Photon Counting Statistics of a Microwave Cavity Coupled with Double Quantum Dots
Abstract
1. Introduction
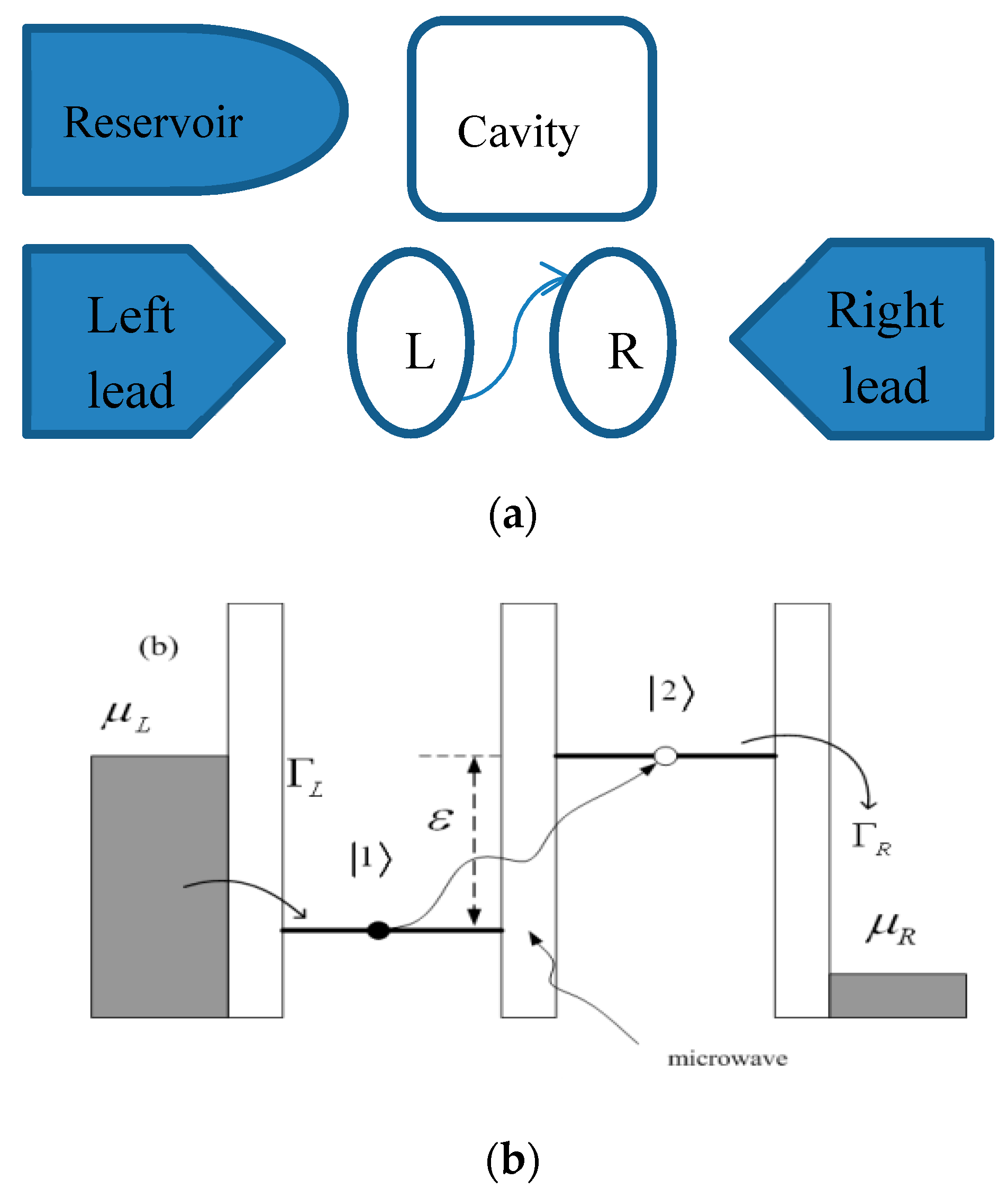
2. Model and Theoretical Formalism
2.1. Hamiltonian Model
2.2. Master Equation
2.3. Photon Emission Counting Statistics
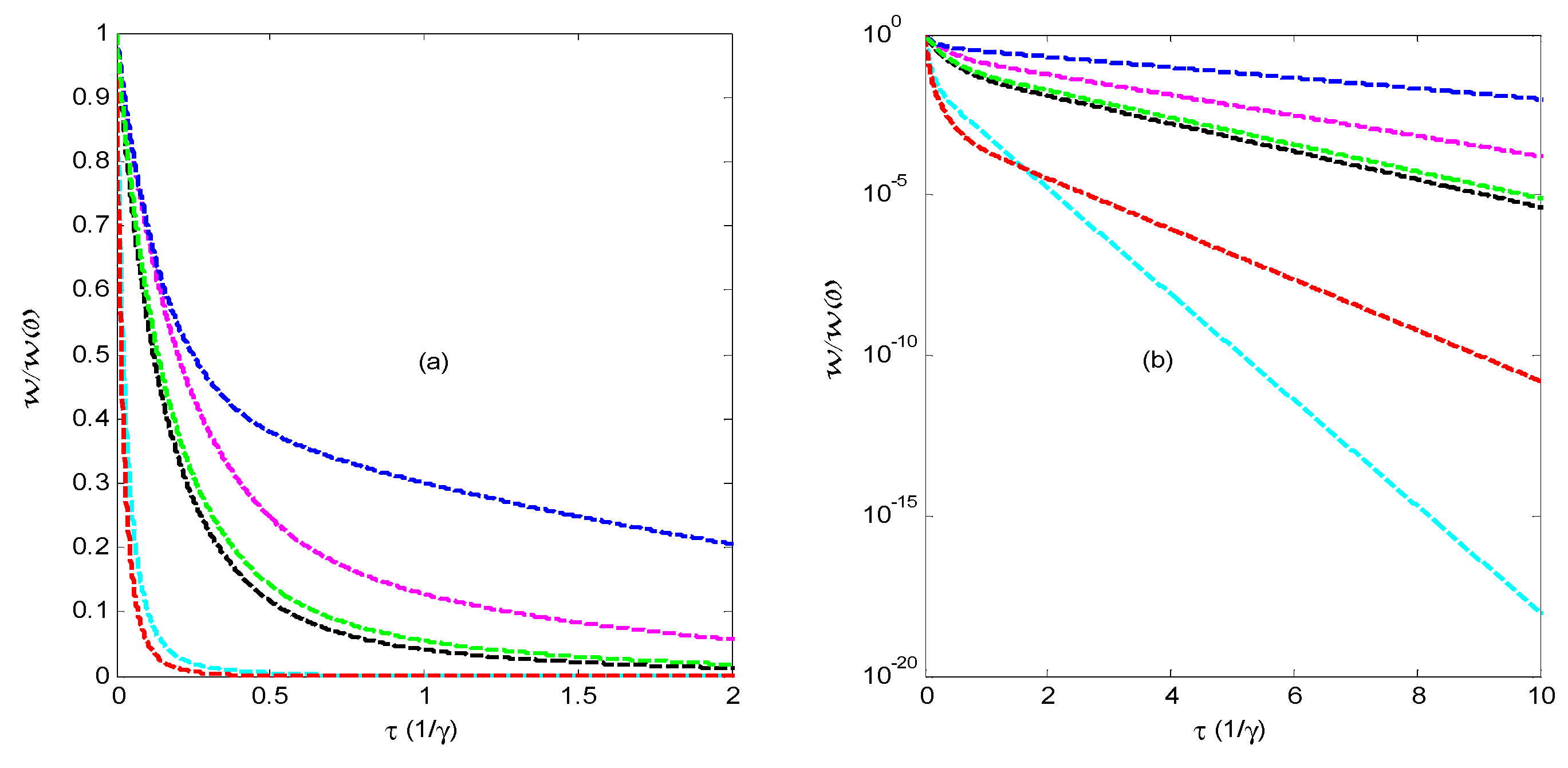
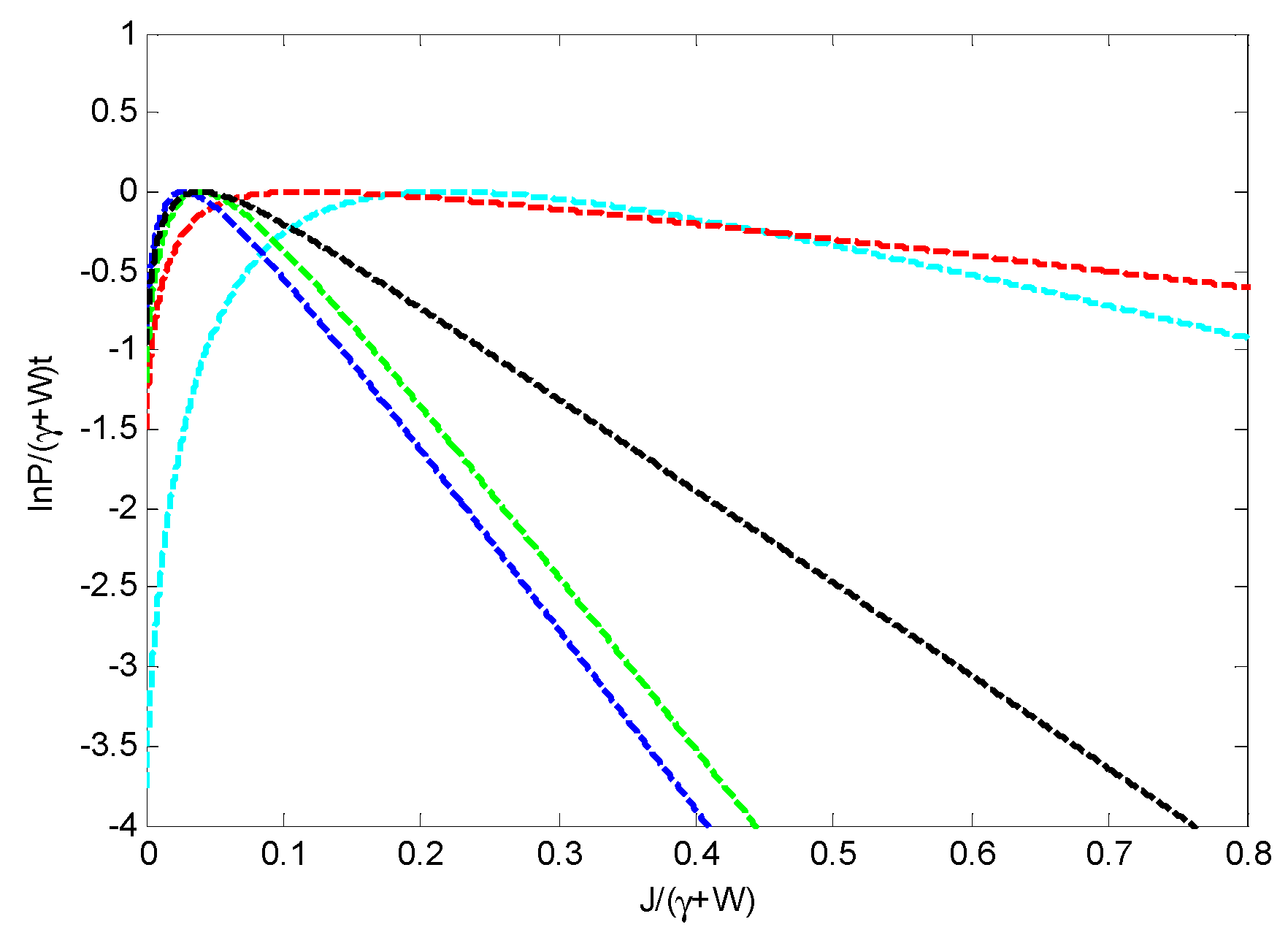
2.3.1. Waiting Time Distributions and Large-Deviation Statistics for Photon Emission
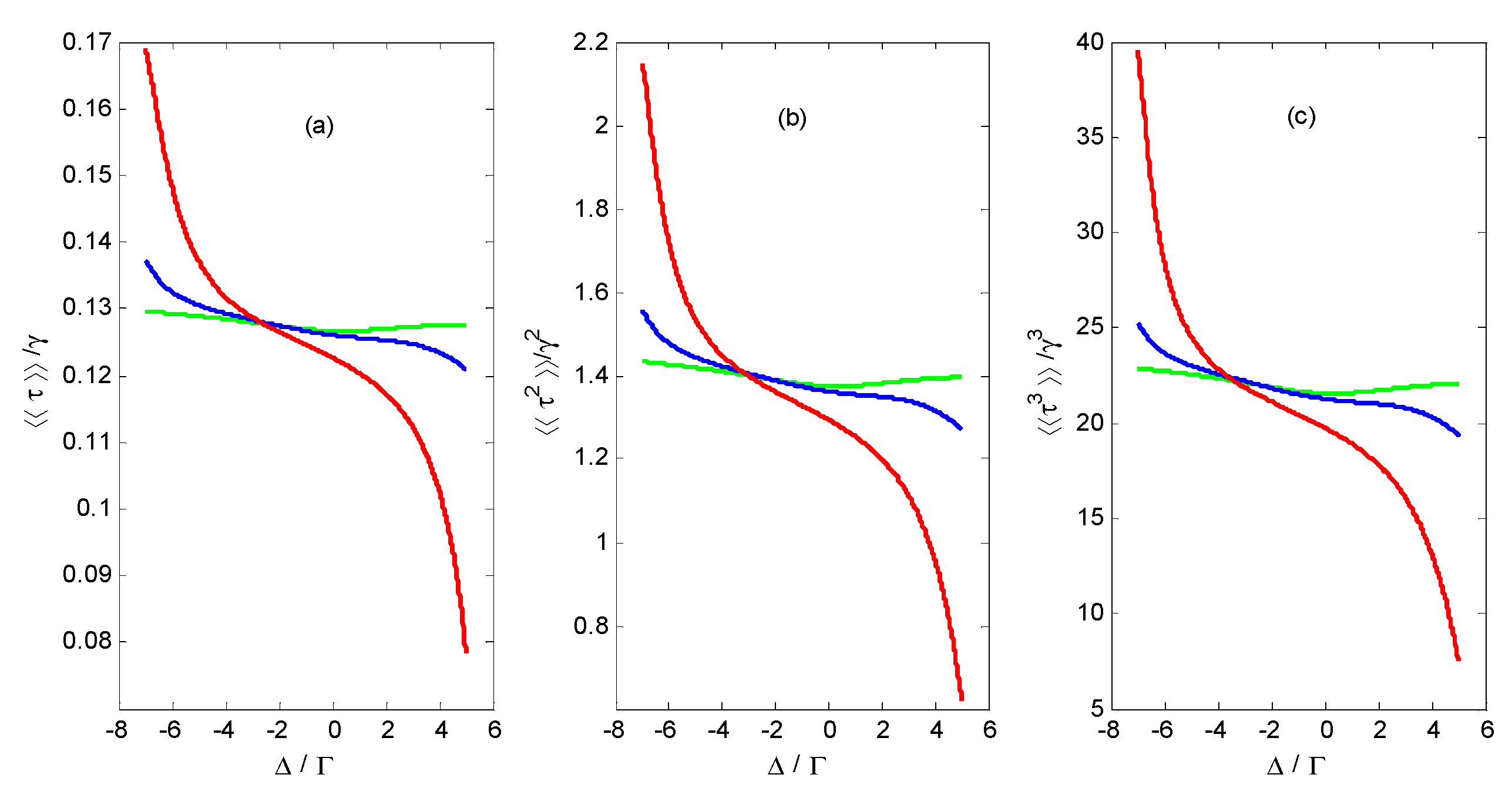
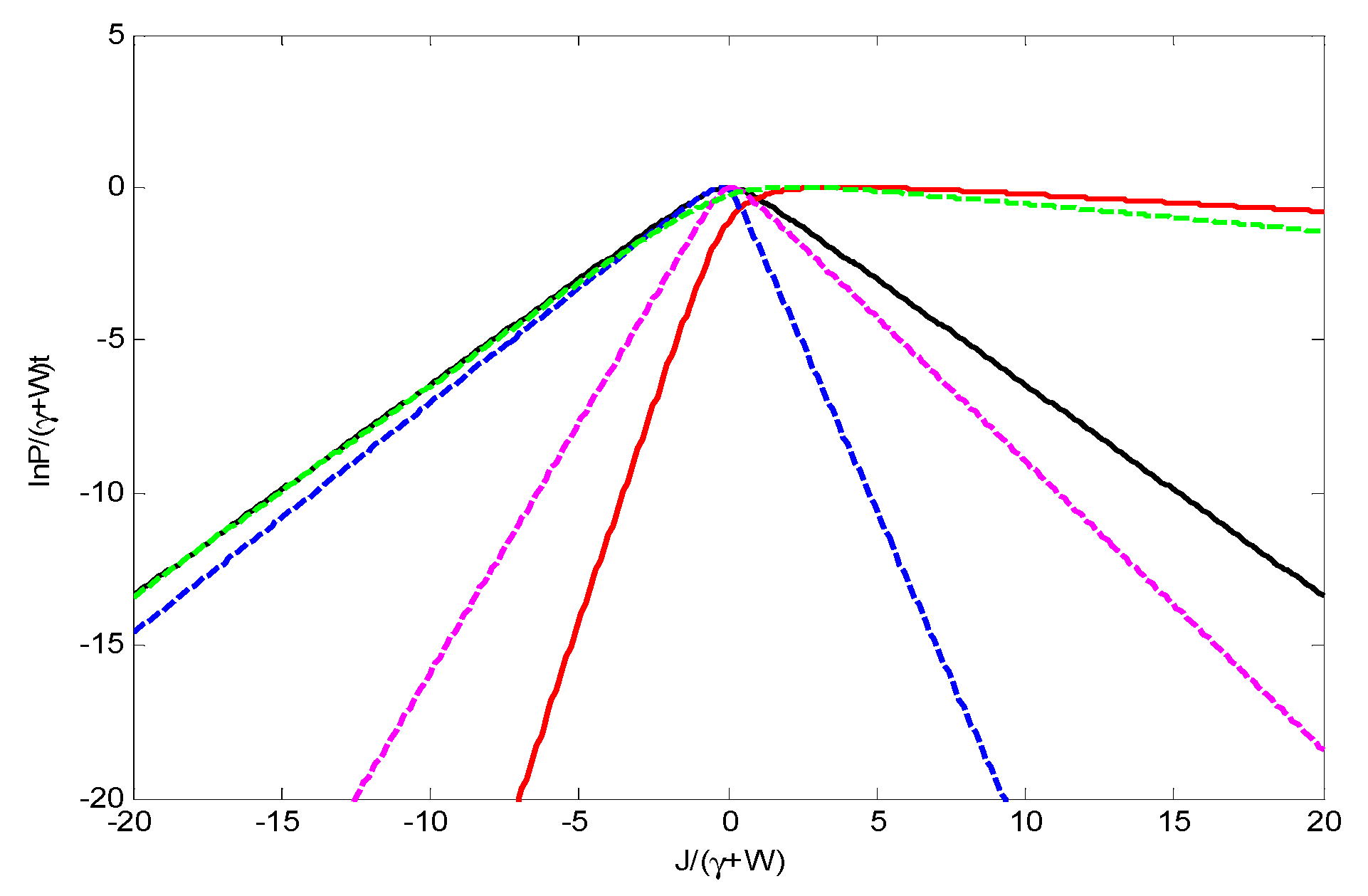
2.3.2. Large-Deviation Statistics for Net Photon Current
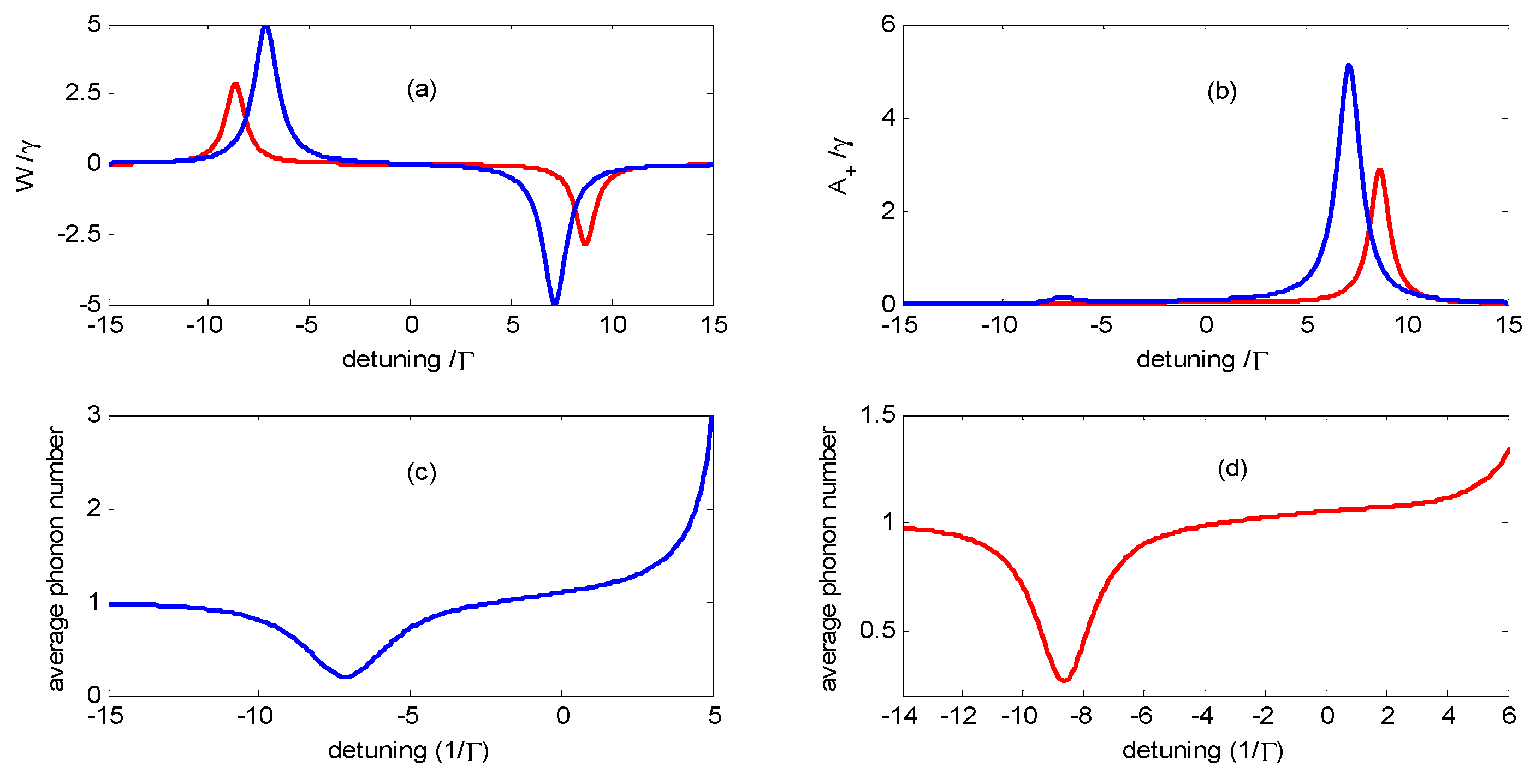
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions and Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Kampen, N.G. Stochastic Processes in Physics and Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, D.R. Renewal Theory; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Tannoudji, C.; Dalibard, J. Single-atom laser spectroscopy. Looking for dark periods in fluorescence light. Europhys. Lett. 1986, 1, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zoller, P.; Marte, M.; Walls, D.F. Quantum jumps in atomic systems. Phys. Rev. A 1987, 35, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, M.; Flindt, C.; Büttiker, M. Distributions of waiting times of dynamic single-electron emitters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 086805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, M.; Haack, G.; Flindt, C.; Büttiker, M. Electron waiting times in mesoscopic conductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 186806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touchette, H. The large deviation approach to statistical mechanics. Phys. Rep. 2009, 478, 1–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrahan, J.P.; Lesanovsky, I. Thermodynamics of quantum jump trajectories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 160601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, X.Q. Counting statistics of photon emissions detected in non-Markovian environment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Ping, J.; Li, S.S.; Li, X.Q.; Yan, Y. Large-deviation analysis for counting statistics in mesoscopic transport. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 115319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žnidarič, M. Large-deviation statistics of a diffusive quantum spin chain and the additivity principle. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 042140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Ji, Z.; Pfeiffer, L.; West, K.W.; Rimberg, A.J. Real-time detection of electron tunnelling in a quantum dot. Nature 2003, 423, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, T.; Hayashi, T.; Tomita, R.; Hirayama, Y. Bidirectional counting of single electrons. Science 2006, 312, 1634–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustavsson, S.; Leturcq, R.; Studer, M.; Ihn, T.; Ensslin, K.; Driscoll, D.C.; Gossard, A.C. Time-resolved detection of single-electron interference. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2547–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Maisi, V.F.; Kambly, D.; Flindt, C.; Pekola, J.P. Full counting statistics of Andreev tunneling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 036801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurzmann, A.; Stegmann, P.; Kerski, J.; Schott, R.; Ludwig, A.; Wieck, A.D.; König, J.; Lorke, A.; Geller, M. Optical detection of single-electron tunneling into a semiconductor quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 247403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbydniewska, E.; Duzynska, A.; Popoff, M.; Hourlier, D.; Lenfant, S.; Judek, J.; Zdrojek, M.; Mélin, T. Charge blinking statistics of semiconductor nanocrystals revealed by carbon nanotube single charge sensors. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6349–6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, J.C.; Gasparinetti, S.; Collodo, M.; Walter, T.; Kurpiers, P.; Eichler, C.; Wallraff, A. Single-shot quantum non-demolition detection of an itinerant microwave photons. Nat. Phys. 2018, 14, 546–549. [Google Scholar]
- Vinjanampathy, S.; Anders, J. Quantum thermodynamics. Cont. Phys. 2016, 57, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M.A.; Chuang, I.L. Quantum Computation and Quantum Information; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Brandes, T. Waiting times and noise in single particle transport. Annalen der Physik 2008, 17, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptaszyński, K. Nonrenewal statistics in transport through quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 045306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptaszyński, K. Waiting time distribution revealing the internal spin dynamics in a double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 035409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sothmann, B. Electronic waiting-time distribution of a quantum-dot spin valve. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 155315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.H.; Flindt, C. Electron waiting times in non-Markovian quantum transport. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 121405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, L.; Pöltl, C.; Governale, M. Waiting time distributions for the transport through a quantum-dot tunnel coupled to one normal and one superconducting lead. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 067002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevallier, D.; Albert, M.; Devillard, P. Probing Majorana and Andreev bound states with waiting times. Eurphys. Lett. 2016, 116, 27005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dasenbrook, D.; Hofer, P.P.; Flindt, C. Electron waiting times in coherent conductors are correlated. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 91, 195420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, G.; Albert, M.; Flindt, C. Distributions of electron waiting times in quantum-coherent conductors. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 205429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brange, F.; Menczel, P.; Flindt, C. Photon counting statistics of a microwave cavity. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 99, 085418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.W.; Wei, D.; Li, S.X.; Johansson, J.R.; Kong, W.C.; Li, H.O.; Jiang, H.W. Coupling two distant double quantum dots with a microwave resonator. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6620–6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbecq, M.R.; Schmitt, V.; Parmentier, F.D.; Roch, N.; Viennot, J.J.; Fève, G.; Huard, B.; Mora, C.; Cottet, A.; Kontos, T. Coupling a quantum dot, fermionic leads, and a microwave cavity on a chip. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 256804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwalla, B.K.; Kulkarni, M.; Mukamel, S.; Segal, D. Giant photon gain in large-scale quantum dot-circuit QED systems. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 121305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.X. Cavity optomechanics: Manipulating photons and phonons towards the single-photon strong coupling. Chin. Phys. B 2018, 27, 024204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Zhang, S.; Zou, J.H.; Chen, L.; Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Feng, M. Fast optical cooling of nanomechanical cantilever with the dynamical Zeeman effect. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 29695–29710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Z.; Ouyang, S.H.; Lam, C.H.; You, J.Q. Cooling a nanomechanical resonator by a triple quantum dot. Europhys. Lett. 2011, 95, 40003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, B.Y.; Li, G.X. Ground-state cooling of a nanomechanical resonator via single-polariton optomechanics in a coupled quantum-dot–cavity system. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 033809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Jin, D.Y.; Qiu, Y.; Lam, C.H.; You, J.Q. Cross-Kerr effect on an optomechanical system. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 93, 023844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.H.; You, J.Q.; Nori, F. Cooling a mechanical resonator via coupling to a tunable double quantum dot. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 075304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.P.; Li, G.X. Ground-state cooling of a nanomechanical resonator with a triple quantum dot via quantum interference. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 86, 053828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renardy, M.; Rogers, R.C. An Introduction to Partial Differential Equations, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rudge, S.L.; Kosov, D.S. Counting quantum jumps: A summary and comparison of fixed-time and fluctuating-time statistics in electron transport. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 151, 034107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockklauser, A.; Scarlino, P.; Koski, J.V.; Gasparinetti, S.; Andersen, C.K.; Reichl, C.; Wegscheider, W.; Ihn, T.; Ensslin, K.; Wallraff, A. Strong coupling cavity QED with gate-defined double quantum dots enabled by a high impedance resonator. Phys. Rev. X 2017, 7, 011030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullans, M.J.; Taylor, J.M.; Petta, J.R. Probing electron-phonon interactions in the charge-photon dynamics of cavity-coupled double quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 97, 035305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Wei, Z.; Meng, H.; Liang, R. Photon Counting Statistics of a Microwave Cavity Coupled with Double Quantum Dots. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4934. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224934
Wang F, Liu W, Wang X, Wei Z, Meng H, Liang R. Photon Counting Statistics of a Microwave Cavity Coupled with Double Quantum Dots. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(22):4934. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224934
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Faqiang, Weici Liu, Xiaolei Wang, Zhongchao Wei, Hongyun Meng, and Ruisheng Liang. 2019. "Photon Counting Statistics of a Microwave Cavity Coupled with Double Quantum Dots" Applied Sciences 9, no. 22: 4934. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224934
APA StyleWang, F., Liu, W., Wang, X., Wei, Z., Meng, H., & Liang, R. (2019). Photon Counting Statistics of a Microwave Cavity Coupled with Double Quantum Dots. Applied Sciences, 9(22), 4934. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224934






