Predicting Factors of Functional Outcome in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Admitted to Neuro-Intensive Care Unit—A Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
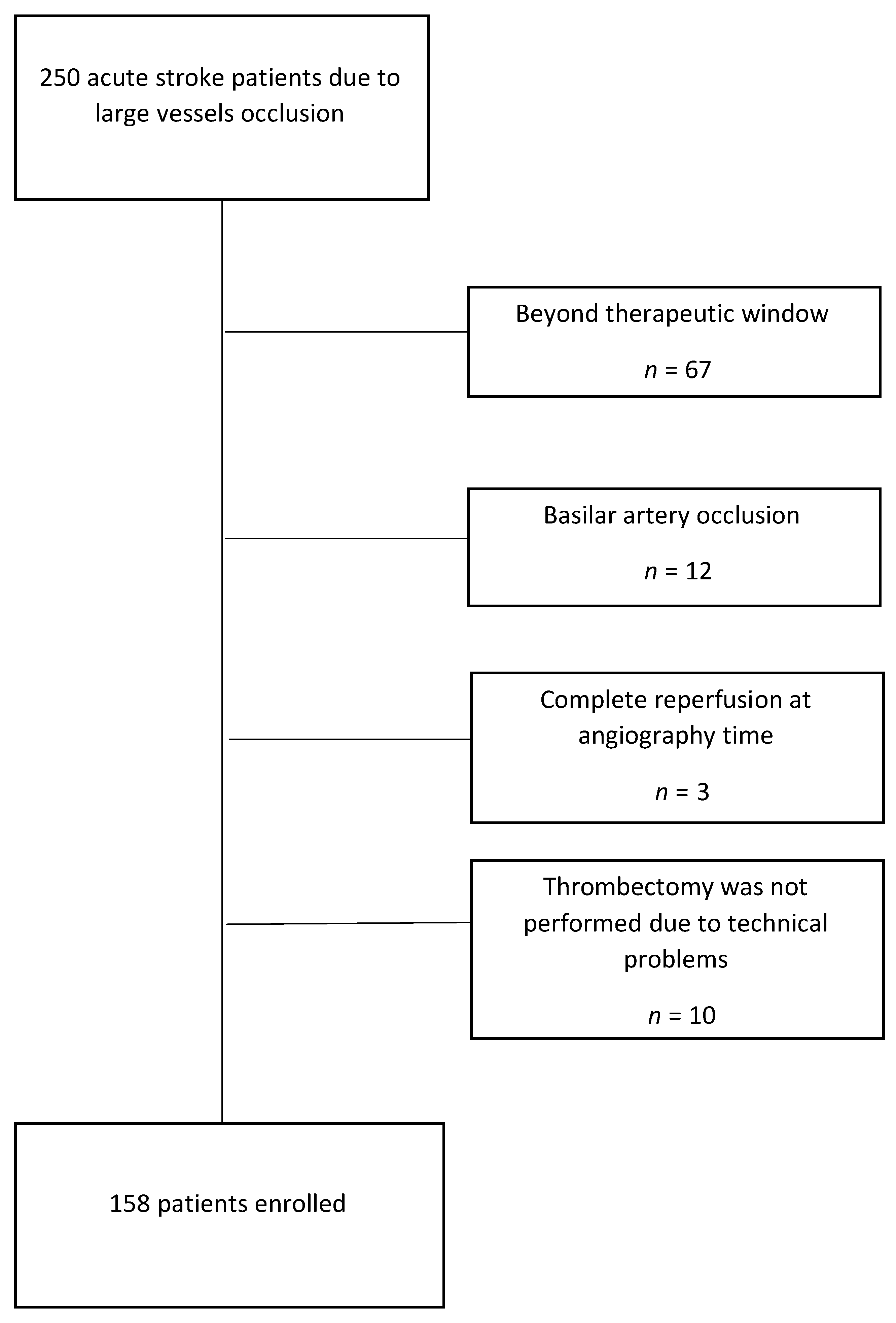
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Predictors of Independency at 3 Months
3.2. Predictors of Independency at 6 Months
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1736–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meschia, J.F.; Bushnell, C.; Boden-Albala, B.; Braun, L.T.; Bravata, D.M.; Chaturvedi, S.; Creager, M.A.; Eckel, R.H.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Fornage, M.; et al. Guidelines for the primary prevention of stroke: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroske Association. Stroke 2014, 45, 3754–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacke, W.; Kaste, M.; Bluhmki, E.; Brozman, M.; Dávalos, A.; Guidetti, D.; Larrue, V.; Lees, K.R.; Medeghri, Z.; Machnig, T.; et al. Thrombolysis with Alteplase 3 to 4.5 Hours after Acute Ischemic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1317–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berkhemer, O.A.; Fransen, P.S.S.; Beumer, D.; van den Berg, L.A.; Lingsma, H.F.; Yoo, A.J.; Schonewille, W.J.; Vos, J.A.; Nederkoorn, P.J.; Wermer, M.J.H.; et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, B.C.V.; Donnan, G.A.; Lees, K.R.; Hacke, W.; Khatri, P.; Hill, M.D.; Goyal, M.; Mitchell, P.J.; Saver, J.L.; Diener, H.; et al. Endovascular stent thrombectomy: The new standard of care for large vessel ischaemic stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Demchuk, A.M.; Menon, B.K.; Eesa, M.; Rempel, J.L.; Thornton, J.; Roy, D.; Jovin, T.G.; Willinsky, R.A.; Sapkota, B.L.; et al. Randomized Assessment of Rapid Endovascular Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saver, J.L.; Goyal, M.; Bonafe, A.; Diener, H.; Levy, E.I.; Pereira, V.M.; Albers, G.W.; Cognard, C.; Cohen, D.J.; Hacke, W.; et al. Stent-Retriever Thrombectomy after Intravenous t-PA vs.t-PA Alone in Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2285–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jovin, T.G.; Chamorro, A.; Cobo, E.; de Miquel, M.A.; Molina, C.A.; Rovira, A.; Román, L.S.; Serena, J.; Abilleira, S.; Ribó, M.; et al. Thrombectomy within 8 Hours after Symptom Onset in Ischemic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2296–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stroke Unit Trialists’ Collaboration. Organised Inpatient (Stroke Unit) Care for Stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, CD000197. Available online: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD000197.pub3/full (accessed on 26 November 2020). [CrossRef]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: 2019 Update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2019, 50, e344–e418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringelstein, E.B.; Chamorro, A.; Kaste, M.; Langhorne, P.; Leys, D.; Lyrer, P.; Thijs, V.; Thomassen, L.; Toni, D.; ESO Stroke Unit Certification Committee. European Stroke Organisation recommendations to establish a stroke unit and stroke center. Stroke 2013, 44, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Venkatasubba Rao, C.P.; Suarez, J.I. Management of Stroke in the Neurocritical Care Unit. Continuum (Minneap. Minn.) 2018, 24, 1658–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faigle, R.; Marsh, E.B.; Llinas, R.H.; Urrutia, V.C.; Gottesman, R.F. ICAT: A simple score predicting critical care needs after thrombolysis in stroke patients. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulder, M.J.H.L.; Ergezen, S.; Lingsma, H.F.; Berkhemer, O.A.; Fransen, P.S.S.; Beumer, D.; van den Berg, L.A.; Nijeholt, G.L.À.; Emmer, B.J.; van der Worp, H.B.; et al. Baseline Blood Pressure Effect on the Benefit and Safety of Intra-Arterial Treatment in MR CLEAN (Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial of Endovascular Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke in the Netherlands). Stroke 2017, 48, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.C.V.; Mitchell, P.J.; Churilov, L.; Yassi, N.; Kleinig, T.J.; Dowling, R.J.; Yan, B.; Bush, S.J.; Dewey, H.M.; Thijs, V.; et al. Tenecteplase versus Alteplase before Thrombectomy for Ischemic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.; Després, J.; Fullerton, H.J.; et al. Executive Summary: Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics--2016 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 133, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Menon, B.K.; van Zwam, W.H.; Dippel, D.W.J.; Mitchell, P.J.; Demchuk, A.M.; Dávalos, A.; Majoie, C.B.L.M.; van der Lugt, A.; de Miquel, M.A.; et al. Endovascular thrombectomy after large-vessel ischaemic stroke: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from five randomised trials. Lancet 2016, 387, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönenberger, S.; Möhlenbruch, M.; Pfaff, J.; Mundiyanapurath, S.; Kieser, M.; Bendszus, M.; Hacke, W.; Bösel, J. Sedation vs. Intubation for Endovascular Stroke TreAtment (SIESTA)—A randomized monocentric trial. Int. J. Stroke 2015, 10, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jia, L.; Fang, F.; Ma, L.; Cai, B.; Faramand, A. General Anesthesia Versus Conscious Sedation for Intracranial Mechanical Thrombectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schönenberger, S.; Uhlmann, L.; Hacke, W.; Schieber, S.; Mundiyanapurath, S.; Purrucker, J.; Nagel, S.; Klose, C.; Pfaff, J.; Bendszus, M.; et al. Effect of Conscious Sedation vs General Anesthesia on Early Neurological Improvement Among Patients with Ischemic Stroke Undergoing Endovascular Thrombectomy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 1986–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnston, K.C.; Bruno, A.; Pauls, Q.; Hall, C.E.; Barrett, K.M.; Barsan, W.; Fansler, A.; van de Bruinhorst, K.; Janis, S.; Durkalski-Mauldin, V.L.; et al. Intensive vs Standard Treatment of Hyperglycemia and Functional Outcome in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: The SHINE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 322, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribo, M.; Molina, C.; Montaner, J.; Rubiera, M.; Delgado-Mederos, R.; Arenillas, J.F.; Quintana, M.; Alvarez-Sabín, J. Acute hyperglycemia state is associated with lower tPA-induced recanalization rates in stroke patients. Stroke 2005, 36, 1705–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Palesch, Y.Y.; Barsan, W.G.; Hanley, D.F.; Hsu, C.Y.; Martin, R.L.; Moy, C.S.; Silbergleit, R.; Steiner, T.; Suarez, J.I.; et al. Intensive Blood-Pressure Lowering in Patients with Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, H.V.; Vivas, M.F.; Ruiz, R.N.; Martínez, J.R.; Navaridas, B.G.; Villa, M.G.; Lázaro, C.L.; Rubio, R.J.; Ortiz, A.M.; Lacal, L.A.; et al. Association between post-procedural hyperoxia and poor functional outcome after mechanical thrombectomy for ischemic stroke: An observational study. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popović, N.; Stefanović-Budimkić, M.; Mitrović, N.; Urošević, A.; Milošević, B.; Pelemiš, M.; Jevtović, D.; Beslać-Bumbaširević, L.; Jovanović, D. The frequency of poststroke infections and their impact on early stroke outcome. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 22, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, J.D.; Kaur, A.; Jyotsna, R.; Sylaja, P.N.; Vijaya, P.; Padma, M.V.; Venkateswaralu, K.; Sukumaran, S.; Mathew, R.; Kaur, P.; et al. Complications in acute stroke in India (CAST-I): A multicenter study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2012, 21, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Yoo, A.J.; Khatri, P.; Tomsick, T.A.; von Kummer, R.; Saver, J.L.; Marks, M.P.; Prabhakaran, S.; Kallmes, D.F.; Fitzsimmons, B.M.; et al. Recommendations on angiographic revascularization grading standards for acute ischemic stroke: A consensus statement. Stroke 2013, 44, 2650–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martino, R.; Foley, N.; Bhogal, S.; Diamant, N.; Speechley, M.; Teasell, R. Dysphagia after stroke: Incidence, diagnosis, and pulmonary complications. Stroke 2005, 36, 2756–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalra, L.; Hodsoll, J.; Irshad, S.; Smithard, D.; Manawadu, D.; STROKE-INF Investigators. Association between nasogastric tubes, pneumonia, and clinical outcomes in acute stroke patients. Neurology 2016, 87, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brogan, E.; Langdon, C.; Brookes, K.; Budgeon, C.; Blacker, D. Can’t swallow, can’t transfer, can’t toilet: Factors predicting infections in the first week post stroke. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eltringham, S.A.; Kilner, K.; Gee, M.; Sage, K.; Bray, B.D.; Smith, C.J.; Pownall, S. Factors Associated with Risk of Stroke-Associated Pneumonia in Patients with Dysphagia: A Systematic Review. Dysphagia 2020, 35, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joundi, R.A.; Saposnik, G.; Martino, R.; Fang, J.; Porter, J.; Kapral, M.K. Outcomes among patients with direct enteral vs nasogastric tube placement after acute stroke. Neurology 2018, 90, e544–e552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, M.; Coccetti, A.; Murdoch, A.; Cardell, E. The impact of aspiration pneumonia and nasogastric feeding on clinical outcomes in stroke patients: A retrospective cohort study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2018, 27, e235–e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, G.; Huang, C.; Chen, W.; Xu, C.; Liu, M.; Xu, H.; Cai, C. Risk factors for decompressive craniectomy after endovascular treatment in acute ischemic stroke. Neurosurg. Rev. 2020, 43, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajjar, K.; Kerr, D.M.; Lees, K.R. Thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. J. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 54, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaghi, S.; Willey, J.Z.; Cucchiara, B.; Goldstein, J.N.; Gonzales, N.R.; Khatri, P.; Kim, L.J.; Mayer, S.A.; Sheth, K.N.; Schwamm, L.H.; et al. Treatment and Outcome of Hemorrhagic Transformation after Intravenous Alteplase in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2017, 48, e343–e361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, C.; Cullell, N.; Torres-Águila, N.; Muiño, E.; Bustamante, A.; Dávalos, A.; López-Cancio, E.; Ribó, M.; Molina, C.A.; Giralt-Steinhauer, E.; et al. Validation of a clinical-genetics score to predict hemorrhagic transformations after rtPA. Neurology 2019, 93, e851–e863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychev, R.; Saver, J.L.; Jahan, R.; Nogueira, R.G.; Goyal, M.; Pereira, V.M.; Gralla, J.; Levy, E.I.; Yavagal, D.R.; Cognard, C.; et al. The impact of general anesthesia, baseline ASPECTS, time to treatment, and IV tPA on intracranial hemorrhage after neurothrombectomy: Pooled analysis of the SWIFT PRIME, SWIFT, and STAR trials. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2020, 12, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, J.C.; Cho, Y.; Kim, B.J.; Bae, H.; Kim, D.; Ryu, W.; Cha, J.; Kim, D.H.; et al. Simple Estimates of Symptomatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Risk and Outcome after Intravenous Thrombolysis Using Age and Stroke Severity. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.J.; Park, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.; Jeong, H.; Park, K.; Rha, J.; Yoon, B.; Ko, S. Blood pressure variability and hemorrhagic transformation in patients with successful recanalization after endovascular recanalization therapy: A retrospective observational study. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 85, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, N.H.; Silverman, A.; Strander, S.M.; Kodali, S.; Wang, A.; Sansing, L.H.; Schindler, J.L.; Falcone, G.J.; Gilmore, E.J.; Jasne, A.S.; et al. Fixed Compared with Autoregulation-Oriented Blood Pressure Thresholds after Mechanical Thrombectomy for Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gariel, F.; Lapergue, B.; Bourcier, R.; Berge, J.; Barreau, X.; Mazighi, M.; Kyheng, M.; Labreuche, J.; Fahed, R.; Blanc, R.; et al. Mechanical Thrombectomy Outcomes with or without Intravenous Thrombolysis. Stroke 2018, 49, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świtońska, M.; Słomka, A.; Korbal, P.; Piekuś-Słomka, N.; Sinkiewicz, W.; Sokal, P.; Żekanowska, E. Association of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio with Treatment Modalities of Acute Ischaemic Stroke: A Pilot Study. Medicina (Kaunas) 2019, 55, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diener, H.; Foerch, C.; Riess, H.; Röther, J.; Schroth, G.; Weber, R. Treatment of acute ischaemic stroke with thrombolysis or thrombectomy in patients receiving anti-thrombotic treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lieschke, F.; Schaefer, J.; Wang, X.; Foerch, C.; van Leyen, K. Dual Antiplatelet Therapy Increases Hemorrhagic Transformation Following Thrombolytic Treatment in Experimental Stroke. Stroke 2019, 50, 3650–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Overall | Poor Outcomes at 90 Days | Good Outcomes at 90 Days | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 158 | 107 (67.72%) | 51 (32.28%) | |
| Age | 73.80 ± 12.60 | 76.33 ± 11.52 | 68.42 ± 13.19 | <0.001 |
| Females | 86 (54.43%) | 59/107 (55.14%) | 27/51 (52.94%) | 0.795 |
| Diabetes | 23 (14.56%) | 20/107 (18.69%) | 3/51 (5.88%) | 0.051 |
| Hypertension | 63 (39.87%) | 43/107 (40.19%) | 20/51 (39.22%) | 10.000 |
| Smoking | 16 (12.21%) | 11/107 (12.36%) | 5/51 (11.90%) | 0.941 |
| Dyslipidemia | 22 (13.92%) | 17/107 (15.89%) | 5/51 (9.80%) | 0.302 |
| AF | 16 (10.13%) | 10/107 (9.35%) | 6/51 (11.76%) | 0.637 |
| Seizures | 2 (1.27%) | 2/107 (1.87%) | 0 | - |
| AED | 1 (0.63%) | 0 | 1/51 (1.96%) | - |
| NGT at discharge | 11 (6.96%) | 9/107 (8.41%) | 2/51 (3.92%) | 0.505 |
| NGT removal | 42 (26.58%) | 20/107 (18.69%) | 22/51 (43.14%) | 0.001 |
| Tracheostomy | 15 (9.55%) | 13/106 (12.26%) | 2/51 (3.92%) | 0.146 |
| Intubation | 117 (74.05%) | 84/107 (78.50%) | 33/51 (64.71%) | 0.064 |
| IV Thrombolysis | 81 (51.27%) | 49/107 (45.79%) | 32/51 (62.75%) | 0.046 |
| DHC | 5 (3.16%) | 3/107 (2.80%) | 2/51 (3.92%) | 0.658 |
| Pneumonia | 17 (10.90%) | 15/106 (14.15%) | 2/50 (4.00%) | 0.095 |
| Sepsis | 1 (0.63%) | 1/107 (0.93%) | 0 | - |
| Septic Shock | - | - | - | - |
| Hemorrhagic transformation | 41 (26.11%) | 30/106 (28.30%) | 11/51 (21.57%) | 0.368 |
| HT1-PH1 | 16 (10.13%) | 10/107 (9.35%) | 6/51 (11.76%) | 0.779 |
| PH2 | 11 (6.96%) | 9/107 (8.41%) | 2/51 (3.92%) | 0.505 |
| 24 h vasopressors infusion | 13 (8.23%) | 11/107 (10.28%) | 2/51 (3.92%) | 0.226 |
| NIHSS | 16.74 ± 5.58 | 18.48 ± 4.72 | 13.07 ± 11.52 | <0.001 |
| Mortality | 40 (25.32%) | 40 (100%) | - | - |
| mTICI 2b/3 | 135 (85.44%) | 84/107 (78.50%) | 50/51 (98.04%) | 0.001 |
| Site of occlusion | 0.090 | |||
| MCA | 111 (70.25%) | 72/107 (67.29%) | 39/51 (76.47%) | |
| ICA | 47 (29.75%) | 35/107 (32.71%) | 12/51 (23.53%) | |
| Left-side occlusion | 88 (55.70%) | 63/107 (58.88%) | 25/51 (49.02%) | 0.243 |
| Mechanical ventilation (n. pts) | 92 (58.23%) | 64/107 (59.81%) | 28/51 (54.90%) | 0.607 |
| Mechanical ventilation (days) | 2.05 ± 3.84 | 2.28 ± 3.64 | 1.48 ± 4.31 | 0.039 |
| LOS-ICU | 3.35 ± 4.74 | 3.69 ± 4.64 | 2.56 ± 4.93 | <0.001 |
| LOS-H | 13.31 ± 13.89 | 13.75 ± 13.56 | 12.27 ± 14.75 | 0.39 |
| Hb-ECU | 13.23 ± 1.66 | 13.24 ± 2.11 | 13.21 ± 1.66 | 0.551 |
| Hb-ICU | 12.33 ± 1.85 | 12.31 ± 1.87 | 12.38 ± 1.82 | 0.961 |
| Trop+ (>0.00) | 60 (37.97%) | 46/107 (42.99%) | 14/51 (27.45%) | 0.060 |
| Var. | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (older) | 0.97 | 0.92–1.02 | 0.247 |
| Female | 0.69 | 0.23–2.03 | 0.510 |
| IV Thrombolysis | 3.78 | 1.20–11.90 | 0.023 |
| NGT-removal | 3.32 | 1.04–10.59 | 0.042 |
| LOS-ICU | 0.90 | 0.69–1.18 | 0.467 |
| mTICI 2b/3 | 5.87 | 0.63–54.54 | 0.120 |
| Mechanical ventilation | 1.02 | 0.74–1.42 | 0.866 |
| Baseline NIHSS | 0.72 | 0.61–.85 | <0.001 |
| Characteristics | Poor Outcome at 180 Days | Good Outcome at 180 Days | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| N | 93 (58.86%) | 65 (41.14%) | |
| Age | 76.92 ± 11.46 | 69.19 ± 12.87 | <0.001 |
| Females | 51/93 (54.84%) | 35/65 (53.85%) | 0.902 |
| Diabetes | 19/93 (20.43%) | 4/65 (6.15%) | 0.012 |
| Hypertension | 40/93 (43.01%) | 23/65 (35.38%) | 0.335 |
| Dyslipidemia | 17/93 (18.28%) | 5/65 (7.69%) | 0.065 |
| AF | 11/93 (11.83%) | 5/65 (7.69%) | 0.437 |
| AED | 0 | 1 (1.54%) | - |
| Seizures | 0 | 2/65 (3.08%) | - |
| NGT at discharge | 9/93 (9.68%) | 2/65 (3.08%) | 0.126 |
| NGT removal | 17/93 (18.28%) | 25/65 (38.46%) | 0.005 |
| Tracheostomy | 8/92 (8.70%) | 7/65 (10.77%) | 0.663 |
| Intubation | 74/93 (79.57%) | 43/65 (66.15%) | 0.058 |
| IV Thrombolysis | 44/93 (47.31%) | 37/65 (56.92%) | 0.234 |
| DHC | 2/93 (2.15%) | 3/65 (4.62%) | 0.403 |
| Pneumonia | 13/92 (14.13%) | 4/64 (6.25%) | 0.190 |
| Sepsis | 1/93 (1.08%) | 0 | - |
| Septic Shock | 0 | 0 | - |
| HT | 30/92 (32.61%) | 11/65 (16.92%) | 0.028 |
| HT1-PH1 | 10/92 (10.75%) | 6/65 (9.23%) | 0.755 |
| PH2 | 9/92 (9.68%) | 2/65 (3.08%) | 0.109 |
| 24h vasopressors infusion | 8/93 (8.60%) | 5/65 (7.69%) | 10.000 |
| NIHSS | 18.83 ± 4.74 | 13.73 ± 5.35 | <0.001 |
| mTICI 2b/3 | 72/93 (77.42%) | 62/65 (95.38%) | 0.001 |
| Site of occlusion | 0.238 | ||
| MCA | 62/93 (66.67%)) | 16/65 (24.62%) | |
| ICA | 31/93 (33.33%) | 16/65 (24.62%) | |
| Left-side occlusion | 54/93 (58.06%) | 34/65 (52.31%) | 0.473 |
| Mechanical ventilation (n. pts) | 57/93 (61.29%) | 35/65 (53.85%) | 0.350 |
| Mechanical ventilation (days) | 1.87 ± 2.69 | 2.37 ± 5.29 | 0.256 |
| LOS-ICU | 3.13 ± 3.44 | 3.48 ± 6.03 | 0.056 |
| LOS-H | 13.32 ± 14.33 | 13.29 ± 13.29 | 0.258 |
| Hb-ECU | 13.11 ± 2.15 | 13.41 ± 1.68 | 0.598 |
| Hb-ICU | 12.20 ± 1.93 | 12.52 ± 1.72 | 0.355 |
| Trop + (>0.00) | 37/93 (39.78%) | 23/65 (35.38%) | 0.575 |
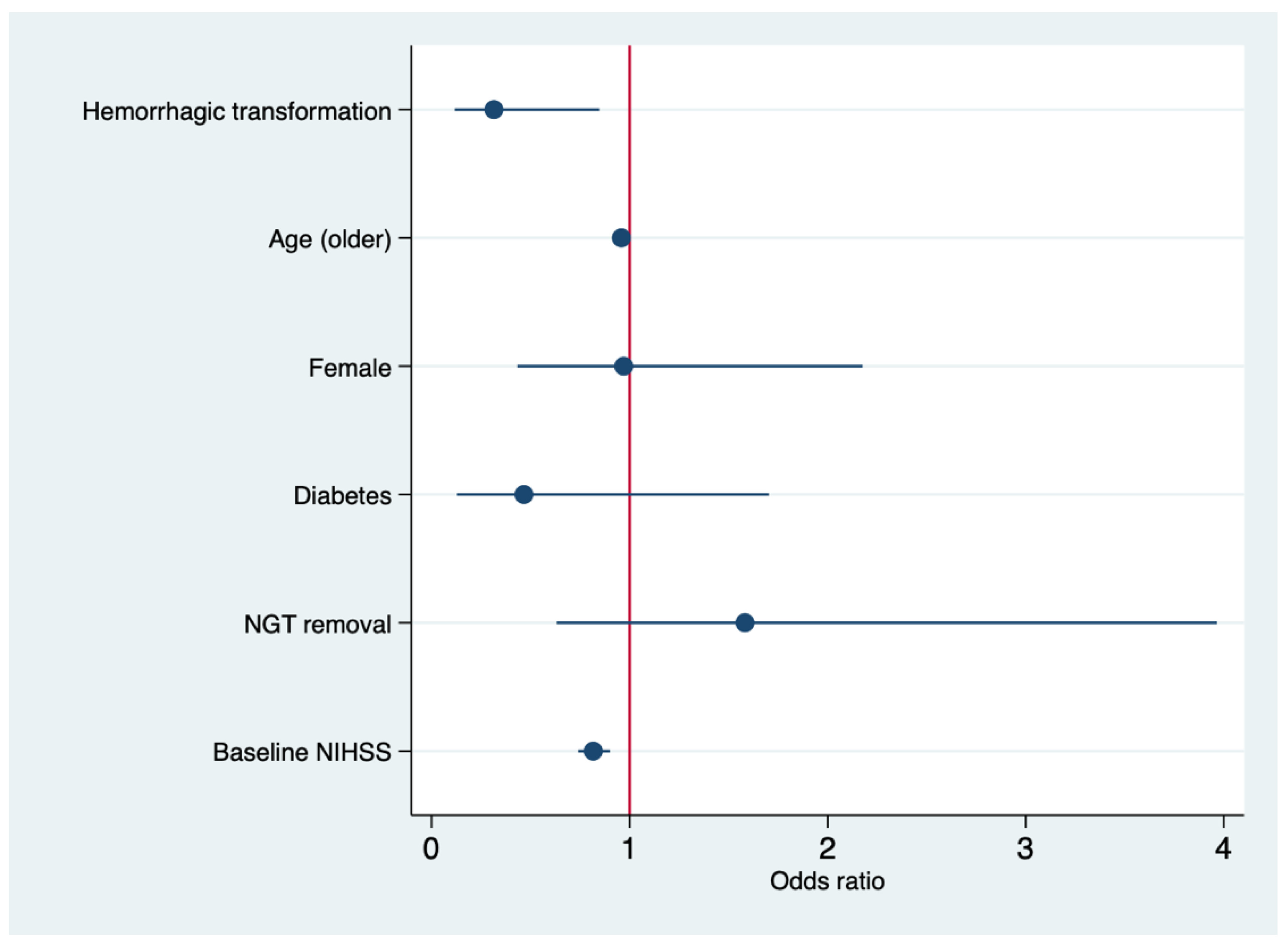
| var. | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (older) | 0.95 | 0.92–0.99 | 0.020 |
| Female | 0.97 | 0.43–2.17 | 0.965 |
| Diabetes | 0.46 | 0.12–1.75 | 0.248 |
| Hemorrhagic transformation | 0.31 | 0.11–0.84 | 0.022 |
| NGT-removal | 1.58 | 0.63–3.96 | 0.328 |
| mTICI2b/3 | 7.86 | 1.65–37.39 | 0.010 |
| Baseline NIHSS | 0.81 | 0.74–0.90 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pilato, F.; Silva, S.; Valente, I.; Distefano, M.; Broccolini, A.; Brunetti, V.; Caliandro, P.; Marca, G.D.; Di Iorio, R.; Frisullo, G.; et al. Predicting Factors of Functional Outcome in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Admitted to Neuro-Intensive Care Unit—A Prospective Cohort Study. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120911
Pilato F, Silva S, Valente I, Distefano M, Broccolini A, Brunetti V, Caliandro P, Marca GD, Di Iorio R, Frisullo G, et al. Predicting Factors of Functional Outcome in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Admitted to Neuro-Intensive Care Unit—A Prospective Cohort Study. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(12):911. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120911
Chicago/Turabian StylePilato, Fabio, Serena Silva, Iacopo Valente, Marisa Distefano, Aldobrando Broccolini, Valerio Brunetti, Pietro Caliandro, Giacomo Della Marca, Riccardo Di Iorio, Giovanni Frisullo, and et al. 2020. "Predicting Factors of Functional Outcome in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Admitted to Neuro-Intensive Care Unit—A Prospective Cohort Study" Brain Sciences 10, no. 12: 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120911
APA StylePilato, F., Silva, S., Valente, I., Distefano, M., Broccolini, A., Brunetti, V., Caliandro, P., Marca, G. D., Di Iorio, R., Frisullo, G., Monforte, M., Morosetti, R., Piano, C., Calandrelli, R., Capone, F., Alexandre, A., Pedicelli, A., Colosimo, C., & Caricato, A. (2020). Predicting Factors of Functional Outcome in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Admitted to Neuro-Intensive Care Unit—A Prospective Cohort Study. Brain Sciences, 10(12), 911. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120911







