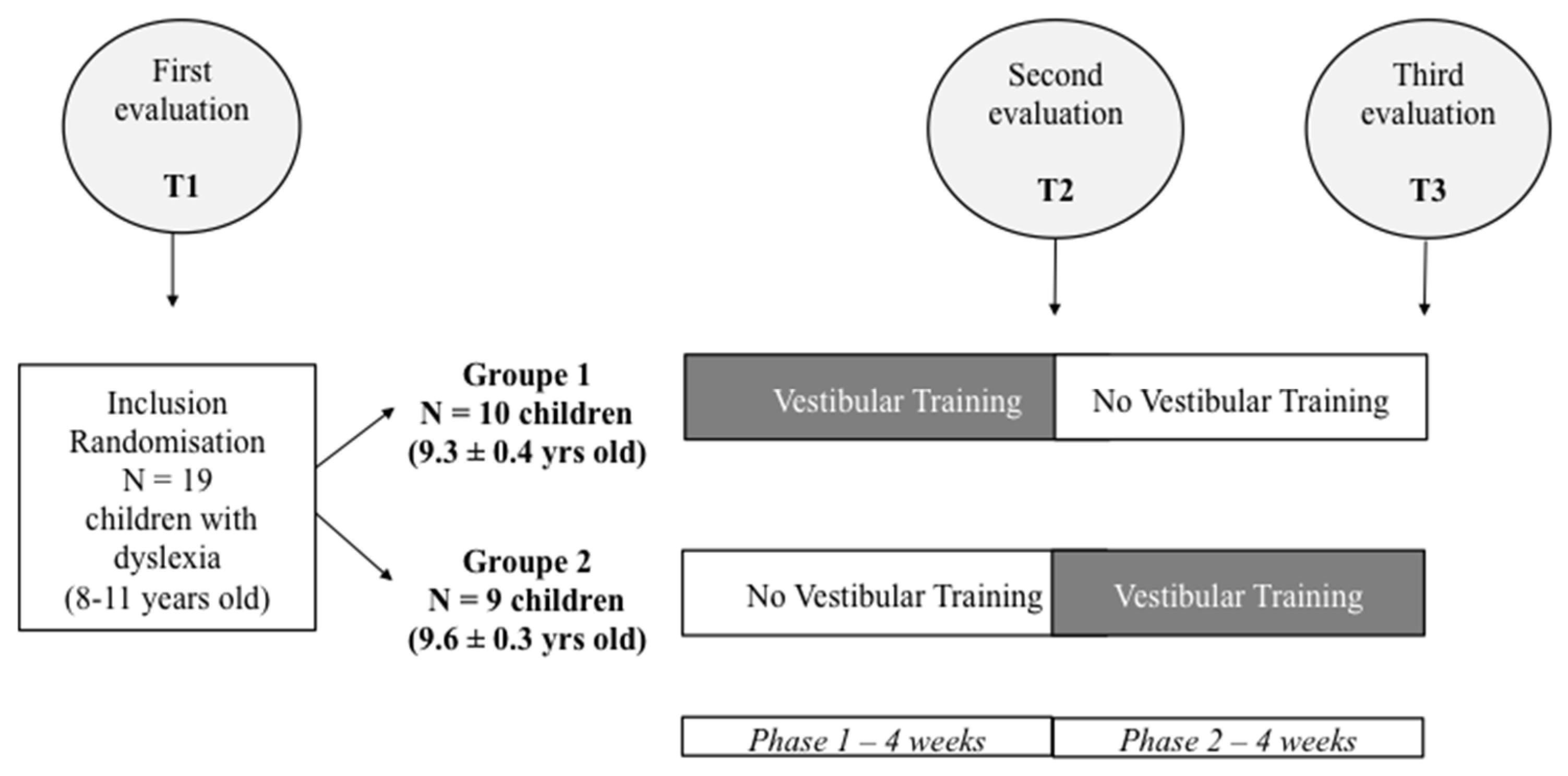
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Reading Task
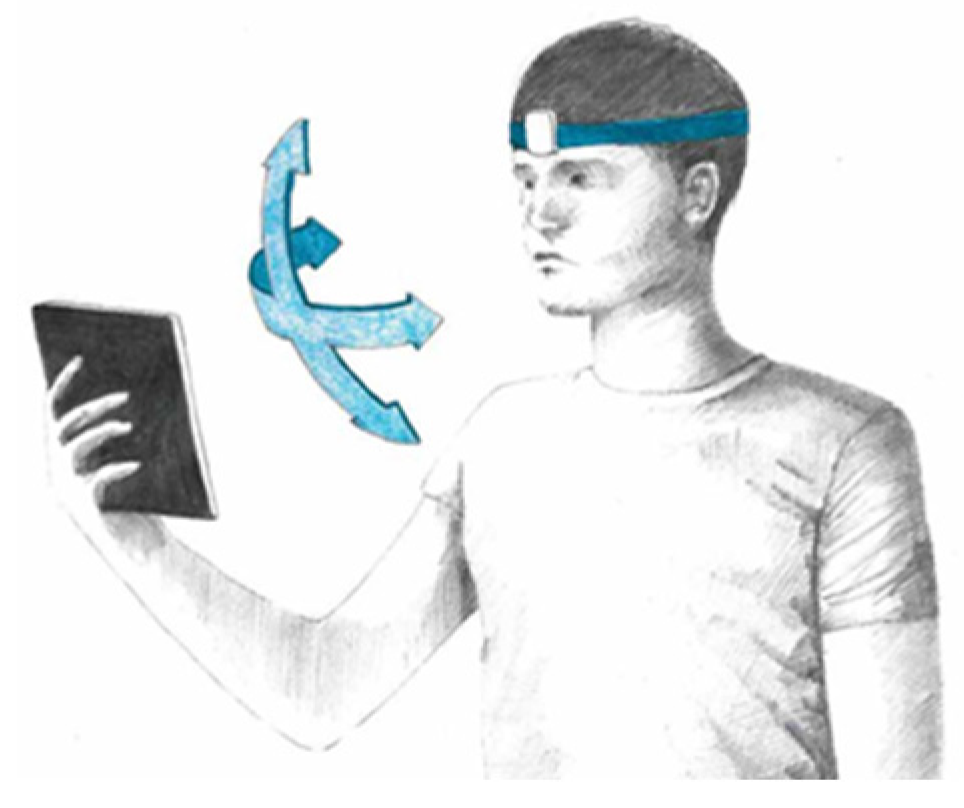
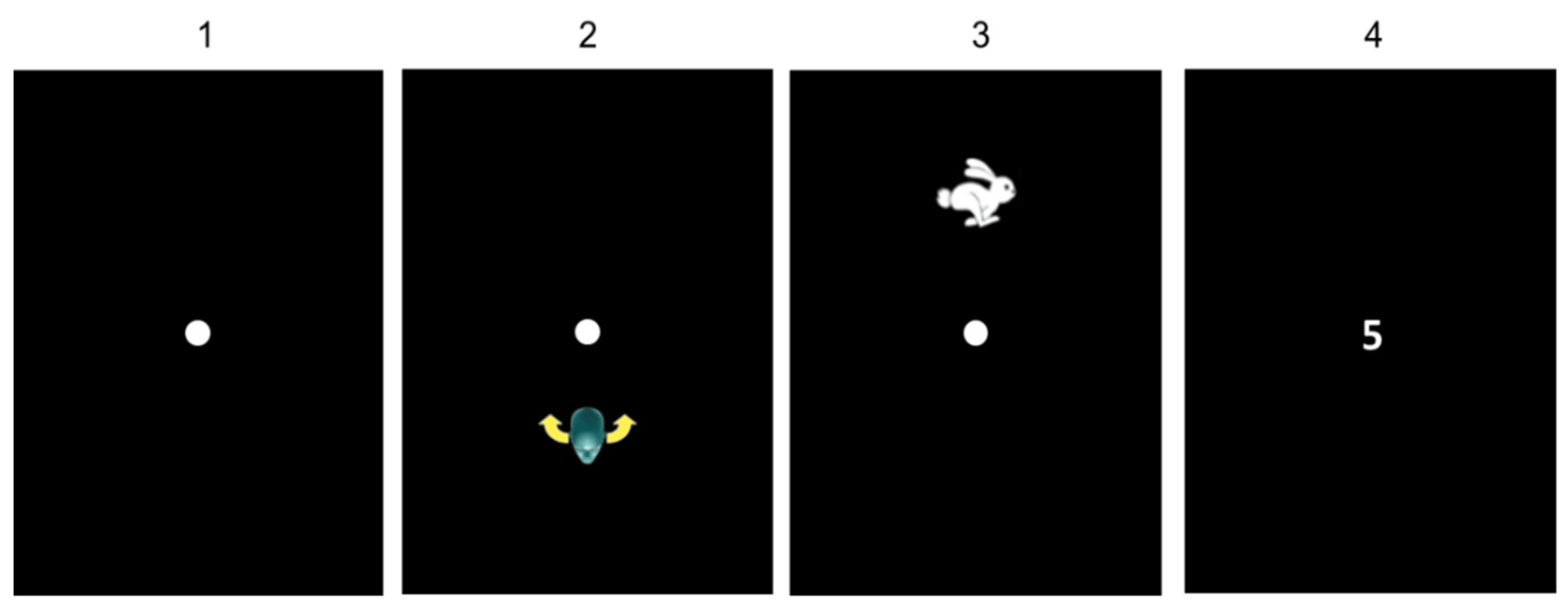
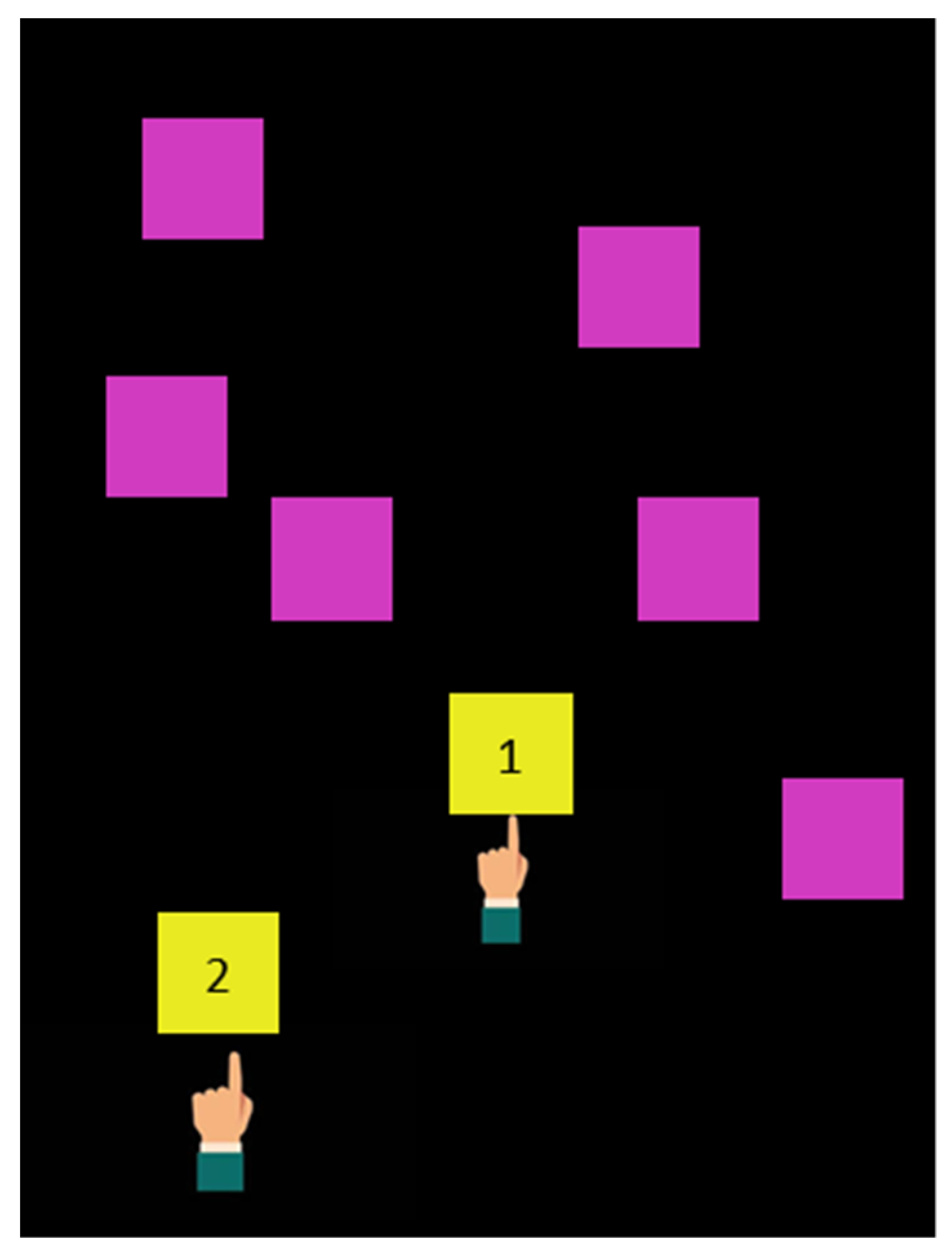
2.4. Vestibular and Cognitive Training Procedure
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
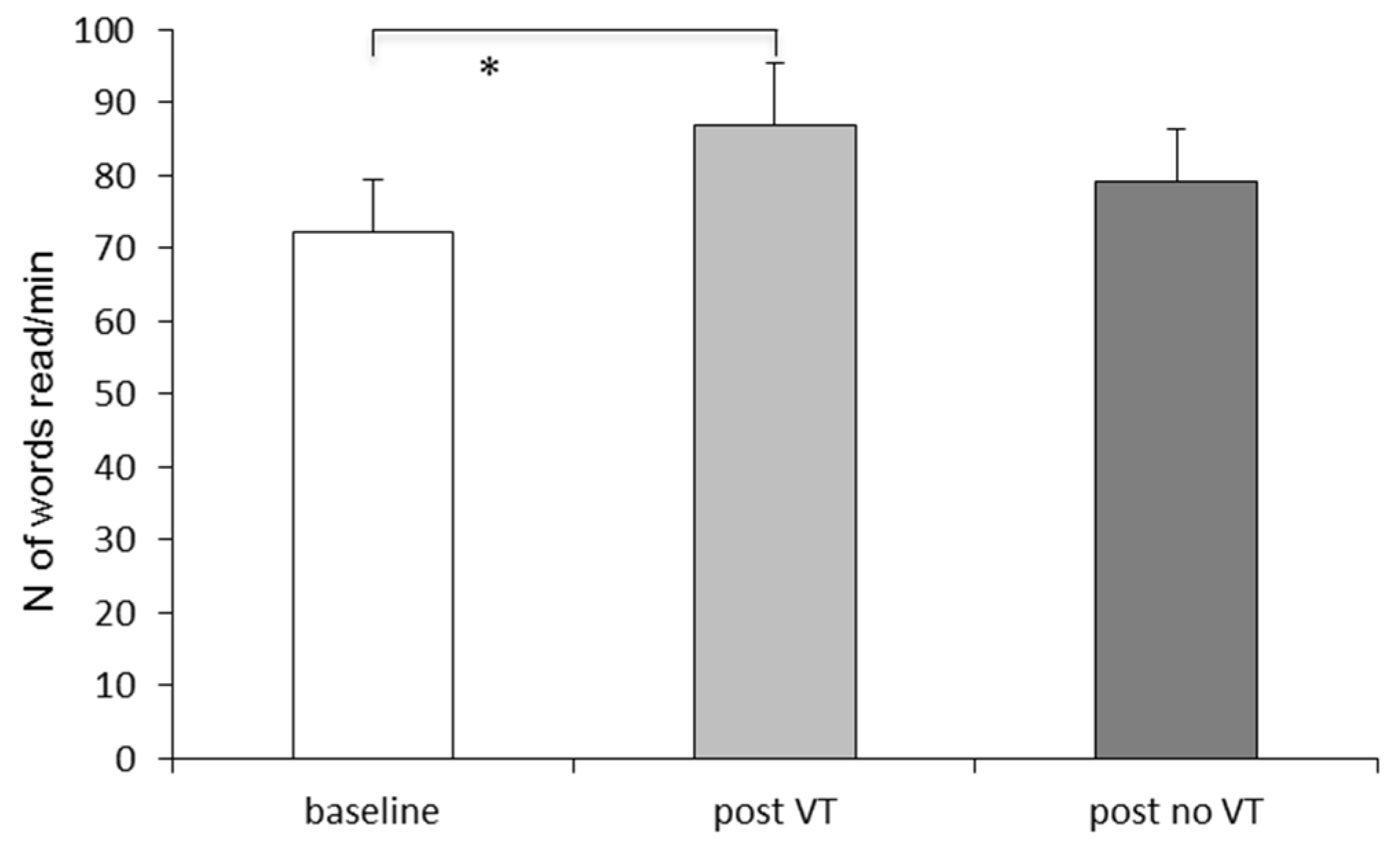
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peterson, R.L.; Pennington, B.F. Developmental dyslexia. Lancet 2012, 379, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, J. What is Developmental Dyslexia? Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Snowling, M.J. Dyslexia, 2nd ed.; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, J.; Levinson, H. Dysmetric dyslexia and dyspraxia: Hypothesis and Study. J. Am. Acad. Child Psychiatry 1973, 12, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, R.I.; Fawcett, A.J. Automaticity: Anew framework for dyslexia research? Cognition 1990, 35, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonnemann, J.; Linkersdörfer, J.; Heselhaus, V.; Hasselhorn, M.; Lindberg, S. Relations between balancing and arithmetic skills in children—Evidence of cerebellar involvement? J. Neurolinguist. 2011, 24, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, M.P.; Bui-Quoc, E.; Gerard, C.-L. The Effect of a Stroop-like Task on Postural Control in Dyslexic Children. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulème, N.; Gerard, C.-L.; Bucci, M.P. The Effect of Training on Postural Control in Dyslexic Children. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe-Nilssen, R.; Helbostad, J.L.; Talcott, J.B.; Toennessen, F.E. Balance and gait in children with dyslexia. Exp. Brain Res. 2003, 150, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoodley, C.J.; Fawcett, A.J.; Nicolson, R.I.; Stein, J.F. Impaired balancing ability in dyslexic children. Exp. Brain Res. 2005, 167, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poblano, A.; Ishiwara, K.; de Lourdes Arias, M.; Garcia-Pedroza, F.; Marin, H.; Trujillo, M. Motor control altera-tion in posturography in learning disabled children. Arch. Med. Res. 2002, 33, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochelle, K.S.H.; Talcott, J.B. Impaired balance in developmental dyslexia? A meta-analysis of the contending evidence. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2006, 47, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facoetti, A.; Lorusso, M.L.; Paganoni, P.; Cattaneo, C.; Galli, R.; Mascetti, G.G. The time course of attentional focusing in dyslexic and normally reading children. Brain Cogn. 2003, 53, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, M.P.; Nassibi, N.; Gerard, C.L.; Bui-Quoc, E.; Seassau, M. Immaturity of the oculomotor saccade and ver-gence interaction in dyslexic children: Evidence from a reading and visual search study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33458. [Google Scholar]
- Seassau, M.; Gérard, C.L.; Bui-Quoc, E.; Bucci, M.P. Binocular saccade coordination in reading and visual search: A developmental study in typical reader and dyslexic children. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiadi, A.; Seassau, M.; Gerard, C.-L.; Bucci, M.P. Differences between Dyslexic and Non-Dyslexic Children in the Performance of Phonological Visual-Auditory Recognition Tasks: An Eye-Tracking Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.L.; De Losa, L.; Bavin, E.L.; Crewther, S.G. Efficacy of dynamic visuo-attentional interventions for reading in dyslexic and neurotypical children: A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 100, 58–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, M.P. Visual training could be useful for improving reading capabilities in dyslexia? Appl. Neuropsychol. Child 2019, 10, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Lin, O.; Wang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Song, Y. Reading Performance Is Enhanced by Visual Texture Discrimination Training in Chinese-Speaking Children with Developmental Dyslexia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldani, S.; Gerard, C.-L.; Peyre, H.; Bucci, M.P. Visual Attentional Training Improves Reading Capabilities in Children with Dyslexia: An Eye Tracker Study During a Reading Task. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solan, H.A.; Larson, S.; Shelley-Tremblay, J.; Ficarra, A.; Silverman, M. Role of Visual Attention in Cognitive Control of Oculomotor Readiness in Students with Reading Disabilities. J. Learn. Disabil. 2001, 34, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solan, H.A.; Shelley-Tremblay, J.; Ficarra, A.; Silverman, M.; Larson, S. Effect of Attention Therapy on Reading Comprehension. J. Learn. Disabil. 2003, 36, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stappen, C.V.; Dricot, L.; Van Reybroeck, M. RAN training in dyslexia: Behavioral and brain correlates. Neuropsychologia 2020, 146, 107566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nation, K.; Adams, J.W.; Bowyer-Crane, C.A.; Snowling, M.J. Working Memory Deficits in Poor Comprehenders Reflect Underlying Language Impairments. J. Exp. Child Psychol. 1999, 73, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Peng, J.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, L.; Mo, L. Specific effects of working memory training on the reading skills of Chinese children with developmental dyslexia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bigelow, R.T.; Agrawal, Y. Vestibular involvement in cognition: Visuospatial ability, attention, executive function, and memory. J. Vestib. Res. 2015, 25, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.F. The vestibular system and cognition. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2017, 30, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldani, S.; Baghdadi, M.; Moscoso, A.; Acquaviva, E.; Gerard, C.-L.; Marcelli, V.; Peyre, H.; Atzori, P.; Delorme, R.; Bucci, M.P. Vestibular Functioning in Children with Neurodevelopmental Disorders Using the Functional Head Impulse Test. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, R.; Colafêmina, J.F. The influence of eye movement and the vestibularocular reflex in reading and writing. Rev. CEFAC 2014, 16, 1791–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solan, H.A.; Shelley-Tremblay, J.; Larson, S. Vestibular Function, Sensory Integration, and Balance Anomalies: A Brief Literature Review. Optom. Vision Dev. 2007, 38, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Sugaya, N.; Arai, M.; Goto, F. Changes in cognitive function in patients with intractable dizziness following vestibular rehabilitation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, A.W.; Schöne, C.G.; Vibert, D.; Caversaccio, M.D.; Mast, F.W. Cognitive Rehabilitation in Bilateral Vestibular Patients: A Computational Perspective. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacquier-Roux, M.; Lequette, C.; Pouget, G.; Valdois, S.; Zorman, M. BALE: Batterie Analytique du Langage Ecrit; Laboratoire Cogni-Sciences: Grenoble, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Berninger, V.W.; Abbott, R.D.; Thomson, J.; Wagner, R.; Swanson, H.L.; Wijsman, E.M.; Raskind, W. Modeling Phonological Core Deficits within a Working Memory Architecture in Children and Adults with Developmental Dyslexia. Sci. Stud. Read. 2006, 10, 165–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J.; Fowler, M. Unstable binocular control in dyslexic children. J. Res. Read. 1993, 16, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eden, G.F.; Stein, J.F.; Wood, H.M.; Wood, F.B. Differences in eye movements and reading problems in dyslexic and non-dyslexic children. Vision Res. 1994, 34, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iles, J.; Walsh, V.; Richardson, A. Visual search performance in dyslexia. Dyslexia 2000, 6, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidyasagar, T.R.; Pammer, K. Dyslexia: A deficit in visuo-spatial attention, not in phonological processing. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2010, 14, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gathercole, S.E.; Baddeley, A.D. Working Memory and Language; Psychology Press: Hove, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Leigh, R.J.; Zee, D.S. The Neurology of Eye Movements; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, C.; Blanke, O. The thalamo cortical vestibular system in animals and humans. Brain Res. Rev. 2011, 67, 119–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehitier, M.; Ebesnard, S.; Smith, P.F. Vestibular pathways involved in cognition. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, P.; Wulff, M.; Finke, K.; Rühl, M.; Brandt, T.; Dieterich, M. Cognitive deficits in patients with a chronic vestibular failure. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbels, B.; Peetermans, O.; Boon, B.; Mertens, G.; Van de Heyning, P.; Van Rompaey, V. Impact of Bilateral Vestibulopathy on Spatial and Nonspatial Cognition: A Systematic Review. Ear Hear. 2018, 40, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pammer, K.; Hansen, P.; Holliday, I.; Cornelissen, P. Attentional shifting and the role of the dorsal pathway in visual word recognition. Neuropsychologia 2006, 44, 2926–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdois, S.; Bosse, M.-L. The cognitive deficits responsible for developmental dyslexia: Review of evidence for a selective visual attentional disorder. Dyslexia 2004, 10, 339–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosse, M.-L.; Tainturier, M.-J.; Valdois, S. Developmental dyslexia: The visual attention span deficit hypothesis. Cognition 2007, 104, 198–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| T1 | T2 | T3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| G1 | 54 ± 10 | 69 ± 11 * | 69 ± 11 * |
| G2 | 92 ± 4 | 89 ± 6 # | 107 ± 8 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caldani, S.; Moiroud, L.; Miquel, C.; Peiffer, V.; Florian, A.; Bucci, M.P. Short Vestibular and Cognitive Training Improves Oral Reading Fluency in Children with Dyslexia. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111440
Caldani S, Moiroud L, Miquel C, Peiffer V, Florian A, Bucci MP. Short Vestibular and Cognitive Training Improves Oral Reading Fluency in Children with Dyslexia. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(11):1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111440
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaldani, Simona, Lionel Moiroud, Carole Miquel, Vanessa Peiffer, Alessandro Florian, and Maria Pia Bucci. 2021. "Short Vestibular and Cognitive Training Improves Oral Reading Fluency in Children with Dyslexia" Brain Sciences 11, no. 11: 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111440
APA StyleCaldani, S., Moiroud, L., Miquel, C., Peiffer, V., Florian, A., & Bucci, M. P. (2021). Short Vestibular and Cognitive Training Improves Oral Reading Fluency in Children with Dyslexia. Brain Sciences, 11(11), 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111440






