Surface Alterations Induced on Endodontic Instruments by Sterilization Processes, Analyzed with Atomic Force Microscopy: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
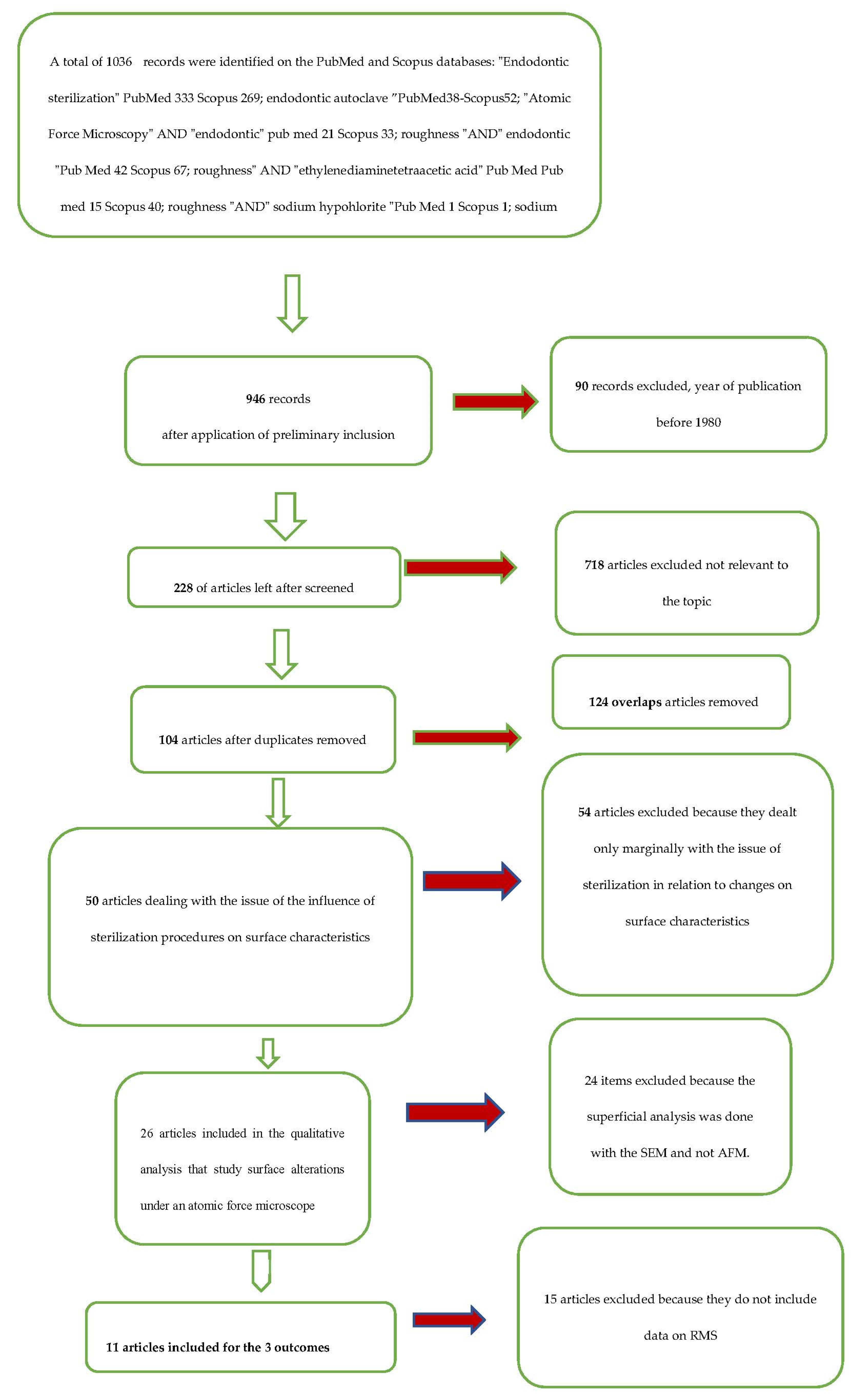
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
- Include all those studies that describe the alterations induced by the sterilization methods of the endodontic instruments, analyzed using atomic force microscopy;
- Include all the articles that describe the alterations induced by root canal irrigants (sodium hypochlorite and EDTA), analyzed using atomic force microscopy;
- The exclusion criteria are to exclude all those studies that do not report data (average and standard deviation) on surface irregularities (AMR, MH, and RMS).
2.2. Research Methodology
2.3. Screening Methodology
- (1)
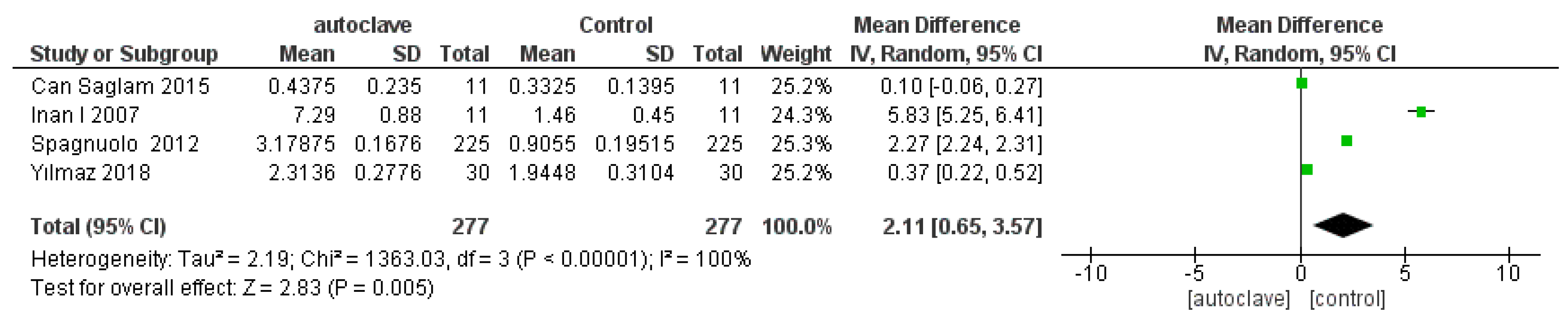
- Primary outcome, variations of the root mean square root (RMS) of endodontic instruments subjected to five autoclave cycles as compared with non-autoclaved control;
- (2)
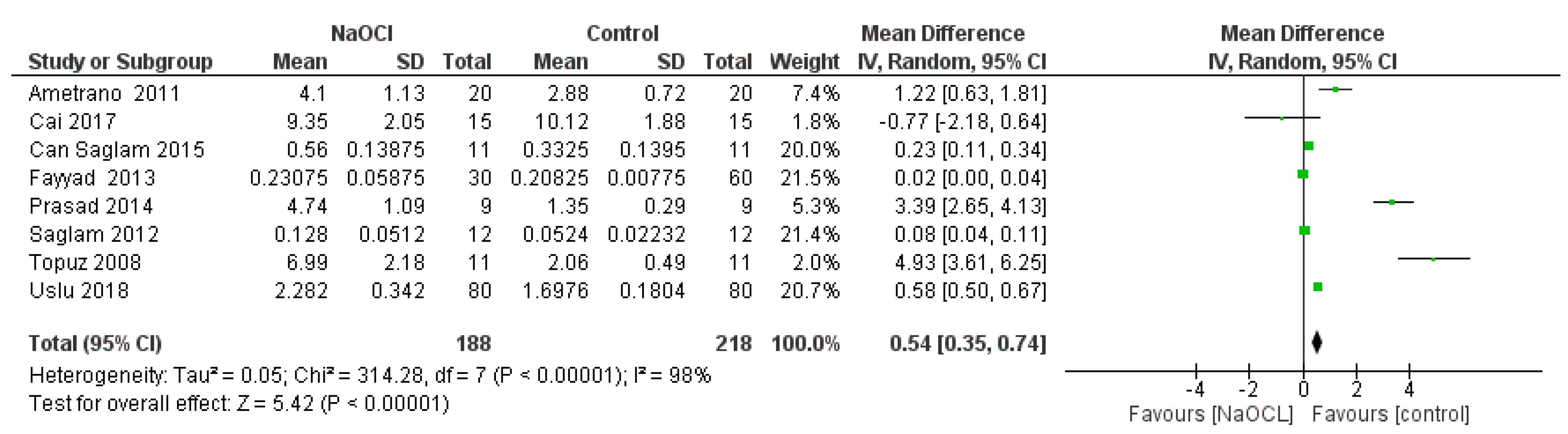
- Secondary outcome, variations of the root mean square (RMS) of endodontic instruments exposed to sodium hypochlorite 5% as compared with the control group;
- (3)
- Tertiary outcome, variations of the root mean square (RMS) of the endodontic instruments described at EDTA 10% as compared with the control group.
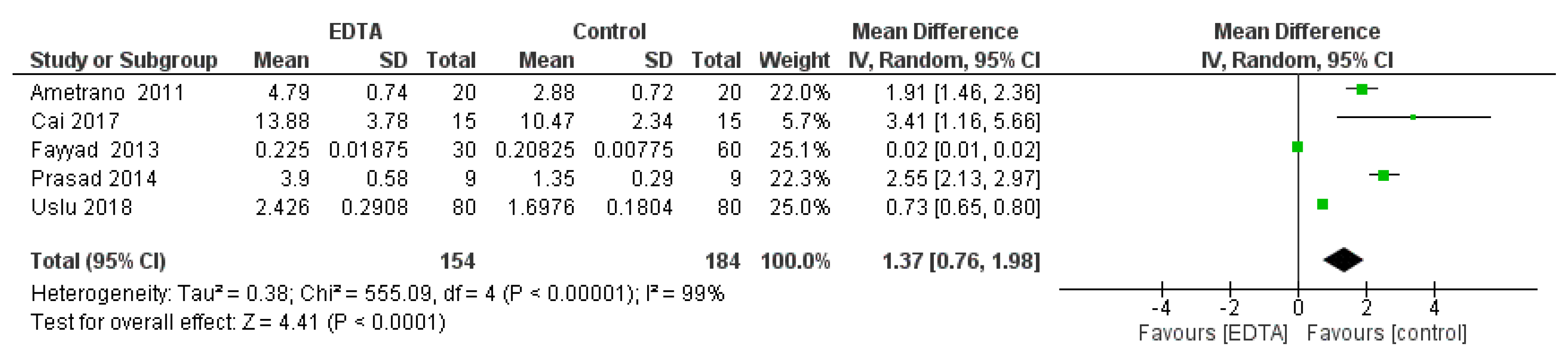
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics and Data Extraction
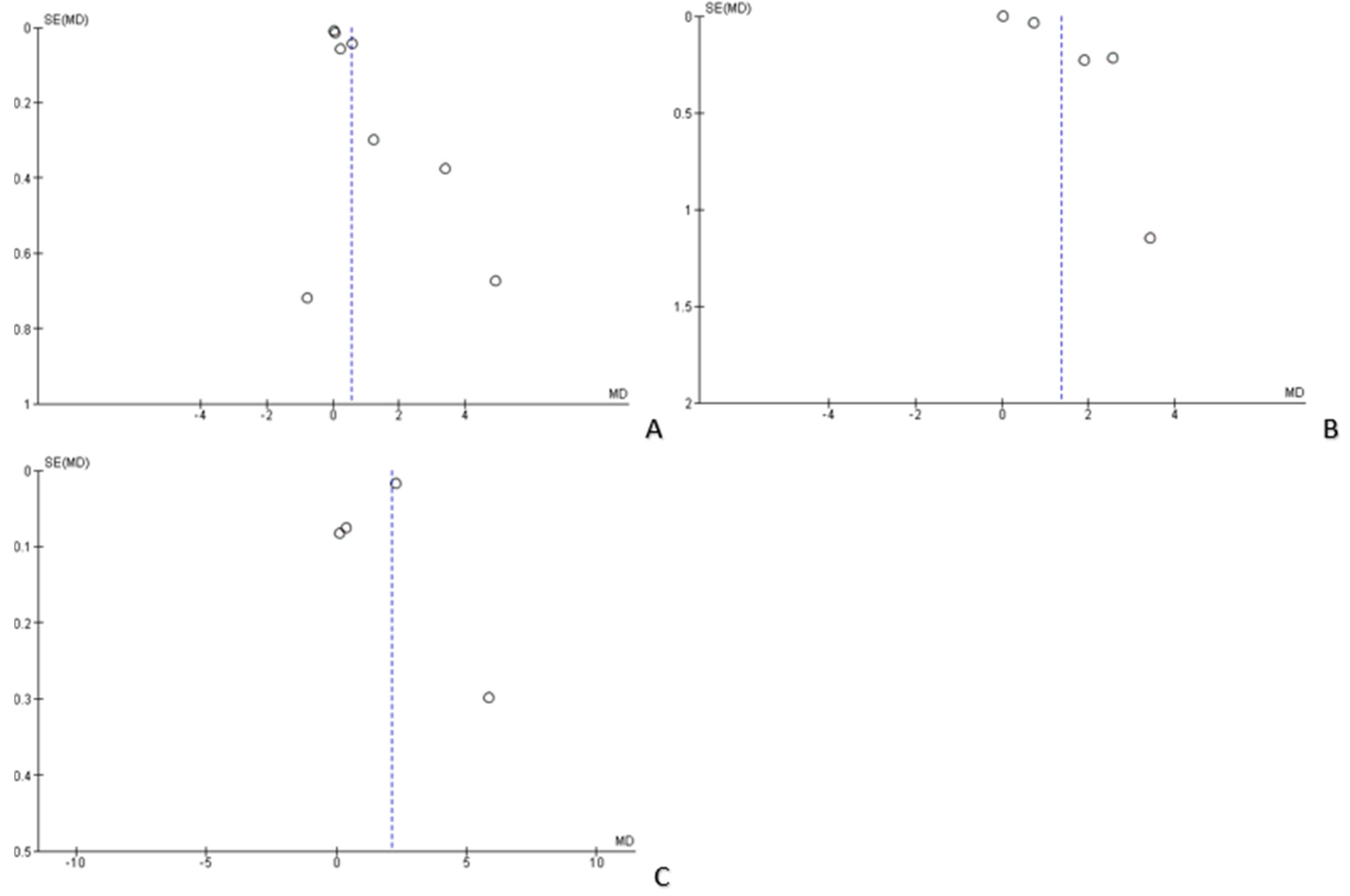
3.2. Risk of Bias
3.3. Data Analysis
4. Discussion
- In 2007, Inan reported statistically significant data for all the instruments of the ProTaper series (S1, S2, F1, F2), and reported that the superficial deterioration induced by the autoclave is greater for ProTaper finished than for ProTaper shaping;
- In 2012, Spagnuolo confirmed, in agreement with Inan’s data, that multiple cycles (autoclave sterilization) modified the surface topography and chemical composition of conventional NiTi (F2 ProTaper) and TiN-coated (alpha kit) instruments, in a statistically significant way (after five autoclave cycles).
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inan, U.; Keskin, C. Torsional Resistance of ProGlider, Hyflex EDM, and One G Glide Path Instruments. J. Endod. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troiano, G.; Dioguardi, M.; Cocco, A.; Zhurakivska, K.; Ciavarella, D.; Muzio, L.L. Increase in [corrected] the glyde path diameter improves the centering ability of F6 Skytaper. Eur. J. Dent. 2018, 12, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laneve, E.; Raddato, B.; Dioguardi, M.; Di Gioia, G.; Troiano, G.; Lo Muzio, L. Sterilisation in Dentistry: A Review of the Literature. Int. J. Dent. 2019, 2019, 6507286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dioguardi, M.; Di Gioia, G.; Illuzzi, G.; Laneve, E.; Cocco, A.; Troiano, G. Endodontic irrigants: Different methods to improve efficacy and related problems. Eur. J. Dent. 2018, 12, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berutti, E.; Angelini, E.; Rigolone, M.; Migliaretti, G.; Pasqualini, D. Influence of sodium hypochlorite on fracture properties and corrosion of ProTaper Rotary instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2006, 39, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dioguardi, M.; Sovereto, D.; Aiuto, R.; Laino, L.; Illuzzi, G.; Laneve, E.; Raddato, B.; Caponio, V.C.A.; Dioguardi, A.; Zhurakivska, K.; et al. Effects of Hot Sterilization on Torsional Properties of Endodontic Instruments: Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Materials 2019, 12, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Coil, J.M.; McLean, A.G.; Hemerling, D.L.; Haapasalo, M. Defects in nickel-titanium instruments after clinical use. Part 5: Single use from endodontic specialty practices. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyurek, T.; Yilmaz, K.; Uslu, G.; Plotino, G. The effect of root canal preparation on the surface roughness of WaveOne and WaveOne Gold files: Atomic force microscopy study. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2018, 43, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, K.; Uslu, G.; Ozyurek, T. Effect of multiple autoclave cycles on the surface roughness of HyFlex CM and HyFlex EDM files: An atomic force microscopy study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 2975–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, U.; Aydin, C.; Uzun, O.; Topuz, O.; Alacam, T. Evaluation of the surface characteristics of used and new ProTaper Instruments: An atomic force microscopy study. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 1334–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyad, D.M.; Mahran, A.H. Atomic force microscopic evaluation of nanostructure alterations of rotary NiTi instruments after immersion in irrigating solutions. Int. Endod. J. 2014, 47, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ametrano, G.; D’Anto, V.; Di Caprio, M.P.; Simeone, M.; Rengo, S.; Spagnuolo, G. Effects of sodium hypochlorite and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on rotary nickel-titanium instruments evaluated using atomic force microscopy. Int. Endod. J. 2011, 44, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casella, G.; Rosalbino, F. Corrosion behaviour of NiTi endodontic instrument. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavian, H.; Iranmanesh, P.; Mojtahedi, H.; Nazeri, R. Effect of Autoclave Cycles on Surface Characteristics of S-File Evaluated by Scanning Electron Microscopy. Iran. Endod. J. 2016, 11, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Green, S. Cochrane Collaboration. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK; Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; 649p. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, C.K.; Mertz, D.; Loeb, M. Newcastle-Ottawa Scale: Comparing reviewers’ to authors’ assessments. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnuolo, G.; Ametrano, G.; D’Anto, V.; Rengo, C.; Simeone, M.; Riccitiello, F.; Amato, M. Effect of autoclaving on the surfaces of TiN -coated and conventional nickel-titanium rotary instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2012, 45, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can Saglam, B.; Gorgul, G. Evaluation of surface alterations in different retreatment nickel-titanium files: AFM and SEM study. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2015, 78, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, G.; Ozyurek, T.; Yilmaz, K. Effect of Sodium Hypochlorite and EDTA on Surface Roughness of HyFlex CM and HyFlex EDM Files. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2018, 81, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topuz, O.; Aydin, C.; Uzun, O.; Inan, U.; Alacam, T.; Tunca, Y.M. Structural effects of sodium hypochlorite solution on RaCe rotary nickel-titanium instruments: An atomic force microscopy study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2008, 105, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.J.; Tang, X.N.; Ge, J.Y. Effect of irrigation on surface roughness and fatigue resistance of controlled memory wire nickel-titanium instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2017, 50, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglam, B.C.; Kocak, S.; Kocak, M.M.; Topuz, O. Effects of irrigation solutions on the surface of ProTaper instruments: A microscopy study. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2012, 75, 1534–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, P.S.; Sam, J.E.; Arvind Kumar, K. The effect of 5% sodium hypochlorite, 17% EDTA and triphala on two different rotary Ni-Ti instruments: An AFM and EDS analysis. J. Conserv. Dent. 2014, 17, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, K.; Kancko, K.; Yabuta, E.; Asaoka, K.; Sakai, J. Fracture of nickel-titanium superelastic alloy in sodium hypochlorite solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 369, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorso, A.; Tripi, T.R.; Rondelli, G.; Condorelli, G.G.; Cantatore, G.; Schafer, E. Pitting corrosion resistance of nickel-titanium rotary instruments with different surface treatments in seventeen percent ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid and sodium chloride solutions. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Database-Provider | Key Words | Search Details | Number of Records | Number of Records after Restriction by Year of Publication (Last 40 Years) | Number of Articles Remaining after the Elimination of Records not Related to the Issue of Sterilization Influence on Endodontic Instruments | Articles After Remove Overlaps Articles | Number of Articles Dealing with the Problem of the Influence of Sterilization Procedures on the Surface Characteristics of Endodontic Instruments | Number of Articles that Have Analyzed the Surface Alterations with Methods Different from the Atomic Force Microscopy | Number of Articles that Analyzed Surface Alterations with Atomic Force Microscopy | Numbers of Articles Included in the Quantitative Analysis for the 3 Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PubMed | “endodontic sterilization” | “endodontic” [All Fields] AND (“sterilization”[All Fields] OR “sterilization”, reproductive”[MeSH Terms] OR (“sterilization”[All Fields] AND “reproductive”[All Fields]) OR “reproductive sterilization”[All Fields] OR “sterilization”[All Fields] OR “sterilization”[MeSH Terms]) | 333 | 291 | 46 | |||||
| PubMed | “endodontic autoclave” | “endodontic” [All Fields] AND “autoclave” [All Fields] | 38 | 38 | 25 | |||||
| PubMed | “atomic force microscopy” AND “endodontic” | “atomic force microscopy” [All Fields] AND “endodontic” [All Fields] | 21 | 21 | 9 | |||||
| PubMed | “roughness” AND “endodontic” | “roughness” [All Fields] AND “endodontic” [All Fields] | 42 | 41 | 11 | |||||
| PubMed | “roughness” AND “ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid” | “roughness” [All Fields] AND (“ethylenediaminetetraacetic” [All Fields] AND “acid” [All Fields]) | 15 | 15 | 2 | |||||
| PubMed | “roughness” AND “sodium hypochlorite” | “roughness” [All Fields] AND (“sodium” [All Fields] AND “hypochlorite” [All Fields]) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| PubMed | “sodium” “hypochlorite” AND “atomic force microscopy” | “sodium hypochlorite” [All Fields] AND “atomic force microscopy” [All Fields] | 40 | 40 | 13 | |||||
| PubMed | “atomic force microscopy” AND “NiTi rotary instruments” | “atomic force microscopy” [All Fields] AND “NiTi rotary instruments” [All Fields] | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Scopus | “endodontic sterilization” | TITLE-ABS-KEY (endodontic AND sterilization) | 269 | 225 | 56 | |||||
| Scopus | “endodontic autoclave” | TITLE-ABS-KEY (endodontic AND autoclave) | 52 | 52 | 25 | |||||
| Scopus | “atomic force microscopy” AND “endodontic” | TITLE-ABS-KEY (“atomic force microscopy” AND “endodontic”) | 33 | 33 | 13 | |||||
| Scopus | “roughness” AND “endodontic” | TITLE-ABS-KEY (“roughness” AND “endodontic”) | 67 | 65 | 12 | |||||
| Scopus | “roughness” AND sodium “hypochlorite” | TITLE-ABS-KEY (“roughness” AND “sodium” AND “hypochlorite”) | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Scopus | “roughness” AND “ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid” | TITLE-ABS-KEY (“roughness” AND “ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid”) | 40 | 40 | 2 | |||||
| Scopus | “sodium hypochlorite” AND “atomic force microscopy” | TITLE-ABS-KEY (“sodium hypochlorite” AND “atomic force microscopy”) | 80 | 80 | 9 | |||||
| Scopus | “atomic force microscopy” AND “NiTi rotary instruments” | TITLE-ABS-KEY (“atomic force microscopy” AND “NiTi rotary instruments”) | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||||
| Total records | 1036 | 946 | 228 | 104 | 50 | 24 | 26 | 11 |
| / | / | Reviewer 2 | Reviewer 2 | Reviewer 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Include | Exclude | Unsure | Total | ||
| Reviewer 1 | include | 11 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| Reviewer 1 | exclude | 2 | 36 | 0 | 38 |
| Reviewer 1 | unsure | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| total | 14 | 36 | 0 | 50 |
| Autor, Data, Journal | Sterilization Method (Autoclave Temperature, Pressure Exposure Time) | Endodontic Instruments (Diameter and Taper at the Tip) | Autoclave Cycles | Number of Instruments | Surfaces Scanned by Instrument | Number of Total Scans | Scanning Surface | Root Mean Square (RMS) ± Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yılmaz et al., 2017, Clin. Oral. Investig. [9] | Autoclave 134 °C, 30 psi for 20 min | HyFlex EDM (25/08) | 0 | 2 | 15 | 30 | 5 × 5 μm | 48.62 ± 7.76 nm |
| 5 | 2 | 15 | 30 | 5 × 5 μm | 57.84 ± 6.94 nm | |||
| Spagnuolo et al., 2012, Int. Endod. J. [17] | Autoclave 121 °C, 15 psi, for 15 min | ProTaper F2 (25/08) | 0 | 15 | 15 | 225 | 15 × 15 μm | 203.75 ± 35.81 nm |
| 5 | 15 | 15 | 225 | 15 × 15 μm | 715.22 nm ± 37.71 | |||
| Can Saglam et al., 2015, Microsc. Res. Tech. [18] | Autoclave 121 °C for 20 min | ProTaper retreatment D1 (30/09) | 0 | 1 | 11 | 11 | 2 × 2 μm | 1.33 ± 0.558 nm |
| 5 | 1 | 11 | 11 | 2 × 2 μm | 1.75 ± 0.940 nm | |||
| Inan et al., 2007, J. Endod. [10] | Autoclave 134 °C for 18 min | ProTaper F2 (25/08) | 0 | 1 | 11 | 11 | 1 × 1 μm | 1.46 ± 0.45 nm |
| 1 | 1 | 11 | 11 | 1 × 1 μm | 7.29 ± 0.88 nm |
| Autor, Data, Journal | Endodontic Instruments (Diameter and Taper at the Tip) | Irrigant Used (Concentration and Exposure Time) | Number of Instruments | Surfaces Scanned by Instrument | Number of Total Scans | Scanning Surface | Root Mean Square (RMS) ± Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uslu et al., 2018, Microsc. Res. Tech. [19] | HyFlex EDM (25/.08) | control | 4 | 20 | 80 | 5 × 5 μm | 42.44 ± 4.51 nm |
| NaOCl 5.25% for 5 min | 4 | 20 | 80 | 5 × 5 μm | 57.05 ± 8.55 nm | ||
| EDTA 17% for 5 min | 4 | 20 | 80 | 5 × 5 μm | 60.65 ± 7.27 nm | ||
| Can Saglam et al., 2015, Microsc. Res. Tech. [18] | ProTaper retreatment D1 (30/09) | Control | 1 | 11 | 11 | 2 × 2 μm | 1.33 ± 0.558 nm |
| NaOCl 2% for 5 min | 1 | 11 | 11 | 2 × 2 μm | 2.24 ± 0.555 nm | ||
| Fayyad et al., 2013, Int. Endod. J. [11] | RaCe | control | 4 | 15 | 60 | 20 × 20 μm | 83.3 ± 3.1 nm |
| NaOCl 5.25% for 5 min | 2 | 15 | 30 | 20 × 20 μm | 92.3 ± 23.5 nm | ||
| EDTA 17% for 5 min | 2 | 15 | 30 | 20 × 20 μm | 90 ± 7.5 nm | ||
| Ametrano et al., 2011, Int. Endod. J. [12] | ProTaper F2 (25/08) | control | 1 | 20 | 20 | 1 × 1 μm | 2.88 ± 0.72 nm |
| NaOCl 5.25% for 5 min | 1 | 20 | 20 | 1 × 1 μm | 4.10 ± 1.13 nm | ||
| EDTA 17% for 5 min | 1 | 20 | 20 | 1 × 1 μm | 4.79 ± 0.74 nm | ||
| Topuz et al., 2008, Oral. Surg. Oral. Med. Oral. Pathol. Oral. Radiol. Endod. [20] | RaCe rotary NiTi files (30.06) | control | 1 | 11 | 11 | 1 × 1 μm | 2.06 ± 0.49 nm |
| NaOCl 5.25% for 5 min | 1 | 11 | 11 | 1 × 1 μm | 6.99 ± 2.18 nm | ||
| Saglam et al. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2012 [22] | ProTapar f3 (30.08) | control | 1 | 12 | 12 | 5 × 5 μm | 1.31 ± 0.558 nm |
| NaOCl 5% for 10 min | 1 | 12 | 12 | 5 × 5 μm | 3.20 ± 1.280 nm | ||
| Prasad et al., 2014, J. Conserv. Dent. [23] | iRaCe-R3 | control | 1 | 9 | 9 | 1 × 1 μm | 1.35 ± 0.29 nm |
| NaOCL 5% | 1 | 9 | 9 | 1 × 1 μm | 4.74 ± 1.09 nm | ||
| EDTA 17% | 1 | 9 | 9 | 1 × 1 μm | 3.90 ± 0.58 nm | ||
| Cai et al., 2017, Int. Endod. J. [21] | HyFlex (25.06) | control | 1 | 15 | 15 | 1 × 1 μm | 10.12 ± 1.88 nm |
| NaOCl 5.25% for 10 min | 1 | 15 | 15 | 1 × 1 μm | 9.35 ± 2.05 nm | ||
| control | 1 | 15 | 15 | 1 × 1 μm | 10.47 ± 2.34 nm | ||
| EDTA 17% for 10 min | 1 | 15 | 15 | 1 × 1 μm | 13.88 ± 3.78 nm |
| Selection | Comparability | Exposure | Score | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | Definition of Cases | Representativeness of Cases | Selection of Controls | Definition of Controls | Comparability of Cases and Controls on the Basis of the Design or Analysis | Ascertainment of Exposure | Same Method of Ascertainment for Cases and Controls | Non-Response Rate | |
| Cai et al., 2017 [21] | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 21 |
| Prasad et al., 2014 [23] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 15 |
| Saglam et al., 2012 [22] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 20 |
| Topuz et al., 2008 [20] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 20 |
| Ametrano et al., 2011 [12] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 17 |
| Fayyad et al., 2013 [11] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 16 |
| Can Saglam et al., 2015 [18] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 20 |
| Uslu et al., 2018 [19] | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 21 |
| Inan et al., 2007 [10] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 20 |
| Yılmaz et al., 2017 [9] | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 21 |
| Spagnuolo et al., 2012 [17] | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 21 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dioguardi, M.; Crincoli, V.; Laino, L.; Alovisi, M.; Laneve, E.; Sovereto, D.; Raddato, B.; Zhurakivska, K.; Mastrangelo, F.; Ciavarella, D.; et al. Surface Alterations Induced on Endodontic Instruments by Sterilization Processes, Analyzed with Atomic Force Microscopy: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4948. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224948
Dioguardi M, Crincoli V, Laino L, Alovisi M, Laneve E, Sovereto D, Raddato B, Zhurakivska K, Mastrangelo F, Ciavarella D, et al. Surface Alterations Induced on Endodontic Instruments by Sterilization Processes, Analyzed with Atomic Force Microscopy: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(22):4948. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224948
Chicago/Turabian StyleDioguardi, Mario, Vito Crincoli, Luigi Laino, Mario Alovisi, Enrica Laneve, Diego Sovereto, Bruna Raddato, Khrystyna Zhurakivska, Filiberto Mastrangelo, Domenico Ciavarella, and et al. 2019. "Surface Alterations Induced on Endodontic Instruments by Sterilization Processes, Analyzed with Atomic Force Microscopy: A Systematic Review" Applied Sciences 9, no. 22: 4948. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224948
APA StyleDioguardi, M., Crincoli, V., Laino, L., Alovisi, M., Laneve, E., Sovereto, D., Raddato, B., Zhurakivska, K., Mastrangelo, F., Ciavarella, D., Lo Russo, L., & Lo Muzio, L. (2019). Surface Alterations Induced on Endodontic Instruments by Sterilization Processes, Analyzed with Atomic Force Microscopy: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences, 9(22), 4948. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224948













