Shear Rate-Dependent Rheological Properties of Mine Tailings: Determination of Dynamic and Static Yield Stresses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results
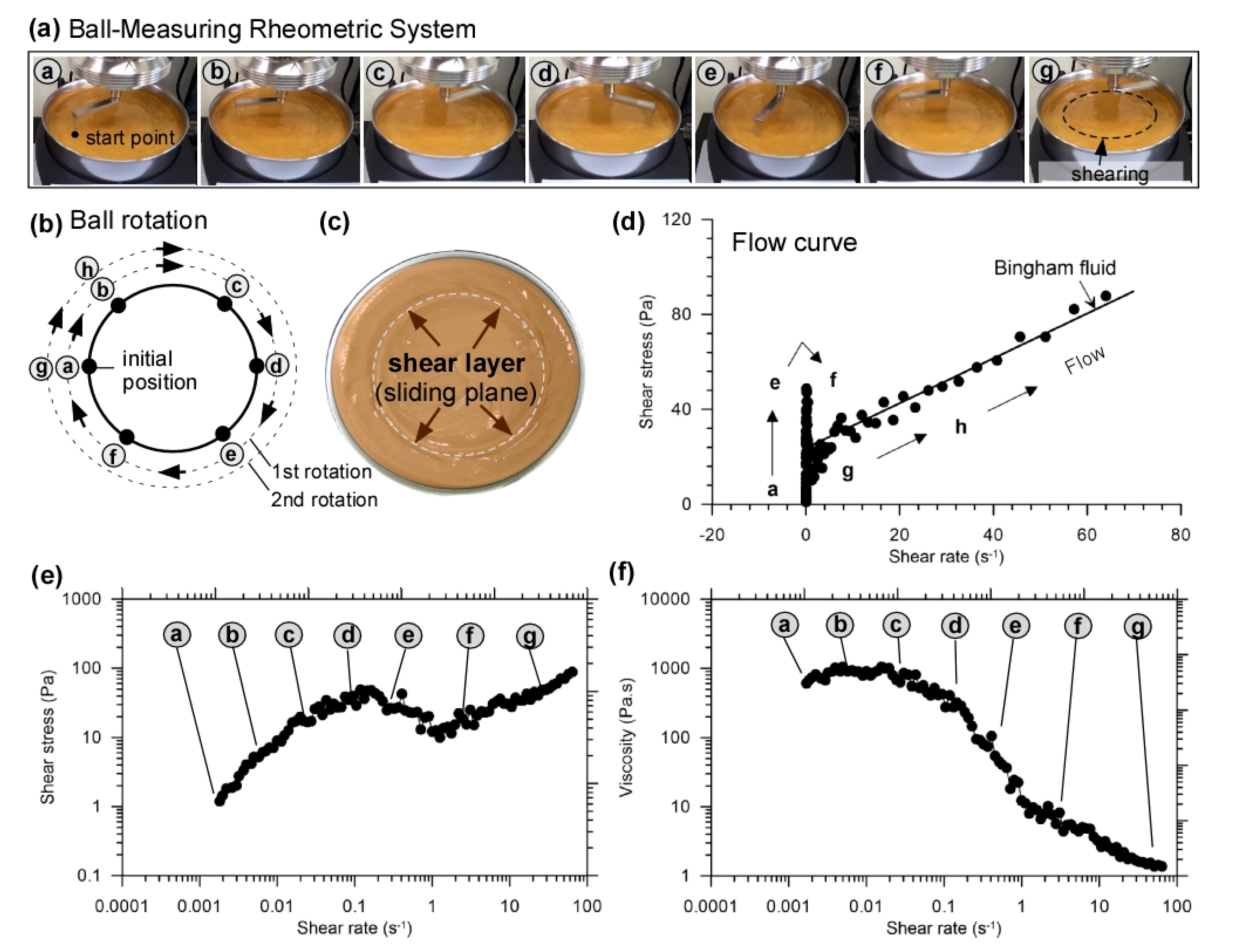
3.1. Rheological Properties of Mine Tailings: Yield Stress and Viscosity
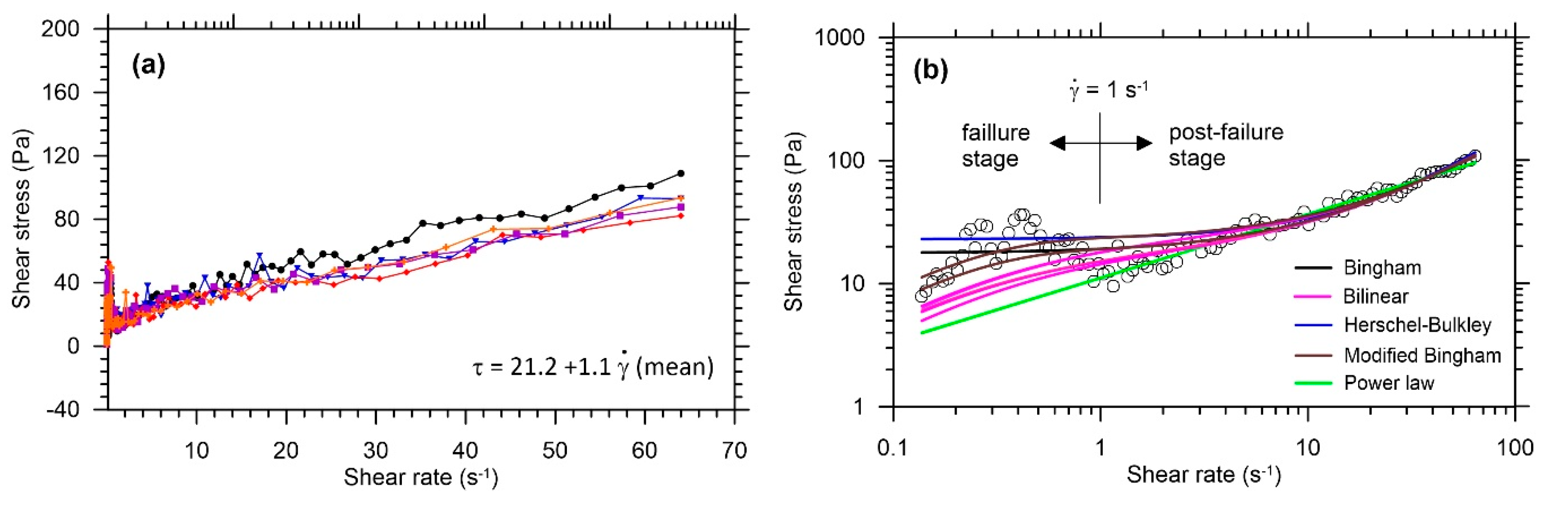
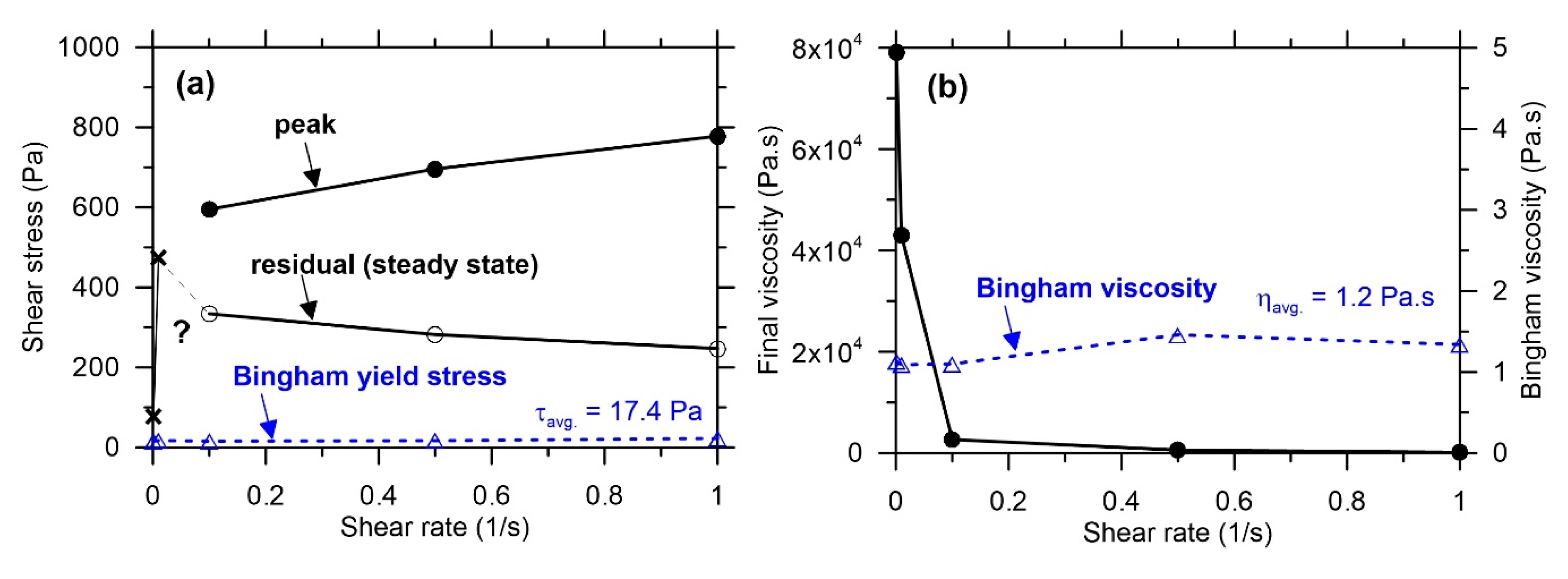
3.2. Shear Rate-Dependent Flow Behavior: Dynamic and Static Yield Stresses
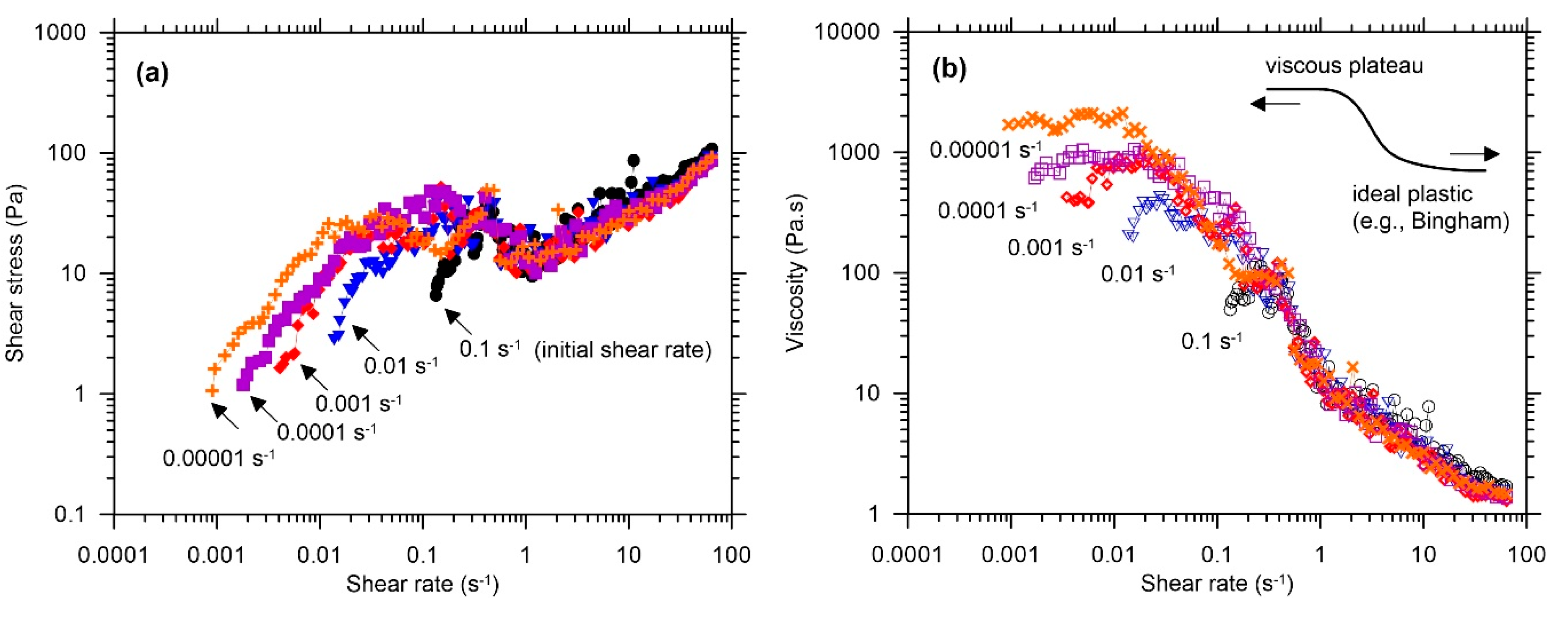
3.2.1. Flow Curve Test: Initial Shear Rate Dependency
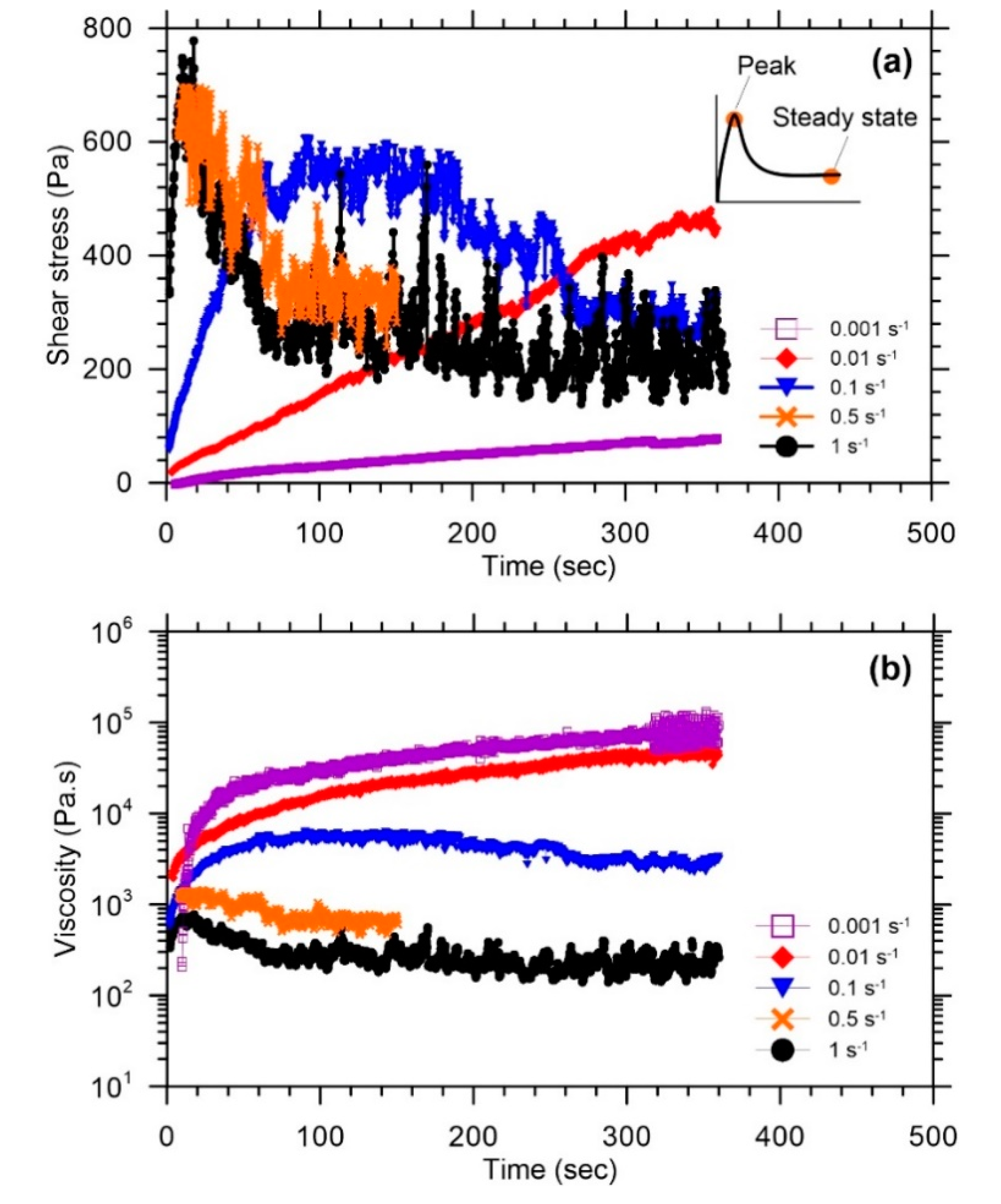
3.2.2. Stress Growth Test: Time Dependency
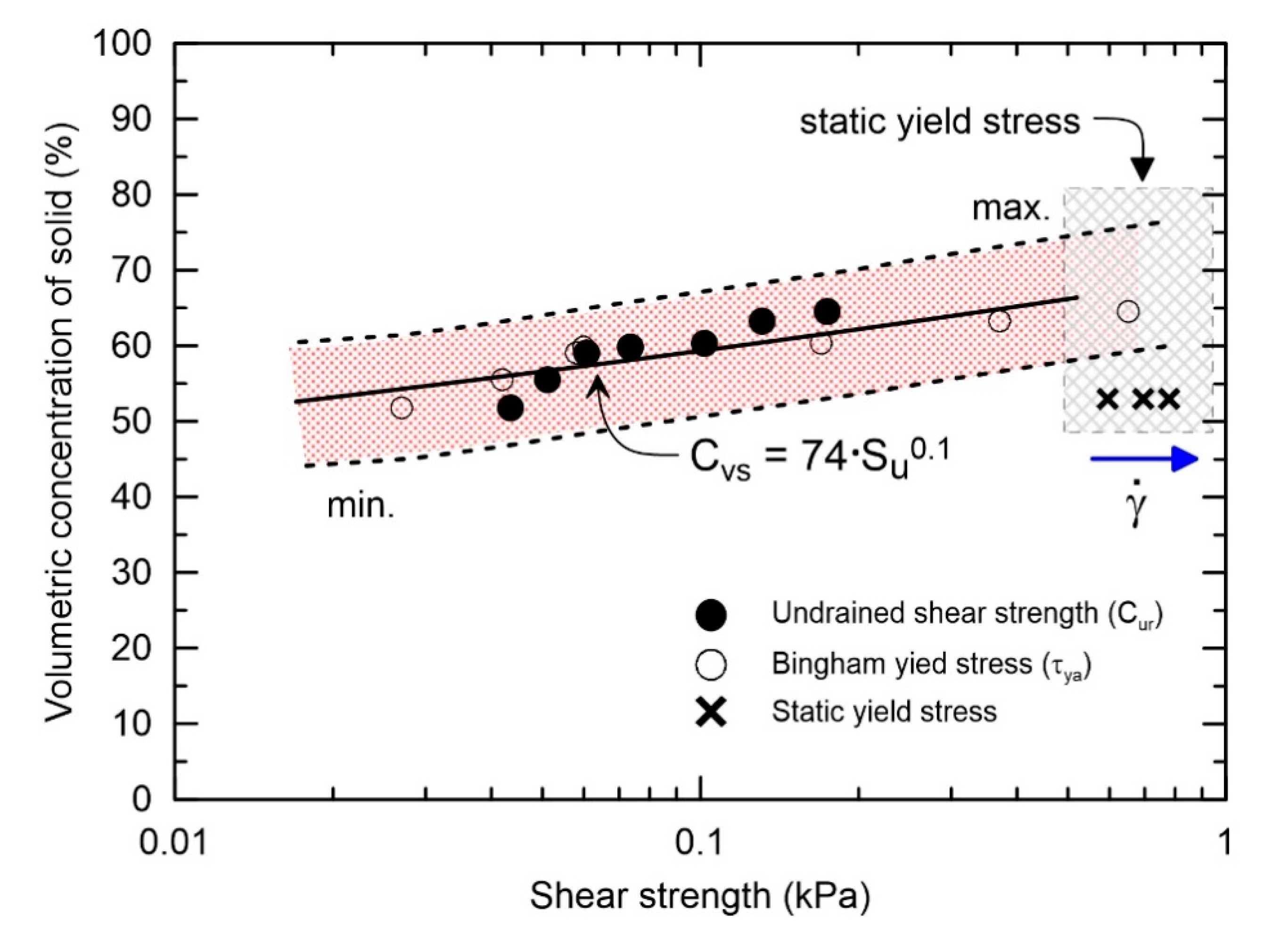
3.3. Rheological Properties and Possible Implications for Debris Flow Modeling
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnes, H.A. The yield stress—A review or ‘παντα ρει’—Everything flows? J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1999, 81, 133–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussot, P.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Huynh, H.T.; Bonn, D. Viscosity bifurcation in thixotropic, yielding fluids. J. Rheol. 2002, 46, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, P.C.F.; Mewis, J.; Bonn, D. Yield stress and thixotropy: On the difficulty of measuring yield stresses in practice. Soft Matt. 2006, 2, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewis, J.; Wagner, N.J. Thixotropy. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147–148, 214–227. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Kawashima, S. Use of creep recovery protocol to measure static yield stress and structural rebuilding of fresh cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 90, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Kawashima, S. Distinguishing dynamic and static yield stress of fresh cement mortars through thixotropy. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2018, 86, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Boger, D.V. Measuring the Flow Properties of Yield Stress Fluids. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1992, 24, 47–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, J.R.; Telford, J.H. Measuring the yield behaviour of structured fluids. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2004, 124, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewis, J. Thixotropy—A general review. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1979, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.A. Thixotropy—A review. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 1997, 70, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, P.; Fall, A.; Chikkadi, V.; Derks, D.; Bonn, D. An attempt to categorize yield stress fluid behaviour. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 5139–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.C.H. Yield stress: A time-dependent property and how to measure it. Rheol. Acta 1986, 25, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santolo, A.S.D.; Pellegrino, A.M.; Evangelista, A.; Coussot, P. Rheological behaviour of reconstituted pyroclastic debris flow. Géotechnique 2012, 62, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H.A.; Walters, K. The yield stress myths? Rheol. Acta 1985, 24, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astarita, G. Letter to the editor: The engineering reality of the yield stress. J. Rheol. 1990, 34, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Mendes, P.R. Modeling the thixotropic behavior of structured fluids. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2009, 164, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.S.; Julien, P.Y. Laboratory Analysis of Mudflow Properties. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1988, 114, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussot, P.; Piau, J.M. On the behavior of fine mud suspensions. Rheol. Acta 1994, 33, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatzmann, M.; Bezzola, G.R.; Minor, H.E.; Windhab, E.J.; Fischer, P. Rheometry for large-particulated fluids: Analysis of the ball measuring system and comparison to debris flow rheometry. Rheol. Acta 2009, 48, 715–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosio, R.; Crosta, G.B. Rheology of concentrated granular suspensions and possible implications for debris flow modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W03412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.S. Rapid Granular Flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1990, 22, 57–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.W.; Wu, Y.H.; Cho, Y.C.; Ji, S.W. Flow behavior and mobility of contaminated waste rock materials in the abandoned Imgi mine in Korea. Geomorphology 2018, 301, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, J.; Parker, G.; Locat, J.; Lee, H. 1D Numerical Model of Muddy Subaqueous and Subaerial Debris Flows. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2001, 127, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.W. Geotechnical and rheological characteristics of waste rock deposits influencing potential debris flow occurrence at the abandoned Imgi Mine, Korea. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 8299–8310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisantino, T.; Fischer, P.; Gentile, F. Rheological characteristics of debris-flow material in South-Gargano watersheds. Nat. Hazards 2010, 54, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaitna, R.; Rickenmann, D.; Schatzmann, M. Experimental study on rheologic behaviour of debris flow material. Acta Geotech. 2007, 2, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.W.; Locat, J.; Leroueil, S.; Malet, J.-P. Rheological properties of fine-grained sediment: The roles of texture and mineralogy. Can. Geotech. J. 2010, 47, 1085–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locat, J.; Demers, D. Viscosity, yield stress, remolded strength, and liquidity index relationships for sensitive clays. Can. Geotech. J. 1988, 25, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, E.C. Fluidity and Plasticity; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1922; p. 440. [Google Scholar]
- Coussot, P.; Tocquer, L.; Lanos, C.; Ovarlez, G. Macroscopic vs. local rheology of yield stress fluids. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2009, 158, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germann, N. Shear banding in semidilute entangled polymer solutions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tika, T.E.; Vaughan, P.R.; Lemos, L.J.L.J. Fast shearing of pre-existing shear zones in soil. Géotechnique 1996, 46, 197–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, H.T.; Roussel, N.; Coussot, P. Aging and free surface flow of a thixotropic fluid. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 033101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bingham | Bilinear | Modified Bingham | Herschel–Bulkley | Power Law | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| τc | ηh | c | ηpN | m | τc-HB | K-HB | n-HB | K | n | ||
| 0.1 | 22.39 | 1.34 | 0.47 | 10.43 | 49.4 | 10.43 | 23.0 | 0.83 | 1.14 | 11.04 | 0.52 |
| 0.01 | 19.75 | 1.46 | 0.08 | 1.52 | 257.05 | 1.52 | 18.0 | 0.69 | 1.13 | 13.01 | 0.42 |
| 0.001 | 15.31 | 1.10 | 0.04 | 0.61 | 384.21 | 0.61 | 15.0 | 1.96 | 0.84 | 10.88 | 0.45 |
| 0.0001 | 17.02 | 1.09 | 0.03 | 0.43 | 674.49 | 0.43 | 12.0 | 1.78 | 0.96 | 11.50 | 0.45 |
| 0.00001 | 15.33 | 1.13 | 0.01 | 0.14 | 1703.47 | 0.14 | 12.0 | 1.90 | 0.91 | 8.98 | 0.53 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, S.-W. Shear Rate-Dependent Rheological Properties of Mine Tailings: Determination of Dynamic and Static Yield Stresses. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4744. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224744
Jeong S-W. Shear Rate-Dependent Rheological Properties of Mine Tailings: Determination of Dynamic and Static Yield Stresses. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(22):4744. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224744
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Sueng-Won. 2019. "Shear Rate-Dependent Rheological Properties of Mine Tailings: Determination of Dynamic and Static Yield Stresses" Applied Sciences 9, no. 22: 4744. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224744
APA StyleJeong, S.-W. (2019). Shear Rate-Dependent Rheological Properties of Mine Tailings: Determination of Dynamic and Static Yield Stresses. Applied Sciences, 9(22), 4744. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9224744




