Bioconcentration, Potential Health Risks, and a Receptor Prediction Model of Metal(loid)s in a Particular Agro-Ecological Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
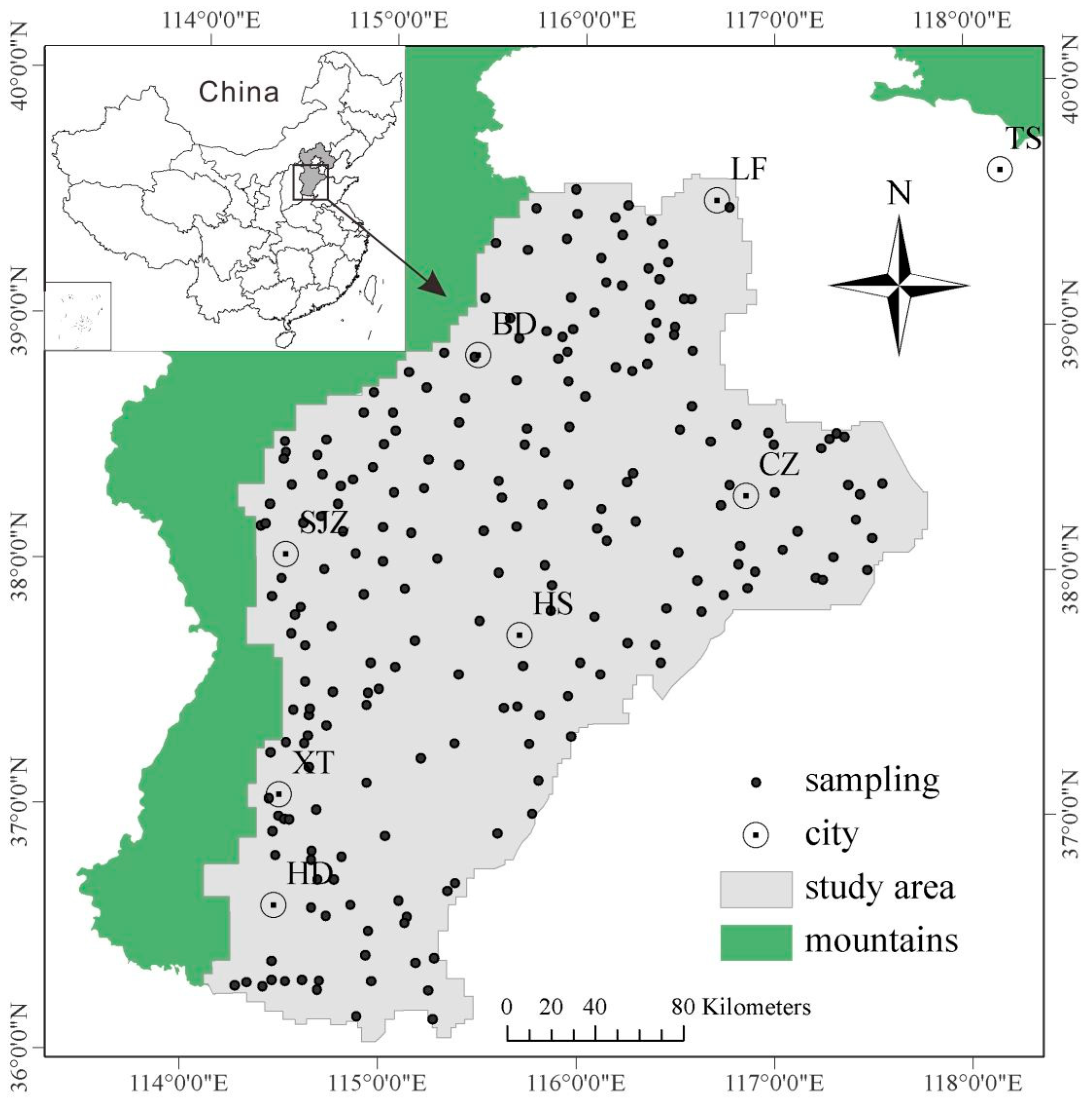
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Index of Geo-Accumulation (Igeo)
2.5. Health Risk Quotient (HQ) Method
2.6. Prediction Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization and Distribution of Metal(loid)s in Soil
3.2. Concentrations of Metal(loid)s in Corn and Wheat
3.3. BCF of Metal(loid)s in Corn and Wheat
3.4. Health Risks
3.5. Receptor Prediction Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doyi, I.; Essumang, D.; Gbeddy, G.; Dampare, S.; Kumassah, E.; Saka, D. Spatial distribution, accumulation and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil and groundwater of the Tano Basin, Ghana. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 165, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwenzi, W.; Muzava, M.; Mapanda, F.; Tauro, T.P. Comparative short-term effects of sewage sludge and its biochar on soil properties, maize growth and uptake of nutrients on a tropical clay soil in Zimbabwe. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Chen, J.B.; Sun, X.S.; Hu, Z.Z.; Fan, D.J. Accumulation and transformation of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Yangtze River estuary to the East China Sea shelf. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwa, E.M.; Meharg, A.A.; Rice, C.M. Risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in agricultural soils and maize tissues from selected districts in Tanzania. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 416, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minari, G.D.; Rosalen, D.L.; Cruz, M.C.; Melo, W.J.; Alves, L.M.C.; Saran, L.M. Agricultural management of an Oxisol affects accumulation of heavy metals. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, Z.U.; Khan, S.; Shah, M.T.; Brusseau, M.L.; Khan, S.A.; Mainhagu, J. Transfer of Heavy Metals from Soils to Vegetables and Associated Human Health Risks at Selected Sites in Pakistan. Pedosphere 2018, 28, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigliotta, G.; Matrella, S.; Cicatelli, A.; Guarino, F.; Castiglione, S. Effects of heavy metals and chelants on phytoremediation capacity and on rhizobacterial communities of maize. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 179, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.H.; Zhu, G.Y.; Li, H.L.; Han, X.M.; Li, J.M.; Ma, Y.B. Accumulation and bioavailability of heavy metals in a soil-wheat/ maize system with long-term sewage sludge amendments. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Huo, S.L.; Yeager, K.M.; Xi, B.D.; Zhang, J.T.; He, Z.S.; Ma, C.Z.; Wu, F.C. Accumulation of arsenic, mercury and heavy metals in lacustrine sediment in relation to eutrophication: Impacts of sources and climate change. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Survey Bulletin on Soil Pollution. Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s of China. 2014. Available online: http://www.mlr.gov.cn/xwdt/jrxw/201404/t20140417_1312998.htm (accessed on 17 April 2014).
- Abbas, M.H.; Abdelhafez, A.A. Role of EDTA in arsenic mobilization and its uptake by maize grown on an As-polluted soil. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood TBibia, I.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Murtaza, B.; Wang Hl Yong, S.O.; Sarkarh, B.; Javed, M.T.; Murtaza, G. Effect of compost addition on arsenic uptake, morphological and physiological attributes of maize plants grown in contrasting soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 178, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruíz-Huerta, E.A.; Garza-Varela, A.; Gómez-Bernal, J.M.; Castillo, F.; Avalos-Borja, M.; SenGupta, B.; Martínez-Villegas, N. Arsenic contamination in irrigation water, agricultural soil and maize crop from an abandoned smelter site in Matehuala, Mexico. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wu, P.J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.F.; Peng, Y.W.; Zhang, S.F.; Cai, G.T.; Gao, G.Q. Heavy metal accumulation, risk assessment and integrated biomarker responses of local vegetables: A case study along the Le’an river. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas-Castor, J.M.; Guzmán-Mar, J.L.; Hernández-Ramírez, A.; Garza-González, M.T.; Hinojosa-Reyes, L. Arsenic accumulation in maize crop (Zea mays): A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488–489, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrugo-Negrete, J.; Pinedo-Hernández, J.; Díez, S. Assessment of heavy metal pollution, spatial distribution and origin in agricultural soils along the Sinú River Basin, Colombia. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.Y.; Zeng, X.B.; Li, L.F.; Pen, C.; Li, S.H. Effects of Land Use on Heavy Metal Accumulation in Soils and Sources Analysis. Agric. Sci. China 2010, 9, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doabi, S.A.; Karami, M.; Afyuni, M.; Yeganeh, M. Pollution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil, atmospheric dust and major food crops in Kermanshah province, Iran. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Lu, C.L.; Peng, H.; Luo, M.; Li, G.K.; Shen, Y.; Ding, H.P.; Zhang, Z.M.; Pan, G.T.; et al. The development dynamics of the maize root transcriptome responsive to heavy metal Pb pollution. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 87–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Li, J.W.; Yue, F.X.; Yan, X.W.; Wang, F.Y.; Bloszies, S.; Wang, Y.F. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculation and biochar amendment on maize growth, cadmium uptake and soil cadmium speciation in Cd-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Kheir, A.M. Maize productivity, heavy metals uptake and their availability in contaminated clay and sandy alkaline soils as affected by inorganic and organic amendments. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajdzik, M.; Halecki, W.; Kalarus, K.; Gąsiorek, M.; Pająk, M. Relationship between heavy metal accumulation and morphometric parameters in European hare (Lepus europaeus) inhabiting various types of landscapes in southern Poland. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Shen, F.; Zhong, G.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J. Concentration and health risk of heavy metals in crops and soils in a zinc-lead mining area in southwest mountainous regions. Acta Sci. Cricumstantiae 2011, 31, 2014–2021. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, C.B.; Cao, S.Z.; Cheng, L.L.; Wu, G.S.; Guo, J.B. Heavy metal accumulation and health risk assessment in soil-wheat system under different nitrogen levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.L.; He, M.M.; Xu, M.; Yan, Z.G.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Guo, G.L.; Nie, J.; Wang, L.Q.; Hou, H.; Li, F.S. Interactive effects between earthworms and maize plants on the accumulation and toxicity of soil cadmium. Soil Boil. Biochem. 2014, 72, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotto, E.; Ceretta, C.A.; Rossato, L.V.; Farias, J.G.; Tiecher, T.L.; DeConti, L.; Schmatz, R.; Brunetto, G.; Schetinger, M.R.C.; Nicoloso, F.T. Triggered antioxidant defense mechanism in maize grown in soil with accumulation of Cu and Zn due to intensive application of pig slurry. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 93, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.K.; Chatterjee, S.; Datta, S.; Veer, V.; Walther, C. Role of phosphate fertilizers in heavy metal uptake and detoxification of toxic metals. Chemosphere 2014, 108, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Liu, L.; Li, D.W.; Zhou, W.N.; Zhou, Z.P.; Zhang, C.F.; Luo, Y.Y.; Wang, H.B.; Li, H.Y. The effect of endophytic Peyronellaea from heavy metal-contaminated and uncontaminated sites on maize growth, heavy metal absorption and accumulation. Fungal Ecol. 2013, 6, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghipour, M.; Jalali, M. Heavy Metal Release from Some Industrial Wastes: Inuence of Organic and Inorganic Acids, Clay Minerals, and Nanoparticles. Pedosphere 2018, 28, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.R.; Ali, S.; Zhang, H.T.; Ouyang, Y.N.; Qiu, B.Y.; Wu, F.B.; Zhang, G.P. The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake by rice plants. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.K.; Li, W.D.; Zhang, C.R.; Wang, S.Q.; Yang, Y.; He, L.Y. Source apportionment of heavy metals in soils using multivariate statistics and geostatistics. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.X.; Li, H.M.; Li, J.Z.; Mao, C.P.; Ji, J.F.; Yuan, X.Y.; Li, T.Y.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L.; Feng, Y.X. Multivariate linear regression model for source apportionment and health risk assessmet of heavy metals from different environmental media. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 165, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, F.; Wang, S.L.; Nan, Z.R.; Ma, J.M.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.Z.; Li, Y.P. Accumulation, spatio-temporal distribution, and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil-corn system around a polymetallic mining area from the Loess Plateau, northwest China. Geoderma 2017, 305, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.G.; Chai, Z.Y.; Mao, Z.C. Using reduction gasification–AFS method quickly measure of arsenic and mercury in the soil of organic food base. Anal. Test. Technol. Instrum. 2002, 8, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R. Analysis Methods of Soil Agricultural Chemistry; China Agricultural Science and Technology Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Walker, D.J.; Clmente, R.; Roig, A. The effects of soil amendment on heavy metal bioavailability in two contaminated Mediterranean soils. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 122, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Wang, D.J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.L. Heavy metal contents, distribution, and prediction in a regional soil–wheat system. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettler, T.A.; Doran, J.W.; Gilbert, T.L. Simplified method for soil particle-size determination to accompany soil-quality analyses. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilbride, C.; Poole, J.; Hutchings, T. A comparison of Cu, Pb, As, Cd, Zn, Fe, Ni and Mn determined by acid extraction/ICP–OES and ex situ field portable X-ray fluorescence analyses. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 143, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, X.; Li, T.; Hu, S.; Ji, J.; Wang, C. Characteristics of heavy metal transfer and their influencing factors in different soil–crop systems of the industrialization region, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryszard, M.; Joanna, K.; Michał, G.; Paweł, Z.; Agnieszka, J.; Tomasz, Z.; Wojciech, K.; Maryla, T.; Kalina, O. Assessment of heavy metals contamination in surface layers of Roztocze National Park forest soils (SE Poland) by indices of pollution. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 839–850. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.H.; Xu, H.Z.; Yu, Q.C.; Li, R.M.; Ma, Z.S.; Cao, F.; Li, H.L. The Investigation and Evaluation of the heavy metal pollution in farmland soil and crop in the Qingyuan of Hebei, China. J. Agro-Envrion. Sci. 2010, 29, 2139–2146. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine river. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Handbook for Non-Cancer Health Effects Evaluation; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Available Information on Assessment Exposure from Pesticides in Food; US Environmental Protection Agency Office of Pesticide Programs: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- USEPA. Risk Assessment Gudience for Superfund Volume I Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); EPA/540/1-89/002; Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 35–52.
- USEPA. Integrated Risk Information System: Lead and Compounds (Inorganic) (CASRN 7439-92-1); Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Huang, M.L.; Zhou, S.L.; Sun, B.; Zhao, Q.G. Heavy metals in wheat grain: Assessment of potential health risk for inhabitants in Kunshan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 405, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Environmental Protection Administration (CEPA). Environmental Quality Standard for Soils (GB15618-2018); Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Ministry of Health of China (MHC). Maximum Levels of Contaminants in Foods (GB2762-2012); Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Chinese Environmental Protection Administration (CEPA). Elemental Background Values of Soils in China; Environmental Science Press of China: Beijing, China, 1990.
- Liu, Y.L.; Liu, S.Q.; Xue, Z.J.; Yan, Y.L.; Hou, D.L. Assessment of Potential Ecological Risk of Soil Heavy Metals in Sewage Irrigated Area of Baoding Suburban. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 10330–10332. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, T.X.; Yang, H.X.; Li, H.F.; Qiao, Y.H.; Su, D.C. Accumulation Characteristics of Heavy Metals in the Soil with Wheat-corn Rotation Systemin North China. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2014, 31, 355–365. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Wang, T.; Louie, P.K.K. Souce apportionment of ambient non-methane hydrocarbons in HongKong: Application of a principal component an anlysis (PCA)/absolute principal component scores (APCS) receptor model. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 129, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, H.L.; Guo, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.M.; Liu, Y.S.; Xu, H.Z. Fraction distribution and risk assessment of soil heavy metals in Anxin-Qingyuan County in Baoding of Heibei. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2016, 43, 140–145. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.L.; Wu, L. Effects of copper concentration on mineral nutrient uptake and copper accumulation in protein of copper tolerant and non-tolerant Lotus purshianus. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1994, 29, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.T.; Rameshbabu, N.; Gandhimathi, R.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Kumar, M.S. Kinetics and Equilibrium Studies for the Removal of Heavy Metals in Both Single and Binary Systems Using Hydroxyapatite. Appl. Water Sci. 2012, 2, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dach, A.; Starmans, D. Heavy metals balance in polish and dutch agronomy: Actual state and previsions for the future. Agriculature Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 107, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, H. Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1995; 889p. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.T.; Luan, W.L.; Guo, H.Q.; Li, S.M.; Song, Z.F.; Gu, H.F. Assessment of the Heavy Metal Pollution and the Potential Ecological Hazard in Soil of Plain Area of Baoding City of Hebei Province. Geoscience 2014, 28, 523–530. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.Q.; Yang, Z.H.; Li, H.L.; Ma, W.J.; Ren, J.F. Environmental quality and anthropogenic pollution assessment of heavy metals in topsoil of Hebei plain. Geol. China 2011, 38, 218–224. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, B.X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.X.; Chai, J.L. An analysis of differences in accumulation of heavy metals in main crops in a tin mining area of Yunnan Province. Geol. Bull. China 2014, 33, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.L.; Nan, Z.R.; Liu, X.W.; Li, Y.; Qin, S.; Ding, H.X. Accumulation and bioavailability of copper and nickel in wheat plants grown in contaminated soils from the oasis, northwest China. Geoderma 2009, 152, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Z.F.; Yuan, X.Y.; Browne, P.; Chen, L.X.; Ji, J.F. The influences of soil properties on Cu and Zn availability in soil and their transfer to wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the Yangtze River delta region, China. Geoderma 2013, 193–194, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Z.; Cheng, G. Accumulation of Cd and Pb in spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in calcareous soil irrigated with wastewater. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 66, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Probst, A.; Liao, B. Metal contamination of soils and crops affected by the Chenzhou lead/zinc mine spill (Hunan, China). Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 339, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pendergrass, A.; Butcher, D.J. Uptake of lead and arsenic in food plants grown in contaminated soil from Barber Orchard, NC. Microchem. J. 2006, 83, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsøe-Petersen, L.; Larsen, E.H.; Larsen, P.B.; Bruun, P. Uptake of Trace Elements and PAHs by Fruit and Vegetables from Contaminated Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3057–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigliotti, G.; Businelli, D.; Giusquiani, P.L. Trace metals uptake and distribution in corn plants grown on a 6-year urban waste compost amended soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1996, 58, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, L.X.; Kang, Z.Q. Characteristics of transfer and their influencing factors of heavy metals in soil crop system of peri-urban agricultural soils of Nanning, South China. Carsologica Sin. 2018, 37, 43–52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Grant, C.A.; Bailey, L.D.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Singh, B.R. management factors which influence cadmium concentrations in crops. In Cadmium in Soils and Plants; MeLaughlin, M.J., Singh, B.R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 151–198. [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin, M.J.; Tiller, K.G.; Naidu, R. Review: The behaviour and environmental impact of contaminants in fertilizers. Soil Res. 1996, 34, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurston, G.D.; Spengler, J.D. A quantitative assessment of source contributions to inhalable particulate matter pollution in metropolitan Boston. Atmos. Environ. 1985, 19, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haji, M.G.; Melesseb, A.M.; Reddic, L. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources using APCS-MLR and PMF receptor modeling techniques in three major rivers of South Florida. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1552–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauve, S.; Hendershot, W.; Allen, H.E. Solid-solution partitioning of metals in contaminated soils: Dependence on pH, total metal burden, and organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Ma, L.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Zheng, L.T. Evolution of heavy metal speciation during the aerobic composting process of sewage sludge. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shan, B.Q.; Tang, W.Z.; Dong, L.X.; Zhang, W.Q.; Pei, Y.S. Heavy metal concentrations and speciation in riverine sediments and the risks posed in three urban belts in the Haihe Basin. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 139, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.G.; Vanthuyne, D.R.; Vandecasteele, B. Influence of hydrological regime on porewater metal concentration sina contaminated sediment-derived soil. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 615–625. [Google Scholar]
- Laing, G.D.; Rinklebe, J.; Vandecasteele, B. Trace metal behavior inestuarine and riverine flood plain soil sand sediments: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3972–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.L.; Er-Rafik, M.; Moller, M. Supercritical carbon dioxide assisted silicon based finishing of cellulosic fabric: A novel approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| mg/kg | Mean | Coefficient of Variable (CV), % | Food Threshold [50] | Local Background Values [51] | Soil Environmental Quality [49] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu corn | 1.40 | 26.75 | - | ||
| Cu wheat | 4.63 | 21.21 | |||
| Cu soil | 25.72 | 58.50 | 21.8 | 100 | |
| Pb2 corn | 0.05 | 71.83 | 0.20 | ||
| Pb3 wheat | 0.06 | 59.07 | |||
| Pb soil | 24.76 | 39.25 | 21.5 | 170 | |
| Zn corn | 21.46 | 17.43 | - | ||
| Zn wheat | 32.07 | 23.08 | |||
| Zn soil | 78.47 | 74.47 | 71.9 | 300 | |
| Cr corn | 0.03 | 68.64 | 1.00 | ||
| Cr wheat | 0.03 | 35.26 | |||
| Cr soil | 67.74 | 10.84 | 68.3 | 250 | |
| Ni corn | 0.22 | 29.52 | 1.00 | ||
| Ni wheat | 0.10 | 48.04 | |||
| Ni soil | 28.84 | 17.20 | 30.8 | 190 | |
| Cd corn | 0.0043 | 79.70 | 0.10 | ||
| Cd3 wheat | 0.03 | 50.71 | |||
| Cd soil | 0.20 | 191.69 | 0.09 | 0.6 | |
| As corn | 0.01 | 68.35 | 0.50 | ||
| As wheat | 0.03 | 76.41 | |||
| As soil | 9.89 | 30.73 | 12.8 | 25 | |
| Hg2 corn | 0.0040 | 92.39 | 0.02 | ||
| Hg1 wheat | 0.0022 | 82.54 | |||
| Hg soil | 0.06 | 62.78 | 0.04 | 3.4 |
| Metal(loid)s | Soil | Corn | Wheat | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | Child | Adult | Child | Adult | Child | |
| HQCu | 6.68 × 10−4 | 1.09 × 10−3 | 8.50 × 10−2 | 0.19 | 0.42 | 0.46 |
| HQPb | 6.43 × 10−3 | 1.04 × 10−2 | 2.99 × 10−2 | 6.76 × 10−2 | 5.60 × 10−2 | 6.15 × 10−2 |
| HQZn | 2.72 × 10−4 | 4.42 × 10−4 | 0.17 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 0.43 |
| HQCd | 3.43 × 10−3 | 5.56 × 10−3 | 1.05 × 10−2 | 2.34 × 10−2 | 3.90 × 10−2 | 4.28 × 10−2 |
| HQCr | 2.0 × 10−5 | 3.25 × 10−5 | 4.35 × 10−5 | 9.54 × 10−5 | 7.93 × 10−5 | 8.69 × 10−5 |
| HQNi | 3.52 × 10−3 | 5.72 × 10−3 | 2.69 × 10−2 | 5.88 × 10−2 | 1.86 × 10−2 | 2.04 × 10−2 |
| HQAs | 7.04 × 10−4 | 1.14 × 10−3 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 0.37 |
| HQHg | 2.07 × 10−4 | 3.37 × 10−4 | 3.22 × 10−2 | 7.03 × 10−2 | 2.6 × 10−2 | 2.85 × 10−2 |
| THQ | 1.52 × 10−2 | 2.48 × 10−2 | 0.47 | 1.04 | 1.29 | 1.42 |
| TTHQadult | 1.78 | |||||
| TTHQchild | 2.48 | |||||
| Crop | Prediction Models by PCS-SMLR for Cu, Zn, and As | R | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | CuBCF = 1.268 *** − 0.034PCS1 *** − 0.022PCS9 *** + 0.015PCS5 * | 0.76 | <000 |
| ZnBCF = 1.627 *** − 0.027PCS1 *** − 0.016PCS14 *** | 0.62 | <000 | |
| AsBCF = −0.611 *** − 0.085PCS5 *** − 0.066PCS11 *** + 0.045PCS14 ** | 0.56 | <000 | |
| Corn | CuBCF = 0.736 *** − 0.06 PCS1 *** + 0.055PCS13 ** − 0.031PCS10 ** | 0.64 | <000 |
| ZnBCF = 1.457 *** − 0.063PCS10 *** + 0.033PCS6 *** | 0.66 | <000 | |
| AsBCF = −0.955 *** − 0.172PCS7 *** − 0.087PCS4 *** | 0.58 | <000 |
| Parameters | Corn | Wheat | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuBCF | ZnBCF | AsBCF | CuBCF | ZnBCF | AsBCF | |
| PH | 0.039 | −0.104 | −0.443 ** | 0.234 ** | 0.097 | −0.117 |
| CaO | −0.027 | −0.071 | −0.225 ** | 0.077 | 0.019 | −0.085 |
| MgO | −0.437 ** | −0.501 ** | −0.281 ** | −0.260 ** | −0.309 ** | −0.221 ** |
| Fe2O3 | −0.513 ** | −0.524 ** | −0.130 * | −0.630 ** | −0.505 ** | −0.362 ** |
| K2O | −0.233 ** | −0.174 ** | 0.136 * | −0.406 ** | −0.297 ** | −0.081 |
| Mn | −0.465 ** | −0.523 ** | −0.220 ** | −0.555 ** | −0.476 ** | −0.445 ** |
| P | −0.122 | −0.046 | 0.148 * | −0.155 * | −0.123 | 0.218 ** |
| N | −0.250 ** | −0.217 ** | 0.144 * | −0.383 ** | −0.310 ** | 0.152 * |
| F | −0.380 ** | −0.418 ** | −0.323 ** | −0.352 ** | −0.310 ** | −0.276 ** |
| Mo | −0.066 | −0.042 | −0.023 | 0.042 | −0.023 | −0.016 |
| B | −0.010 | −0.112 | −0.354 ** | −0.036 | −0.077 | −0.330 ** |
| TOC | −0.331 ** | −0.284 ** | 0.063 | −0.512 ** | −0.381 ** | −0.064 |
| CeC | −0.492 ** | −0.468 ** | −0.225 ** | −0.576 ** | −0.465 ** | −0.392 ** |
| clay | −0.303 ** | −0.347 ** | −0.073 | −0.378 ** | −0.336 ** | −0.264 ** |
| available Mn | −0.235 ** | −0.158 * | 0.055 | −0.408 ** | −0.236 ** | −0.144 * |
| available Fe | −0.098 | −0.129 | 0.191 ** | −0.298 ** | −0.220 ** | 0.092 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, K.; Song, Z. Bioconcentration, Potential Health Risks, and a Receptor Prediction Model of Metal(loid)s in a Particular Agro-Ecological Area. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091902
Cai K, Song Z. Bioconcentration, Potential Health Risks, and a Receptor Prediction Model of Metal(loid)s in a Particular Agro-Ecological Area. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(9):1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091902
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Kui, and Zefeng Song. 2019. "Bioconcentration, Potential Health Risks, and a Receptor Prediction Model of Metal(loid)s in a Particular Agro-Ecological Area" Applied Sciences 9, no. 9: 1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091902
APA StyleCai, K., & Song, Z. (2019). Bioconcentration, Potential Health Risks, and a Receptor Prediction Model of Metal(loid)s in a Particular Agro-Ecological Area. Applied Sciences, 9(9), 1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091902




