Correlation Structures of PM2.5 Concentration Series in the Korean Peninsula
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
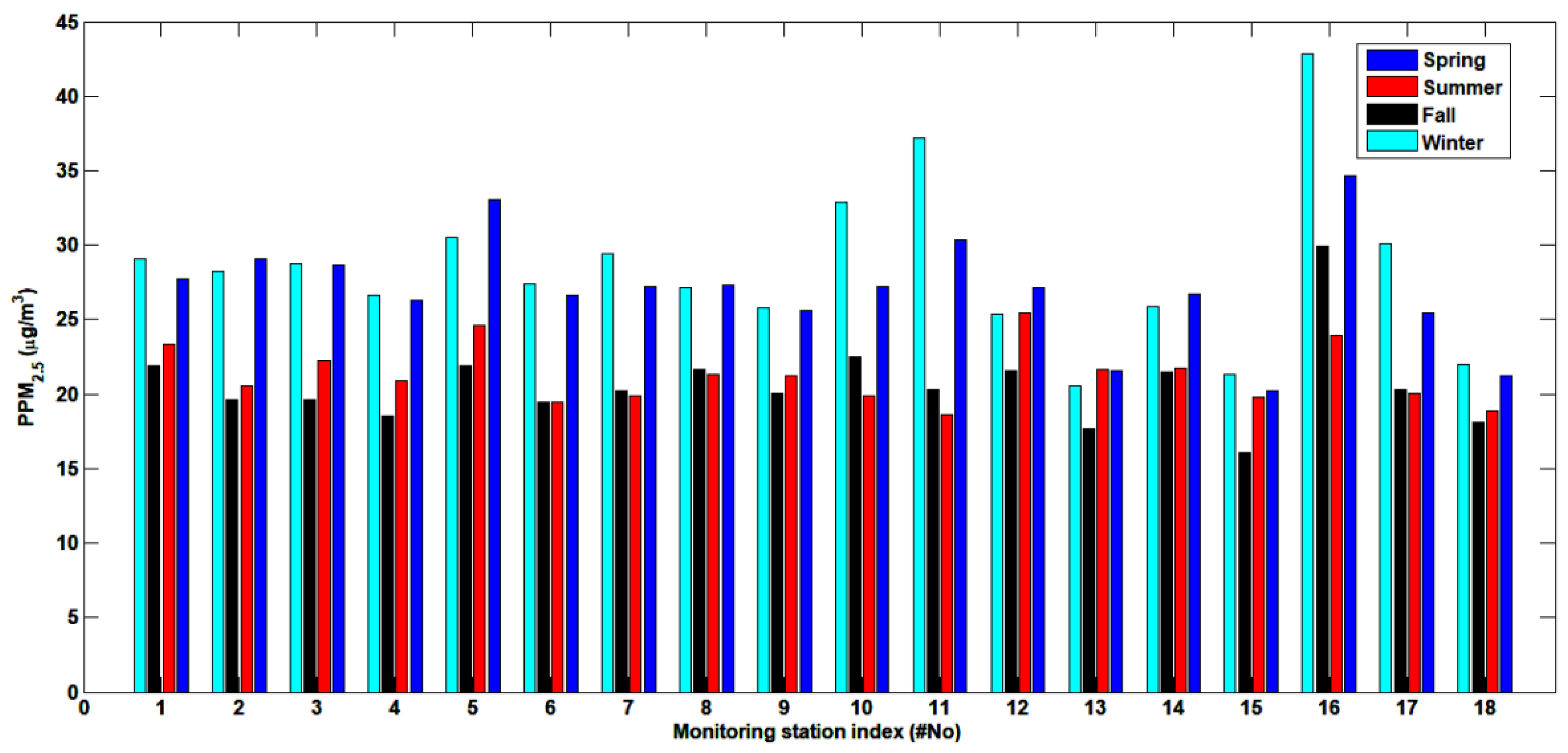
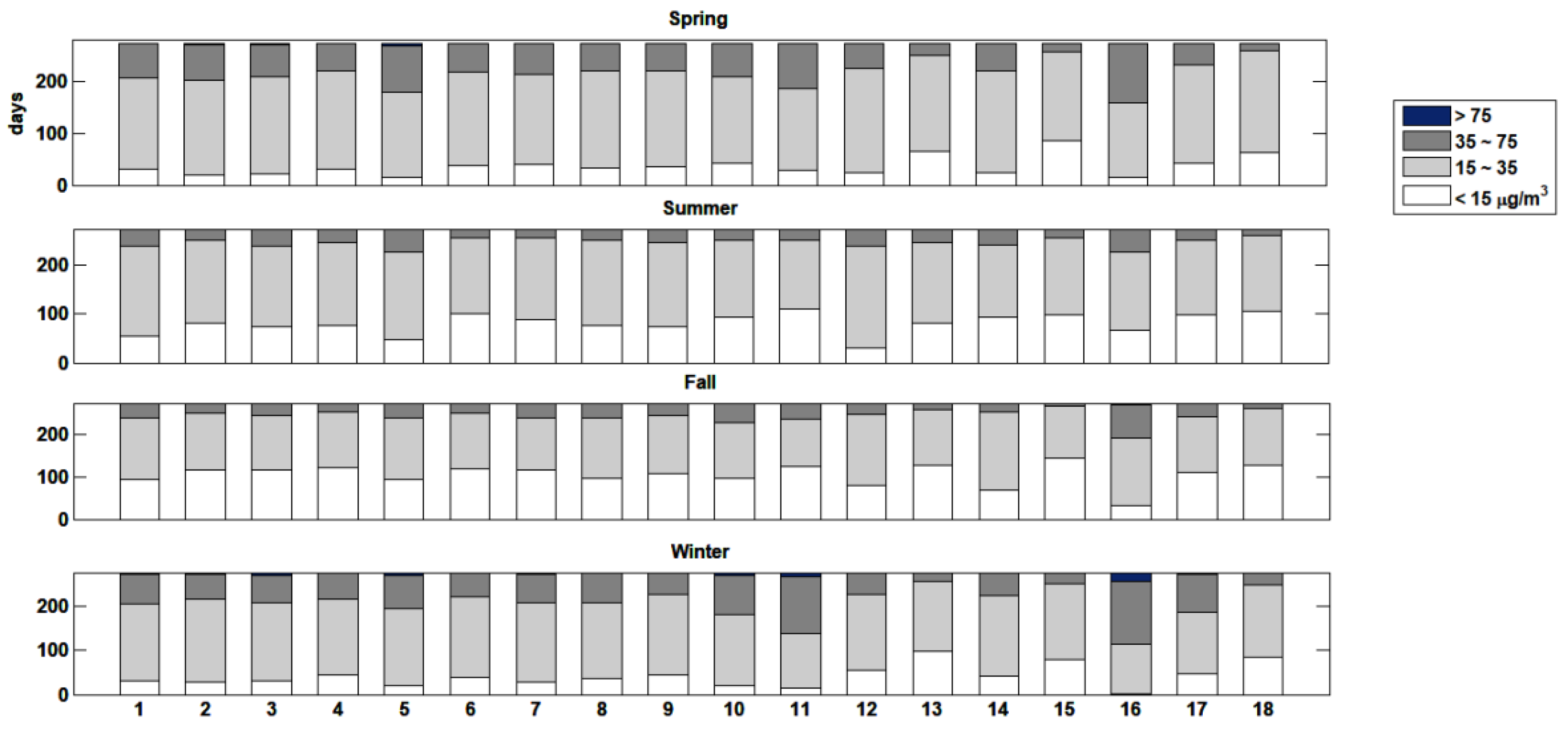
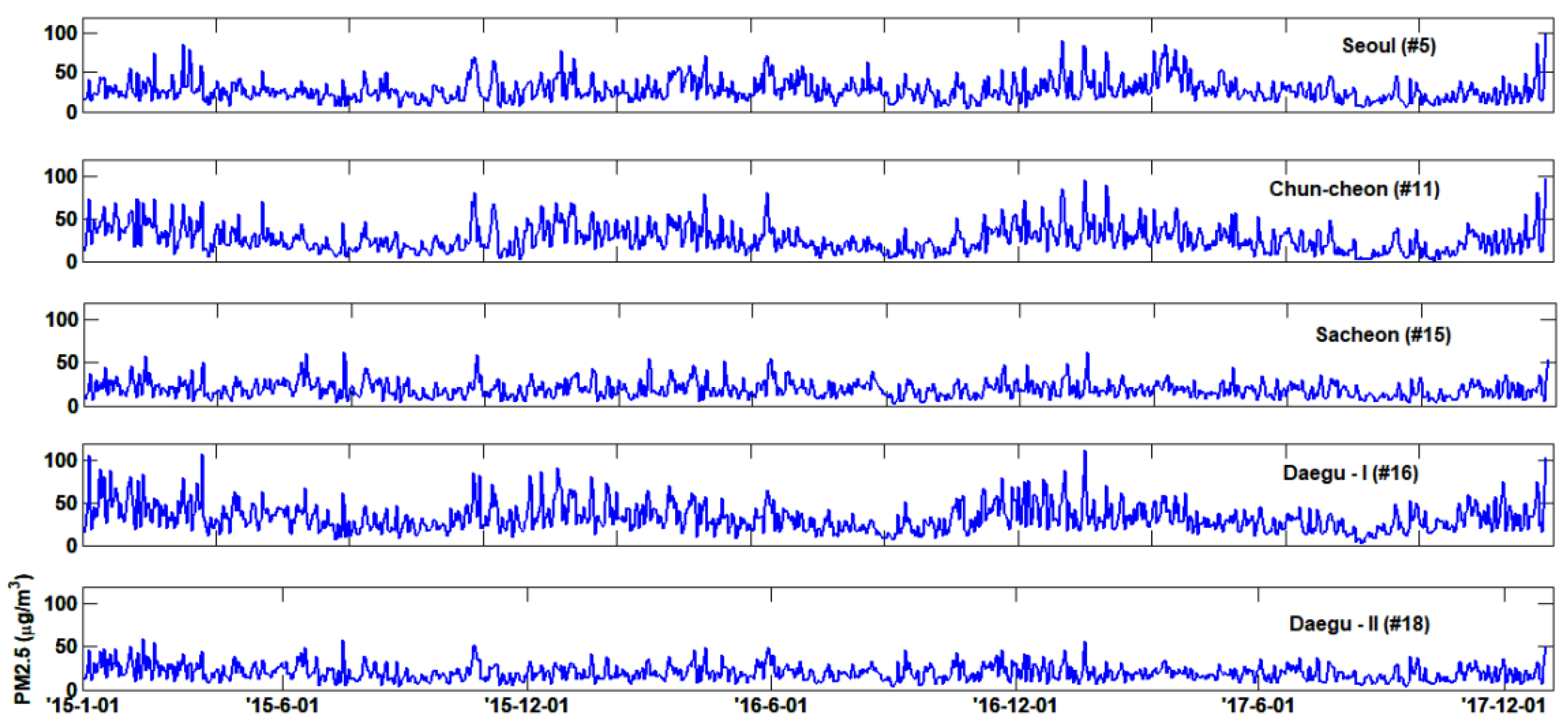
2.1. Data
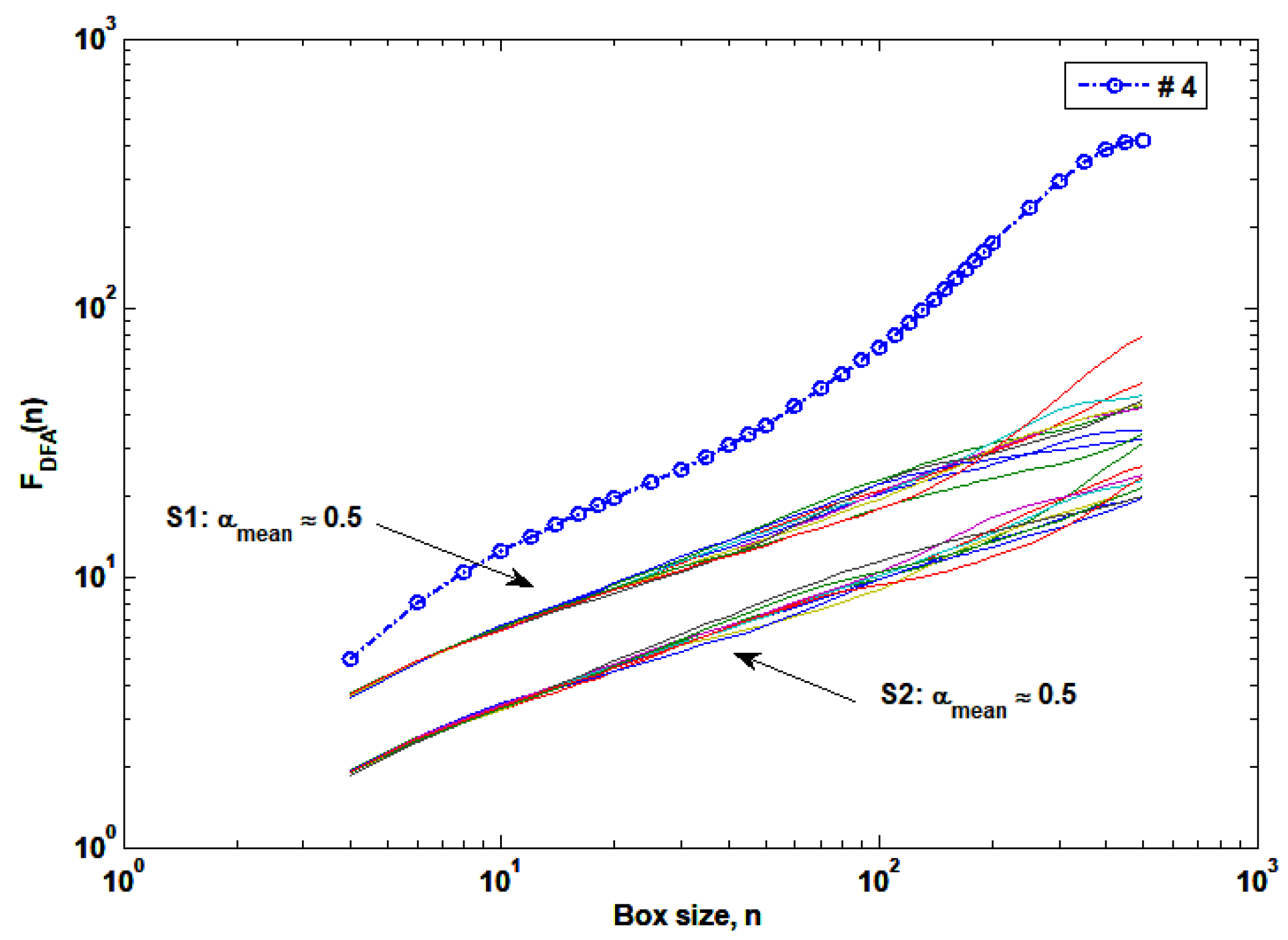
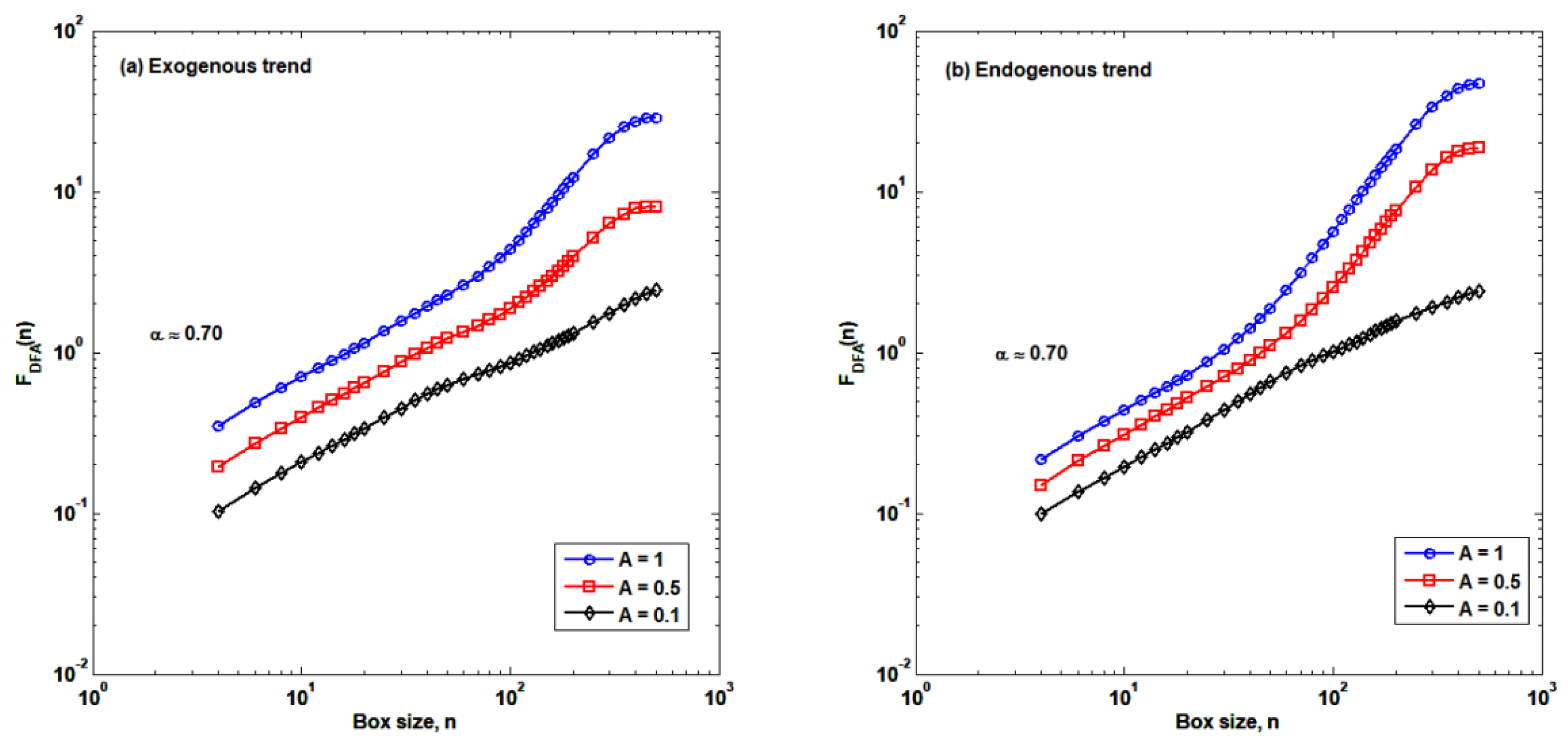
2.2. Detrended Fluctuation Analysis (DFA)
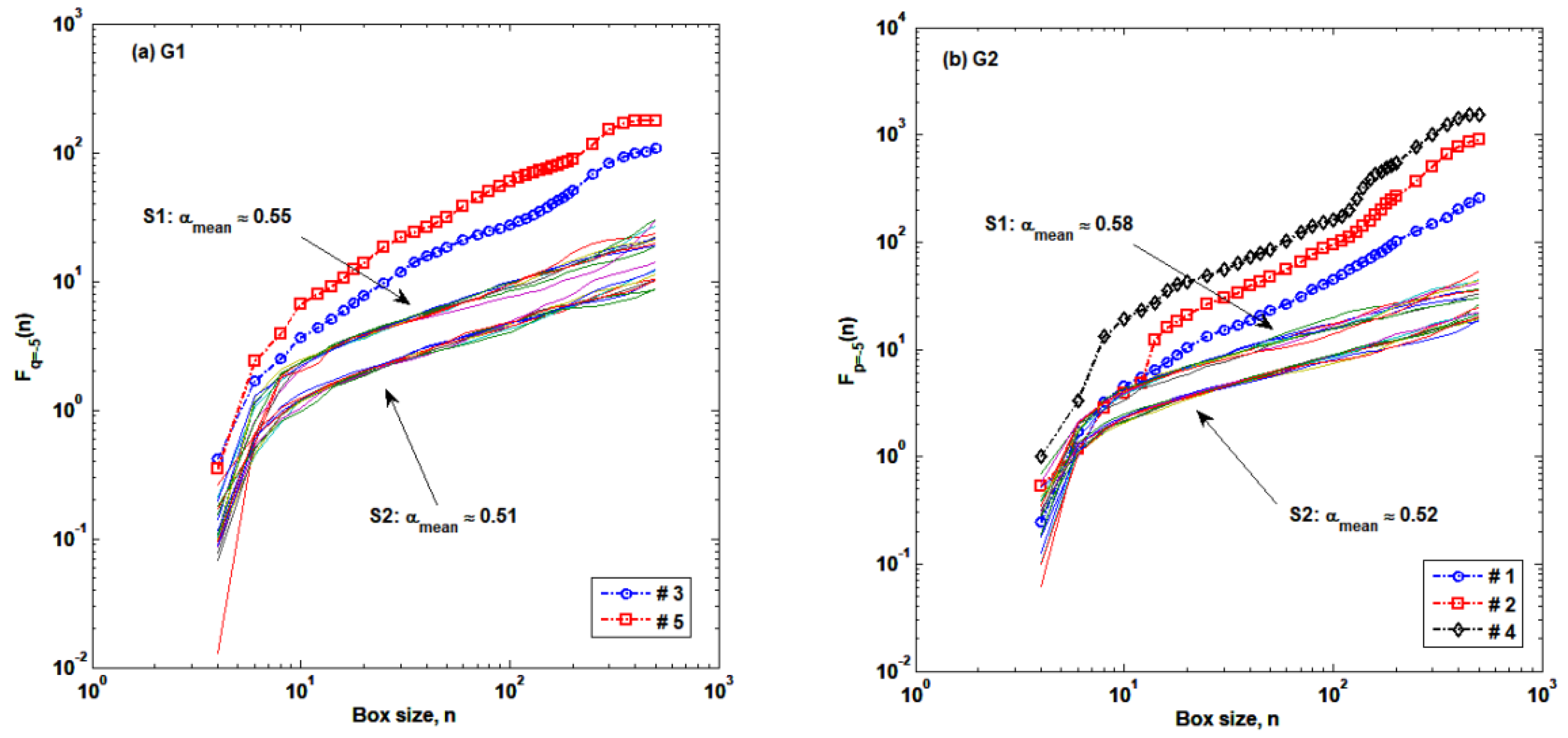
2.3. Multifractal Detrended Fluctuation Analysis (MFDFA)
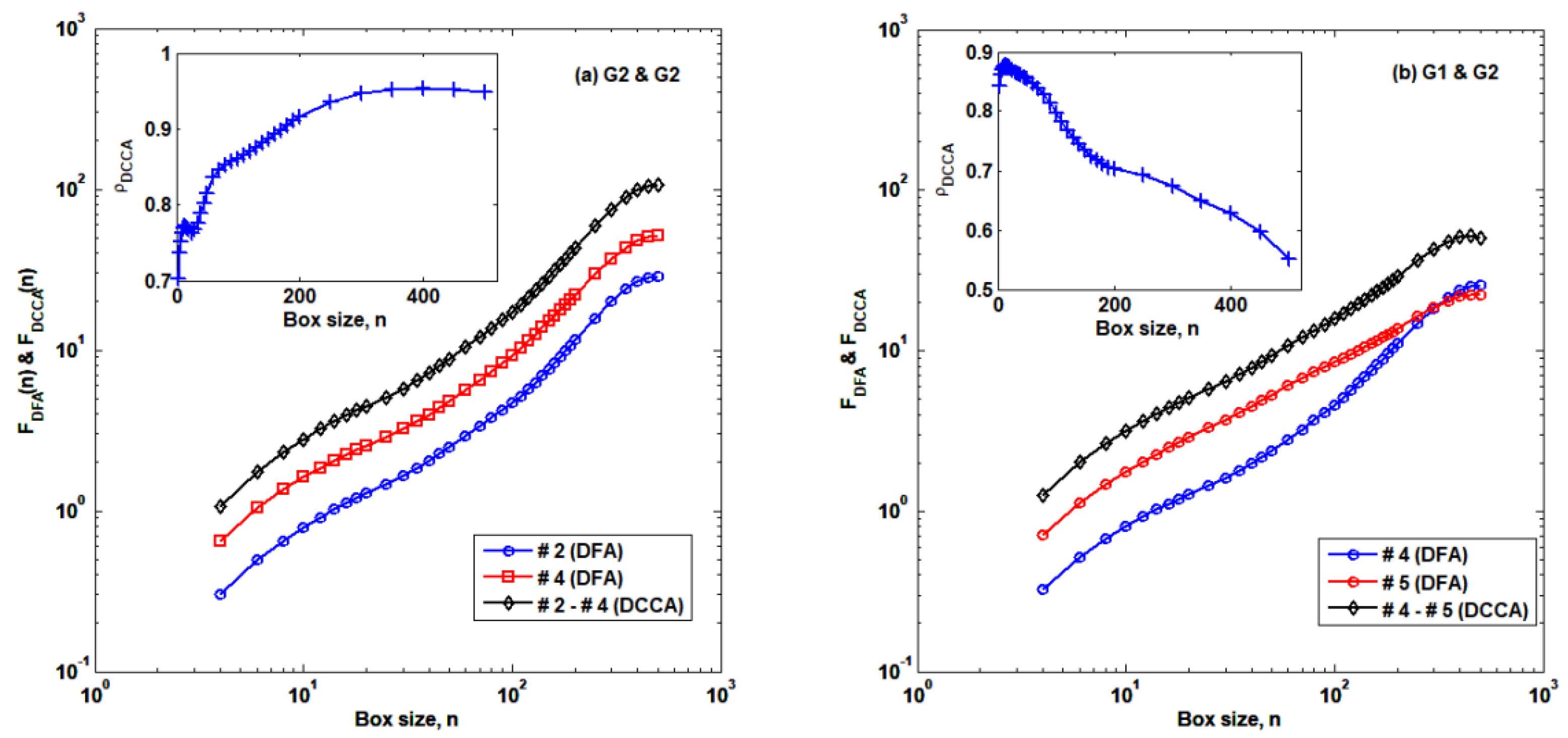
2.4. Detrended Cross-Correlation Analysis (DCCA)
3. Results
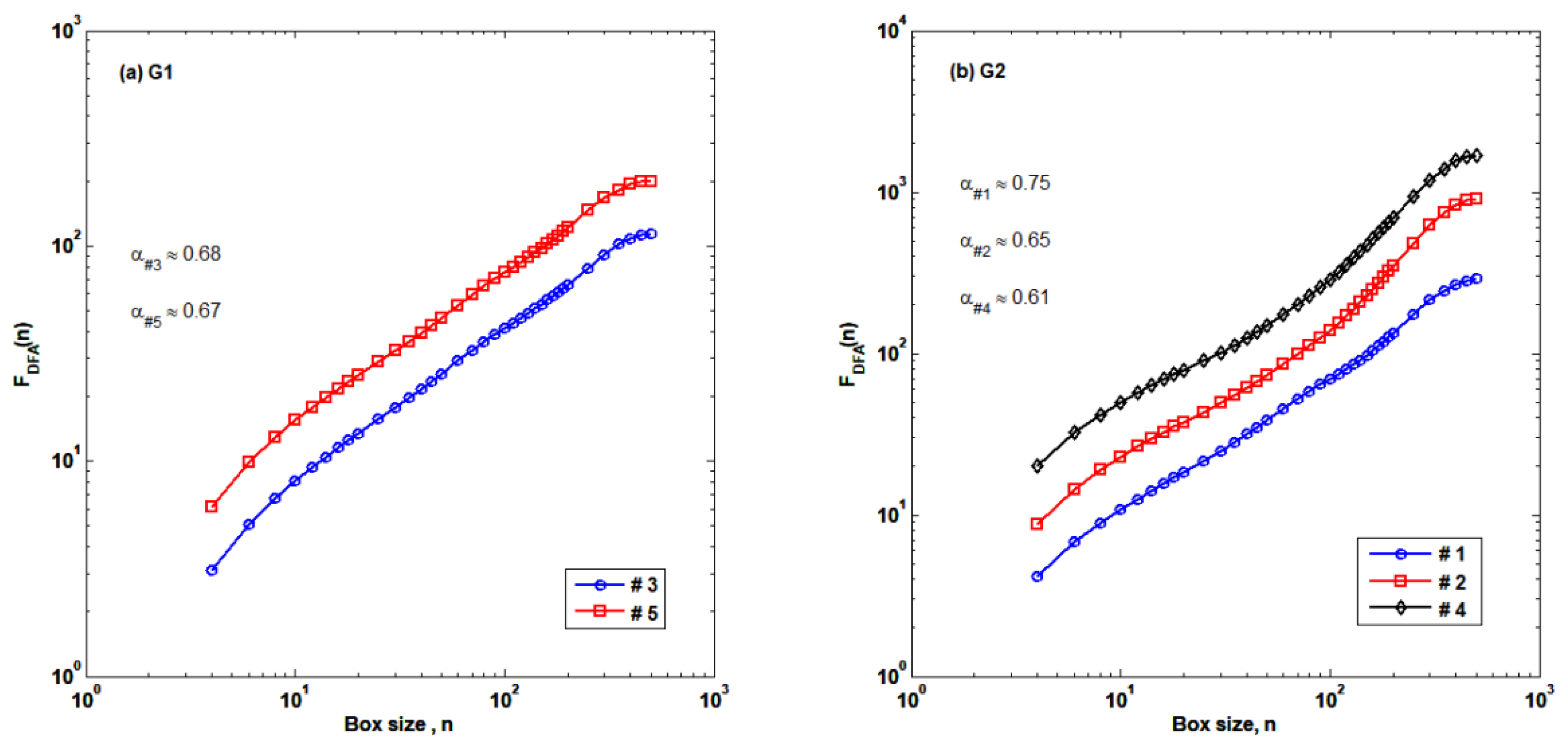
3.1. Autocorrelation Structures
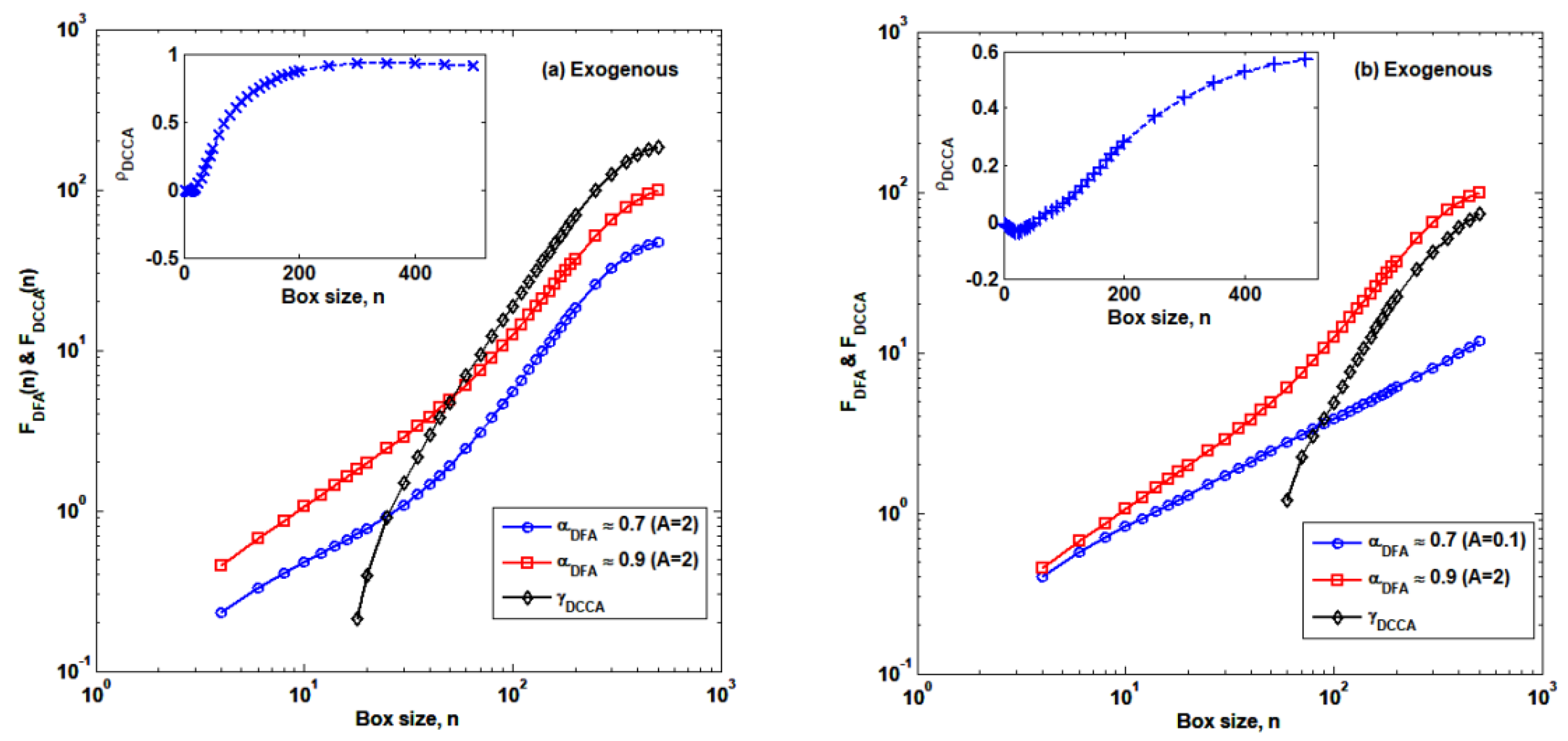
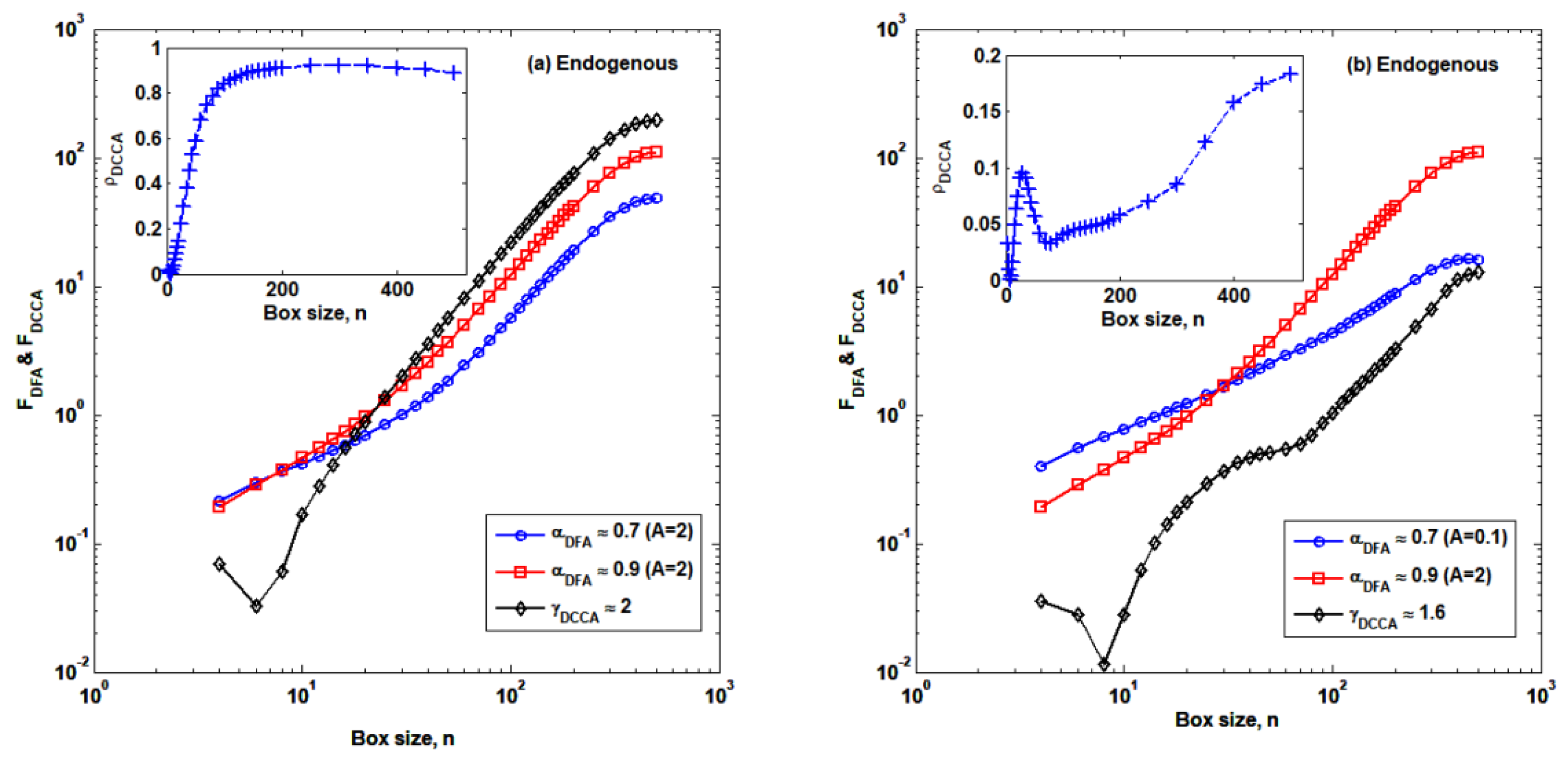
3.2. Cross-Correlation Structures
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M.M.B., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., et al., Eds.; Cambridge: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-10766-182-0.
- He, K.; Yang, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, X.; Chan, C.K.; Cadle, S.; Chan, T.; Mulawa, P. The characteristics of PM2.5 in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4959–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Tan, J.; Zhao, Q.; Du, Z.; He, K.; Ma, Y.; Duan, F.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Q. Characteristics of PM2.5 speciation in representative megacities and across China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 5207–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, W.; Yu, Y.; Hu, B.; Xin, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Bi, X.; Zhang, G.; et al. Characteristics of PM2.5 mass concentrations and chemical species in urban and background areas of China: Emerging results from the CARE-China network. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 8849–8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, S.; Xiong, Q.; Yang, X.; Qi, M.; Zhao, W.; Wang, X. Characteristics of PM2.5 chemical compositions and their effect on atmospheric visibility in urban Beijing, China during the heating season. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windsor, H.L.; Toumi, R. Scaling and persistence of UK pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4545–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ni, Z.; Ni, L. Multifractal detrended cross-correlation analysis between PM2.5 and meteorological factors. Physica A 2015, 438, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ni, Z.; Ni, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, L. Asymmetric multifractal detrending moving average analysis in time series of PM2.5 concentration. Physica A 2016, 457, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ni, Z.; Ni, L. Asymmetric multiscale behavior in PM2.5 time series: Based on asymmetric MS-DFA. Physica A 2016, 461, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hasan, Y.A. Machine learning algorithms for predicting roadside fine particulate matter concentration level in Hong Kong Central. Comput. Ecol. Softw. 2013, 3, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Lu, X.; Chang, Y.; Xue, W. Heavy metal contamination in dust from kindergartens and elementary schools in Xi’an, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 2701–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, J.; Jin, L.; Wang, J. Artificial neural networks forecasting of PM2.5 pollution using air mass trajectory based geographic model and wavelet transformation. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 107, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Xu, J.; Meng, W.; Pu, W. Seasonal and diurnal variations of ambient PM2.5 concentration in urban and rural environments in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2893–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, A.P.K.; Mickley, L.J.; Jacob, D.J. Correlations between fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and meteorological variables in the United States: Implications for the sensitivity of PM2.5 to climate change. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3976–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotsos, C.; Ondov, J.; Efstathiou, M. Scaling properties of air pollution in Athens, Greece and Baltimore, Maryland. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4041–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraz, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Femat, R.; Echeverria, J.C.; Alvarez-Ramirez, J. Statistical persistence of air pollutants (O3, SO2, NO2 and PM10) in Mexico City. Physica A 2015, 427, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-K.; Buldyrev, S.V.; Havlin, S.; Simons, M.; Stanley, H.E.; Goldberger, A.L. Mosaic organization of DNA nucleotides. Phys. Rev. E 1994, 49, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Ch.Ivanov, P.; Chen, Z.; Carpena, P.; Stanley, H.E. Effect of trends on detrended fluctuation analysis. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 011114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ivanov, P.C.; Hu, K.; Stanley, H.E. Effect of nonstationarities on detrended fluctuation analysis. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 041107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatic, D.; Stanley, H.E.; Podobnik, B. Detrended cross-correlation analysis for non-stationary time series with periodic trends. Europhys. Lett. 2011, 94, 18007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.; Min, S. Effect of Outliers and Non-consecutive Data Points on the Detrended Cross-Correlation Analysis. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2018, 72, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, X.; Tong, D.; Davis, S.J.; Zhao, H.; Geng, G.; Feng, T.; Zheng, B.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; et al. Transboundary health impacts of transported global air pollution and international trade. Nature 2017, 543, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podobnik, B.; Stanley, H.E. Detrended cross-correlation analysis: A new method for analyzing two nonstationary time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 084102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantelhardt, J.W.; Zschiegner, S.A.; Koscielny-Bunde, E.; Havlin, S.; Bunde, A.; Stanley, H.E. Multifractal detrended fluctuation analysis of nonstationary time series. Physica A 2002, 316, 87–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buldyrev, S.V.; Goldberger, A.L.; Havlin, S.; Mantegna, R.N.; Matsa, M.E.; Peng, C.-K.; Simons, M.; Stanley, H.E. Long-range correlation properties of coding and noncoding DNA sequences: GenBank analysis. Phys. Rev. E 1995, 51, 5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feder, J. Fractals; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Zebende, G.F. DCCA cross-correlation coefficient: Quantifying level of cross-correlation. Physica A 2011, 390, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podobnik, B.; Jiang, Z.-Q.; Zhou, W.-X.; Stanley, H.E. Statistical tests for power-law cross-correlated processes. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 066118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiler, J.; Eubank, S.; Longtin, A.; Galdrikian, B.; Farmer, J.D. Testing for nonlinearity in time series: The method of surrogate data. Physica D 1992, 58, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podobnik, B.; Ivanov, P.C.; Biljakovic, K.; Horvatic, D.; Stanley, H.E.; Grosse, I. Fractionally integrated process with power-law correlations in variables and magnitudes. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 72, 026121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, G.; Min, S. Correlation Structures of PM2.5 Concentration Series in the Korean Peninsula. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5441. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9245441
Lim G, Min S. Correlation Structures of PM2.5 Concentration Series in the Korean Peninsula. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(24):5441. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9245441
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Gyuchang, and Seungsik Min. 2019. "Correlation Structures of PM2.5 Concentration Series in the Korean Peninsula" Applied Sciences 9, no. 24: 5441. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9245441
APA StyleLim, G., & Min, S. (2019). Correlation Structures of PM2.5 Concentration Series in the Korean Peninsula. Applied Sciences, 9(24), 5441. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9245441





