Osteopontin and Integrin Mediated Modulation of Post-Synapses in HIV Envelope Glycoprotein Exposed Hippocampal Neurons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Primary Hippocampal Neuron Culture
2.2. SiRNA Silencing and Treatments
2.3. Immunofluorescence
2.4. Image Analysis
2.5. Experimental Groups
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
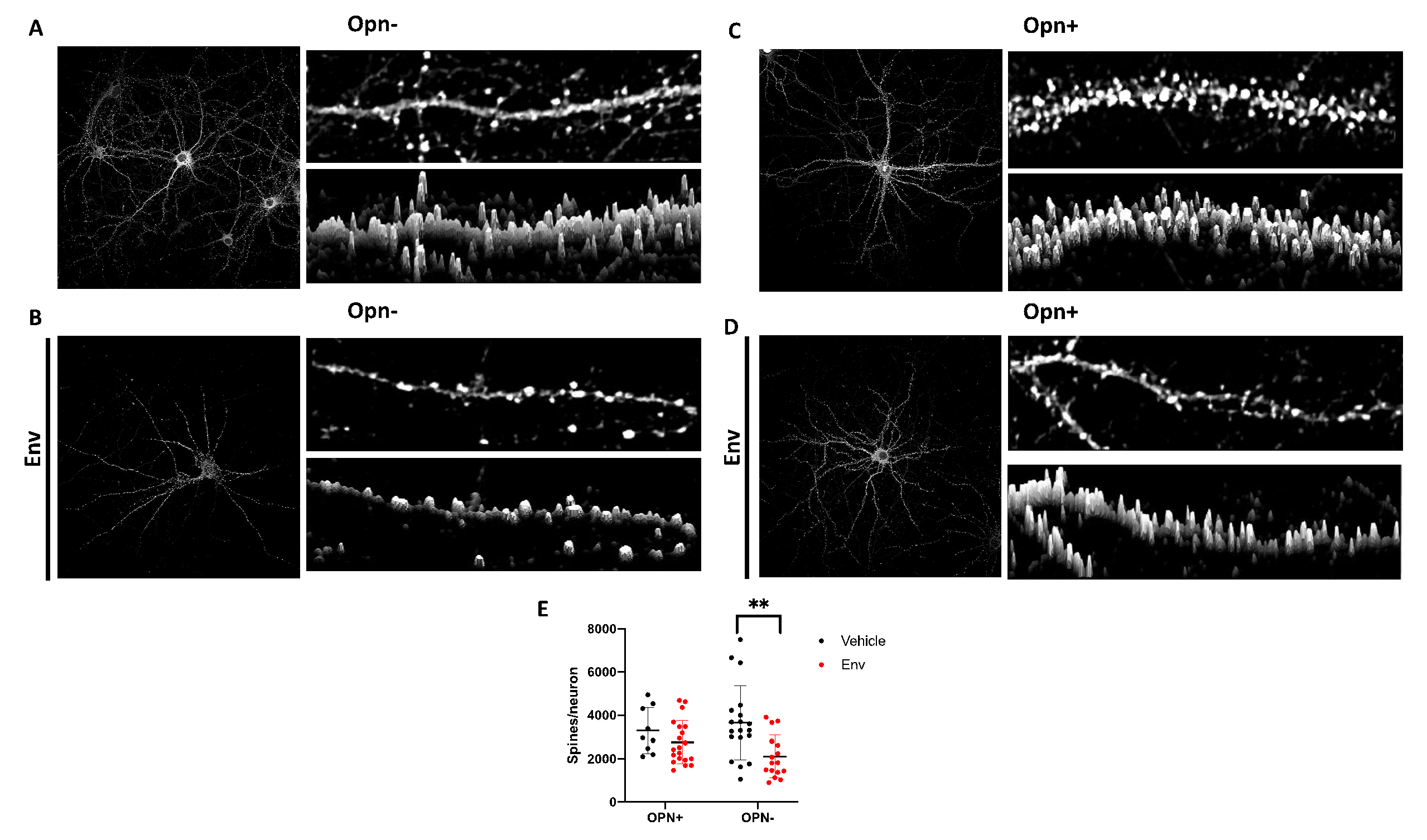
3.1. HIV-1 Env Mediates Post-Synaptic Remodeling by Decreasing the Number of Dendritic Spines, but Co-Treatment with Opn Reverses This Damage
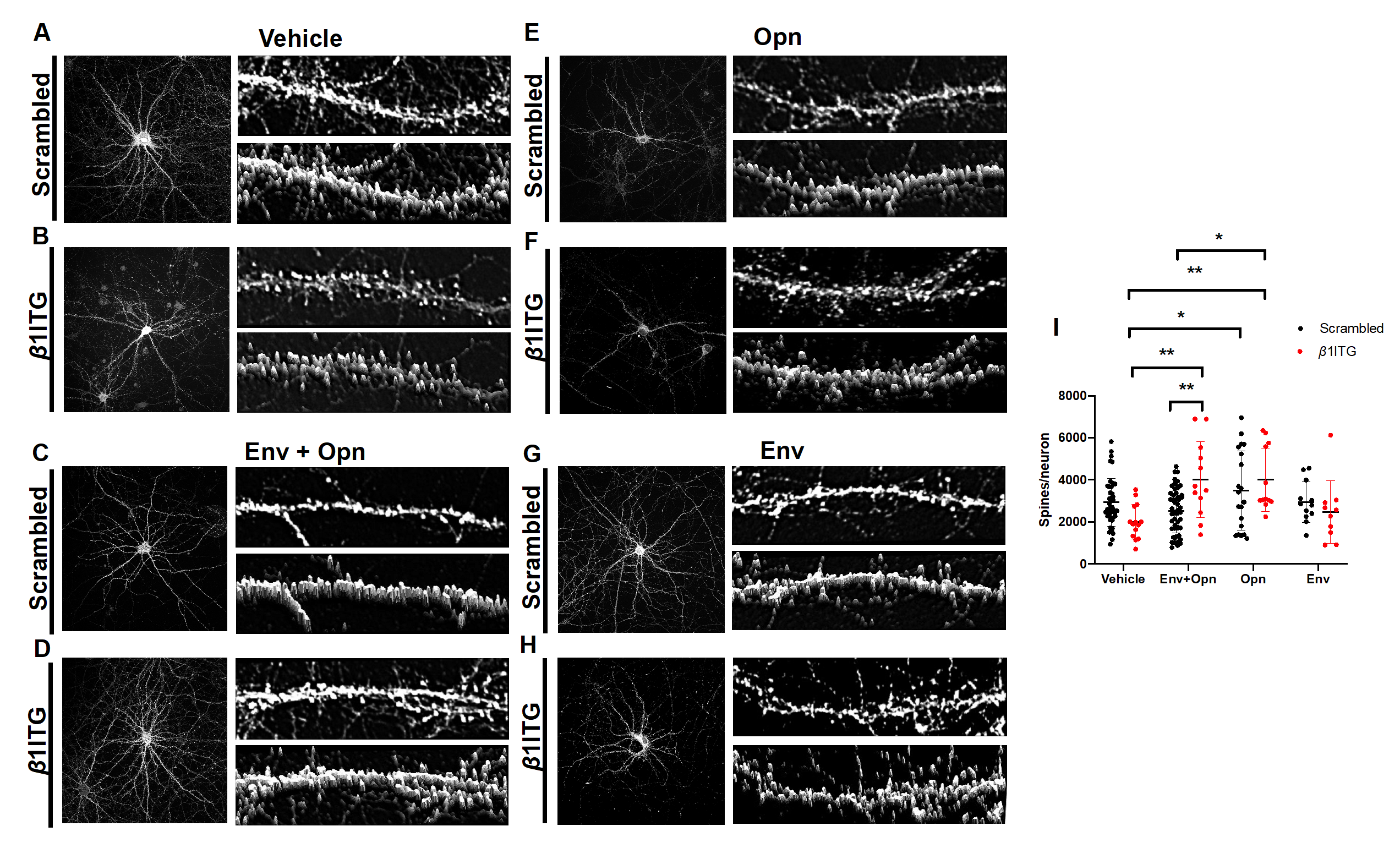
3.2. Opn Acts Independently of Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Component, β1 Integrin, to Regulate Hippocampal Post-Synapses in the Presence of HIV-1 Env
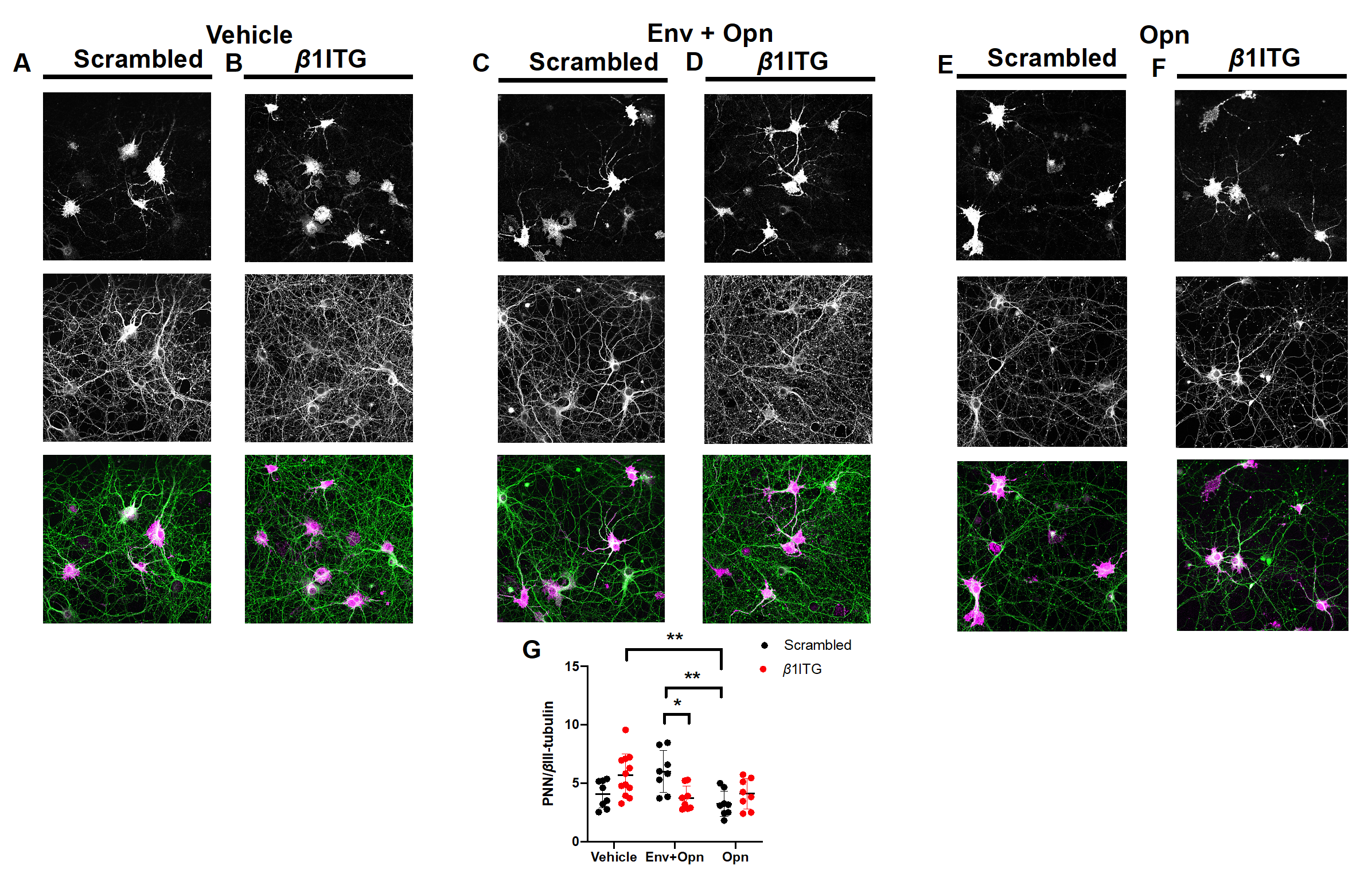
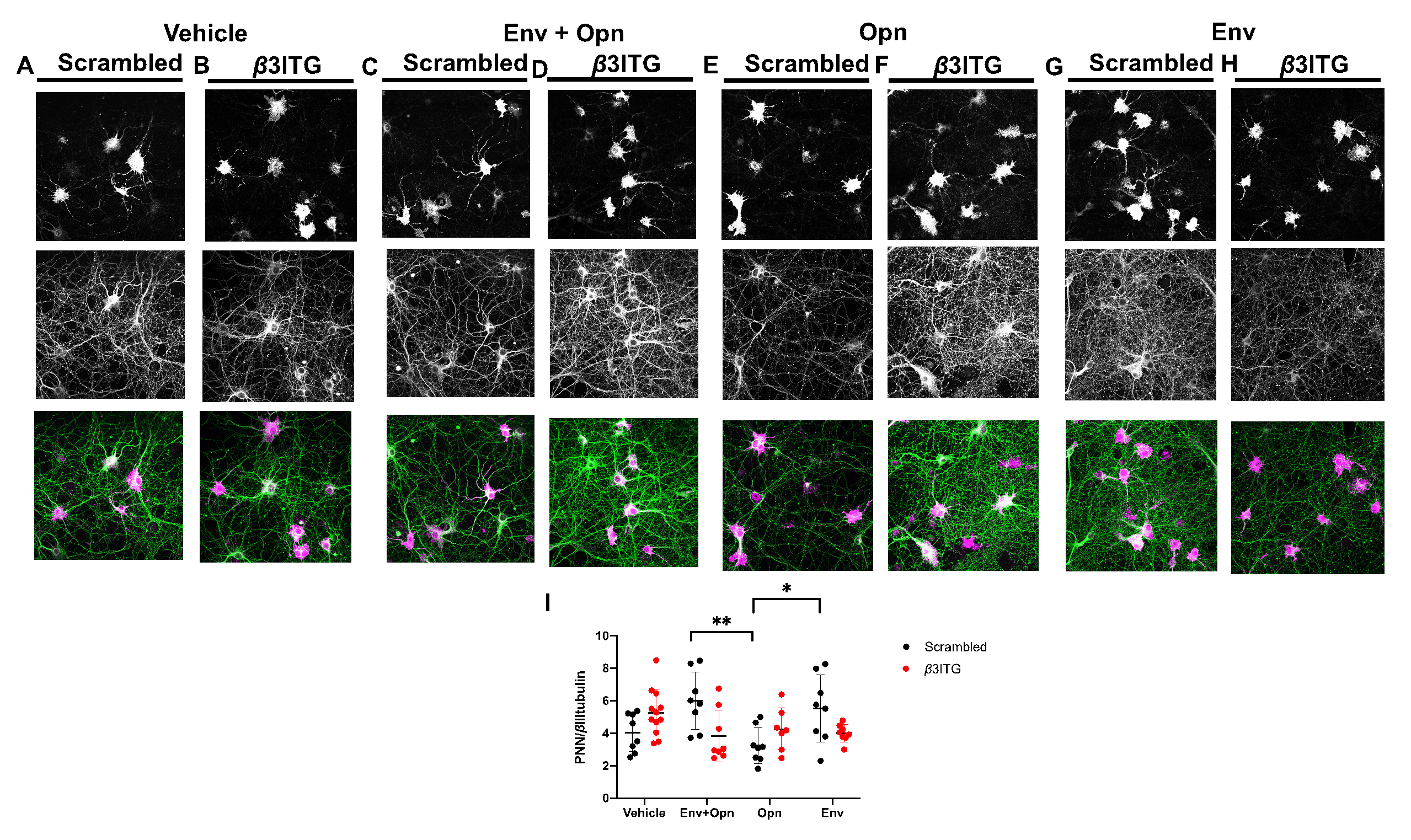
3.3. Perineuronal Net (PNN) Expression Is Decreased in β1 Integrin Silenced Neurons Co-Treated with HIV-1 Env and Opn, and in Neurons Treated Only with Opn Compared to Vehicle Controls
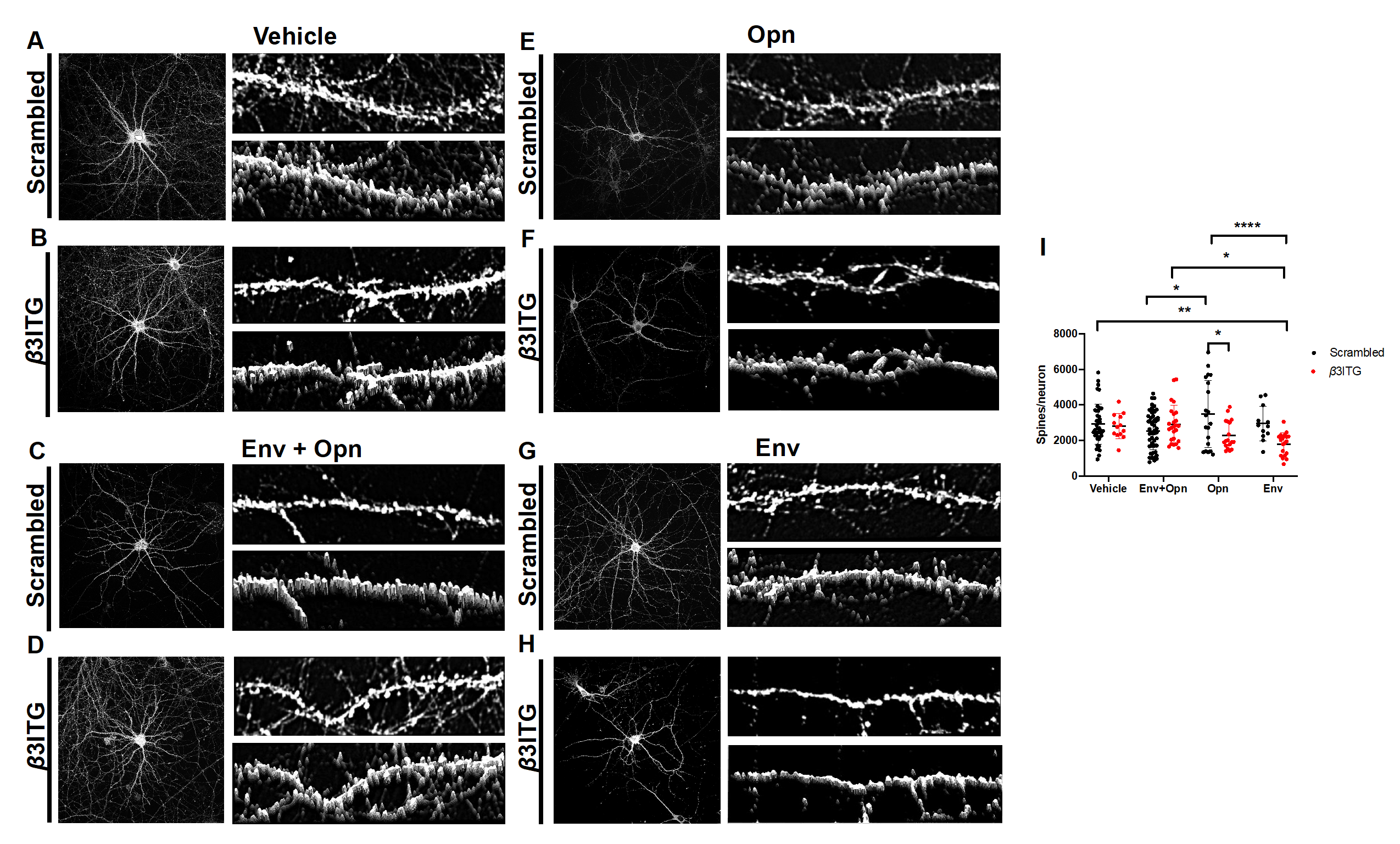
3.4. β3 Integrins Are Required for Opn Induced Upregulation of Post-Synaptic Dendritic Spines
3.5. In HIV-1 Env and Opn Treated Neurons, PNN Expression Is not Regulated by β3 Integrins
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saylor, D.; Dickens, A.M.; Sacktor, N.; Haughey, N.; Slusher, B.; Pletnikov, M.; Mankowski, J.L.; Brown, A.; Volsky, D.J.; McArthur, J.C. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder—pathogenesis and prospects for treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 12, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, M.; Garden, G.; Lipton, S.A. Pathways to neuronal injury and apoptosis in HIV-associated dementia. Nature 2001, 410, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocchetti, I.; Bachis, A.; Avdoshina, V. Neurotoxicity of human immunodeficiency virus-1: Viral proteins and axonal transport. Neurotox. Res. 2011, 21, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toggas, S.M.; Masliah, E.; Mucke, L. Prevention of HIV-1 gp120-induced neuronal damage in the central nervous system of transgenic mice by the NMDA receptor antagonist memantine. Brain Res. 1996, 706, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Ghorpade, A.; Niemann, D.; Cotter, R.L.; Thylin, M.R.; Epstein, L.; Swartz, J.M.; Shepard, R.B.; Liu, X.; Nukuna, A.; et al. Lymphotropic Virions Affect Chemokine Receptor-Mediated Neural Signaling and Apoptosis: Implications for Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1-Associated Dementia. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 8256–8267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Banks, W.A. Role of the immune system in HIV-associated neuroinflammation and neurocognitive implications. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 45, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.R.; Ruiz, A.P.; Prasad, V.R. Viral and cellular factors underlying neuropathogenesis in HIV associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND). Aids Res. Ther. 2014, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toggas, S.M.; Masliah, E.; Rockenstein, E.M.; Rail, G.F.; Abraham, C.R.; Mucke, L. Central nervous system damage produced by expression of the HIV-1 coat protein gpl20 in transgenic mice. Nature 1994, 367, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, A.; Psooy, K.; Martin, C.; Knudsen, B.; Magnuson, D.S.; Haughey, N.; Geiger, J.D. Identification of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat epitope that is neuroexcitatory and neurotoxic. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Shin, A.H.; Thayer, S.A. Activation of cannabinoid type 2 receptors inhibits HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein gp120-induced synapse loss. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 80, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Brandimarti, R.; Musser, B.J.; Resue, D.M.; Fatatis, A.; Meucci, O. The Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 Regulates Cell-Cycle Proteins in Neurons. J. NeuroVirology 2003, 9, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol, F.; Kitabgi, P.; Boudin, H. The chemokine SDF-1 differentially regulates axonal elongation and branching in hippocampal neurons. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.M.; Islam, T.; Adams, R.; Nerle, S.; Kamara, M.; Eger, C.; Marder, K.; Cohen, B.; Schifitto, G.; McArthur, J.C.; et al. Osteopontin enhances HIV replication and is increased in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid of HIV-infected individuals. J. NeuroVirology 2011, 17, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, K.; Lucas, C.-H.G.; White, T.; Hairston, T.-K.; Rameau, T.; Brown, A.M. Cortical neurons are a prominent source of the proinflammatory cytokine osteopontin in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. J. NeuroVirology 2015, 21, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdo, T.H.; Ellis, R.J.; Fox, H.S. Osteopontin Is Increased in HIV-Associated Dementia. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.L.; Reeves, T.M.; Phillips, L.L. Osteopontin expression in acute immune response mediates hippocampal synaptogenesis and adaptive outcome following cortical brain injury. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 261, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Sun, N.; Rittling, S.R.; Denhardt, D.T.; Young, W. Osteopontin-Deficient Mice Exhibit Less Inflammation, Greater Tissue Damage, and Impaired Locomotor Recovery from Spinal Cord Injury Compared with Wild-Type Controls. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 3603–3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabenstein, M.; Hucklenbroich, J.; Willuweit, A.; Ladwig, A.; Fink, G.R.; Schroeter, M.; Langen, K.-J.; Rueger, M.A. Osteopontin mediates survival, proliferation and migration of neural stem cells through the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Stem Cell Res. 2015, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, Y.U.; Sleeman, J.; Fujii, H.; Herrlich, P.; Hotta, H.; Tanaka, K.; Chikuma, S.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K.; Murakami, M.; et al. CD44 variants but not CD44s cooperate with beta1-containing integrins to permit cells to bind to osteopontin independently of arginine-glycine-aspartic acid, thereby stimulating cell motility and chemotaxis. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 219–226. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Dammer, E.B.; Zhang-Brotzge, X.; Chen, S.; Duong, D.; Seyfried, N.T.; Kuan, C.-Y.; Sun, Y.-Y. Osteopontin is a Blood Biomarker for Microglial Activation and Brain Injury in Experimental Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy. eNeuro 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agah, E.; Zardoui, A.; Saghazadeh, A.; Ahmadi, M.; Tafakhori, A.; Rezaei, N. Osteopontin (OPN) as a CSF and blood biomarker for multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisaki, Y.; Niikura, M.; Watanabe, M.; Onishi, K.; Tanabe, S.; Moriwaki, Y.; Okuda, T.; Ohara, S.; Murayama, S.; Takao, M.; et al. Selective Expression of Osteopontin in ALS-resistant Motor Neurons is a Critical Determinant of Late Phase Neurodegeneration Mediated by Matrix Metalloproteinase-9. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzelli, P.L.; Caccavano, A.; Avdoshina, V.; Mocchetti, I.; Wu, J.-Y.; Conant, K. Increased matrix metalloproteinase levels and perineuronal net proteolysis in the HIV-infected brain; relevance to altered neuronal population dynamics. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 323, 113077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vivo, L.; Landi, S.; Panniello, M.; Baroncelli, L.; Chierzi, S.; Mariotti, L.; Spolidoro, M.; Pizzorusso, T.; Maffei, L.; Ratto, G. Extracellular matrix inhibits structural and functional plasticity of dendritic spines in the adult visual cortex. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-B.; Bozdagi, O.; Nikitczuk, J.S.; Zhai, Z.W.; Zhou, Q.; Huntley, G.W. Extracellular proteolysis by matrix metalloproteinase-9 drives dendritic spine enlargement and long-term potentiation coordinately. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19520–19525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennekinne, L.; Colasse, S.; Triller, A.; Renner, M. Differential Control of Thrombospondin over Synaptic Glycine and AMPA Receptors in Spinal Cord Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 11432–11439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.H.; Afroz, S.; Reinhard, S.M.; Palacios, A.R.; Tapia, K.; Binder, D.K.; Razak, K.A.; Ethell, I.M. Genetic Reduction of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Promotes Formation of Perineuronal Nets Around Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons and Normalizes Auditory Cortex Responses in Developing Fmr1 Knock-Out Mice. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 28, 3951–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahles, F.; Findeisen, H.M.; Bruemmer, D. Osteopontin: A novel regulator at the cross roads of inflammation, obesity and diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denhardt, D.T.; Noda, M.; O’Regan, A.W.; Pavlin, D.; Berman, J.S. Osteopontin as a means to cope with environmental insults: Regulation of inflammation, tissue remodeling, and cell survival. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roszkowska, M.; Skupień-Jaroszek, A.; Wójtowicz, T.; Konopka, A.; Gorlewicz, A.; Kisiel, M.; Bekisz, M.; Ruszczycki, B.; Doleżyczek, H.; Rejmak-Kozicka, E.; et al. CD44: A novel synaptic cell adhesion molecule regulating structural and functional plasticity of dendritic spines. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 4055–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard-Trifilo, J.A.; Kramár, E.A.; Torp, R.; Pineda, E.A.; Lynch, G.; Gall, C.; Lin, C.-Y. Integrin signaling cascades are operational in adult hippocampal synapses and modulate NMDA receptor physiology. J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 834–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, P.M.D.; Humphries, M.J.; Relton, J.; Rothwell, N.J.; Verkhratsky, A.; Gibson, R.M.; Verkhratsky, A. Integrin-binding RGD peptides induce rapid intracellular calcium increases and MAPK signaling in cortical neurons. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2007, 34, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Ethell, I.M. Integrins control dendritic spine plasticity in hippocampal neurons through NMDA receptor and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-mediated actin reorganization. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilja, J.; Ivaska, J. Integrin activity in neuronal connectivity. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs212803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeachie, A.B.; Cingolani, L.A.; Goda, Y.A. Stabilising influence: Integrins in regulation of synaptic plasticity. Neurosci. Res. 2011, 70, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortillo, S.; Elste, A.; Ge, Y.C.; Patil, S.B.; Hsiao, K.; Huntley, G.W.; Davis, R.L.; Benson, D.L. Compensatory redistribution of neuroligins and N-cadherin following deletion of synaptic beta 1-integrin. J. Comp. Neurol. 2012, 520, 2041–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfiridaki, A.; Miyakis, S.; Pappa, C.; Tsirakis, G.; Alegakis, A.; Kotsis, V.; Stathopoulos, E.N.; Alexandrakis, M.G. Circulating osteopontin: A dual marker of bone destruction and angiogenesis in patients with multiple myeloma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2011, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.S.; Jeong, S.-H.; Kim, J.-W.; Choi, Y.S.; Leissner, P.; Brechot, C. Diagnostic Performance of Alpha-Fetoprotein, Protein Induced by Vitamin K Absence, Osteopontin, Dickkopf-1 and Its Combinations for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liu, J.; Ye, Z.; Huang, J.; He, F.; Xiao, W.; Hu, X.; Luo, Z. CaMKII-Mediated CREB Phosphorylation Is Involved in Ca2+-Induced BDNF mRNA Transcription and Neurite Outgrowth Promoted by Electrical Stimulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorovski, Z.; Asrar, S.; Liu, J.; Saw, N.M.N.; Joshi, K.; Cortez, M.A.; Snead, O.C.; Xie, W.; Jia, Z. LIMK1 Regulates Long-Term Memory and Synaptic Plasticity via the Transcriptional Factor CREB. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 35, 1316–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbig, H.; Bidmon, H.J.; Blohm, U.; Zilles, K. Wisteria floribunda agglutinin labeling patterns in the human cortex: A tool for revealing areal borders and subdivisions in parallel with immunocytochemistry. Anat. Embryol. 2001, 203, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma, M.; Kim, J.; Kato, A.; Kawato, S. Src Kinase Dependent Rapid Non-genomic Modulation of Hippocampal Spinogenesis Induced by Androgen and Estrogen. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, M.C.; Figuera-Losada, M.; Rojas, C.; Slusher, B. Targeting the Glutamatergic System for the Treatment of HIV-Associated Neurocognitive Disorders. J. Neuroimmune Pharm. 2013, 8, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitting, S.; Ignatowska-Jankowska, B.; Bull, C.; Skoff, R.P.; Lichtman, A.H.; Wise, L.E.; Fox, M.A.; Su, J.; Medina, A.E.; Krahe, T.E.; et al. Synaptic dysfunction in the hippocampus accompanies learning and memory deficits in human immunodeficiency virus type-1 Tat transgenic mice. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 73, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avdoshina, V.; Caragher, S.; Wenzel, E.D.; Taraballi, F.; Mocchetti, I.; Harry, G.J. The viral protein gp120 decreases the acetylation of neuronal tubulin: Potential mechanism of neurotoxicity. J. Neurochem. 2017, 141, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaney, V.E.; O’Neill, A.M.; Hoefer, M.M.; Maung, R.; Sanchez, A.B.; Kaul, M. IFN beta Protects Neurons from Damage in a Murine Model of HIV-1 Associated Brain Injury. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maung, R.; Hoefer, M.M.; Sanchez, A.B.; Sejbuk, N.E.; Medders, K.E.; Desai, M.K.; Catalan, I.C.; Dowling, C.C.; De Rozieres, C.M.; Garden, G.; et al. CCR5 Knockout Prevents Neuronal Injury and Behavioral Impairment Induced in a Transgenic Mouse Model by a CXCR4-using HIV-1 Glycoprotein 1201. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 1895–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, M.J.; Fiches, G.; Hayashi, T.; Zhu, J.; Fiches, G. Current Strategies for Elimination of HIV-1 Latent Reservoirs Using Chemical Compounds Targeting Host and Viral Factors. Aids Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2019, 35, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.J.; Langford, D.; Masliah, E. HIV and antiretroviral therapy in the brain: Neuronal injury and repair. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-Y.; Choi, J.-S.; Lim, S.-W.; Cha, J.-H.; Chun, M.-H.; Chung, J.-W. Expression of osteopontin mRNA in developing rat brainstem and cerebellum. Cell Tissue Res. 2001, 306, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamiya, M.; Tanabe, S.; Muramatsu, R. Microglia promote the proliferation of neural precursor cells by secreting osteopontin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 513, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnihotri, R.; Crawford, H.C.; Haro, H.; Matrisian, L.M.; Havrda, M.C.; Liaw, L. Osteopontin, a Novel Substrate for Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 (Stromelysin-1) and Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 (Matrilysin). J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 28261–28267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, B.; Schack, L.; Kläning, E.; Sørensen, E.S. Osteopontin Is Cleaved at Multiple Sites Close to Its Integrin-binding Motifs in Milk and Is a Novel Substrate for Plasmin and Cathepsin D. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7929–7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivins, J.K.; Yurchenco, P.D.; Lander, A.D. Regulation of Neurite Outgrowth by Integrin Activation. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 6551–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-L.; Wang, M.-J.; Sudhir, P.-R.; Chen, G.-D.; Chi, C.-W.; Chen, J.-Y. Osteopontin Promotes Integrin Activation through Outside-In and Inside-Out Mechanisms: OPN-CD44V Interaction Enhances Survival in Gastrointestinal Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2089–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Fu, M.G.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A. Methamphetamine potentiates HIV-1 gp120-mediated autophagy via Beclin-1 and Atg5/7 as a pro-survival response in astrocytes. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, W.; Tang, S.-J. HIV-associated synaptic degeneration. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedringhaus, M.; Chen, X.; Dzakpasu, R.; Conant, K. MMPs and Soluble ICAM-5 Increase Neuronal Excitability within In Vitro Networks of Hippocampal Neurons. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lonskaya, I.; Partridge, J.; Lalchandani, R.R.; Chung, A.; Lee, T.; Vicini, S.; Hoe, H.-S.; Lim, S.T.; Conant, K. Soluble ICAM-5, a Product of Activity Dependent Proteolysis, Increases mEPSC Frequency and Dendritic Expression of GluA1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Tian, L.; Smirnov, S.; Vihinen, H.; Llano, O.; Vick, K.; Davis, R.L.; Rivera, C.; Gahmberg, C.G. Interactions between ICAM-5 and beta 1 integrins regulate neuronal synapse formation. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Wei, Y.Y.; Chen, H.T.; Fong, Y.C.; Hsu, C.J.; Tsai, C.H.; Hsu, H.C.; Liu, S.H.; Tang, C.H. Osteopontin Increases Migration and MMP-9 Up-Regulation Via alpha v beta 3 Integrin, FAK, ERK, and NF-kappa B-Dependent Pathway in Human Chondrosarcoma Cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 221, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiya, S.; Givvimani, S.; Bhatnagar, S.; Qipshidze, N.; Tyagi, S.C.; Kumar, A. Osteopontin-stimulated expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 causes cardiomyopathy in the mdx model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 2723–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Jiang, C.; Chen, H.; Nian, Y.; Bai, Z.; Ha, C. The involvement of osteopontin and matrix metalloproteinase- 9 in the migration of endometrial epithelial cells in patients with endometriosis. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2015, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavis, P.; Westbrook, G. Integrins mediate functional pre- and postsynaptic maturation at a hippocampal synapse. Nature 2001, 411, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmud, F.J.; Boucher, T.; Liang, S.; Brown, A.M. Osteopontin and Integrin Mediated Modulation of Post-Synapses in HIV Envelope Glycoprotein Exposed Hippocampal Neurons. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060346
Mahmud FJ, Boucher T, Liang S, Brown AM. Osteopontin and Integrin Mediated Modulation of Post-Synapses in HIV Envelope Glycoprotein Exposed Hippocampal Neurons. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(6):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060346
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmud, Farina J., Thomas Boucher, Shijun Liang, and Amanda M. Brown. 2020. "Osteopontin and Integrin Mediated Modulation of Post-Synapses in HIV Envelope Glycoprotein Exposed Hippocampal Neurons" Brain Sciences 10, no. 6: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060346
APA StyleMahmud, F. J., Boucher, T., Liang, S., & Brown, A. M. (2020). Osteopontin and Integrin Mediated Modulation of Post-Synapses in HIV Envelope Glycoprotein Exposed Hippocampal Neurons. Brain Sciences, 10(6), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060346





