Nanopowder Fluidization Using the Combined Assisted Fluidization Techniques of Particle Mixing and Flow Pulsation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
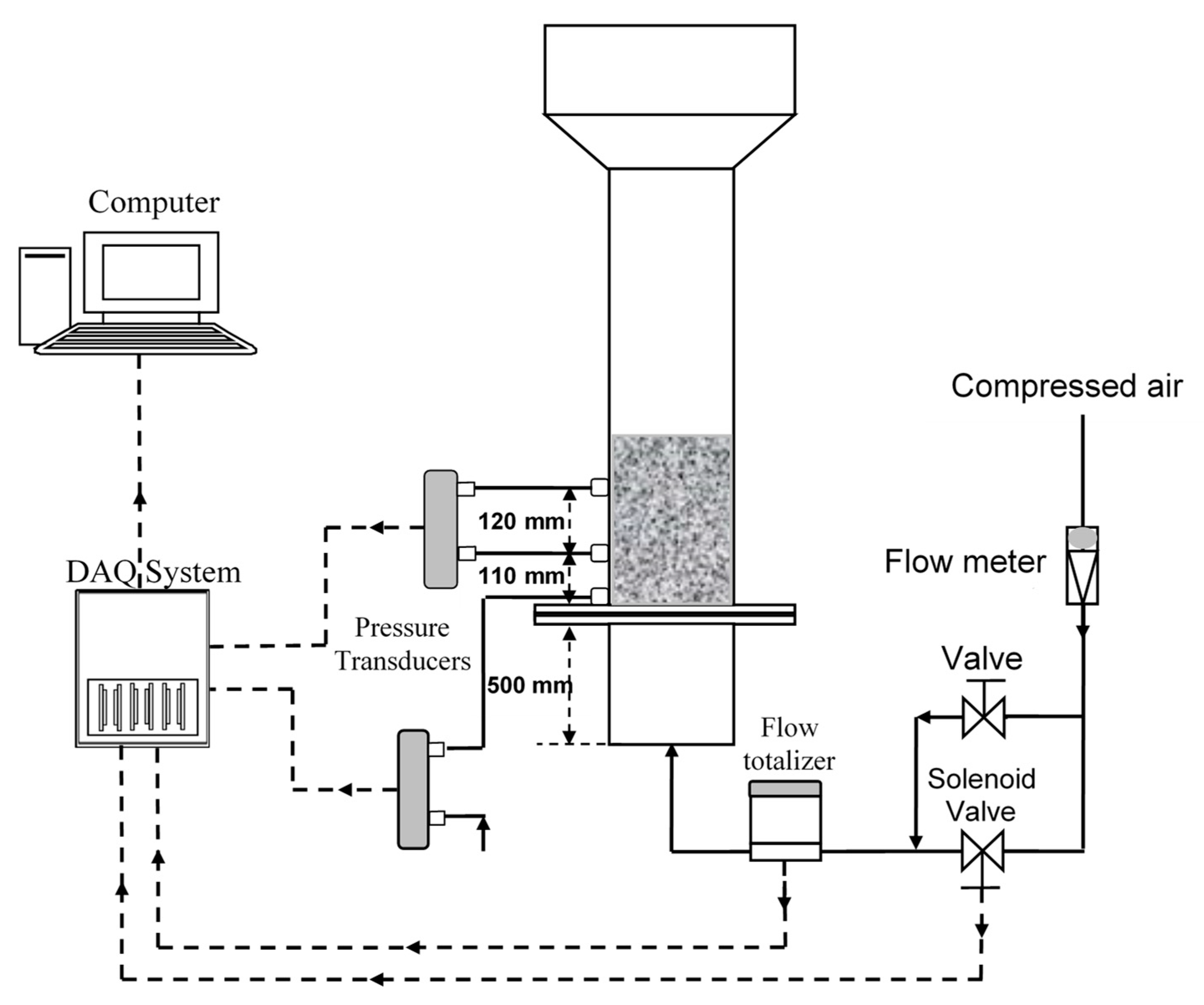
2. Experimental
- Unassisted fluidization experiments were carried out by first gradually increasing the velocity followed by a gradual defluidization.
- Before carrying out the fluidization and defluidization experiment, 4.5 vol % Geldart group A particles were added and thoroughly mixed with the nanopowder.
- The inlet air flow to the fluidized bed was pulsed at 0.1 Hz.
- Steps 2 and 3 were repeated after increasing the fraction of group A particles to 8.6 vol %.
3. Mathematical Equations Used
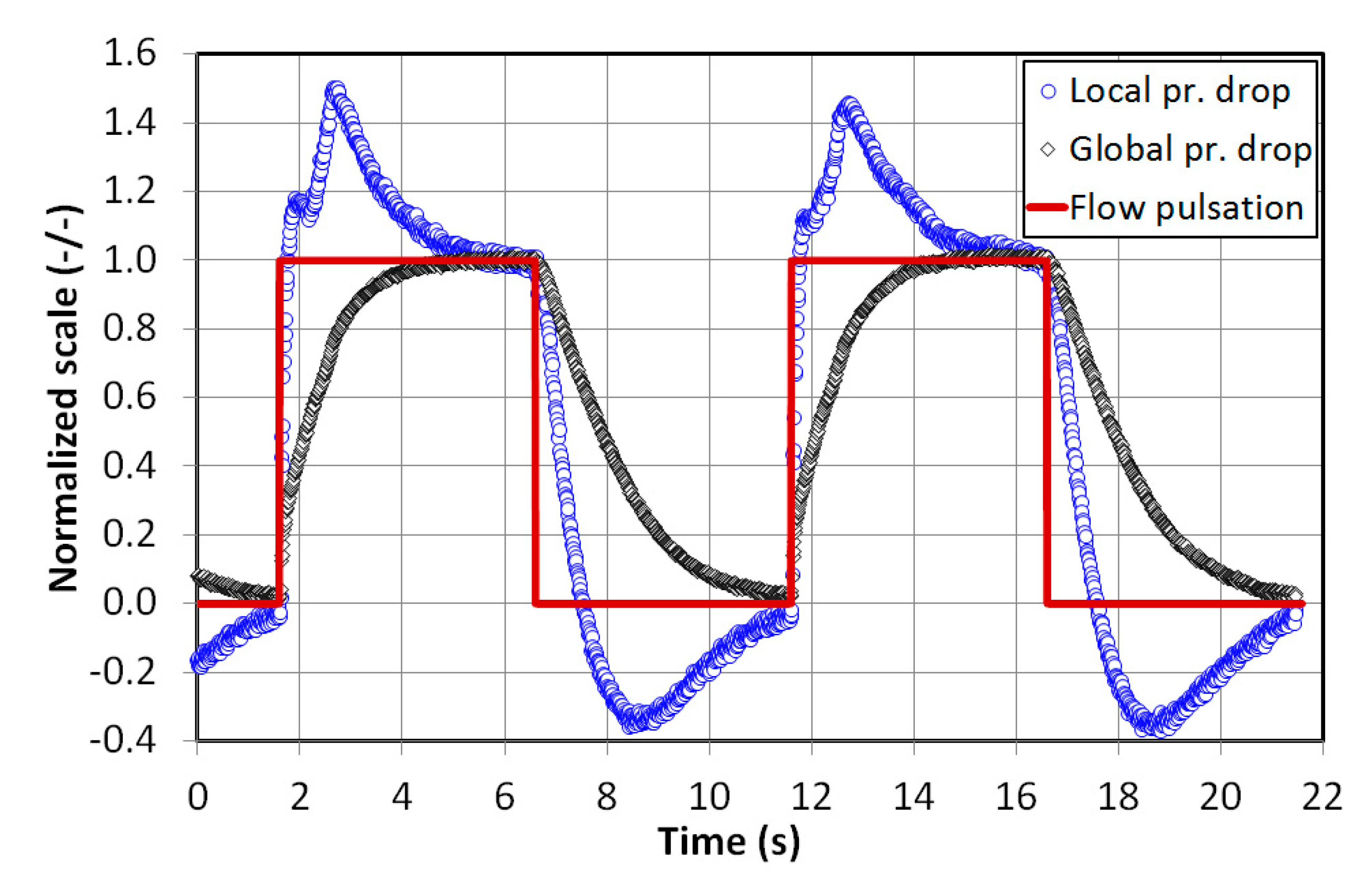
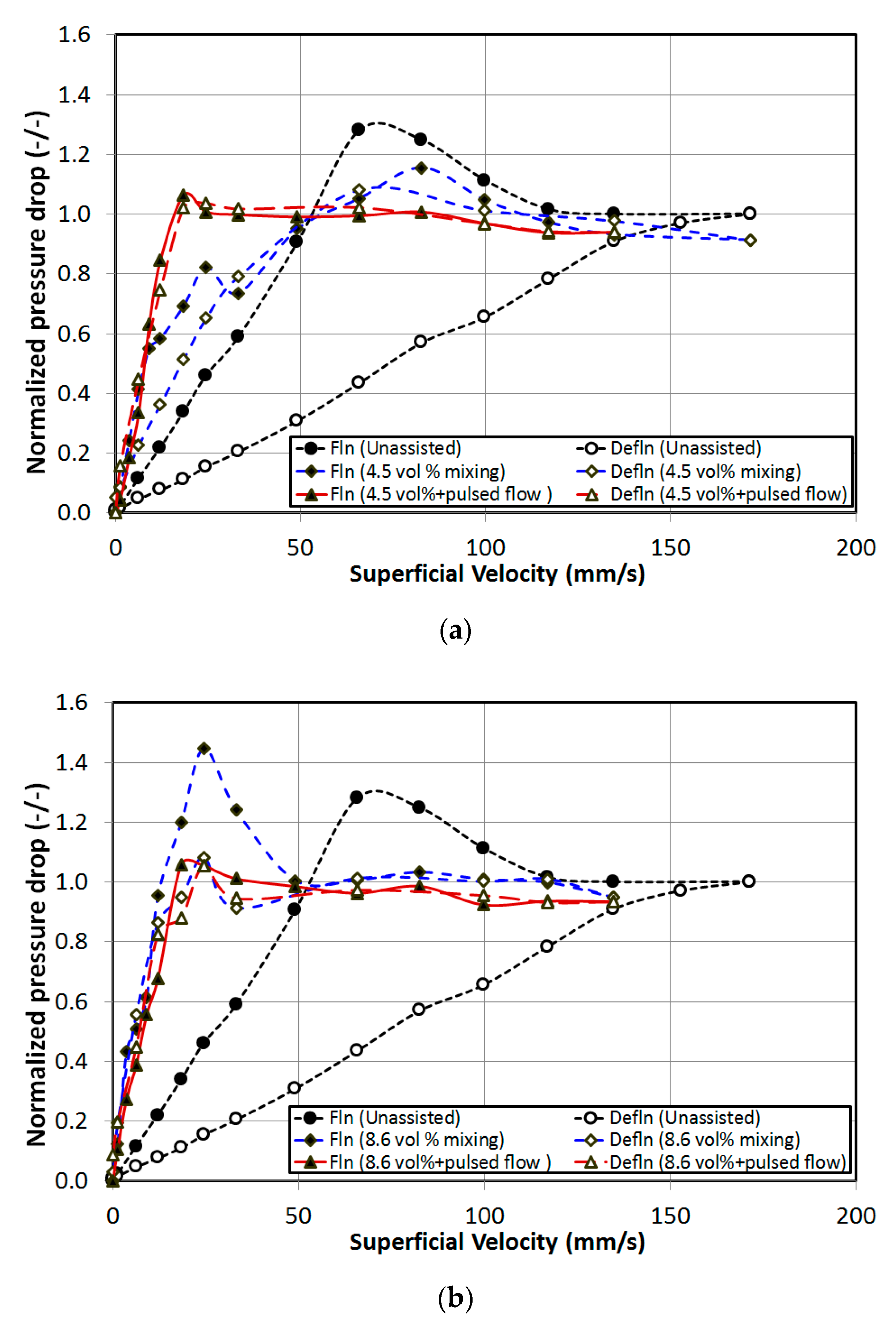
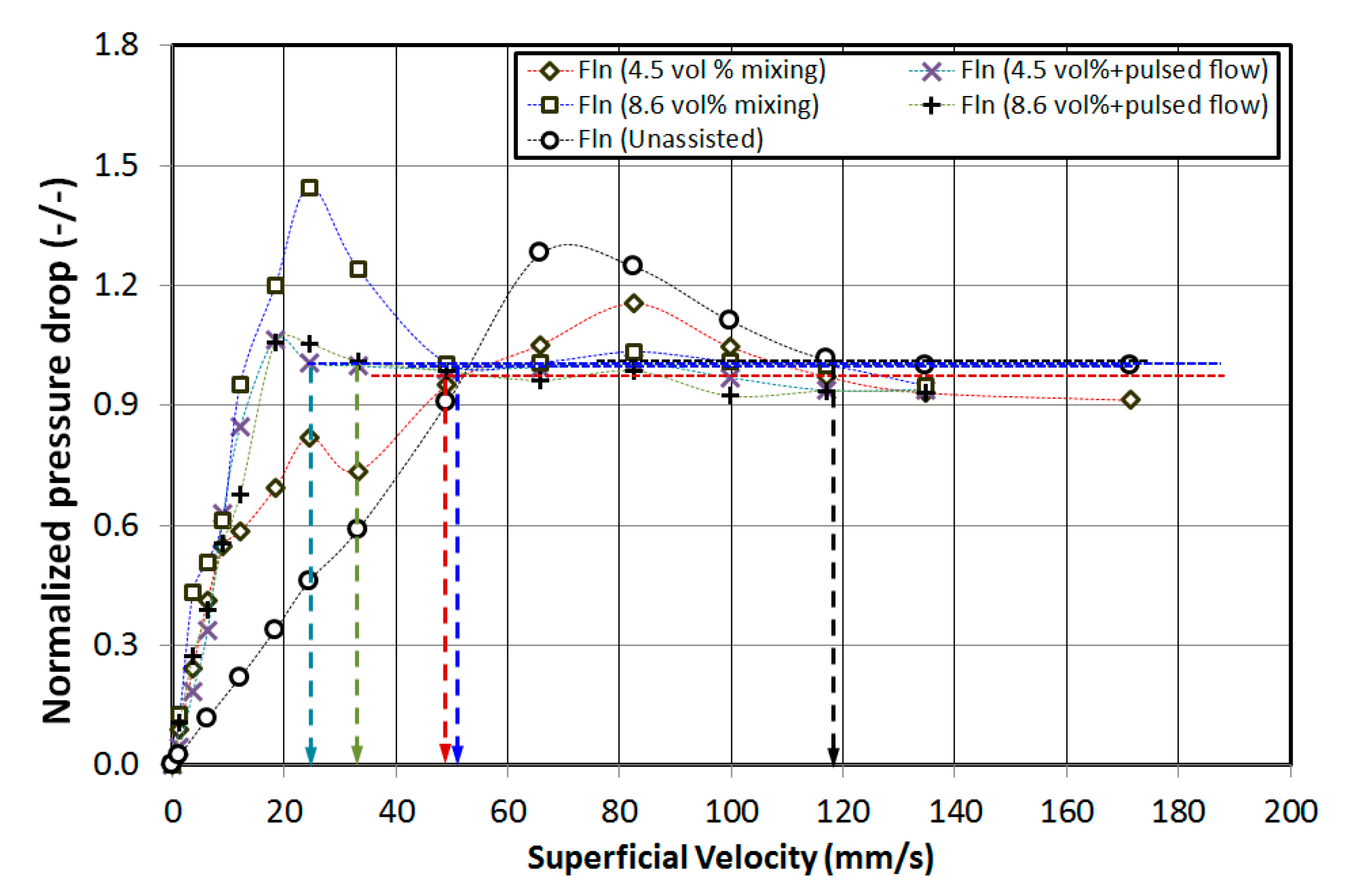
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| mean diameter of nanoparticle agglomerates (µm) | |
| diameter of the component (µm) | |
| distance between pressure taps (m) | |
| solid mass in the bed (kg) | |
| pressure drop calculated from the Ergun equation (Pa) | |
| average pressure drop (Pa) | |
| pressure transient recorded at ‘ith’ time (Pa) | |
| superficial velocity of the fluid (m/s) | |
| minimum fluidization velocity (m/s) | |
| volume of the solids in the bed (m3) | |
| specific volume of the species (-/-) | |
| specific volume of the mixture (-/-) | |
| volume fraction of the species (-/-) | |
| Greek Symbols | |
| bed porosity (-/-) | |
| bed porosity at incipient fluidization (-/-) | |
| bulk density (kg/m3) | |
| air density (kg/m3) | |
| true solid density (kg/m3) | |
| air viscosity at room temperature (N·s m–2) | |
| standard deviation (Pa) |
References
- Van Ommen, J.R.; Valverde, J.M.; Pfeffer, R. Fluidization of nanopowders: A review. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wei, F. Review on the nanoparticle fluidization science and technology. China J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 24, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Al-Ghurabi, E.H.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Asif, M. Effect of adding Geldart group A particles on the collapse of fluidized bed of hydrophilic nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghurabi, E.; Ajbar, A.; Asif, M. Improving Fluidization Hydrodynamics of Group C Particles by Mixing with Group B Particles. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettieri, P.; Macrì, D. Effect of Process Conditions on Fluidization. KONA Powder Part. J. 2016, 33, 86–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, E.K.; Celeste, B. Combined effects of mechanical and acoustic vibrations on fluidization of cohesive powders. Powder Technol. 2006, 163, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, A.; Salameh, S.; Ciacchi, L.C.; Kreutzer, M.T.; van Ommen, J.R. Contact mechanics of highly porous oxide nanoparticle agglomerates. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, A.; Rahman, F.; Wang, S.; Rhodes, M. Enhanced fluidization of nanoparticles with gas phase pulsation assistance. Powder Technol. 2015, 284, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabanian, J.; Jafari, R.; Chaouki, J. Fluidization of Ultrafine Powders. Int. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2012, 4, 16–50. [Google Scholar]
- Shabanian, J.; Chaouki, J. Influence of interparticle forces on solids motion in a bubbling gas-solid fluidized bed. Powder Technol. 2016, 299, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Rahman, F.; Rhodes, M.J. Nanoparticle fluidization and Geldart’s classification. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 3455–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, J.M.; Castellanos, A. Fluidization, bubbling and jamming of nanoparticle agglomerates. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 6947–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldart, D. Types of gas fluidization. Powder Technol. 1973, 7, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, S.; Gómez-Hernández, J.; Goulas, A.; Van Bui, H.; van Ommen, J.R. Advances in scalable gas-phase manufacturing and processing of nanostructured solids: A review. Particuology 2017, 30, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Pacek, A.W. De-agglomeration of goethite nano-particles using ultrasonic comminution device. Powder Technol. 2008, 187, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Orwa, M.G.; Pacek, A.W. De-agglomeration of hydrophobic and hydrophilic silica nano-powders in a high shear mixer. Powder Technol. 2009, 195, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhu, J. Parametric study of fine particle fluidization under mechanical vibration. Powder Technol. 2006, 161, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, J.M. Acoustic streaming in gas-fluidized beds of small particles. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 8792–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliyaperumal, S.; Barghi, S.; Zhu, J.; Briens, L.; Rohani, S. Effects of acoustic vibration on nano and sub-micron powders fluidization. Powder Technol. 2011, 210, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, G.; Yu, Q.; Pfeffer, R.; Dave, R.N.; Nam, C.H. Sound assisted fluidization of nanoparticle agglomerates. Powder Technol. 2004, 141, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Diao, R.; Zhou, T.; Wang, H.; Kage, H.; Mawatari, Y. Behavior of magnetic Fe3O4 nano-particles in magnetically assisted gas-fluidized beds. Adv. Powder Technol. 2011, 22, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Dave, R.N.; Zhu, C.; Quevedo, J.A.; Pfeffer, R. Enhanced fluidization of nanoparticles in an oscillating magnetic field. AIChE J. 2005, 51, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, J.M.; Castellanos, A.; Quintanilla, M.A.S.; Gilabert, F.A. Effect of inclination on gas-fluidized beds of fine cohesive powders. Powder Technol. 2008, 182, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, J. Magnetically assisted gas-solid fluidization in a tapered vessel: Part, I. Magnetization-LAST mode. Particuology 2009, 7, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Asif, M.; Ajbar, A. Bed collapse behavior of pulsed fluidized beds of nano-powder. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Al-Ghurabi, E.H.; Ajbar, A.; Mohammed, Y.A.; Boumaza, M.; Asif, M. Effect of Frequency on Pulsed Fluidized Beds of Ultrafine Powders. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Asif, M. Fluidization of nano-powders: Effect of flow pulsation. Powder Technol. 2012, 225, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, E.; Pitt, K.; Smith, R. A review of pulsed flow fluidisation; the effects of intermittent gas flow on fluidised gas-solid bed behaviour. Powder Technol. 2016, 292, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, A.; van Ommen, J.R.; Nijenhuis, J.; Wang, X.S.; Coppens, M.-O.; Rhodes, M.J. Improved Drying in a Pulsation-Assisted Fluidized Bed. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Asif, M. Effect of particle mixing on the hydrodynamics of fluidized bed of nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2017, 310, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raganati, F.; Chirone, R.; Ammendola, P. Effect of Temperature on Fluidization of Geldart’s Group A and C Powders: Role of Interparticle Forces. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 12811–12821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghurabi, E.; Ajbar, A.; Asif, M. Enhancement of CO2 Removal Efficacy of Fluidized Bed Using Particle Mixing. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Liang, X.; Zhou, T.; Wang, J.; Tang, W. Fluidization of mixed SiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles by adding coarse particles. Powder Technol. 2014, 267, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajbar, A.; Alhumazi, K.; Asif, M. Improvement of the Fluidizability of Cohesive Powders through Mixing with Small Proportions of Group A Particles. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2005, 83, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammendola, P.; Chirone, R. Aeration and mixing behaviours of nano-sized powders under sound vibration. Powder Technol. 2010, 201, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirone, R.; Raganati, F.; Ammendola, P.; Barletta, D.; Lettieri, P.; Poletto, M. A comparison between interparticle forces estimated with direct powder shear testing and with sound assisted fluidization. Powder Technol. 2018, 323, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajbar, A.; Bakhbakhi, Y.; Ali, S.; Asif, M. Fluidization of nano-powders: Effect of sound vibration and pre-mixing with group A particles. Powder Technol. 2011, 206, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla, M.A.S.; Valverde, J.M.; Castellanos, A.; Lepek, D.; Pfeffer, R.; Dave, R.N. Nanofluidization as affected by vibration and electrostatic fields. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 5559–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, Q. Fluidization in combined acoustic-magnetic field for mixtures of ultrafine particles. China Particuol. 2007, 5, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Ali, S.S. Bed collapse dynamics of fluidized beds of nano-powder. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Hernández, J.; Sánchez-Delgado, S.; Wagner, E.; Mudde, R.F.; van Ommen, J.R. Characterization of TiO2 nanoparticles fluidization using X-ray imaging and pressure signals. Powder Technol. 2017, 316, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogre, C.; Thakurdesai, A.U.; van Ommen, J.R.; Salameh, S. Long-term fluidization of Titania nanoparticle agglomerates. Powder Technol. 2017, 316, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

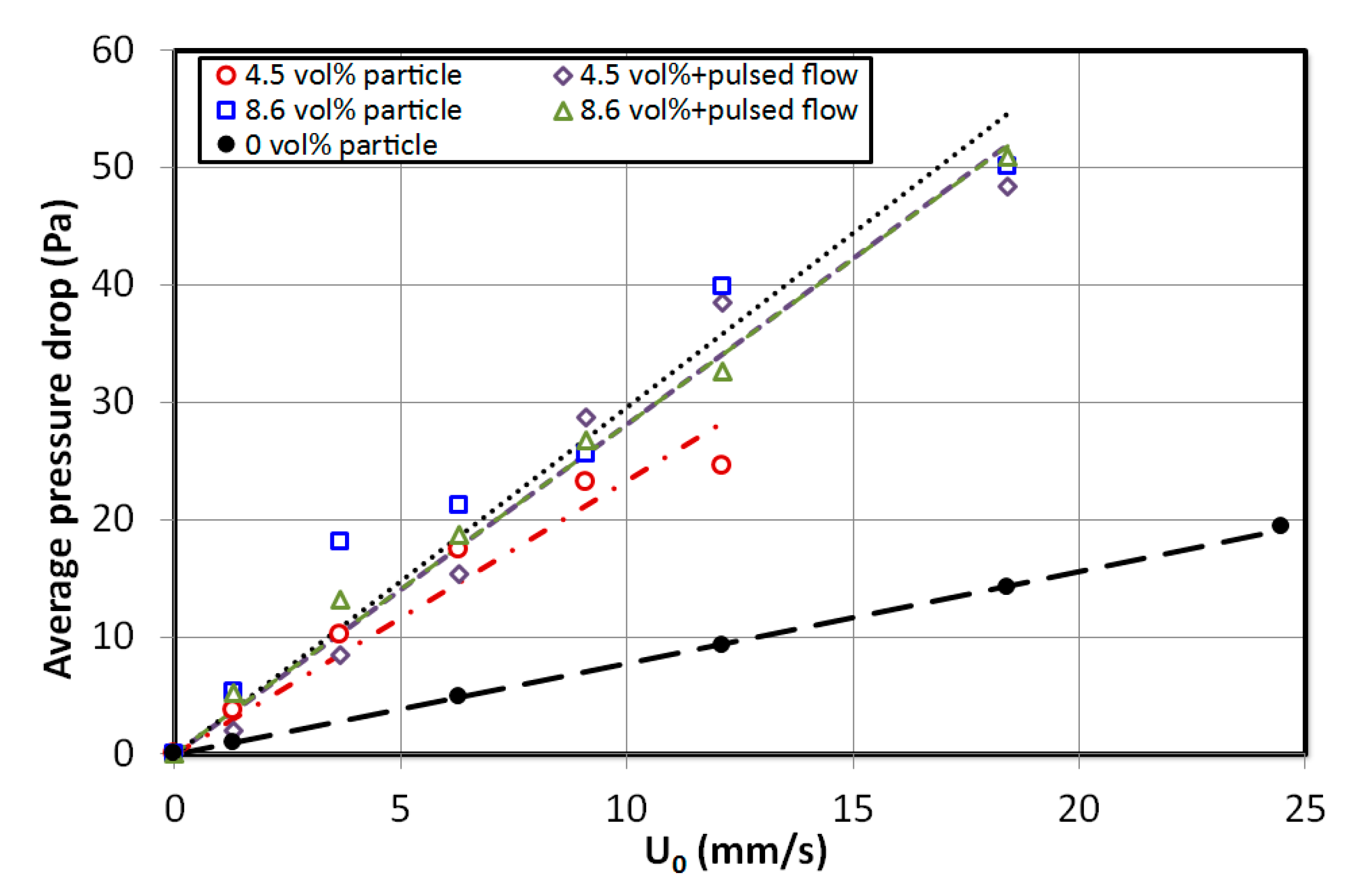
| Incipient Fluidization | ||
|---|---|---|
| (mm/s) | (-/-) | |
| Unassisted | 118.3 | 0.984 |
| 4.5 vol % particle | 47.0 | 0.973 |
| 4.5 vol % + 0.1 Hz pulse | 25.0 | 0.971 |
| 8.6 vol % particle | 49.4 | 0.970 |
| 8.6 vol % + 0.1 Hz pulse | 33.0 | 0.969 |
| Assisted Fluidization Techniques | Porosity (ε) | Effective Diameter | Mean Agglomerate Diameter | Agglomerate Size Reduction | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (-/-) | (µm) | (µm) | (%) | (-/-) | |
| Unassisted | 0.979 | 14.05 | 14.05 | - | 0.997 |
| 4.5 vol % particle | 0.971 | 11.62 | 9.50 | 32.4 | 0.910 |
| 4.5 vol % + 0.1 Hz pulse | 0.970 | 10.65 | 8.49 | 39.6 | 0.992 |
| 8.6 vol % particle | 0.967 | 11.50 | 7.25 | 48.4 | 0.924 |
| 8.6 vol % + 0.1 Hz pulse | 0.969 | 11.21 | 6.93 | 50.7 | 0.975 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, S.S.; Basu, A.; Alfadul, S.M.; Asif, M. Nanopowder Fluidization Using the Combined Assisted Fluidization Techniques of Particle Mixing and Flow Pulsation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030572
Ali SS, Basu A, Alfadul SM, Asif M. Nanopowder Fluidization Using the Combined Assisted Fluidization Techniques of Particle Mixing and Flow Pulsation. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(3):572. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030572
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Syed Sadiq, Avijit Basu, Sulaiman M. Alfadul, and Mohammad Asif. 2019. "Nanopowder Fluidization Using the Combined Assisted Fluidization Techniques of Particle Mixing and Flow Pulsation" Applied Sciences 9, no. 3: 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030572
APA StyleAli, S. S., Basu, A., Alfadul, S. M., & Asif, M. (2019). Nanopowder Fluidization Using the Combined Assisted Fluidization Techniques of Particle Mixing and Flow Pulsation. Applied Sciences, 9(3), 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030572






