Featured Application
The process proposed in this study could be an effective method for the treatment of high-tech industrial wastewater to meet the new tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH) discharge limit.
Abstract
Nitrogen-containing wastewater is an important issue in optoelectronic and semiconductor industries. Wastewater containing nitrogen compounds such as ammonium, monoethanolamine (MEA), and tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH) must be properly treated due to concerns about health and environmental effects. MnCe-GAC (granular activated carbon) processes were developed in this study for the treatment of TMAH-contaminated wastewater in high-tech industries. The MnCe-GAC processes could effectively remove ammonium, MEA, and TMAH from aqueous solutions. The removal efficiencies of ammonium and MEA by these processes were better than observed for TMAH. Parameters affecting TMAH removal such as type of process, type of wastewater (synthetic or real), pH, salts, and t-butanol were investigated. In general, removal efficiencies of TMAH by various processes were in the following order: MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 > MnCe-GAC/O3 > MnCe-GAC/H2O2 > MnCe-GAC > GAC. The negative effect of sulfate and nitrate on pollutant removal might be due to the salting-out effect. Based on t-butanol experiments, the main degradation mechanisms of TMAH by the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process likely involved hydroxyl radicals. The process proposed in this study could be an effective alternative method for the treatment of high-tech industrial wastewater to meet the new TMAH discharge limit.
1. Introduction
Nitrogen-containing wastewater is an important issue in high-tech industries such as optoelectronic and semiconductor manufacturing industries. For example, in thin-film transistor liquid crystal display (TFT-LCD) manufacturing processes, wastewater containing high concentrations of nitrogen compounds (such as ammonium (NH4+), monoethanolamine (MEA), or tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH)) is generated [1,2]. TMAH is a caustic developing fluid, widely used in the manufacture of TFT-LCD and light emitting diodes (TFT-LED) and in semiconductor industries as a developer or etchant [2,3,4]. For example, a TFT-LCD factory (sixth generation) could generate 30,000 cubic meter per day (CMD) of TMAH-containing wastewater [5]. In Japan, one factory could discharge roughly 2500 tons of TMAH per year [6]. In addition, MEA is used as a stripper in the manufacture of TFT-LCD [7]. Exposure to TMAH may result in muscle weakness, muscular paralysis, dyspnea, hyperglycemia, respiratory deterioration, alkaline chemical burns, and/or sudden death [8,9,10]. For example, Lin et al. [10] reported on three fatal incidents in Taiwan due to TMAH exposure. TMAH must be properly treated before discharge due to its health and environmental effects [11]. These pollutants in wastewater discharged from TFT-LCD manufacturing factories are already being legislatively regulated in Taiwan and Japan [9]. In addition, the TMAH effluent standard at the Hsinchu Industrial Science Park, Taiwan, was modified from 60 to 30 mg/L in 2015 due to human health and environmental concerns. High concentrations of TMAH solutions from factories could be physicochemically recovered and recycled, while wastewater containing lower concentrations of TMAH (in the order of hundreds of mg/L) can be treated in wastewater treatment facilities [9,12].
Common treatment processes for nitrogen-containing wastewater include adsorption [13,14,15], biological processes [9,11], ozonation [16], chemical oxidation [17], electrodialysis [18], and UV/persulfate [19,20]. Although wastewater containing high concentrations of TMAH can be treated by Fenton oxidation and catalytic oxidation processes, costs of these processes can be very high [11]. The TFT-LCD industry contributed more than 100 billion dollars annually due to the growing demand in electronic products [2]. There is a need to develop effective processes for the removal of nitrogen-containing wastewater because meeting the new TMAH effluent standard will not be an easy task. An alternative effective treatment process (MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2) for the treatment of nitrogen-containing wastewater is proposed and investigated in this study.
2. Materials and Methods
Samples of wastewaters discharged from four optoelectronic (Plants 1–4) and six semiconductor (Plants 5–10) plants in Central Taiwan Science Park, Taiwan, were collected and analyzed in this research, and their temperature, conductivity, suspended solids (SS), chemical oxygen demand (COD), biological oxygen demand (BOD), nitrate, sulfate, ammonium, and TMAH are summarized in Table 1. Plant 1 is a LCD glass substrate (LCD-GS) manufacturing factory, Plant 2 is a photovoltaic cell (PV) and TFT-LCD manufacturing factory, Plants 3–4 are TFT-LCD manufacturing factories, Plant 5 is an integrated circuit (IC) design and manufacturing factory (including flash memory (FM) and dynamic random access memory (DRAM), Plants 6–9 are IC manufacturing factories, and Plant 10 is an IC packaging and testing factory (IC-P&T). Plant 3 is a typical TF-LCD manufacturing plant with a relatively high wastewater flow rate (12,381 CMD) and pollutant concentrations (SS 79.4 mg/L, COD 296.6 mg/L, BOD 169.43 mg/L, NH3-N 9.78 mg/L, TMAH 100.21 mg/L) among these plants. It was chosen for the subsequent real wastewater test. The experimental set-up of MnCe-GAC (granular activated carbon) processes (Figure 1) made it possible to explore ten treatment processes: GAC, MnCe-GAC, O3, GAC/O3, MnCe-GAC/O3, H2O2, GAC/H2O2, MnCe-GAC/H2O2, GAC/O3/H2O2, and MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2. Since salts might be present in wastewaters, the effect of three model salts (including sulfate, nitrate, and carbonate) on the processes was investigated. Both synthetic (ammonium, MEA, or TMAH) and real wastewater (Plant 3) samples were treated by the above processes. A known amount of solid (1.0 g of GAC or MnCe-GAC) was packed in a column (internal diameter 1.1 cm, column height 3.9 cm, flow rate 100 mL/min). A vessel (500 mL) was filled with known concentrations of a target solution (ammonium, MEA, or TMAH) with pH adjusted to the desired values (3, 7, or 11), and the solution was circulated through the column as indicated in Figure 1. A known amount of O3 and/or H2O2 was added into the system as the process required. Samples were collected, filtered, and analyzed in triplicate within acceptable analytical error (±5%). TMAH, monomethylamine (MH, CH6ClN), dimethylamine (DH, C2H8ClN), and trimethylamine (TH, C3H10ClN) concentrations were analyzed by Dionex ICS-1100 ion chromatography system with Ion Pac CS19A IC columns and Dionex CERSTM 300.

Table 1.
Characteristics of wastewaters discharged from high-tech industry plants (n = 3).
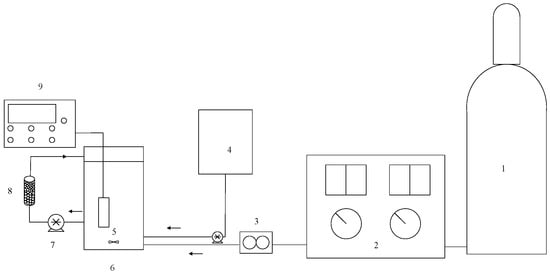
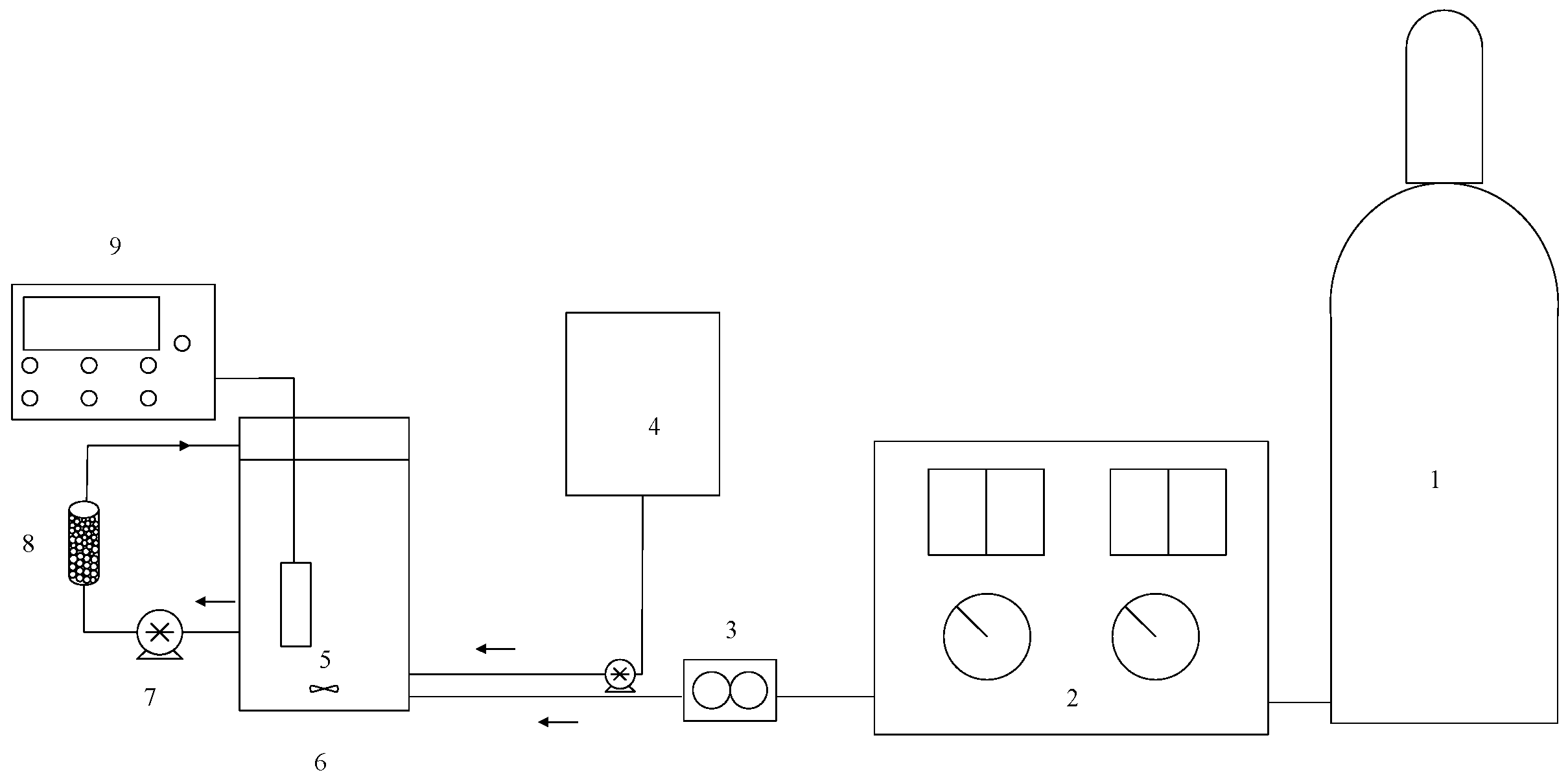
Figure 1.
Experimental set-up of MnCe-GAC processes (1—oxygen cylinder, 2—ozone generator, 3—flow meter, 4—hydrogen peroxide storage tank, 5—mixer, 6—reactor, 7—peristaltic pump, 8—activated carbon, 9—pH meter).
MnCe-GAC was prepared by impregnating Mn and Ce oxides onto GAC (F400, Calgon Carbon Corporation) surfaces. For example, known amounts of Mn(NO3)2·4H2O and Ce(NO3)3·6H2O solids (molar ratio of Mn:Ce = 6:4) were dissolved in deionized water. A known amount of GAC was immersed in the above solution and sonicated for 30 min before being dried in an oven at 90 °C for 12 h. The resulting mixture was heated at 200 °C for 120 min and then washed several times with deionized water to remove detachable Mn and Ce oxides. The resulting composite (MnCe-GAC) was dried at 105 °C and stored at room temperature until needed. Apparent bulk density, particle density, and pore volume fraction of GAC were 0.54 kg/L, 0.78 kg/L, and 0.82 kg/L, respectively. Prior to being used in this study, GAC was sieved so that the particle size was between 0.425 and 0.600 mm, washed several times with deionized water, and baked in an oven at 200 °C. The BET-pecific surface areas and surface morphology of MnCe-GAC and GAC were examined by ASAP 2010 accelerated surface area and porosimetry system (Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA) and field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) (SEM, ABT-150S, Topcon, Japan), respectively.
The amount of Mn and Ce impregnated on MnCe-GAC was measured by extracting MnCe-GAC in a HNO3 (10%) solution for 3 h at 180 °C. Total Mn or Ce in the extracted solution was measured by inductively coupled plasma (ICP-AES, Kontron, S-35). The amount of Mn and Ce on the spent MnCe-GAC (after treatment) was measured as well. The loss of Mn and Ce on MnCe-GAC after the treatment processes was determined by comparing the amount of Mn and Ce between newly prepared MnCe-GAC and spent MnCe-GAC. All labware were acid washed and thoroughly rinsed with deionized water. Chemicals used in this study were reagent grade, unless specified. Hydrogen peroxide (35%) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co. H2O2 was added into the reactor by a syringe pump at a constant feed rate. Ozone was produced by the ozone generator OW-K2/O (Taiwan) and was introduced into the reactor via a fine bubble diffusor. A standard iodometric titration method was used to determine the concentration of ozone [21].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Wastewater Composition from Photoelectric and Semiconductor Factories
Wastewaters from four photoelectric (Plants1–4) and six semiconductor (Plants 5–10) plants were shown in Table 1. Most of these plants (except Plant 10) had higher TMAH concentrations than the discharge limit (30 mg/L).
3.2. Characteristics of MnCe-GAC
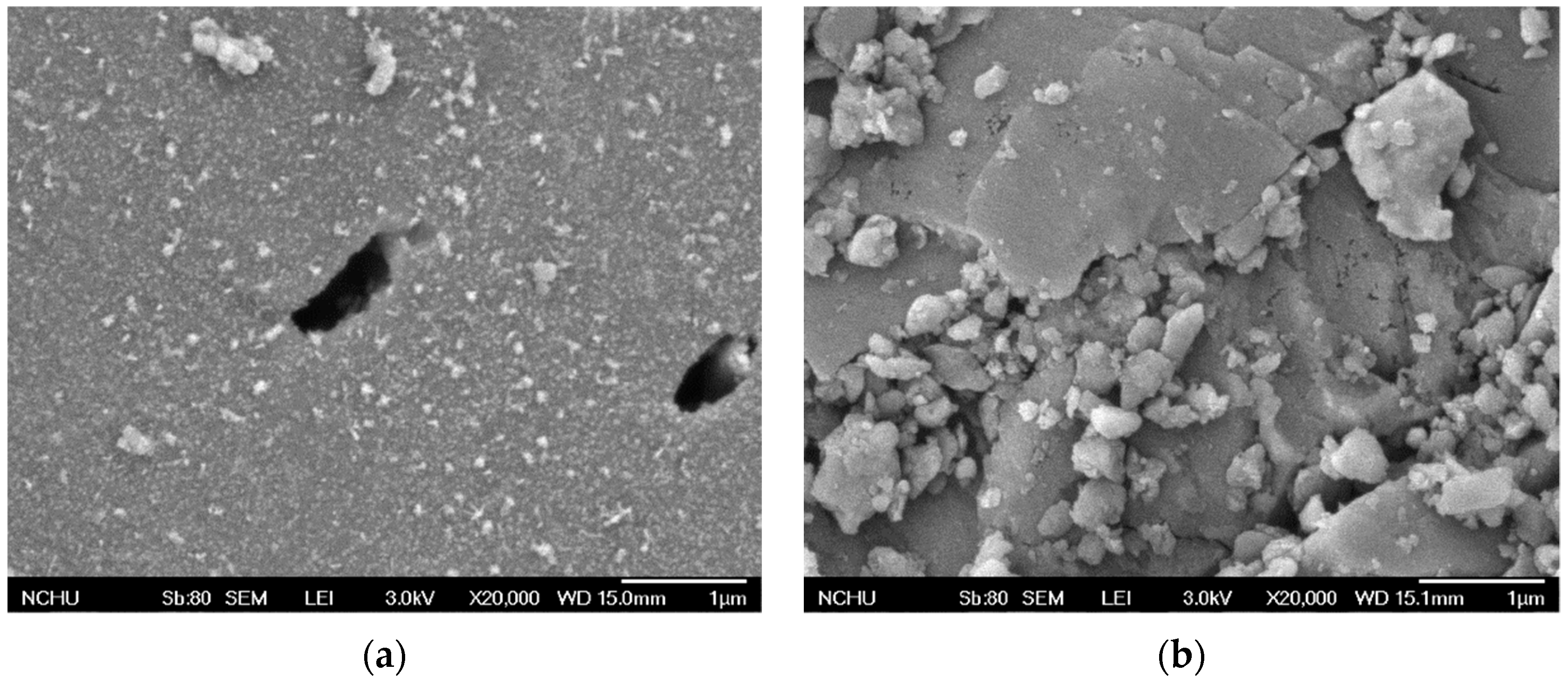
The BET-specific surface areas for GAC and MnCe-GAC were approximately 811 and 590 m2/g, respectively. The lower surface area of MnCe-GAC indicated that some of the pores of GAC might be blocked by the impregnation of Mn and Ce on the GAC surface. Surface characteristics of GAC and MnCe-GAC were further examined by SEM as shown in Figure 2a and b, respectively. The amount of Mn and Ce on MnCe-GAC surfaces was approximately 65.1 mg Mn/g (SD = 1.5 mg Mn/g) and 27.0 mg Ce/g (SD = 1.1 mg Ce/g), respectively. The loss of Mn and Ce on MnCe-GAC was determined by comparing the amount of Mn and Ce on MnCe-GAC before and after the treatment processes. In these tests, the total loss of Mn and Ce was less than 6%. This result indicated that MnCe-GAC has the potential to be reused.
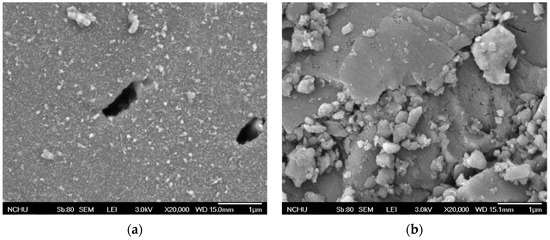
Figure 2.
SEM images of (a) GAC and (b) MnCe-GAC.
3.3. Removal of Ammonium, MEA, and TMAH by Various Processes (Synthetic Wastewater)
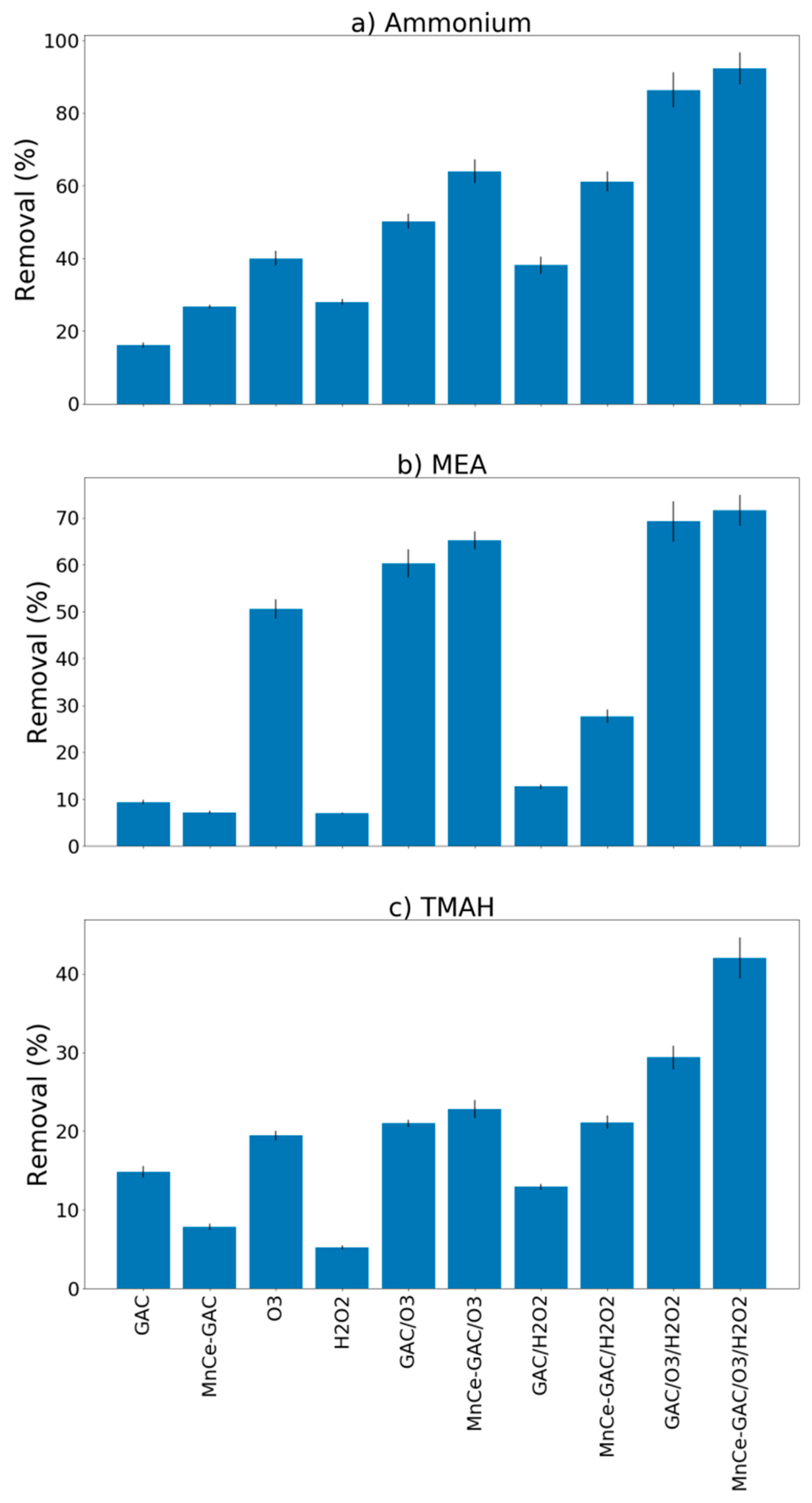
Removal results for ammonium, MEA, and TMAH by the processes examined in this study (GAC, MnCe-GAC, O3, H2O2, GAC/O3, GAC/H2O2, MnCe-GAC/O3, MnCe-GAC/H2O2, GAC/O3/H2O2, and MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2) are shown in Figure 3 (pH 11, Co = 100 mg/L, V = 0.5 L, solid 1g, 0.25 mmol O3/min, 0.125 mmol H2O2/min, 30 min). In general, the removal efficiencies of ammonium and MEA by these processes were better than that of TMAH. For example, the removal efficiencies of ammonium, MEA, and TMAH by MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 were 92.3, 71.6, and 42.0%, respectively. This result is in agreement with Lei et al. [11]. They reported that the degradation rate of MEA was significantly higher than that of TMAH. In addition, the ozone processes (O3, GAC/O3, and MnCe-GAC/O3) had slightly better removal efficiencies (40, 50, and 64% for ammonium removal, respectively) than the H2O2 processes (H2O2, GAC/H2O2, and MnCe-GAC/H2O2; 28, 38, and 61% ammonium removal, respectively) (Figure 3). The removal of ammonium and MEA by the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process was slightly better than that observed for the GAC/O3/H2O2 process. However, the removal of TMAH by the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process (42%) was significantly greater than that observed for the GAC/O3/H2O2 process (29%) (Figure 3). The addition of H2O2 could improve the removal of pollutants in wastewater in ozonation processes and it might be due to the formation of •OH radicals by the conjugated base of H2O2 with ozone [16,22,23,24,25]. In addition, an overdose of H2O2 might act as a scavenger and react with •OH instead of ozone. Therefore, the overall removal efficiency might be hindered by the overdose of H2O2. Therefore, the ratio of H2O2/O3 applied in the process is important. The stoichiometric molar ratio of H2O2/O3 being 1/2 [16] was applied in the study to ensure high efficiency of the treatment processes. As shown in Figure 3, MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 had the highest removal efficiencies among these processes for ammonium, MEA, and TMAH removal. This result indicated that the removal mechanism of the process is a combination of adsorption and degradation via catalysis/oxidation. The addition of H2O2 could improve the removal of pollutants in wastewater in ozonation processes. Therefore, this process was used in the subsequent experiments.
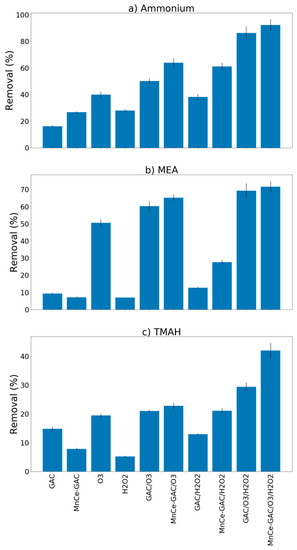
Figure 3.
Removal of (a) Ammonium, (b) Monoethanolamine (MEA), and (c) Tetramethylammonium hydroxide (TMAH) by various processes (pH 11, Co = 100 mg/L, V = 0.5 L, solid 1g, 0.25 mmol O3/min, 0.125 mmol H2O2/min, 30 min).
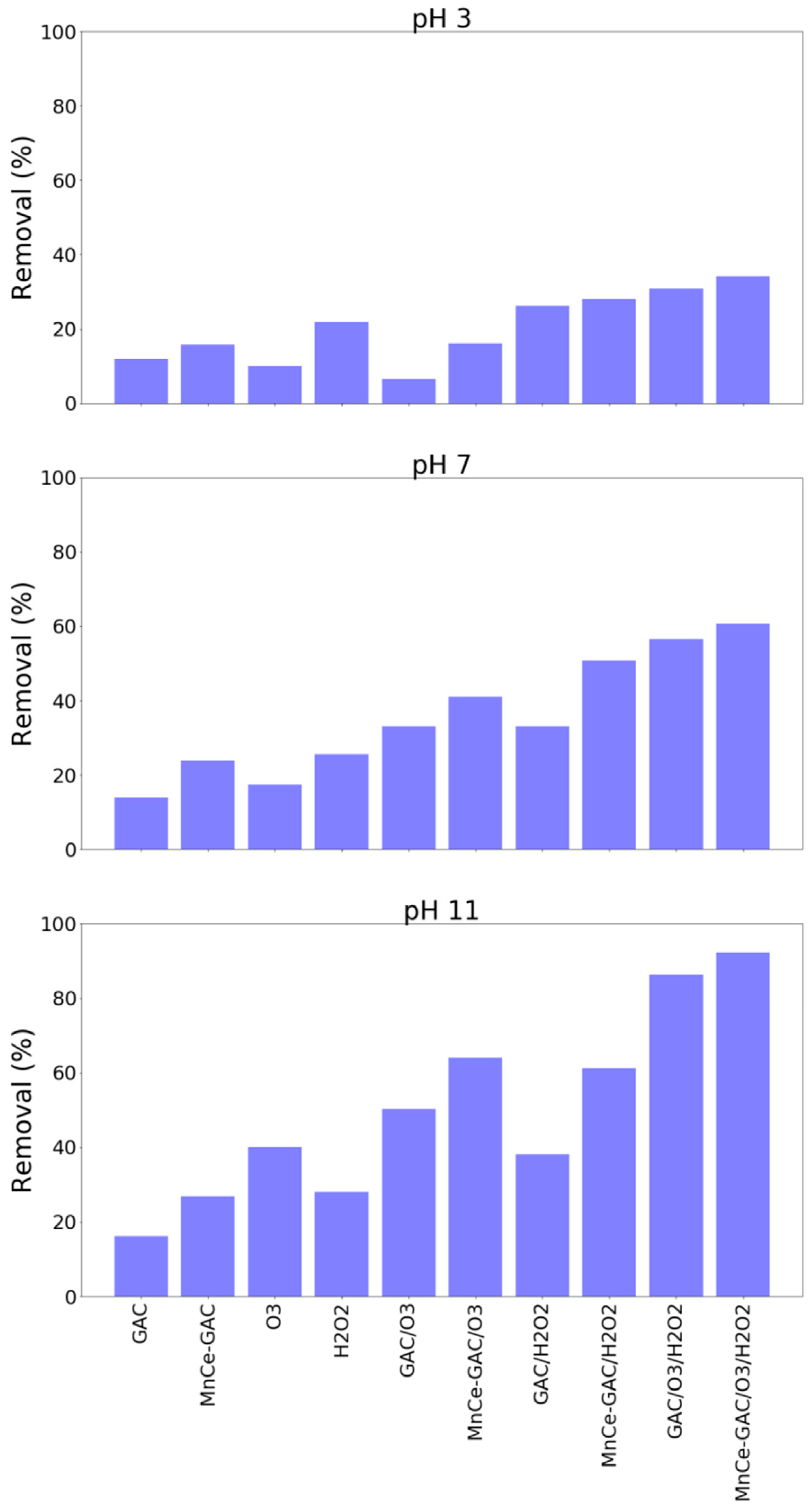
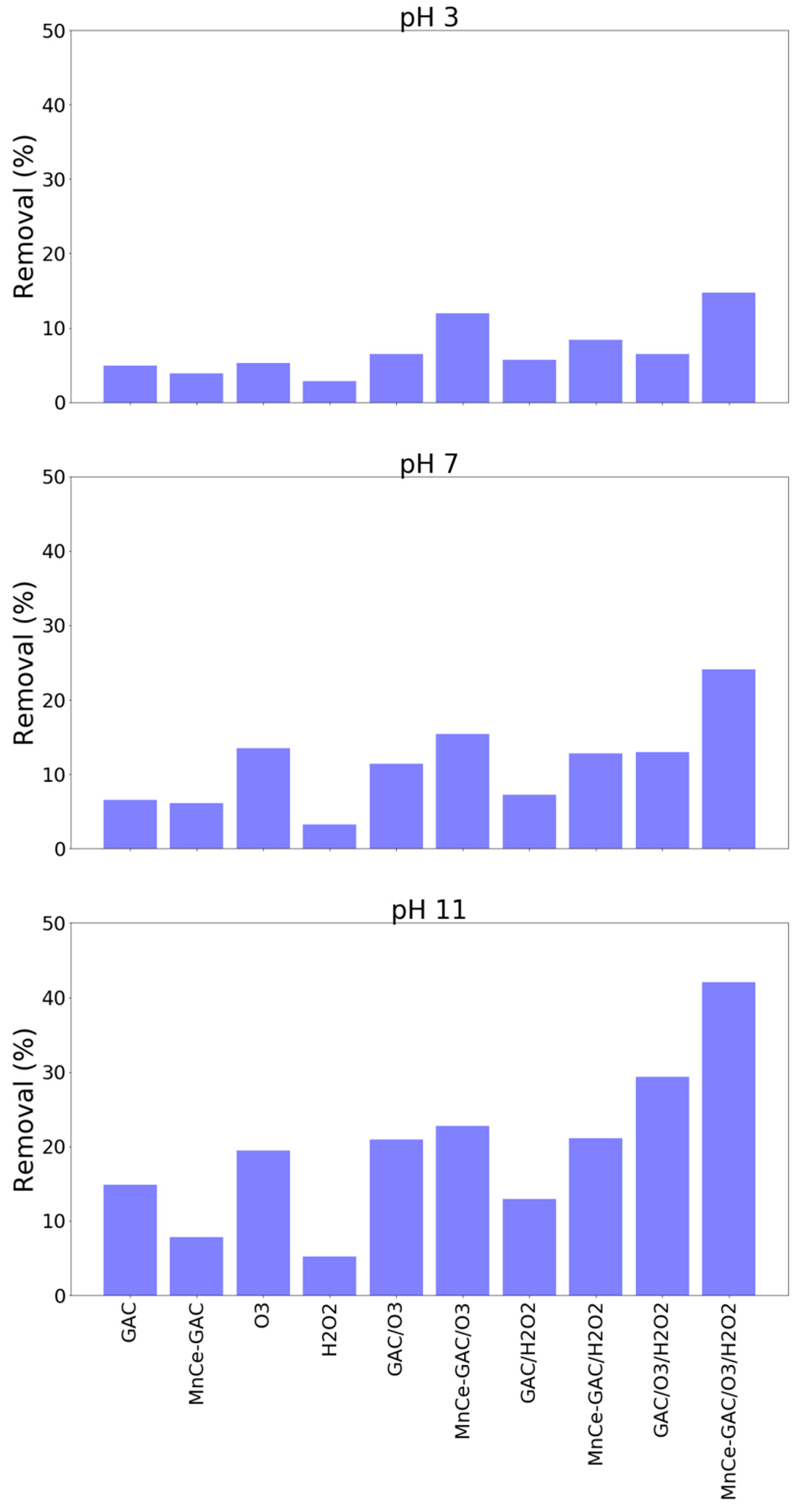
The solution pH played a significant role in these processes. A higher solution pH (pH 11) had a better ammonium removal than those of pH 3 and pH 7 (Figure 4). For example, the removal of ammonium at pH 3, 7, and 11 by the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process were 34, 61, and 92%, respectively (Co = 100 mg/L, V = 0.5 L, solid 1g, 0.25 mmol O3/min, 0.125 mmol H2O2/min, 30 min). Similar results were obtained for the removal of TMAH by these processes (Figure 5). The solution pH had a significant impact on the removal of TMAH. In general, the order of removal efficiencies of TMAH is as follows: pH 11 > pH 7 > pH 3. At high pH values, ozone decomposes into nonselective hydroxyl radicals which oxidize organic pollutants. Similar pH effect was observed in the findings reported by Lu et al. [26] and the authors investigated using activated carbon/silver catalytic combined with ozone and hydrogen peroxide for the removal of TMAH. On the other hand, under acidic or neutral conditions, the direct attack on organic pollutants by molecular ozone occurs. In general, hydroxyl radicals could destroy organic compounds more effectively than ozone [16,27].
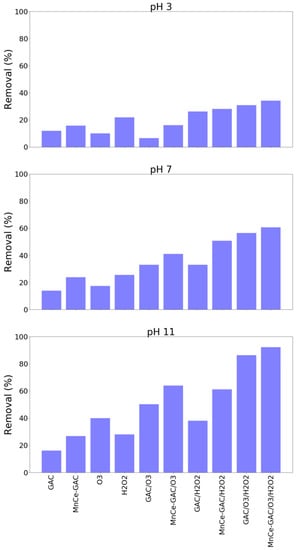
Figure 4.
Removal of ammonium by various processes at various solution pH (Co = 100 mg/L, V = 0.5 L, solid 1 g, 0.25 mmol O3/min, 0.125 mmol H2O2/min, 30 min).
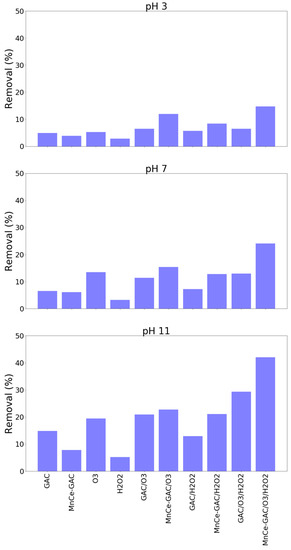
Figure 5.
Removal of TMAH by various processes at various solution pH (Co = 100 mg/L, V = 0.5 L, solid 1 g, 0.25 mmol O3/min, 0.125 mmol H2O2/min, 30 min).
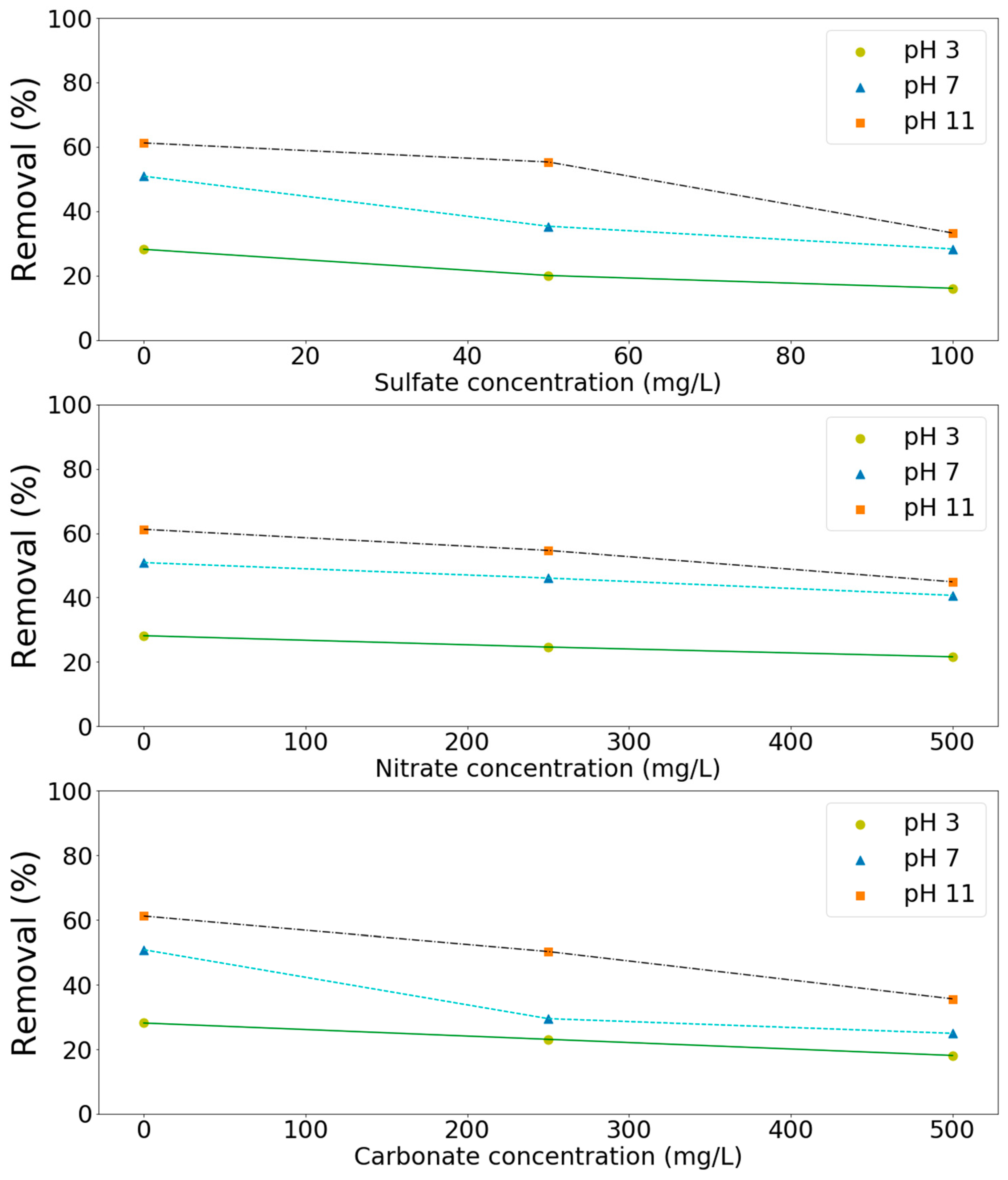
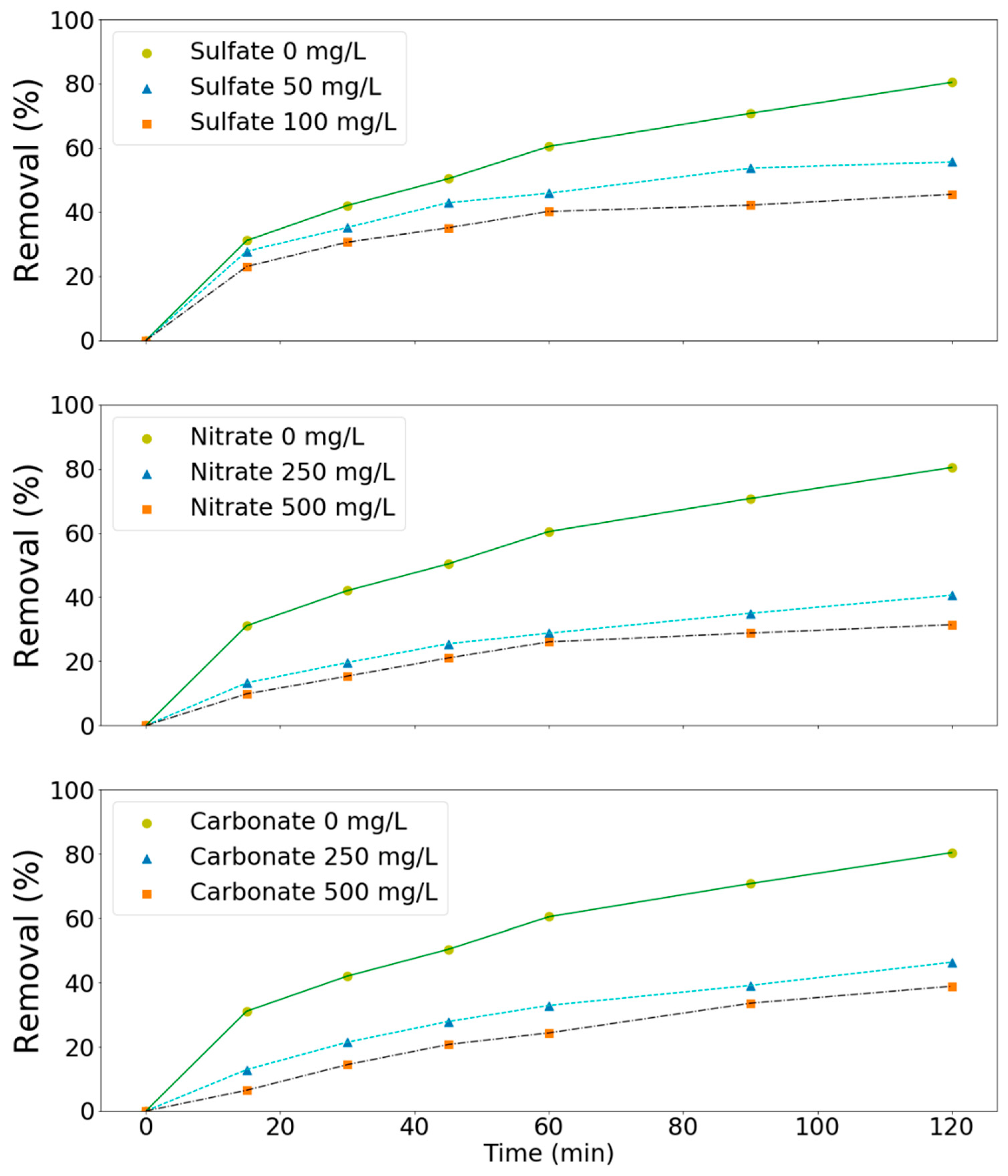
Since significant amounts of salts might be present in the wastewater, the effect of these salts on the processes has to be investigated in order to be able to apply the processes effectively in practice. Three types of salts such as sulfates, nitrates, and carbonates were chosen in this study as model compounds. As shown in Figure 6, these salts had a negative effect (Figure 6) on the removal of these pollutants at the tested pH values (3, 7, and 11). For example, ammonium removal decreased from 61 to 33, 45, and 36% due to the presence of sulfates (100 mg/L), nitrates (500 mg/L), and carbonates (500 mg/L) in solution, respectively (Figure 6). TMAH removal decreased from 80 to 46, 41, and 46% in aqueous solutions containing sulfates (100 mg/L), nitrates (250 mg/L), and carbonates (250 mg/L), respectively (Figure 7). Salts can affect the ozone oxidation process in several ways. For example, the presence of a salt generally lowers the solubility of a gas (salting out). A change in ozone solubility can be observed in the salt-containing solutions [28,29]. Rischbieter et al. [28] reported that sulfates and nitrates could reduce the solubility of ozone significantly with Henry constants about 15.3 and 12.1 kPa m3 mol−1, respectively (salt concentration 0.5 kmol m−3). Salts can also influence the size distribution of gas bubbles in a bubble column. They might inhibit bubble coalescence, resulting in a lower average bubble diameter. As a result, mass transfer rates might increase [30,31]. Carbonate ions are well-known species for scavenging the radicals involved in ozone decomposition [28,29,32]. On the other hand, sulfate, phosphate, nitrate, and chloride ions are extremely slow in reacting with •OH. Their scavenging effect can generally be neglected [33]. Therefore, the negative effect of sulfates and nitrates on pollutants removal might due to the salting-out effect.
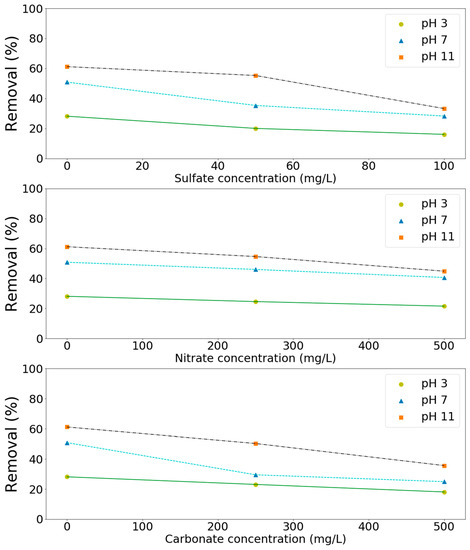
Figure 6.
Effect of salts on the removal of ammonium by the MnCe-GAC/H2O2 process (Co = 100 mg/L, V = 0.5 L, solid 1 g, 0.25 mmol O3/min, 0.125 mmol H2O2/min, 30 min).
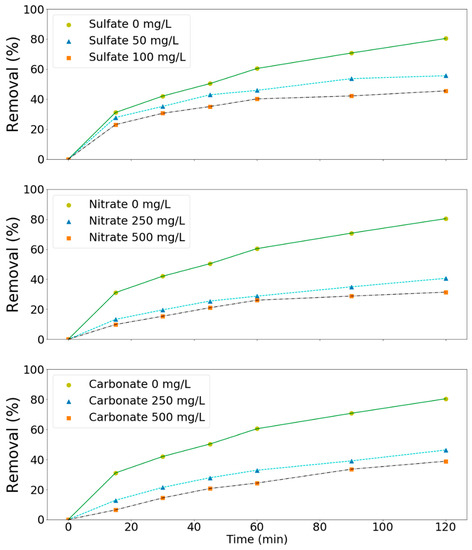
Figure 7.
Effect of salts on the removal of TMAH by the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process (Co = 100 mg/L, V = 0.5 L, solid 1 g, 0.25 mmol O3/min, 0.125 mmol H2O2/min, 30 min).
This study proposed that MnCe-GAC could enhance the formation of free radicals (such as hydroxyl radicals) in the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process and subsequent oxidation of adsorbed pollutants [34,35]. This assumption was tested by the addition of t-butanol. t-Butanol has a high rate constant with •OH as shown in Equation (1) [36].
CH3C(CH3) 2OH +•OH → CH2C(CH3) 2OH + H2O (k= 6.0*108 M−1s−1)
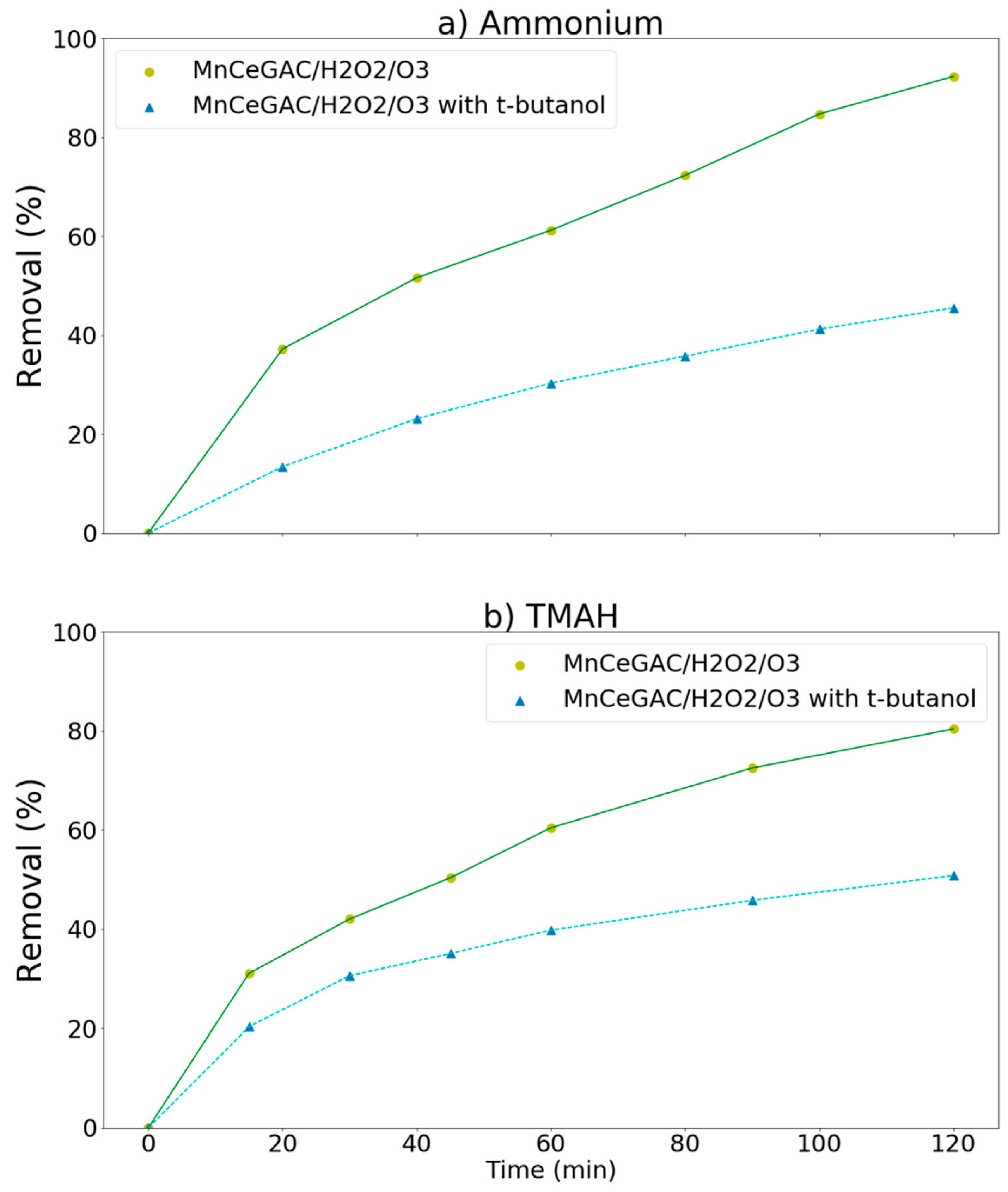
t-Butanol could be used as a hydroxyl radical scavenger [37] and served as an •OH-scavenger in this study. If the removal of pollutants were significantly hindered by the addition of t-butanol, it indicated that the hydroxyl radical reaction might play an important role in the removal processes. The effect of t-butanol on the removal of ammonium and TMAH by the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process is shown in Figure 8a,b, respectively. As indicated in the figure, the removal of ammonium as well as TMAH was significantly reduced due to the presence of t-butanol. For examples, the removal of ammonium decreased from 92 to 46% and the removal of TMAH decreased from 80 to 51%. The removal efficiencies of ammonium and TMAH were reduced to 46 and 29%, respectively, due to the presence of t-butanol. In agreement with the findings of Wang et al. [38], this result indicated that the hydroxyl radical reaction might play an important role in the removal processes. Kim and Choi [39] reported that •OH could initiate the degradation of TMAH by either abstracting H-atoms or adding hydrocarbon molecules. Chen et al. [40] reported that metal oxide catalysts (such as Mn-Ce-O composites) were efficient catalysts and they possessed many oxidation states to facilitate electron transfer processes in the radical-producing step of wet oxidation.
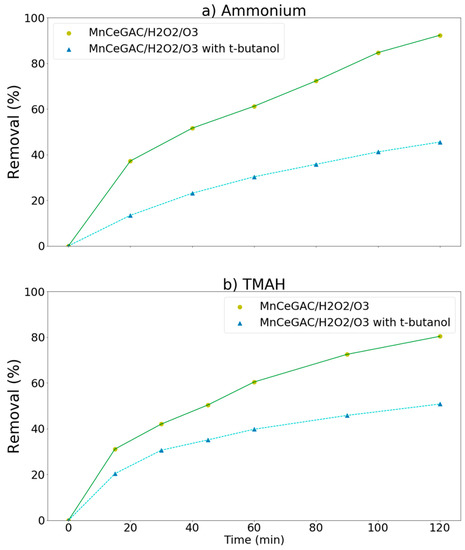
Figure 8.
Effect of t-butanol on the removal of ammonium and TMAH by the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process (Co = 100 mg/L, V = 0.5 L, solid 1 g, 0.25 mmol O3/min, 0.125 mmol H2O2/min).
3.4. Real Wastewater
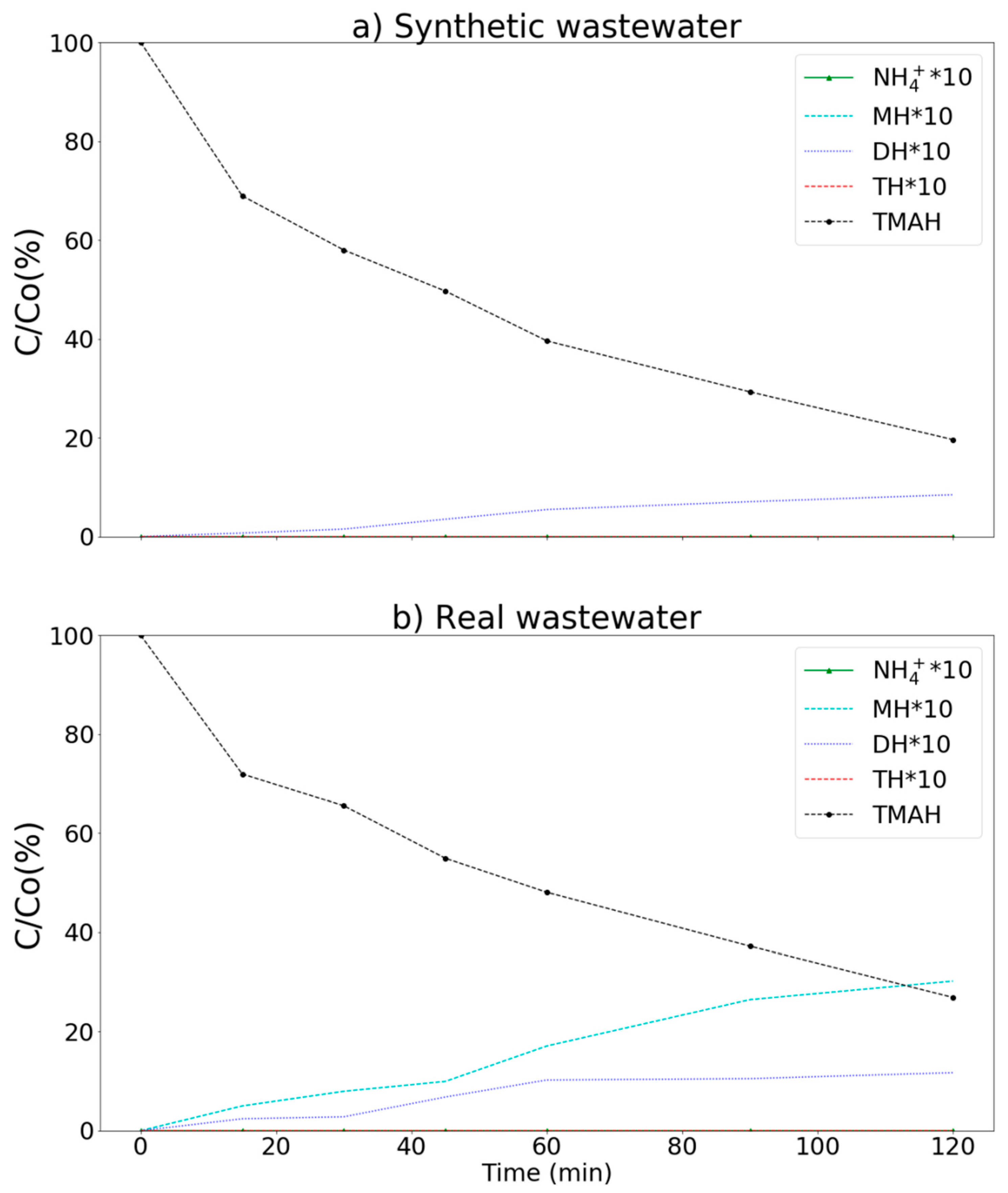
The intermediate products produced during TMAH degradation [12] by the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process, including NH4+, MH, DH, and TH are presented in Figure 9. More than 80 and 73% of TMAH were removed in synthetic and real wastewaters, respectively. For example, in real wastewater, the concentrations of NH4+, MH, DH, TH, and TMAH were under detection limit (ND), 3.38, 1.17, ND, and 26.89 mg/L, respectively (120 min). Both NH4+ and TH were not observed in the aqueous solution. A small amount of MH and DH (less than 3.5 mg/L) was observed in the process. This result indicated that the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process could remove TMAH efficiently to meet the discharge limit of the Science Park (30 mg/L) for both synthetic and real wastewaters.
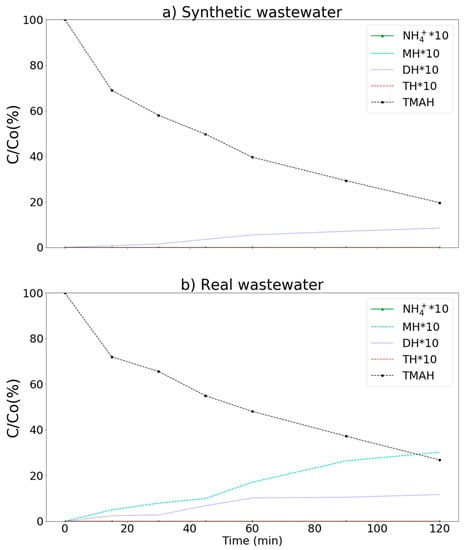
Figure 9.
Degradation of TMAH by the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process. (a) synthetic (Co = 100 mg/L) and (b) real wastewater samples (Co = 100 mg/L, V = 0.5 L, solid 1 g, 0.25 mmol O3/min, 0.125 mmol H2O2/min).
3.5. Reaction Kinetics
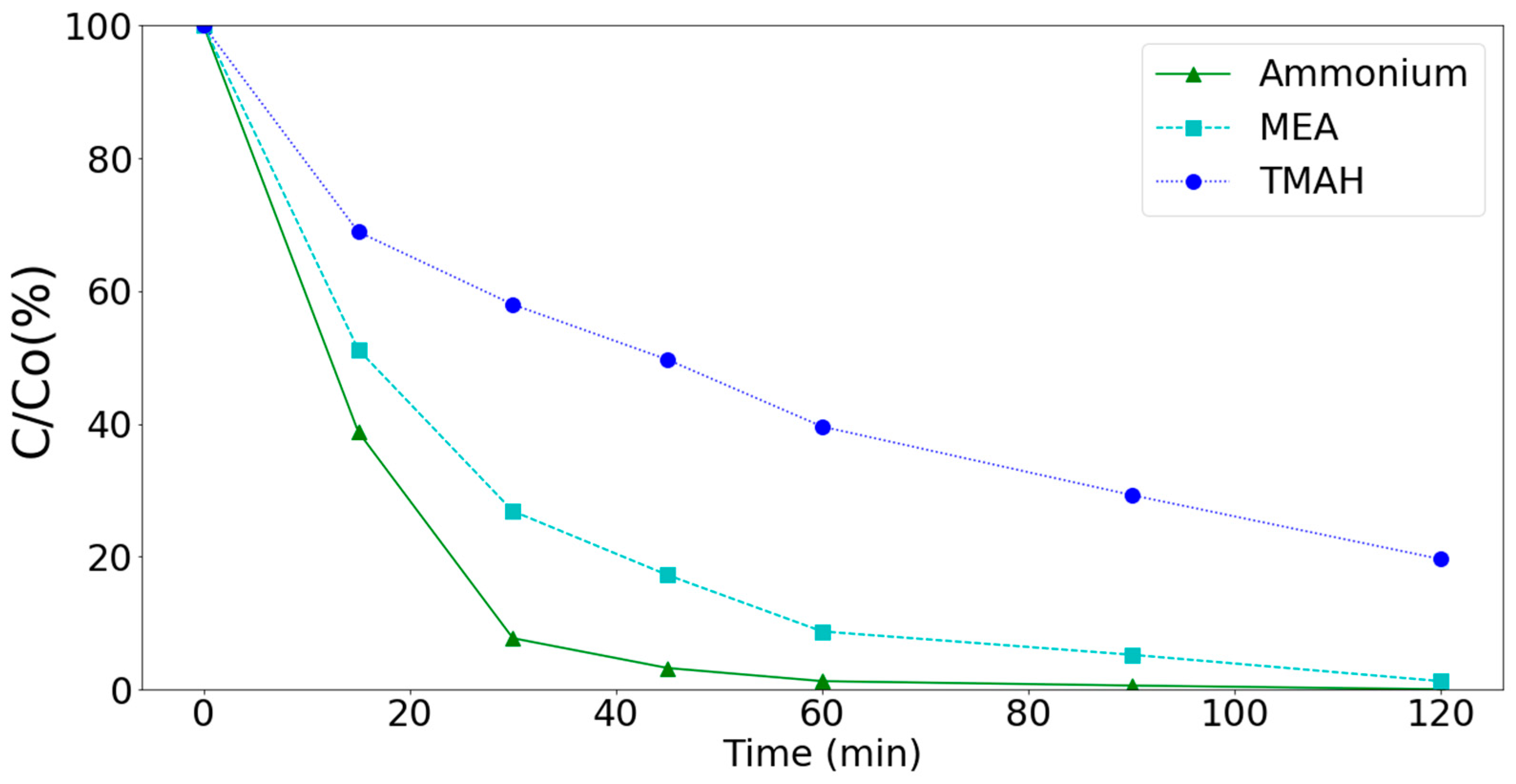
Experimental results indicated that the MnCe-GAC processes could effectively remove ammonium, MEA, and TMAH from aqueous solutions. In general, the removal of ammonium and MEA by these processes were better than that of TMAH as shown in Figure 10. Since the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process had the highest removal efficiency among these processes, reaction kinetics of the process was investigated. A suitable model could help in future design and implementation of the process. Many sophisticated models such as pore diffusion, homogeneous surface diffusion, and heterogeneous diffusion models have been developed to describe various kinetics processes. However, these models might not be convenient for practical use due to the mathematical complexity of these models [41,42]. Therefore, four simplified models (pseudo-first-order equation or generalized first order equation [41,42,43], pseudo-second-order equation [2], intra-particle diffusion model [2,38,43,44,45,46], and liquid film diffusion [46]) were applied in this research.
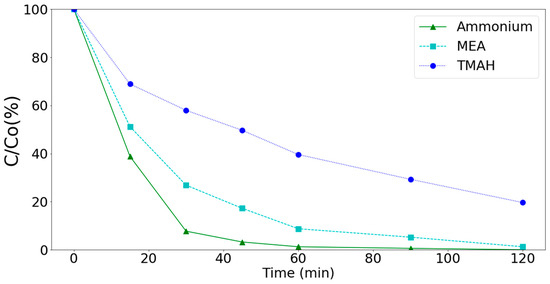
Figure 10.
Degradation of ammonium, MEA, and TMAH by the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process (Co = 100 mg/L, V = 0.5 L, solid 1 g, 0.25 mmol O3/min, 0.125 mmol H2O2/min).
Pseudo-first-order equation:
In the above equations, qt is the amount of adsorbate adsorbed (mg g−1) at time t (min), qe is the maximum adsorption capacity (mg g−1), and K1 is the pseudo-first-order rate constant (min−1) for the process.
Pseudo-second-order equation:
In the above equations, K2 is the pseudo-second-order rate constant (g mg−1 min−1).
Intra-particle diffusion model (or Weber and Morris’ method):
In the above equation, Cp is the intercept (mg g−1) and Kp is the intra-particle diffusion rate constant (mg min−0.5 g−1).
Liquid film diffusion model:
In the above equation, KL is the liquid film diffusion rate constant (min−1) for the adsorption process.
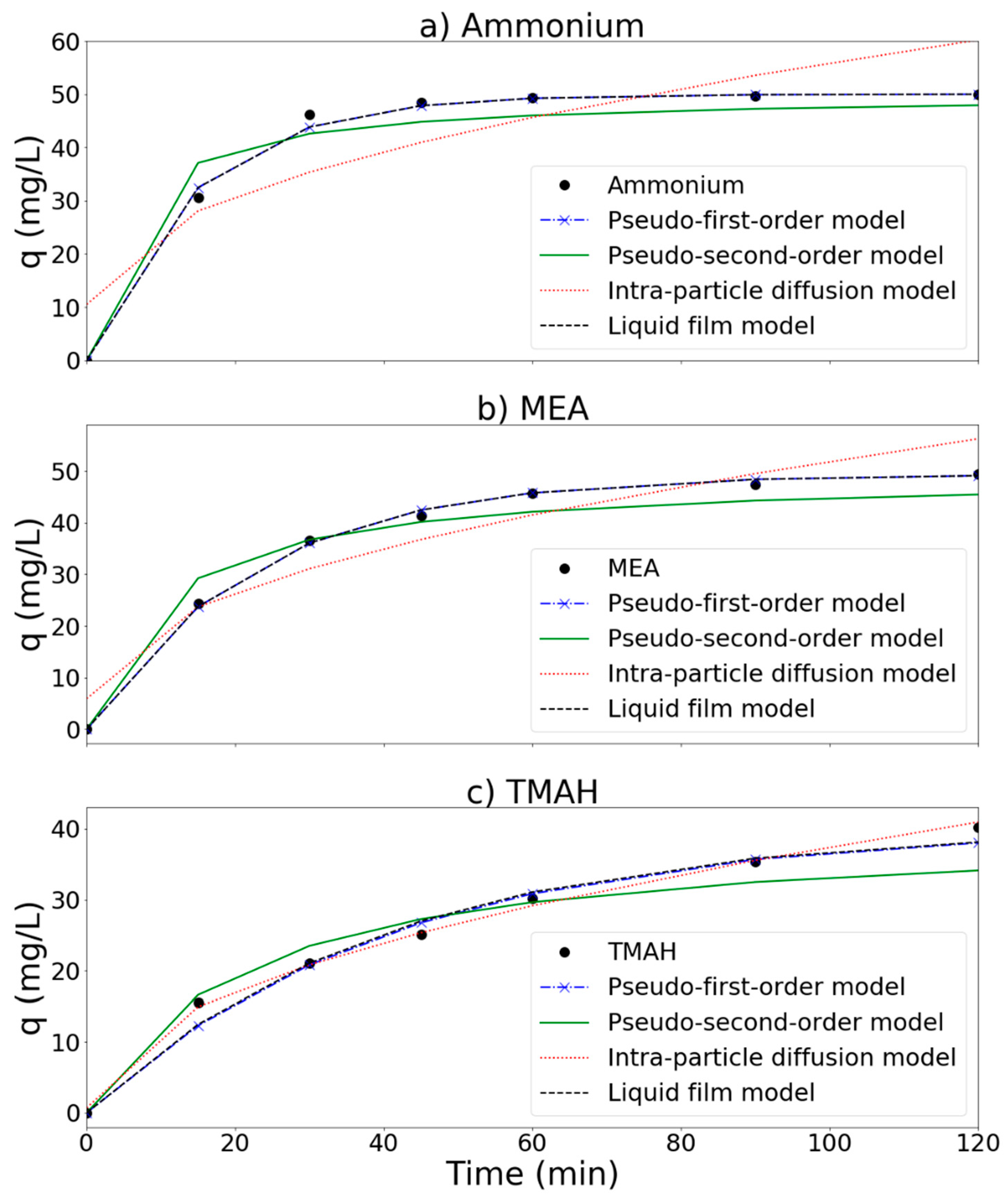
Experimental and simulation results are presented in Figure 11 and Table 2. To evaluate these models, root mean square error (RMSE) was calculated as follows:
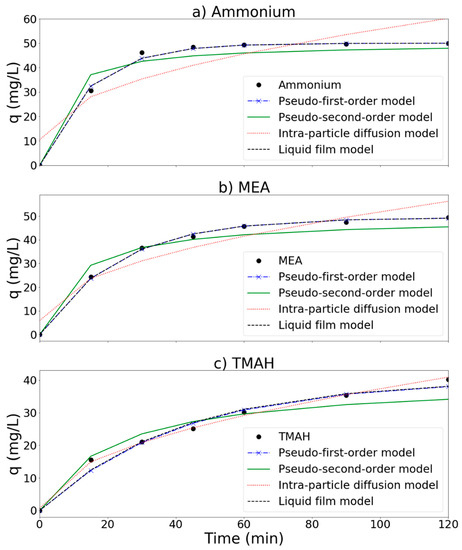
Figure 11.
Removal of (a) ammonium, (b) MEA, and (c) TMAH by the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process, respectively (Co = 100 mg/L, V = 0.5 L, solid 1 g, 0.25 mmol O3/min, 0.125 mmol H2O2/min).

Table 2.
Simulation results with various kinetic models.
In the above equation, qexp and qpre are model experimental and predicted values, respectively, and N is the number of data points.
In general, a model with a smaller RMSE value is a better fit model. According to RMSE results (Table 2), both pseudo-first-order equation and liquid film diffusion models seem to fit the removal process of ammonium and MEA well with smaller RMSE values (1.31 and 0.43 for ammonium and MEA, respectively). This result is similar to the findings reported by Wang et al. [38], who reported that liquid film diffusion was probably the rate limiting step in an MnCe-AC/O3 process for the removal of humic acid in solution. On the other hand, the intra-particle diffusion model can better describe the removal process of TMAH (with lower RMSE = 0.38). The pseudo-second order model was unable to fit these systems as indicated by a larger RMSE value. Based on the above simulations, liquid film diffusion is probably the rate limiting step for the removal of ammonium and MEA. Both ammonium and MEA probably transported from the bulk of the solution into the solid phase through the liquid film. For the removal of TMAH, it seemed that intra-particle diffusion played an important role in the process. TMAH was first adsorbed onto the MnCe-GAC surface, and then oxidized via catalytic reactions. This result is similar to the results presented by Fan et al. (2006), who reported that the intra-particle diffusion model was the best fitted model for GAC/H2O2 and FeGAC/H2O2 processes for the removal of acid black 24.
4. Conclusions
An MnCe-GAC process combining O3 and H2O2 was evaluated in this research for the removal of nitrogen-containing wastewater, typical of high-tech industries. Experimental results indicated that the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process could effectively lower ammonium, MEA, and TMAH concentrations to the desired levels. The presence of salts (carbonates, nitrates, or sulfates) interfered with the removal of these pollutants. Model simulation results indicated that the rate limiting step for the removal of ammonium and MEA is liquid film diffusion. On the other hand, intra-particle diffusion is probably the rate limiting step for the removal of TMAH by the MnCe-GAC/O3/H2O2 process. The process proposed in this study could be an effective alternative method for the treatment of high-tech industrial wastewater.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.-J.F. and D.T.C.; Funding acquisition, H.-J.F. and D.P.; Investigation, D.T.C., D.P., J.-J.Z. and H.-J.F.; Methodology, D.T.C., H.-J.F. and J.-J.Z.; Writing—review & editing, D.T.C., D.P. and H.-J.F.
Funding
This work was supported by Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, R.O.C. (Grant no. MOST 107-2637-E-241-005) and Korea Environment Industry & Technology Institute (KEITI) through Advanced Water Management Research Program, funded by Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE) (Grant 83089).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Su, C.-C.; Chen, C.-M.; Anotai, J.; Lu, M.-C. Removal of monoethanolamine and phosphate from thin-film transistor liquid crystal display (tft-lcd) wastewater by the fluidized-bed fenton process. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 222, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligaray, M.; Futalan, C.M.; de Luna, M.D.; Wan, M.-W. Removal of chemical oxygen demand from thin-film transistor liquid-crystal display wastewater using chitosan-coated bentonite: Isotherm, kinetics and optimization studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 175, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubel, I.; Kramkowska, M.; Rola, K. Silicon anisotropic etching in tmah solutions containing alcohol and surfactant additives. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 178, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhuri, V.; Son, D.-H.; Lee, D.-G.; Sakong, S.; Jeong, Y.-H.; Cho, I.-T.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-T.; Cristoloveanu, S.; Bae, Y.; et al. 1/f noise characteristics of algan/gan finfets with and without tmah surface treatment. Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 147, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan-Foo, C.; Show-Ying, Y.; Huey-Song, Y.; Pan, J.R. Anaerobic treatment of tetra-methyl ammonium hydroxide (tmah) containing wastewater. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2008, 21, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, J.; Murayama, N.; Matsumoto, S. Recovery of tetra-methyl ammonium hydroxide from waste solution by ion exchange resin. Resour. Process. 2006, 53, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hori, H.; Wachi, S.; Iwamura, K.; Sano, T. Visible light-induced decomposition of monoethanolamine in water using graphitic carbon nitride as a photocatalyst. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2018, 351, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.L.; Su, S.B.; Chen, J.L.; Chang, C.P.; Guo, H.R. Tetramethylammonium ion causes respiratory failure related mortality in a rat model. Resuscitation 2012, 83, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yoshinaga, K.; Wu, J.-H.; Chen, W.-Y.; Terashima, M.; Goel, R.; Pangallo, D.; Yasui, H. Kinetic analysis of biological degradation for tetramethylammonium hydroxide (tmah) in the anaerobic activated sludge system at ambient temperature. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 114, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Yang, C.C.; Ger, J.; Deng, J.F.; Hung, D.Z. Tetramethylammonium hydroxide poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. (Phila) 2010, 48, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Lu, L.A.; Lin, J.G. Biodegradation of tetramethylammonium hydroxide (tmah) in completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite (canon) process. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 210, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, C.N.; Whang, L.M.; Chen, P.C. Biological treatment of thin-film transistor liquid crystal display (tft-lcd) wastewater using aerobic and anoxic/oxic sequencing batch reactors. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prahas, D.; Liu, J.C.; Ismadji, S.; Wang, M.-J. Adsorption of tetramethylammonium hydroxide on activated carbon. J. Environ. Eng. 2012, 138, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Lin, K.-Y.A.; Lu, C. Efficient adsorptive removal of tetramethylammonium hydroxide (tmah) from water using graphene oxide. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Lu, C.; Lin, K.-Y.A. Comparisons of kinetics, thermodynamics and regeneration of tetramethylammonium hydroxide adsorption in aqueous solution with graphene oxide, zeolite and activated carbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 326, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, C.-S.; Chuang, K.-J.; Lin, Y.-F.; Chen, H.-W.; Ma, C.-M. Application of ozone related processes to mineralize tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide in aqueous solution. Int. J. Photoenergy 2013, 2013, 191742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, K.; Okamura, J.; Taira, T.; Sano, K.; Toyoda, A.; Ikeda, M. An efficient treatment technique for tmah wastewater by catalytic oxidation. IEEE Trans. Semicond. Manuf. 2001, 14, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Xu, T. Electrodialysis process for the recycling and concentrating of tetramethylammonium hydroxide (tmah) from photoresist developer wastewater. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 18356–18361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-W.; Liang, C. Oxidative degradation of tmah solution with uv persulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, K.S.; Liang, C. Oxidative degradation of tetramethylammonium hydroxide (tmah) by uv/persulfate and associated acute toxicity assessment. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2017, 52, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federation, W.E.; American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto, N.; Nakamura, E. Bromate formation characteristics of uv irradiation, hydrogen peroxide addition, ozonation, and their combination processes. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 107293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A.; Chelme-Ayala, P.; Drzewicz, P.; Martin, J.W.; Gamal El-Din, M. Effects of ozone and ozone/hydrogen peroxide on the degradation of model and real oil-sands-process-affected-water naphthenic acids. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2015, 37, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, G.; Vega, S.R.; Fick, J.; Tysklind, M.; Ledin, A.; La Cour Jansen, J.; Andersen, H.R. Removal of pharmaceuticals in wwtp effluents by ozone and hydrogen peroxide. Water SA 2014, 40, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gottschalk, C.; Libra, J.; Saupe, A. Ozonation of Water and Waste Water: A Practical Guide to Understanding Ozone and its Application; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; p. 189. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.-W.; Peng, Y.-P.; Chang, C.-N. Applying an activated carbon/silver catalyst to the decomposition of the aqueous solutions of tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 88, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.-P.; Xie, D.-M.; Wei, H.; Liu, W.-P. Degradation of sulfosalicylic acid by o3/uv o3/tio2/uv, and o3/v-o/tio2: A comparative study. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2005, 27, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rischbieter, E.; Stein, H.; Schumpe, A. Ozone solubilities in water and aqueous salt solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2000, 45, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotelo, J.L.; Beltrán, F.J.; González, M.; Domínguez, J. Effect of high salt concentrations on ozone decomposition in water. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2008, 24, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christenson, H.K.; Yaminsky, V.V. Solute effects on bubble coalescence. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.B.; Tsouris, C.; DePaoli, D.W.; Thomas Klasson, K. Ozonation of soluble organics in aqueous solutions using microbubbles. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2001, 23, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boncz, M.A.; Bruning, H.; Rulkens, W.H.; Zuilhof, H.; Sudhölter, E.J.R. The effect of salts on ozone oxidation processes. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2005, 27, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoigné, J. Chemistry of aqueous ozone and transformation of pollutants by ozonation and advanced oxidation processes. In Quality and Treatment of Drinking Water II; Hrubec, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1998; pp. 83–141. [Google Scholar]
- Tizaoui, C.; Bouselmi, L.; Mansouri, L.; Ghrabi, A. Landfill leachate treatment with ozone and ozone/hydrogen peroxide systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 140, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peixoto, A.L.C.; Silva, M.B.; Izário Filho, H.J. Leachate treatment process at a municipal stabilized landfill by catalytic ozonation: An exploratory study from taguchi orthogonal array. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 26, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, G.V.; Greenstock, C.L.; Helman, W.P.; Ross, A.B. Critical review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 513–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Khan, H.M.; Sayed, M.; Cooper, W.J. Advanced oxidation for the treatment of chlorpyrifos in aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.-M.; Lu, C.-S.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chang, D.T.; Fan, H.-J. Landfill leachate treatment with mn and ce oxides impregnated gac–ozone treatment process. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 482, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, W. Kinetics and mechanisms of photocatalytic degradation of (ch3)nnh4-n+ (0 ≤ n ≤ 4) in tio2 suspension: The role of oh radicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2019–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sayari, A.; Adnot, A.; Larachi, F. Composition-activity effects of mn–ce–o composites on phenol catalytic wet oxidation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 32, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Wilczak, A.; Keinath, T.M. Kinetics of sorption and desorption of copper (ii) and lead (ii) on activated carbon. Water Environ. Res. 1993, 65, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.J.; Shu, H.Y.; Tajima, K. Decolorization of acid black 24 by the fegac/h2o2 process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 128, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, N.; Sundaram, M.M. Kinetics and mechanism of removal of methylene blue by adsorption on various carbons—A comparative study. Dye. Pigment. 2001, 51, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onundi, Y.B.; Mamun, A.A.; Al khatib, M.; Ahmed, Y.M. Adsorption of copper, nickel and lead ions from synthetic semiconductor industrial wastewater by palm shell activated carbon. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khateeb, L.A.; Almotiry, S.; Salam, M.A. Adsorption of pharmaceutical pollutants onto graphene nanoplatelets. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 248, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).