Pre-Concentration Based on Cloud Point Extraction for Ultra-Trace Monitoring of Lead (II) Using Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation
2.2. Materials and Reagents
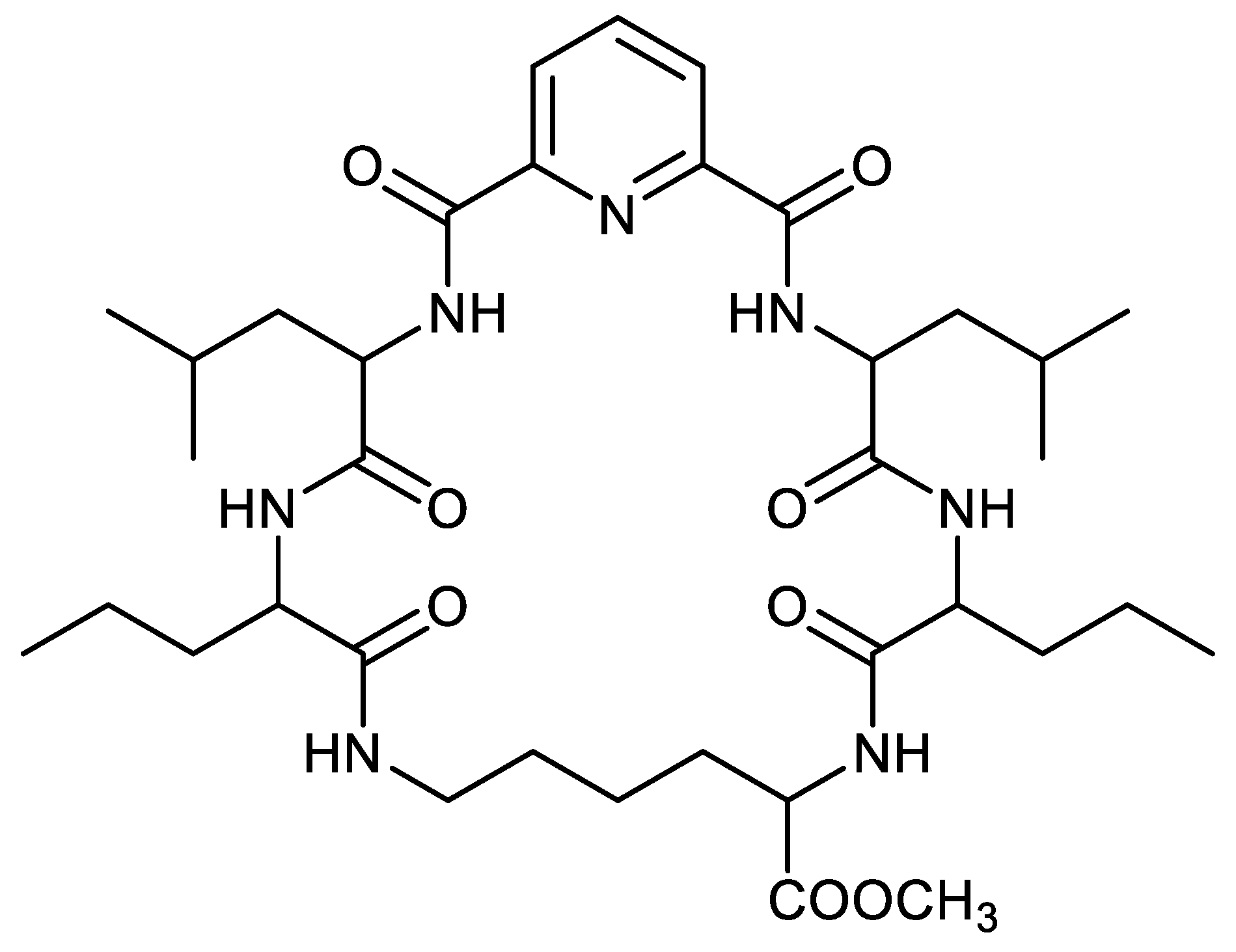
2.3. Procedure for CPE
3. Results and Discussion
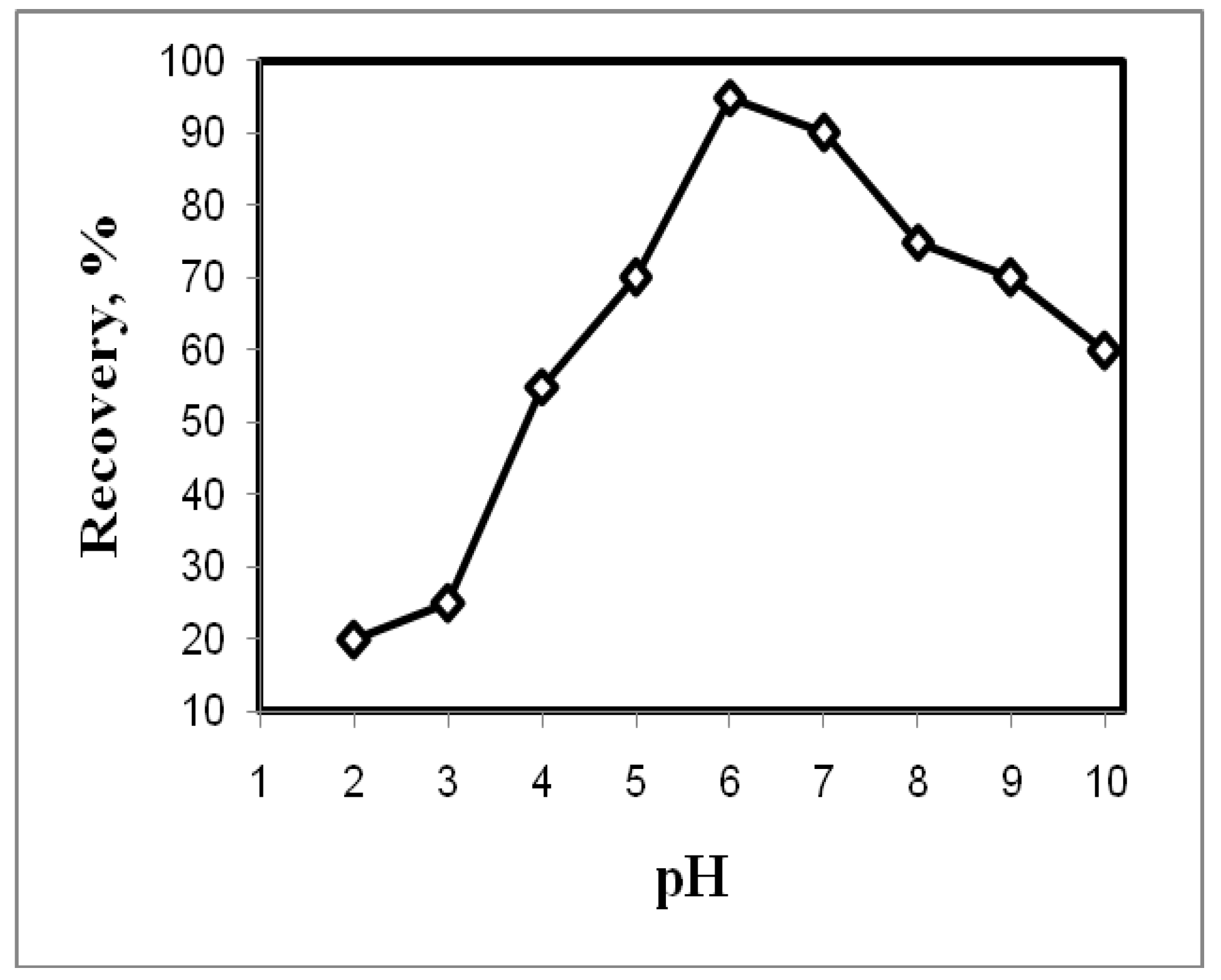
3.1. Effect of pH
3.2. Ligand Concentration Effect
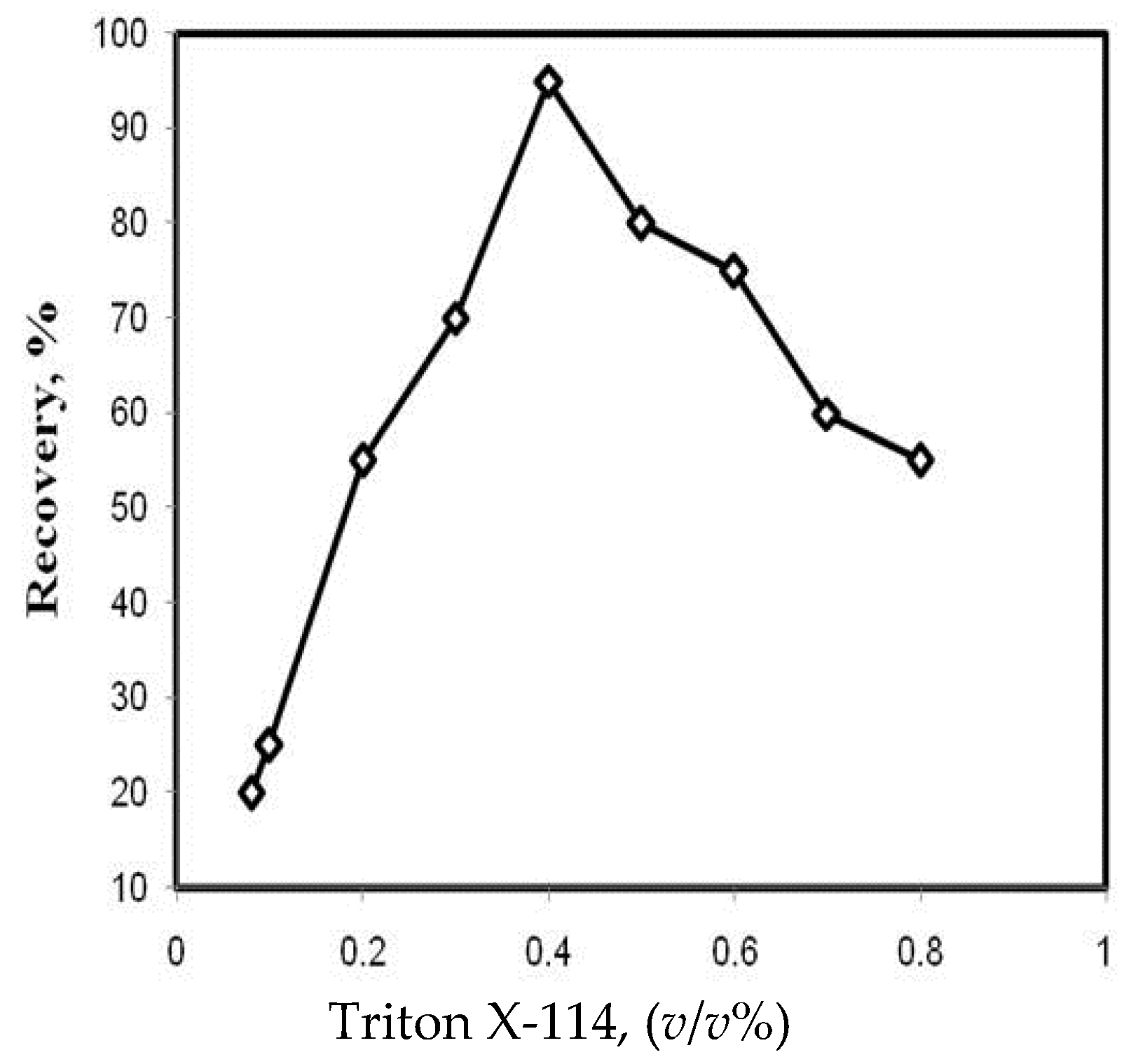
3.3. Effect of Triton X-114 Concentration
3.4. Incubation Time and Equilibrium Temperature Effects
3.5. Effect of Diverse Ions
3.6. Figure of Merit and Results
3.7. Analysis of Natural Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tautkus, S.; Steponeniene, L.; Kazlauskas, R. Accumulation of sadmium and zinc in bottom sediments ofdifferent waters of Lithuania. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2007, 72, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, H.I.; Kazi, T.G.; Jamali, M.K.; Kazi, G.H.; Arain, M.B.; Jalbani, N.; Shar, G.Q.; Sarfaraz, R.A. Evaluation of toxic metals in biological samples (scalp hair, blood and urine) of steel mill workers by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2006, 22, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolann, B.J.; Rahil-Khazen, R.; Henriksen, H.; Isrenn, R.; Ulvik, R.J. Evaluation of methods for trace-element determination with emphasis on their usability in the clinical routine laboratory. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2007, 67, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nriagu, J.O.; Pacyna, J.M. Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace metals. Nature 1988, 333, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gercel, O.; Gercel, H.F. Adsorption of lead(II) ions from aqueous solutions by activated carbon prepared from biomass plant material of Euphorbia rigida. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 132, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezio, M.S.D.; Palomeque, M.E.; Band, B.S.F. A sensitive spectrophotometric method for lead determination by flow injection analysis with on-line preconcentration. Talanta 2004, 63, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Health Criteria and Other Supporting Information, Geneva, 2nd ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; Volume 2, p. 973. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, F.; Kazi, T.G.; Naeemullah, A.H.I.; Soylak, M. Temperature controlled ionic liquid-dispersive liquid phase microextraction for determination of trace lead level in blood samples prior to analysis by flame atomic absorption spectrometry with multivariate optimization. Microchem. J. 2012, 101, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokalıoğlu, Ş.; Yılmaz, V.; Kartal, Ş. Solid phase extraction of Cu(II), Ni(II), Pb(II), Cd(II) and Mn(II) ions with 1-(2-thiazolylazo)-2-naphthol loaded Amberlite XAD-1180. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 152, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenduzler, E.; Turker, A.R.; Yalcınkaya, O. Separation and preconcentration of trace manganese from various samples with Amberlyst 36 column and determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2006, 69, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, F.; Kazi, T.G.; Afridi, H.I.; Naeemullah; Arain, M.B.; Baig, J.A. Cloud point extraction for determination of lead in blood samples of children, using different ligands prior to analysis by flame atomic absorption spectrometry: A multivariate study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, A.M.; Dadfarnia, S.; Dehghani, Z. On-line solid phase extraction system using 1,10-phenanthroline immobilized on surfactant coated alumina for the flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of copper and cadmium. Talanta 2009, 79, 1066–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Hu, B.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M. Cloud point extraction for speciation of chromium in water samples by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Water Res. 2005, 39, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.G.; Jiang, G.B.; Cai, Y.Q.; He, B.; Liu, J.F. Determination of cadmium at the nanogram per liter level in seawater by graphite furnace AAS using cloud point extraction. At. Spectrosc. 2004, 25, 170–197. [Google Scholar]
- Boyukbayram, A.E.; Volkan, M. Cloud point preconcentration of germanium and determination by hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2000, 55, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burguera, J.L.; Burguera, M. Analytical applications of organized assemblies for on-line spectrometric determinations: Present and future. Talanta 2004, 64, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medel, A.S.; Campa, M.R.F.; Gonzales, E.B.; Gonzales, M.L.F. Organised surfactant assemblies in analytical atomic spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 1999, 54, 251–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalikas, C.D. Micelle-mediated extraction as a tool for separation and preconcentration in metal analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, H.; Kamidate, T.; Watanabe, H. Micelle-mediated extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 780, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, A.B. Cloud point extraction and spectrofluorimetric determination of aluminium and zinc in foodstuffs and water samples. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 1698–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrakian, T.; Afkhami, A.; Mousavi, A. Spectrophotometric determination of trace amounts of uranium(VI) in water samples after mixed micelle-mediated extraction. Talanta 2007, 71, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Liang, P.; Ding, Q.; Cao, J. Cloud Point Extraction Preconcentration of Manganese(II) from Natural Water Samples Using 1-Phenyl-3-methyl-4-benzoyl-5-pyrazolone and Triton X-100 and Determination by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Anal. Sci. 2006, 22, 911–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Teo, K.C. Determination of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc in water samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry after cloud point extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 450, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Teo, K.C. Determination of cobalt and nickel in water samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry after cloud point extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 434, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleologos, E.K.; Giokas, D.L.; Tzouwara-Karayanni, S.M.; Karayannis, M.I. Micelle mediated methodology for the determination of free and bound iron in wines by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 458, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luconi, M.O.; Silva, M.F.; Olsina, R.A.; Ferna’ndez, L.P. Cloud point extraction of lead in saliva via use of nonionic PONPE 7.5 without added chelating agents. Talanta 2000, 51, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgendy, F.A.; Khalifa, M.K.; Kamel, A.H. Cloud point extraction for pre-concentration determination of palladium in water and food samples by visual and flame atomic absorption spectroscopy. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2015, 4, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.S.M.; Abou Ghalia, M.H.; Abdel-Galil, E.A.; Mohamed, A.H.K. New lead (II) selective membrane potentiometric sensors based on chiral 2,6-bis-pyridinecarboximide derivatives. Talanta 2003, 60, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokrollahi, A.; Ghaedi, M.; Hossaini, O.; Khanjari, N.; Soylak, M. Cloud point extraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometry combination for copper(II) ion in environmental and biological samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, M.; Shokrollahi, A.; Nikham, K.; Nikham, E.; Najibi, A.; Soylak, M. Cloud point extraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of cadmium(II), lead(II), palladium(II) and silver(I) in environmental samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1022–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.Z.; Shamspur, T.; Afzali, D.; Taher, M.A.; Baghelani, Y.M. Applicability of cloud point extraction for the separation trace amount of lead ion in environmental and biological samples prior to determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Arabian J. Chem. 2016, 9, S610–S615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Deng, Q.; Ji, S.; Yang, S.; Peng, L. Design of rapidly synergistic cloud point extraction of ultra-trace lead combined with flame atomic absorption spectrometry determination. Microchem. J. 2012, 100, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citak, D.; Tuzen, M. A novel preconcentration procedure using cloud point extraction for determination of lead, cobalt and copper in water and food samples using flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, E.L.; Roldan, P.S. Simultaneous flow injection preconcentration of lead and cadmium using cloud point extraction and determination by atomic absorption spectrometry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surme, Y.; Narin, I.; Soylak, M.; Yuruk, H.; Dogan, M. Cloud point extraction procedure for flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of lead(II) in sediment and water samples. Microchim. Acta 2007, 157, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xiao, S.; Wu, X.; Fang, K.; Liu, W. Determination of lead in water samples by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry after cloud point extraction. Talanta 2005, 67, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candir, S.; Narin, I.; Soylak, M. Ligandless cloud point extraction of Cr(III), Pb(II), Cu(II), Ni(II), Bi(III), and Cd(II) ions in environmental samples with Tween 80 and flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Talanta 2008, 77, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luconi, M.O.; Olsina, R.A.; Fernandez, L.P.; Silva, M.F. Determination of lead in human saliva by combined cloud point extraction–capillary zone electrophoresis with indirect UV detection. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 128, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavallali, H.; Asrari, E.; Attaran, A.M.; Tabandeh, M. Sensitive determination of lead in soil and water samples by cloud point extraction-flame atomic absorption spectrometry method. Int. J. Chem. Technol. Res. 2010, 2, 1731–1737. [Google Scholar]
- Maranhao, T.A.; Borges, D.L.G.; da Veiga, M.A.M.S.; Curtius, A.J. Cloud point extraction for the determination of cadmium and lead in biological samples by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2005, 60, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Foreign Ions | Interferent/Pb(II) Ratio |
|---|---|
| Na+, K+, NH4+ | 5000 |
| Co2+, Ni2+ | 3000 |
| Ca2+, Mg2+ | 4000 |
| Mn2+ | 2000 |
| Cd2+ | 2000 |
| Zn2+ | 1000 |
| Fe2+ | 800 |
| Cu2+ | 500 |
| Hg2+ | 700 |
| Parameter | Analytical Feature |
|---|---|
| Enrichment factor | 50 |
| Limit of detection (ng/mL) | 4 |
| Regression equation | Y = 0.0198 C + 0.0360 |
| Correlation coefficient (r2) | 0.9981 |
| Linear range (ng/mL) | 7–250 |
| %RSD | 1.9 |
| Enrichment Method | System | Detection Method | Linear Range, (ng/mL) | RSD, % | Detection Limit, (ng/mL) | Enrichment Factor | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPE | APDC DDTC | FAAS | 5–20 | 6.88 8.74 | 1.14 | 56 42 | [11] |
| CPE | TAN | FAAS | 1.1–160 | 3.5 | 1.1 | 55.6 | [23] |
| CPE | PAN | FAAS | 7.5–3500 | 1.6 | 5.27 | 30 | [31] |
| RS-CPE | APDC DDTC | FAAS | Up to 40 | 4.9 | 4.3 | 39 | [32] |
| CPE | 1-PTSC | FAAS | 0.5–10.0 | 1.7–4.8 | 4.8 | 25 | [33] |
| CPE | TAN | FI-FAAS | 50–250 | 1.6–3.2 | 4.5 | 15 | [34] |
| CPE | BCB | FAAS | − | <6.4 | 7.5 | 25 | [35] |
| CPE | 5-Br-PADAP | GFAAS | 0.1–30 | 2.8 | 0.08 | 50 | [36] |
| CPE | Tween 80 | FAAS | 2–12 | ≤6 | 7.2 | 10 | [37] |
| CPE | PONPE 7.5 | Capillary zone electrophoresis | 12–400 | 3.6 | 11.4 | − | [38] |
| CPE | PAN | FAAS | 20–300 | 2.7 | 8.0 | 50 | [39] |
| CPE | DDTP | FAAS | − | − | 40 ng/g | 18 | [40] |
| CPE | DLNL | FAAS | 7–250 | 1.9 | 4.0 | 50 | Present work |
| Sample | Amount of Pb(II), (ng/mL) * | Recovery, % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Added | Found | ||
| River water | − | 25.6 ± 0.3 | − |
| 10 | 35.9 ± 1.1 | 101.30 | |
| 20 | 45.2 ± 2.2 | 99.10 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
H. Kamel, A.; E. Amr, A.E.-G.; A. Al-Omar, M.; A. Elsayed, E. Pre-Concentration Based on Cloud Point Extraction for Ultra-Trace Monitoring of Lead (II) Using Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4752. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224752
H. Kamel A, E. Amr AE-G, A. Al-Omar M, A. Elsayed E. Pre-Concentration Based on Cloud Point Extraction for Ultra-Trace Monitoring of Lead (II) Using Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(22):4752. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224752
Chicago/Turabian StyleH. Kamel, Ayman, Abd El-Galil E. Amr, Mohamed A. Al-Omar, and Elsayed A. Elsayed. 2019. "Pre-Concentration Based on Cloud Point Extraction for Ultra-Trace Monitoring of Lead (II) Using Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry" Applied Sciences 9, no. 22: 4752. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224752
APA StyleH. Kamel, A., E. Amr, A. E.-G., A. Al-Omar, M., & A. Elsayed, E. (2019). Pre-Concentration Based on Cloud Point Extraction for Ultra-Trace Monitoring of Lead (II) Using Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Applied Sciences, 9(22), 4752. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224752








