Immunohistochemical Evidence for Glutamatergic Regulation of Nesfatin-1 Neurons in the Rat Hypothalamus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Groups and Injections
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Immunofluorescence
2.5. Cell Counting and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nesfatin-1, c-Fos and Glutamate Receptor Immunoreactivity in the Hypothalamic Neurons
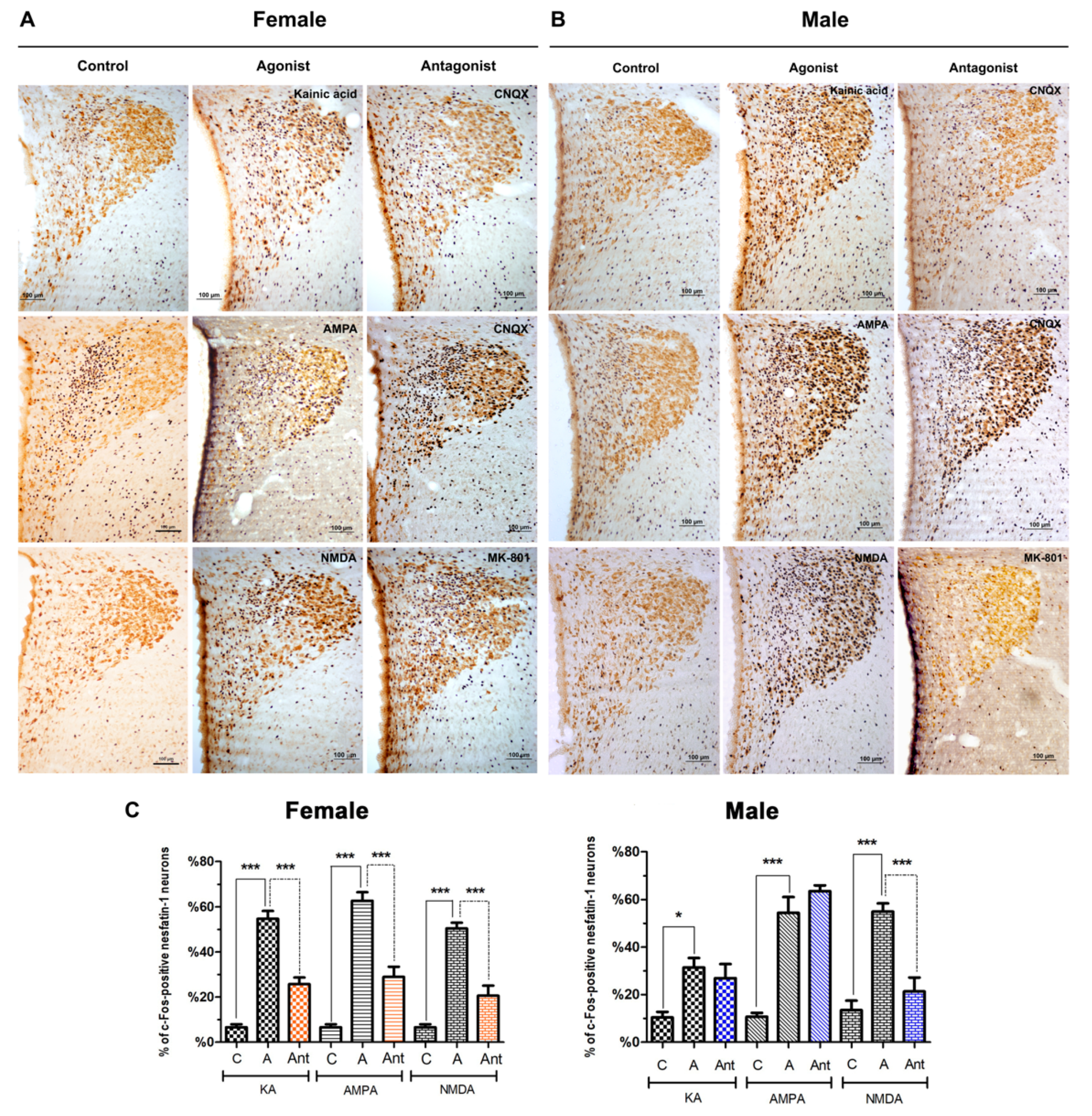
3.2. Effects of Glutamatergic Agonists and Antagonists on the Activation of Nesfatin-1 Neurons
3.2.1. Supraoptic Nucleus
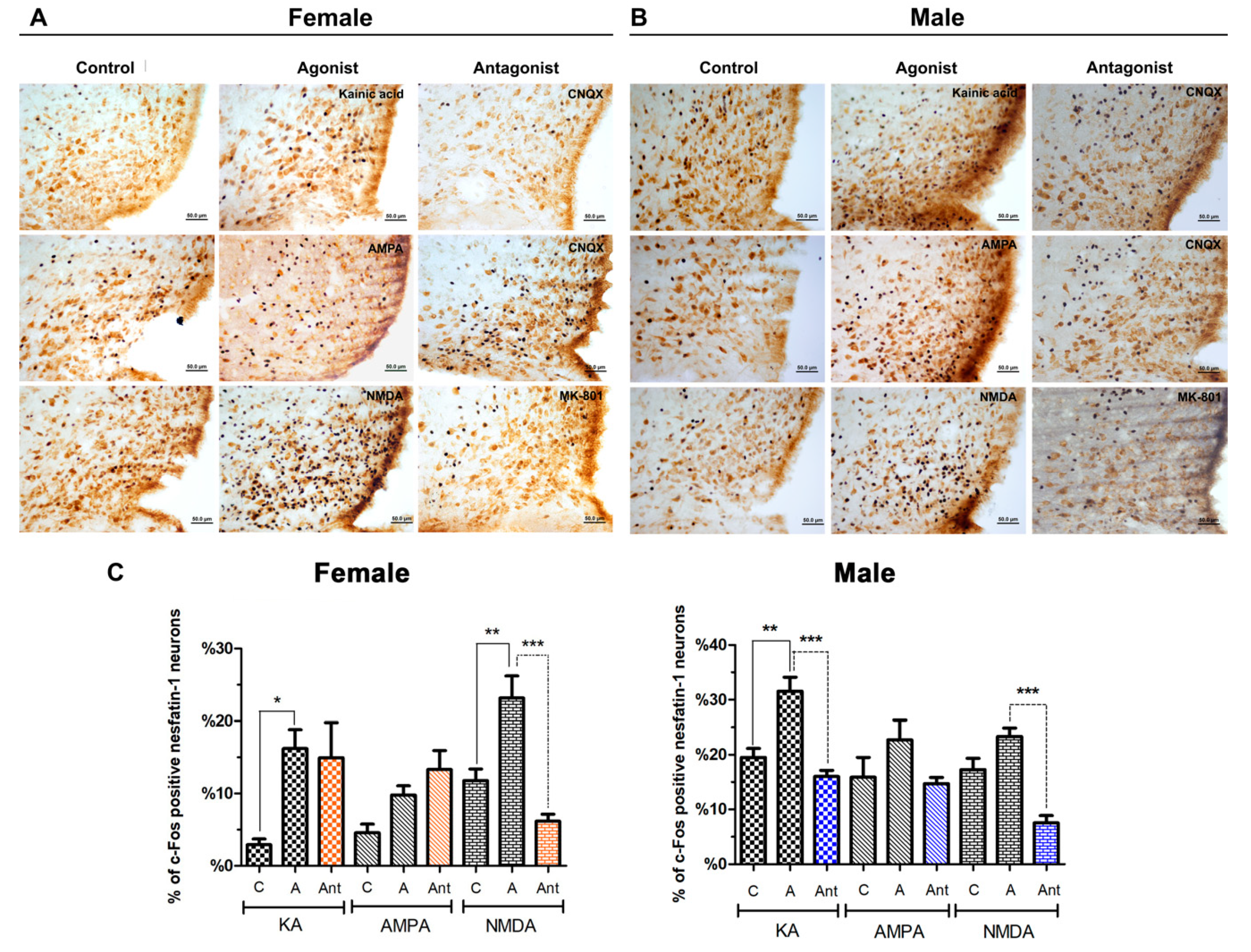
3.2.2. Paraventricular Nucleus
3.2.3. Arcuate Nucleus
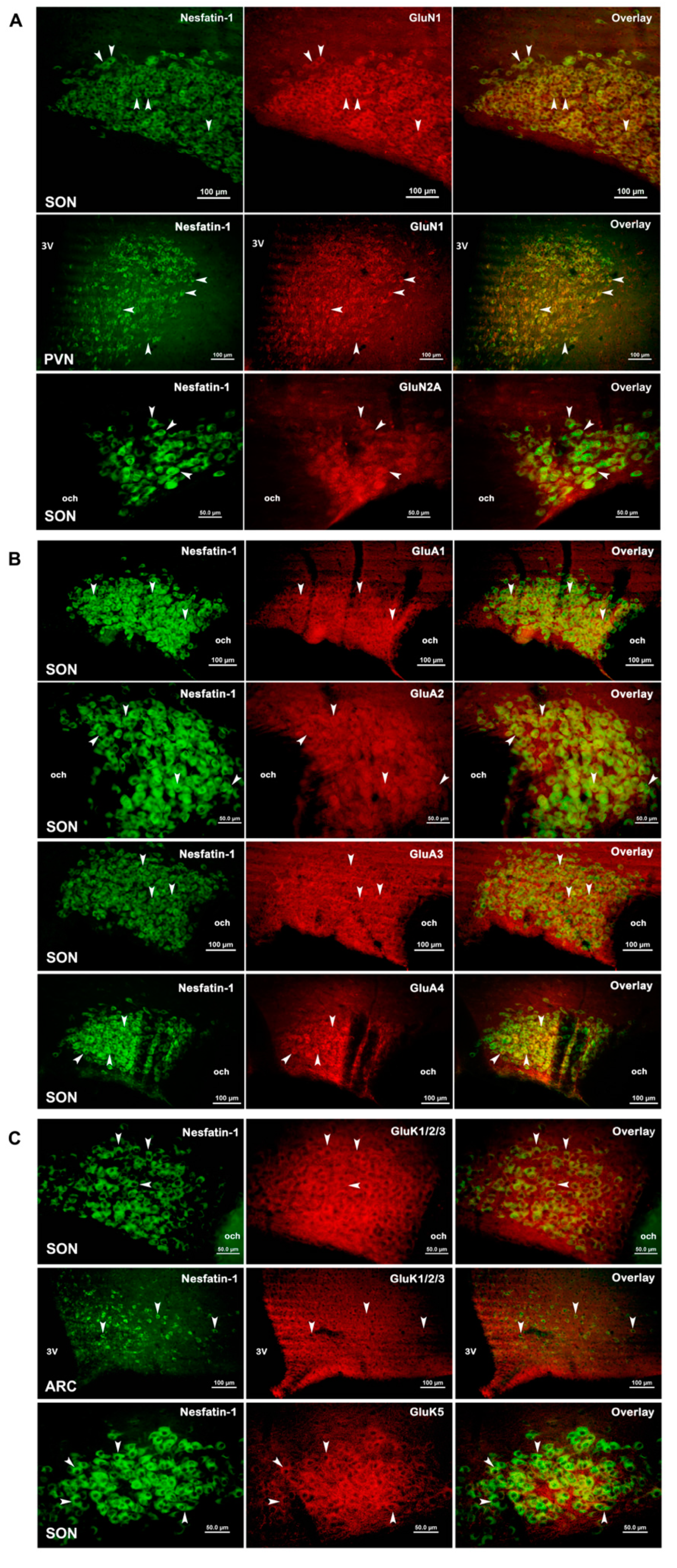
3.3. Expression of Glutamate Receptor Subunits in Nesfatin-1 Neurons
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Glutamatergic Agonists and Antagonists on the Activation of Nesfatin-1 Neurons
4.2. Expressions of Glutamate Receptor Subunit Proteins in Nesfatin-1 Neurons
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | Avidin-biotin complex |
| AMPA | α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid |
| ARC | Arcuate nucleus |
| DAB | Diaminobenzidine |
| DMH | Dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus |
| GluRs | Glutamate receptor subunits |
| LH | Lateral hypothalamic area |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| PVN | Paraventricular nucleus |
| SON | Supraoptic nucleus |
| VMH | Ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus |
References
- Oh, S.; Shimizu, H.; Satoh, T. Identification of nesfatin-1 as a satiety molecule in the hypothalamus. Nature 2006, 443, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Galiano, D.; Navarro, V.M.; Gaytan, F.; Tena-Sempere, M. Expanding roles of NUCB2/nesfatin-1 in neuroendocrine regulation. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 45, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengel, A.; Tache, Y. Nesfatin-1-Role as possible new potent regulator of food intake. Regul. Pept. 2010, 163, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.H.; Hung, H.C.; Kastin, A.J. Nesfatin-1 crosses the blood brain barrier without saturation. Peptides 2007, 28, 2223–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, T.O.; Samson, W.K.; Niehoff, M.L.; Banks, W.A. Permeability of the blood-brain barrier to a novel satiety molecule nesfatin-1. Peptides 2007, 28, 2372–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brailoiu, G.C.; Dun, S.L.; Brailoiu, E.; Inan, S.; Yang, J.; Chang, J.K.; Dun, N.J. Nesfatin-1: Distribution and interaction with a G protein-coupled receptor in the rat brain. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 5088–5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.S.; Brismar, H.; Broberger, C. Distribution and Neuropeptide Coexistence of Nucleobindin-2 Mrna/Nesfatin-Like Immunoreactivity in the Rat CNS. Neuroscience 2008, 156, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, M.; Stengel, A.; Wang, L.X.; Lambrecht, N.W.G.; Tache, Y. Nesfatin-1 immunoreactivity in rat brain and spinal cord autonomic nuclei. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 452, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel-Stengel, M.; Wang, L.X.; Stengel, A.; Tache, Y. Localization of nesfatin-1 neurons in the mouse brain and functional implication. Brain Res. 2011, 1396, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, R.; Levata, L.; Lehnert, H.; Schulz, C. Nesfatin-1: Functions and physiology of a novel regulatory peptide. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 232, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, P.; Teuffel, P.; Lembke, V.; Kobelt, P.; Goebel-Stengel, M.; Hofmann, T.; Rose, M.; Klapp, B.F.; Stengel, A. Nesfatin-130-59 injected intracerebroventricularly differentially affects food intake microstructure in rats under normal weight and diet-induced obese conditions. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brann, D.W.; Mahesh, V.B. Excitatory amino acids: Function and significance in reproduction and neuroendocrine regulation. Front. Neuroendocrin. 1994, 15, 3–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brann, D.W. Glutamate: A major excitatory transmitter in neuroendocrine regulation. Neuroendocrinology 1995, 61, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollmann, M.; Heinemann, S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1994, 17, 31–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelkey, K.A.; Mcbain, C.J. Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors in Synaptic Plasticity. In The Glutamate Receptors, 1st ed.; Gereau, R.W., Swanson, G.T., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2008; Volume XI, pp. 179–247. [Google Scholar]
- Eyigor, O.; Centers, A.; Jennes, L. Distribution of ionotropic glutamate receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat hypothalamus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2001, 431, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettler, B.; Mulle, C. Review: Neurotransmitter receptors II. AMPA and kainate receptors. Neuropharmacology 1995, 34, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Mishina, M. Structure and function of the NMDA receptor channel. Neuropharmacology 1995, 34, 1219–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, S.M.; Sharp, F.R.; Curran, T. Expression of c-fos protein in brain: Metabolic mapping at the cellular level. Science 1988, 240, 1328–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, G.E.; Smith, M.S.; Verbalis, J.G. c-Fos and related immediate early gene products as markers of activity in neuroendocrine systems. Front. Neuroendocrin. 1993, 14, 173–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, K.J. Measurement of Immediate-Early Gene Activation- c-fos and Beyond. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2008, 20, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, G.E.; Lyo, D. Anatomical markers of activity in neuroendocrine systems: Are we all ‘fos-ed out’? J. Neuroendocrinol. 2002, 14, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, B.; Guvenc, G.; Altinbas, B.; Niaz, N.; Yalcin, M. Modulation of nesfatin-1 induced cardiovascular effects by the central cholinergic system. Neuropeptides 2018, 70, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.B.; Arnold, A.P.; Berkley, K.J.; Blaustein, J.D.; Eckel, L.A.; Hampson, E.; Herman, J.P.; Marts, S.; Sadee, W.; Steiner, M.; et al. Strategies and methods for research on sex differences in brain and behavior. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 1650–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2009; pp. Plate 37–Plate 56. [Google Scholar]
- Niciu, M.J.; Kelmendi, B.; Sanacora, G. Overview of glutamatergic neurotransmission in the nervous system. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 100, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minbay, F.Z.; Eyigor, O.; Çavusoglu, I. Kainic acid activates oxytocinergic neurons through non-NMDA glutamate receptors. Int. J. Neurosci. 2006, 116, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gynther, M.; Petsalo, A.; Hansen, S.H.; Bunch, L.; Pickering, D.S. Blood-Brain Barrier permeability and brain uptake mechanism of kainic acid and dihydrokainic acid. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, C.; Tercero, I.; Pineda, A.; Burgos, J.S. Simvastatin is the statin that most efficiently protects against kainate-induced excitotoxicity and memory impairment. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 24, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankir, M.K.; Parkinson, J.R.; Bloom, S.R.; Bell, J.D. The effects of glutamate receptor agonists and antagonists on mouse hypothalamic and hippocampal neuronal activity shown through manganese enhanced MRI. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 968–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gok-Yurtseven, D.; Kafa, I.M.; Minbay, Z.; Eyigor, O. Glutamatergic activation of A1 and A2 noradrenergic neurons in the rat brain stem. Croat. Med. J. 2019, 60, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, D.J.; Braun, C.J.; Duncan, G.E.; Qian, Y.; Fernandes, A.; Crews, F.T.; Breese, G.R. Regional specificity of ethanol and NMDA action in brain revealed with Fos-like immunohistochemistry and differential routes of drug administration. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 1662–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.W.; Park, J.W.; Suh, M.H.; Suh, S.I.; Choe, B.K. Persistent expression of Fas/FasL mRNA in the mouse hippocampus after a single NMDA injection. J. Neurochem. 1998, 71, 1773–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsikostas, D.D.; Sanchez del Rio, M.; Waeber, C.; Huang, Z.; Cutrer, F.M.; Moskowitz, M.A. Non-NMDA glutamate receptors modulate capsaicin induced c-fos expression within trigeminal nucleus caudalis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 127, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyigor, O.; Minbay, Z.; Cavusoglu, I. Activation of orexin neurons through non-NMDA glutamate receptors evidenced by c-Fos immunohistochemistry. Endocrine 2010, 37, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyigor, O.; Minbay, Z.; Kafa, I.M. Glutamate and Orexin Neurons. Vitam. Horm. 2012, 89, 209–222. [Google Scholar]
- Serter, S.; Gok Yurtseven, D.; Cakir, C.; Minbay, Z.; Eyigor, O. Glutamatergic Activation of Neuronostatin Neurons in the Periventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, Y. Gonadal steroid action and brain sex differentiation in the rat. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2009, 21, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayada, C.; Toru, Ü.; Korkut, Y. Nesfatin-1 and its effects on different systems. Hippokratia. 2015, 19, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Malarkey, E.B.; Parpura, V. Mechanisms of glutamate release from astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Pol, A.N.; Hermans-Borgmeyer, I.; Hofer, M.; Ghosh, P.; Heinemann, S. Ionotropic glutamate receptor gene expression in hypothalamus: Localization of AMPA kainate and NMDA receptor RNA with in situ hybridization. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 343, 428–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.P.; Eyigor, O.; Ziegler, D.R.; Jennes, L. Expression of ionotropic glutamate receptor subunit mRNAs in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 2000, 422, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyigor, O.; Minbay, Z.; Cavusoglu, I.; Jennes, L. Localization of kainate receptor subunit GluR5-immunoreactive cells in the rat hypothalamus. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 136, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petralia, R.S.; Wang, Y.X.; Wenthold, R.J. Histological and ultrastructural localization of the kainate receptor subunits, KA2 and GluR6/7, in the rat nervous system using selective antipeptide antibodies. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 349, 85–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petralia, R.S.; Wang, Y.X.; Wenthold, R.J. The NMDA receptor subunits NR2A and NR2B show histological and ultrastructural localization patterns similar to those of NR1. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 6102–6120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, F.C.; Sladek, C.D. NMDA receptor subunit expression in the supraoptic nucleus of adult rats: Dominance of NR2B and NR2D. Brain Res. 2011, 1388, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, J.R. Homomeric and heteromeric ion channels formed from the kainite type subunits GluR6 and KA2 have very small, but different, unitary conductance. J. Neurophysiol. 1996, 76, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, A.; Weiss, B.; Ogden, A.M.; Knauss, J.L.; Oler, J.; Ho, K.; Large, T.H.; Bleakman, D. Pharmacological characterization of glutamatergic agonists and antagonists at recombinant human homomeric and heteromeric kainate receptors in vitro. Neuropharmacology 2004, 46, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, S.; Iizuka, M.; Wakamori, M.; Akiba, I.; Imoto, K.; Barsoumian, E.L. Stable expression of human homomeric and heteromeric AMPA receptor subunits in HEK293 cells. Recept. Channels 2000, 7, 139–150. [Google Scholar]
- Monyer, H.; Sprengel, R.; Schoepfer, R.; Herb, A.; Higuchi, M.; Lomeli, H.; Burnashev, N.; Sakmann, B.; Seeburg, P.H. Heteromeric NMDA receptors: Molecular and functional distinction of subtypes. Science 1992, 256, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.L. Structural biology of glutamate receptor ion channel complexes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2016, 41, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 ) was localized in the nucleus with a black chromogen reaction, so the active nesfatin-1 neurons are distinguished by the presence of c-Fos-positive nuclei. (B) Nesfatin-1 neurons are labeled with green fluorochrome. (C) Glutamate receptor subunit (GluN1 as the example in this figure) proteins are labeled with red fluorochrome. (D) Nesfatin-1 neurons expressing GluN1 subunit protein are monitored in yellow. Arrows point out a double-labeled neuron.
) was localized in the nucleus with a black chromogen reaction, so the active nesfatin-1 neurons are distinguished by the presence of c-Fos-positive nuclei. (B) Nesfatin-1 neurons are labeled with green fluorochrome. (C) Glutamate receptor subunit (GluN1 as the example in this figure) proteins are labeled with red fluorochrome. (D) Nesfatin-1 neurons expressing GluN1 subunit protein are monitored in yellow. Arrows point out a double-labeled neuron.
 ) was localized in the nucleus with a black chromogen reaction, so the active nesfatin-1 neurons are distinguished by the presence of c-Fos-positive nuclei. (B) Nesfatin-1 neurons are labeled with green fluorochrome. (C) Glutamate receptor subunit (GluN1 as the example in this figure) proteins are labeled with red fluorochrome. (D) Nesfatin-1 neurons expressing GluN1 subunit protein are monitored in yellow. Arrows point out a double-labeled neuron.
) was localized in the nucleus with a black chromogen reaction, so the active nesfatin-1 neurons are distinguished by the presence of c-Fos-positive nuclei. (B) Nesfatin-1 neurons are labeled with green fluorochrome. (C) Glutamate receptor subunit (GluN1 as the example in this figure) proteins are labeled with red fluorochrome. (D) Nesfatin-1 neurons expressing GluN1 subunit protein are monitored in yellow. Arrows point out a double-labeled neuron.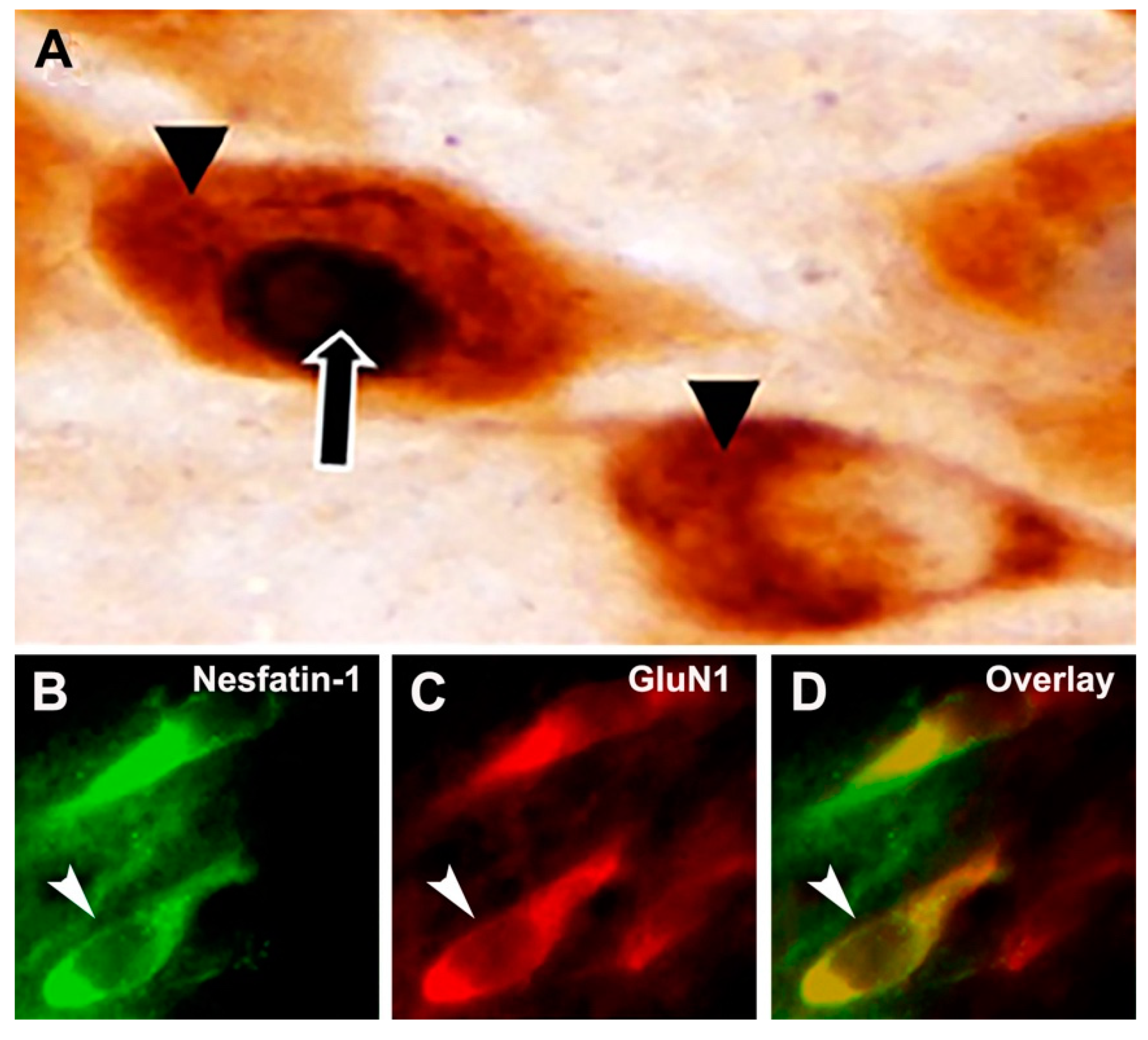


| Antibodies | Dilution | Incubation Time | Temperature | Supplier | Catalog Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rabbit anti-c-Fos | 1:10,000 | 24 h | RT | Oncogene | PC-38 |
| Rabbit anti-Nesfatin-1 | 1:20,000 | 24 h | RT | Phoenix Pharmaceuticals | H-003-22 |
| Mouse anti-GluN1 (IgG) | 1:300 | 48 h | +4 °C | BD Pharmingen | 556,308 |
| Mouse anti-GluN2A (IgG) | 1:1,000 | 48 h | +4 °C | Millipore | MAB5216 |
| Mouse anti-GluA1 (IgG) | 1:500 | 48 h | +4 °C | Acris | AM60040PU-N |
| Mouse anti-GluA2 (IgG) | 1:1,000 | 48 h | +4 °C | Millipore | MAB397 |
| Mouse anti-GluA3 (IgG) | 1:1,000 | 48 h | +4 °C | Millipore | MAB5416 |
| Goat anti-GluA4 (IgG) | 1:500 | 48 h | +4 °C | LifeSpan BioSciences | LS-B3606 |
| Mouse anti-GluK1/2/3 (IgM) | 1:900 | 48 h | +4 °C | Chemicon | MAB379 |
| Goat anti-GluK5 (IgG) | 1:2,000 | 72 h | +4 °C | Santa Cruz | sc-8915 |
| Hypothalamic Nuclei | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Subunits | Supraoptic Nucleus | Paraventricular Nucleus | Arcuate Nucleus |
| GluN1 | +++ | ++ | ++ |
| GluN2A | +++ | + | + |
| GluA1 | +++ | + | ++ |
| GluA2 | +++ | ++ | + |
| GluA3 | +++ | + | + |
| GluA4 | ++ | ++ | + |
| GluK1/2/3 | +++ | + | + |
| GluK5 | +++ | ++ | ++ |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gok Yurtseven, D.; Serter Kocoglu, S.; Minbay, Z.; Eyigor, O. Immunohistochemical Evidence for Glutamatergic Regulation of Nesfatin-1 Neurons in the Rat Hypothalamus. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090630
Gok Yurtseven D, Serter Kocoglu S, Minbay Z, Eyigor O. Immunohistochemical Evidence for Glutamatergic Regulation of Nesfatin-1 Neurons in the Rat Hypothalamus. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(9):630. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090630
Chicago/Turabian StyleGok Yurtseven, Duygu, Sema Serter Kocoglu, Zehra Minbay, and Ozhan Eyigor. 2020. "Immunohistochemical Evidence for Glutamatergic Regulation of Nesfatin-1 Neurons in the Rat Hypothalamus" Brain Sciences 10, no. 9: 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090630
APA StyleGok Yurtseven, D., Serter Kocoglu, S., Minbay, Z., & Eyigor, O. (2020). Immunohistochemical Evidence for Glutamatergic Regulation of Nesfatin-1 Neurons in the Rat Hypothalamus. Brain Sciences, 10(9), 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090630





