Quantification of Trans-Resveratrol-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles by a Validated Reverse-Phase HPLC Photodiode Array
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Chromatographic Parameters
2.3. Method Validation
2.3.1. Accuracy
2.3.2. Precision
2.3.3. Linearity
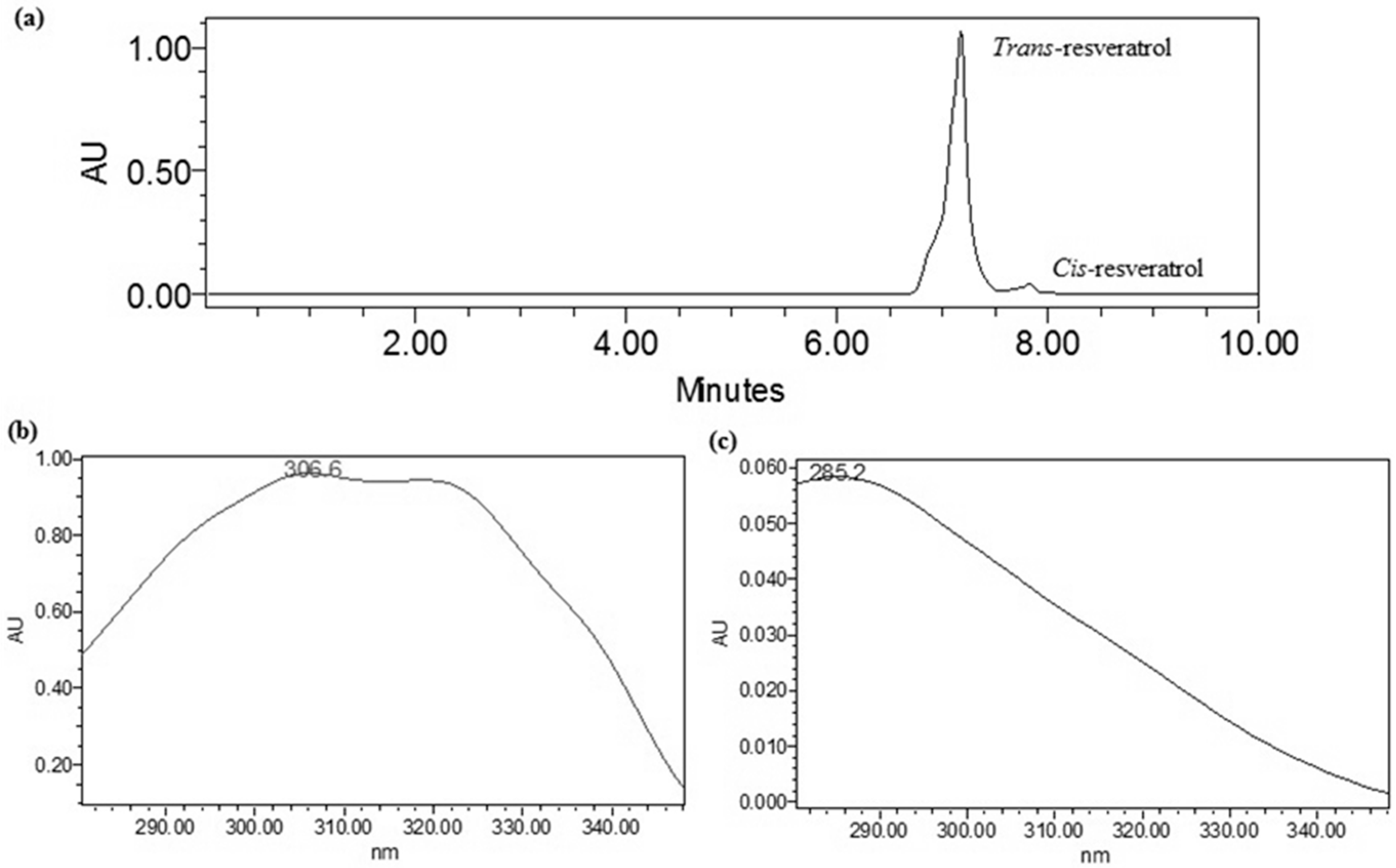
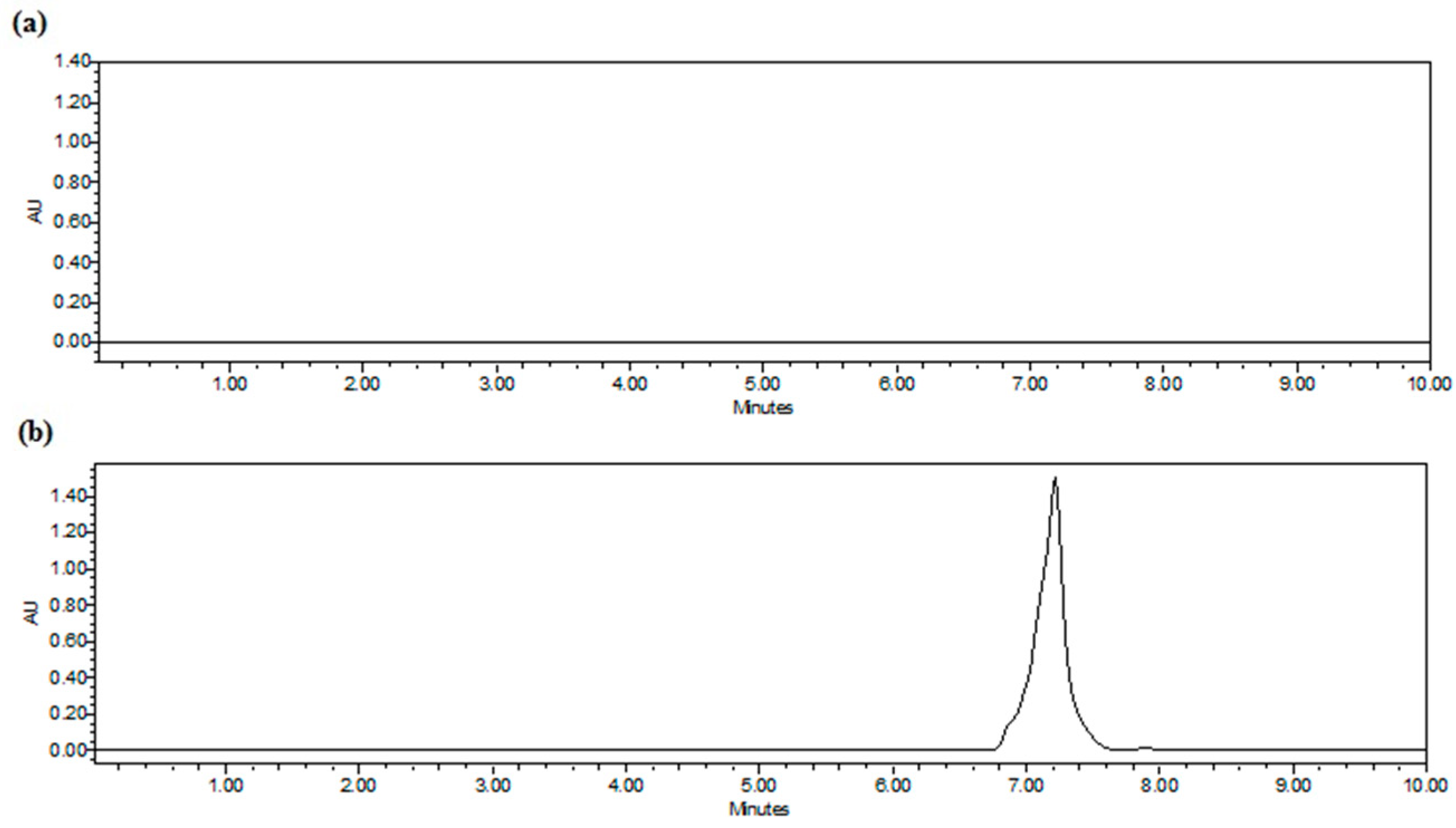
2.3.4. Specificity
2.3.5. Limit of Detection (LOD) and Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
2.3.6. Robustness
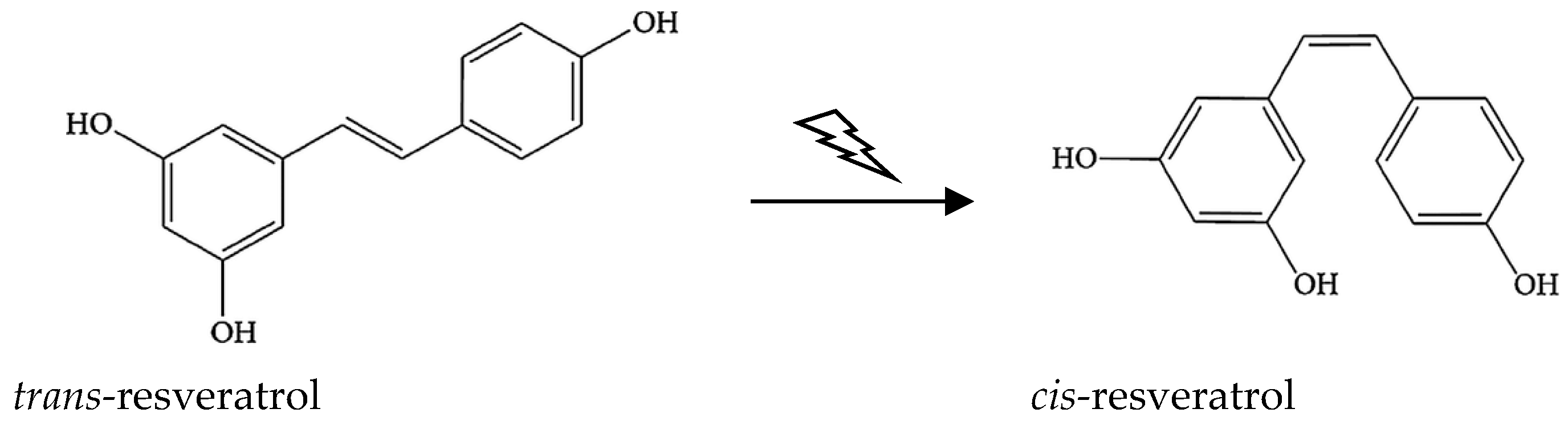
2.4. Measurement of tRES Stability under UV Exposure
2.5. Production and Characterization of SLN
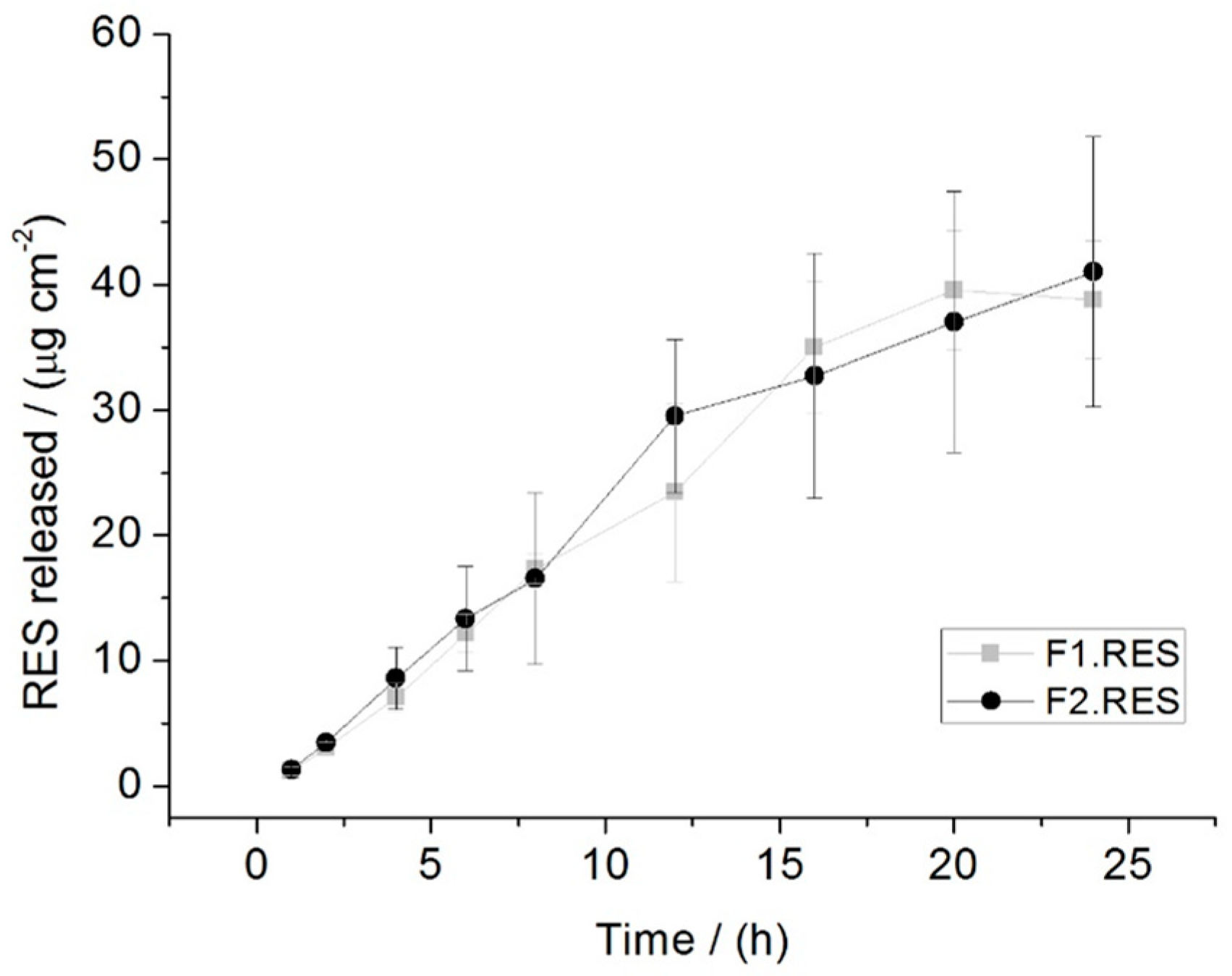
2.6. Drug Release Data Modeling
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| ANVISA | National Agency for Sanitary Vigilance Agency |
| BCS | Biopharmaceutics Classification System |
| DL | Detection limit |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| HPTLC | High-performance thin-layer chromatography |
| HPLC-DAD | High-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection |
| HHT | Hydroxyl heptadecatrienoate |
| ICH | International Conference on Harmonization |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantification |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| PDA | Photodiode array |
| QL | Quantification limit |
| R2 | Regression coefficient |
| RSD | relative standard deviation |
| RDC | Resolução da Diretoria Colegiada |
| RP-C18 | Reverse phase C18 |
| SLN | Solid lipid nanoparticles |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| tRES | trans-Resveratrol |
| US | Ultrasound |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Orhan, I.E.; Barreca, D.; Battino, M.; Belwal, T.; Bishayee, A.; Daglia, M.; Devkota, H.P.; Echeverría, J.; et al. Resveratrol, a popular dietary supplement for human and animal health. Anim. Sci. Papers Rep. 2019, 37, 103–118. [Google Scholar]
- Gehm, B.D.; McAndrews, J.M.; Chien, P.-Y.; Jameson, J.L. Resveratrol, a polyphenolic compound found in grapes and wine, is an agonist for the estrogen receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14138–14143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amri, A.; Chaumeil, J.; Sfar, S.; Charrueau, C. Administration of resveratrol: What formulation solutions to bioavailability limitations? J. Control. Release 2012, 158, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristl, J.; Teskač, K.; Caddeo, C.; Abramović, Z.; Šentjurc, M. Improvements of cellular stress response on resveratrol in liposomes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 73, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidon, G.L.; Lennernäs, H.; Shah, V.P.; Crison, J.R. A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: The correlation of in vitro drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orallo, F. Comparative studies of the antioxidant effects of cis-and trans-resveratrol. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yáñez, M.; Fraiz, N.; Cano, E.; Orallo, F. Inhibitory effects of cis-and trans-resveratrol on noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake and on monoamine oxidase activity. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 2006, 344, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiras, T.S.; Neves-Petersen, M.T.; Petersen, S.B. Activation energy of light induced isomerization of resveratrol. J. Fluoresc. 2011, 21, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, A.; Novellino, E. Nutraceuticals in hypercholesterolaemia: An overview. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1450–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, A.; Novellino, E. To Nutraceuticals and Back: Rethinking a Concept. Foods 2017, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, A.; D’Addezio, L.; Camilli, E.; Piccinelli, R.; Turrini, A.; Marletta, L.; Marconi, S.; Lucarini, M.; Lisciani, S.; Gabrielli, P.; et al. From Plant Compounds to Botanicals and Back: A Current Snapshot. Molecules 2018, 23, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M. Extractable and Non-Extractable Antioxidants. Molecules 2019, 24, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, A.; Novellino, E. Nutraceuticals - shedding light on the grey area between pharmaceuticals and food. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, A.; Cammarata, S.M.; Capone, G.; Ianaro, A.; Tenore, G.C.; Pani, L.; Novellino, E. Nutraceuticals: Opening the debate for a regulatory framework. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 659–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daliu, P.; Santini, A.; Novellino, E. From pharmaceuticals to nutraceuticals: Bridging disease prevention and management. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Souto, E.B.; Cicala, C.; Caiazzo, E.; Izzo, A.A.; Novellino, E.; Santini, A. Polyphenols: A concise overview on the chemistry, occurrence, and human health. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2221–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucarini, M.; Durazzo, A.; Romani, A.; Campo, M.; Lombardi-Boccia, G.; Cecchini, F. Bio–Based Compounds from Grape Seeds: A Biorefinery Approach. Molecules 2018, 23, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolinsky, V.W.; Dyck, J.R. Calorie restriction and resveratrol in cardiovascular health and disease. BBA-Mol. Basis. Dis. 2011, 1812, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovski, G.; Gurusamy, N.; Das, D.K. Resveratrol in cardiovascular health and disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1215, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-Q.; Wu, B.-J.; Pan, W.H.; Zhang, X.-M.; Liu, J.-H.; Chen, M.-M.; Chao, F.-P.; Chao, H.-M. Resveratrol mitigates rat retinal ischemic injury: The roles of matrix metalloproteinase-9, inducible nitric oxide, and heme oxygenase-1. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 29, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasnyó, P.; Molnár, G.A.; Mohás, M.; Markó, L.; Laczy, B.; Cseh, J.; Mikolás, E.; Szijártó, I.A.; Mérei, A.; Halmai, R. Resveratrol improves insulin sensitivity, reduces oxidative stress and activates the Akt pathway in type 2 diabetic patients. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, R.; Souto, S.B.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Machado, A.L.; Severino, P.; Jose, S.; Santini, A.; Fortuna, A.; Garcia, M.L.; Silva, A.M.; et al. Sugar-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Syndrome-Review of Classical and New Compounds: Part-I. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2019, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, R.; Souto, S.B.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Machado, A.L.; Severino, P.; Jose, S.; Santini, A.; Silva, A.M.; Fortuna, A.; Garcia, M.L.; et al. Sugar-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Syndrome-Strategies for In Vivo Administration: Part-II. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, A.Y.; Wang, Q.; Simonyi, A.; Sun, G.Y. Resveratrol as a therapeutic agent for neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 41, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wight, R.D.; Tull, C.A.; Deel, M.W.; Stroope, B.L.; Eubanks, A.G.; Chavis, J.A.; Drew, P.D.; Hensley, L.L. Resveratrol effects on astrocyte function: Relevance to neurodegenerative diseases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 426, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuzhu, G.; Komai-Koma, M.; Leung, B.P.; Howe, H.S.; McSharry, C.; McInnes, I.B.; Xu, D. Resveratrol modulates murine collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting Th17 and B-cell function. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace-Asciak, C.R.; Hahn, S.; Diamandis, E.P.; Soleas, G.; Goldberg, D.M. The red wine phenolics trans-resveratrol and quercetin block human platelet aggregation and eicosanoid synthesis: Implications for protection against coronary heart disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 1995, 235, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qiao, H.; Liu, T.; Yang, Z.; Xu, L.; Xu, Y.; Ge, H.M.; Tan, R.-X.; Li, E. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus infection by oligomeric stilbenoids through ROS generation. Antivir. Res. 2012, 95, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, Y.; Singh, R. Resveratrol and cellular mechanisms of cancer prevention. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1215, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzo, K.O.; Souto, A.A.; Lopes, T.G.; Zanin, R.F.; Gomez, M.V.; Souza, A.H.; Campos, M.M. Evidence for the analgesic activity of resveratrol in acute models of nociception in mice. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimojo, A.A.M.; Fernandes, A.R.V.; Ferreira, N.R.E.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Santana, M.H.A.; Souto, E.B. Evaluation of the Influence of Process Parameters on the Properties of Resveratrol-Loaded NLC Using 2(2) Full Factorial Design. Antioxidants (Basel) 2019, 8, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, S.; Anju, S.S.; Cinu, T.A.; Aleykutty, N.A.; Thomas, S.; Souto, E.B. In vivo pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of resveratrol-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for brain delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 474, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Peng, Y.; Yao, J.; Sui, L.; Gu, A.; Wang, J. Anticancer Activity and Molecular Mechanism of Resveratrol–Bovine Serum Albumin Nanoparticles on Subcutaneously Implanted Human Primary Ovarian Carcinoma Cells in Nude Mice. Cancer Biother. Radiopharma. 2010, 25, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, K.-H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.W.; Quach, C.H.T.; Moon, S.-H.; Cho, Y.S.; Lee, K.-H. Resveratrol-loaded polymeric nanoparticles suppress glucose metabolism and tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 478, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doktorovova, S.; Kovacevic, A.B.; Garcia, M.L.; Souto, E.B. Preclinical safety of solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: Current evidence from in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.B.; Silva, A.M. Nanotoxicology applied to solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers - a systematic review of in vitro data. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Doktorovova, S. Chapter 6 - Solid lipid nanoparticle formulations pharmacokinetic and biopharmaceutical aspects in drug delivery. Methods Enzymol 2009, 464, 105–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Muller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles: Effect on bioavailability and pharmacokinetic changes. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2010, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teskač, K.; Kristl, J. The evidence for solid lipid nanoparticles mediated cell uptake of resveratrol. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 390, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianzani, C.; Zara, G.P.; Maina, G.; Pettazzoni, P.; Pizzimenti, S.; Rossi, F.; Gigliotti, C.L.; Ciamporcero, E.S.; Daga, M.; Barrera, G. Drug delivery nanoparticles in skin cancers. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. HPLC method development and validation-an overview. J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2013, 4, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Paulo, L.; Domingues, F.; Queiroz, J.A.; Gallardo, E. Development and Validation of an Analytical Method for the Determination of trans- and cis-Resveratrol in Wine: Analysis of Its Contents in 186 Portuguese Red Wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2157–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICH. Harmonised Tripartite Guideline, Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology Q2 (R1), International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. 2015. Available online: http://www.ich.org/products/guidelines/quality/article/quality-guidelines.html (accessed on 20 October 2019).
- ANVISA-Brasil. Guia Para Validação de Métodos Analíticos e Bioanalíticos; ANVISA, Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária, Ed.; Diário Oficial da União: Brasília, Brasil, 2003; p. 47.
- Nemen, D.; Lemos-Senna, E. Preparação e caracterização de suspensões coloidais de nanocarreadores lipídicos contendo resveratrol destinados à administração cutânea. Quim. Nova 2011, 34, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.; Lopes, C.M.; Fonseca, J.; Soares, M.E.; Santos, D.; Souto, E.B.; Ferreira, D. Risperidone release from solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN): Validated HPLC method and modelling kinetic profile. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2012, 8, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel-Moral, S.; Teixeira, M.C.; Fernandes, A.R.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Arráez-Román, D.; Martínez-Férez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Souto, E.B. Polyphenols-enriched Hibiscus sabdariffa extract-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC): Optimization by multi-response surface methodology. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detoni, C.B.; Souto, G.D.; da Silva, A.L.M.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S. Photostability and Skin Penetration of Different E-Resveratrol-Loaded Supramolecular Structures. Photochem. Photobiol. 2012, 88, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agayan, R.R.; Horvath, T.; McNaughton, B.H.; Anker, J.N.; Kopelman, R. Optical manipulation of metal-silica hybrid nanoparticles. In Proceedings of the Optical Science and Technology, International Society for Optics and Photonics, the SPIE 49th Annual Meeting, Denver, CO, USA, 18 October 2004; pp. 502–513. [Google Scholar]
- Bertelli, A.; Giovannini, L.; Bernini, W.; Migliori, M.; Fregoni, M.; Bavaresco, L.; Bertelli, A. Antiplatelet activity of cis-resveratrol. Drug Exp. Clin. Res. 1995, 22, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Pragst, F.; Herzler, M.; Erxleben, B.T. Systematic toxicological analysis by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection (HPLC-DAD). Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2004, 42, 1325–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, R.S.; Antunes, M.V.; Linden, R. Determinação de citrato de sildenafila e de tadalafila por cromatografia líquida de ultraeficiência com detecção por arranjo de diodos (CLUE-DAD). Quim. Nova 2010, 33, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonda, C.; Zhang, J.; Pavlovic, A. The photostability and photostabilization of trans-resveratrol. Cosmet. Toiletries 2011, 126, 652. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, D.; Guerrini, A.; Bruni, R.; Brognara, E.; Borgatti, M.; Gambari, R.; Maietti, S.; Sacchetti, G. trans-Resveratrol in nutraceuticals: Issues in retail quality and effectiveness. Molecules 2012, 17, 12393–12405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Snyder, L.R.; Kirkland, J.J.; Glajch, J.L. Practical HPLC Method Development, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, A.R.; Reis, S.; Segundo, M.A. Development and Validation of a HPLC Method Using a Monolithic Column for Quantification of trans-Resveratrol in Lipid Nanoparticles for Intestinal Permeability Studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3114–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Rocha Lindner, G.; Khalil, N.M.; Mainardes, R.M. Resveratrol-loaded polymeric nanoparticles: Validation of an HPLC-PDA method to determine the drug entrapment and evaluation of its antioxidant activity. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 506083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agnihotri, S.A.; Mallikarjuna, N.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Recent advances on chitosan-based micro-and nanoparticles in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2004, 100, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Adibkia, K.; Valizadeh, H.; Shadbad, M.R.S.; Nokhodchi, A.; Omidi, Y.; Mohammadi, G.; Nezhadi, S.H.; Hasan, M. Kinetic analysis of drug release from nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci 2008, 11, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grassi, M.; Voinovich, D.; Franceschinis, E.; Perissutti, B.; Filipovic-Grcic, J. Theoretical and experimental study on theophylline release from stearic acid cylindrical delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2003, 92, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.C.; Carbone, C.; Souto, E.B. Beyond liposomes: Recent advances on lipid based nanostructures for poorly soluble/poorly permeable drug delivery. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 68, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Andreani, T.; Macedo, A.S.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Santana, M.H.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Current State-of-Art and New Trends on Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN and NLC) for Oral Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. 2012, 2012, 750891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, R.H.; Runge, S.; Ravelli, V.; Mehnert, W.; Thunemann, A.F.; Souto, E.B. Oral bioavailability of cyclosporine: Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) versus drug nanocrystals. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 317, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Severino, P.; Basso, R.; Santana, M.H. Encapsulation of antioxidants in gastrointestinal-resistant nanoparticulate carriers. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1028, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.M.; Martins-Lopes, P.; Souto, E.B. Nanoparticulate carriers (NPC) for oral pharmaceutics and nutraceutics. Pharmazie 2010, 65, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santos, I.S.; Ponte, B.M.; Boonme, P.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Nanoencapsulation of polyphenols for protective effect against colon–rectal cancer. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel-Moral, S.; Teixeira, M.C.; Fernandes, A.R.; Arráez-Román, D.; Martínez-Férez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Souto, E.B. Lipid nanocarriers for the loading of polyphenols—A comprehensive review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 260, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daliu, P.; Santini, A.; Novellino, E. A decade of nutraceutical patents: Where are we now in 2018, Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2018, 28, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, A.; Ferreira, N.R.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Cicero, N.; Mamouni, S.E.; Silva, A.M.; Nowak, I.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B. Development and Optimization of Alpha-Pinene-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) Using Experimental Factorial Design and Dispersion Analysis. Molecules 2019, 24, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zielinska, A.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Ferreira, N.R.; Silva, A.M.; Nowak, I.; Souto, E.B. Anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activity of citral: Optimization of citral-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) using experimental factorial design and LUMiSizer(R). Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 553, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, I.; Zielinska, A.; Ferreira, N.R.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Optimization of linalool-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles using experimental factorial design and long-term stability studies with a new centrifugal sedimentation method. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, R.; Wu, L.; Zhang, C.; Davis, R.M.; Xu, B. Natural product-based nanomedicine: Recent advances and issues. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 6055–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abenavoli, L.; Izzo, A.A.; Milić, N.; Cicala, C.; Santini, A.; Capasso, R. Milk thistle (Silybum marianum): A concise overview on its chemistry, pharmacological, and nutraceutical uses in liver diseases. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2202–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredients/% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA | SPC | P407 | MP | PP | RES | MQ Water g | |
| F1 | 5.0 | - | 3.5 | 0.18 | 0.02 | - | Sq * |
| F2 | 5.0 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 0.18 | 0.02 | - | Sq * |
| F1.RES | 5.0 | - | 3.5 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.1 | Sq * |
| F2.RES | 5.0 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.1 | Sq * |
| Precision | Accuracy | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | tRES Concentration/(μg/mL) | Intraday | Interday | Experimental Concentration/(μg/mL) *** | Recovery/(%) | ||
| SD */(AU) | RSD **/(%) | SD */(AU) | RSD **/(%) | ||||
| 1 | 1.0 | 10,916 | 2.87 | 19150 | 4.83 | 4.626 ± 0.009 | 92.53 ± 0.19 |
| 2 | 9867 | 2.35 | |||||
| 3 | 632 | 0.16 | |||||
| 1 | 50.0 | 9623 | 0.05 | 662346 | 3.17 | 50.57 ± 0.228 | 101.15 ± 0.46 |
| 2 | 91,404 | 0.45 | |||||
| 3 | 205,253 | 0.95 | |||||
| 1 | 100.0 | 66,372 | 0.16 | 1439947 | 3.47 | 99.64 ± 0.170 | 99.64 ± 0.170 |
| 2 | 68,212 | 0.17 | |||||
| 3 | 84,338 | 0.19 | |||||
| Parameters | Retention Time/(min.) | RSD/(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow | 0.8 mL/min | 8.22 ± 0.007 * | 0.52 |
| 1.0 mL/min | 7.24 ± 0.009 * | 0.64 | |
| 1.2 mL/min | 6.53 ± 0.015 * | 0.52 | |
| Column temperature | 25 °C | 7.24 ± 0.009 ** | 0.64 |
| 30 °C | 7.15 ± 0.100 ** | 0.26 | |
| 35 °C | 7.06 ± 0.006 ** | 0.70 | |
| Mathematical Models | Regression Coefficient (R2) | |
|---|---|---|
| F1.RES | F2.RES | |
| Korsmeyer-Peppas | 0.9680 | 0.9752 |
| Higuchi | 0.8469 | 0.8734 |
| First Order | 0.9757 | 0.9814 |
| Weibull | 0.9916 | 0.9939 |
| Zero Order | 0.9700 | 0.9683 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rigon, R.B.; Fachinetti, N.; Severino, P.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Atanasov, A.G.; El Mamouni, S.; Chorilli, M.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B. Quantification of Trans-Resveratrol-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles by a Validated Reverse-Phase HPLC Photodiode Array. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224961
Rigon RB, Fachinetti N, Severino P, Durazzo A, Lucarini M, Atanasov AG, El Mamouni S, Chorilli M, Santini A, Souto EB. Quantification of Trans-Resveratrol-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles by a Validated Reverse-Phase HPLC Photodiode Array. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(22):4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224961
Chicago/Turabian StyleRigon, Roberta B., Naiara Fachinetti, Patrícia Severino, Alessandra Durazzo, Massimo Lucarini, Atanas G. Atanasov, Soukaina El Mamouni, Marlus Chorilli, Antonello Santini, and Eliana B. Souto. 2019. "Quantification of Trans-Resveratrol-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles by a Validated Reverse-Phase HPLC Photodiode Array" Applied Sciences 9, no. 22: 4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224961
APA StyleRigon, R. B., Fachinetti, N., Severino, P., Durazzo, A., Lucarini, M., Atanasov, A. G., El Mamouni, S., Chorilli, M., Santini, A., & Souto, E. B. (2019). Quantification of Trans-Resveratrol-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles by a Validated Reverse-Phase HPLC Photodiode Array. Applied Sciences, 9(22), 4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224961












