Dysfunctional Incidental Olfaction in Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): An Electroencephalography (EEG) Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Data Acquisition
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Behavioural Data
2.4.2. EEG Data
3. Results
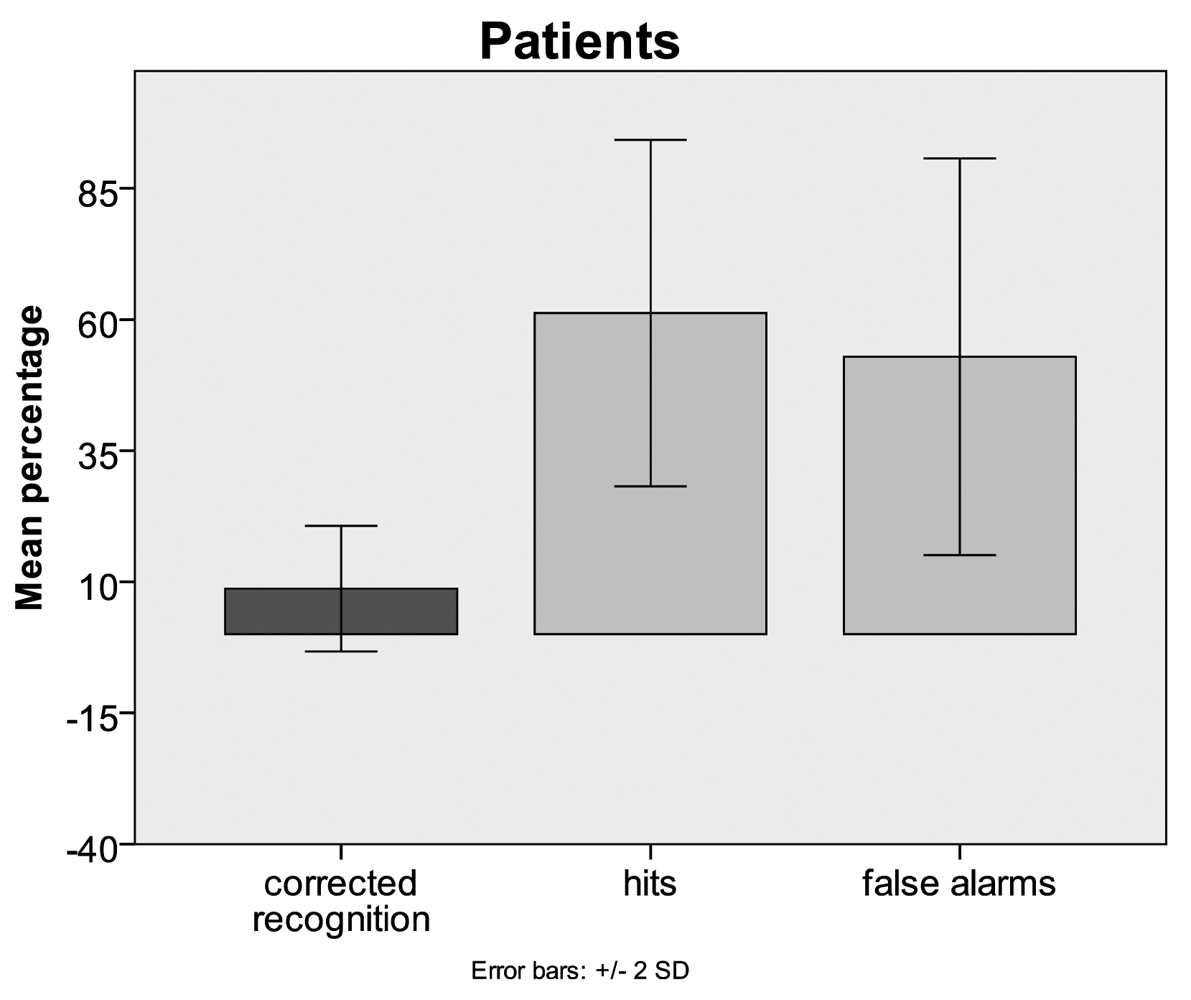
3.1. Behavioural Data

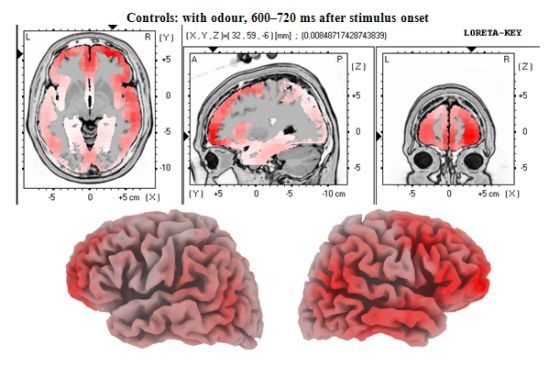
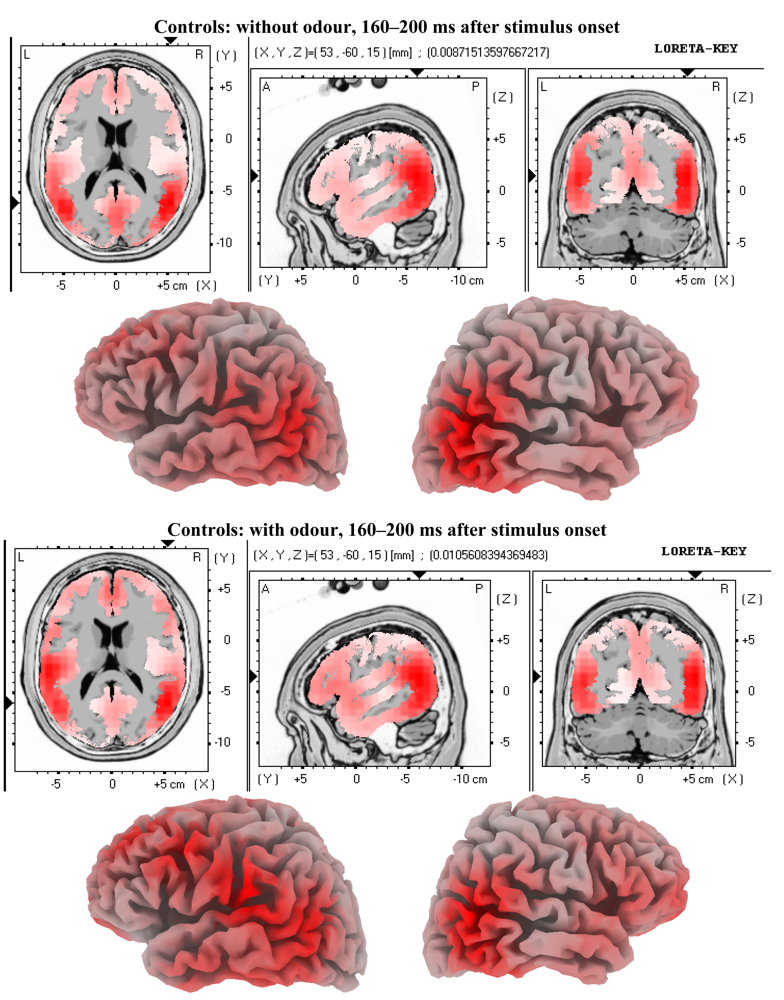
3.2. EEG Data
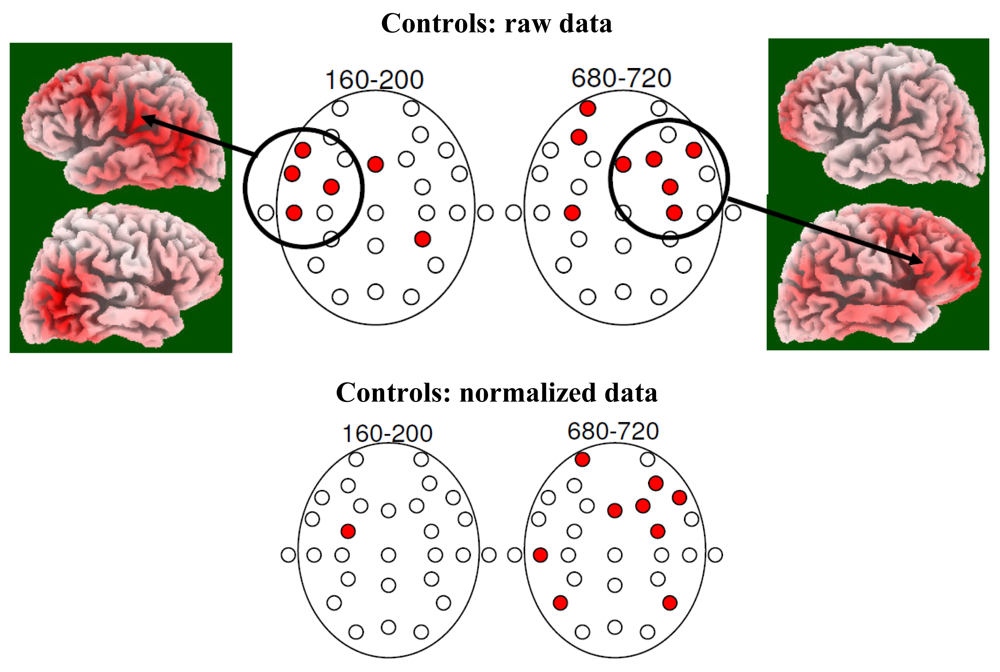
4. Discussion
4.1. Behaviour
4.2. Electrophysiology

Acknowledgments
References
- Walla, P.; Hufnagl, B.; Lehrner, J.; Mayer, D.; Lindinger, G.; Imhof, H.; Deecke, L.; Lang, W. Olfaction and face encoding in humans: A magnetoencephalographic (MEG) study. Cogn. Brain Res. 2003, 15, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, R.C.; Smith, G.E.; Waring, S.C.; Ivnik, R.J.; Kokmen, E.; Tangelos, E.G. Aging, memory, and mild cognitive impairment. Int. Psychogeriatr. 1997, 9, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, R.C.; Smith, G.E.; Waring, S.C. Mild cognitive impairment, clinical characterization and outcome. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier, S.; Reisberg, B.; Zaudig, M.; Petersen, R.C.; Ritchie, K.; Broich, K.; Belleville, S.; Brodaty, H.; Bennett, D.; Chertkow, H.; et al. International Psychogeriatric Association Expert Conference on mild cognitive impairment. Lancet 2006, 367, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Petrella, J.R.; Prince, S.E.; Wang, L.; Hellegers, C.; Doraiswamy, P.M. Prognostic value of posteromedial cortex deactivation in mild cognitive impairment. PLoS One 2007, 2, e1104. [Google Scholar]
- Moretti, D.V.; Frisoni, G.B.; Fracassi, C.; Pievani, M.; Geroldi, C.; Binetti, G.; Rossini, P.M.; Zanetti, O. MCI patients' EEGs show group differences between those who progress and those who do not progress to AD. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 32, 563–571. [Google Scholar]
- Hebert, L.E.; Scherr, P.A.; Bienias, J.L.; Bennett, D.A.; Evans, D.A. Alzheimer disease in the US population: prevalence estimates using the 2000 census. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Missonnier, P.; Deiber, M.P.; Gold, G.; Herrmann, F.R.; Millet, P.; Michon, A.; Fazio-Costa, L.; Ibañez, V.; Giannakopoulos, P. Working memory load-related electroencephalographic parameters can differentiate progressive from stable mild cognitive impairment. Neuroscience 2007, 150, 346–356. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.L.; Fenstermacher, E.; Bates, J.; Blacker, D.; Sperling, R.A.; Dickerson, B.C. Hippocampal activation in adults with mild cognitive impairment predicts subsequent cognitive decline. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 79, 630–635. [Google Scholar]
- Devanand, D.P.; Liu, X.; Tabert, M.H.; Pradhaban, G.; Cuasay, K.; Bell, K.; de Leon, M.J.; Doty, R.L.; Stern, Y.; Pelton, G.H. Combining early markers strongly predicts conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 64, 871–879. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, S.C.; Baxter, L.C.; Susskind-Wilder, L.; Connor, D.J.; Sabbagh, M.N.; Caselli, R.J. Hippocampal adaptation to face repetition in healthy elderly and mild cognitive impairment. Neuropsychologia 2004, 42, 980–989. [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson, B.C.; Salat, D.H.; Greve, D.N.; Chua, E.F.; Rand-Giovannetti, E.; Rentz, D.M.; Bertram, L.; Mullin, K.; Tanzi, R.E.; Blacker, D.; et al. Increased hippocampal activation in mild cognitive impairment compared to normal aging and AD. Neurology 2005, 65, 404–411. [Google Scholar]
- Püregger, E.; Walla, P.; Deecke, L.; Dal-Bianco, P. Magnetoencephalographic—features related to mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage 2003, 20, 2235–2244. [Google Scholar]
- Eibenstein, A.; Fioretti, A.B.; Simaskou, M.N.; Sucapane, P.; Mearelli, S.; Mina, C.; Amabile, G.; Fusetti, M. Olfactory screening test in mild cognitive impairment. Neurol. Sci. 2005, 26, 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, R.S.; Schneider, J.A.; Arnold, S.E.; Tang, Y.; Boyle, P.A.; Bennett, D.A. Olfactory identification and incidence of mild cognitive impairment in older age. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2007, 64, 802–808. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, R.S.; Arnold, S.E.; Schneider, J.A.; Boyle, P.A.; Buchman, A.S.; Bennett, D.A. Olfactory impairment in presymptomatic Alzheimer's disease. Annu. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1170, 730–735. [Google Scholar]
- Lehrner, J.; Pusswald, G.; Gleiss, A.; Auff, E.; Dal-Bianco, P. Odor identification and self-reported olfactory functioning in patients with subtypes of mild cognitive impairment. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2009, 23, 818–830. [Google Scholar]
- Fusetti, M.; Fioretti, A.B.; Silvagni, F.; Simaskou, M.; Sucapane, P.; Necozione, S.; Eibenstein, A. Smell and preclinical Alzheimer disease: Study of 29 patients with amnesic mild cognitive impairment. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 39, 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, J.M.; Hummel, T.; Kratzsch, T.; Lötsch, J.; Skarke, C.; Frölich, L. Olfactory function in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: An investigation using psychophysical and electrophysiological techniques. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2003, 160, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Walla, P.; Endl, W.; Lindinger, G.; Deecke, L.; Lang, W. Implicit memory within a word recognition task: An event-related potential study in human subjects. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 269, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Walla, P.; Hufnagl, B.; Lehrner, J.; Mayer, D.; Lindinger, G.; Imhof, H.; Deecke, L.; Lang, W. Olfaction and depth of word processing: a magnetoencephalographic (MEG) study. Neuroimage 2003, 18, 104–116. [Google Scholar]
- Walla, P.; Mayer, D.; Deecke, L.; Lang, W. How chemical information processing interferes with face processing: A magnetoencephalographic (MEG) study. Neuroimage 2005, 24, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Walla, P. Olfaction and its dynamic influence on word and face processing: Cross-modal integration. Prog. Neurobiol. 2008, 84, 192–209. [Google Scholar]
- Walla, P.; Imhof, H.; Lang, W. A gender difference related to the effect of a background odor: A Magnetoencephalographic (MEG) study. J. Neural Transm. 2009, 116, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Walla, P.; Hufnagl, B.; Lehrner, J.; Mayer, D.; Lindinger, G.; Deecke, L.; Lang, W. Evidence of conscious and subconscious olfactory information processing during word encoding: a magnetoencephalographic (MEG) study. Cogn. Brain Res. 2002, 14, 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Crook, T.H.; Larrabee, G.J. Unveröffentlichtes Manual der Crook'schen Testbatterie; Memory Assessment Clinics: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Folstein, M.F. Mini mental state. J. Psychol. Res. 1975, 12, 196–198. [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield, R.C. The assessment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh Inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971, 9, 97–113. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, G.; Wood, C.C. Scalp distributions of eventrelated potentials: An ambiguity associated with analysis of variance models. Electroencephal. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1985, 62, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Michel, C.M.; Lehmann, D. Low resolution electromagnetic tomography: Anewmethod for localizing electrical activity in the brain. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1994, 18, 49–65. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, J.M.; Hummel, T.; Kratzsch, T.; Lotsch, J.; Skarke, C.; Frohlich, L. Olfactory function in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: An investigation using psychophysical and electrophysiological techniques. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic, J.; Jones-Gotman, M.; De Sousa, K.; Chertkow, H. Olfaction in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 693–706. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick, M.A.; Combest, W.; Newton, M.; Teske, Y.; Cavendish, J.; McGee, R.; Przychodzin, D. Combining olfaction and cognition measures to screen for mild cognitive impairment. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2006, 2, 565–570. [Google Scholar]
- Wesson, D.W.; Wilson, D.A.; Nixon, R.A. Should olfactory dysfunction be used as a biomarker of Alzheimer's disease? Expert Rev. Neurother. 2010, 10, 633–635. [Google Scholar]
- Mesholam, R.I.; Moberg, P.J.; Mahr, R.N.; Doty, R.L. Olfaction in neurodegenerative disease: A meta-analysis of olfactory functioning in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Arch. Neurol. 1998, 55, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Devanand, D.P.; Michaels-Marston, K.S.; Liu, X.; Pelton, G.H.; Padilla, M.; Marder, K.; Bell, K.; Stern, Y.; Mayeux, R. Olfactory deficits in patients with mild cognitive impairment predictAlzheimer's disease at follow-up. Am. J. Psychiatry 2000, 157, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/)
Share and Cite
Walla, P.; Duregger, C.; Deecke, L.; Dal-Bianco, P. Dysfunctional Incidental Olfaction in Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): An Electroencephalography (EEG) Study. Brain Sci. 2011, 1, 3-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci1010003
Walla P, Duregger C, Deecke L, Dal-Bianco P. Dysfunctional Incidental Olfaction in Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): An Electroencephalography (EEG) Study. Brain Sciences. 2011; 1(1):3-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci1010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalla, Peter, Cornelia Duregger, Lüder Deecke, and Peter Dal-Bianco. 2011. "Dysfunctional Incidental Olfaction in Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): An Electroencephalography (EEG) Study" Brain Sciences 1, no. 1: 3-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci1010003
APA StyleWalla, P., Duregger, C., Deecke, L., & Dal-Bianco, P. (2011). Dysfunctional Incidental Olfaction in Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): An Electroencephalography (EEG) Study. Brain Sciences, 1(1), 3-15. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci1010003