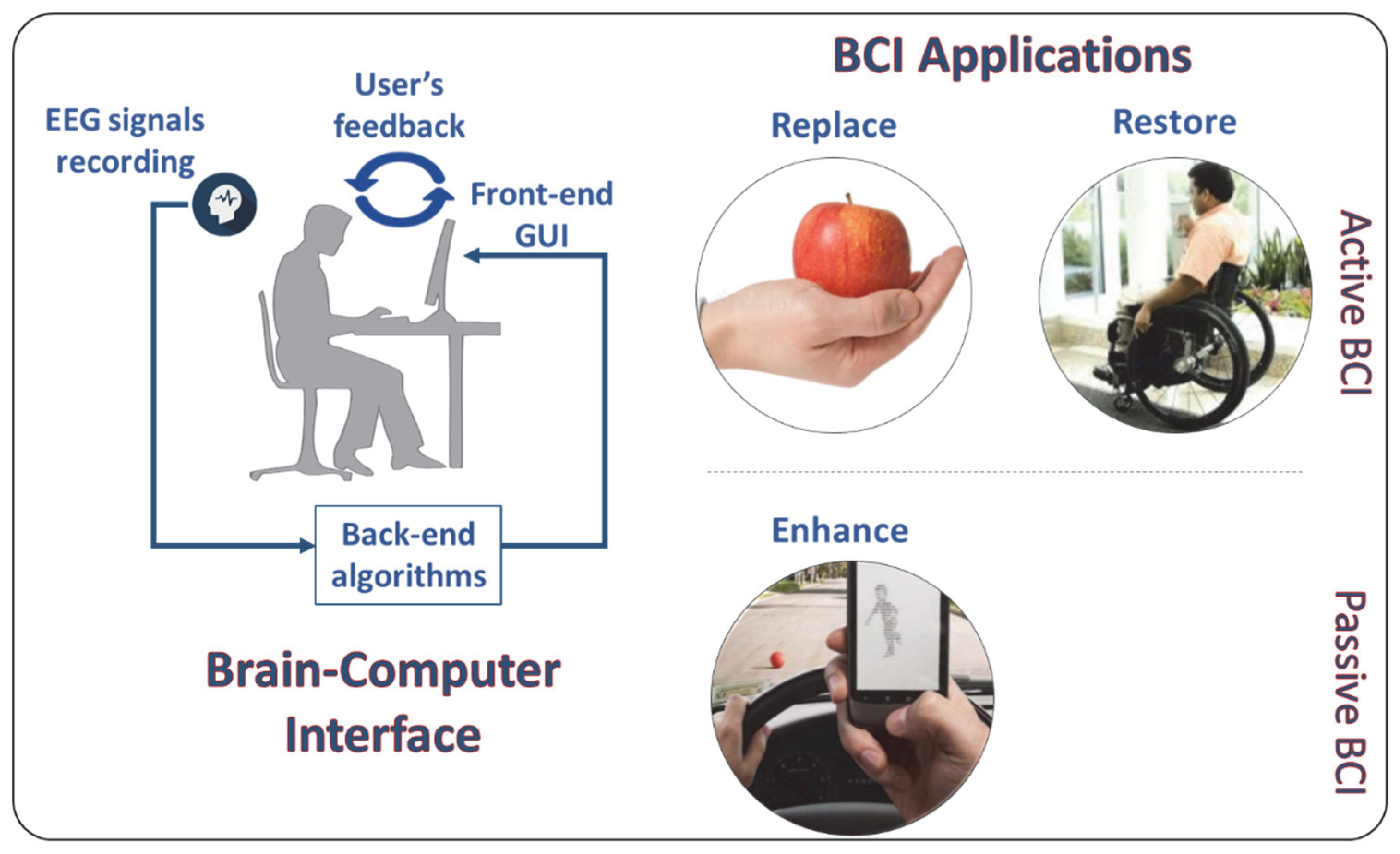
Brain–Computer Interfaces: Toward a Daily Life Employment
Abstract
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N.; McFarland, D.J.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Vaughan, T.M. Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonathan Wolpaw and Elizabeth Winter Wolpaw, Brain-Computer Interfaces—Jonathan Wolpaw; Elizabeth Winter Wolpaw—Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 1–424.
- Abiri, R.; Borhani, S.; Sellers, E.W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, X. A comprehensive review of EEG-based brain-computer interface paradigms. J. Neural Eng. 2019, 16, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloise, F.; Aricò, P.; Schettini, F.; Salinari, S.; Mattia, D.; Cincotti, F. Asynchronous gaze-independent event-related potential-based brain-computer interface. Artif. Intell. Med. 2013, 59, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichiorri, F.; Morone, G.; Petti, M.; Toppi, J.; Pisotta, I.; Molinari, M.; Paolucci, S.; Inghilleri, M.; Astolfi, L.; Cincotti, F.; et al. Brain-computer interface boosts motor imagery practice during stroke recovery. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 77, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Flumeri, G.; Borghini, G.; Aricò, G.; Sciaraffa, P.; Lanzi, N.; Pozzi, P.; Vignali, S.; Lantieri, V.; Bichicchi, C.; Simone, A.; et al. EEG-Based Mental Workload Neurometric to Evaluate the Impact of Different Traffic and Road Conditions in Real Driving Settings. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankertz, B.; Acqualagna, L.; Dähne, S.; Haufe, S.; Schultze-Kraft, M.; Sturm, I.; Ušćumlic, M.; Wenzel, M.A.; Curio, G.; Müller, K.R. The Berlin brain-computer interface: Progress beyond communication and control. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartocci, G.; Maglione, A.G.; Vecchiato, G.; Di Flumeri, G.; Colosimo, A.; Scorpecci, A.; Marsella, P.; Giannantonio, S.; Malerba, P.; Borghini, G.; et al. Mental workload estimations in unilateral deafened children. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, Milan, Italy, 30 August–3 September 2015; pp. 1654–1657. [Google Scholar]
- Zander, T.O.; Kothe, C. Towards Passive Brain-Computer Interfaces: Applying Brain-Computer Interface Technology to Human-Machine Systems in General. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeriani, D.; Cinel, C.; Poli, R. Brain-computer interfaces for human augmentation. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchiato, G.; Borghini, G.; Aricò, P.; Graziani, I.; Maglione, A.G.; Cherubino, P.; Babiloni, F. Investigation of the effect of EEG-BCI on the simultaneous execution of flight simulation and attentional tasks. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2016, 54, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astolfi, L.; Toppi, J.; Borghini, G.; Vecchiato, G.; He, E.J.; Roy, A.; Cincotti, F.; Salinari, S.; Mattia, D.; He, B.; et al. Cortical activity and functional hyperconnectivity by simultaneous EEG recordings from interacting couples of professional pilots. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 4752–4755. [Google Scholar]
- Sciaraffa, N.; Borghini, G.; Aricò, P.; di Flumeri, G.; Colosimo, A.; Bezerianos, A.; Thakor, N.V.; Babiloni, F. Brain Interaction during Cooperation: Evaluating Local Properties of Multiple-Brain Network. Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, T.O.; Jatzev, S. Context-aware Brain-Computer Interfaces: Exploring the Information Space of User, Technical System and Environment. J. Neural Eng. 2012, 9, 016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghini, G.; Aricò, P.; di Flumeri, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Colosimo, A.; Herrero, M.-T.; Bezerianos, A.; Thakor, N.V.; Babiloni, F. A new perspective for the training assessment: Machine learning-based neurometric for augmented user’s evaluation. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Flumeri, G.; De Crescenzio, F.; Berberian, B.; Ohneiser, O.; Kramer, J.; Aricò, P.; Borghini, G.; Babiloni, F.; Bagassi, S.; Piastra, S. Brain–Computer Interface-Based Adaptive Automation to Prevent Out-Of-The-Loop Phenomenon in Air Traffic Controllers Dealing With Highly Automated Systems. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, M.; Di Flumeri, G.; Aricò, P.; Sciaraffa, N.; Babiloni, F.; Borghini, G. Neurophysiological Vigilance Characterisation and Assessment: Laboratory and Realistic Validations Involving Professional Air Traffic Controllers. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezeika, A.; Benda, M.; Stawicki, P.; Gembler, F.; Saboor, A.; Volosyak, I. Brain–computer interface spellers: A review. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schettini, F.; Aloise, F.; Aricò, P.; Salinari, S.; Mattia, D.; Cincotti, F. Self-calibration algorithm in an asynchronous P300-based brain–computer interface. J. Neural Eng. 2014, 11, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aricó, P.; Borghini, G.; Di Flumeri, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Colosimo, A.; Babiloni, F. Passive BCI in operational environments: Insights, recent advances, and future trends. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietro, A.; Gianluca, B.; Gianluca, d.; Nicolina, S.; Fabio, B. Passive BCI Beyond the Lab: Current Trends and Future Directions. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Lühmann, A.; Müller, K.-R. Headgear For Mobile Neurotechnology: Looking Into Alternatives For Eeg And Nirs Probes. In Proceedings of the Berlin Brain Computer Interface View Project M3ba: Mobile, Modular, Multimodal Biosignal Acquisition: Hybrid Eeg-Nirs For Neurotechnology Out Of The Lab View Project pr, Graz, Austria, 18–22 September 2017; pp. 496–501. [Google Scholar]
- Tallgren, P.; Vanhatalo, S.; Kaila, K.; Voipio, J. Evaluation of commercially available electrodes and gels for recording of slow EEG potentials. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2005, 116, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Gordo, M.A.; Sanchez Morillo, D.; Pelayo Valle, F. Dry EEG electrodes. Sensors 2014, 14, 12847–12870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Flumeri, G.; Aricò, P.; Borghini, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Di Florio, A.; Babiloni, F. The dry revolution: Evaluation of three different eeg dry electrode types in terms of signal spectral features, mental states classification and usability. Sensors 2019, 19, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aricò, P.; Sciaraffa, N.; Babiloni, F. Brain–Computer Interfaces: Toward a Daily Life Employment. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10030157
Aricò P, Sciaraffa N, Babiloni F. Brain–Computer Interfaces: Toward a Daily Life Employment. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(3):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10030157
Chicago/Turabian StyleAricò, Pietro, Nicolina Sciaraffa, and Fabio Babiloni. 2020. "Brain–Computer Interfaces: Toward a Daily Life Employment" Brain Sciences 10, no. 3: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10030157
APA StyleAricò, P., Sciaraffa, N., & Babiloni, F. (2020). Brain–Computer Interfaces: Toward a Daily Life Employment. Brain Sciences, 10(3), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10030157






