Is Instructional Scaffolding a Better Strategy for Teaching Writing to EFL Learners? A Functional MRI Study in Healthy Young Adults
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Developing EFL Writing through Scaffolding Instruction
1.2. Relationship between Brain Activation and Language Processing
1.3. Relationship between Brain Activation and Writing Activities
1.4. Study Aims
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design
2.2. Participants
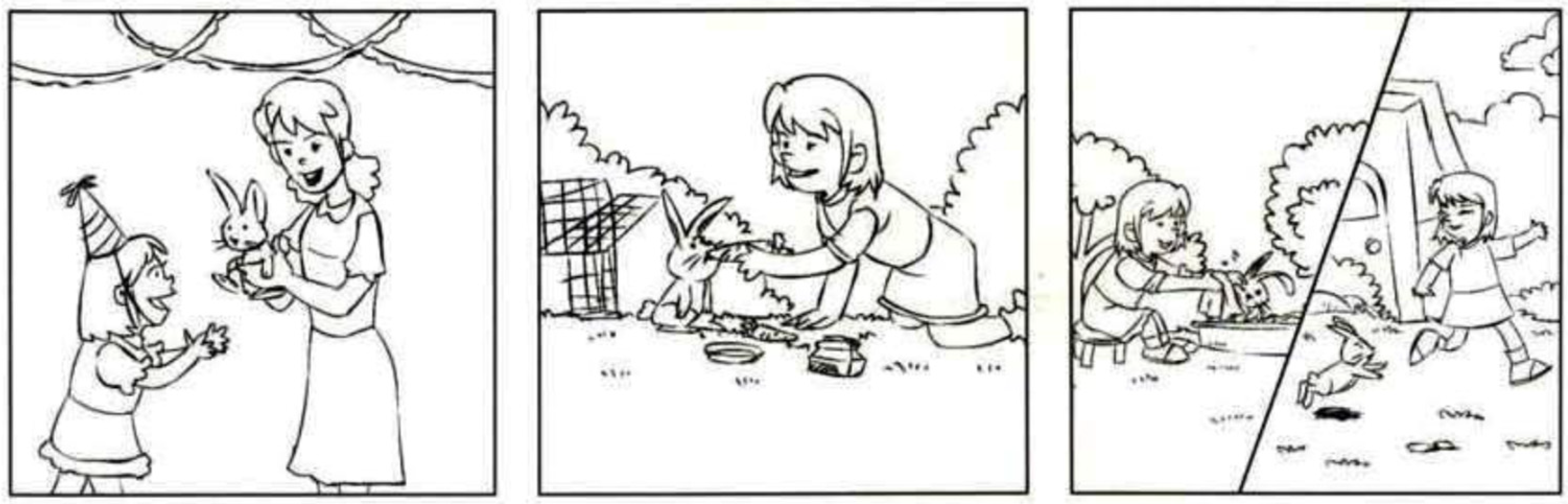
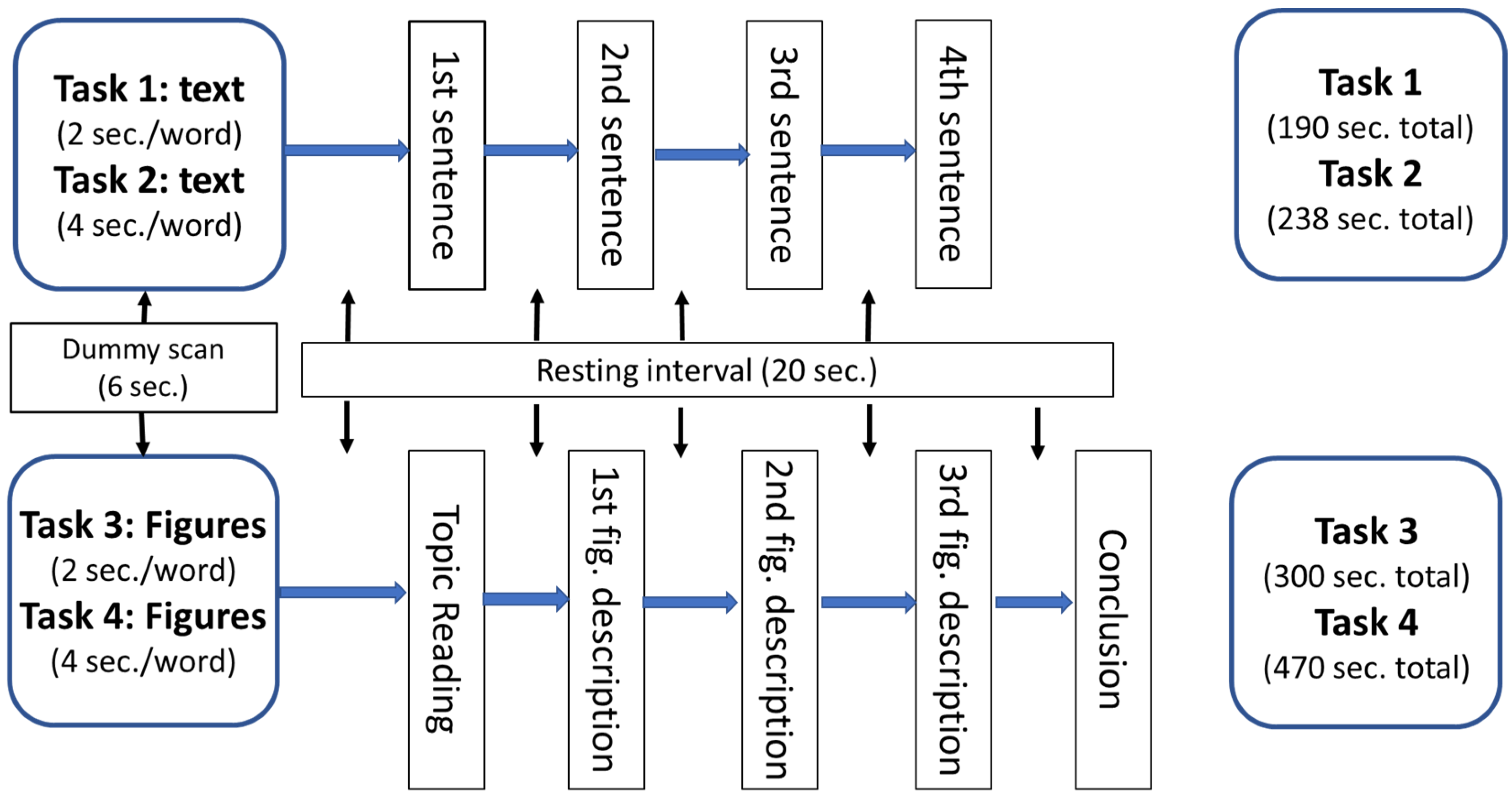
2.3. Writing Tasks
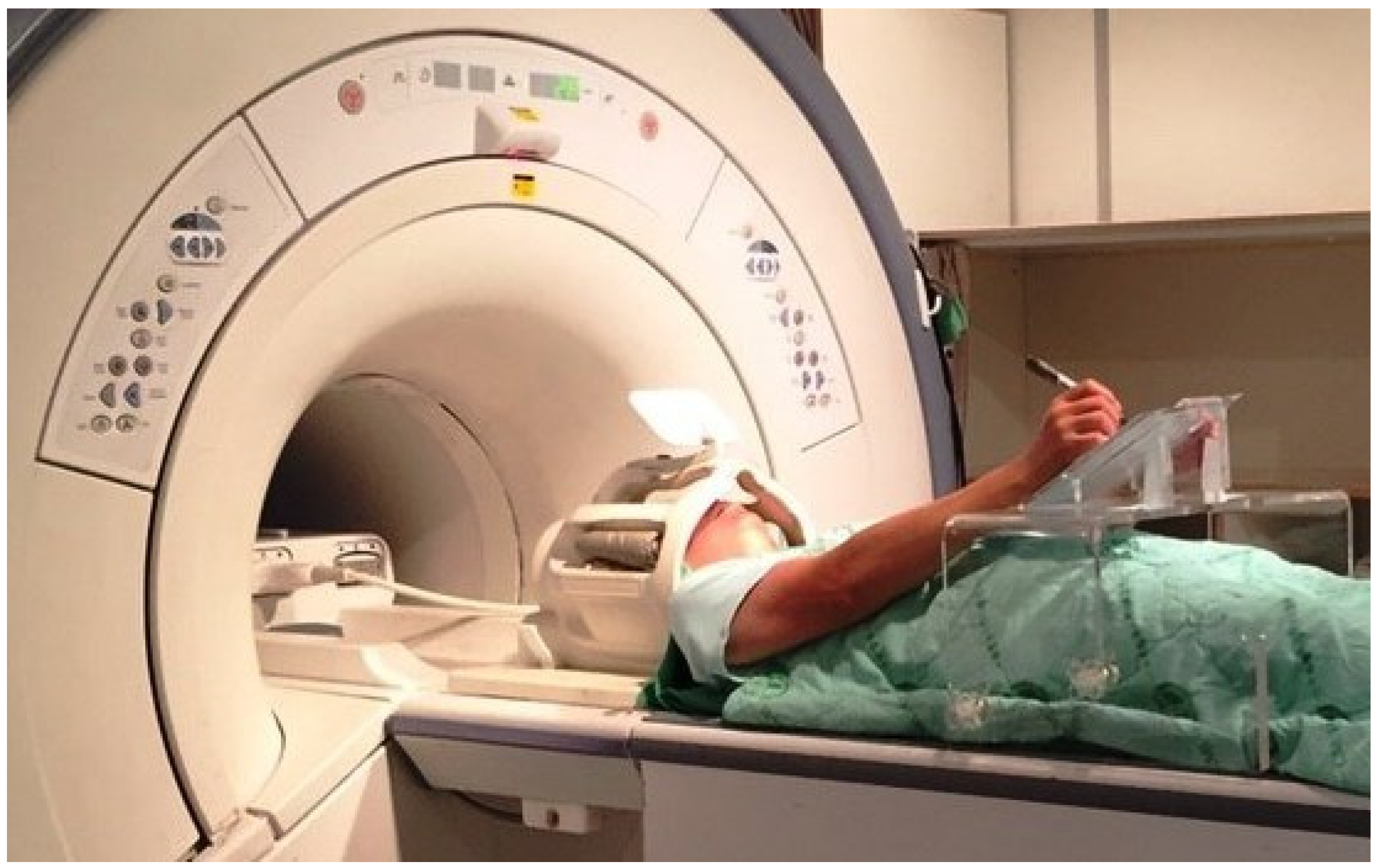
2.4. Data Collection
2.4.1. Procedures
2.4.2. Instruments
- Instrument 1: Writing outcomes
- Instrument 2: fMRI images
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Writing Outcomes
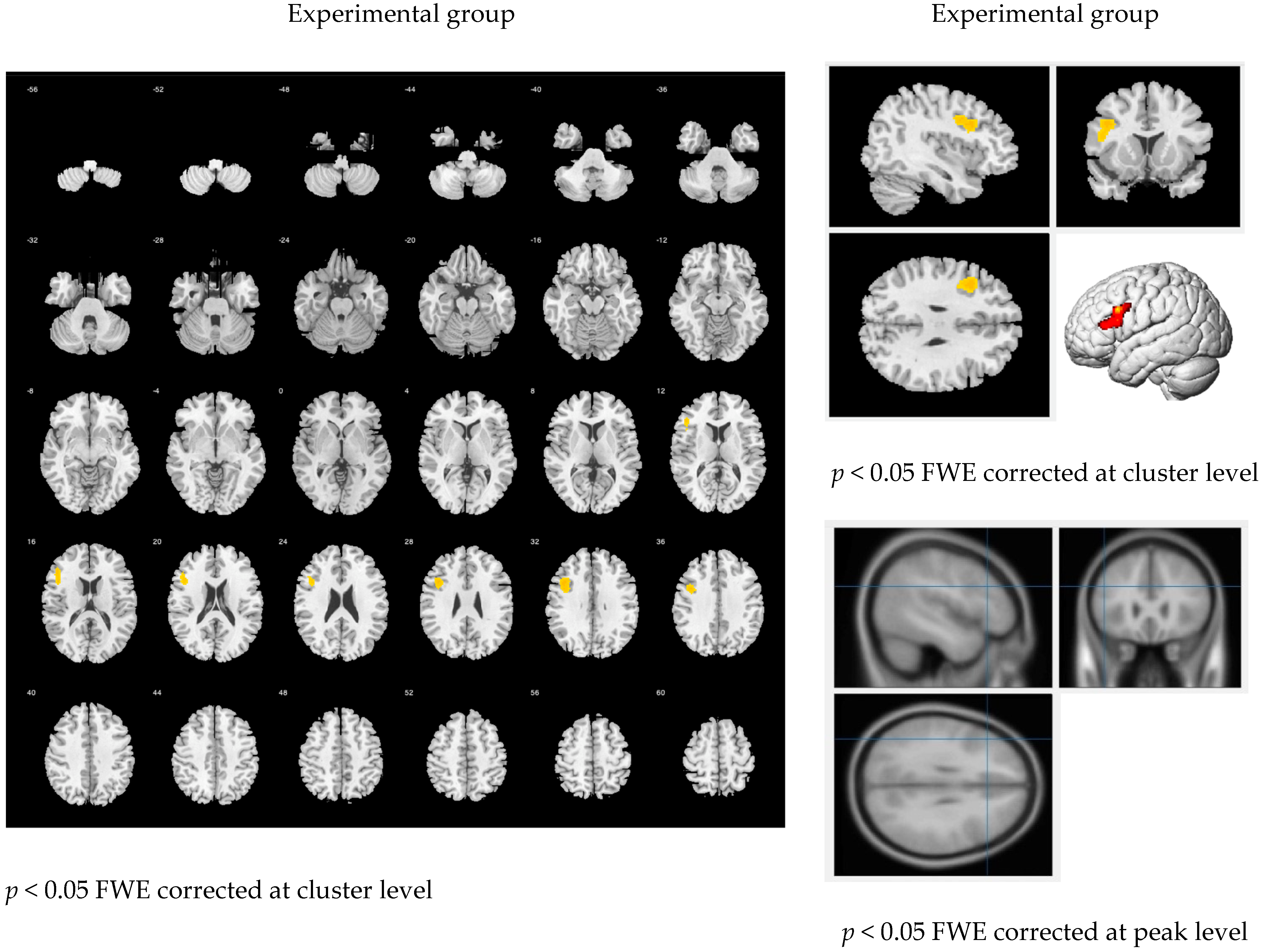
3.2. Brain Images
3.2.1. The Main Effect of the Handwriting Tasks
3.2.2. The Language Effects among Different Tasks
3.2.3. Learning Effects through Scaffolding Instruction
4. Discussion
4.1. Writing Outcomes
4.2. Brain Images
4.3. Implications and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Writing Task Samples

Appendix B. Additional Facilities


Appendix C. Further MANOVA Test
| Dependent Variables | df/ df Error | F | Group | Means | 99.9% Confidence Interval | Cohen’s d | Effect Size r | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| Task 1 | Readability | 1 | 0.01 | Experiment | 4.02 | 3.36 | 4.69 | 0.08 | 0.04 |
| 50 | Comparison | 4.05 | 3.37 | 4.73 | |||||
| Speed | 1 | 0.04 | Experiment | 4.03 | 3.19 | 4.74 | 0.07 | 0.03 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 3.97 | 3.25 | 4.83 | |||||
| Holistic | 1 | 0.09 | Experiment | 4.10 | 3.43 | 4.64 | 0.21 | 0.10 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 4.17 | 3.61 | 4.85 | |||||
| Task 2 | Readability | 1 | 1.64 | Experiment | 3.93 | 3.29 | 4.57 | 0.37 | 0.18 |
| 50 | Comparison | 3.58 | 2.93 | 4.23 | |||||
| Speed | 1 | 1.63 | Experiment | 4.03 | 3.42 | 4.65 | 0.38 | 0.19 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 3.70 | 3.07 | 4.32 | |||||
| Content | 1 | 20.20 ** | Experiment | 3.73 | 3.21 | 4.35 | 1.37 | 0.57 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.67 | 2.03 | 3.20 | |||||
| Structure | 1 | 13.94 ** | Experiment | 3.67 | 3.15 | 4.25 | 1.14 | 0.50 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.81 | 2.21 | 3.33 | |||||
| Grammar | 1 | 3.29 | Experiment | 2.96 | 2.40 | 3.60 | 0.61 | 0.29 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.51 | 1.85 | 3.07 | |||||
| Vocabulary | 1 | 10.40 | Experiment | 3.20 | 2.63 | 3.90 | 1.02 | 0.45 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.37 | 1.67 | 2.95 | |||||
| Punctuation | 1 | 0.44 | Experiment | 3.54 | 2.93 | 4.26 | 0.28 | 0.14 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 3.36 | 2.63 | 3.99 | |||||
| Holistic | 1 | 4.49 | Experiment | 3.48 | 2.95 | 4.09 | 0.70 | 0.33 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.97 | 2.35 | 3.51 | |||||
| Task 3 | Readability | 1 | 1.53 | Experiment | 3.97 | 3.24 | 4.62 | 0.27 | 0.14 |
| 50 | Comparison | 3.61 | 2.95 | 4.36 | |||||
| Speed | 1 | 22.71 ** | Experiment | 4.06 | 3.41 | 4.67 | 1.31 | 0.55 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.78 | 2.16 | 3.45 | |||||
| Content | 1 | 20.43 ** | Experiment | 3.92 | 3.28 | 4.58 | 1.33 | 0.55 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.67 | 1.99 | 3.32 | |||||
| Structure | 1 | 20.61 ** | Experiment | 4.07 | 3.41 | 4.74 | 1.31 | 0.55 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.78 | 2.09 | 3.45 | |||||
| Grammar | 1 | 26.06 ** | Experiment | 4.20 | 3.53 | 4.84 | 1.42 | 0.58 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.79 | 2.14 | 3.47 | |||||
| Vocabulary | 1 | 42.83 ** | Experiment | 4.17 | 3.55 | 4.74 | 1.83 | 0.67 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.52 | 1.93 | 3.14 | |||||
| Punctuation | 1 | 8.52 | Experiment | 4.22 | 3.65 | 4.80 | 0.85 | 0.39 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 3.51 | 2.92 | 4.09 | |||||
| Holistic | 1 | 23.94 ** | Experiment | 4.13 | 3.54 | 4.68 | 1.36 | 0.56 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.94 | 2.37 | 3.54 | |||||
| Task 4 | Readability | 1 | 3.70 | Experiment | 3.68 | 3.11 | 4.22 | 0.53 | 0.26 |
| 50 | Comparison | 3.22 | 2.67 | 3.80 | |||||
| Speed | 1 | 10.05 | Experiment | 3.89 | 3.37 | 4.48 | 0.98 | 0.44 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 3.16 | 2.55 | 3.68 | |||||
| Content | 1 | 17.75 ** | Experiment | 3.45 | 2.88 | 4.08 | 1.27 | 0.54 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.38 | 1.74 | 2.96 | |||||
| Structure | 1 | 11.46 | Experiment | 3.36 | 2.81 | 4.01 | 1.06 | 0.47 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.51 | 1.85 | 3.08 | |||||
| Grammar | 1 | 2.25 | Experiment | 2.83 | 2.33 | 3.45 | 0.57 | 0.27 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.49 | 1.86 | 2.99 | |||||
| Vocabulary | 1 | 8.35 | Experiment | 3.15 | 2.57 | 3.88 | 0.94 | 0.43 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.39 | 1.64 | 2.97 | |||||
| Punctuation | 1 | 1.69 | Experiment | 3.42 | 2.81 | 4.15 | 0.48 | 0.23 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 3.06 | 2.32 | 3.68 | |||||
| Holistic | 1 | 5.83 | Experiment | 3.33 | 2.79 | 3.95 | 0.78 | 0.36 | |
| 50 | Comparison | 2.74 | 2.11 | 3.29 | |||||
References
- Benko, S.L. Scaffolding: An ongoing process to support adolescent writing development. J. Adolesc. Adult Lit. 2012, 56, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwieter, J.W. Developing second language writing through scaffolding in the ZPD: A magazine project for an authentic audience. J. Coll. Teach. Learn. 2010, 7, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karimpoor, M.; Churchill, N.W.; Tam, F.; Fischer, C.E.; Schweizer, T.A.; Graham, S.J. Functional MRI of handwriting tasks: A study of healthy young adults interacting with a novel touch-sensitive tablet. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseini, S.H.; Bruno, J.L.; Baker, J.M.; Gundran, A.; Harbott, L.K.; Gerdes, J.C.; Reiss, A.L. Neural, physiological, and behavioral correlates of visuomotor cognitive load. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H. New insights into the process of peer review for EFL writing: A process-oriented socio-cultural perspective. Learn. Instr. 2018, 58, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paas, F.; Ayres, P. Cognitive load theory: A broader view on the role of memory in learning and education. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2014, 26, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourssi, A. Theoretical and practical linguistic shifting from product/guided writing to process writing and recently to the innovated writing process approach in teaching writing for second/foreign language learners. Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2013, 3, 731. [Google Scholar]
- Sweller, J. Cognitive load theory, learning difficulty, and instructional design. Learn. Instr. 1994, 4, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyuga, S.; Singh, A.-M. Rethinking the boundaries of cognitive load theory in complex learning. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2016, 28, 831–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vygotsky, L. Zone of proximal development. Mind Soc. Dev. High. Psychol. Process. 1987, 5291, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Cabell, S.Q.; Tortorelli, L.S.; Gerde, H.K. How do I write…? Scaffolding preschoolers’ early writing skills. Read. Teach. 2013, 66, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyland, K. Genre pedagogy: Language, literacy and L2 writing instruction. J. Second Lang. Writ. 2007, 16, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodd, J.M.; Vitello, S.; Woollams, A.M.; Adank, P. Localising semantic and syntactic processing in spoken and written language comprehension: An Activation Likelihood Estimation meta-analysis. Brain Lang. 2015, 141, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, E. The Oscillatory Nature of Language; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Quiñones, I.; Molinaro, N.; Mancini, S.; Hernández-Cabrera, J.A.; Carreiras, M. Where agreement merges with disagreement: fMRI evidence of subject–verb integration. NeuroImage 2014, 88, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, J.; Meltzer-Asscher, A.; Barbieri, E.; Thompson, C. Neural correlates of processing passive sentences. Brain Sci. 2013, 3, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, S.M.; DeMarco, A.T.; Henry, M.L.; Gesierich, B.; Babiak, M.; Mandelli, M.L.; Miller, B.L.; Gorno-Tempini, M.L. What role does the anterior temporal lobe play in sentence-level processing? Neural correlates of syntactic processing in semantic variant primary progressive aphasia. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2014, 26, 970–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shetreet, E.; Friedmann, N. The processing of different syntactic structures: fMRI investigation of the linguistic distinction between wh-movement and verb movement. J. Neurolinguist. 2014, 27, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, B.; Obleser, J.; Kalberlah, C.; Haynes, J.-D.; Friederici, A.D. Dissociable neural imprints of perception and grammar in auditory functional imaging. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2012, 33, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flick, G.; Pylkkänen, L. Isolating syntax in natural language: MEG evidence for an early contribution of left posterior temporal cortex. Cortex 2020, 127, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obleser, J.; Kotz, S.A. Expectancy constraints in degraded speech modulate the language comprehension network. Cereb. Cortex 2010, 20, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, I.; Blumstein, S.E.; Myers, E.B.; Hutchison, E. Recruitment of anterior and posterior structures in lexical–semantic processing: An fMRI study comparing implicit and explicit tasks. Brain Lang. 2008, 105, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snijders, T.M.; Vosse, T.; Kempen, G.; Van Berkum, J.J.A.; Petersson, K.M.; Hagoort, P. Retrieval and unification of syntactic structure in sentence comprehension: An fMRI study using word-category ambiguity. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 19, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kambara, T.; Tsukiura, T.; Yokoyama, S.; Takahashi, K.; Shigemune, Y.; Miyamoto, T.; Takahashi, D.; Sato, S.; Kawashima, R. Differential contributions of the inferior parietal and inferior frontal regions to the processing of grammatical and semantic relationships in wh-questions. Lang. Sci. 2013, 37, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, J.A.; McArdle, J.J.; Schafer, R.J.; Braun, A.R. Neural aspects of sentence comprehension: Syntactic complexity, reversibility, and reanalysis. Cereb. Cortex 2010, 20, 1853–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, L.; Obleser, J.; Anwander, A.; Friederici, A.D. Linking ordering in Broca’s area to storage in left temporo-parietal regions: The case of sentence processing. NeuroImage 2012, 62, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friederici, A.D.; Kotz, S.A.; Scott, S.K.; Obleser, J. Disentangling syntax and intelligibility in auditory language comprehension. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2010, 31, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Newman, S.D. The effect of presentation paradigm on syntactic processing: An event-related fMRI study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2010, 31, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segaert, K.; Menenti, L.; Weber, K.; Petersson, K.M.; Hagoort, P. Shared syntax in language production and language comprehension—an fMRI study. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 22, 1662–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planton, S.; Jucla, M.; Roux, F.-E.; Démonet, J.-F. The “handwriting brain”: A meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies of motor versus orthographic processes. Cortex 2013, 49, 2772–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, C.; Erhard, K.; Ortheil, H.-J.; Kaza, E.; Kessler, C.; Lotze, M. Neural correlates of creative writing: An fMRI Study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2013, 34, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.R. GEPT and English language teaching and testing in Taiwan. Lang. Assess. Q. 2012, 9, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H. Explanation of the Grading Standard for English Writing Ability in the 2020 College Entrance Examination; College Entrance Examination Center: Taipei, Taiwan, 2020; Volume 312. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- SPSS. IBM SPSS Statistics Version 21; International Business Machines Corp: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Friston, K.J.; Ashburner, J.T.; Kiebel, S.; Nichols, T.E.; Penny, W.D. Statistical Parametric Mapping: The Analysis of Functional Brain Images; Elsevier/Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardo, M.V.; Auyeung, B.; Holt, R.J.; Waldman, J.; Ruigrok, A.N.V.; Mooney, N.; Bullmore, E.T.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Kundu, P. Improving effect size estimation and statistical power with multi-echo fMRI and its impact on understanding the neural systems supporting mentalizing. NeuroImage 2016, 142, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.-G. Statistical power analyses using G* Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawagoe, T.; Onoda, K.; Yamaguchi, S. The neural correlates of “mind blanking”: When the mind goes away. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 4934–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffstaedter, F.; Grefkes, C.; Caspers, S.; Roski, C.; Palomero-Gallagher, N.; Laird, A.R.; Fox, P.T.; Eickhoff, S.B. The role of anterior midcingulate cortex in cognitive motor control: Evidence from functional connectivity analyses. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 2741–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hervais-Adelman, A.; Egorova, N.; Golestani, N. Beyond bilingualism: Multilingual experience correlates with caudate volume. Brain Struct. Funct. 2018, 223, 3495–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Task | Criterion 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Transcribe in Chinese | readability | speed | - | - | - | - | - | holistic |
| 2 | Translate in English | readability | speed | content | structure | grammar | vocabulary | punctuation | holistic |
| 3 | Draft in Chinese | readability | speed | content | structure | grammar | vocabulary | punctuation | holistic |
| 4 | Draft in English | readability | speed | content | structure | grammar | vocabulary | punctuation | holistic |
| Dependent Variables | df/ df Error | F | Group | Means | 99.9% Confidence Interval | Cohen’s d | Effect Size r | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| Task 1 | Readability | 1 | 0.08 | Experiment | 4.00 | 3.35 | 4.65 | 0.08 | 0.04 |
| 51 | Comparison | 4.08 | 3.41 | 4.74 | |||||
| Speed | 1 | 0.06 | Experiment | 3.96 | 3.19 | 4.74 | 0.07 | 0.03 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 4.04 | 3.25 | 4.83 | |||||
| Holistic | 1 | 0.61 | Experiment | 4.04 | 3.43 | 4.64 | 0.21 | 0.10 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 4.23 | 3.61 | 4.85 | |||||
| Task 2 | Readability | 1 | 1.78 | Experiment | 3.93 | 3.29 | 4.57 | 0.37 | 0.18 |
| 51 | Comparison | 3.58 | 2.93 | 4.23 | |||||
| Speed | 1 | 1.89 | Experiment | 4.04 | 3.42 | 4.65 | 0.38 | 0.19 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 3.69 | 3.07 | 4.32 | |||||
| Content | 1 | 24.79 ** | Experiment | 3.78 | 3.21 | 4.35 | 1.37 | 0.57 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.62 | 2.03 | 3.20 | |||||
| Structure | 1 | 17.23 ** | Experiment | 3.70 | 3.15 | 4.25 | 1.14 | 0.50 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.77 | 2.21 | 3.33 | |||||
| Grammar | 1 | 4.84 | Experiment | 3.00 | 2.40 | 3.60 | 0.61 | 0.29 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.46 | 1.85 | 3.07 | |||||
| Vocabulary | 1 | 13.68 | Experiment | 3.26 | 2.63 | 3.90 | 1.02 | 0.45 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.31 | 1.67 | 2.95 | |||||
| Punctuation | 1 | 1.10 | Experiment | 3.59 | 2.93 | 4.26 | 0.28 | 0.14 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 3.31 | 2.63 | 3.99 | |||||
| Holistic | 1 | 6.38 | Experiment | 3.52 | 2.95 | 4.09 | 0.70 | 0.33 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.93 | 2.35 | 3.51 | |||||
| Task 3 | Readability | 1 | 0.93 | Experiment | 3.93 | 3.24 | 4.62 | 0.27 | 0.14 |
| 51 | Comparison | 3.65 | 2.95 | 4.36 | |||||
| Speed | 1 | 22.69 ** | Experiment | 4.04 | 3.41 | 4.67 | 1.31 | 0.55 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.81 | 2.16 | 3.45 | |||||
| Content | 1 | 22.90 ** | Experiment | 3.93 | 3.28 | 4.58 | 1.33 | 0.55 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.65 | 1.99 | 3.32 | |||||
| Structure | 1 | 22.79 ** | Experiment | 4.07 | 3.41 | 4.74 | 1.31 | 0.55 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.77 | 2.09 | 3.45 | |||||
| Grammar | 1 | 26.64 ** | Experiment | 4.19 | 3.53 | 4.84 | 1.42 | 0.58 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.81 | 2.14 | 3.47 | |||||
| Vocabulary | 1 | 43.90 ** | Experiment | 4.15 | 3.55 | 4.74 | 1.83 | 0.67 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.54 | 1.93 | 3.14 | |||||
| Punctuation | 1 | 9.48 | Experiment | 4.22 | 3.65 | 4.80 | .85 | 0.39 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 3.50 | 2.92 | 4.09 | |||||
| Holistic | 1 | 24.40 ** | Experiment | 4.11 | 3.54 | 4.68 | 1.36 | 0.56 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.96 | 2.37 | 3.54 | |||||
| Task 4 | Readability | 1 | 3.71 | Experiment | 3.67 | 3.11 | 4.22 | 0.53 | 0.26 |
| 51 | Comparison | 3.23 | 2.67 | 3.80 | |||||
| Speed | 1 | 12.86 | Experiment | 3.93 | 3.37 | 4.48 | 0.98 | 0.44 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 3.12 | 2.55 | 3.68 | |||||
| Content | 1 | 21.43 ** | Experiment | 3.48 | 2.88 | 4.08 | 1.27 | 0.54 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.35 | 1.74 | 2.96 | |||||
| Structure | 1 | 14.75 ** | Experiment | 3.41 | 2.81 | 4.01 | 1.06 | 0.47 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.46 | 1.85 | 3.08 | |||||
| Grammar | 1 | 4.19 | Experiment | 2.89 | 2.33 | 3.45 | 0.57 | 0.27 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.42 | 1.86 | 2.99 | |||||
| Vocabulary | 1 | 11.72 | Experiment | 3.22 | 2.57 | 3.88 | 0.94 | 0.43 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.31 | 1.64 | 2.97 | |||||
| Punctuation | 1 | 3.09 | Experiment | 3.48 | 2.81 | 4.15 | 0.48 | 0.23 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 3.00 | 2.32 | 3.68 | |||||
| Holistic | 1 | 8.02 | Experiment | 3.37 | 2.79 | 3.95 | 0.78 | 0.36 | |
| 51 | Comparison | 2.70 | 2.11 | 3.29 | |||||
| Structure | Anatomy | Abbreviation | Hemisphere | x, y, z | T-Value | Cluster Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lateralized Regions | ||||||
| Precentral_L | Primary Motor Cortex | M1 | L | −40, −24, 58 | 14.16 | 2074 |
| Postcentral_L | Primary Somatosensory Cortex | S1 | L | −36, −36, 58 | 11.45 | 2465 |
| Supp_Motor_Area_L | Supplementary Motor Area | SMA | L | −8, −8, 64 | 10.01 | 1412 |
| SupraMarginal_L | Supramarginal Gyrus | SMG | L | −44, −30, 24 | 8.19 | 599 |
| Thal_VPL_L | Thalamus | THA | L | −16, −20, 8 | 8.28 | 158 |
| Angular_R | Angular Gyrus | ANG | R | 30, −58, 44 | 6.03 | 96 |
| Bilateral Regions | ||||||
| Frontal_Sup_R | Superior Frontal Gyrus | SFG | R | 26, −4, 54 | 7.68 | 495 |
| Frontal_Sup_L | L | −24, −8, 54 | 8.95 | 527 | ||
| Frontal_Inf_Oper_R | Inferior Frontal Gyrus | IFG | R | 54, 8, 26 | 7.51 | 366 |
| Frontal_Inf_Oper_L | (pars opercularis) | Broca’s area | L | −54, 6, 14 | 6.47 | 160 |
| Rolandic_Oper_R | Rolandic operculum | ROL | R | 40, 2, 14 | 5.88 | 148 |
| Rolandic_Oper_L | L | −44, −2, 14 | 7.97 | 616 | ||
| Insula_R | Insula | INS | R | 34, 20, 12 | 7.47 | 470 |
| Insula_L | L | −32, 18, 12 | 5.17 | 280 | ||
| Cingulate_Mid_R | Midcingulate Cortex | MCC | R | 10, 0, 34 | 5.5 | 249 |
| Cingulate_Mid_L | L | −10, 0, 36 | 5.55 | 363 | ||
| Parietal_Sup_R | Superior Parietal Gyrus | SPG | R | 24, −60, 54 | 8.2 | 685 |
| Parietal_Sup_L | L | −26, −60, 62 | 8.44 | 1103 | ||
| Parietal_Inf_R | Inferior Parietal Gyrus | IPG | R | 36, −44, 50 | 5.55 | 246 |
| Parietal_Inf_L | L | −38, −42, 44 | 6.28 | 994 | ||
| Temporal_Mid_R | Middle Temporal Gyrus | MTG | R | 50, −60, −2 | 6.98 | 285 |
| Temporal_Mid_L | L | −46, −66, 8 | 6.25 | 388 | ||
| Temporal_Inf_R | Inferior Temporal Gyrus | ITG | R | 50, −58, −12 | 9.95 | 422 |
| Temporal_Inf_L | L | −46, −54, −14 | 6.83 | 227 | ||
| Occipital_Mid_R | Middle Occipital Gyrus | MOG | R | 34, −72, 24 | 6.45 | 493 |
| Occipital_Mid_L | L | −44, −68, 0 | 7.84 | 524 | ||
| Occipital_Inf_R | Inferior Occipital Gyrus | IOG | R | 40, −72, −12 | 7.74 | 303 |
| Occipital_Inf_L | L | −44, −72, −16 | 6.44 | 581 | ||
| Fusiform_R | Fusiform Gyrus | FFG | R | 38, −56, −22 | 6.89 | 938 |
| Fusiform_L | (VWFA) | L | −42, −58, −18 | 5.86 | 230 | |
| Cerebellum | ||||||
| Vermis_6 | Cerebellum | (global maxima) | -- | 6, −62, −20 | 14.48 | 371 |
| Cerebellum_4_5_R | R | 16, −52, −22 | 12.26 | 732 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tai, H.-C.; Chen, C.-M.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Lee, B.-O.; Setiya Dewi, Y. Is Instructional Scaffolding a Better Strategy for Teaching Writing to EFL Learners? A Functional MRI Study in Healthy Young Adults. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111378
Tai H-C, Chen C-M, Tsai Y-H, Lee B-O, Setiya Dewi Y. Is Instructional Scaffolding a Better Strategy for Teaching Writing to EFL Learners? A Functional MRI Study in Healthy Young Adults. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(11):1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111378
Chicago/Turabian StyleTai, Hung-Cheng, Chun-Ming Chen, Yuan-Hsiung Tsai, Bih-O Lee, and Yulis Setiya Dewi. 2021. "Is Instructional Scaffolding a Better Strategy for Teaching Writing to EFL Learners? A Functional MRI Study in Healthy Young Adults" Brain Sciences 11, no. 11: 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111378
APA StyleTai, H.-C., Chen, C.-M., Tsai, Y.-H., Lee, B.-O., & Setiya Dewi, Y. (2021). Is Instructional Scaffolding a Better Strategy for Teaching Writing to EFL Learners? A Functional MRI Study in Healthy Young Adults. Brain Sciences, 11(11), 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111378






