Impaired Expression of Tetraspanin 32 (TSPAN32) in Memory T Cells of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ex Vivo Study
2.1.1. Cell Isolation and Real-Time PCR
2.1.2. Real-Time PCR
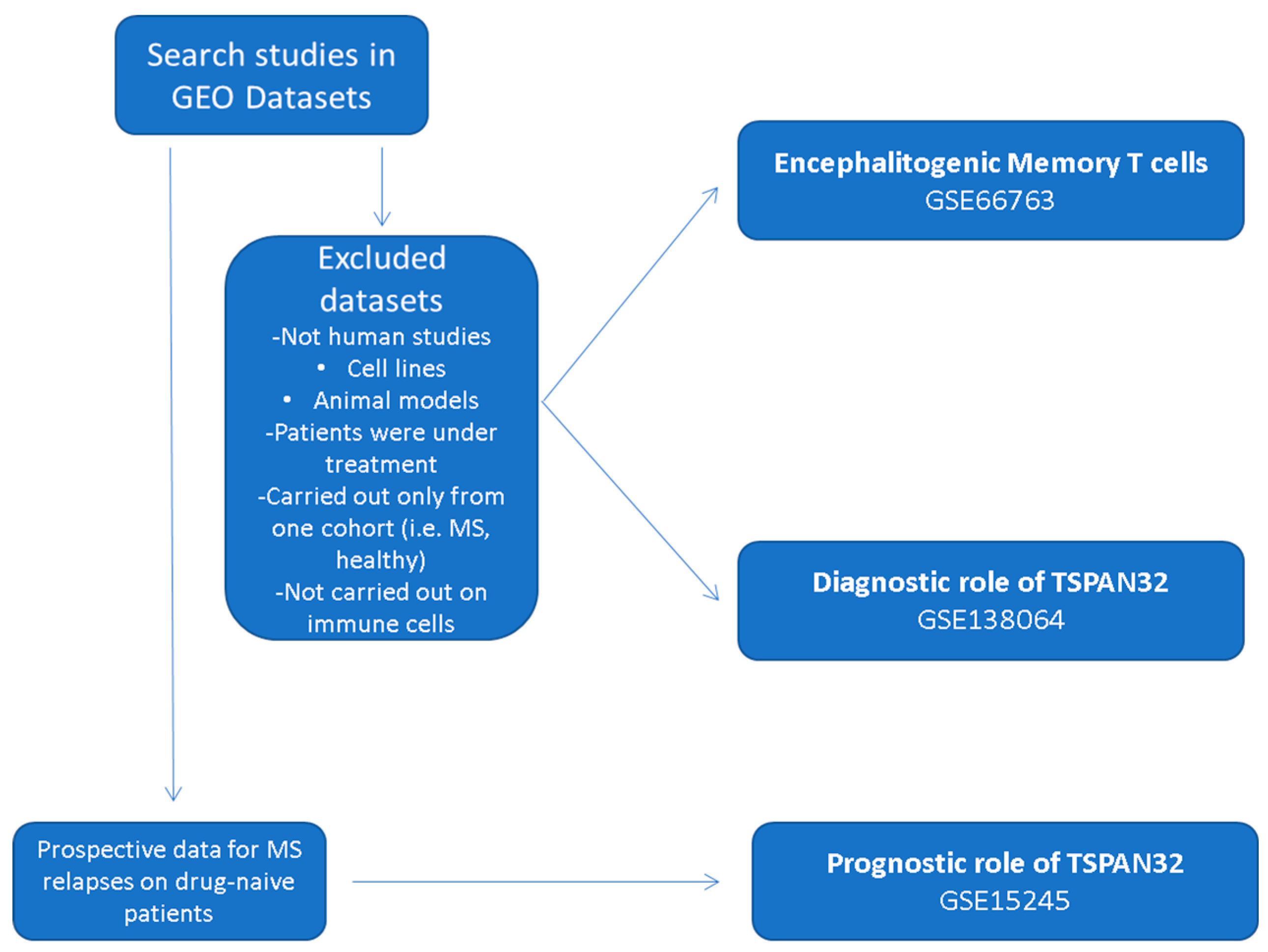
2.2. In Silico Analysis
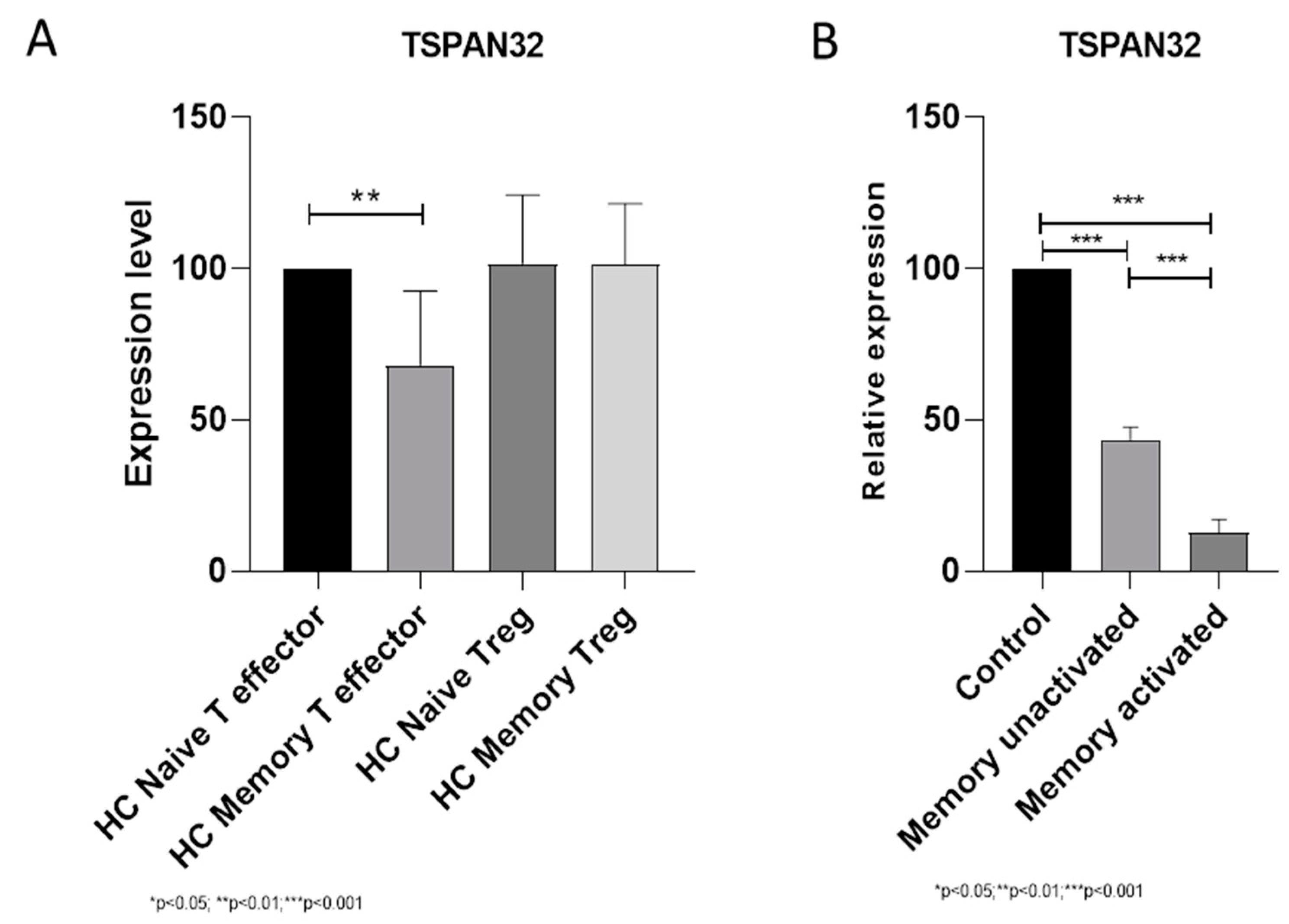
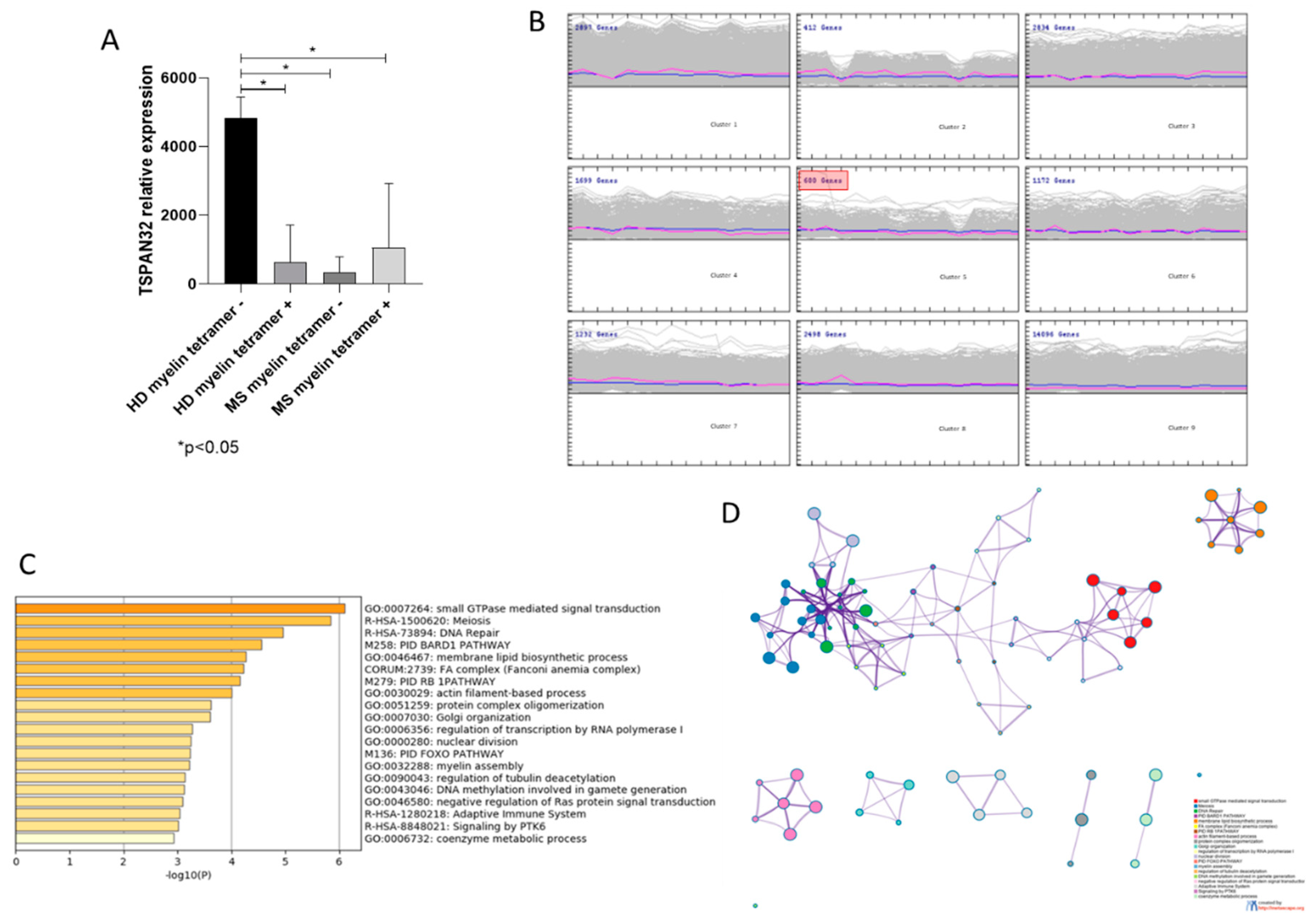
2.2.1. TSPAN32 in Memory T Cells from MS Patients
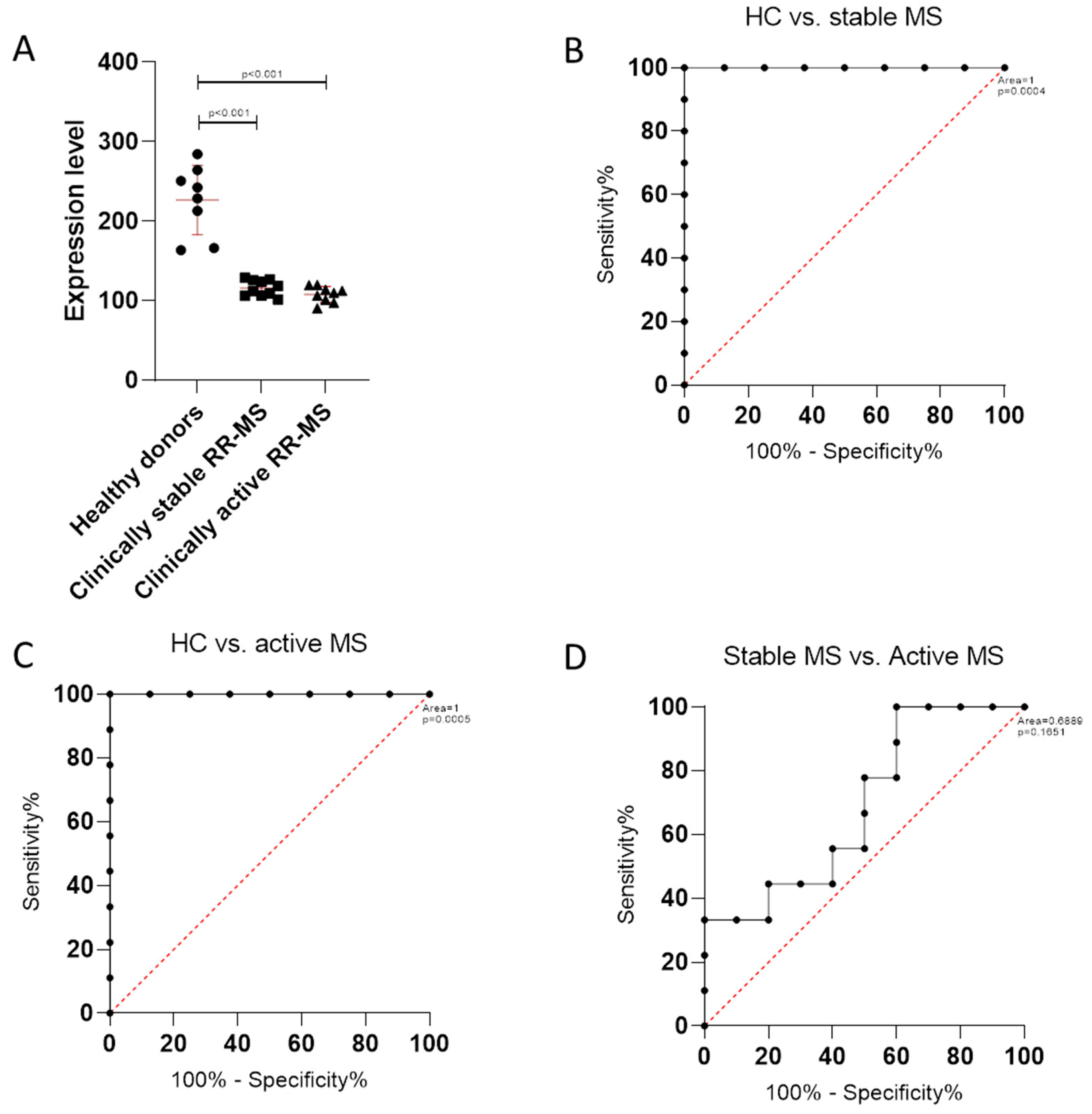
2.2.2. TSPAN32 in PBMCs from MS Patients
2.2.3. Predictive Analysis of TSPAN32 in MS
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
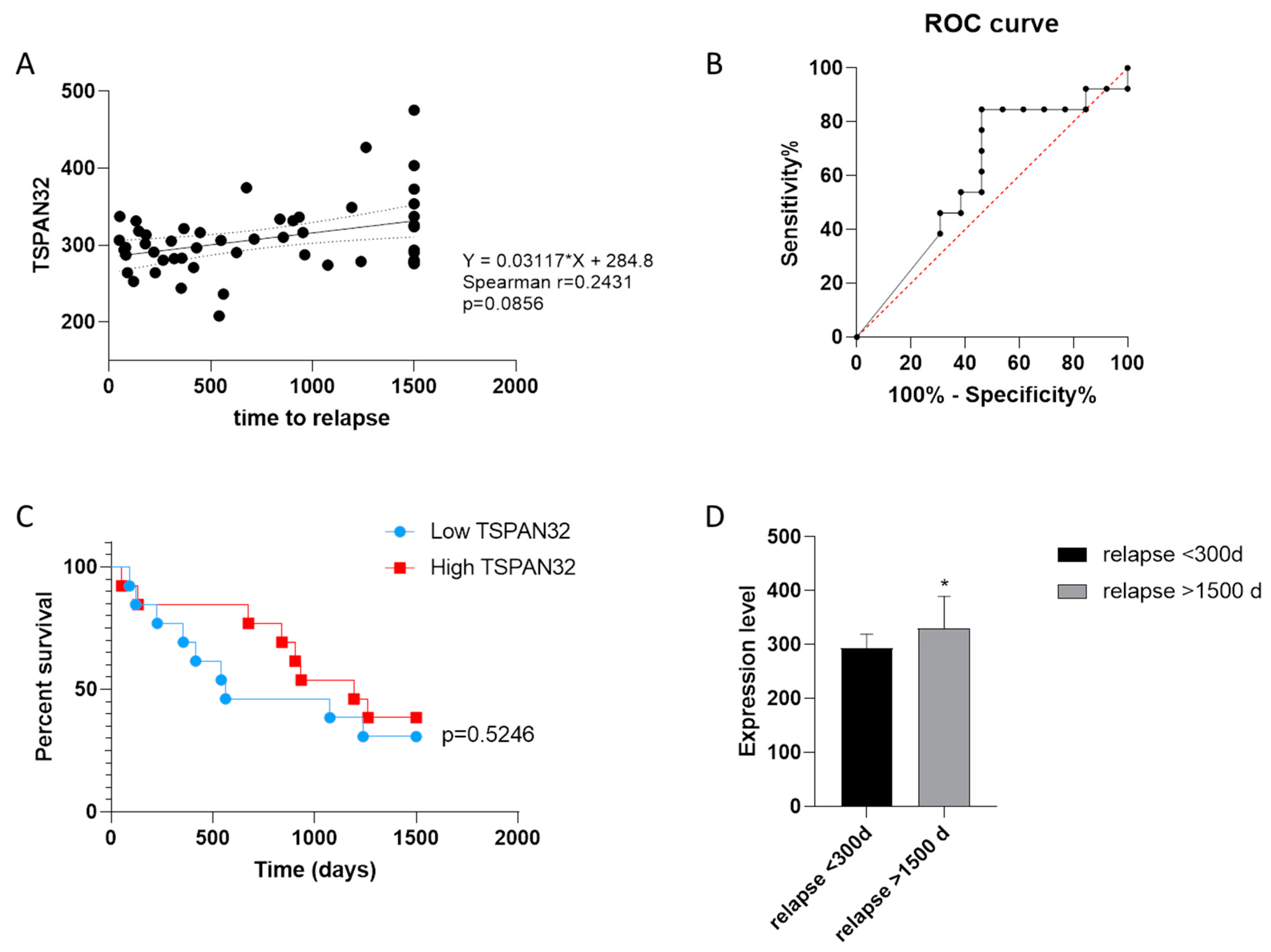
3.1. TSPAN32 in Memory T Cells
3.2. TSPAN32 Expression in PBMCs from MS Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Termini, C.M.; Gillette, J.M. Tetraspanins Function as Regulators of Cellular Signaling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrin, S.; Jouannet, S.; Boucheix, C.; Rubinstein, E. Tetraspanins at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 3641–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, S.; Shoham, T. The tetraspanin web modulates immune-signalling complexes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebel-Binay, S.; Lagaudrière, C.; Fradelizi, D.; Conjeaud, H. CD82, member of the tetra-span-transmembrane protein family, is a costimulatory protein for T cell activation. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, X.G.; Yashiro, Y.; Abe, R.; Toyooka, K.; Wood, C.R.; Morris, J.; Long, A.; Ono, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Hamaoka, T.; et al. A role for CD9 molecules in T cell activation. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 184, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Spriel, A.B.; Puls, K.L.; Sofi, M.; Pouniotis, D.; Hochrein, H.; Orinska, Z.; Knobeloch, K.-P.; Plebanski, M.; Wright, M.D. A regulatory role for CD37 in T cell proliferation. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 2953–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Müller, U.; Campbell, K.S. Normal development but differentially altered proliferative responses of lymphocytes in mice lacking CD81. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 4217–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.D.; Geary, S.M.; Fitter, S.; Moseley, G.W.; Lau, L.-M.; Sheng, K.-C.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Stanley, E.G.; Jackson, D.E.; Ashman, L.K. Characterization of mice lacking the tetraspanin superfamily member CD151. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 5978–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarrant, J.M.; Groom, J.; Metcalf, D.; Li, R.; Borobokas, B.; Wright, M.D.; Tarlinton, D.; Robb, L. The absence of Tssc6, a member of the tetraspanin superfamily, does not affect lymphoid development but enhances in vitro T-cell proliferative responses. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 5006–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.D.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Campo, G.; Corsico, F.; Presti, M.; Bramanti, P.; Mangano, K.; Petralia, M.C.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. Modulation of Tetraspanin 32 (TSPAN32) Expression in T Cell-Mediated Immune Responses and in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffaroni, M.; Rossini, S.; Ghezzi, A.; Parma, R.; Cazzullo, C.L. Decrease of CD4+ CD45+ T-cells in chronic-progressive multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 1990, 237, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.; Bartholomew, B.; Lobo, S. Isolation of myelin basic protein-specific T cells predominantly from the memory T-cell compartment in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 45, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, P.J.; Lovett-Racke, A.; Phillips, S.M.; Racke, M.K. Differential requirements of naïve and memory T cells for CD28 costimulation in autoimmune pathogenesis. Histol. Histopathol. 1999, 14, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lovett-Racke, A.E.; Trotter, J.L.; Lauber, J.; Perrin, P.J.; June, C.H.; Racke, M.K. Decreased dependence of myelin basic protein-reactive T cells on CD28-mediated costimulation in multiple sclerosis patients. A marker of activated/memory T cells. J. Clin. Invest. 1998, 101, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Goods, B.A.; Raddassi, K.; Nepom, G.T.; Kwok, W.W.; Love, J.C.; Hafler, D.A. Functional inflammatory profiles distinguish myelin-reactive T cells from patients with multiple sclerosis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 287ra74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Bao, R.; Li, L.; Deisenhammer, F.; Arnason, B.G.W.; Reder, A.T. Interferon-β corrects massive gene dysregulation in multiple sclerosis: Short-term and long-term effects on immune regulation and neuroprotection. EBioMedicine 2019, 49, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, M.; Tuller, T.; Rubinstein, U.; Or-Bach, R.; Achiron, A. Prediction of acute multiple sclerosis relapses by transcription levels of peripheral blood cells. BMC Med. Genom. 2009, 2, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, C.; Ramirez, R.N.; El-Ali, N.C.; Gomez-Cabrero, D.; Tegner, J.; Merkenschlager, M.; Conesa, A.; Mortazavi, A. Building gene regulatory networks from scATAC-seq and scRNA-seq using Linked Self Organizing Maps. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unternaehrer, J.J.; Chow, A.; Pypaert, M.; Inaba, K.; Mellman, I. The tetraspanin CD9 mediates lateral association of MHC class II molecules on the dendritic cell surface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittelbrunn, M.; Yanez-Mo, M.; Sancho, D.; Ursa, A.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. Cutting Edge: Dynamic Redistribution of Tetraspanin CD81 at the Central Zone of the Immune Synapse in Both T Lymphocytes and APC. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 6691–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, K.-C.; van Spriel, A.B.; Gartlan, K.H.; Sofi, M.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Ashman, L.; Wright, M.D. Tetraspanins CD37 and CD151 differentially regulate Ag presentation and T-cell co-stimulation by DC. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartlan, K.H.; Belz, G.T.; Tarrant, J.M.; Minigo, G.; Katsara, M.; Sheng, K.-C.; Sofi, M.; van Spriel, A.B.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Plebanski, M.; et al. A Complementary Role for the Tetraspanins CD37 and Tssc6 in Cellular Immunity. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3158–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, M.; Edström, M.; Gawel, D.; Nestor, C.E.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Barrenäs, F.; Tojo, J.; Kockum, I.; Olsson, T.; et al. Integrated genomic and prospective clinical studies show the importance of modular pleiotropy for disease susceptibility, diagnosis and treatment. Genome Med. 2014, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzone, L.; Scola, L.; Zanghì, A.; Biondi, A.; Di Cataldo, A.; Libra, M.; Candido, S. Integrated analysis of colorectal cancer microRNA datasets: Identification of microRNAs associated with tumor development. Aging 2018, 10, 1000–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candido, S.; Lupo, G.; Pennisi, M.; Basile, M.; Anfuso, C.; Petralia, M.; Gattuso, G.; Vivarelli, S.; Spandidos, D.; Libra, M.; et al. The analysis of miRNA expression profiling datasets reveals inverse microRNA patterns in glioblastoma and Alzheimer’s disease. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.D.; Mazzon, E.; Mangano, K.; Basile, M.S.; Cavalli, E.; Mammana, S.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Petralia, M.C. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Involvement of the Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Gene Network in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Genes 2019, 10, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.D.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Cavalli, E.; Bramanti, P.; Nania, R.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Petralia, M.C. Upregulation of IL-1 Receptor Antagonist in a Mouse Model of Migraine. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petralia, M.C.; Mazzon, E.; Fagone, P.; Falzone, L.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Basile, M.S. Retrospective follow-up analysis of the transcriptomic patterns of cytokines, cytokine receptors and chemokines at preconception and during pregnancy, in women with post-partum depression. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 2055–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagone, P.; Mazzon, E.; Cavalli, E.; Bramanti, A.; Petralia, M.C.; Mangano, K.; Al-Abed, Y.; Bramati, P.; Nicoletti, F. Contribution of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor superfamily of cytokines in the pathogenesis of preclinical and human multiple sclerosis: In silico and in vivo evidences. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 322, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Mazzon, E.; Fagone, P.; Mangano, K.; Mammana, S.; Cavalli, E.; Basile, M.S.; Bramanti, P.; Scalabrino, G.; Lange, A.; et al. Prevention of clinical and histological signs of MOG-induced experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by prolonged treatment with recombinant human EGF. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 332, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, E.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Mangano, K.; Di Marco, R.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P.; Petralia, M.C. Upregulated Expression of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor, Its Analogue D-Dopachrome Tautomerase, and the CD44 Receptor in Peripheral CD4 T Cells from Clinically Isolated Syndrome Patients with Rapid Conversion to Clinical Defined Multiple Sclerosis. Medicina 2019, 55, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagone, P.; Mazzon, E.; Mammana, S.; Di Marco, R.; Spinasanta, F.; Basile, M.S.; Petralia, M.C.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Mangano, K. Identification of CD4+ T cell biomarkers for predicting the response of patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis to natalizumab treatment. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, E.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Mammana, S.; Pennisi, M.; Fagone, P.; Kalfin, R.; Martinovic, V.; Ivanovic, J.; Andabaka, M.; et al. In Silico and In Vivo Analysis of IL37 in Multiple Sclerosis Reveals Its Probable Homeostatic Role on the Clinical Activity, Disability, and Treatment with Fingolimod. Molecules 2019, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petralia, M.C.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Cutuli, M.; Di Marco, R.; Scandurra, F.; Saraceno, A.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Mangano, K. Effects of Treatment with the Hypomethylating Agent 5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine in Murine Type II Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, E174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, E.; Mazzon, E.; Mammana, S.; Basile, M.S.; Lombardo, S.D.; Mangano, K.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P.; Petralia, M.C. Overexpression of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor and Its Homologue D-Dopachrome Tautomerase as Negative Prognostic Factor in Neuroblastoma. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petralia, M.C.; Mazzon, E.; Fagone, P.; Russo, A.; Longo, A.; Avitabile, T.; Nicoletti, F.; Reibaldi, M.; Basile, M.S. Characterization of the Pathophysiological Role of CD47 in Uveal Melanoma. Molecules 2019, 24, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.D.; Presti, M.; Mangano, K.; Petralia, M.C.; Basile, M.S.; Libra, M.; Candido, S.; Fagone, P.; Mazzon, E.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. Prediction of PD-L1 Expression in Neuroblastoma via Computational Modeling. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, K.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Di Marco, R.; Bramanti, P.; Mammana, S.; Petralia, M.C.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F. Pathogenic role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor in glioblastoma and its targeting with specific inhibitors as novel tailored therapeutic approach. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17951–17970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammana, S.; Fagone, P.; Cavalli, E.; Basile, M.; Petralia, M.; Nicoletti, F.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. The Role of Macrophages in Neuroinflammatory and Neurodegenerative Pathways of Alzheimer’s Disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, and Multiple Sclerosis: Pathogenetic Cellular Effectors and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammana, S.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E.; Cavalli, E.; Basile, M.S.; Fagone, P.; Petralia, M.C.; McCubrey, J.A.; Nicoletti, F.; Mangano, K. Preclinical evaluation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in animal models of multiple sclerosis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 8263–8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagone, P.; Mangano, K.; Quattrocchi, C.; Cavalli, E.; Mammana, S.; Lombardo, G.A.G.; Pennisi, V.; Zocca, M.-B.; He, M.; Al-Abed, Y.; et al. Effects of NO-Hybridization on the Immunomodulatory Properties of the HIV Protease Inhibitors Lopinavir and Ritonavir. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 117, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paskas, S.; Mazzon, E.; Basile, M.S.; Cavalli, E.; Al-Abed, Y.; He, M.; Rakocevic, S.; Nicoletti, F.; Mijatovic, S.; Maksimovic-Ivanic, D. Lopinavir-NO, a nitric oxide-releasing HIV protease inhibitor, suppresses the growth of melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Invest. New Drugs 2019, 37, 1014–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, M.; Mazzon, E.; Krajnovic, T.; Draca, D.; Cavalli, E.; Al-Abed, Y.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Mijatovic, S.; Maksimovic-Ivanic, D. Anticancer and Differentiation Properties of the Nitric Oxide Derivative of Lopinavir in Human Glioblastoma Cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarević, M.; Mazzon, E.; Momčilović, M.; Basile, M.S.; Colletti, G.; Petralia, M.C.; Bramanti, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Miljković, Đ. The H₂S Donor GYY4137 Stimulates Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in BV2 Cells While Suppressing the Secretion of TNF and Nitric Oxide. Molecules 2018, 23, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, H.F.; Martin, R. Multiple sclerosis: A complicated picture of autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goverman, J. Autoimmune T cell responses in the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, A.; Hafler, D.A. Multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemler, M.E. Targeting of tetraspanin proteins--potential benefits and strategies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basile, M.S.; Mazzon, E.; Mangano, K.; Pennisi, M.; Petralia, M.C.; Lombardo, S.D.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P.; Cavalli, E. Impaired Expression of Tetraspanin 32 (TSPAN32) in Memory T Cells of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10010052
Basile MS, Mazzon E, Mangano K, Pennisi M, Petralia MC, Lombardo SD, Nicoletti F, Fagone P, Cavalli E. Impaired Expression of Tetraspanin 32 (TSPAN32) in Memory T Cells of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(1):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10010052
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasile, Maria Sofia, Emanuela Mazzon, Katia Mangano, Manuela Pennisi, Maria Cristina Petralia, Salvo Danilo Lombardo, Ferdinando Nicoletti, Paolo Fagone, and Eugenio Cavalli. 2020. "Impaired Expression of Tetraspanin 32 (TSPAN32) in Memory T Cells of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis" Brain Sciences 10, no. 1: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10010052
APA StyleBasile, M. S., Mazzon, E., Mangano, K., Pennisi, M., Petralia, M. C., Lombardo, S. D., Nicoletti, F., Fagone, P., & Cavalli, E. (2020). Impaired Expression of Tetraspanin 32 (TSPAN32) in Memory T Cells of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Brain Sciences, 10(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10010052






