Reduction in Epigenetic Age Acceleration Is Related to Empathy in Mothers with Neglectful Caregiving
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Psychological Measures
2.3. Procedure
2.4. DNAm Assay and Methylation Analyses
2.5. DNAm PhenoAge Clock
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
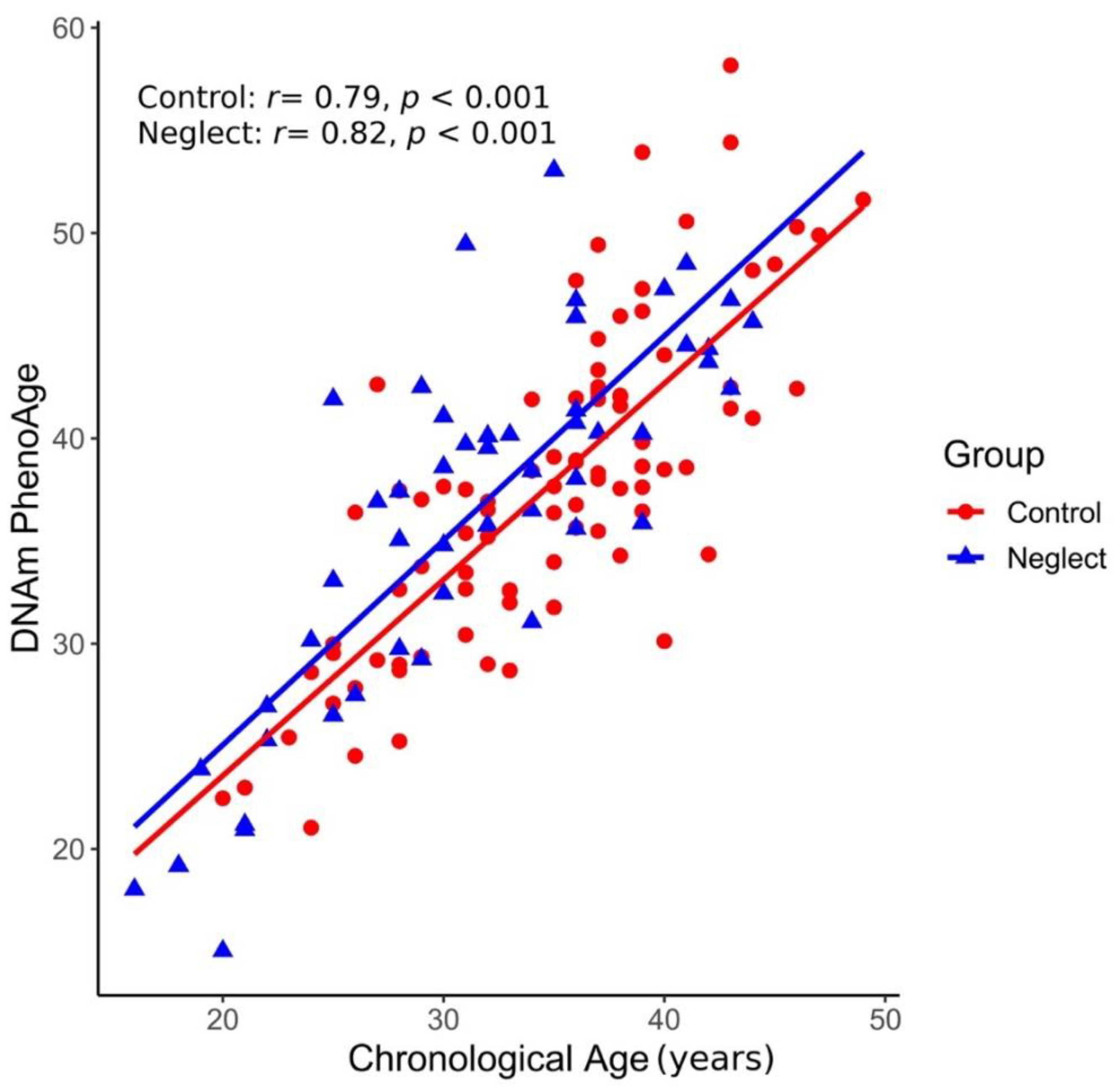
3.1. Epigenetic Age Acceleration (EAA) in Neglect and Control Groups
3.2. Selection of Variables for the ANCOVA Model
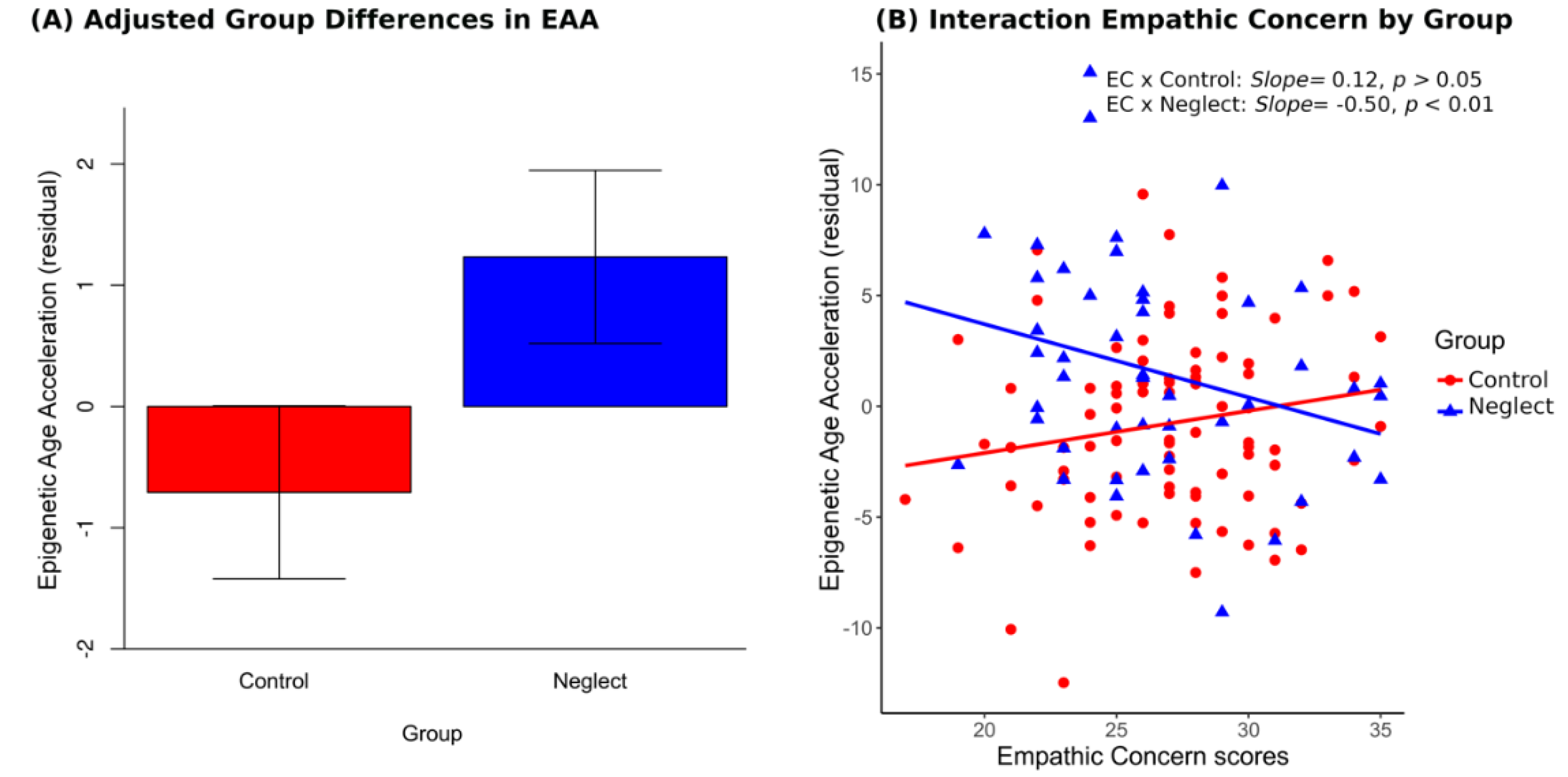
3.3. Group, Empathic Concern and Covariate Effects on EAA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Petersen, A.C.; Joseph, J.; Feit, M. New Directions in Child Abuse and Neglect Research; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Stoltenborgh, M.; Bakermans-Kranenburg, M.J.; van Ijzendoorn, M.H. The Neglect of Child Neglect: A Meta-Analytic Review of the Prevalence of Neglect. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2013, 48, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Child Maltreatment 2017; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Weinfield, N.S.; Sroufe, L.A.; Egeland, B.; Carlson, E. Individual Differences in Infant-Caregiver Attachment: Conceptual and Empirical Aspects of Security. In Handbook of Attachment: Theory, Research, and Clinical Applications; Cassidy, J., Shaver, P.R., Eds.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Teicher, M.H.; Samson, J.A.; Anderson, C.M.; Ohashi, K. The Effects of Childhood Maltreatment on Brain Structure, Function and Connectivity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 652–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffee, S.R. Child Maltreatment and Risk for Psychopathology in Childhood and Adulthood. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2017, 13, 525–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strathearn, L.; Giannotti, M.; Mills, R.; Kisely, S.; Najman, J.; Abajobir, A. Long-Term Cognitive, Psychological, and Health Outcomes Associated with Child Abuse and Neglect. Pediatrics 2020, 146, e20200438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelton, L.H. The Continuing Role of Material Factors in Child Maltreatment and Placement. Child Abuse Negl. 2015, 41, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horan, J.M.; Widom, C.S. Cumulative Childhood Risk and Adult Functioning in Abused and Neglected Children Grown Up. Dev. Psychopathol. 2015, 27, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, T.M.; Nurius, P.; Song, C.; Fleming, C.M.; Jones, T.M.; Nurius, P.; Song, C.; Fleming, C.M. Modeling Life Course Pathways from Adverse Childhood Experiences to Adult Mental Health. Child Abuse Negl. 2018, 80, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransquet, P.D.; Wrigglesworth, J.; Woods, R.L.; Ernst, M.E.; Ryan, J. The Epigenetic Clock as a Predictor of Disease and Mortality Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, E.J.; Maniates, H.; Nugent, N.; Maihofer, A.X.; Armstrong, D.; Ratanatharathorn, A.; Ashley-Koch, A.E.; Garrett, M.; Kimbrel, N.A.; Lori, A.; et al. Traumatic Stress and Accelerated DNA Methylation Age: A Meta-Analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 92, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannas, A.S.; Arloth, J.; Carrillo-Roa, T.; Iurato, S.; Röh, S.; Ressler, K.J.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Smith, A.K.; Bradley, B.; Heim, C.; et al. Lifetime Stress Accelerates Epigenetic Aging in an Urban, African American Cohort: Relevance of Glucocorticoid Signaling. Genome Biol. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutter, M. Resilience in the Face of Adversity. Protective Factors and Resistance to Psychiatric Disorder. Br. J. Psychiatry 1985, 147, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, P.W. Principles and Challenges of Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Analysis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knafo, A.; Jaffee, S.R. Gene–Environment Correlation in Developmental Psychopathology. Dev. Psychopathol. 2013, 25, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horvath, S.; Raj, K. DNA Methylation-Based Biomarkers and the Epigenetic Clock Theory of Ageing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorito, G.; Polidoro, S.; Dugué, P.-A.; Kivimaki, M.; Ponzi, E.; Matullo, G.; Guarrera, S.; Assumma, M.B.; Georgiadis, P.; Kyrtopoulos, S.A.; et al. Social Adversity and Epigenetic Aging: A Multi-Cohort Study on Socioeconomic Differences in Peripheral Blood DNA Methylation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.; Smart, M.; Gorrie-Stone, T.; Hannon, E.; Mill, J.; Bao, Y.; Burrage, J.; Schalkwyk, L.; Kumari, M. Socioeconomic Position and DNA Methylation Age Acceleration Across the Life Course. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 187, 2346–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, C.P.; Hayes, M.G.; Lee, N.R.; McDade, T.W.; Jones, M.J.; Kobor, M.S.; Kuzawa, C.W.; Eisenberg, D.T.A. Reproduction Predicts Shorter Telomeres and Epigenetic Age Acceleration among Young Adult Women. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essex, M.J.; Boyce, W.T.; Hertzman, C.; Lam, L.; Armstrong, J.; Neumann, S.; Kobor, M.S.; Essex, M.J.; Boyce, W.T.; Hertzman, C.; et al. Epigenetic Vestiges of Early Developmental Adversity: Childhood Stress Exposure and DNA Methylation in Adolescence. Child Dev. 2013, 84, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whalley, H.C.; Gibson, J.; Marioni, R.; Walker, R.M.; Clarke, T.-K.; Howard, D.M.; Adams, M.J.; Hall, L.; Morris, S.; Deary, I.J.; et al. Accelerated Epigenetic Ageing in Major Depressive Disorder. Genomics 2017, 210666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levine, M.E.; Lu, A.T.; Quach, A.; Chen, B.H.; Assimes, T.L.; Hou, L.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Stewart, J.D.; Li, Y.; Whitsel, E.A.; et al. An Epigenetic Biomarker of Aging for Lifespan and Healthspan. Aging 2018, 10, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murata, Y.; Fujii, A.; Kanata, S.; Fujikawa, S.; Ikegame, T.; Nakachi, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Jinde, S.; Kasai, K.; Bundo, M.; et al. Evaluation of the Usefulness of Saliva for DNA Methylation Analysis in Cohort Studies. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2019, 39, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bell, C.G.; Lowe, R.; Adams, P.D.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Beck, S.; Bell, J.T.; Christensen, B.C.; Gladyshev, V.N.; Heijmans, B.T.; Horvath, S.; et al. DNA Methylation Aging Clocks: Challenges and Recommendations. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marioni, R.E.; Shah, S.; McRae, A.F.; Ritchie, S.J.; Muniz-Terrera, G.; Harris, S.E.; Gibson, J.; Redmond, P.; Cox, S.R.; Pattie, A.; et al. The Epigenetic Clock Is Correlated with Physical and Cognitive Fitness in the Lothian Birth Cohort 1936. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quach, A.; Levine, M.E.; Tanaka, T.; Lu, A.T.; Chen, B.H.; Ferrucci, L.; Ritz, B.; Bandinelli, S.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Beasley, J.M.; et al. Epigenetic Clock Analysis of Diet, Exercise, Education, and Lifestyle Factors. Aging 2017, 9, 419–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eisenberg, N.; Fabes, R.A. Empathy: Conceptualization, Measurement, and Relation to Prosocial Behavior. Motiv. Emot. 1990, 14, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, M.L. Empathy and Moral Development: Implications for Caring and Justice; Cambridge Univ. Press: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Preston, S.D.; De Waal, F.B. Preston, S.D.; De Waal, F.B. Empathy: Its Ultimate and Proximate Bases. Behav. Brain Sci. 2002, 25, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tucker, D.M.; Luu, P.; Derryberry, D. Love Hurts: The Evolution of Empathic Concern through the Encephalization of Nociceptive Capacity. Dev. Psychopathol. 2005, 17, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decety, J.; Norman, G.J.; Berntson, G.C.; Cacioppo, J.T. A Neurobehavioral Evolutionary Perspective on the Mechanisms Underlying Empathy. Prog. Neurobiol. 2012, 98, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, J.I.; Romeo, R.D.; Lupien, S.J. Effects of Stress across the Lifespan. Stress 2011, 14, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, M.J.; León, I.; García-Pentón, L.; Hernández-Cabrera, J.A.; Quiñones, I. Neglectful Maternal Caregiving Involves Altered Brain Volume in Empathy-Related Areas. Dev. Psychopathol. 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, D.; Manly, J.T.; Cicchetti, D. Defining Child Maltreatment: The Interface between Policy and Research. Child Abuse Child Dev. Soc. Policy 1993, 8, 7–73. [Google Scholar]
- Dube, S.R.; Anda, R.F.; Felitti, V.J.; Edwards, V.J.; Croft, J.B. Adverse Childhood Experiences and Personal Alcohol Abuse as an Adult. Addict. Behav. 2002, 27, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hidalgo, V.; Menéndez, S.; Sánchez, J.; López, I.; Jiménez, L.; Lorence, B. Inventario de Situaciones Estresantes y de Riesgo; Universidad de Sevilla: Sevilla, Spain, 2005. (in press) [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein, D.P.; Fink, L. Childhood Trauma Questionnaire: A RetrospecTive Self-Report (CTQ); NCS Pearson, Inc.: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, A.; Gallardo-Pujol, D.; Pereda, N.; Arntz, A.; Bernstein, D.P.; Gaviria, A.M.; Labad, A.; Valero, J.; Gutiérrez-Zotes, J.A. Initial Validation of the Spanish Childhood Trauma Questionnaire-Short Form: Factor Structure, Reliability and Association with Parenting. J. Interpers. Violence 2013, 28, 1498–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrando, L.; Bobes, J.; Gibert, J.; Soto, M.; Soto, O. MINI Entrevista Neuropsiquitrica Internacional (MINI International Neuropsychiatric Interview, MINI). Instrum. Detección Orientación Diagnóstica 2000, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, M.H. A Multidimensional Approach to Individual Differences in Empathy. JSAS Cat. Sel. Doc. Psychol. 1980, 10, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Albéniz, A.; De Paúl, J.; Etxeberría, J.; Montes, M.P.; Torres, E. Adaptación de Interpersonal Reactivity Index (IRI) al Español. Psicothema 2003, 15, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Köster, J.; Rahmann, S. Snakemake—A Scalable Bioinformatics Workflow Engine. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2520–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fortin, J.-P.; Triche, T.J.; Hansen, K.D. Preprocessing, Normalization and Integration of the Illumina HumanMethylationEPIC Array with Minfi. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Langie, S.A.S.; De Boever, P.; Taylor, J.A.; Niu, L. RELIC: A Novel Dye-Bias Correction Method for Illumina Methylation BeadChip. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teschendorff, A.E.; Marabita, F.; Lechner, M.; Bartlett, T.; Tegner, J.; Gomez-Cabrero, D.; Beck, S. A Beta-Mixture Quantile Normalization Method for Correcting Probe Design Bias in Illumina Infinium 450 k DNA Methylation Data. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Just, A.C.; Heiss, J.A. Ewastools: EWAS Tools. 2018. Available online: https://github.com/hhhh5/ewastools/blob/master/DESCRIPTION (accessed on 19 March 2020).
- Adalsteinsson, B.T.; Gudnason, H.; Aspelund, T.; Harris, T.B.; Launer, L.J.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Smith, A.V.; Gudnason, V. Heterogeneity in White Blood Cells Has Potential to Confound DNA Methylation Measurements. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiao, C.; Zhang, C.; Dai, R.; Xia, Y.; Wang, K.; Giase, G.; Chen, C.; Liu, C. Positional Effects Revealed in Illumina Methylation Array and the Impact on Analysis. Epigenomics 2018, 10, 643–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mulder, T.M.; Kuiper, K.C.; van der Put, C.E.; Stams, G.-J.J.; Assink, M. Risk Factors for Child Neglect: A Meta-Analytic Review. Child Abuse Negl. 2018, 77, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toepfer, P.; O’Donnell, K.J.; Entringer, S.; Garg, E.; Heim, C.M.; Lin, D.T.S.; MacIsaac, J.L.; Kobor, M.S.; Meaney, M.J.; Provençal, N.; et al. Dynamic DNA Methylation Changes in the Maternal Oxytocin Gene Locus (OXT) during Pregnancy Predict Postpartum Maternal Intrusiveness. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 103, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, D.; Nishitani, S.; Shimada, K.; Kasaba, R.; Fujisawa, T.X.; Tomoda, A. Epigenetic Modification of the Oxytocin Gene Is Associated with Gray Matter Volume and Trait Empathy in Mothers. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2021, 123, 105026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, E.S.K.; Herres, J.; Dilks, K.E.; Rahim, F.; Trentacosta, C.J. Understanding of Emotions and Empathy: Predictors of Positive Parenting with Preschoolers in Economically Stressed Families. J. Child Fam. Stud. 2019, 28, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-C.; McFatter, R. Empathy and Distress: Two Distinct but Related Emotions in Response to Infant Crying. Infant Behav. Dev. 2012, 35, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, J.A.; Borelli, J.L.; Smiley, P.A. Assessing Parental Empathy: A Role for Empathy in Child Attachment. Attach. Hum. Dev. 2015, 17, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, N.; Miller, P.A. The Relation of Empathy to Prosocial and Related Behaviors. Psychol. Bull. 1987, 101, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grühn, D.; Rebucal, K.; Diehl, M.; Lumley, M.; Labouvie-Vief, G. Empathy across the Adult Lifespan: Longitudinal and Experience-Sampling Findings. Emotion 2008, 8, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, R.; Vuillier, L.; Hui, B.P.; Kogan, A. Caring Helps: Trait Empathy Is Related to Better Coping Strategies and Differs in the Poor versus the Rich. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, B.H.; Assimes, T.L.; Ferrucci, L.; Horvath, S.; Levine, M.E. The Role of Epigenetic Aging in Education and Racial/Ethnic Mortality Disparities among Older U.S. Women. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 104, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.; Leckman, J.F.; Mayes, L.C.; Newman, M.-A.; Feldman, R.; Swain, J.E. Perceived Quality of Maternal Care in Childhood and Structure and Function of Mothers’ Brain. Dev. Sci. 2010, 13, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hannighofer, J.; Foran, H.; Hahlweg, K.; Zimmermann, T. Impact of Relationship Status and Quality (Family Type) on the Mental Health of Mothers and Their Children: A 10-Year Longitudinal Study. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lo, C.K.M.; Chan, K.L.; Ip, P. Insecure Adult Attachment and Child Maltreatment: A Meta-Analysis. Trauma Violence. Abuse 2019, 20, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietromonaco, P.R.; Beck, L.A. Adult Attachment and Physical Health. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2019, 25, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.J.; Bagby, R.M. New Trends in Alexithymia Research. Psychother. Psychosom. 2004, 73, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Gudiel, H.; Fañanás, L.; Horvath, S.; Zannas, A.S. Psychosocial Stress and Epigenetic Aging. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2020, 150, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Control Group (n = 87) M (SD) or % | Neglect Group (n = 50) M (SD) or % | t(135)/χ2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age of mother | 34.72 (6.37) | 31.36 (7.28) | 2.82 ** |
| Number of pregnancies | 1.66 (0.73) | 2.48 (1.3) | −4.13 *** |
| Mean age of the target child | 3.67 (2.11) | 3.59 (2.56) | 0.20 |
| Two-parent family % | 72 | 50 | 6.0 * |
| Level of education (%) | 16.62 *** | ||
| Primary school | 43 | 80 | |
| ≥Secondary school | 57 | 20 | |
| Rural areas (%) | 26 | 44 | 3.68 |
| Unemployment (%) | 58 | 70 | 1.31 |
| Financial assistance % | 24 | 68 | 23.63 *** |
| Ancestry of mother % | 7.8 * | ||
| African | 0 | 0.02 | |
| European | 0.88 | 0.98 | |
| Latin American | 0.12 | 0 | |
| Immune cells (proportion) | 1.09 (0.09) | 1.12 (0.06) | −1.65 |
| Epithelial cells (proportion) | 0.02 (0.08) | 0.01 (0.05) | 0.81 |
| Comparisons | Control Group (n = 87) M (SD) | Neglect Group (n = 50) M (SD) | t(135) | δ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Empathy | ||||
| Empathic concern | 26.66 (4.26) | 26.98 (3.79) | −0.45 | 0.08 |
| Personal distress | 18.54 (4.25) | 18.08 (4.52) | 0.58 | 0.10 |
| Perspective taking | 24.33 (4.80) | 24.80 (3.90) | −0.61 | 0.11 |
| Fantasy | 20.3 (4.64) | 21.3 (4.5) | −1.17 | 0.21 |
| Intensity events | 11.59 (7.70) | 16,66 (8.70) | −3.52 *** | 0.62 |
| Child maltreatment | 33.98 (11.25) | 47.22 (21.37) | −4.06 *** | 0.72 |
| Psychiatric disorders | −0.26 (0.80) | 0.40 (1.14) | −3.59 *** | 0.64 |
| Correlations | EAA (r) | EAA (r) | ||
| Empathy | ||||
| Empathic concern | 0.19 * | −0.27 * | ||
| Personal distress | −0.20 | 0.03 | ||
| Perspective taking | 0.05 | 0.12 | ||
| Fantasy | 0.03 | −0.12 |
| Variables | F(1126) | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Empathic concern | 0.06 | 0.80 |
| Family type | 5.28 | 0.02 |
| Educational level | 5.17 | 0.02 |
| Group | 4.21 | 0.04 |
| Empathic concern × Group | 9.25 | 0.00 |
| Family type × Group | 5.17 | 0.02 |
| Educational level × Group | 5.46 | 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrero-Roldán, S.; Rodrigo, M.J.; Hernández-Cabrera, J.A.; Mitchell, C.; López, M.; Alcoba-Florez, J.; Fisher, J.; Espinosa, F.; León, I. Reduction in Epigenetic Age Acceleration Is Related to Empathy in Mothers with Neglectful Caregiving. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111376
Herrero-Roldán S, Rodrigo MJ, Hernández-Cabrera JA, Mitchell C, López M, Alcoba-Florez J, Fisher J, Espinosa F, León I. Reduction in Epigenetic Age Acceleration Is Related to Empathy in Mothers with Neglectful Caregiving. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(11):1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111376
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrero-Roldán, Silvia, María José Rodrigo, Juan A. Hernández-Cabrera, Colter Mitchell, Maykel López, Julia Alcoba-Florez, Jonah Fisher, Fernanda Espinosa, and Inmaculada León. 2021. "Reduction in Epigenetic Age Acceleration Is Related to Empathy in Mothers with Neglectful Caregiving" Brain Sciences 11, no. 11: 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111376
APA StyleHerrero-Roldán, S., Rodrigo, M. J., Hernández-Cabrera, J. A., Mitchell, C., López, M., Alcoba-Florez, J., Fisher, J., Espinosa, F., & León, I. (2021). Reduction in Epigenetic Age Acceleration Is Related to Empathy in Mothers with Neglectful Caregiving. Brain Sciences, 11(11), 1376. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11111376







