Correlation between Spatial-Temporal Variation in Landscape Patterns and Surface Water Quality: A Case Study in the Yi River Watershed, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
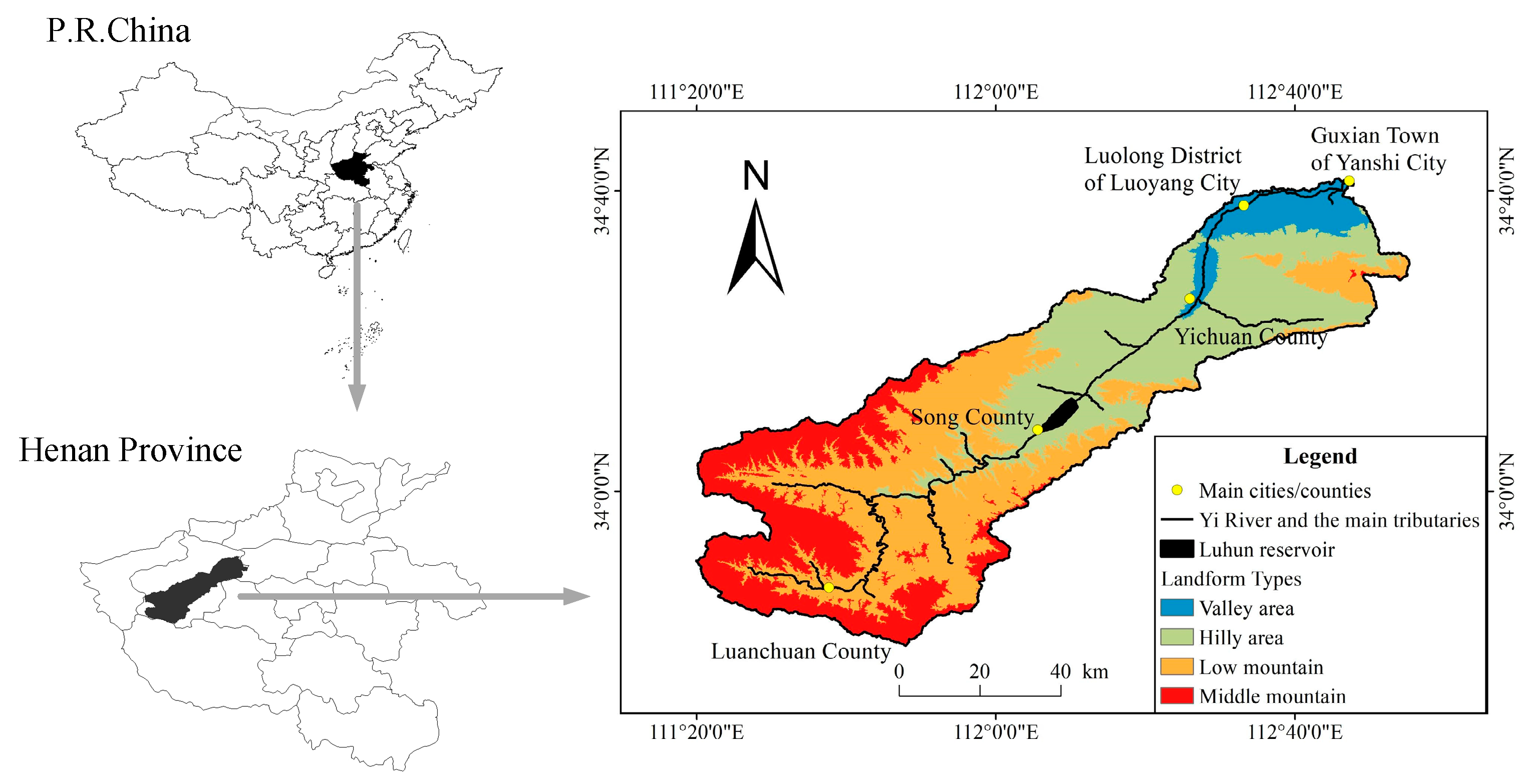
2.1. Site Description
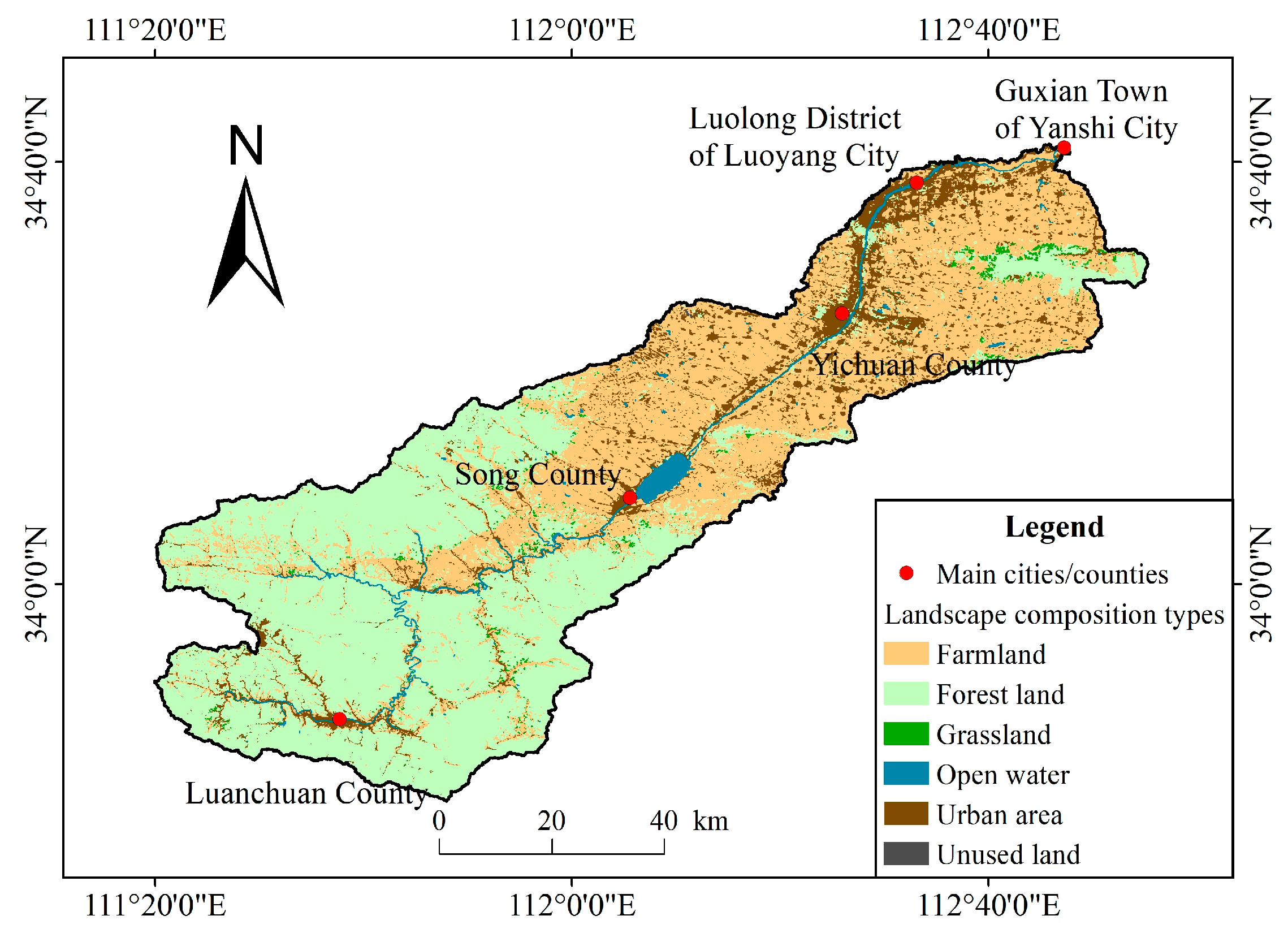
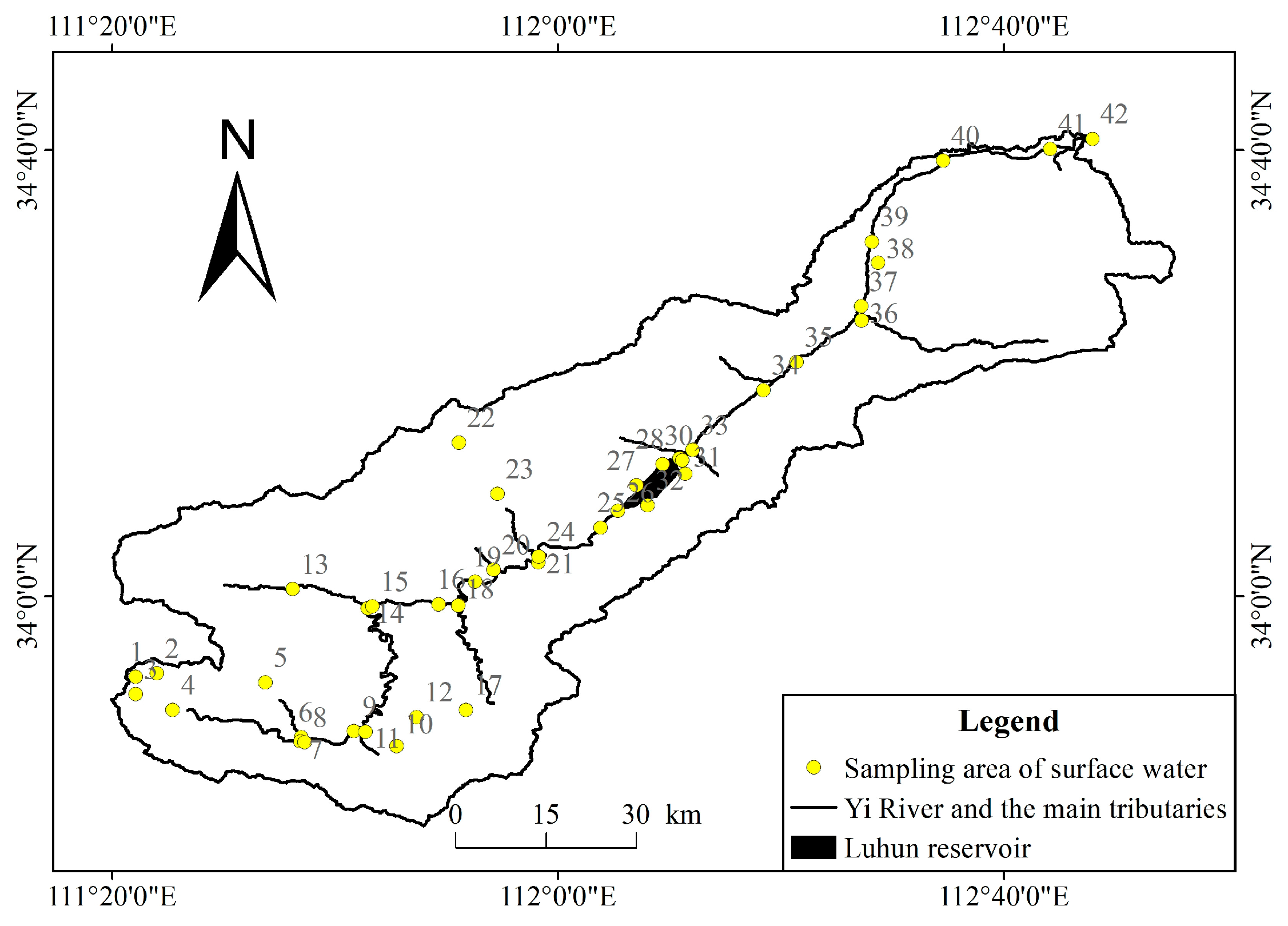
2.2. Data Resources
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. Landscape Indices Analysis
2.3.2. Mapping Analysis
2.3.3. PCA
2.3.4. Correlation Analysis
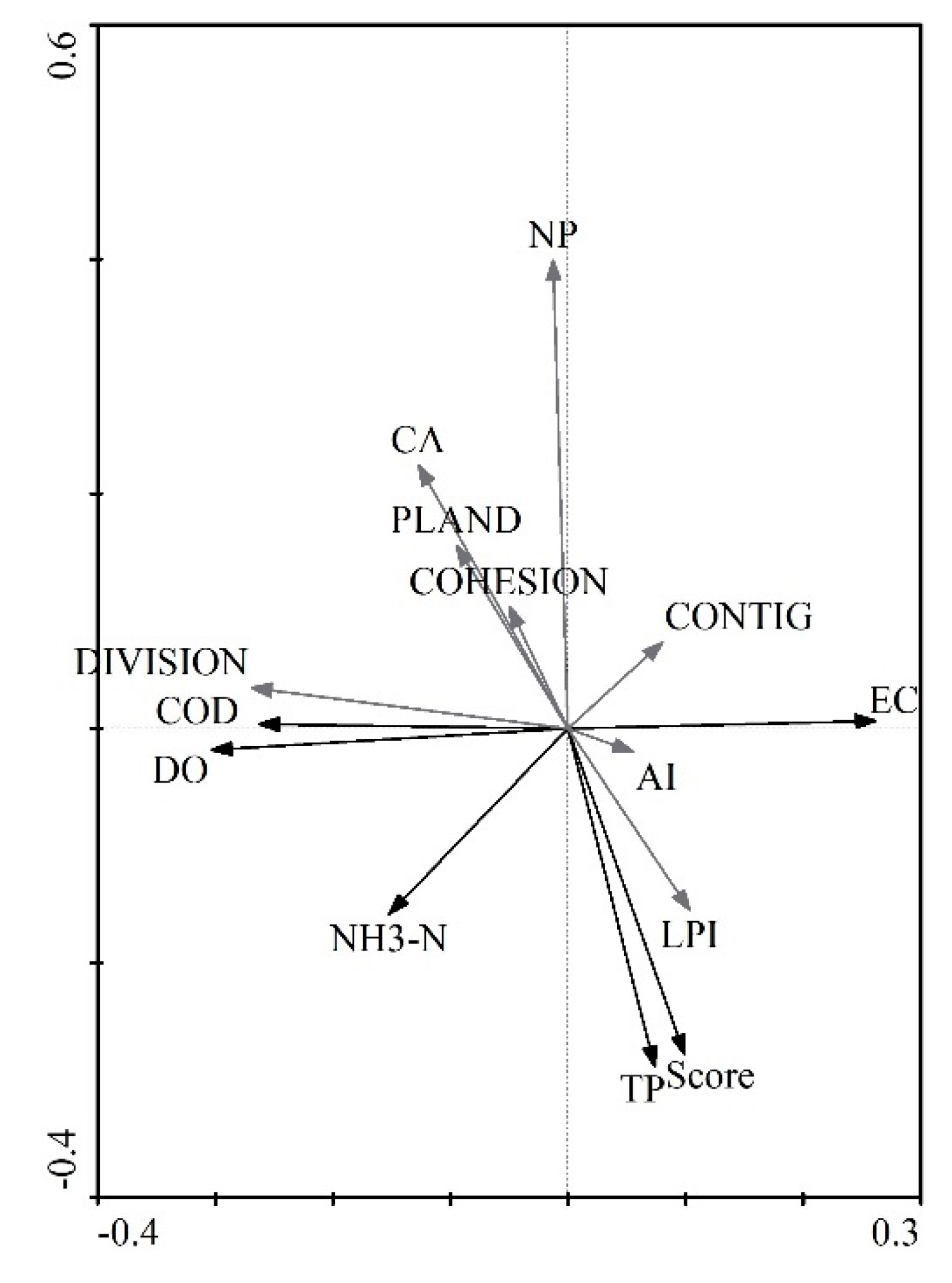
2.3.5. RDA
3. Results
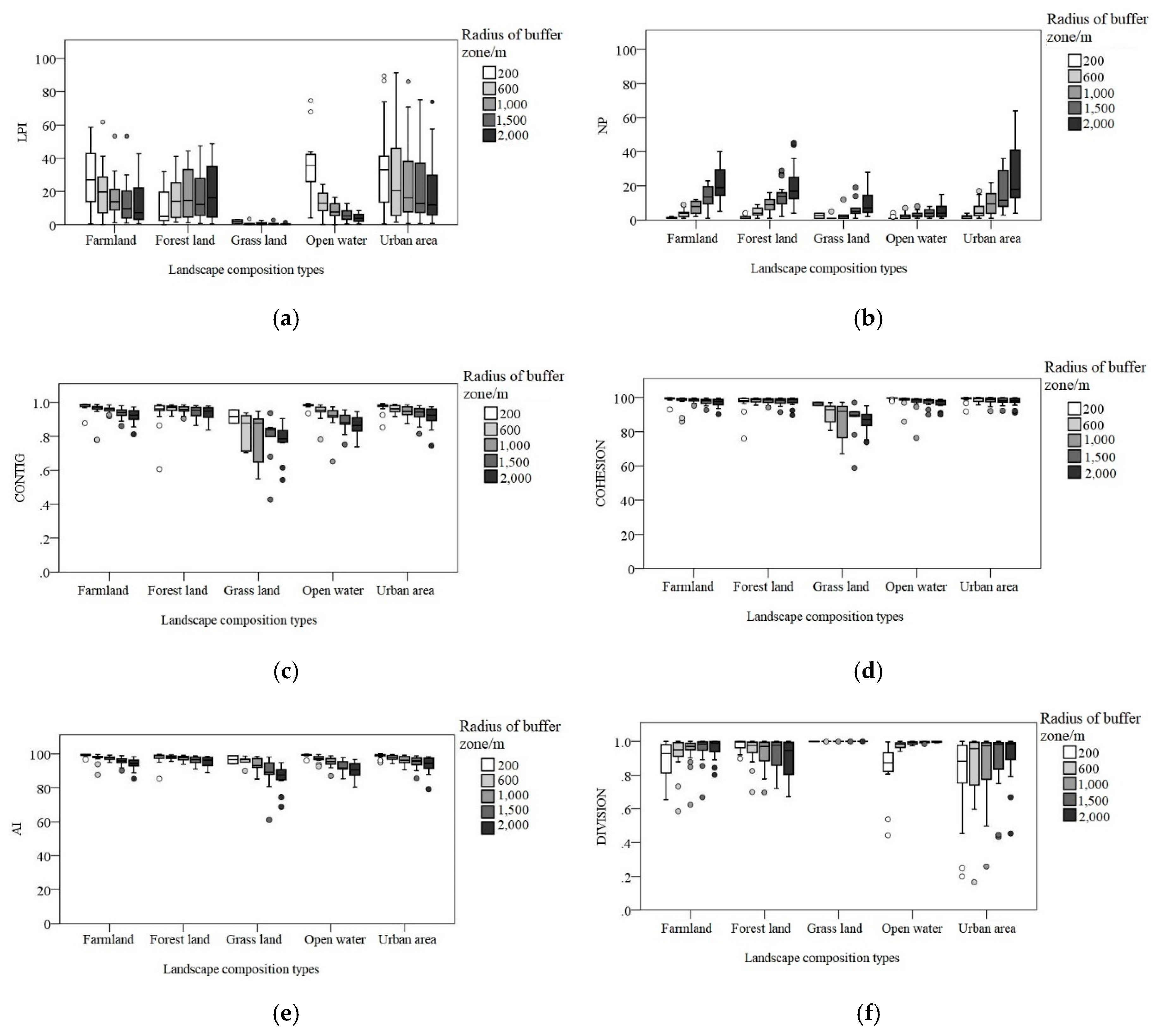
3.1. Landscape Indices Analysis
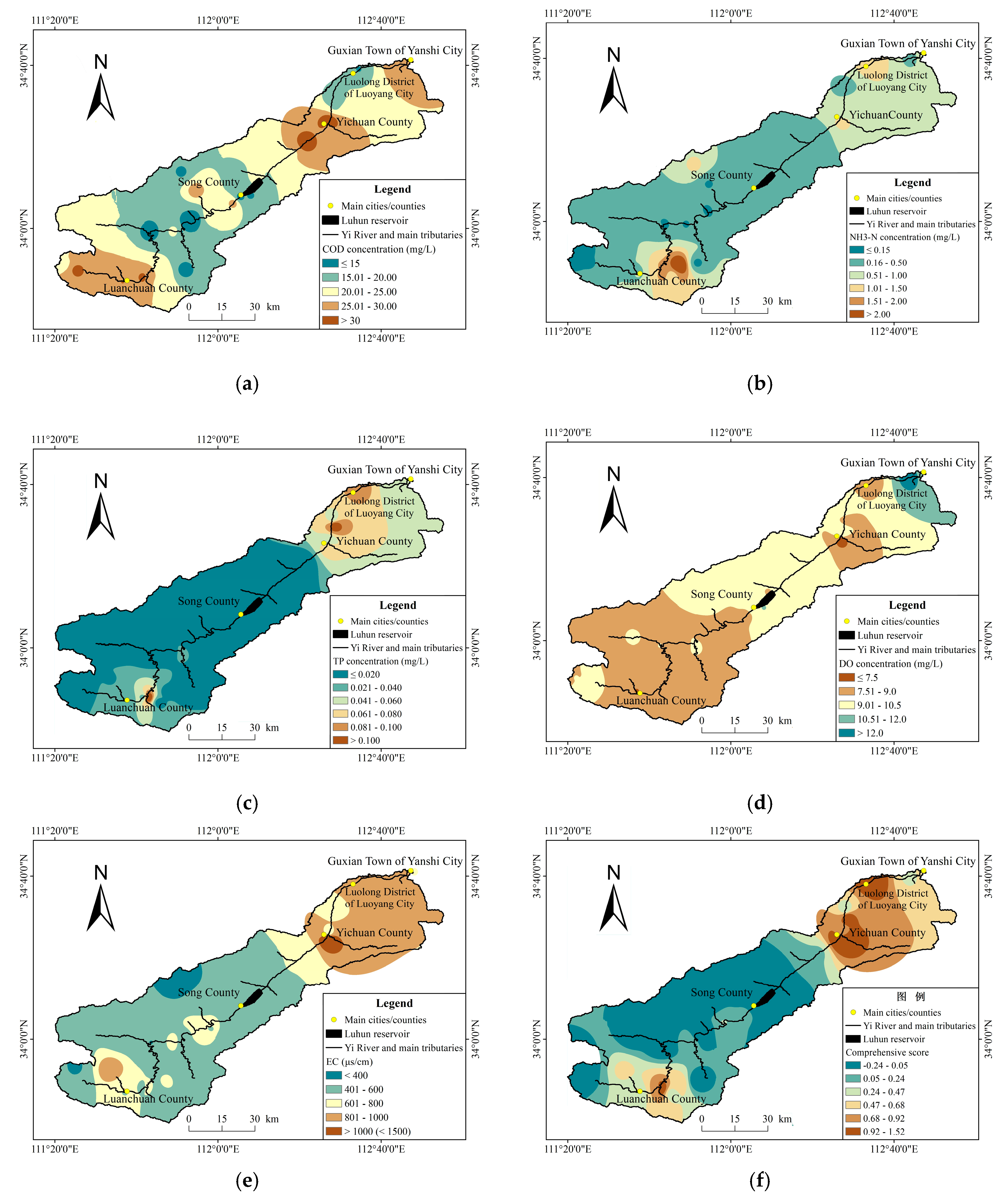
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Surface Water Quality
3.3. Correlation Between Landscape Patterns and Surface Water Quality
3.3.1. Landscape Composition and Surface Water Quality
3.3.2. Landscape Configuration and Surface Water Quality
3.4. Impacting Strengths of Landscape Composition and Configuration on Surface Water Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Landscape Composition on Surface Water Quality
4.2. Effects of Landscape Configuration on Surface Water Quality
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, G. Influence of land use and land cover patterns on seasonal water quality at multi-spatial scales. Catena 2017, 151, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Chen, L.; Ma, K. The effect of land use Chang on the regional environment in the Yangjuangou catchment in the Loess Plateau of China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1999, 54, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Gao, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, Q. River water quality change and its relationship with landscape pattern under the urbanization: A case study of Suzhou City in Taihu Basin. J. Lake Sci. 2017, 29, 827–835. [Google Scholar]
- Lawler, J.J. Landscape pattern and ecological process: An important update of a classic textbook. Ecology 2017, 98, 2231–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Hwang, S.; Lee, S.; Hwang, H.; Sung, H. Landscape ecological approach to the relationships of land use patterns in watersheds to water quality characteristics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrane, S.J. Impacts of urbanization on hydrological and water quality dynamics and urban water management: A review. Hydrol. Sci. J. J. Sci. Hydrol. 2016, 61, 2295–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janardan, M.; Heejun, C. Landscape and anthropogenic factors affecting spatial patterns of water quality trends in a large river basin, South Korea. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 26–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Cao, C.; Guo, M.; Chen, L. Correlation analysis between the spatial characteristics of land use/cover-landscape patter and surface-water quality in the Ebinur Lake area. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 7438–7452. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, D.; Wen, Y.; Wei, J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, J. Relationships between landscape spatial characteristics and surface water quality in the Liu Xi River watershed. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 246–253. [Google Scholar]
- Tscharntke, T.; Batáry, P.; Dormann, C.F. Set-aside management: How do succession, sowing patterns and landscape context affect biodiversity? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 143, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prager, K.; Reed, M.; Scott, A. Encouraging collaboration for the provision of ecosystem services at a landscape scale—Rethinking agri-environmental payments. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, S.M.; Mchale, M.R.; Hess, G.R. Beyond impervious: Urban land-cover pattern variation and implications for watershed management. Environ. Manag. 2016, 58, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, Y.; Qian, G.; Niu, J.; Liang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, A. What is sustainability science? Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Turner, M.G. Importance of landscape heterogeneity in sustaining hydrologic ecosystem services in an agricultural watershed. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Du, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. From natural regionalization, land change to landscape service: The development of integrated physical geography in China. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 1819–1833. [Google Scholar]
- Sabit, M.; Nasirdin, N.; Mamut, A. Analysis on the change in land use/cover ecological service value in Tomur National Reserve. Geogr. Res. 2016, 35, 2116–2124. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, P.; Kong, X.; Yu, L. Effects of land-use and landscape pattern on nitrogen and phosphorus exports in Caohai wetland watershed. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2016, 36, 2983–2989. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Xiang, J. Correlation between the water quality and land use composition in the river side area—A case of Chaohu Lake basin in China. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2011, 20, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, K.; Lee, S.; Hwang, H.; Jang, J. The effects of spatial variability of land use on stream water quality in a costal watershed. Paddy Water Environ. 2008, 6, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, M.; Yackulic, C.B.; Lim, Y.; Arce-Nazario, J.A. Influence of land use on water quality in a tropical landscape: A multi-scale analysis. Landsc. Ecol. 2011, 26, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Lin, G.; Kang, W. The effects of sloping landscape features on water quality in the upper and middle reaches of the Chishui River Watershed. Geogr. Res. 2018, 37, 704–716. [Google Scholar]
- Roces-Díaz, J.V.; Vayreda, J.; Banqué-Casanovas, M.; Díaz-Varela, E.; Bonet, J.A.; Brotons, L.; de-Miguel, S.; Herrando, S.; Martínez-Vilaltaah, J. The spatial level of analysis affects the patterns of forest ecosystem services supply and their relationships. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1270–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billmire, M.; Koziol, B.W. Landscape and flow path-based nutrient loading metrics for evaluation of in-stream water quality in Saginaw Bay, Michigan. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, D.G.; Marques, S.P.; Garabini, C.T.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Paglia, A.P. The effects of landscape patterns on ecosystem services: Meta-analyses of landscape services. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 33, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Basnyat, P.; Teeter, L.D.; Flynn, K.M.; Lockaby, B.G. Relationships between landscape characteristics and nonpoint source pollution inputs to coastal estuaries. Environ. Manag. 1999, 23, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.T.Y.; Chen, W. Modeling the relationship between land use and surface water quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 66, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Turner, M.G. Spatial interactions among ecosystem services in an urbanizing agricultural watershed. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12149–12154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, M.; Zhu, X. Relationship between landscape pattern and river water quality in Wujingang region, Taihu Lake watershed. Environ. Sci. 2010, 31, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar]
- King, R.S.; Baker, M.E.; Whigham, D.F.; Weller, D.E.; Jordan, T.E.; Hurd, K.M.K. Spatial considerations for linking watershed land cover to ecological indicators in streams. Ecol. Appl. 2005, 15, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jiang, M.; Yuan, Y. Spatial heterogeneity of water quality in Xiaoxingkai Lake. Wetl. Sci. 2015, 13, 166–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Mou, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Z. Spatial and temporal variability of water quality of city river in south Jiangsu. Environ. Pollut. Control. 2012, 34, 28–33. [Google Scholar]

| Abbreviation | Description | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| CA | Total (class) area | Total area of patches of a certain landscape composition type. A fundamental measure of landscape composition. |
| PLAND | Percentage of landscape | Percentage of CA in total landscape area. Another fundamental measure of landscape composition. |
| LPI | Largest patch index | Percentage of the area of the largest patch of a certain landscape composition type in the landscape total area. It helps confirm the dominant landscape composition type. |
| NP | Number of patches | Total number of patches of a certain landscape composition type, which can reflect landscape spatial pattern and describe the heterogeneity of a landscape. |
| CONTIG | Contiguity index | Average contiguity index among patches of certain landscape composition types. |
| COHESION | Patch cohesion index | Physical connectivity of patches in the same landscape composition type that can describe the connectivity among patches. |
| AI | Aggregation index | Adjacency relation among pixels that can aggregate into patches in certain landscape composition types. |
| DIVISION | Landscape division index | Possibility of two random pixels not in the same patch of being a certain landscape composition type, which reflects the spatial pattern of the landscape. |
| Surface Water Quality Indicators | Principal Component 1 | Principal Component 2 |
|---|---|---|
| COD | 0.42 | 0.66 |
| NH3–N | 0.74 | 0.11 |
| TP | 0.85 | 0.01 |
| DO | −0.32 | 0.81 |
| EC | 0.78 | −0.15 |
| Variance contribution rate (%) | 42.98 | 42.42 |
| Accumulating contribution rate (%) | 42.98 | 85.40 |
| Radius (m) | Indicator | Farmland | Forest Land | Grass Land | Urban Area | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLAND | LPI | PLAND | LPI | PLAND | LPI | PLAND | LPI | ||
| 200 | COD | −0.33 | −0.32 | −0.60 * | −0.60 * | — | — | 0.43 | 0.39 |
| NH3–N | −0.07 | −0.07 | −0.40 | −0.40 | — | — | 0.13 | 0.14 | |
| TP | −0.40 | -0.31 | 0.01 | 0.12 | — | — | 0.29 | 0.14 | |
| DO | −0.15 | −0.25 | 0.07 | 0.27 | — | — | −0.12 | −0.06 | |
| EC | −0.25 | −0.34 | −0.24 | 0.55 * | — | — | 0.29 | 0.13 | |
| Score 1 | −0.35 | −0.32 | −0.43 | −0.39 | — | — | 0.37 | 0.33 | |
| 600 | COD | 0.09 | −0.07 | −0.15 | −0.15 | −0.20 | −0.20 | 0.20 | 0.31 |
| NH3–N | 0.04 | −0.04 | −0.36 | −0.33 | −0.30 | −0.30 | 0.25 | 0.20 | |
| TP | −0.45 | −0.42 | -0.32 | −0.28 | −0.30 | −0.30 | 0.43 | 0.41 | |
| DO | 0.57 ** | 0.46 * | −0.01 | −0.003 | 0.50 | 0.50 | −0.38 | −0.32 | |
| EC | −0.25 | −0.21 | −0.35 | −0.33 | −0.20 | −0.20 | 0.45 * | 0.42 | |
| Score | −0.10 | −0.20 | −0.37 | −0.32 | −0.40 | −0.40 | 0.39 | 0.38 | |
| 1000 | COD | 0.12 | 0.06 | −0.29 | −0.26 | −0.57 | −0.54 | 0.25 | 0.23 |
| NH3–N | 0.09 | 0.08 | −0.34 | −0.39 | −0.21 | −0.11 | 0.27 | 0.27 | |
| TP | −0.44 | −0.27 | −0.27 | −0.29 | −0.11 | 0.00 | 0.40 | 0.43 | |
| DO | 0.35 | 0.39 | −0.22 | −0.14 | 0.39 | 0.43 | −0.33 | −0.34 | |
| EC | 0.10 | 0.13 | −0.41 | −0.43 | −0.36 | −0.43 | 0.40 | 0.37 | |
| Score | −0.04 | -0.03 | −0.36 | −0.40 | −0.43 | −0.36 | 0.40 | 0.39 | |
| 1500 | COD | 0.09 | 0.13 | −0.35 | −0.27 | −0.46 | −0.50 | 0.29 | 0.22 |
| NH3–N | 0.04 | 0.11 | −0.30 | −0.32 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.25 | 0.35 | |
| TP | −0.46 * | −0.33 | −0.20 | −0.15 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.41 | 0.49 * | |
| DO | 0.64 ** | 0.70 ** | −0.33 | −0.24 | −0.38 | −0.49 | −0.25 | −0.20 | |
| EC | −0.10 | −0.06 | −0.41 | −0.37 | −0.44 | −0.31 | 0.44 | 0.38 | |
| Score | −0.10 | −0.02 | −0.33 | −0.31 | −0.14 | −0.20 | 0.39 | 0.42 | |
| 2000 | COD | 0.06 | 0.04 | −0.32 | −0.28 | −0.50 | −0.48 | 0.46 * | 0.37 |
| NH3–N | −0.01 | 0.03 | −0.33 | −0.21 | −0.01 | 0.09 | 0.35 | 0.51 * | |
| TP | −0.45 * | −0.40 | −0.15 | −0.06 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.47 * | 0.62 ** | |
| DO | 0.56 * | 0.61 ** | −0.33 | −0.26 | −0.37 | −0.58 | −0.01 | −0.08 | |
| EC | −0.12 | −0.10 | −0.34 | −0.27 | −0.38 | −0.19 | 0.48 * | 0.48 * | |
| Score | −0.14 | −0.11 | −0.31 | −0.22 | −0.25 | −0.27 | 0.51 * | 0.60 ** | |
| Indicator | NP | CONTIG | COHESION | DIVISION | AI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | −0.13 | −0.67 * | −0.57 * | 0.60 * | −0.59 * |
| NH3–N | −0.43 | −0.26 | −0.27 | 0.42 | −0.11 |
| TP | −0.87 ** | 0.34 | 0.30 | −0.12 | 0.45 |
| DO | −0.47 | −0.14 | −0.32 | 0.44 | 0.15 |
| EC | 0.52 * | 0.53 | 0.51 | −0.39 | 0.47 |
| Score | −0.52 | −0.28 | −0.25 | 0.40 | −0.13 |
| Indicator | NP | CONTIG | COHESION | DIVISION | AI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | −0.23 | 0.42 | 0.33 | −0.40 | 0.40 |
| NH3–N | −0.47 * | 0.43 | 0.46 * | −0.49 * | 0.44 |
| TP | −0.50 * | 0.56 ** | 0.61 ** | −0.60 ** | 0.54 * |
| DO | 0.08 | −0.04 | −0.16 | 0.10 | −0.05 |
| EC | −0.32 | 0.56 * | 0.43 | −0.45 * | 0.52 * |
| Score | −0.49 * | 0.56 * | 0.56 ** | −0.59 ** | 0.55 * |
| Axis. | Eigenvalue | Correlation Coefficient | Contribution to Surface Water Quality (%) | Accumulating Contribution to Surface Water Quality and Variation in Landscape Indices (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.072 | 0.288 | 7.2 | 96.1 |
| 2 | 0.002 | 0.312 | 7.4 | 98.9 |
| 3 | 0.001 | 0.086 | 7.5 | 100.0 |
| 4 | 0.000 | 0.129 | 7.5 | 100.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bian, Z.; Liu, L.; Ding, S. Correlation between Spatial-Temporal Variation in Landscape Patterns and Surface Water Quality: A Case Study in the Yi River Watershed, China. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061053
Bian Z, Liu L, Ding S. Correlation between Spatial-Temporal Variation in Landscape Patterns and Surface Water Quality: A Case Study in the Yi River Watershed, China. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(6):1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061053
Chicago/Turabian StyleBian, Ziqi, Lyuyi Liu, and Shengyan Ding. 2019. "Correlation between Spatial-Temporal Variation in Landscape Patterns and Surface Water Quality: A Case Study in the Yi River Watershed, China" Applied Sciences 9, no. 6: 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061053
APA StyleBian, Z., Liu, L., & Ding, S. (2019). Correlation between Spatial-Temporal Variation in Landscape Patterns and Surface Water Quality: A Case Study in the Yi River Watershed, China. Applied Sciences, 9(6), 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9061053





