Influence of Topiramate on the Synaptic Endings of the Temporal Lobe Neocortex in an Experimental Model of Hyperthermia-Induced Seizures: An Ultrastructural Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Model of Febrile Seizures
2.3. Preparation for Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.4. Measurement of Neuronal Synapses and Quantitative Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
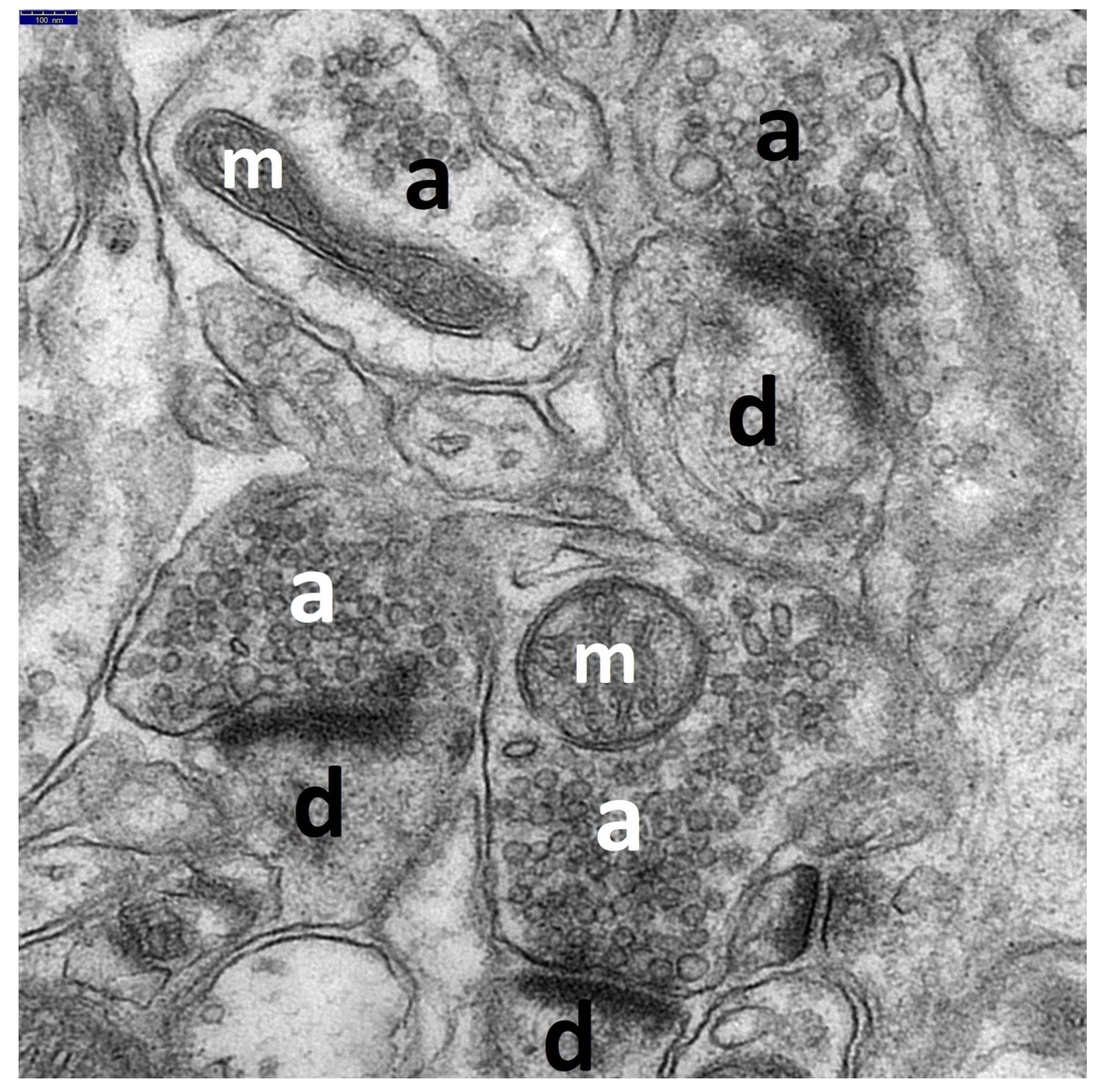
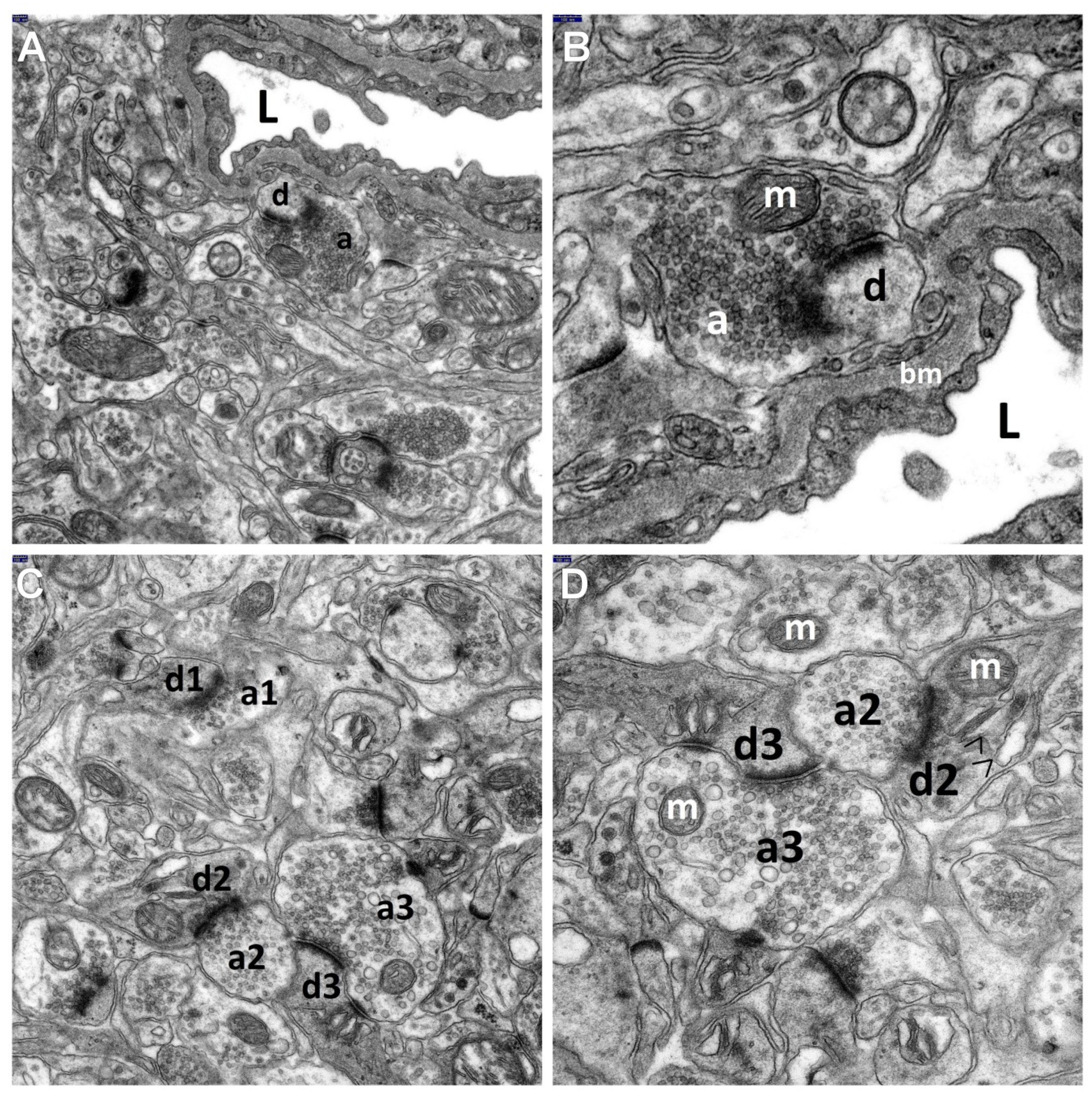
3.1. Decriptive Ultrastructural Study
3.1.1. HS Group
3.1.2. HS + TPM Group (the Antiepileptic Administered Immediately after the Induction of Febrile Seizures)
3.1.3. TPM + HS Group (the Antiepileptic Administered Prior to Febrile Seizures)
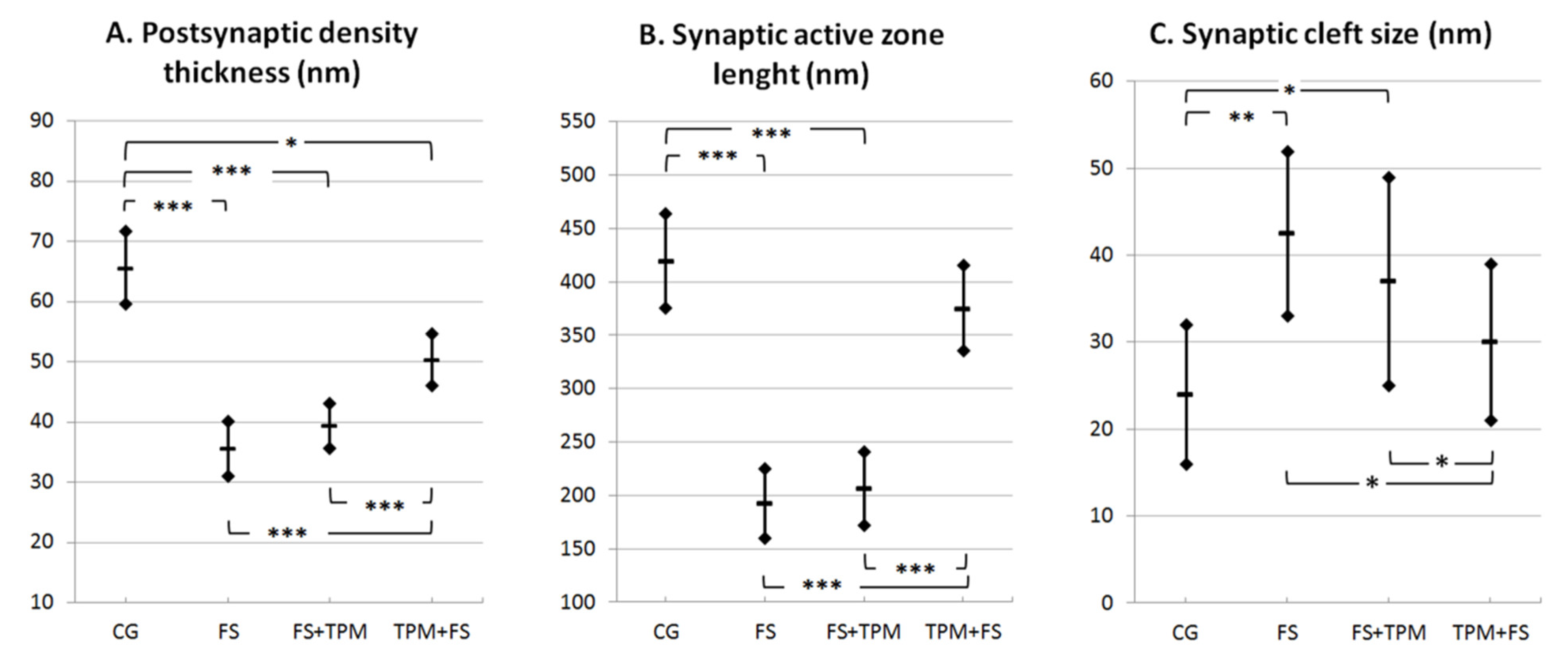
3.2. Morphometric Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Scott, R.C. Consequences of febrile seizures in childhood. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2014, 26, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.K.; Hon, K.L.; Leung, T.N. Febrile seizures: An overview. Drugs Context 2018, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, K.P.; Baram, T.Z.; Shinnar, S. Origins of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: Febrile Seizures and Febrile Status Epilepticus. Neurotherapeutics 2014, 11, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shinnar, S.; Glauser, T.A. Febrile seizures. J. Child Neurol. 2002, 17 (Suppl. S1), S44–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, F.U. Febrile seizures: Treatment and prognosis. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafstrom, C.E. The incidence and prevalence of febrile seizures. In Febrile Seizures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- De Nijs, L.; Choe, K.; Steinbusch, H.; Schijns, O.; Dings, J.; van den Hove, D.L.A.; Rutten, B.P.F.; Hoogland, G. DNA methyltransferase isoforms expression in the temporal lobe of epilepsy patients with a history of febrile seizures. Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millichap, J.J.; Millichap, J. Clinical Features and Evaluation of Febrile Seizures; UpToDate, Inc.: Waltham, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, B.; Chen, Z. Generation of Febrile Seizures and Subsequent Epileptogenesis. Neurosci. Bull. 2016, 32, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swijsen, A.; Brone, B.; Rigo, J.M.; Hoogland, G. Long-lasting enhancement of GABA(A) receptor expression in newborn dentate granule cells after early-life febrile seizures. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 1516–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendrowski, K.; Sobaniec, W. Hippocampus, hippocampal sclerosis and epilepsy. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassi, L.; Meroni, A.; Deleo, F.; Villani, F.; Mai, R.; Russo, G.L.; Colombo, N.; Avanzini, G.; Falcone, C.; Bramerio, M.; et al. Temporal lobe epilepsy: Neuropathological and clinical correlations in 243 surgically treated patients. Epileptic. Disord. 2009, 11, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sendrowski, K.; Sobaniec, W.; Sobaniec-Lotowska, M.E.; Artemowicz, B. Topiramate as a neuroprotectant in the experimental model of febrile seizures. Adv. Med. Sci. 2007, 52 (Suppl. S1), 161–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bresnahan, R.; Hounsome, J.; Jette, N.; Hutton, J.L.; Marson, A.G. Topiramate add-on therapy for drug-resistant focal epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, CD001417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Quan, Q.Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.C.; Zhao, G.; Jiang, W. Effects of lamotrigine and topiramate on hippocampal neurogenesis in experimental temporal-lobe epilepsy. Brain Res. 2010, 1313, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyazi, A.; Khajeh, A.; Baghbani, A. Comparison of Effectiveness of Topiramate and Diazepam in Preventing Risk of Recurrent Febrile Seizure in Children under Age of 2 Years. Iran. J. Child Neurol. 2018, 12, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Labate, A.; Siniscalchi, A.; Mumoli, L.; Aguglia, U.; Quattrone, A.; Gambardella, A. Topiramate and temporal lobe epilepsy: An open-label study. Epileptic Disord. 2012, 14, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.N.; Wang, Y.P. Topiramate for juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 1, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manitpisitkul, P.; Shalayda, K.; Todd, M.; Wang, S.S.; Ness, S.; Ford, L. Pharmacokinetics and safety of adjunctive topiramate in infants (1–24 months) with refractory partial-onset seizures: A randomized, multicenter, open-label phase 1 study. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepien, K.; Tomaszewski, M.; Czuczwar, S.J. Profile of anticonvulsant activity and neuroprotective effects of novel and potential antiepileptic drugs—An update. Pharmacol. Rep. 2005, 57, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, M.G.; Yao, D.; Huang, X.X.; Zhang, T.; Deng, X.Q. Comparison of impact on seizure frequency and epileptiform discharges of children with epilepsy from topiramate and phenobarbital. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 993–997. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Artemowicz, B.; Sobaniec, W. Neuroprotection possibilities in epileptic children. Rocz. Akad. Med. Bialymst. 2005, 50 (Suppl. S1), 91–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Ueshima, S.; Ouchida, M.; Mashimo, T.; Nishiki, T.; Sendo, T.; Serikawa, T.; Matsui, H.; Ohmori, I. Therapy for hyperthermia-induced seizures in Scn1a mutant rats. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, M.; Yu, X.; Ye, X.; Wang, X.; Shan, P. The Efficacy and Safety of Topiramate in the Prevention of Pediatric Migraine: An Update Meta-Analysis. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreou, A.P.; Goadsby, P.J. Topiramate in the treatment of migraine: A kainate (glutamate) receptor antagonist within the trigeminothalamic pathway. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 1343–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manhapra, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Arias, A.J. Topiramate Pharmacotherapy for Alcohol Use Disorder and Other Addictions: A Narrative Review. J. Addict. Med. 2019, 13, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, J.W., 3rd; Sombati, S.; DeLorenzo, R.J.; Coulter, D.A. Cellular actions of topiramate: Blockade of kainate-evoked inward currents in cultured hippocampal neurons. Epilepsia 2000, 41 (Suppl. S1), 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lason, W.; Dudra-Jastrzebska, M.; Rejdak, K.; Czuczwar, S.J. Basic mechanisms of antiepileptic drugs and their pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic interactions: An update. Pharmacol. Rep. 2011, 63, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motaghinejad, M.; Motevalian, M. Involvement of AMPA/kainate and GABAA receptors in topiramate neuroprotective effects against methylphenidate abuse sequels involving oxidative stress and inflammation in rat isolated hippocampus. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 784, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motaghinejad, M.; Motevalian, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Heidari, M.; Madjd, Z. Topiramate Confers Neuroprotection Against Methylphenidate-Induced Neurodegeneration in Dentate Gyrus and CA1 Regions of Hippocampus via CREB/BDNF Pathway in Rats. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 31, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motaghinejad, M.; Motevalian, M.; Falak, R.; Heidari, M.; Sharzad, M.; Kalantari, E. Neuroprotective effects of various doses of topiramate against methylphenidate-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in isolated rat amygdala: The possible role of CREB/BDNF signaling pathway. J. Neural. Transm. 2016, 123, 1463–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, C.F.; Simeone, T.A.; Maar, T.E.; Smith-Swintosky, V.; White, H.S.; Schousboe, A. Modulation by topiramate of AMPA and kainate mediated calcium influx in cultured cerebral cortical, hippocampal and cerebellar neurons. Neurochem. Res. 2004, 29, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Teng, J.; Zhang, Y. The protective action of topiramate on dopaminergic neurons. Med. Sci. Monit. 2010, 16, 307–312. [Google Scholar]
- Lotowska, J.; Sobaniec, P.; Sobaniec-Lotowska, M.; Szukiel, B.; Lukasik, M.; Lotowska, S. Effects of topiramate on the ultrastructure of synaptic endings in the hippocampal CA1 and CA3 sectors in the rat experimental model of febrile seizures: The first electron microscopy report. Folia Neuropathol. 2019, 57, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotowska, J.M.; Sobaniec-Lotowska, M.E.; Sendrowski, K.; Sobaniec, W.; Artemowicz, B. Ultrastructure of the blood-brain barrier of the gyrus hippocampal cortex in an experimental model of febrile seizures and with the use of a new generation antiepileptic drug—Topiramate. Folia Neuropathol. 2008, 46, 57–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lotowska, J.M.; Sobaniec-Lotowska, M.E.; Sobaniec, W. Ultrastructural features of astrocytes in the cortex of the hippocampal gyrus and in the neocortex of the temporal lobe in an experimental model of febrile seizures and with the use of topiramate. Folia Neuropathol. 2009, 47, 268–277. [Google Scholar]
- Sobaniec-Lotowska, M.E.; Lotowska, J.M. The neuroprotective effect of topiramate on the ultrastructure of pyramidal neurons of the hippocampal CA1 and CA3 sectors in an experimental model of febrile seizures in rats. Folia Neuropathol. 2011, 49, 230–236. [Google Scholar]
- Sendrowski, K.; Sobaniec, W.; Sobaniec-Łotowska, M.; Artemowicz, B. The neuroprotective effects of topiramate in the experimental model of febrile seizures in rats. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillery, R.W. Early electron microscopic observations of synaptic structures in the cerebral cortex: A view of the contributions made by George Gray (1924–1999). Trends Neurosci. 2000, 23, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.L.; Han, T.Z.; Yang, D.W.; Chen, M.X. Morphological alteration of the hippocampal synapses in rats prenatally exposed to magnetic resonance imaging magnetic fields. Sheng Li Xue Bao 2003, 55, 705–710. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y.; Fu, R. Repeated febrile convulsions impair hippocampal neurons and cause synaptic damage in immature rats: Neuroprotective effect of fructose-1,6-diphosphate. Neural. Regen. Res. 2014, 9, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.J.; Shi, Z.S.; Xia, L.X.; Zhu, L.H.; Zeng, L.; Nie, J.H.; Xu, Z.C.; Ruan, Y.W. Changes in synaptic plasticity and expression of glutamate receptor subunits in the CA1 and CA3 areas of the hippocampus after transient global ischemia. Neuroscience 2016, 327, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semple, B.D.; Blomgren, K.; Gimlin, K.; Ferriero, D.M.; Noble-Haeusslein, L.J. Brain development in rodents and humans: Identifying benchmarks of maturation and vulnerability to injury across species. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 106, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsujimoto, S. The prefrontal cortex: Functional neural development during early childhood. Neuroscientist 2008, 14, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, D.K.; Nagelhus, E.A.; Ottersen, O.P. Aquaporin-4 and epilepsy. Glia 2012, 60, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, M.M.; Kitchen, P.; Iliff, J.J.; Bill, R.M. Aquaporin 4 and glymphatic flow have central roles in brain fluid homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 22, 650–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, M.M.; Kitchen, P.; Halsey, A.; Wang, M.X.; Tornroth-Horsefield, S.; Conner, A.C.; Badaut, J.; Iliff, J.J.; Bill, R.M. Emerging Roles for Dynamic Aquaporin-4 Subcellular Relocalization in Cns Water Homeostasis. Brain 2021, awab311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchen, P.; Salman, M.M.; Halsey, A.M.; Clarke-Bland, C.; MacDonald, J.A.; Ishida, H.; Vogel, H.J.; Almutiri, S.; Logan, A.; Kreida, S.; et al. Targeting Aquaporin-4 Subcellular Localization to Treat Central Nervous System Edema. Cell 2020, 181, 784–799.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, U.; Wiemann, M. Topiramate Decelerates Bicarbonate-Driven Acid-Elimination of Human Neocortical Neurons: Strategic Significance for its Antiepileptic, Antimigraine and Neuroprotective Properties. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 19, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtal, K.; Borowicz, K.K.; Blaszczyk, B.; Czuczwar, S.J. Interactions of excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists with antiepileptic drugs in three basic models of experimental epilepsy. Pharmacol. Rep. 2006, 58, 587–598. [Google Scholar]
- Armijo, J.A.; Shushtarian, M.; Valdizan, E.M.; Cuadrado, A.; de las Cuevas, I.; Adin, J. Ion channels and epilepsy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 1975–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sendrowski, K.; Rusak, M.; Sobaniec, P.; Ilendo, E.; Dabrowska, M.; Bockowski, L.; Koput, A.; Sobaniec, W. Study of the protective effect of calcium channel blockers against neuronal damage induced by glutamate in cultured hippocampal neurons. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurses, C.; Orhan, N.; Ahishali, B.; Yilmaz, C.U.; Kemikler, G.; Elmas, I.; Cevik, A.; Kucuk, M.; Arican, N.; Kaya, M. Topiramate reduces blood-brain barrier disruption and inhibits seizure activity in hyperthermia-induced seizures in rats with cortical dysplasia. Brain Res. 2013, 1494, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niebauer, M.; Gruenthal, M. Topiramate reduces neuronal injury after experimental status epilepticus. Brain Res. 1999, 837, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sobaniec, P.; Lotowska, J.M.; Sobaniec-Lotowska, M.E.; Zochowska-Sobaniec, M. Influence of Topiramate on the Synaptic Endings of the Temporal Lobe Neocortex in an Experimental Model of Hyperthermia-Induced Seizures: An Ultrastructural Study. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111433
Sobaniec P, Lotowska JM, Sobaniec-Lotowska ME, Zochowska-Sobaniec M. Influence of Topiramate on the Synaptic Endings of the Temporal Lobe Neocortex in an Experimental Model of Hyperthermia-Induced Seizures: An Ultrastructural Study. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(11):1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111433
Chicago/Turabian StyleSobaniec, Piotr, Joanna Maria Lotowska, Maria Elzbieta Sobaniec-Lotowska, and Milena Zochowska-Sobaniec. 2021. "Influence of Topiramate on the Synaptic Endings of the Temporal Lobe Neocortex in an Experimental Model of Hyperthermia-Induced Seizures: An Ultrastructural Study" Brain Sciences 11, no. 11: 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111433
APA StyleSobaniec, P., Lotowska, J. M., Sobaniec-Lotowska, M. E., & Zochowska-Sobaniec, M. (2021). Influence of Topiramate on the Synaptic Endings of the Temporal Lobe Neocortex in an Experimental Model of Hyperthermia-Induced Seizures: An Ultrastructural Study. Brain Sciences, 11(11), 1433. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111433





