A Numerical Model to Estimate the Soil Thermal Conductivity Using Field Experimental Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
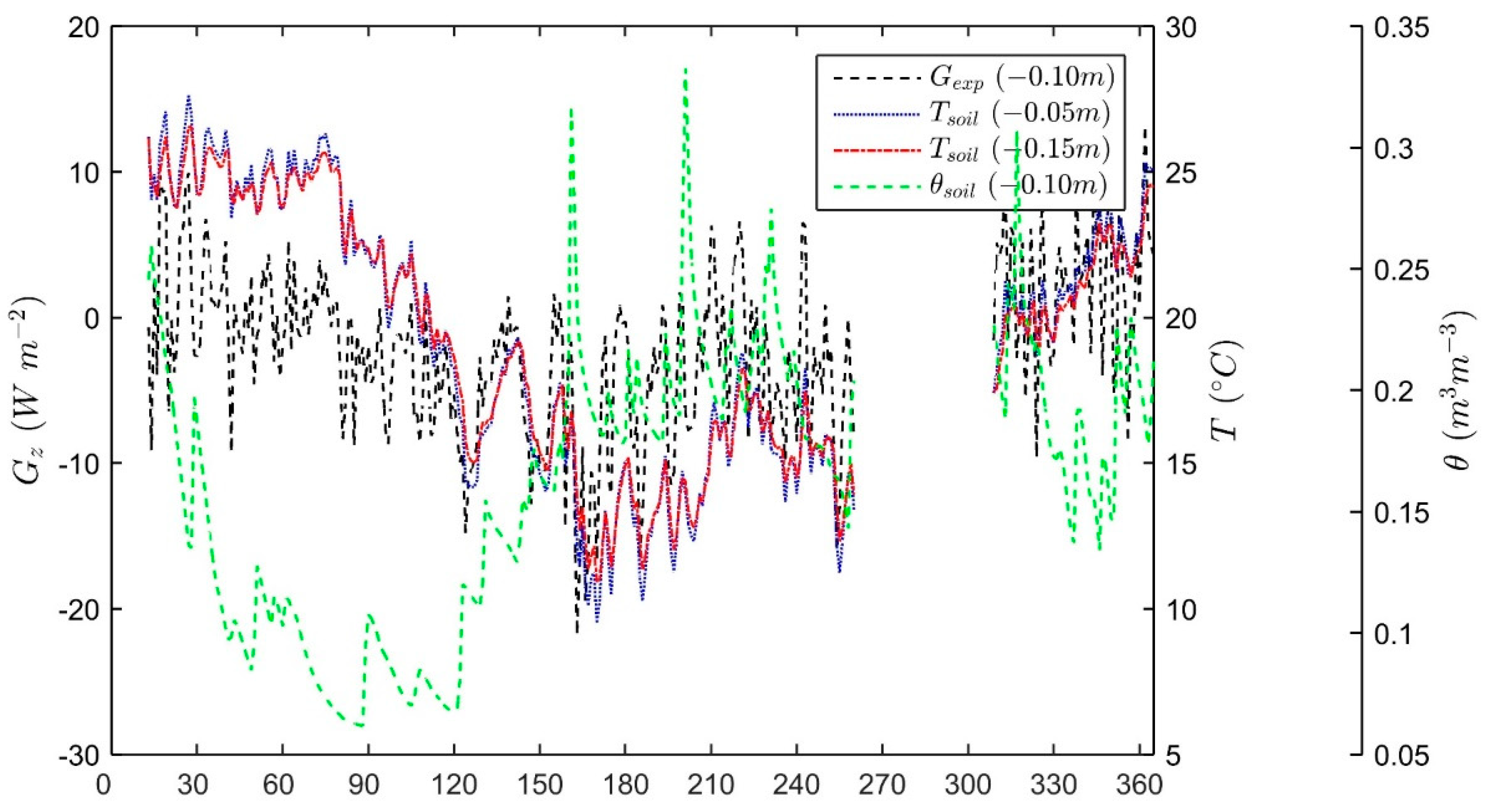
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Proposed Model
Data Fitting: Least Squares Approximation
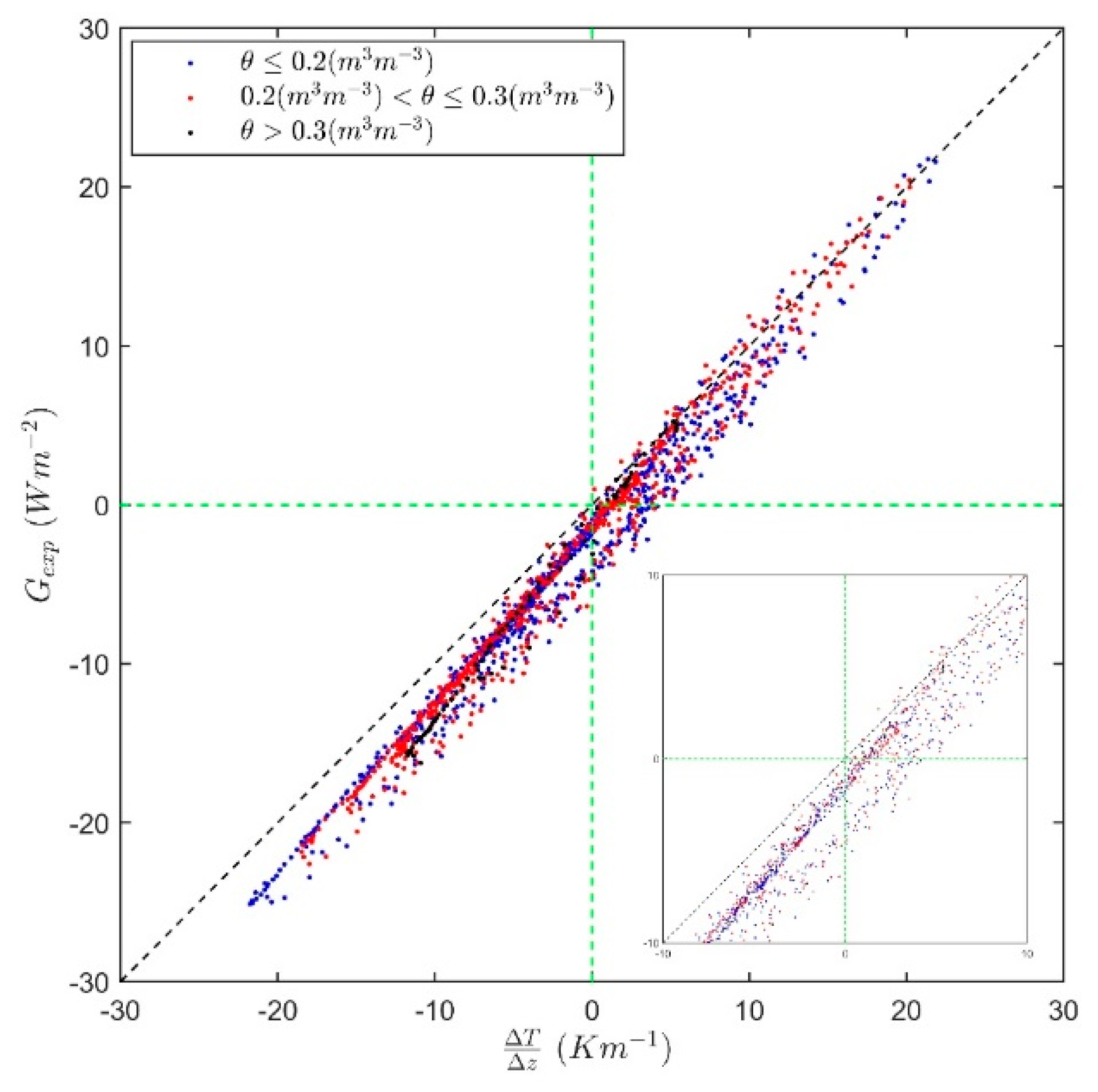
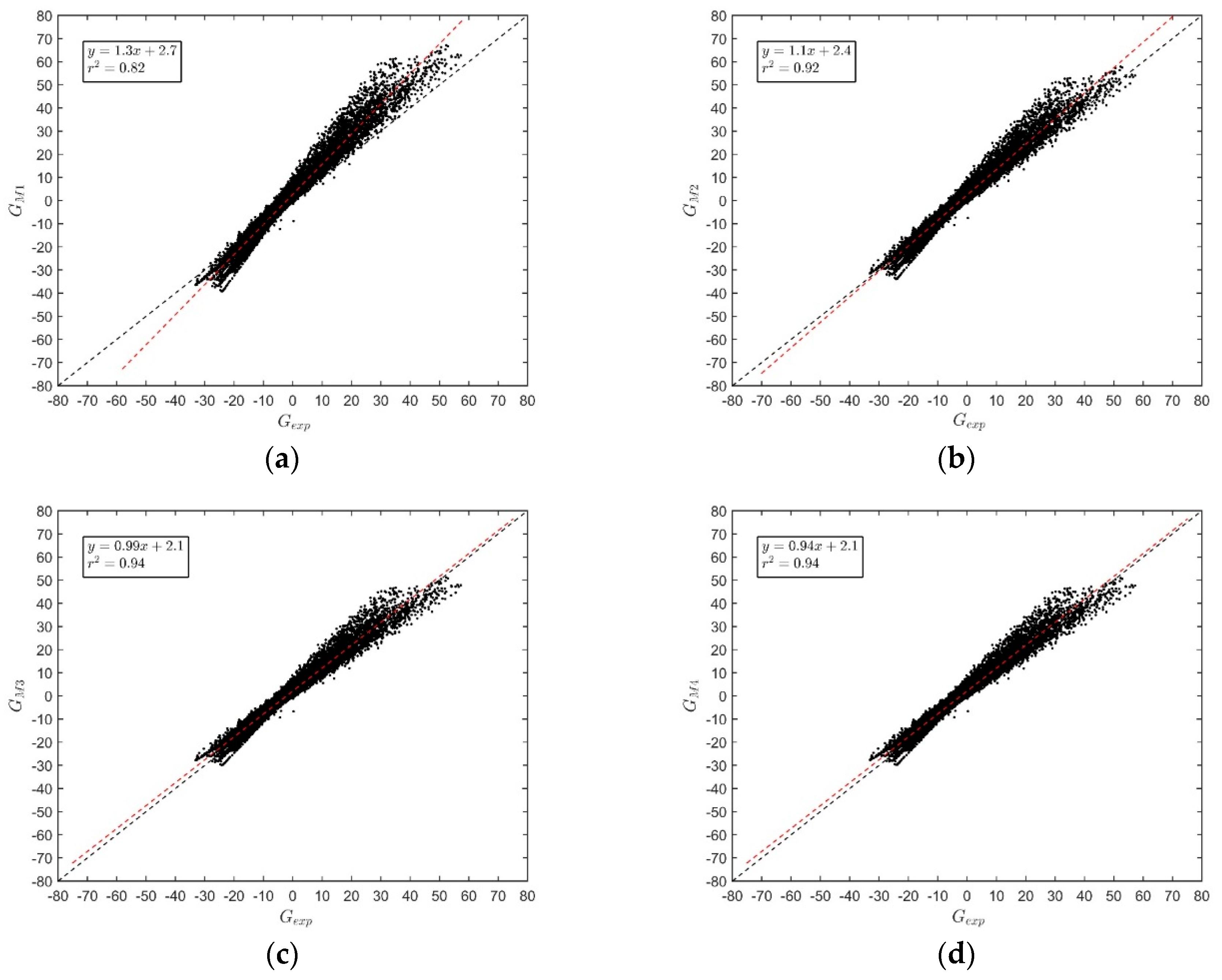
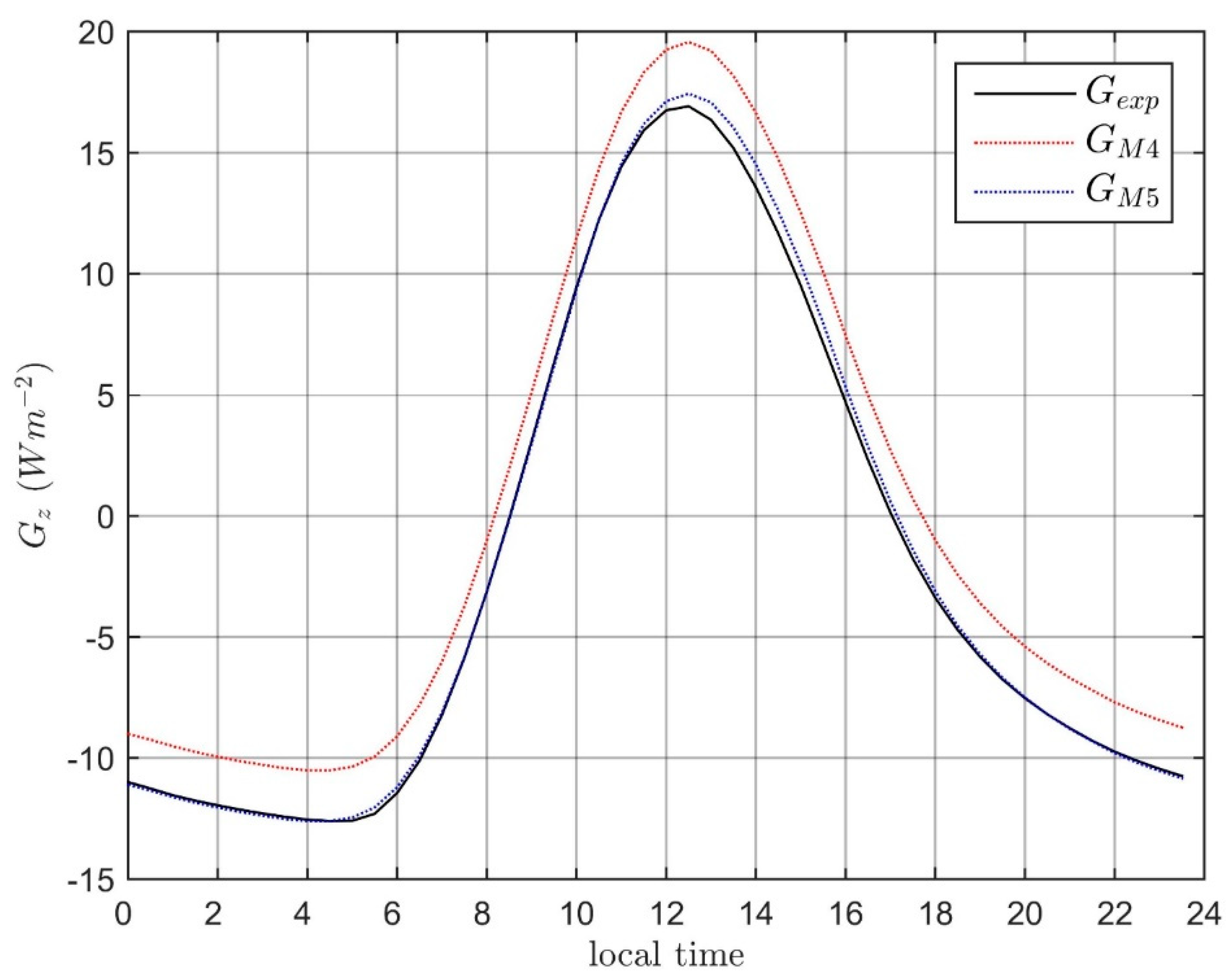
2.3. Numerical Models Calibration and Validation
- Method 1 (): Isolating in Equation (2) and calculating the average value of ;
- Method 2 (): Isolating in Equation (2) and calculating the average value of for the observed data whose temperature variation () is equal to or greater than ;
- Method 3 (): Isolating in Equation (2) and calculating the average value of for the 13-h data (local time). This time was chosen because it presents, in general, a greater variation of the temperature in relation to the depth than the other times;
- Method 4 (): Least squares method applied to Equation (2);
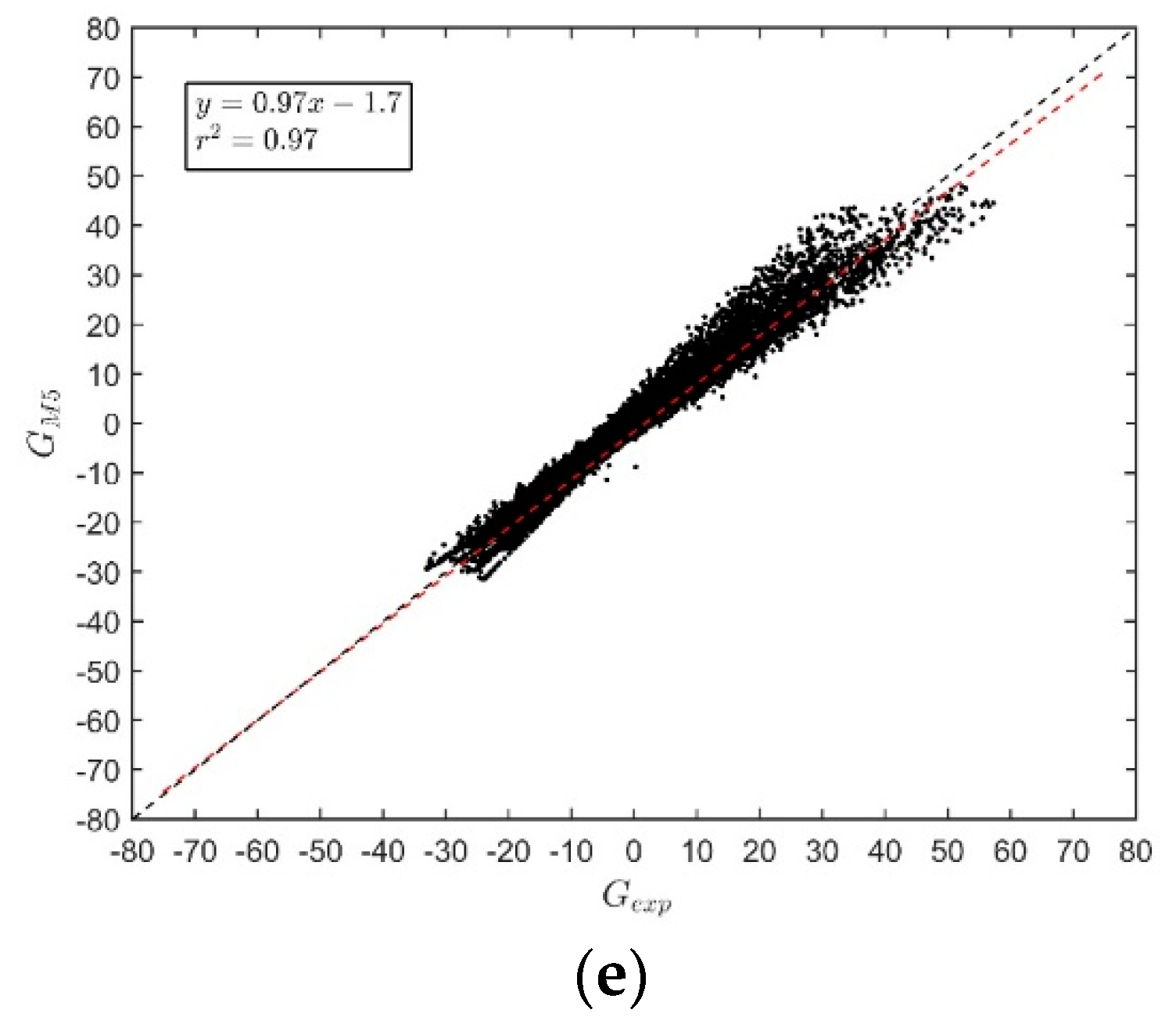
- Method 5 (): Least squares method applied to Equation (3).
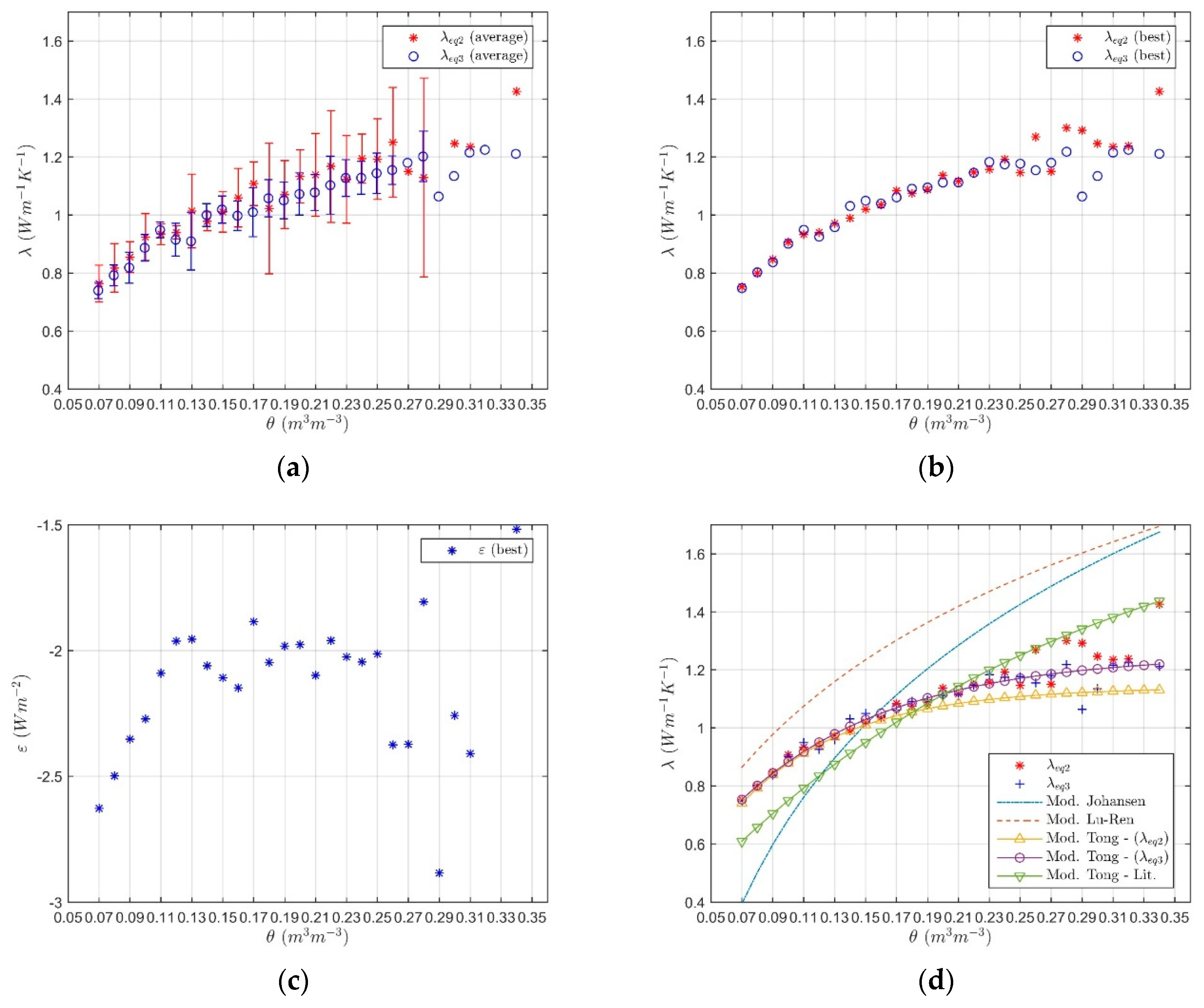
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Campbell, G.S. Soil Physics with Basic: Transport Models for Soil-Plant Systems. In Developments in Soil Science 14, 1st ed.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- de Vries, D.A. Thermal Properties of Soils. In Physics of Plant Environment; van Wijk, W.R., Ed.; North-Holland Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Lu, S.; Horton, R.; Ren, T. An Empirical Model for Estimating Soil Thermal Conductivity from Texture, Water Content, and Bulk Density. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, L. Estimation of Ground Heat Flux from Soil Temperature over a Bare Soil. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 129, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, W.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, W. Estimation from Soil Temperature of Soil Thermal Diffusivity and Heat Flux in Sub-Surface Layers. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2016, 158, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.; Gao, Z.; Horton, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, L. An Empirical Model for Estimating Soil Thermal Conductivity from Soil Water Content and Porosity. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 17, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Lu, Y.; Peng, W.; Ju, Z.; Ren, T. A Generalized Relationship between Thermal Conductivity and Matric Suction of Soils. Geoderma 2019, 337, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhou, G.; Jiang, X. Measurement of Thermal Conductivity for Frozen Soil at Temperatures Close to 0 °C. Measurement 2019, 140, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, A.W. Heat Transmission in Low Conductivity Materials. In Thermal Conductivity; Tye, R.P., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1969; Volume 1, pp. 301–405. [Google Scholar]
- de Vries, D.A.; Peck, A.J. On the Cylindrical Probe Method of Measuring Thermal Conductivity with Special Reference to Soils. Part 1. Extension of Theory and Discussion of Probe Characteristics. Aust. J. Phys. 1958, 11, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Padmakumar, G.P.; Sharma, V.; Singh, D.N.; Baghini, M.S. A Methodology to Determine Thermal Conductivity of Soils from Flux Measurement. Geomech. Geoengin. Int. J. 2015, 11, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, K.L.; Kluitenberg, G.J.; Horton, R. Measurement of Soil Thermal Properties with a Dual-probe Heat-pulse Technique. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluitenberg, G.J.; Bristow, K.L.; Das, B.S. Error Analysis of the Heat Pulse Method for Measuring Soil Heat Capacity, Diffusivity and Conductivity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1995, 59, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, S.M.; Kluitenberg, G.J.; Bristow, K.L. Rapid Numerical Estimation os Soil Thermal Properties for a Broad Class of Heat-Pulse Emitter Geometries. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1996, 7, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsner, T.E.; Sauer, T.J.; Horton, R. Field Tests of the Soil Heat Flux Plate Method and Some Alternatives. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Heitman, J.; Horton, R.; Ren, T. Field Evaluation and Improvement of the Plate Method for Measuring Soil Heat Flux Density. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 214–215, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, H.S.; Jaeger, J.C. Conduction of Heat in Solids, 4th ed.; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Liebethal, C.; Foken, T. Evaluation of Six Parameterization Approaches for the Ground Heat Flux. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2007, 88, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Hou, X.; Wei, Z. Comparative Study of the Soil Thermal Regime in Arid and Semi-Humid Areas. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.R. The Theory of Heat Flux Meters. J. Geophys. Res. 1961, 66, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, T.J. Heat Flux Density. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Part 4; Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C., Eds.; SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 2002; pp. 1233–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Mayocchi, C.L.; Bristow, K.L. Soil Surface Heat Flux: Some General Questions and Comments on Measurments. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 75, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, M.; Hadas, A. Analysis of the Performance of an Improved Soil Heat Flux Transducer. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1973, 37, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimball, B.A.; Jackson, R.D.; Nakayama, F.S.; Idso, S.B.; Reginato, R.J. Soil-Heat Flux Determination: Temperature Gradient Method with Computed Thermal Conductivities. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1976, 40, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.P.; Prueger, J.H.; Hatfield, J.L.; Ramalingam, K.; Hipps, L.E. Variability in Soil Heat Flux from a Mesquite Dune Site. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 103, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, D.R.; Baker, J.M. In Situ Measurement of Soil Heat Flux with the Gradient Method. Vadose Zone J. 2003, 2, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, T.J.; Meek, D.W.; Ochsner, T.E.; Harris, A.R.; Horton, R. Errors in Heat Flux Measurement by Flux Plates of Contrasting Design and Thermal Conductivity. Vadose Zone J. 2003, 2, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, T.J.; Ochsner, T.E.; Horton, R. Soil Heat Flux Plates: Heat Flow Distortion and Thermal Contact Resistance. Agron. J. 2007, 99, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusinkveld, B.G.; Jacobs, A.F.G.; Holtslag, A.A.M.; Berkowicz, S.M. Surface Energy Balance Closure in an Arid Region: Role of Soil Heat Flux. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2004, 122, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhao, L.; Wu, T.; Wang, Q.; Ding, Y.; Yao, J.; Wu, X.; Hu, G.; Xiao, Y.; Du, Y.; et al. Soil Thermal Conductivity and its Influencing Factors at the Tanggula Permafrost Region on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 264, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubert, G.C.D.; Roberti, D.R.; Pereira, L.S.; Quadros, F.L.F.; Velho, H.F.C.; de Moraes, O.L.L. Evapotranspiration of the Brazilian Pampa Biome: Seasonality and Influential Factors. Water 2018, 10, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated World Map of the Köppen-Geiger Climate Classification. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences Discussions. Eur. Geosci. Union 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoef, A.; van den Hurk, B.J.J.M.; Jacobs, A.F.G.; Heusinkveld, B.G. Thermal Soil Properties for Vineyard (EFEDA-I) and Savanna (HAPEX-Sahel) Sites. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1996, 78, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bou-Zeid, E. A Novel Approach for the Estimation of Soil Ground Heat Flux. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 154–155, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, O. Thermal Conductivity of Soils (CRREL draft transl. 637, 1977). Ph.D. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Ren, T.; Gong, Y.; Horton, R. An Improved Model for Predicting Soil Thermal Conductivity from Water Content at Room Temperature. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różański, A.; Stefaniuk, D. Prediction of Soil Solid Thermal Conductivity from Soil Separates and Organic Matter Content: Computational Micromechanics Approach. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2016, 67, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Calibration | Validation | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | Day | Night | Daily | Day | Night | |||
| Method 1 ( | 1.331 | - | 5.56 | 7.31 | 2.92 | 0.82 | 0.71 | 0.77 |
| Method 2 ( | 1.148 | - | 3.86 | 5.08 | 1.97 | 0.92 | 0.86 | 0.89 |
| Method 3 ( | 1.014 | - | 3.24 | 3.97 | 2.28 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.86 |
| Method 4 ( | 1.011 | - | 3.23 | 3.95 | 2.30 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.85 |
| Method 5 ( | 0.993 | -2.216 | 2.43 | 3.06 | 1.58 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.93 |
| Original—Tong Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | |||
| RMSE |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romio, L.C.; Roberti, D.R.; Buligon, L.; Zimmer, T.; Degrazia, G.A. A Numerical Model to Estimate the Soil Thermal Conductivity Using Field Experimental Data. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4799. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224799
Romio LC, Roberti DR, Buligon L, Zimmer T, Degrazia GA. A Numerical Model to Estimate the Soil Thermal Conductivity Using Field Experimental Data. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(22):4799. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224799
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomio, Leugim Corteze, Débora Regina Roberti, Lidiane Buligon, Tamires Zimmer, and Gervásio Annes Degrazia. 2019. "A Numerical Model to Estimate the Soil Thermal Conductivity Using Field Experimental Data" Applied Sciences 9, no. 22: 4799. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224799
APA StyleRomio, L. C., Roberti, D. R., Buligon, L., Zimmer, T., & Degrazia, G. A. (2019). A Numerical Model to Estimate the Soil Thermal Conductivity Using Field Experimental Data. Applied Sciences, 9(22), 4799. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224799





